Study on the Interfacial Functionary Mechanism of Rare-Earth-Solution-Modified Bamboo-Fiber-Reinforced Resin Matrix Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Formulation and Designation of Composites
2.2. Fabrication of Composites
2.3. Measurements
2.3.1. Mechanical Characterization
2.3.2. Morphological Characterization
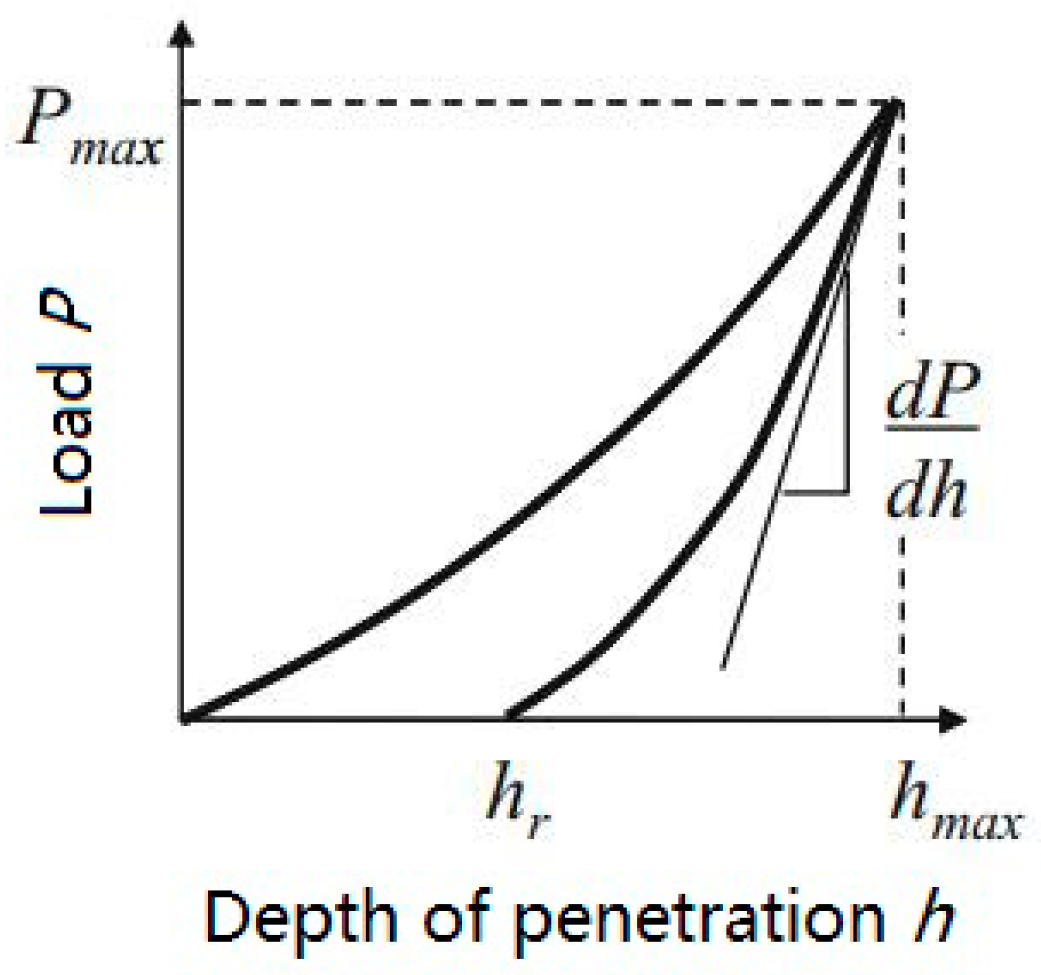
2.3.3. Characterization of the Interfacial Bonding Properties
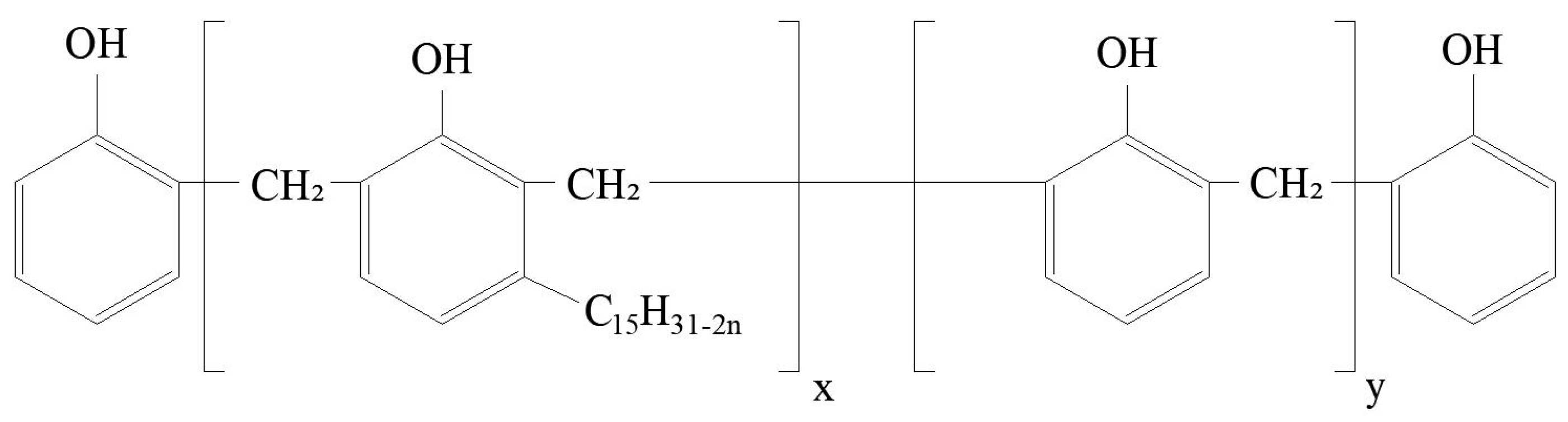
2.3.4. FT-IR Spectroscopy
2.3.5. XPS Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
