Characterisation of Electrical and Stiffness Properties of Conductive Textile Coatings with Metal Flake-Shaped Fillers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Substrate
2.1.2. Coating Formulation
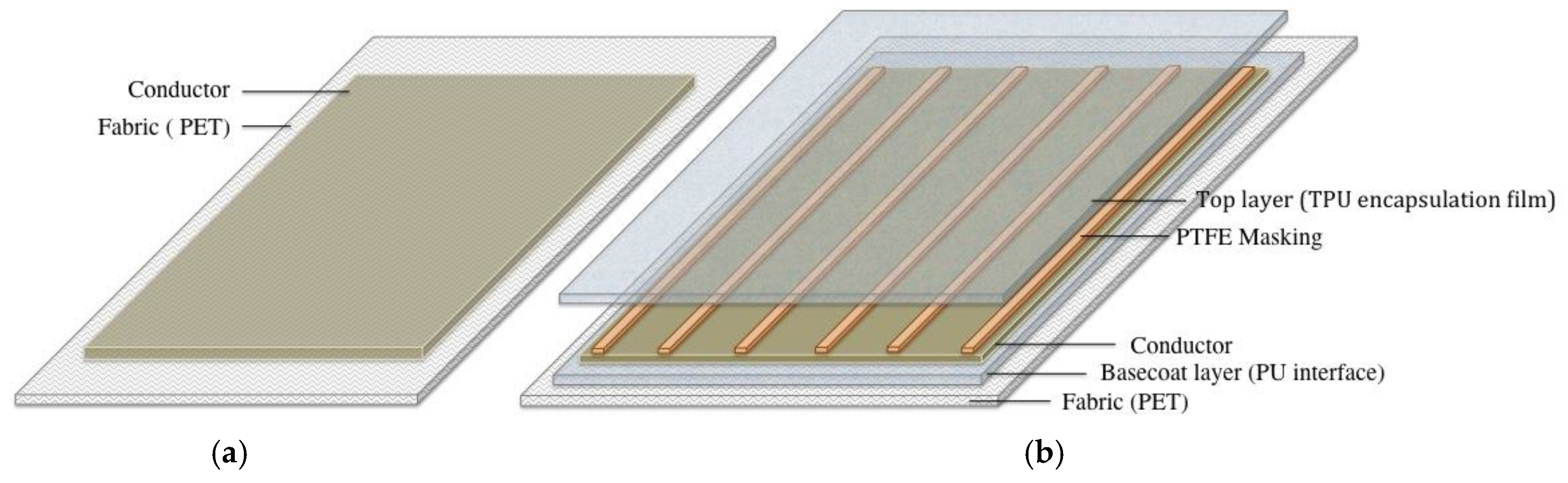
2.1.3. Sample Manufacturing
2.2. Characterisation
2.2.1. Viscosity
2.2.2. Surface Topography and Morphology
2.2.3. Flexural Stiffness
2.2.4. Electrical Resistance
2.3. Durability Test
2.3.1. Washing
2.3.2. Abrasion
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of the Formulation Type and Coating Parameters on the Physical, Electrical and Mechanical Properties
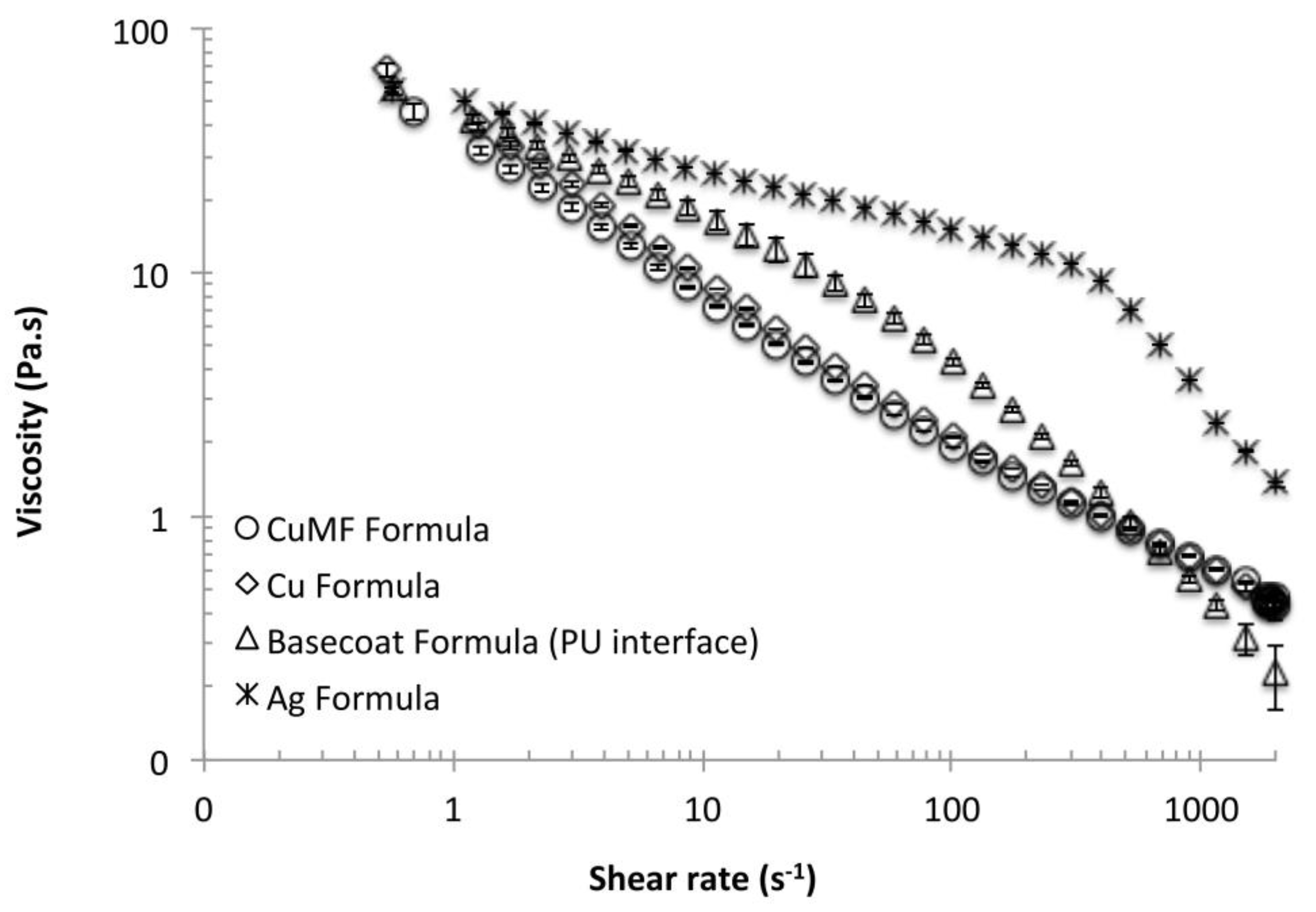
3.1.1. Viscosity Behaviour of the Formulations
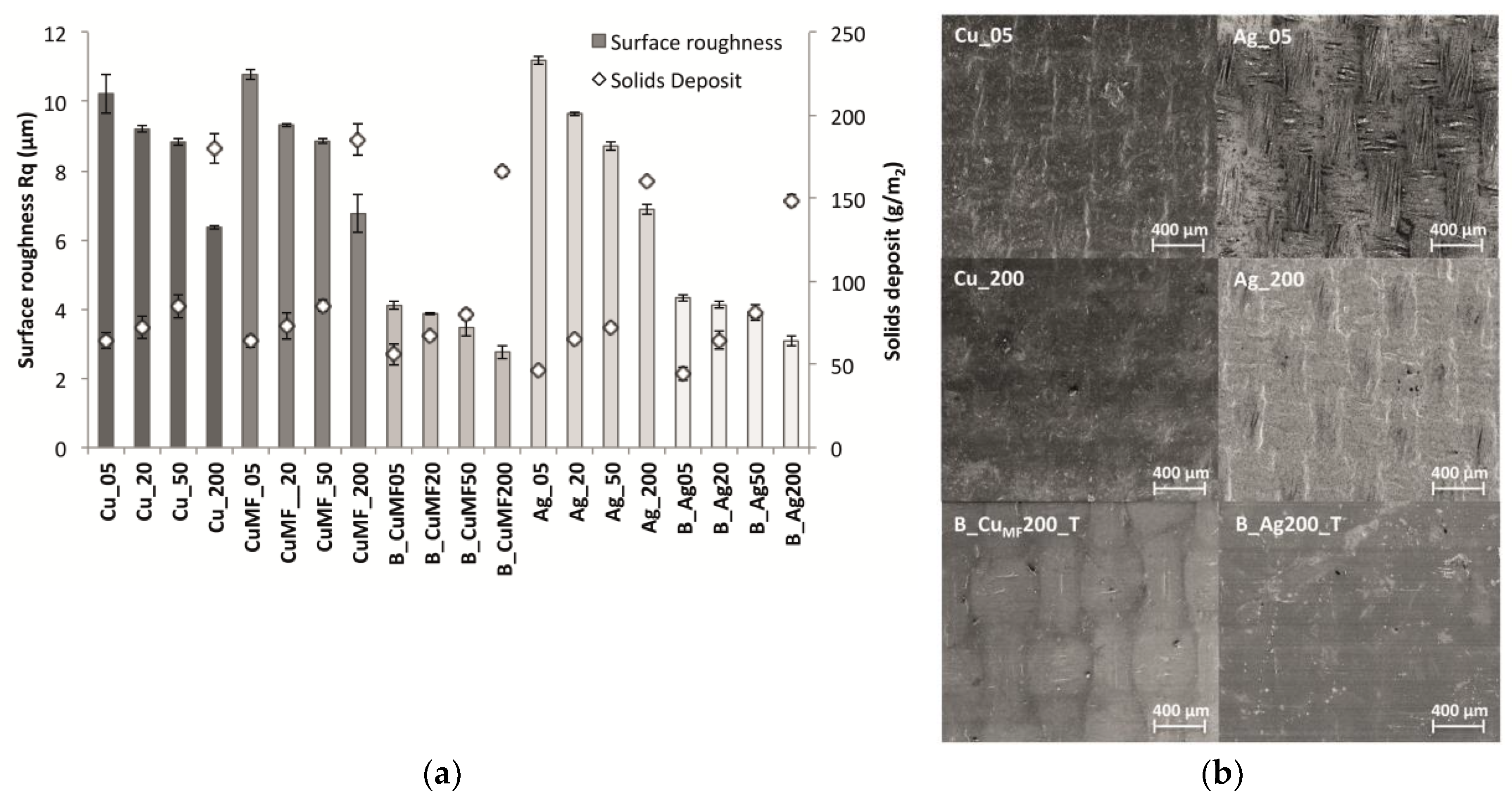
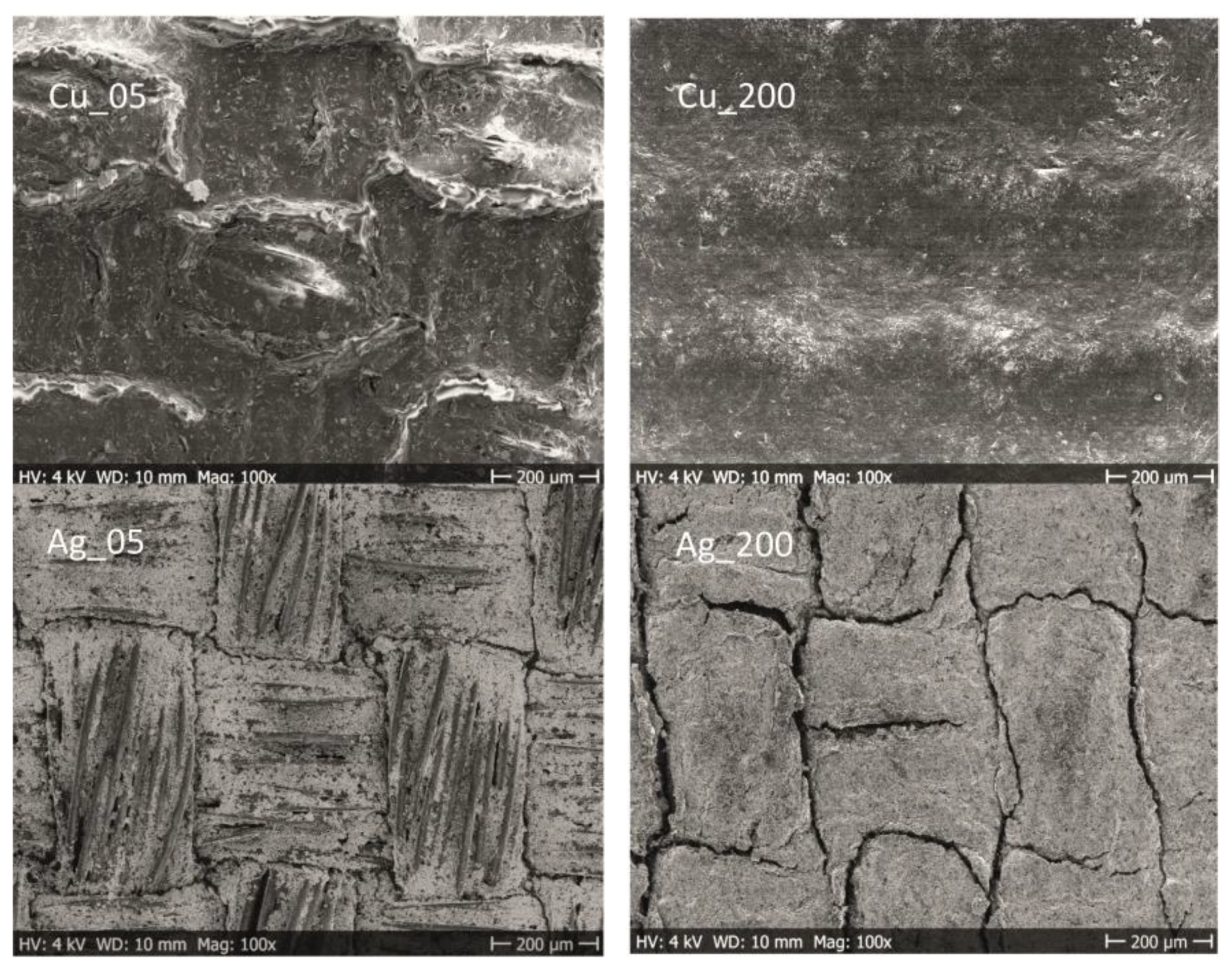
3.1.2. Influence of Solids Deposit on Surface Topography and Morphology
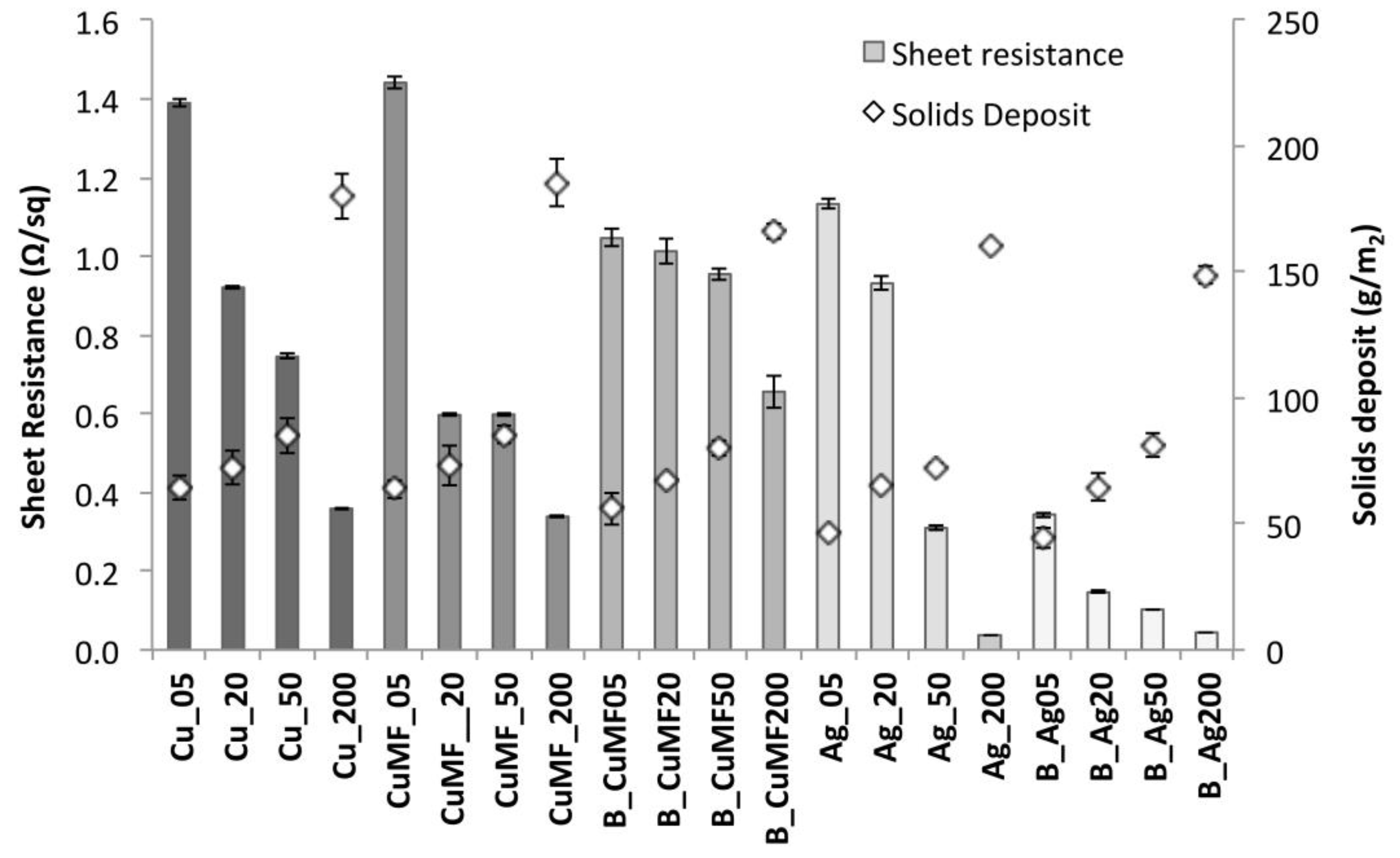
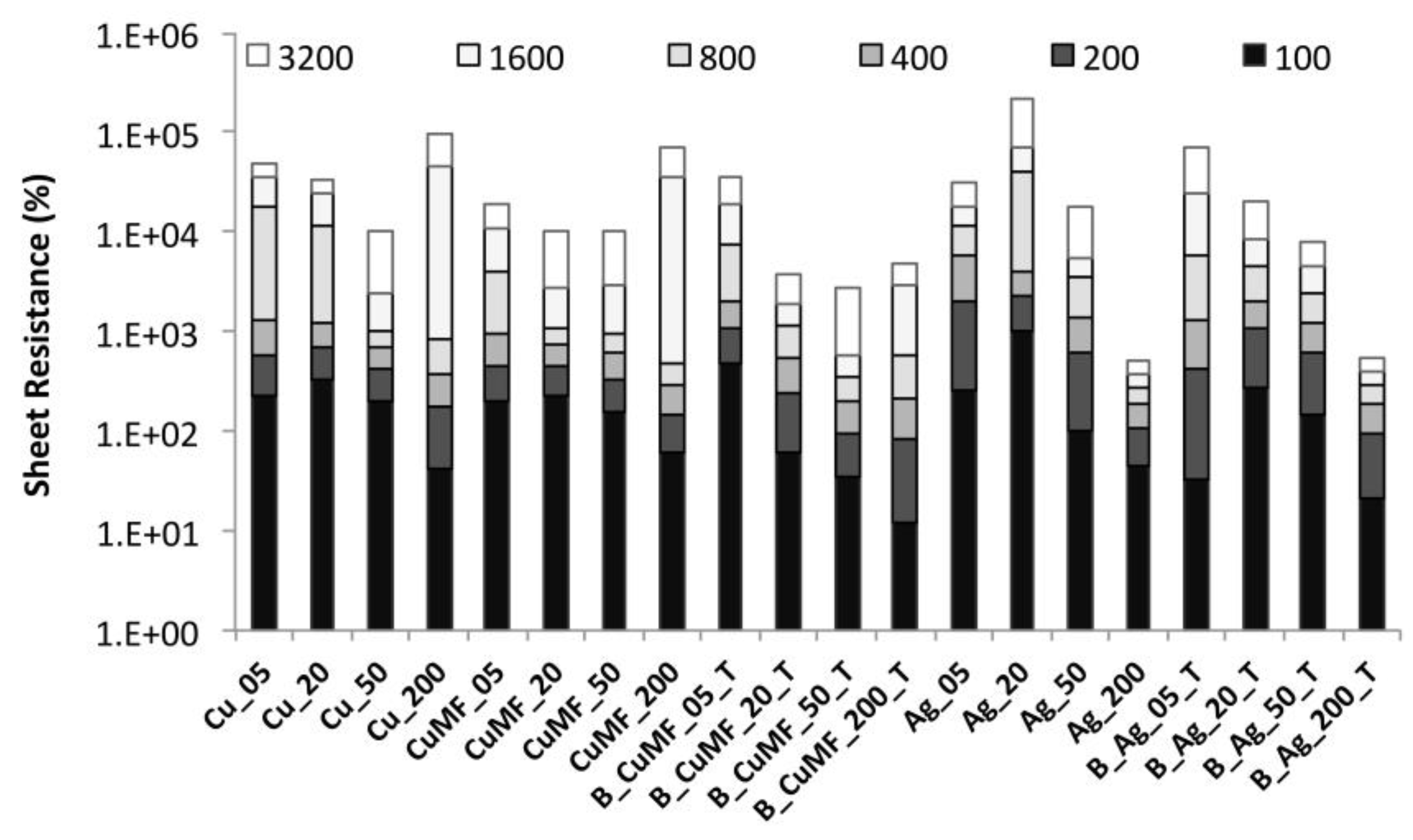
3.1.3. Influence of Solids Deposit on Electrical Resistance
3.1.4. Influence of Solids Deposit and Construction on Fabric Flexibility
3.2. Influence of Durability Testing on the Morphology and Electrical Properties
3.2.1. Influence of Washing on the Morphology
3.2.2. Influence of Washing on the Electrical Resistance
