Properties of Concrete Prepared with Recycled Aggregates Treated by Bio-Deposition Adding Oxygen Release Compound
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Recycled Mortar Aggregates
2.1.2. Bacterial Strain and Cultivation
2.1.3. Cement
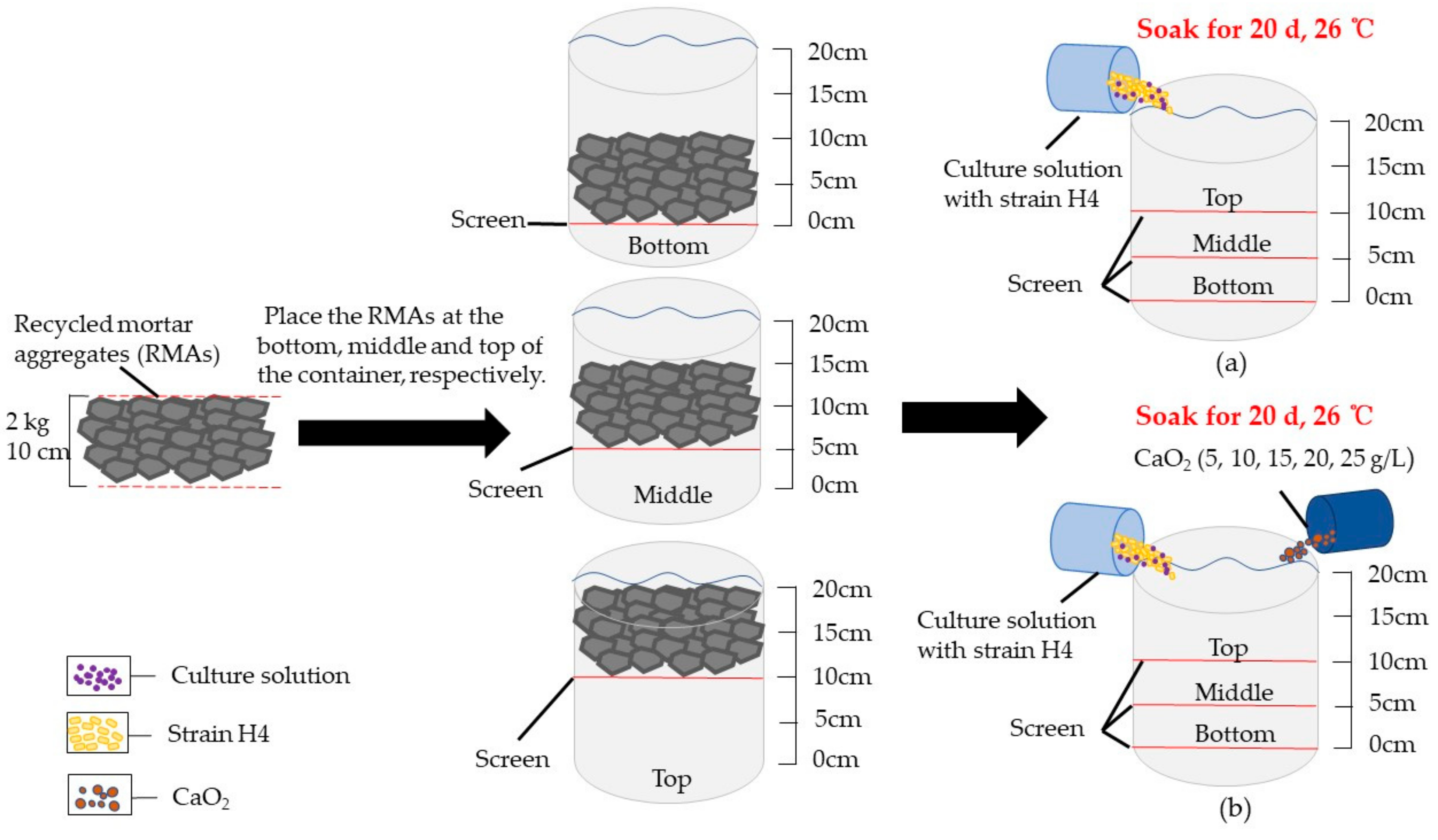
2.2. Bio-Deposition Treatment Method for RMA