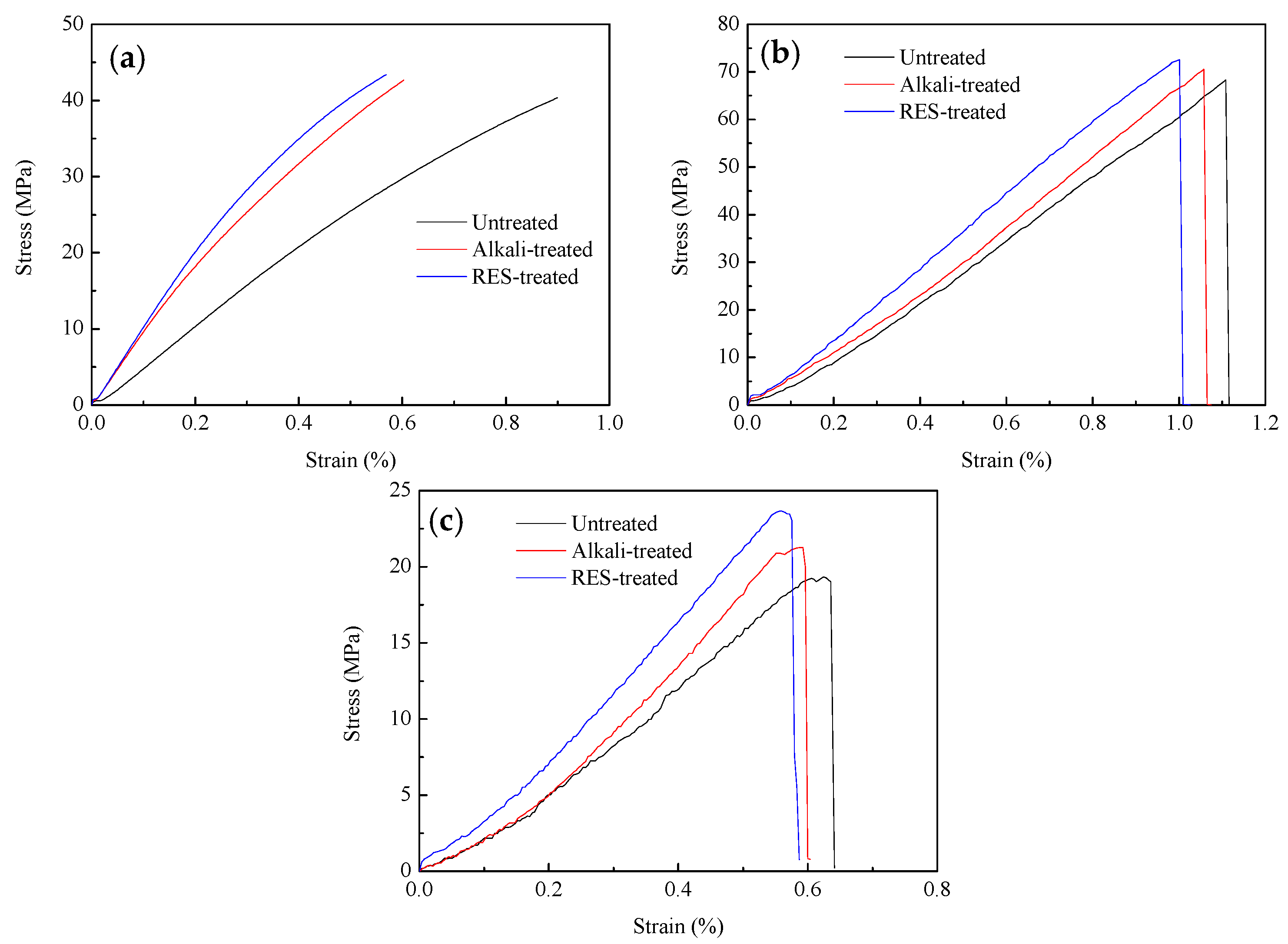
3.1. Characterization of Mechanical Properties
3.2. Morphology Analysis
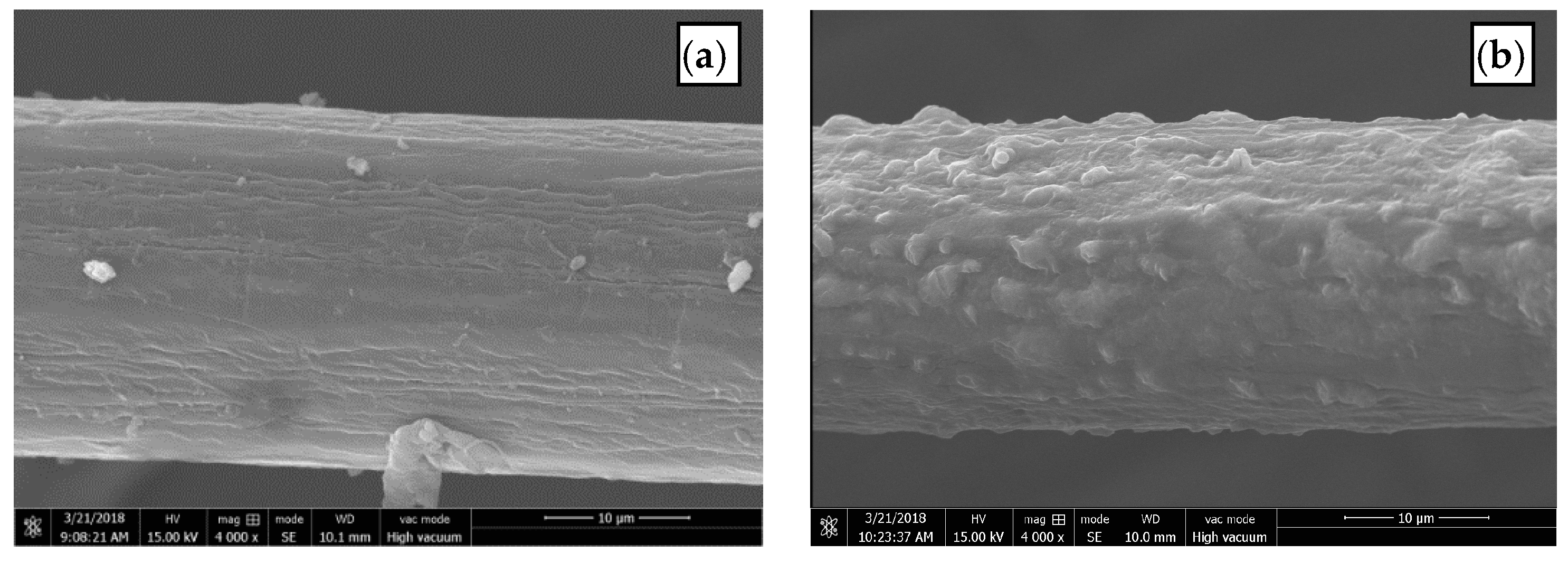
3.2.1. Surface Morphology of BF
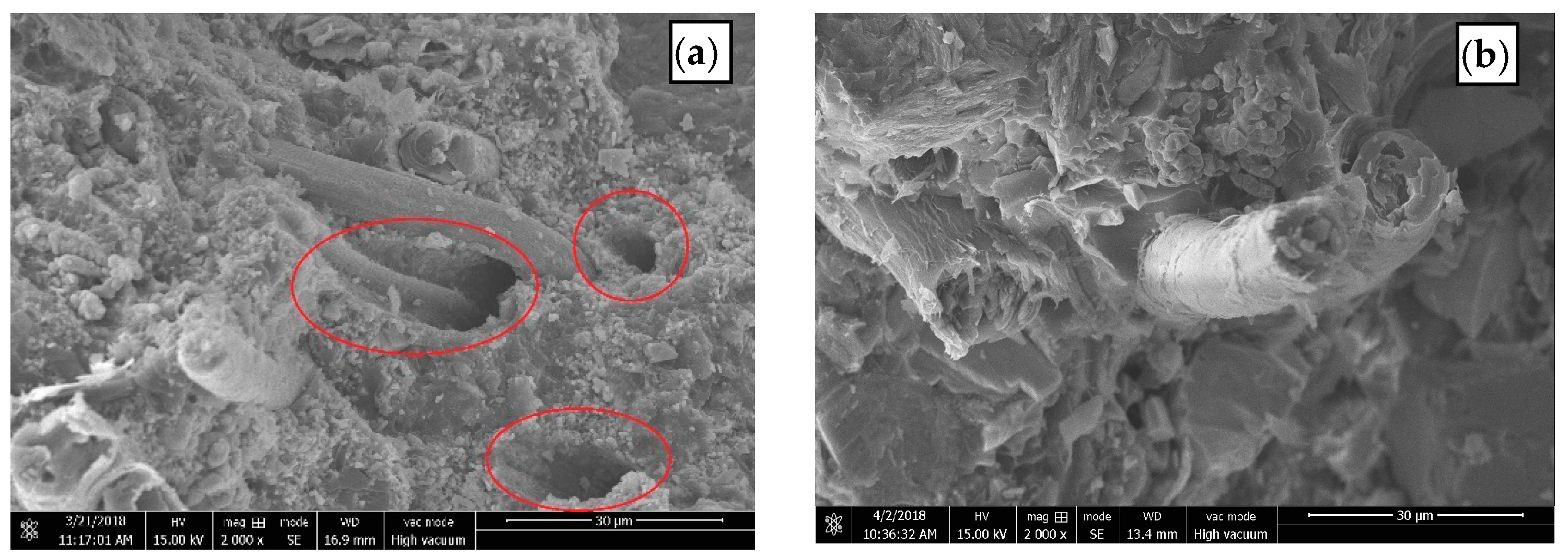
3.2.2. Fracture Morphology of Composites
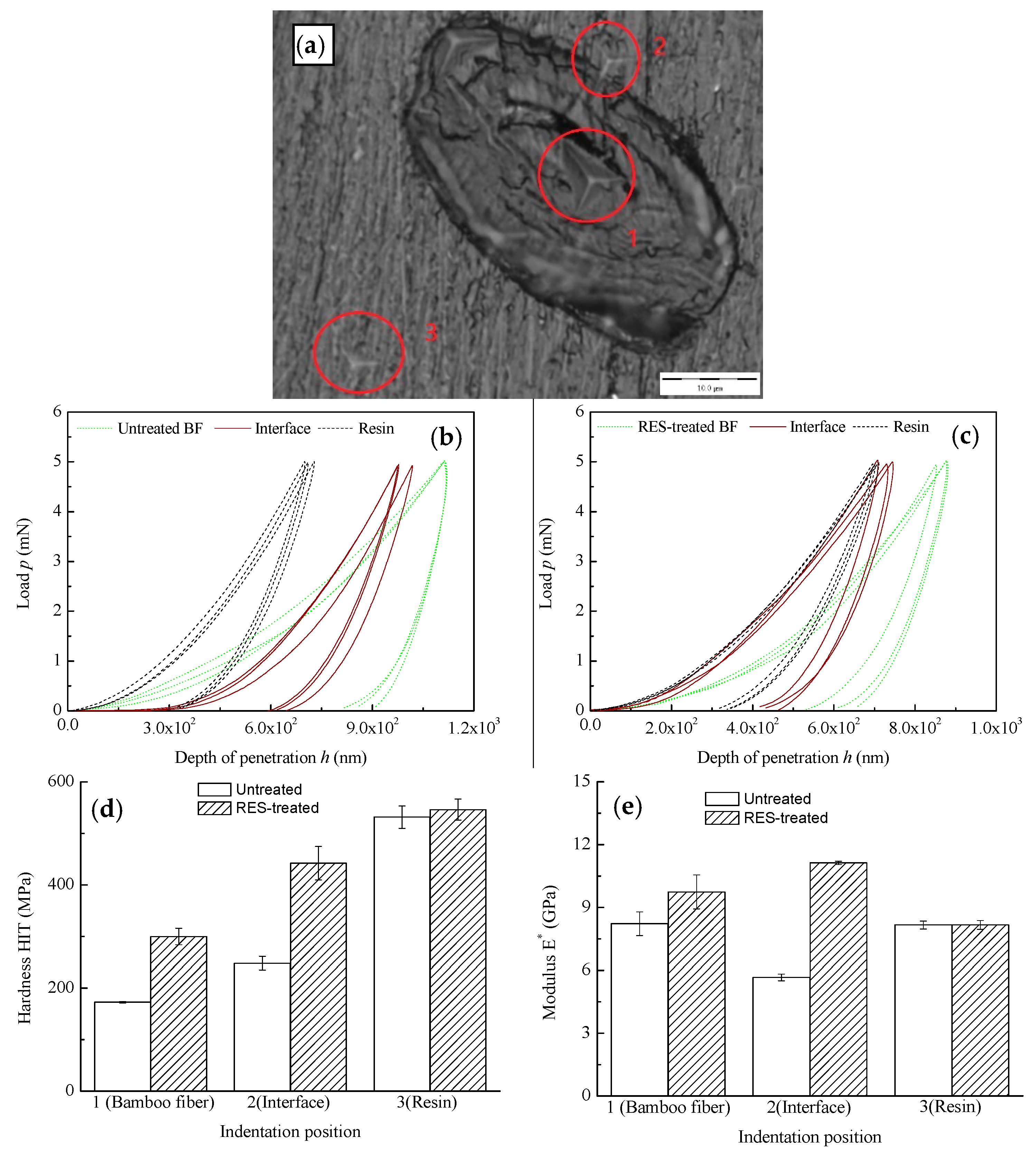