3.2.3. Encapsulation and Drying in between Washing Cycles.
3.2.4. Influence of Abrasion on the Electrical Resistance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Jin, H.; Nayeem, M.O.G.; Lee, S.; Matsuhisa, N.; Inoue, D.; Yokota, T.; Hashizume, D.; Someya, T. Highly Durable Nanofiber-Reinforced Elastic Conductors for Skin-Tight Electronic Textiles. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 7905–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topp, K.; Haase, H.; Degen, C.; Illing, G.; Mahltig, B. Coatings with metallic effect pigments for antimicrobial and conductive coating of textiles with electromagnetic shielding properties. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2014, 11, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasap, S.; Koughia, C.; Ruda, H.E. Electrical Conduction in Metals and Semiconductors. In Springer Handbook of Electronic and Photonic Materials; Kasap, S., Capper, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, R.; Ganta, D.; Guzman, C. Mechanical, in-situ electrical and thermal properties of wearable conductive textile yarn coated with polypyrrole/carbon black composite. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 6, 016307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, M.K.; Alkhidir, T.; Samad, Y.A.; Liao, K. Graphene-clad textile electrodes for electrocardiogram monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.; Torah, R.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. The development of screen printed conductive networks on textiles for biopotential monitoring applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 206, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, K. Recent Advances in Soft E-Textiles. Inventions 2018, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazani, I.; Hertleer, C.; De Mey, G.; Guxho, G.; Van Langenhove, L. Dry cleaning of electroconductive layers screen printed on flexible substrates. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merilampi, S.; Laine-Ma, T.; Ruuskanen, P. The characterization of electrically conductive silver ink patterns on flexible substrates. Microelectron. Reliab. 2009, 49, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Torah, R.; Wei, Y.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. Waterproof and durable screen printed silver conductive tracks on textiles. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon Paul, R.T.; Kai, Y.; Steve, B.; John, T. An investigation into the durability of screen-printed conductive tracks on textiles. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhisa, N.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Yokota, T.; Jinno, H.; Kuribara, K.; Sekitani, T.; Someya, T. Printable elastic conductors with a high conductivity for electronic textile applications. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komolafe, A.O.; Torah, R.N.; Yang, K.; Tudor, J.; Beeby, S.P. Durability of screen printed electrical interconnections on woven textiles. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 65th Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), San Diego, CA, USA, 26–29 May 2015; pp. 1142–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Wagener, S.; Dommershausen, N.; Jungnickel, H.; Laux, P.; Mitrano, D.; Nowack, B.; Schneider, G.; Luch, A. Textile Functionalization and Its Effects on the Release of Silver Nanoparticles into Artificial Sweat. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5927–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limpiteeprakan, P.; Babel, S.; Lohwacharin, J.; Takizawa, S. Release of silver nanoparticles from fabrics during the course of sequential washing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22810–22818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Rimmele, E.; Wichser, A.; Erni, R.; Height, M.; Nowack, B. Presence of nanoparticles in wash water from conventional silver and nano-silver textiles. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7208–7219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliga, A.R.; Skoglund, S.; Odnevall Wallinder, I.; Fadeel, B.; Karlsson, H.L. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: The role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvidsson, R.; Molander, S.; Sandén, B.A. Assessing the Environmental Risks of Silver from Clothes in an Urban Area. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2014, 20, 1008–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunda, M.; Kumar, P.; Katiyar, M. Review of Mechanical Characterization Techniques for Thin Films Used in Flexible Electronics. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 42, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnik, M.A.; Pinenq, P.; Krüger, C.; Zhang, J.; Yaneff, P.V. Crosslinking vs. interdiffusion rates in melamine-formaldehyde cured latex coatings: A model for waterborne automotive basecoat. J. Coat. Technol. 