2.3. Test Methods
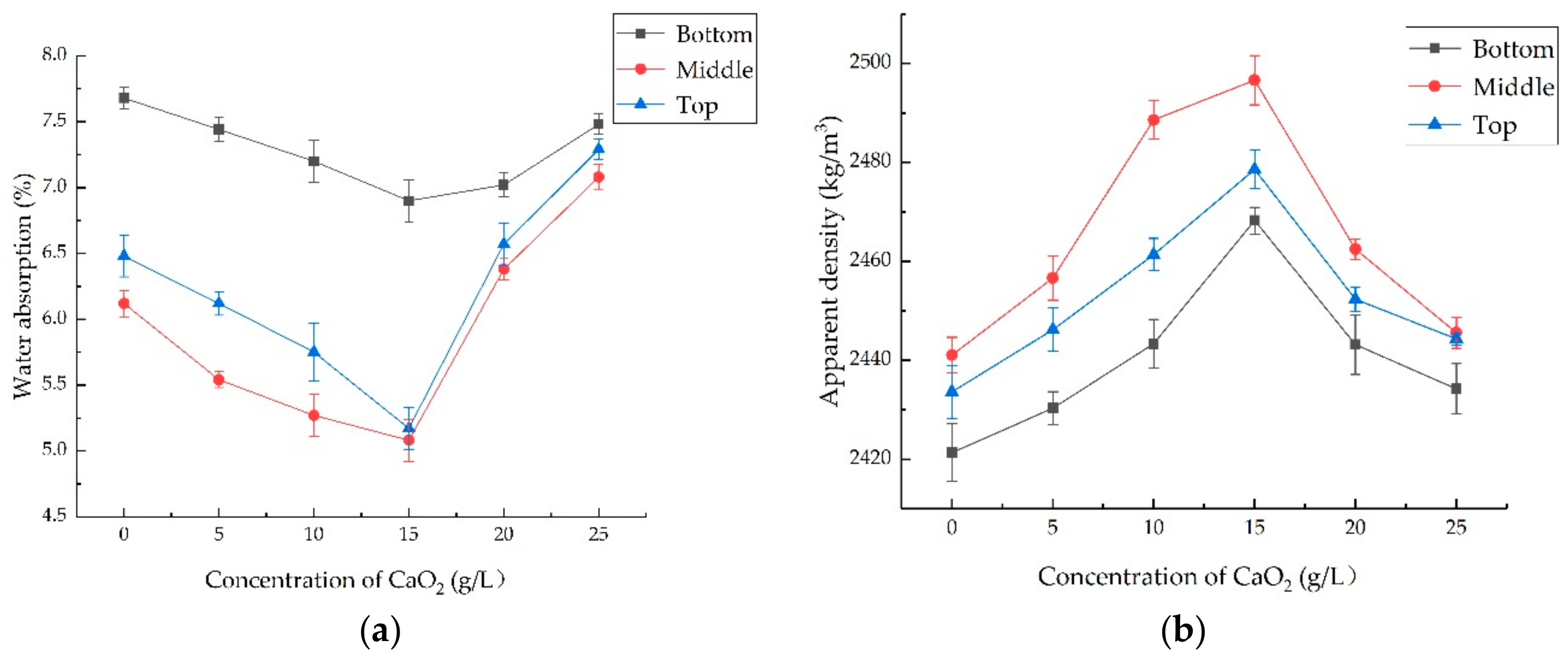
2.3.1. Water Absorption
2.3.2. Apparent Density
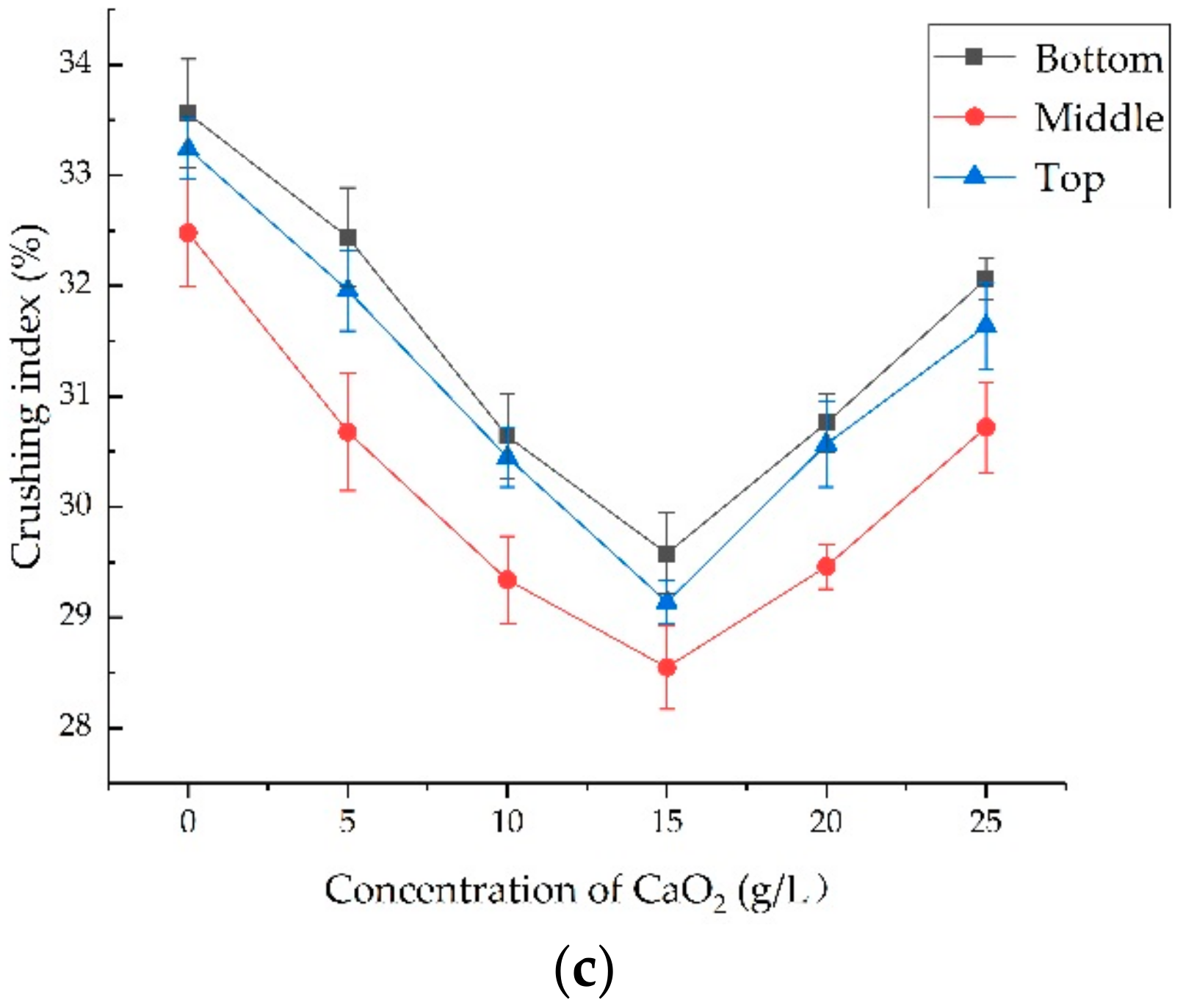
2.3.3. Crushing Index
- C = crushing index (%)
- m0 = weight of the RMA (g)
- m1 = weight of RMA after crushing test (g)
- Csa = The total crushing index (%) was accurate to 0.1%.