3.3. Characterization of Interfacial Bonding Properties
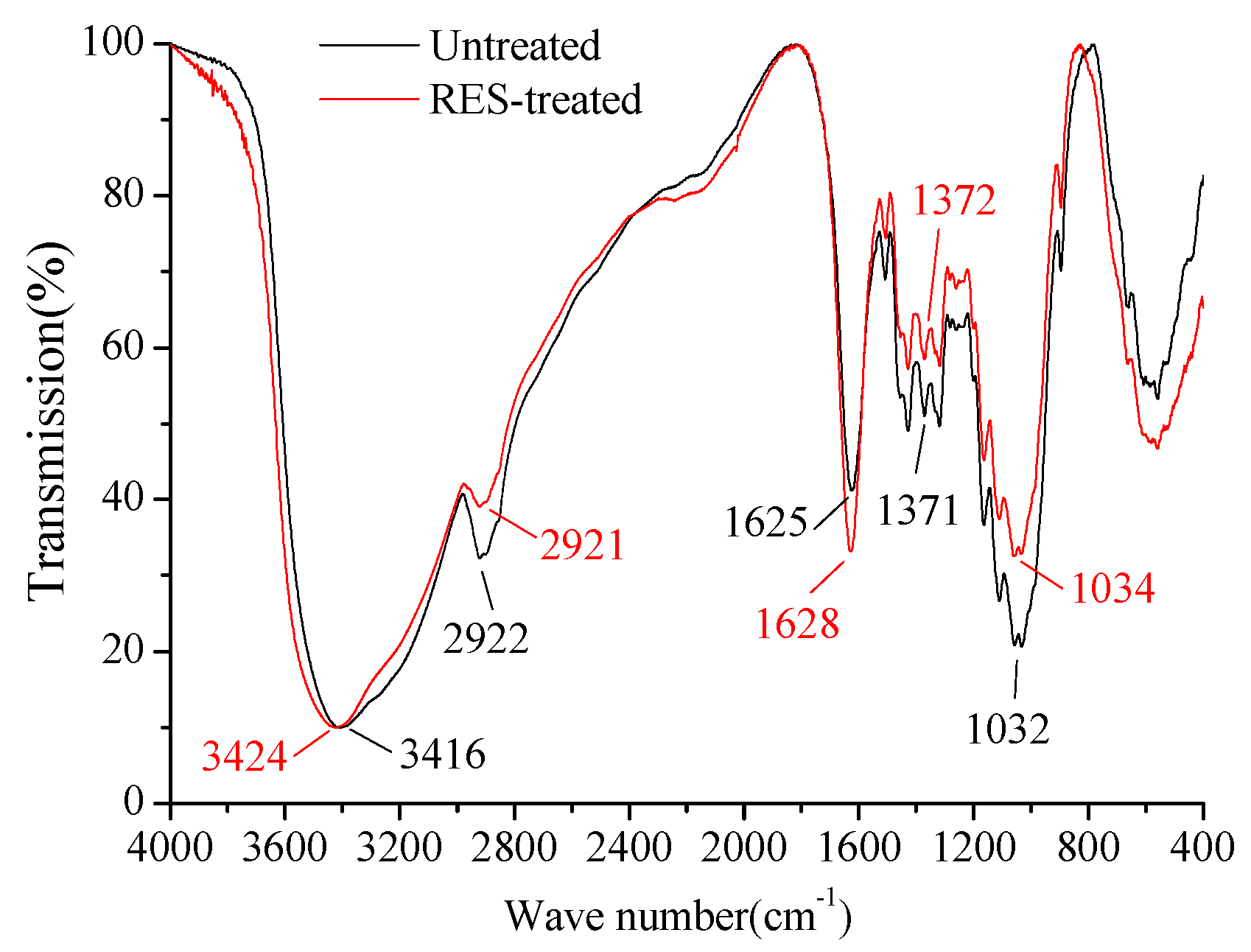
3.4. Infrared Spectroscopic Analysis
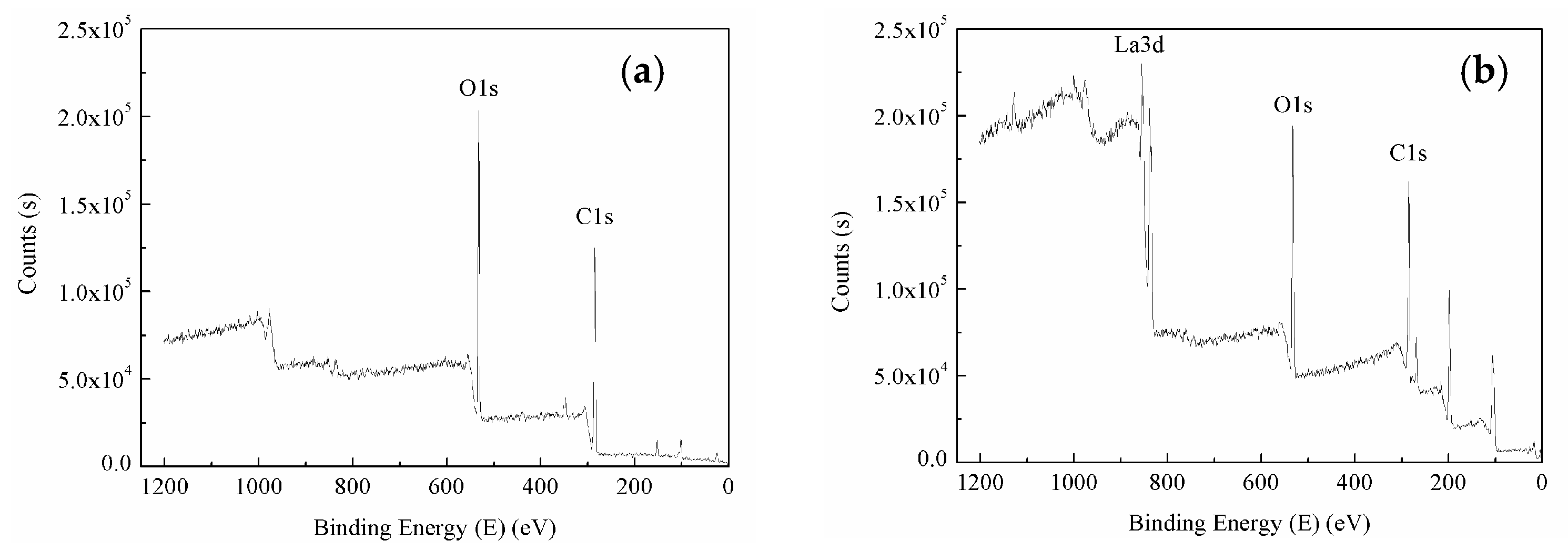
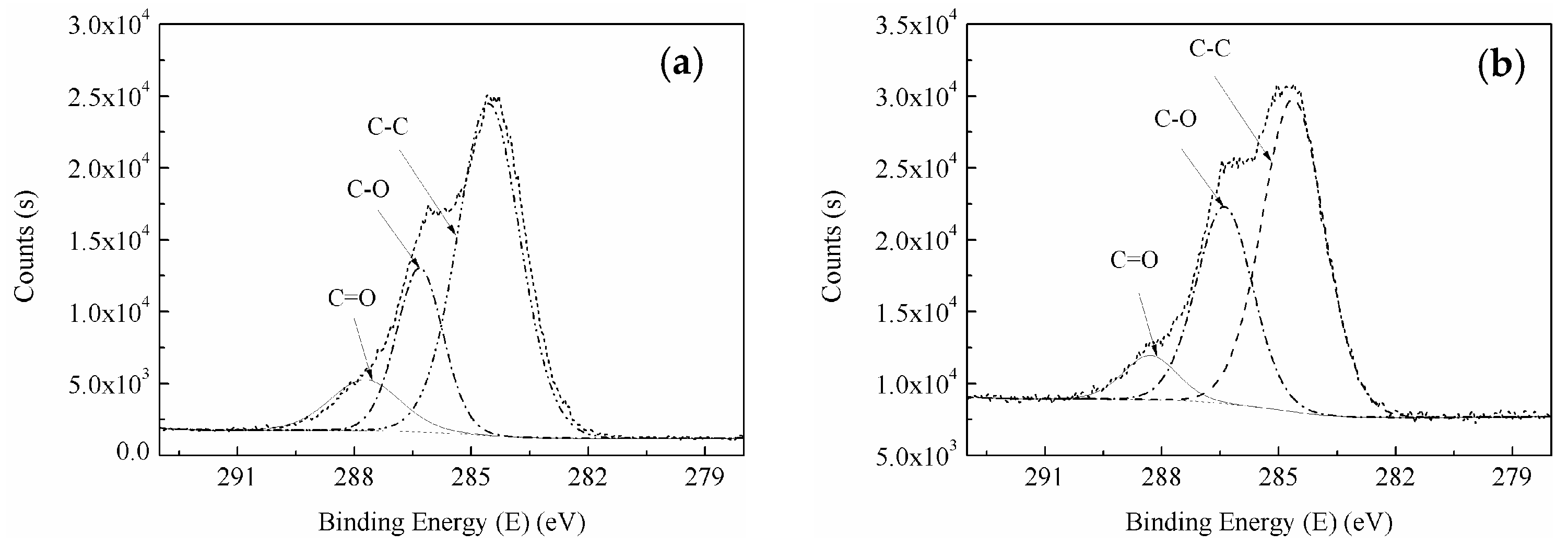
3.5. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Analysis