1999, 71, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerfeldt, M.; Strååt, M.; Walkenström, P. Influence of coating parameters on textile and electrical properties of a poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene): Poly(styrene sulfonate)/polyurethane-coated textile. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 2164–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Shear Rate (Formulation) | Solids Deposit (Conductor) | Drying Temp:Time | Annealing Temp:Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (s−1) | (g/m2) | (°C:min) | (°C:min) | |
| Cu_05 | 2000 | 64 | 80:5 | 150:2 |
| Cu_20 | 500 | 72 | 80:10 | 150:3 |
| Cu_50 | 200 | 85 | 80:15 | 150:4 |
| Cu_200 | 50 | 180 | 80:20 | 150:5 |
| CuCL_05 | 2000 | 64 | 80:5 | 150:2 |
| CuCL_20 | 500 | 73 | 80:10 | 150:3 |
| CuCL_50 | 200 | 85 | 80:15 | 150:4 |
| CuCL_200 | 50 | 185 | 80:20 | 150:5 |
| B_CuMF05_T | 2000 | 56 | 80:5 | 150:2 |
| B_CuMF20_T | 500 | 67 | 80:10 | 150:3 |
| B_CuMF50_T | 200 | 80 | 80:15 | 150:4 |
| B_CuMF200_T | 50 | 166 | 80:20 | 150:5 |
| Ag_05 | 2000 | 47 | - | 130:20 |
| Ag_20 | 500 | 65 | - | 130:30 |
| Ag_50 | 200 | 72 | - | 130:50 |
| Ag_200 | 50 | 160 | - | 150:40 |
| B_Ag05_T | 2000 | 44 | - | 130:20 |
| B_Ag20_T | 500 | 64 | - | 130:30 |
| B_Ag50_T | 200 | 81 | - | 130:50 |
| B_Ag200_T | 50 | 149 | - | 150:40 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malm, V.; Seoane, F.; Nierstrasz, V. Characterisation of Electrical and Stiffness Properties of Conductive Textile Coatings with Metal Flake-Shaped Fillers. Materials 2019, 12, 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12213537
Malm V, Seoane F, Nierstrasz V. Characterisation of Electrical and Stiffness Properties of Conductive Textile Coatings with Metal Flake-Shaped Fillers. Materials. 2019; 12(21):3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12213537
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalm, Veronica, Fernando Seoane, and Vincent Nierstrasz. 2019. "Characterisation of Electrical and Stiffness Properties of Conductive Textile Coatings with Metal Flake-Shaped Fillers" Materials 12, no. 21: 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12213537
APA StyleMalm, V., Seoane, F., & Nierstrasz, V. (2019). Characterisation of Electrical and Stiffness Properties of Conductive Textile Coatings with Metal Flake-Shaped Fillers. Materials, 12(21), 3537. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12213537





