Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of NiTi46 Alloy Consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering
Abstract
1. Introduction
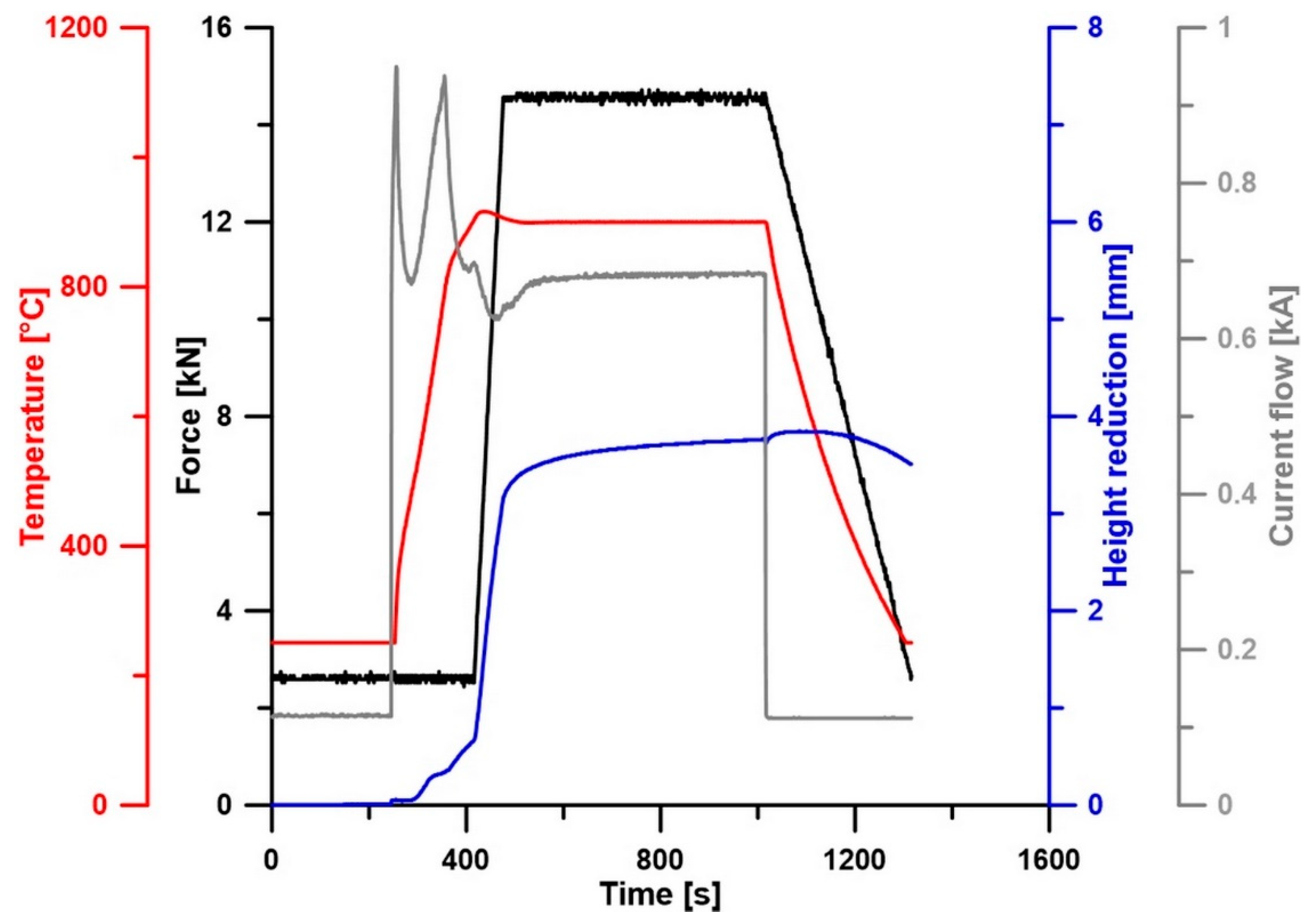
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
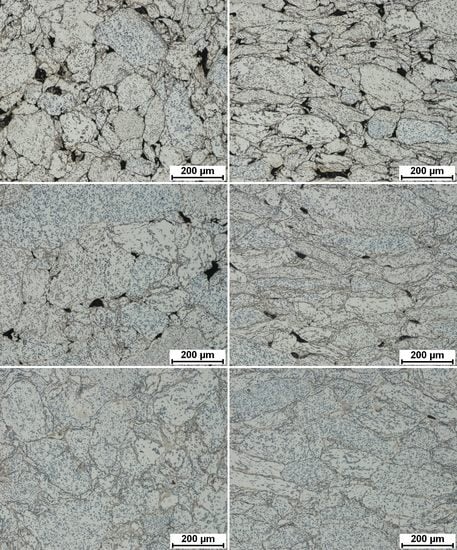
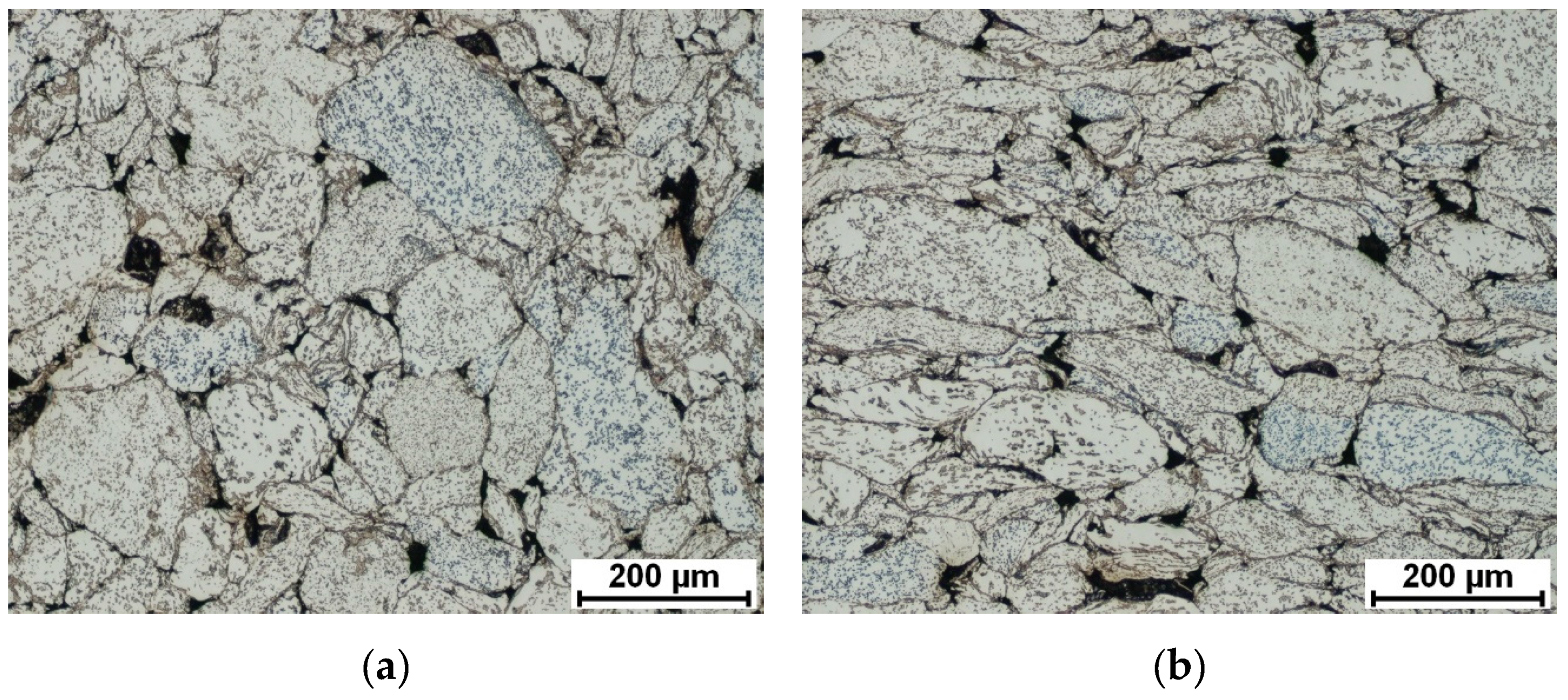
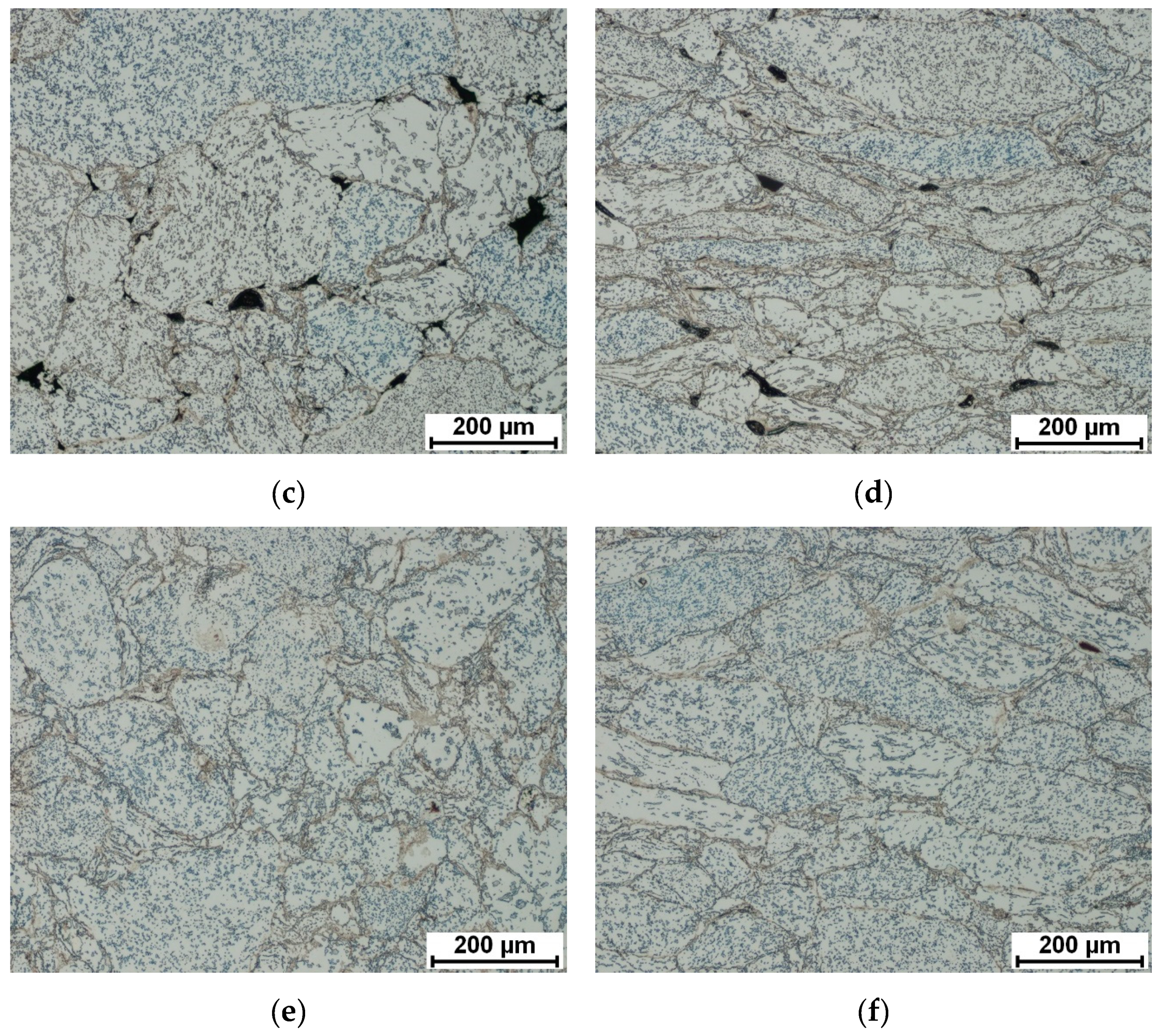
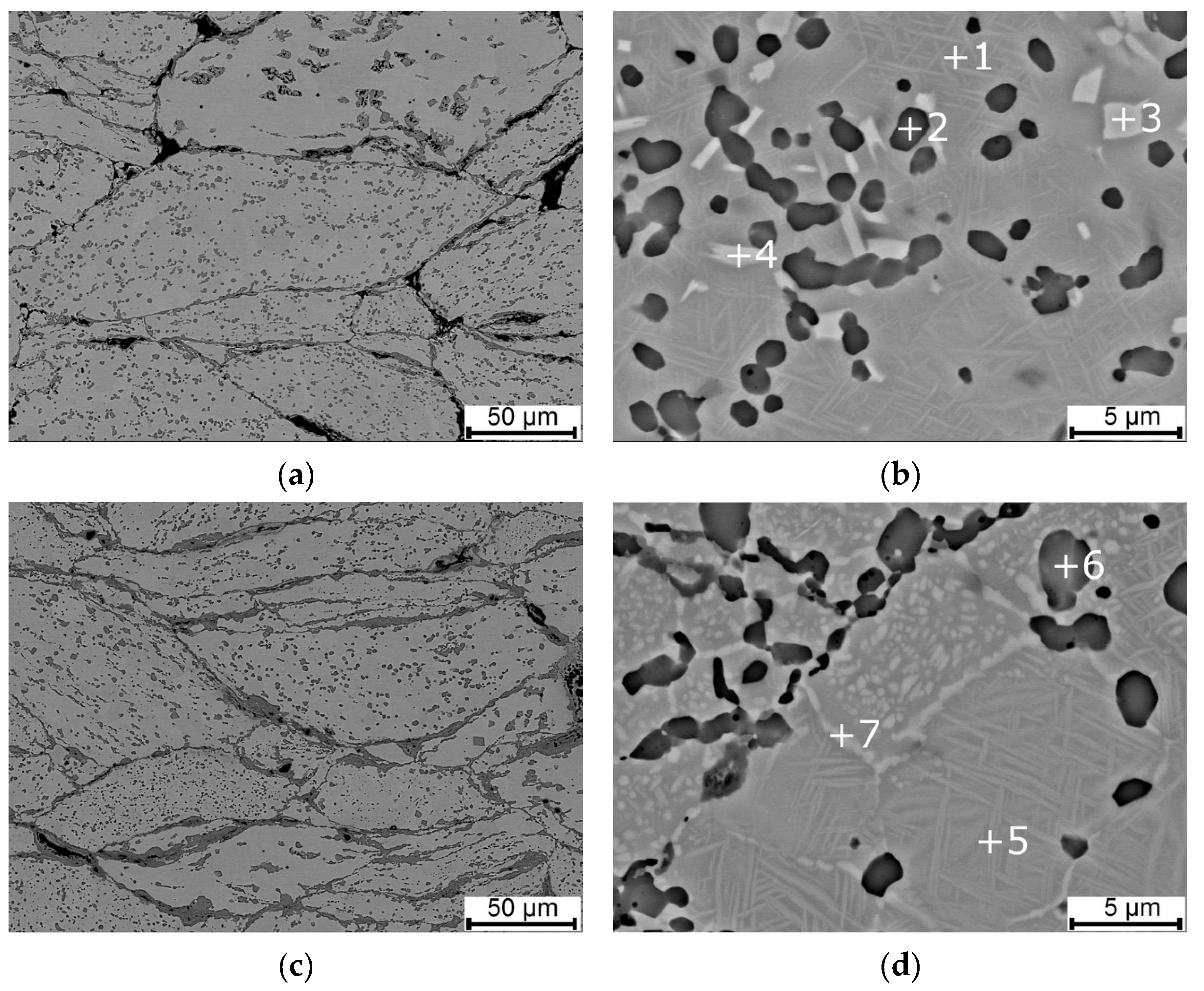
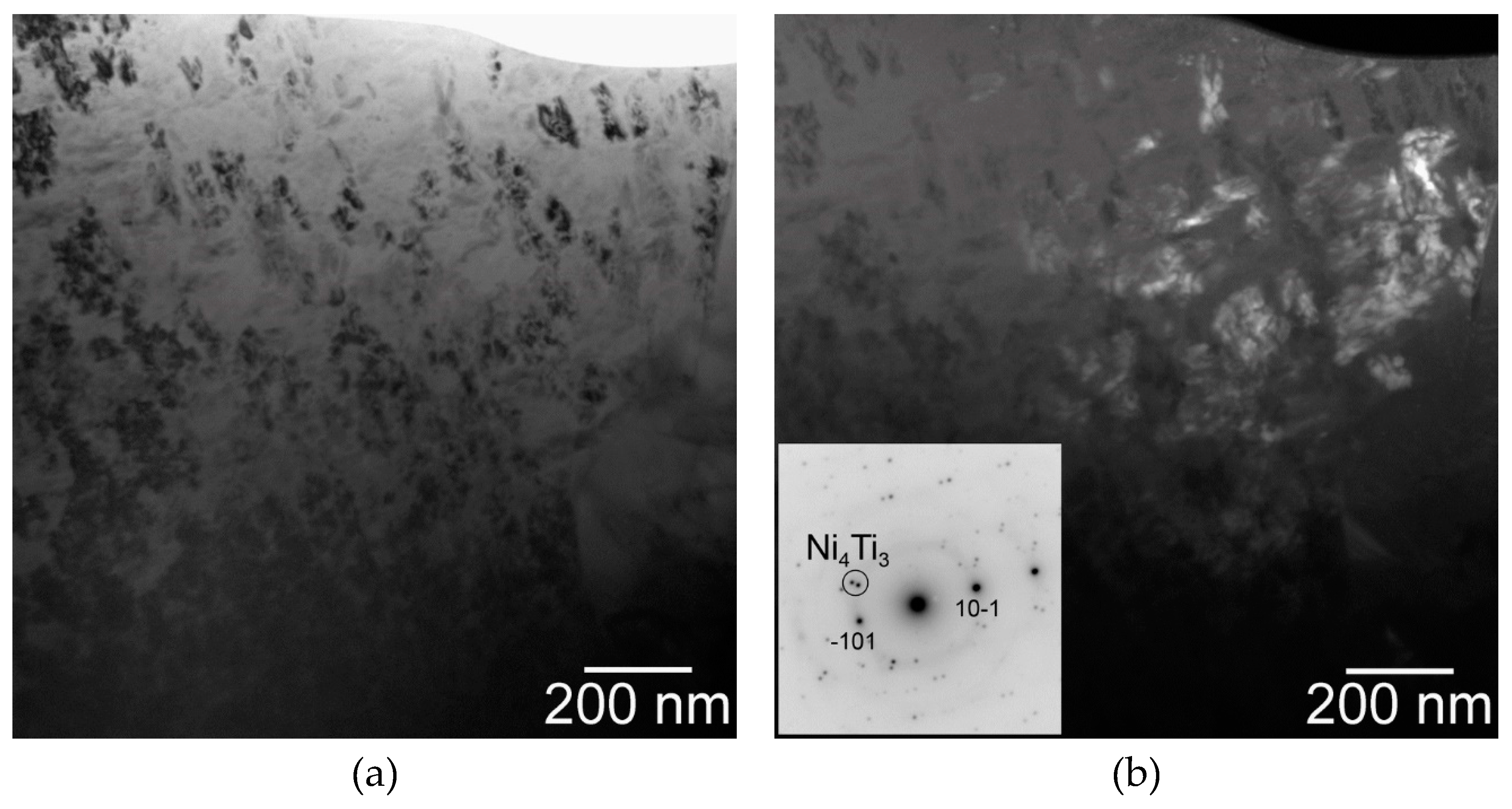
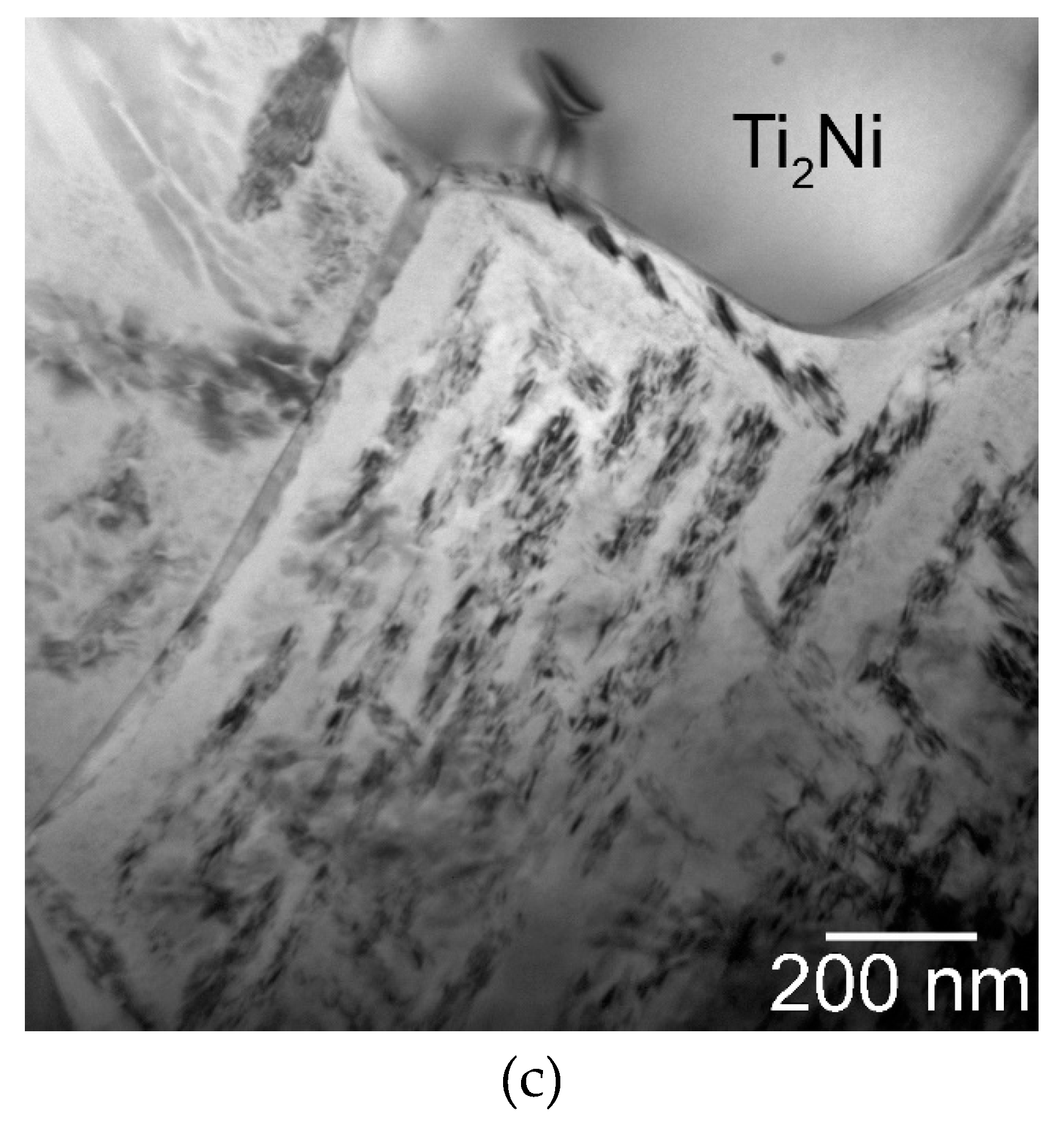
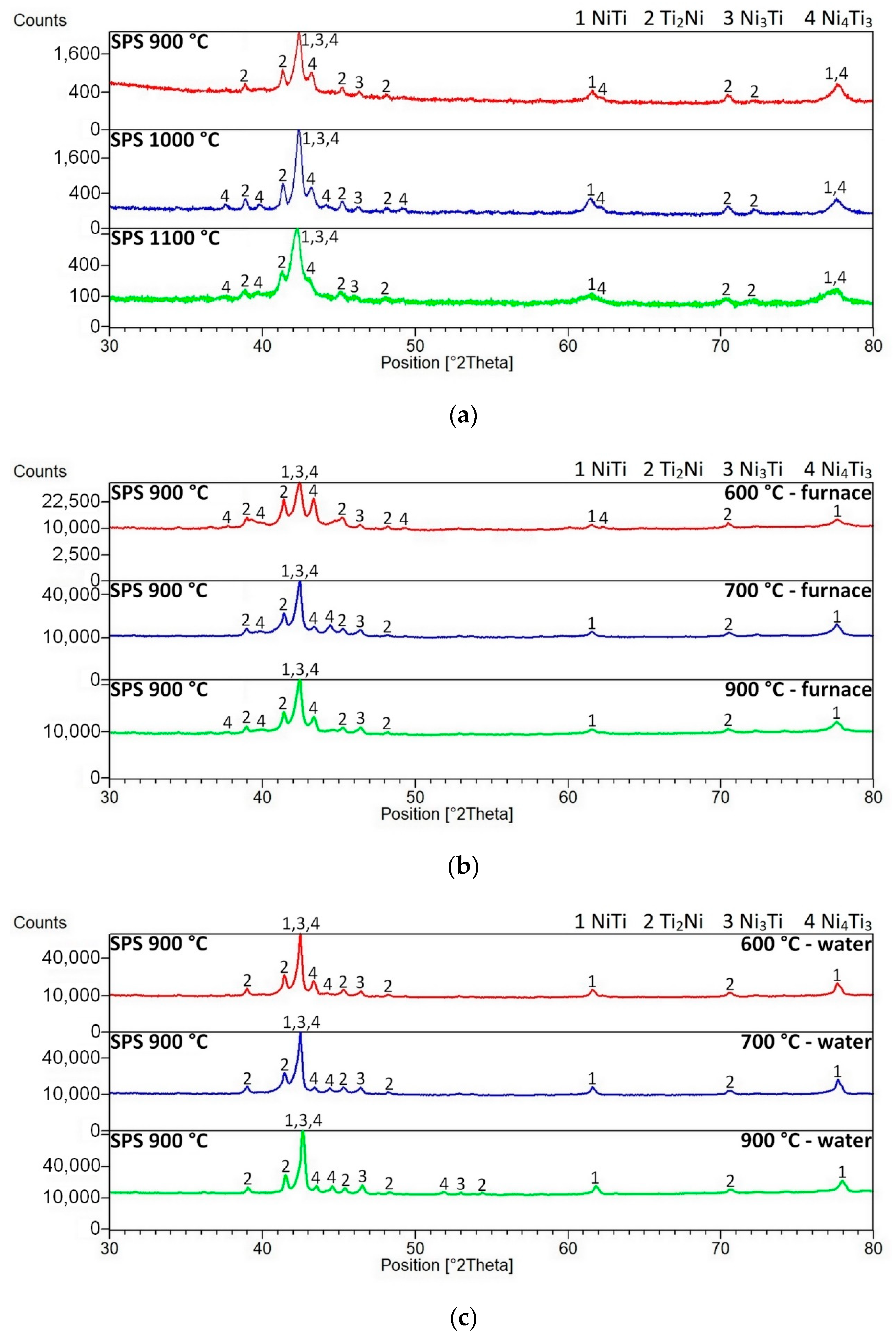
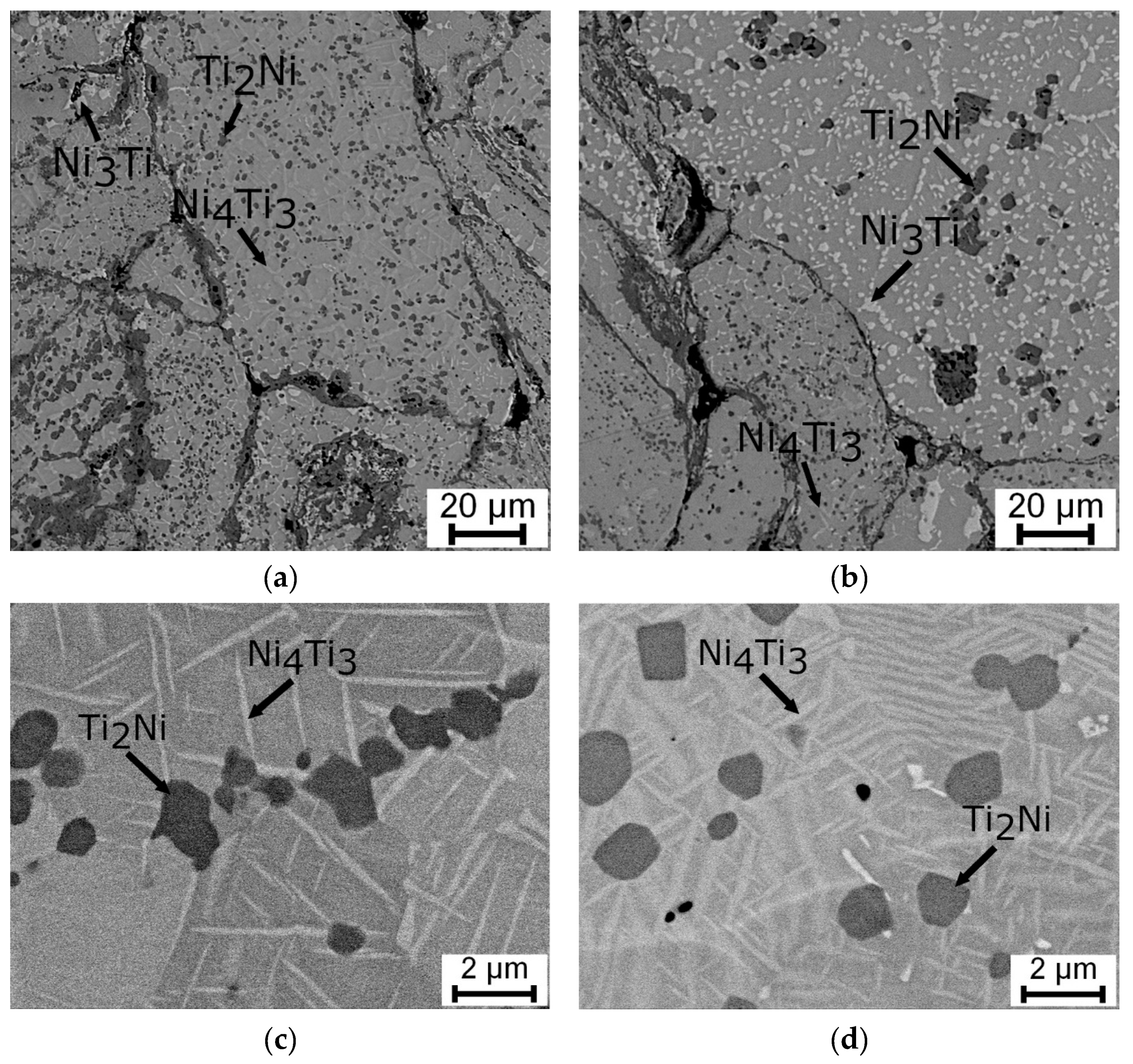
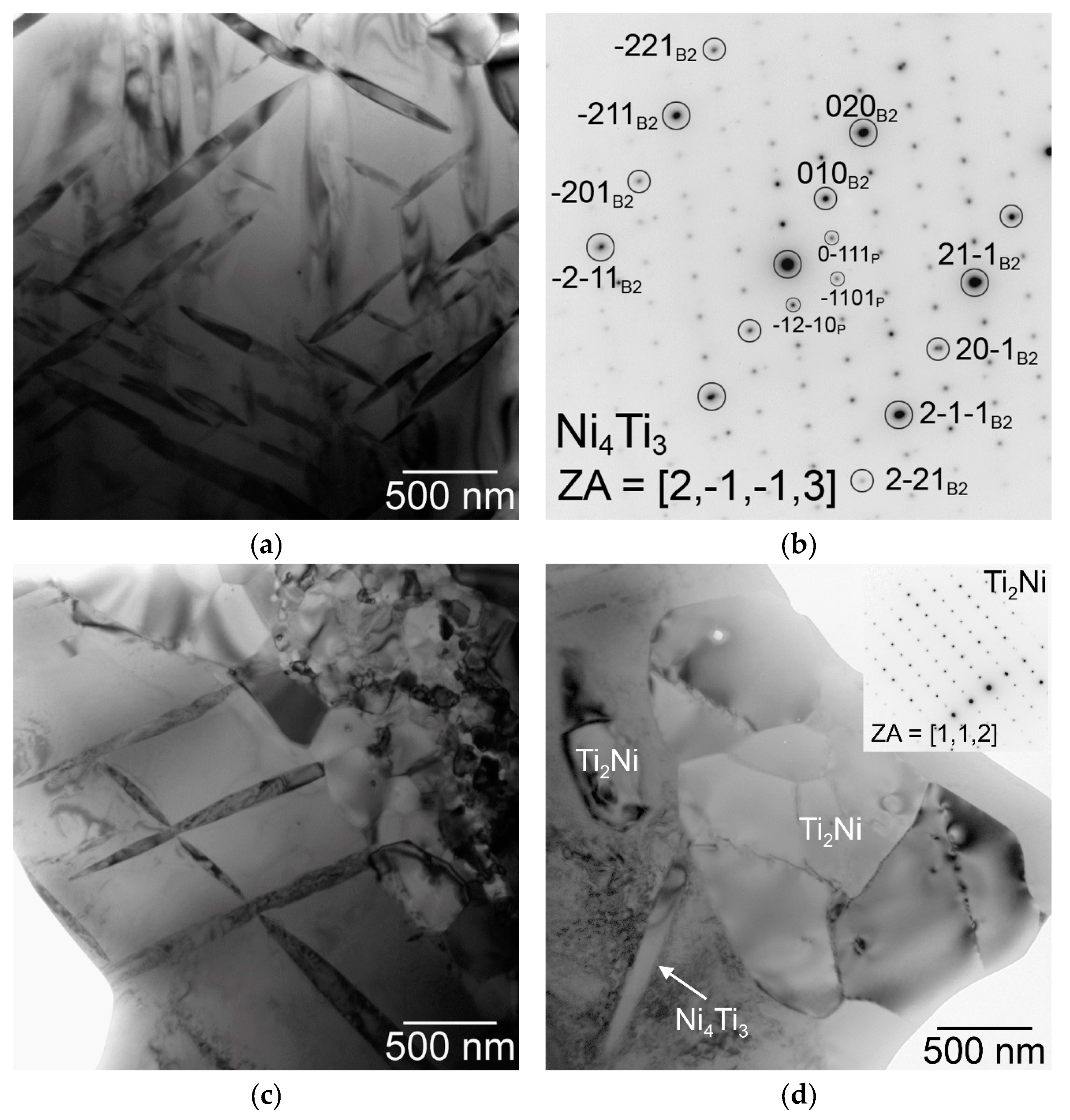
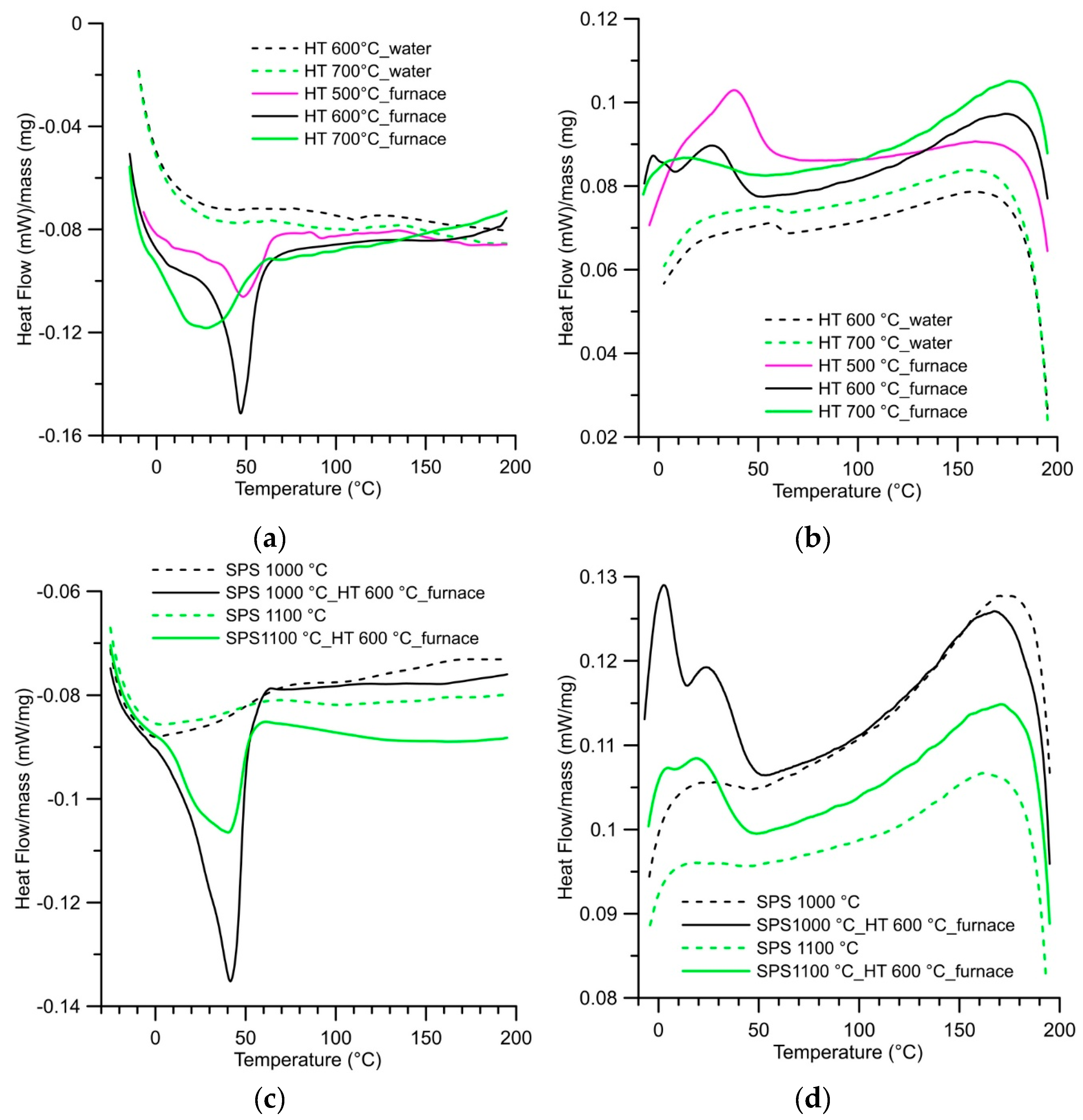
3.1. Microstructure, Phase Composition, and Phase Transformation
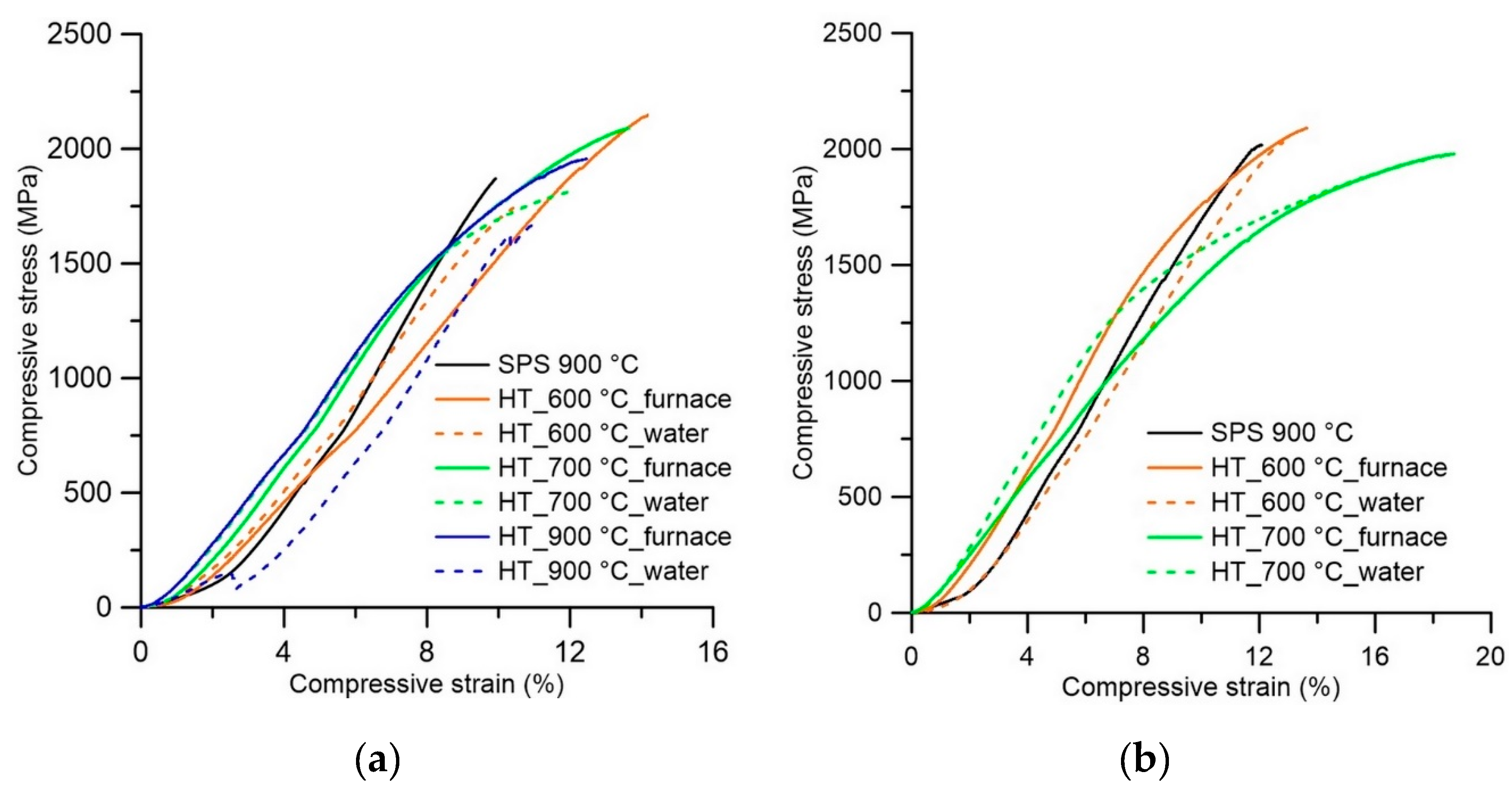
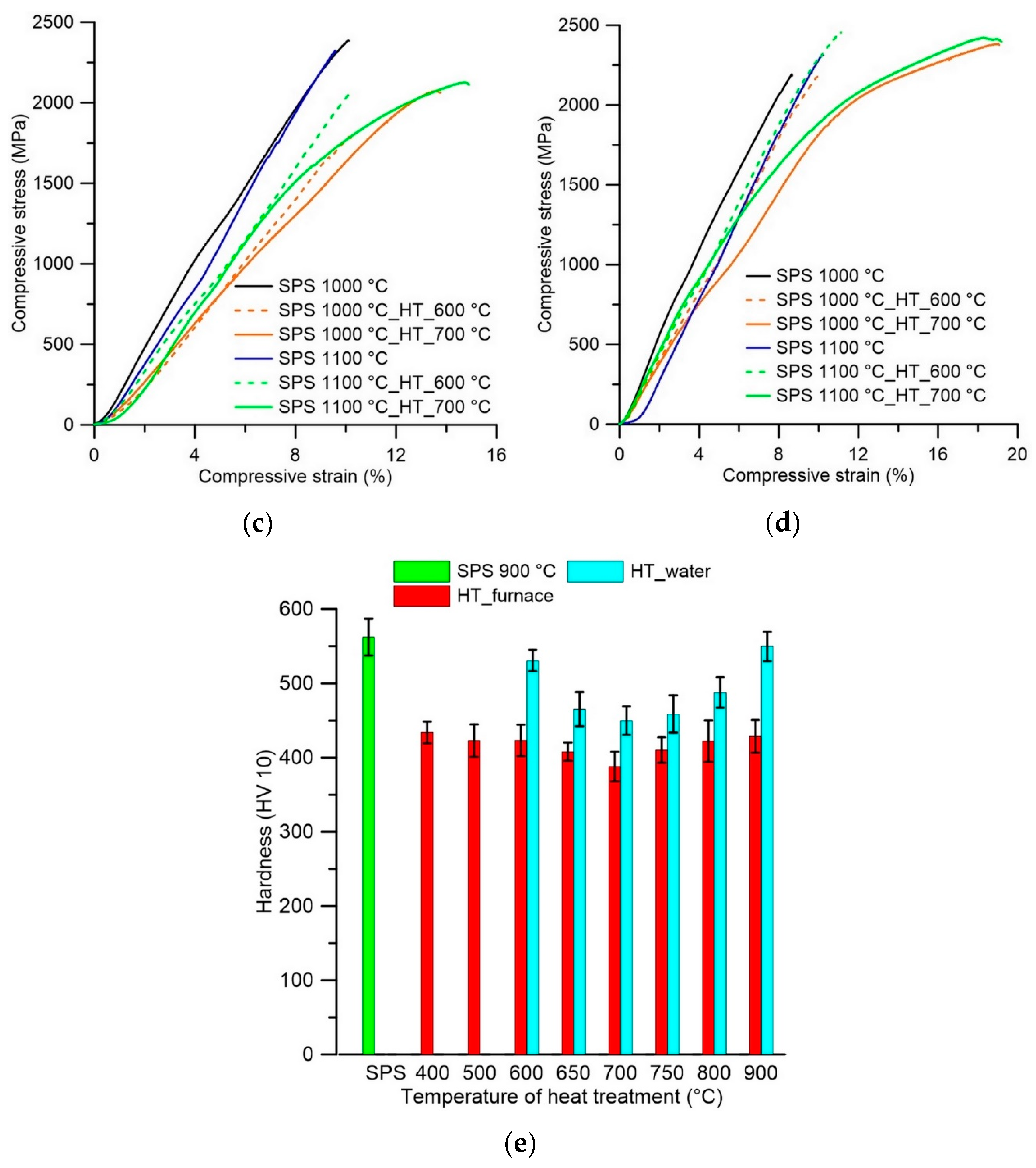
3.2. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Humbeeck, J. Shape Memory Alloys: A Material and a Technology. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2001, 3, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil-Allafi, J.; Dlouhy, A.; Eggeler, G. Ni4Ti3-precipitation during aging of NiTi shape memory alloys and its influence on martensitic phase transformations. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 4255–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Sundman, B.; Sandström, R.; Qiu, C. New modelling of the B2 phase and its associated martensitic transformation in the Ti–Ni system. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 3457–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayan, N.; Saikrishna, C.N.; Ramaiah, K.V.; Bhaumik, S.K.; Nair, K.S.; Mittal, M.C. Vacuum induction melting of NiTi shape memory alloys in graphite crucible. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 465, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Frenzel, J.; Neuking, K.; Eggeler, G. On the reaction between NiTi melts and crucible graphite during vacuum induction melting of NiTi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3971–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvildeev, V.N.; Panov, D.V.; Boldin, M.S.; Nokhrin, A.V.; Blagoveshchensky, Y.V.; Sakharov, N.V.; Shotin, S.V.; Kotkov, D.N. Structure and properties of advanced materials obtained by Spark Plasma Sintering. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 109, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, C.; Senthilkumar, V.; Biswas, K.; Yadav, S. Densification and microstructural evolution of spark plasma sintered NiTi shape memory alloy. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 2456–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Průša, F.; Šesták, J.; Školáková, A.; Novák, P.; Haušild, P.; Karlík, M.; Minárik, P.; Kopeček, J.; Laufek, F. Application of SPS consolidation and its influence on the properties of the FeAl20Si20 alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 761, 138020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Vanka, T.; Nová, K.; Stoulil, J.; Pruša, F.; Kopeček, J.; Haušild, P.; Laufek, F. Structure