3.5.1. Wide-Scan Photoelectron Spectra of BF
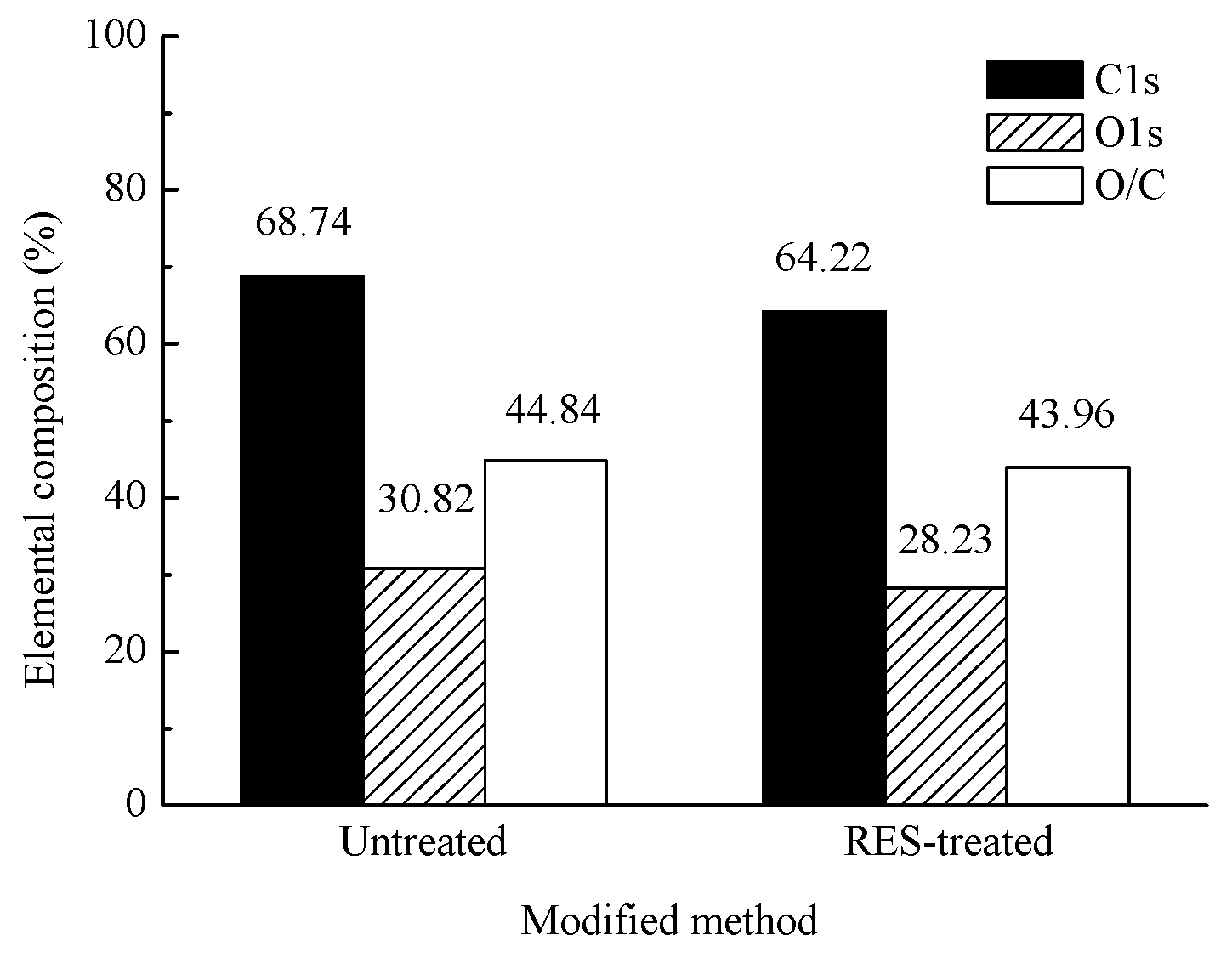
3.5.2. Narrow-Scan Photoelectron Spectra of BF
3.6. Mechanism of RES Modification
4. Conclusions
- The RES modification on the mechanical properties (tensile strength, flexural strength, fracture toughness, and impact strength) of composites is better than that of alkali treatment, especially in regard to the improvement of fracture toughness. The surface of BF modified by RES becomes rough and the surface area increases, which improves the mechanical meshing force between the fiber and the matrix.