- a1, a2, a3, and a4 = the crushing index of fine RMA with different particle sizes of 2.50 mm, 1.25 mm, 0.63 mm, and 0.315 mm, respectively.
- c1, c2, c3, and c4 = the corresponding residual weights (%)
2.3.4. Characterization of the Surface of RMA by SEM-EDS
2.4. Concrete Properties
2.4.1. Slump
2.4.2. Compressive Strength of Concrete
3. Results and Discussion
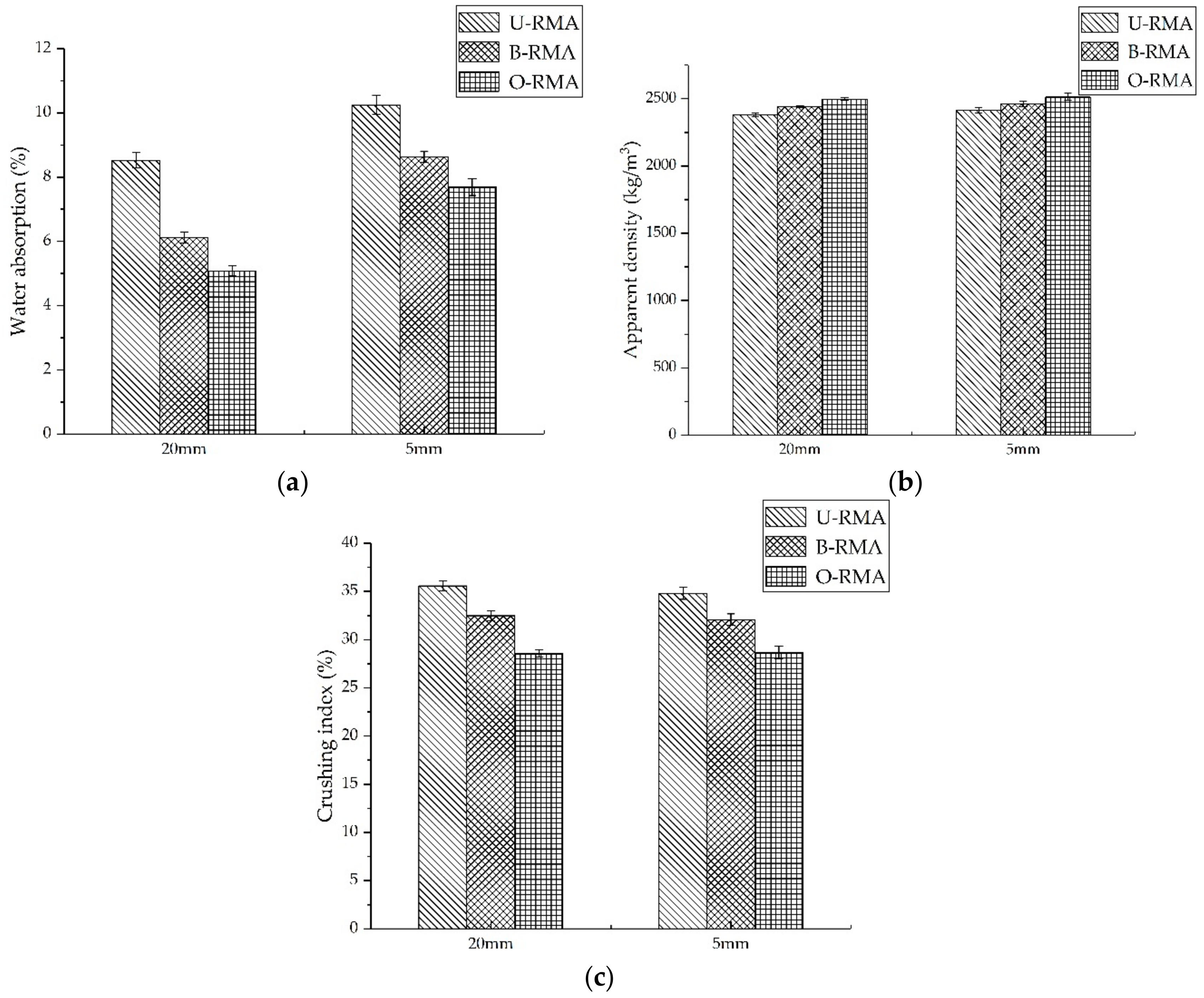
3.1. The Optimal Treatment Method for the o-Bio-Deposition
3.2. Properties of Concrete
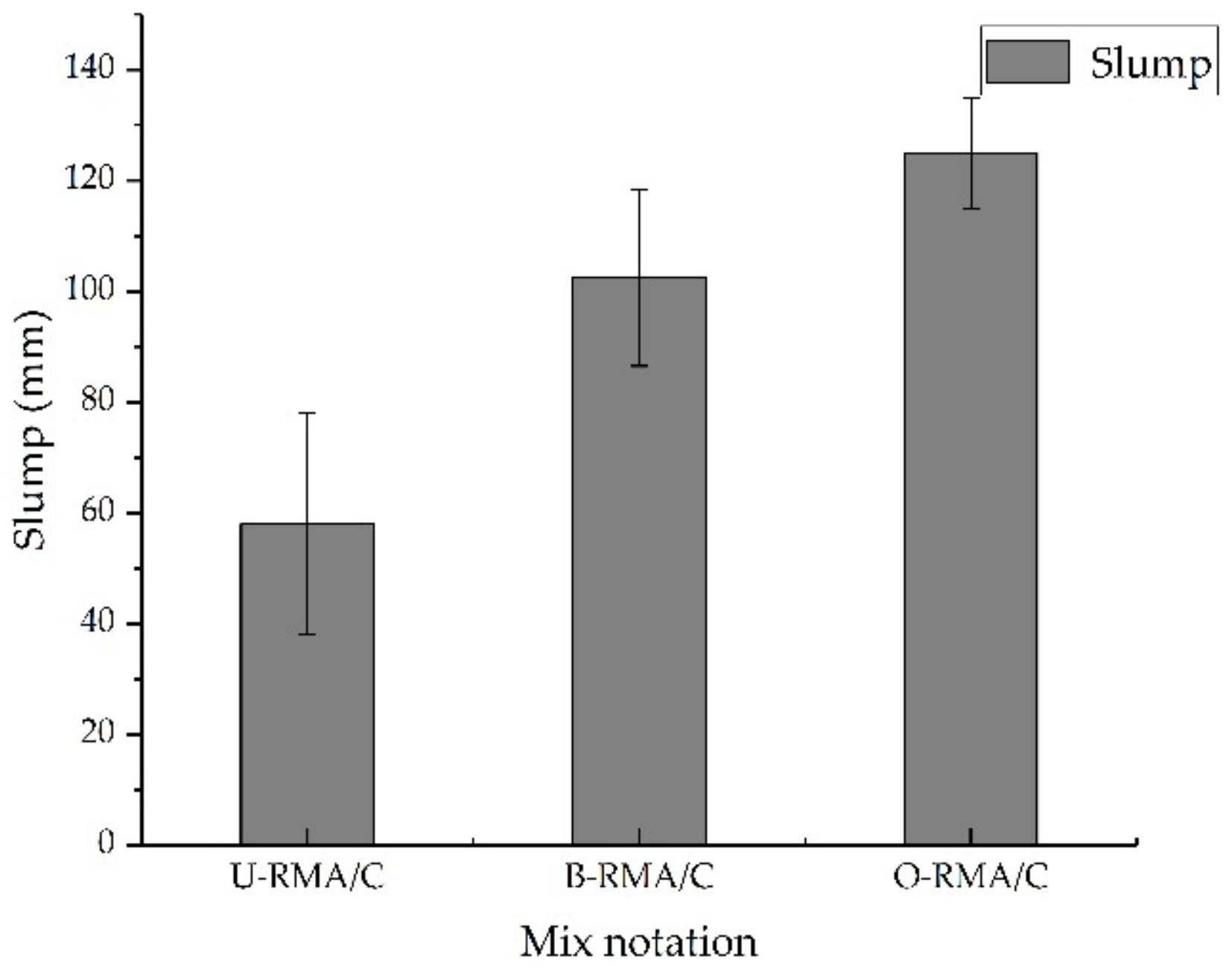
3.2.1. Slump of Concrete Mixtures
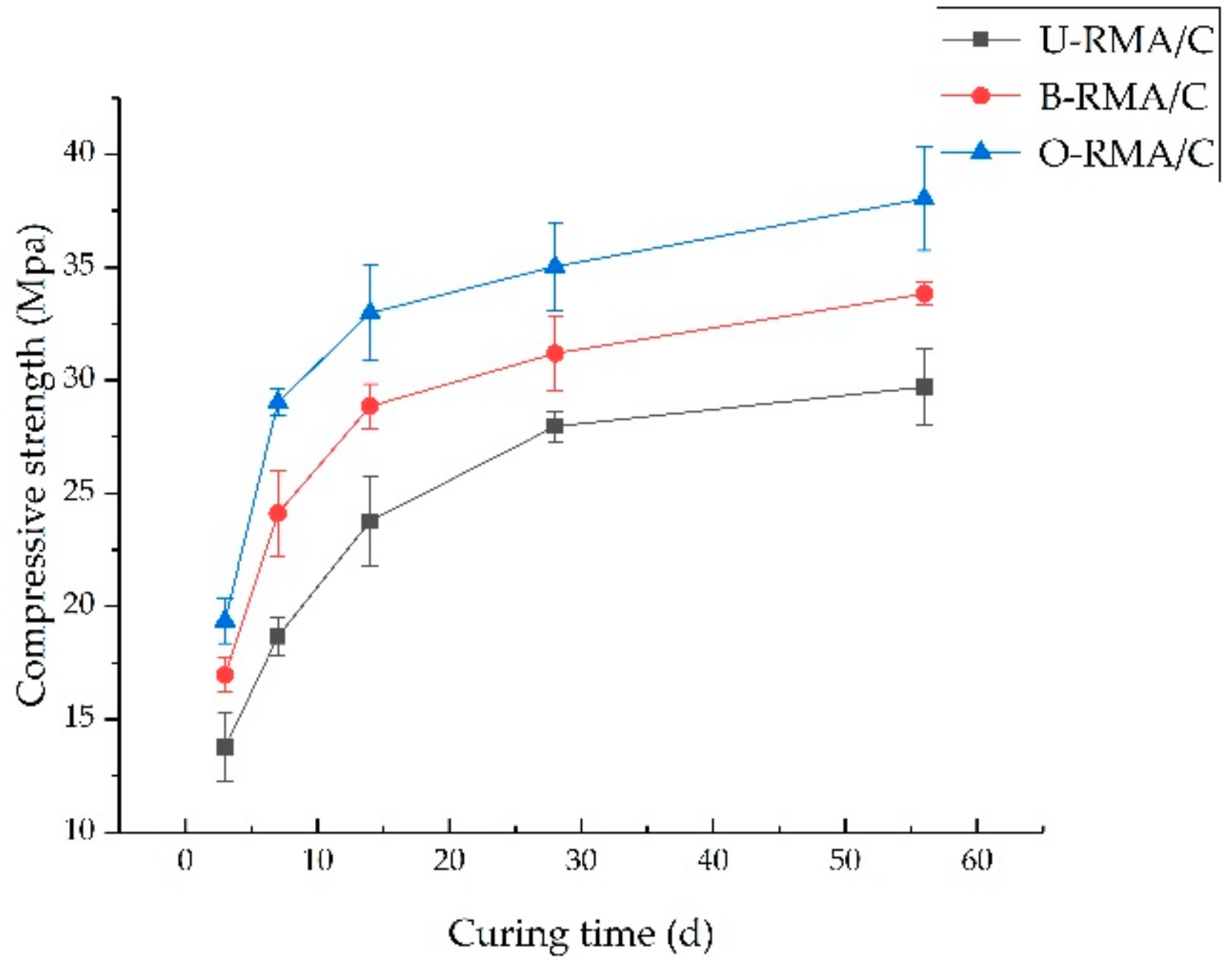