and properties of Fe-Al-Si alloy prepared by mechanical alloying. Materials 2019, 12, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusa, F.; Vojtech, D.; Kucera, V.; Bernatikova, A. Preparation of Ultrafine-Grained and Nano-crystalline Materials by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. Chem. Listy 2017, 111, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Novák, P.; Kubatík, T.; Vystrčil, J.; Hendrych, R.; Kříž, J.; Mlynár, J.; Vojtěch, D. Powder metallurgy preparation of Al–Cu–Fe quasicrystals using mechanical alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering. Intermetallics 2014, 52, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, I.; Vojtěch, D.; Michalcová, A.; Kubatík, T.F. High-strength bulk nano-crystalline silver prepared by selective leaching combined with spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 627, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Mejzlíková, L.; Michalcová, A.; Čapek, J.; Beran, P.; Vojtěch, D. Effect of SHS conditions on microstructure of NiTi shape memory alloy. Intermetallics 2013, 42, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Školáková, A.; Pignol, D.; Průša, F.; Salvetr, P.; Kubatík, T.F.; Perriere, L.; Karlík, M. Finding the energy source for self-propagating high-temperature synthesis production of NiTi shape memory alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 181, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Jiang, Y.H.; Zhou, R. Superelastic behaviors of biomedical porous NiTi alloy with high porosity and large pore size prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 644, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Taya, M.; Kang, Y.; Kawasaki, A. Compression behavior of porous NiTi shape memory alloy. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adharapurapu, R.R.; Jiang, F.; Vecchio, K.S. Aging effects on hardness and dynamic compressive behavior of Ti–55Ni (at.%) alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamei, A.A.; Dehghani, K. A study on the mechanical behavior and microstructural evolution of Ni60wt.%–Ti40wt.% (60Nitinol) intermetallic compound during hot deformation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 123, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdel, A.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Shamsolhodaei, A.; Krooß, P.; Niendorf, T. Room temperature superelastic responses of NiTi alloy treated by two distinct thermomechanical processing schemes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 684, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Fu, M.W.; Lin, J.; Ning, Y.Q. Effect of low-temperature aging treatment on thermally- and stress-induced phase transformations of nanocrystalline and coarse-grained NiTi wires. Mater. Des. 2017, 131, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocich, R.; Szurman, I.; Kursa, M.; Fiala, J. Investigation of influence of preparation and heat treatment on deformation behaviour of the alloy NiTi after ECAE. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 512, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, H.E.; Kaya, I.; Tobe, H.; Basaran, B.; Nagasako, M.; Kainuma, R.; Chumlyakov, Y. Shape memory behavior of high strength Ni54Ti46 alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 580, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, Z.X.; An, J.; Chua, C.K.; Shen, Y.F.; Kuo, C.N.; Liu, Y. Effect of heat treatment on repetitively scanned SLM NiTi shape memory alloy. Materials 2019, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saedi, S.; Turabi, A.S.; Taheri Andani, M.; Haberland, C.; Karaca, H.; Elahinia, M. The influence of heat treatment on the thermomechanical response of Ni-rich NiTi alloys manufactured by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 677, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, L.J.; Zhang, F.X.; Zhang, H. Thermal stability and hardening behavior in superelastic Ni-rich Nitinol alloys with Al addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 708, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, M.; Wayman, C.M.; Honma, T. Precipitation processes in near-equiatomic TiNi shape memory alloys. Metall. Trans. A 1986, 17, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvetr, P.; Novák, P.; Moravec, H. Ni-Ti alloys produced by powder metallurgy. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 15, 689–694. [Google Scholar]
- Salvetr, P.; Kubatík, T.F.; Pignol, D.; Novák, P. Fabrication of Ni-Ti Alloy by Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis and Spark Plasma Sintering Technique. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroz, D.; Kwarciak, J.; Morawiec, H. Effect of ageing on martensitic transformation in NiTi shape memory alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 1988, 23, 4127–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrnezhaad, S.K.; Mirabolghasemi, S.H. Optimum temperature for recovery and recrystallization of 52Ni48Ti shape memory alloy. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 1945–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Otsuka, K.; Ueki, T.; Mitose, K. Recovery and recrystallization processes in Ti-Pd-Ni high-temperature shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
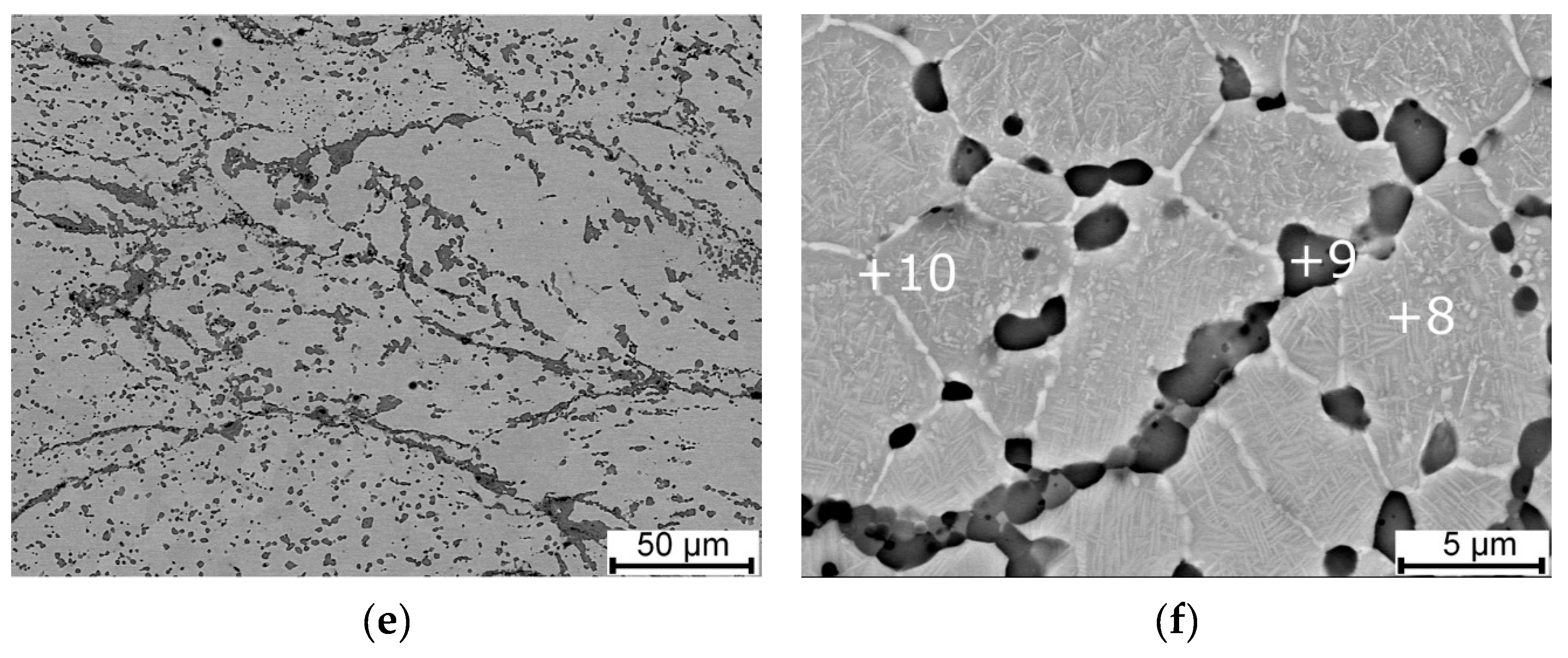
| Parameter | Direction | Spark Plasma Sintering Temperature | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 900 °C | 1000 °C | 1100 °C | ||
| Porosity (%) | Perpendicular | 1.6 ± 0.09 | 0.7 ± 0.16 | ˂ 0.1 |
| Longitudinal | 1.4 ± 0.09 | 0.1 ± 0.06 | ˂ 0.1 | |
| Area fraction of the Ti2Ni phase (%) | 13.8 ± 2.41 | 17.0 ± 2.22 | 11.9 ± 1.22 | |
| Area | Ni (wt.%) | Ti (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 54.4 | 45.6 |
| 2 | 38.0 | 62.0 |
| 3 | 72.4 | 27.6 |
| 4 | 68.6 | 31.4 |
| 5 | 55.5 | 44.5 |
| 6 | 38.0 | 62.0 |
| 7 | 58.7 | 41.3 |
| 8 | 55.2 | 44.8 |
| 9 | 37.6 | 62.4 |
| 10 | 59.1 | 40.9 |
| Sample | Crystallite Size (nm) |
|---|---|
| SPS 900 °C | 47 |