- The RES modification can improve the hardness and elastic modulus of the BF and the interface between BF and the resin matrix; in particular, the interfacial zone has a larger elastic modulus than BF and the resin matrix, which indicates the formation of chemical bonds between the modified BF and the resin matrix during the composite process.
- The O–H stretching vibration frequency increased and the bandwidth narrowed after the RES modification, which indicates that the hydrogen bonds among large molecular chains of cellulose were weakened, the hydrophilicity of BF decreased, and the interfacial compatibility between BF and the resin matrix was improved.
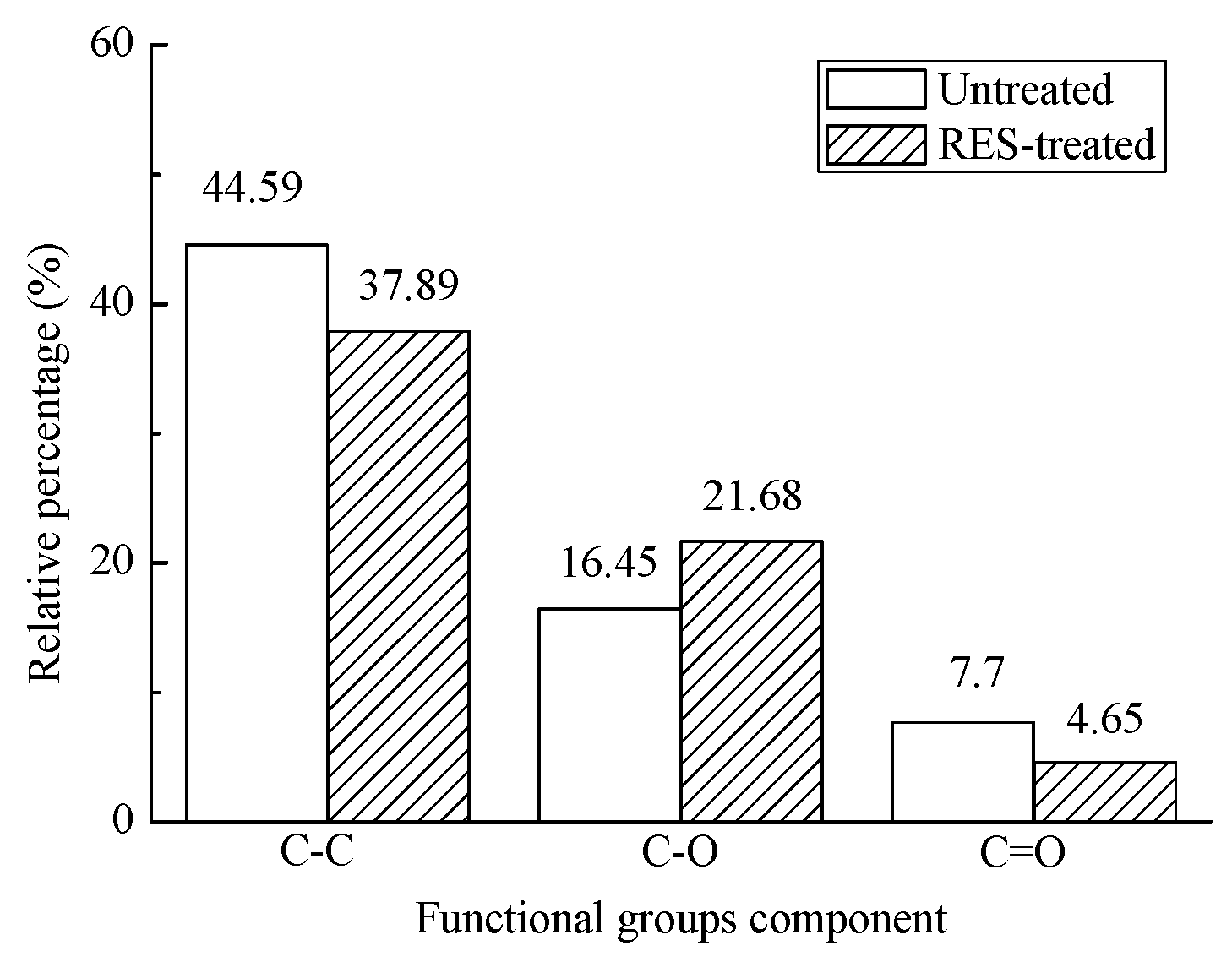
- The RES modification caused the relative contents of C and O on the BF’s surface and the O/C rate to decrease, indicating that modification of the BF by use of RES can reduce the hydroxyl concentration of the BF’s surface, reduce the polarity and hydrophilicity of the natural BF, and improve interfacial bonding properties between the fiber and the resin matrix.
