A Comparative Study on the Effects of Au, ZnO and AZO Seed Layers on the Performance of ZnO Nanowire-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Seed Layers Preparation
2.2. ZnO Nanowires Synthesis
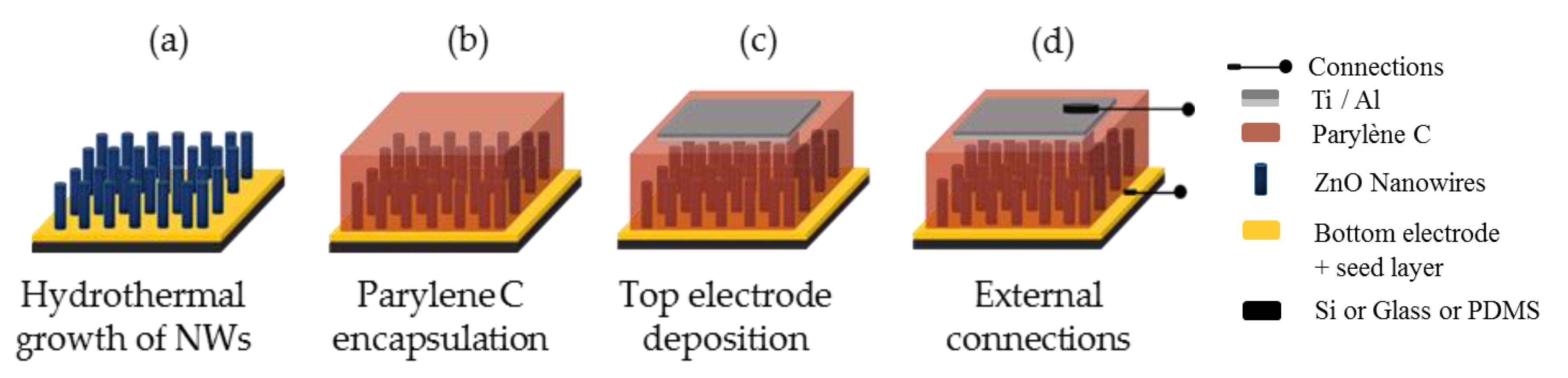
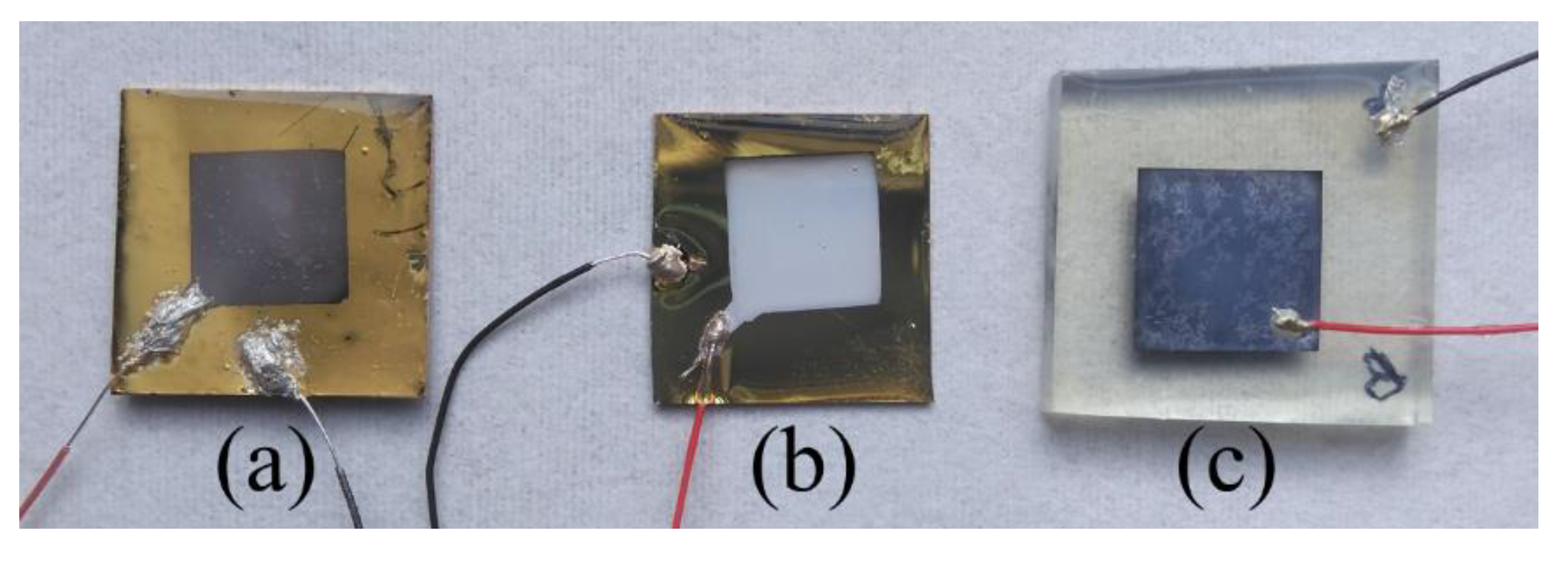
2.3. Nanogenerator Fabrication
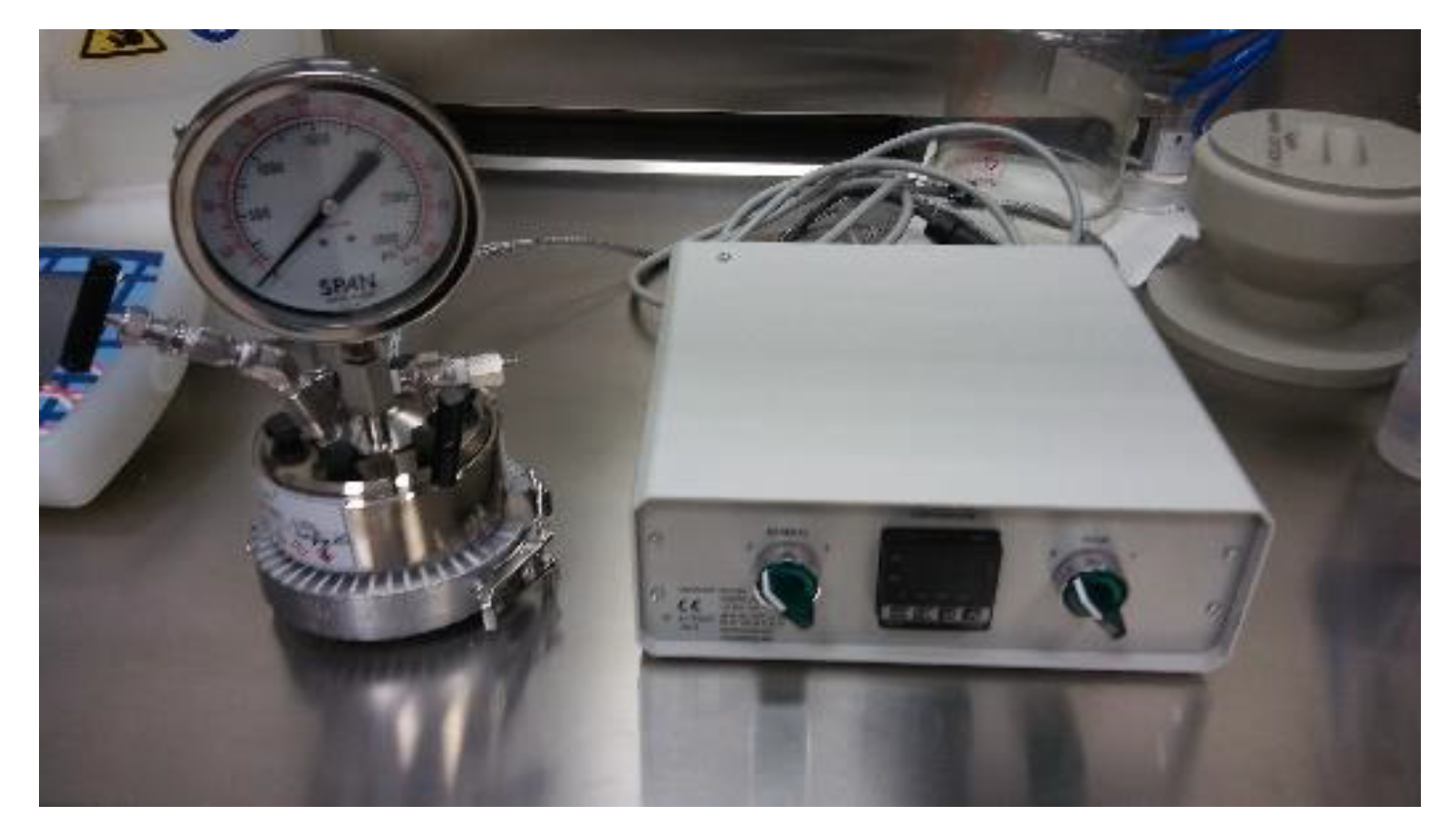
2.4. Characterizations
3. Results
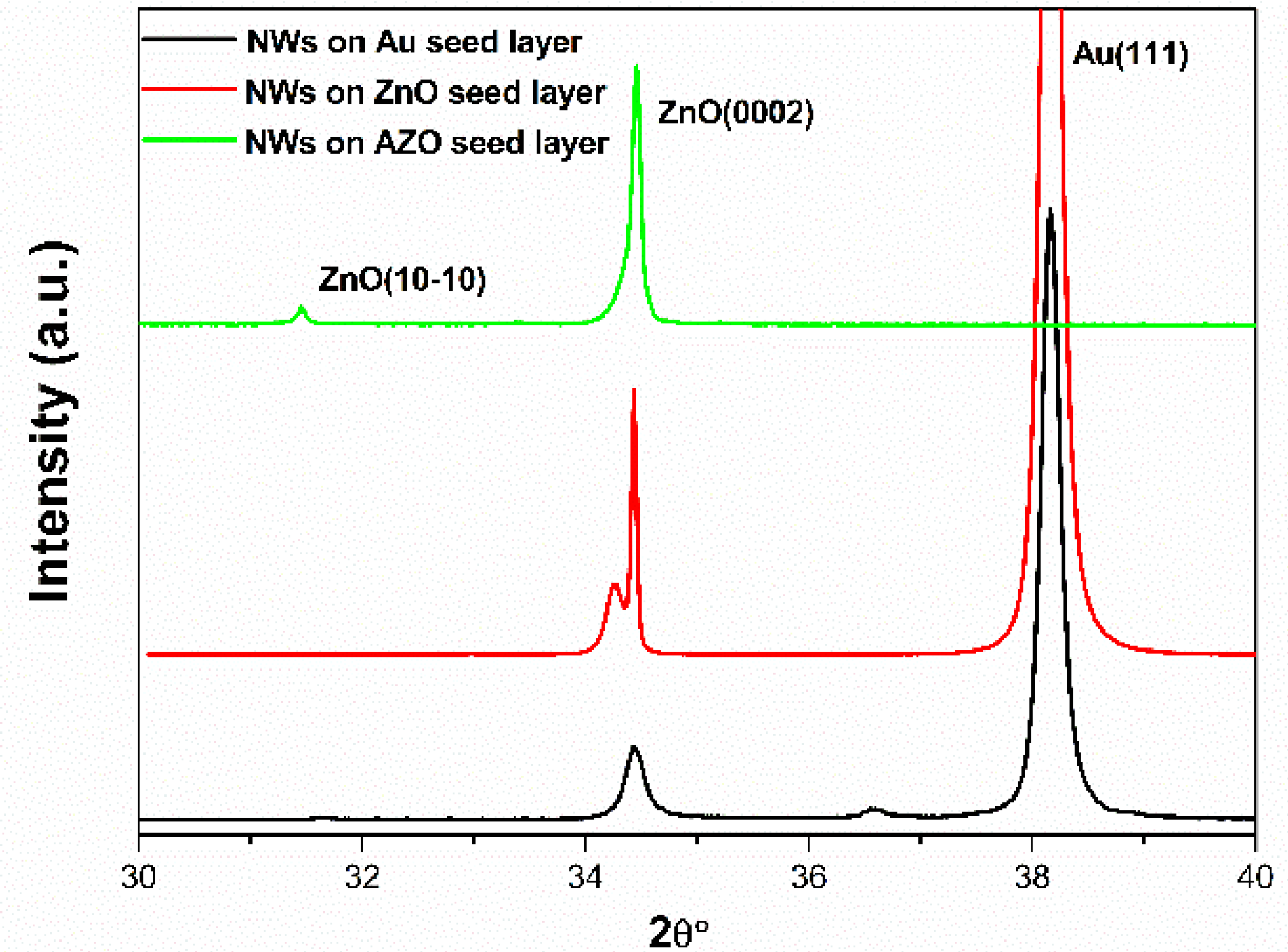
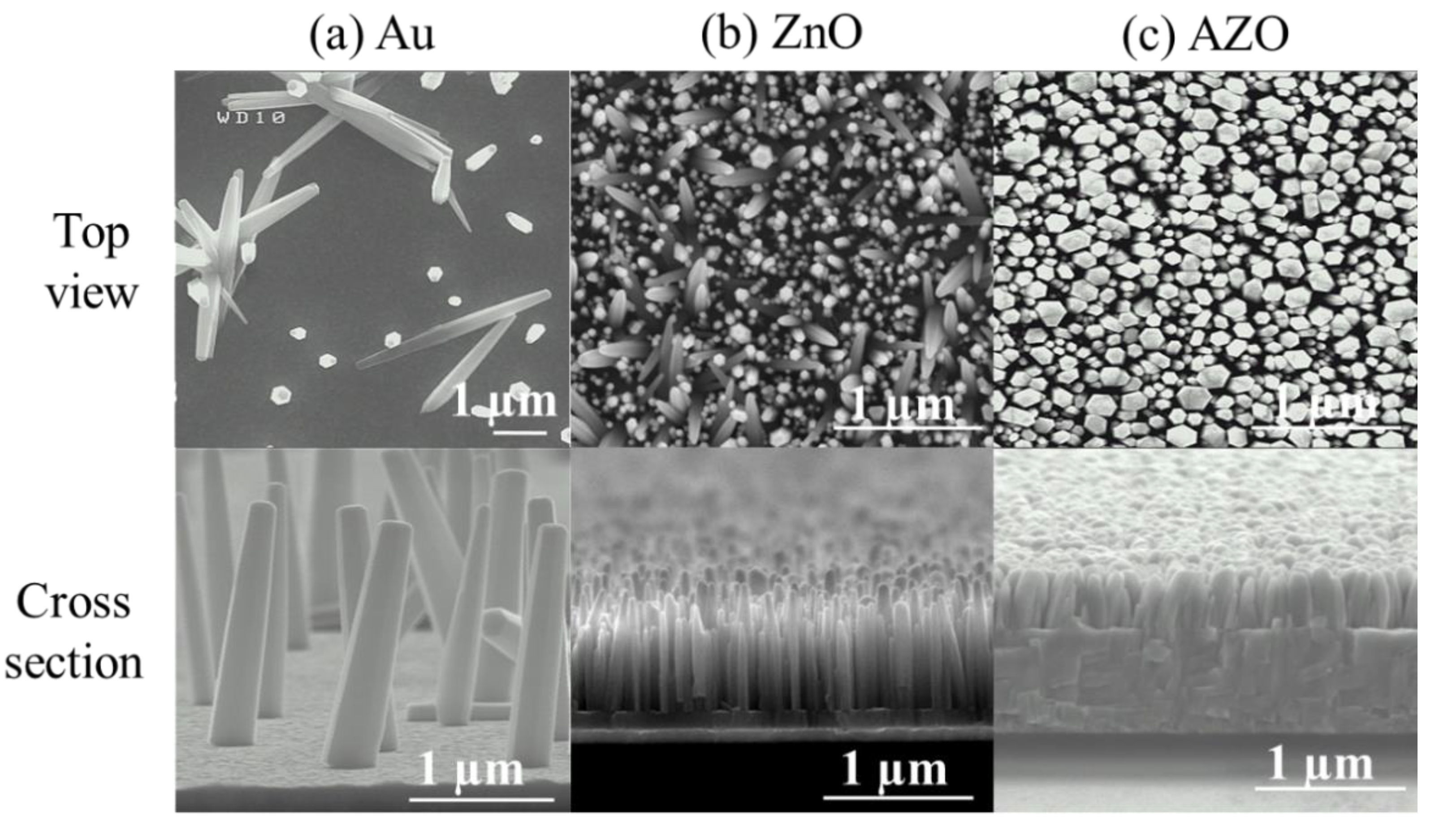
3.1. Structural Characterizations
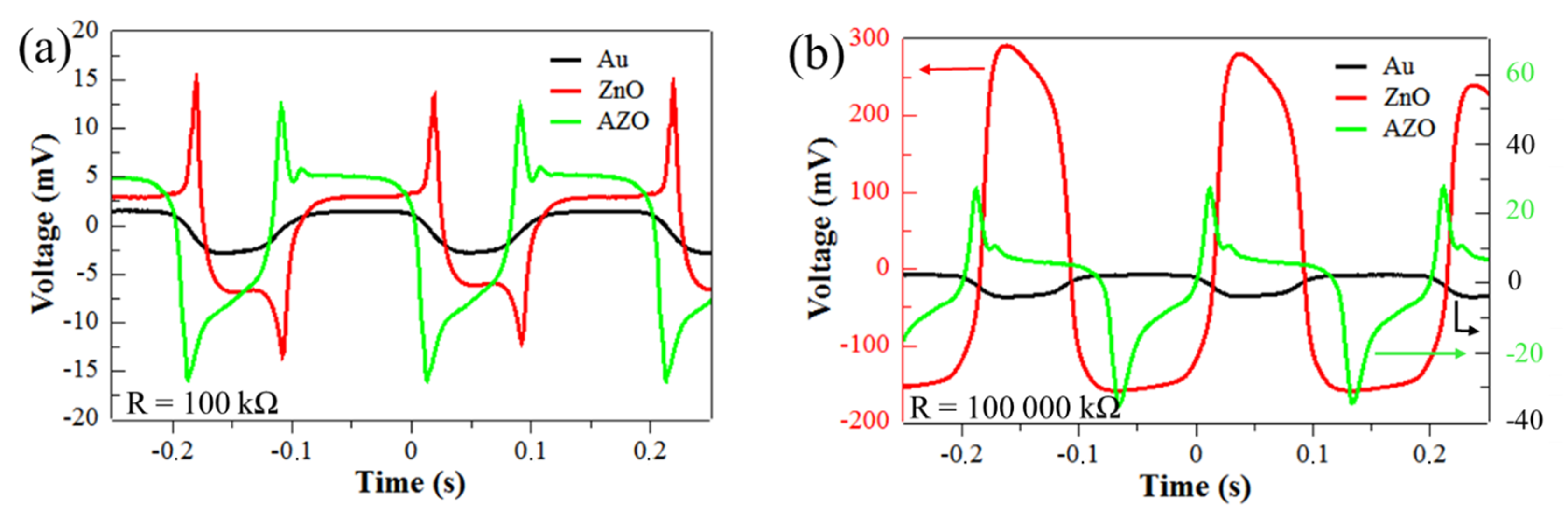
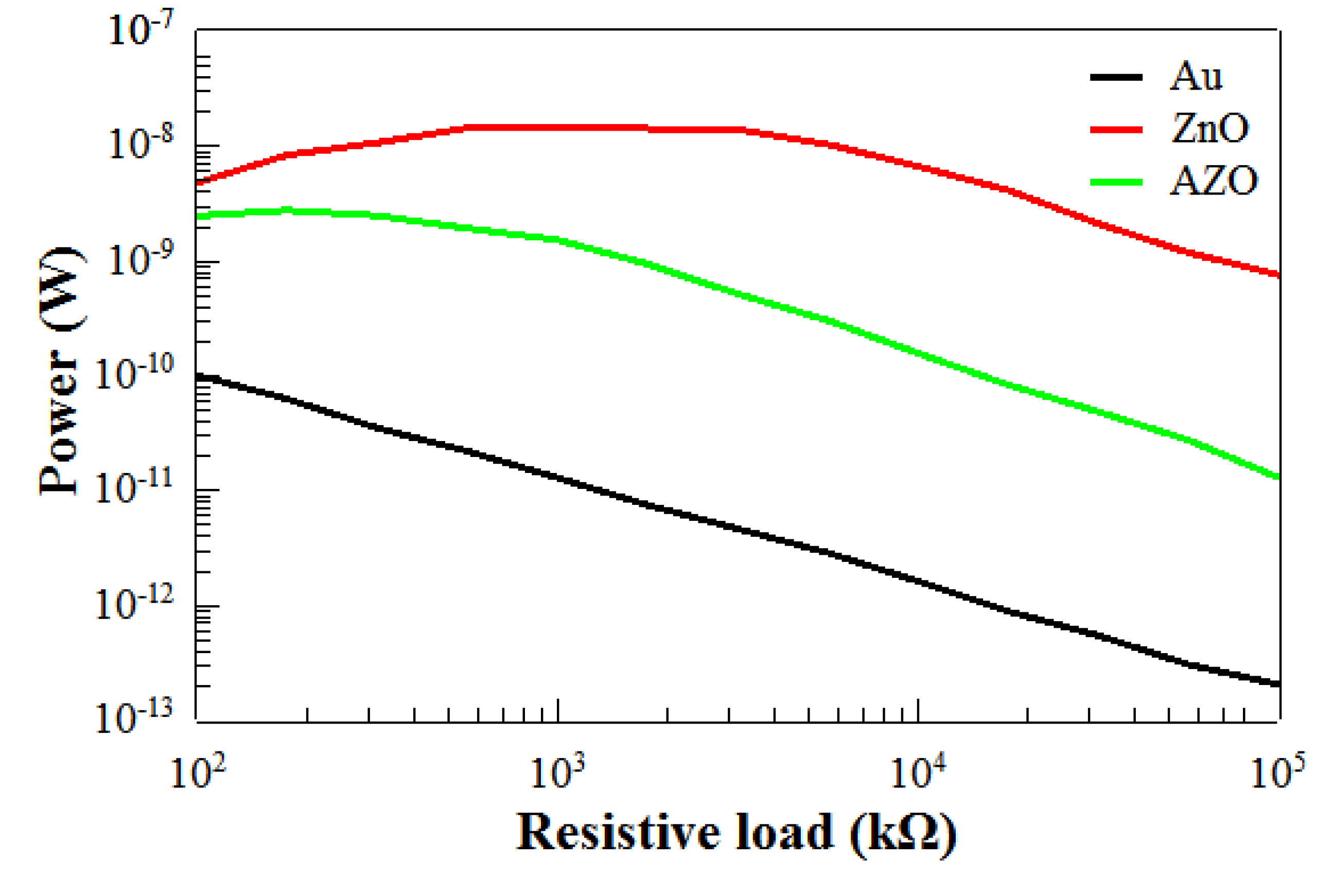
3.2. Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Device Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Khandelwal, G.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Alluri, N.R.; Vivekanathan, V.; Raj, N.P.M.J.; Kim, S.J. Trash to energy: A facile, robust and cheap approach for mitigating environment pollutant using household triboelectric nanogenerator ward cost-effective solar energy use. Appl. Energy 2018, 219, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Yao, N.; Shi, Y. 1.6 V Nanogenerator for mechanical energy harvesting using PZT nanofibers. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2133–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Yang, J.; Bai, P.; Su, Y.; Jing, Q.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting energy from the natural vibration of human walking. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11317–11324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudem, B.; Huynh, N.D.; Kim, W.; Kim, D.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Choi, D. Nanopillar-array architectured PDMS-based triboelectric nanogenerator integrated with a windmill model for effective wind energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2017, 42, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudem, B.; Kim, D.H.; Yu, J.S. Triboelectric nanogenerators with gold-thin-film-coated conductive textile as floating electrode for scavenging wind energy. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Zeng, W.; Wang, H.; Qian, M.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z. Self-Assembled Biomolecular 1D Nanostructures for Aqueous Sodium-Ion Battery. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudem, B.; Kim, D.H.; Bharat, L.K.; Yu, J.S. Highly-flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators with silver nanowires and barium titanate embedded composite films for mechanical energy harvesting. Appl. Energy 2018, 230, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsidjodoung, P.; Le Pierrès, N.; Luo, L. A Review of potential materials for thermal energy storage on building applications. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 327–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, C.; Cuevas, A.; De Wolf, S. High-efficiency crystalline silicon solar cells: status and perspectives. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1552–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Yeh, M.H.; Pan, C.; Lin, L.; Yu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, Z.L. A Streaming Potential/Current-Based Microfluidic Direct Current Generator for Self-Powered Nanosystems. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6482–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, W.; Pradel, K.C.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Pyroelectric nanogenerators for harvesting thermoelectric energy. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2833–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sun, M.; Wei, X.; Shan, C.; Chen, Q. 1D Piezoelectric Material Based Nanogenerators: Methods, Materials and Property Optimization. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Wang, S.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Hybridizing energy conversion and storage in a mechanical-to-electrochemical process for self-charging power cell. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5048–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.B.; Chang, J.; Koh, K.; Lin, L.; Cho, Y.S. High quality Mn-doped (Na,K)NbO3 nanofibers for flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 10576–10582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakua, I.; Afzulpurkar, N. Piezoelectric energy generation and harvesting at the nano-scale: materials and devices. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2013, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, M.; Novak, N.; Rojas, V.; Patel, S.; Vaish, R.; Koruza, J.; Rossetti, G.A., Jr.; Rödel, J. BaTiO3-based piezoelectrics: Fundamentals, current status, and perspectives. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2017, 4, 041305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alluri, N.; Selvarajan, S.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Saravanakumar, B.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, S.J. Piezoelectric BaTiO3/alginate spherical composite beads for energy harvesting and self-powered wearable flexion sensor. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 142, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Bai, S.; Yuan, M.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Jing, T. Lead zirconate titanate nanowire textile nanogenerator for wearable energy-harvesting and self-powered devices. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6231–6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Jia, W.; Qian, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Hou, X.; Mu, J.; Geng, W.; Cho, J.; He, J.; et al. High-performance PZT-based stretchable piezoelectric nanogenerator. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadaud, K.; Morini, F.; Dahiya, A.S.; Justeau, C.; Boubenia, S.; Rajeev, K.P.; Alquier, D.; Poulin-Vittrant, G. Double buffer circuit for the characterization of piezoelectric nanogenerators based on ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 063901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, G.C.; Chang, H.; Wang, J.H. Fabrication of ZnO nanowires