3.2.2. Compressive Strength
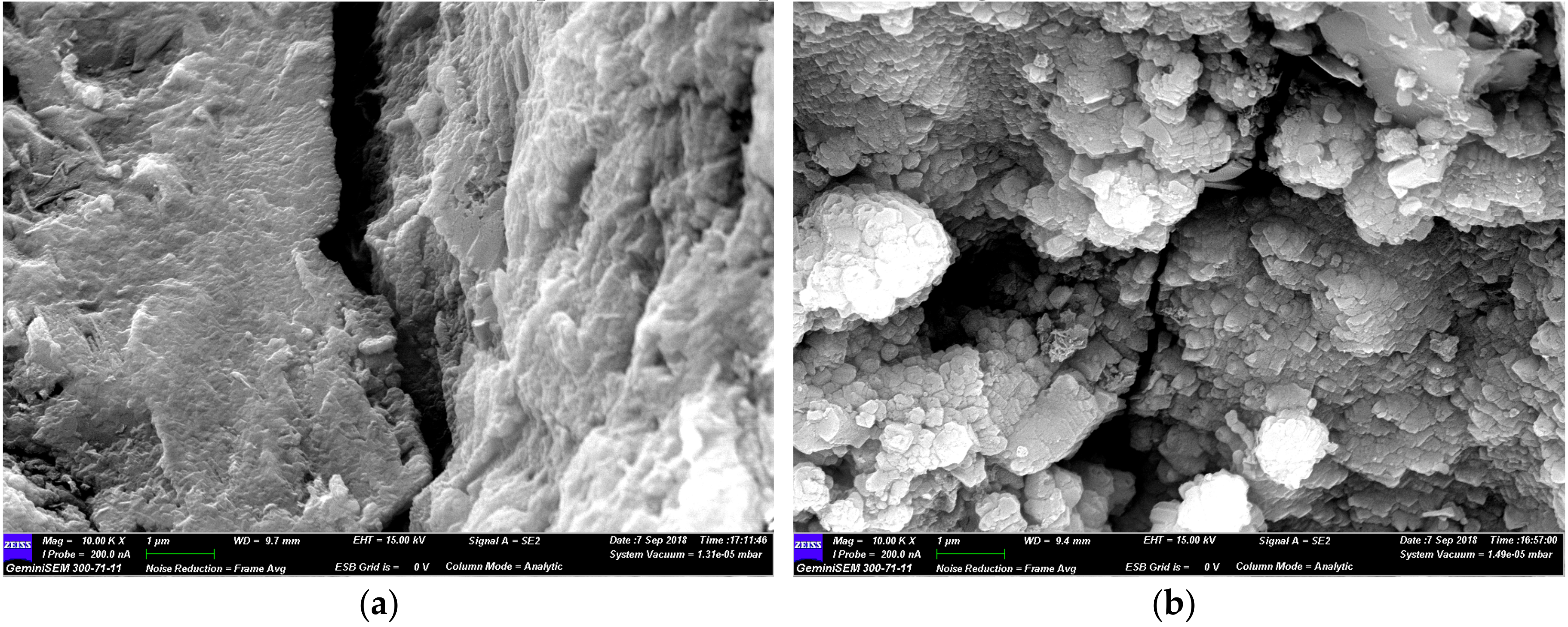
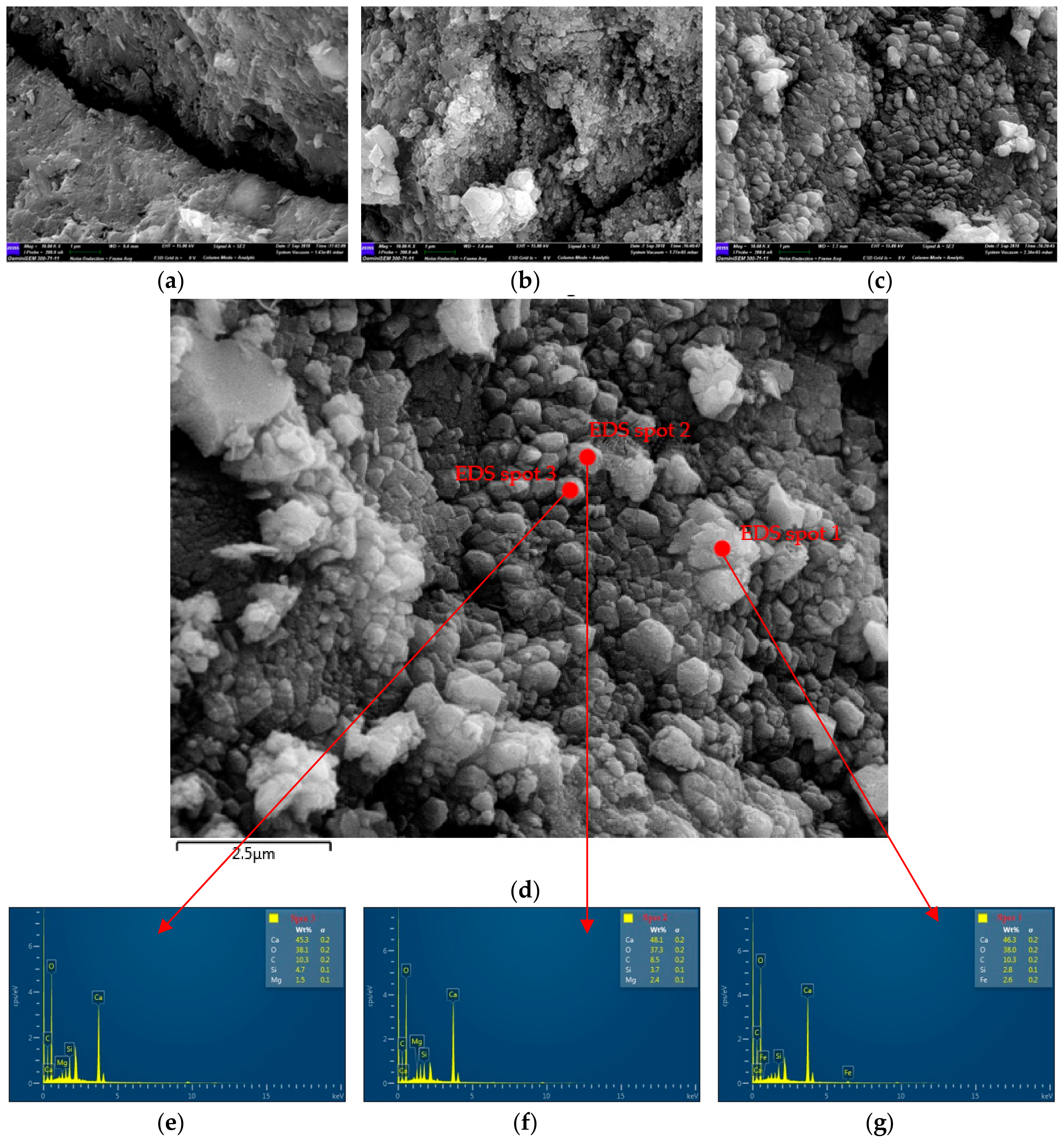
3.2.3. SEM Analysis of Micro-Cracks in Concretes
4. Conclusions
- Upon comparing the properties of RMA under different treatment methods, we determined that the treatment method of o-bio-deposition involves immersing the aggregates in the middle of the container and adding 15 g/L CaO2 to the bacterial solution of Bacillus alkalophilus H4. The water absorption and crushing index of 20-mm O-RMA are 40.4% and 19.8% higher than those of U-RMA, respectively. The properties of the O-RMA are superior to that of the B-RMA.