| SPS 1000 °C | 34 |
| SPS 1100 °C | 20 |
| SPS 900 °C-HT 600 °C-furnace | 25 |
| SPS 900 °C-HT 700 °C-furnace | 122 |
| SPS 900 °C-HT 900 °C-furnace | 28 |
| SPS 900 °C-HT 600 °C-water | 84 |
| SPS 900 °C-HT 700 °C-water | 129 |
| SPS 900 °C-HT 900 °C-water | 57 |
| SPS Temperature | 900 °C | 1000 °C | 1100 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV 10)/Std. dev. (±) | 562/25 | 596/20 | 624/23 | |
| Longitudinal | UCS (MPa) | 1903 | 2116 | 2315 |
| Agt (%) | 8.7 | 8.7 | 8.7 | |
| Perpendicular | UCS (MPa) | 1953 | 2212 | 2243 |
| Agt (%) | 7.4 | 9.4 | 8.6 | |
| Sample | Heat Treatment Regime | Hardness (HV 10)/Std. dev. (±) | Direction | UCS (MPa) | Agt (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPS 900 °C | 600 °C-furnace | 423/21 | Perpendicular | 2163 | 10.5 |
| Longitudinal | 2089 | 11.6 | |||
| SPS 900 °C | 600 °C-water | 531/14 | Perpendicular | 1508 | 7.6 |
| Longitudinal | 1994 | 9.9 | |||
| SPS 900 °C | 700 °C-furnace | 388/20 | Perpendicular | 1430 | 9.3 |
| Longitudinal | 1907 | 16.3 | |||
| SPS 900 °C | 700 °C-water | 450/19 | Perpendicular | 1566 | 9.3 |
| Longitudinal | 1878 | 13.7 | |||
| SPS 900 °C | 900 °C-furnace | 429/22 | Perpendicular | 1957 | 11.1 |
| SPS 900 °C | 900 °C-water | 550/20 | Perpendicular | 1670 | - |
| SPS 1000 °C | 600 °C-furnace | 504/21 | Perpendicular | 2089 | 9.5 |
| Longitudinal | 2235 | 9.2 | |||
| SPS 1000 °C | 700 °C-furnace | 444/14 | Perpendicular | 2099 | 12.5 |
| Longitudinal | 2355 | 18.5 | |||
| SPS 1100 °C | 600 °C-furnace | 509/22 | Perpendicular | 2295 | 10.0 |
| Longitudinal | 2488 | 10.6 | |||
| SPS 1100 °C | 700 °C-furnace | 448/10 | Perpendicular | 2163 | 13.6 |
| Longitudinal | 2465 | 19.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salvetr, P.; Dlouhý, J.; Školáková, A.; Průša, F.; Novák, P.; Karlík, M.; Haušild, P. Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of NiTi46 Alloy Consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials 2019, 12, 4075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244075
Salvetr P, Dlouhý J, Školáková A, Průša F, Novák P, Karlík M, Haušild P. Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of NiTi46 Alloy Consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials. 2019; 12(24):4075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244075
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalvetr, Pavel, Jaromír Dlouhý, Andrea Školáková, Filip Průša, Pavel Novák, Miroslav Karlík, and Petr Haušild. 2019. "Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of NiTi46 Alloy Consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering" Materials 12, no. 24: 4075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244075
APA StyleSalvetr, P., Dlouhý, J., Školáková, A., Průša, F., Novák, P., Karlík, M., & Haušild, P. (2019). Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of NiTi46 Alloy Consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering. Materials, 12(24), 4075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244075