arrays by anodization and high-vacuum die casting technique, and their piezoelectric properties. Sensors 2016, 16, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K. Review: Environmental friendly lead-free piezoelectric materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 5049–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Song, J. Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janotti, A.; Van de Walle, C.G. Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2009, 72, 126501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, T.; Sun, R.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, W.; Wang, Z. Hollow, porous, and yttrium functionalized ZnO nanospheres with enhanced gas-sensing performances. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2013, 178, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Yang, R.; Zhou, J.; Qin, Y.; Xu, C.; Hu, Y.; Xu, S. Lateral nanowire/nanobelt based nanogenerators, piezotronics and piezo-phototronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 2010, 70, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Abbasi, M.A.; Wissting, J.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Harvesting piezoelectric potential from zinc oxide nanoflowers grown on textile fabric substrate. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 2013, 7, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Abbasi, M.A.; Hussain, M.; Ibupoto, Z.H.; Wissting, J.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Piezoelectric nanogenerator based on zinc oxide nanorods grown on textile cotton fabric. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 193506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin-Vittrant, G.; Oshman, C.; Opoku, C.; Dahiya, A.S.; Camara, N.; Alquier, D.; Tran Huu Hue, L.P.; Lethiecq, M. Fabrication and Characterization of ZnO Nanowire-based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators for Low Frequency Mechanical Energy Harvesting. Phys. Procedia 2015, 70, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, C.; Dahiya, A.S.; Oshman, C.; Daumont, C.; Cayrel, F.; Poulin-Vittrant, G.; Alquier, D.; Camara, N. Fabrication of high performance field-effect transistors and practical Schottky contacts using hydrothermal ZnO nanowires. Nanotechnol. 