- SEM-EDS showed that there are many pores and micro-cracks in the U-RMA, the width of which vary from 0.02 µm to 1.2 µm. The particles on the surface of the O-RMA were CaCO3 as indicated by EDS analyses. Several CaCO3 crystals could be seen on the surface and cracks of the O-RMA that completely fill the micro-cracks.
- The compressive strength and slump of the B-RMA/C and O-RMA/C increased compared with U-RMA/C, and the increase in compressive strength of the O-RMA/C is 25.3% at 28 d. In addition, according to the SEM images of the micro-cracks of concrete, it was found that the micro-cracks of the O-RMA/C were filled by hydration products, and improved the compressive strength of concrete.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, J.; Li, W.; Poon, C. Recent studies on mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete in China—A review. Sci. Chin. Technol. Sci. 2012, 55, 1463–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azúa, G.; González, M.; Arroyo, P.; Kurama, Y. Recycled coarse aggregates from precast plant and building demolitions: Environmental and economic modeling through stochastic simulations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Minocha, A.K.; Deoliya, R.; Maiti, S. Recycled aggregate from C&D waste & its use in concrete—A breakthrough towards sustainability in construction sector: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Juan, M.S.; Gutiérrez, P.A. Study on the influence of attached mortar content on the properties of recycled concrete aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisku, N.; Joshi, H.; Ansari, M.; Panda, S.K.; Nayak, S.; Dutta, S.C. A critical review and assessment for usage of recycled aggregate as sustainable construction material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 721–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, P.; Abhiram, K.; Manoj, B. Properties of treated recycled aggregates and its influence on concrete strength characteristics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Shui, Z.H.; Lam, L. Effect of microstructure of ITZ on compressive strength of concrete prepared with recycled aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2004, 18, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verian, K.P.; Ashraf, W.; Cao, Y. Properties of recycled concrete aggregate and their influence in new concrete production. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 133, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.-C.; Poon, C.-S.; Etxeberria, M. Influence of recycled aggregates on long term mechanical properties and pore size distribution of concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 33, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, L.; West, J.S.; Tighe, S.L. The effect of recycled concrete aggregate properties on the bond strength between RCA concrete and steel reinforcement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2011, 41, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakradhara Rao, M.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Barai, S.V. Influence of field recycled coarse aggregate on properties of concrete. Mater. Struct. 2011, 44, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Chong, L.; Xie, Z. Performance enhancement of recycled concrete aggregate—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Shi, C.; Guan, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, Y.; Ling, T.-C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete—A review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 89, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiao, J.; Poon, C.S. Dynamic compressive behavior of recycled aggregate concrete. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 4451–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangan, K.; Dayanithy, A.; Prakash, S.O. Influence of treatment methods on the bond strength of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build.Mater. 2016, 120, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, W.M.; Yang, J.; Su, H.; Mo, K.H.; Li, L.; Xie, J. Quality Improvement techniques for recycled concrete aggregate: A review. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2019, 17, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Mueller, A. Development of thermo-mechanical treatment for recycling of used concrete. Mater. Struct. 2012, 45, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Tam, C.M.; Le, K.N. Removal of cement mortar remains from recycled aggregate using pre-soaking approaches. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 50, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Qian, X.; Chen, P.; Xu, Y.; Guo, J. An environmentally friendly method to improve the quality of recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-G.; Kou, S.-C.; Poon, C.-S.; Dai, J.-G.; Li, Q.-Y. Influence of silane-based water repellent on the durability properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 35, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.-C.; Poon, C.-S. Properties of concrete prepared with PVA-impregnated recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaeth, V.; Djerbi Tegguer, A. Improvement of recycled concrete aggregate properties by polymer treatments. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2013, 2, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Cui, L.; Qian, X.; Chen, P.; Fang, Y. Consolidating recycled concrete aggregates using phosphate solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 200, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, B.; Poon, C.S.; Liu, Q.; Kou, S.; Shi, C. Experimental study on CO2 curing for enhancement of recycled aggregate properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 67, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.