2015, 26, 355704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlemcani, T.S.; Justeau, C.; Nadaud, K.; Poulin-Vittrant, G.; Alquier, D. Deposition Time and Annealing effects of ZnO seed layer on enhancing vertical alignment of piezoelectric ZnO nanowires. Chemosens. 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, C.; Sanchez-Jimenez, P.E.; Datta, A.; Boughey, F.L.; Whiter, R.A.; Sahonta, S.L.; Kar-Narayan, S. Template-assisted hydrothermal growth of aligned zinc oxide nanowires for piezoelectric energy harvesting applications. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13678–13683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubenia, S.; Dahiya, A.S.; Poulin-Vittrant, G.; Morini, F.; Nadaud, K.; Alquier, D. A facile hydrothermal approach for the density tunable growth of ZnO nanowires and their electrical characterizations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamieniecki, E.; Foggiato, G. Analysis and control of electrically active contaminants by surface charge analysis. In Handbook of Semiconductor Wafer Cleaning Technology; Noyes Publications: Westwood, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 497–535. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Qin, Y.; Xu, C.; Wei, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered nanowire devices. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zöpfl, T.; Klare, S.; Wachutka, G.; Schrag, G. Characterisation of the intrinsic stress in micromachined parylene membranes. In Proceedings of the Spie Europe Microtechnologies For The New Millennium, Dresden, Germany, 4–6 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Qiu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Song, W.; Xu, J.; Zong, Y.; Feng, Q.; Sun, X. Patterned growth of ZnO nanowires on flexible substrates for enhanced performance of flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 063901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.L.; Bae, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoon, G.C.; Gupta, M.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Park, J.; Kim, S.-W. Depletion width engineering via surface modification for high performance semiconducting piezoelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2014, 8, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moni, P.; Al-obeidi, A.; Gleason, K.K. Vapor deposition routes to conformal polymer thin films. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorham, W.F. A New, General synthetic method for the preparation of linear poly-p-xylylenes. J. Polym. Sci. 1966, 4, 3027–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Meng, E. Micromachining of Parylene C for bioMEMS. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golda-Cepa, M.; Brzychczy-Wloch, M.; Engvall, K.; Aminlashgari, N.; Hakkarainen, M.; Kotarba, A. Microbiological investigations of oxygen plasma treated parylene C surfaces for metal implant coating. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 52, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshman, C.; Opoku, C.; Dahiya, A.S.; Alquier, D.; Camara, N.; Poulin-Vittrant, G. Measurement of Spurious Voltages in ZnO Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2016, 25, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Utashiro, K.; Abe, Y.; Kawamura, M. Structural properties of zinc oxide nanorods grown on Al-doped zinc oxide seed layer and their applications in dye-sensitized solar cells. Materials 2014, 7, 2522–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.W.; Peng, S.M.; Wu, J.S.; Shih, W.S.; Wu, C.S.; Tang, I.T. Effect of seed layer on the growth of well-aligned ZnO nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2009, 70, 1359–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, P.K.; Dhara, S.; Chakraborty, R. Effect of ZnO seed layer on the catalytic growth of vertically aligned ZnO nanorod arrays. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 122, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Y.; Lee, C.Y.; Tseng, T.Y. Copper-catalyzed ZnO nanowires on silicon (1 0 0) grown by vapor–liquid–solid process. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 247, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemin, S.; Consonni, V.; Appert, E.; Puyoo, E.; Rapenne, L.; Roussel, H. Critical Nucleation Effects on the Structural relationship between ZnO Seed layer and nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 25106–25111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymshits, A.; Iagher, L.; Etgar, L. Parameters influencing the growth of ZnO nanowires as efficient low temperature flexible perovskite-based solar cells. Materials 2016, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Abbasi, M.A.; Khan, A.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Comparative Study of Energy Harvesting from ZnO Nanorods Using Different Flexible Substrates. Energy Harvest. Syst. 2014, 1, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadaud, K.; Poulin-Vittrant, G.; Alquier, D. Effect of the excitation waveform on the average power and peak power delivered by a piezoelectric generator. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 2019. accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakooti, M.H.; Patterson, B.A.; Hwang, H.S.; Sodano, H.A. ZnO nanowire interfaces for high strength multifunctional composites with embedded energy harvesting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Electrostatic potential in a bent piezoelectric nanowire. The fundamental theory of nanogenerator and nanopiezotronics. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


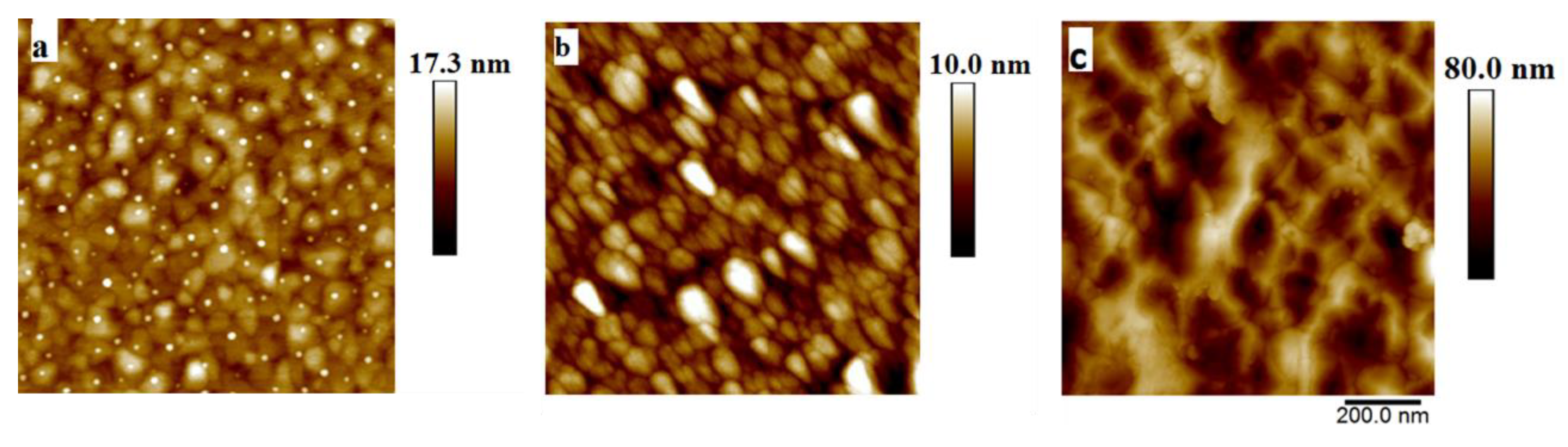

| Sample | Seed Layer | Thickness (nm) | Substrate |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Au | 200 | Si |
| B | ZnO | 100 | Si |