-C.; Zhan, B.-j.; Poon, C.-S. Use of a CO2 curing step to improve the properties of concrete prepared with recycled aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 45, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Bang, S.S. Microbiologically induced sealant for concrete crack remediation. In Proceedings of the 16th Engineering Mechanics Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–18 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jonkers, H.M.; Thijssen, A.; Muyzer, G.; Copuroglu, O.; Schlangen, E. Application of bacteria as self-healing agent for the development of sustainable concrete. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Van Tittelboom, K.; De Belie, N.; Verstraete, W. Use of silica gel or polyurethane immobilized bacteria for self-healing concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalhori, H.; Bagherpour, R. Application of carbonate precipitating bacteria for improving properties and repairing cracks of shotcrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Vandevyvere, B.; Vanhessche, S.; Schoon, J.; Boon, N.; De Belie, N. Microbial carbonate precipitation for the improvement of quality of recycled aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Tng, D.Q.S.; Yang, E.-H. Surface treatment of recycled concrete aggregates through microbial carbonate precipitation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 57, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, J.; Rodríguez-Robles, D.; Wang, J.; De Belie, N.; Morán-del Pozo, J.M.; Guerra-Romero, M.I.; Juan-Valdés, A. Quality improvement of mixed and ceramic recycled aggregates by biodeposition of calcium carbonate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabiec, A.M.; Klama, J.; Zawal, D.; Krupa, D. Modification of recycled concrete aggregate by calcium carbonate biodeposition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-R.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Zhang, X.-T.; Kou, S.-C. Improving the properties of recycled concrete aggregate with bio-deposition approach. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 94, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Wu, R.S.; Li, Y.M.; Zhong, J.Y.; Deng, X.; Liu, B.; Han, N.X.; Xing, F. Screening of bacteria for self-healing of concrete cracks and optimization of the microbial calcium precipitation process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6661–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.L.; Wang, C.G.; Wang, Q.L.; Feng, J.L.; Pan, W.; Zheng, X.C.; Liu, B.; Han, N.X.; Xing, F.; Deng, X. A binary concrete crack self-healing system containing oxygen-releasing tablet and bacteria and its Ca(2+)-precipitation performance. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 10295–10306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T17671-1999. Testing Method for Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortar, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (SAC) & General Administration of Quality Supervision; Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China (AQSIQ): Beijing, China, 1999.
- JGJ52-2006. Standard for Technical Requirements and Test Method of Sand and Crushed Stone (or Gravel) for Ordinary Concrete; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- JGJ55-2011. Specification For Mix Proportion Design of Ordinary Concrete; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- GB/T25177–2010. Recycled Coarse Aggregate for Concrete; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- GB/T50080-2016. Standard for Test Method of Performance on Ordinary Fresh Concrete; Ministry of Construction of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Zhang, J.; Mai, B.; Cai, T.; Luo, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, B.; Han, N.; Xing, F.; Deng, X. Optimization of a binary concrete crack self-healing system containing bacteria and oxygen. Materials 2017, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knop, Y.; Peled, A. Setting behavior of blended cement with limestone: Influence of particle size and content. Mater. Struct. 2015, 49, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Notation 1 | Proportion (kg/m3) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/c Ratio | Sand Ratio | Cement | Fine Aggregates | Coarse Aggregates | Water | |
| U-RMA/C | 0.5 | 40 | 370 | 738 | 1107 | 185 + 36.7 |
| B-RMA/C | 0.5 | 40 | 370 | 738 | 1107 | 185 + 22.1 |
| O-RMA/C | 0.5 | 40 | 370 | 738 | 1107 | 185 + 14.7 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, P.; Wang, X.; Kou, S. Properties of Concrete Prepared with Recycled Aggregates Treated by Bio-Deposition Adding Oxygen Release Compound. Materials 2019, 12, 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132147
Zhu Y, Li Q, Xu P, Wang X, Kou S. Properties of Concrete Prepared with Recycled Aggregates Treated by Bio-Deposition Adding Oxygen Release Compound. Materials. 2019; 12(13):2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132147
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yaguang, Quanquan Li, Peizhen Xu, Xiangrui Wang, and Shicong Kou. 2019. "Properties of Concrete Prepared with Recycled Aggregates Treated by Bio-Deposition Adding Oxygen Release Compound" Materials 12, no. 13: 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132147
APA StyleZhu, Y., Li, Q., Xu, P., Wang, X., & Kou, S. (2019). Properties of Concrete Prepared with Recycled Aggregates Treated by Bio-Deposition Adding Oxygen Release Compound. Materials, 12(13), 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132147