| C | AZO | 500 | Glass |
| Sample | Density (NWs/µm2) | Diameter (µm) | Length (µm) | Aspect RATIO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (Au) | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.38 ± 0.13 | 1.78 ± 0.20 | 4.7 |
| B (ZnO) | 35.4 ± 0.2 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.57 ± 0.18 | 8 |
| C (AZO) | 52.9 ± 0.5 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | 0.48 ± 0.08 | 3.4 |
| Sample | VOC (mV) | ISC (nA) | Ppk (nW) | ROpt (kΩ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (Au) | <4 | <15 | - | - |
| B (ZnO) | 272 | 214 | 17 | 562 |
| C (AZO) | 36 | 157 | 3 | 177 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Justeau, C.; Slimani Tlemcani, T.; Poulin-Vittrant, G.; Nadaud, K.; Alquier, D. A Comparative Study on the Effects of Au, ZnO and AZO Seed Layers on the Performance of ZnO Nanowire-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. Materials 2019, 12, 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162511
Justeau C, Slimani Tlemcani T, Poulin-Vittrant G, Nadaud K, Alquier D. A Comparative Study on the Effects of Au, ZnO and AZO Seed Layers on the Performance of ZnO Nanowire-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. Materials. 2019; 12(16):2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162511
Chicago/Turabian StyleJusteau, Camille, Taoufik Slimani Tlemcani, Guylaine Poulin-Vittrant, Kevin Nadaud, and Daniel Alquier. 2019. "A Comparative Study on the Effects of Au, ZnO and AZO Seed Layers on the Performance of ZnO Nanowire-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators" Materials 12, no. 16: 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162511
APA StyleJusteau, C., Slimani Tlemcani, T., Poulin-Vittrant, G., Nadaud, K., & Alquier, D. (2019). A Comparative Study on the Effects of Au, ZnO and AZO Seed Layers on the Performance of ZnO Nanowire-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. Materials, 12(16), 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12162511