- During the modification process, La3+ coordinates with the oxidation of the hydroxyl of BF and chemically adsorbs onto the surface of BF. La3+ can also be coordinated with the oxygen groups on the molecular chain of phenolic resin, which forms a stable structure of rare earth complexes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mittal, V.; Saini, R.; Sinha, S. Natural fiber-mediated epoxy composites—A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 99, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohit, K.; Dixit, S. A review-future aspect of natural fiber reinforced composite. Polym. Renew. Resour. 2016, 7, 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Pozo Morales, A.; Güemes, A.; Fernandez-Lopez, A.; Carcelen Valero, V.; De La Rosa Llano, S. Bamboo–polylactic acid (PLA) composite material for structural applications. Materials 2017, 10, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramamoorthy, S.K.; Skrifvars, M.; Persson, A. A review of natural fibers used in biocomposites: Plant, animal and regenerated cellulose fibers. Polym. Rev. 2015, 55, 107–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Oqla, F.M.; Sapuan, S.M. Natural fiber reinforced polymer composites in industrial applications: Feasibility of date palm fibers for sustainable automotive industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 66, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, T.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. A review of the recent developments in biocomposites based on natural fibres and their application perspectives. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 77, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, H.O.; Jha, K.; Tyagi, Y.K. Tribological behavior of short sisal fiber reinforced epoxy composite. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2017, 25, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmala, U.; Hashim, J.; Ahmad, M.M.H.M. A review on tribological performance of natural fibre polymeric composites. Tribol. Int. 2015, 83, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, S.; Cruz, J.; Toro, A. Friction and wear in sliding contact of cast iron against phenolic resin composites reinforced with carbonaceous fibres from plantain fibre bundles. Lubr. Sci. 2013, 25, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Fu, Z.; Yun, R.; Jiang, S.; Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Matejka, V.; Kukutschova, J.; Peknikova, V.; Prikasky, M. Effects of walnut shells on friction and wear performance of eco-friendly brake friction composites. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2014, 228, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.H.; Wei, C.; Zeng, M.; Xiong, X.M.; Liu, H.X.; Lv, J.; Qin, A.M. Friction properties of sisal fiber reinforced nano-SiO2 phenol formaldehyde resin brake composites. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 490–491, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekomaya, O.; Jamiru, T.; Sadiku, R.; Huan, Z. Negative impact from the application of natural fibers. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, P.S.; Portier, R.; Raman, A. Studies on polymer-wood interface bonding: Effect of coupling agents and surface modification. J. Compos. Mater. 1999, 33, 1064–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Paul, S.A.; Pothan, L.A.; Deepa, B. Natural fibres: Structure, properties and applications. In Cellulose Fibers: Bio- and Nano-Polymer Composites; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 3–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A. Synthesis, chemical resistance, and water absorption of bamboo fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Reihmane, S.; Gassan, J. Properties and modification methods for vegetable fibers for natural fiber composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 59, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumithra, H.; Sidda Reddy, B. A review on tribological behaviour of natural reinforced composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2018, 37, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Gassan, J. Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibres. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.; Francucci, G. PHB coating on jute fibers and its effect on natural fiber composites performance. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 50, 2047–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzounis, L.; Debnath, S.; Rooj, S.; Fischer, D.; Mäder, E.; Das, A.; Stamm, M.; Heinrich, G. High performance natural rubber composites with a hierarchical reinforcement structure of carbon nanotube modified natural fibers. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orue, A.; Jauregi, A.; Unsuain, U.; Labidi, J.; Eceiza, A.; Arbelaiz, A. The effect of alkaline and silane treatments on mechanical properties and breakage of sisal fibers and poly (lactic acid)/sisal fiber composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 84, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, V.; Scalici, T.; Nicoletti, F.; Vitale, G.; Prestipino, M.; Valenza, A. A new eco-friendly chemical treatment of natural fibres: Effect of sodium bicarbonate on properties of sisal fibre and its epoxy composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 85, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdoğan, U.H.; Seki, Y.; Aydoğdu, G.; Kutlu, B.; Akşit, A. Effect of different surface treatments on the properties of jute. J. Nat. Fibers 2016, 13, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, S.S.; Hasan, S.M.N.; Hossain, M.J.; Hasan, M. Chemical modification effect on the mechanical properties of coir fiber. Eng. J. 2012, 16, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Keer, L.M. Influence of surface modification on the microstructure and thermo-mechanical properties of bamboo fibers. Materials 2015, 8, 6597–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, M.; Chakraborty, D. Influence of alkali treatment on the fine structure and morphology of bamboo fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 5050–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiropoulos, N.E.; Baillie, C.A.; Hodgkinson, J.M. Engineering and characterisation of the interface in flax fibre/polypropylene composite materials. Part II. The effect of surface treatments on the interface. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2002, 33, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothan, L.A.; George, C.N.; Jacob, M.; Thomas, S. Effect of chemical modification on the mechanical and electrical properties of banana fiber. Polyest. Compos. 2007, 41, 2371–2386. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, M.; Wu, H.; Qiu, F.; Wang, X. Interface bond improvement of sisal fibre reinforced polylactide composites with added epoxy Oligomer. Materials 2018, 11, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Gao, C.; Ye, S. Effect of bamboo fiber modification on tribological performance of brake composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 150–151, 1801–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Gao, C.; Zheng, K.; Lin, Y.; Yang, F. Effect of steam explosion process on tribological performance of bamboo fiber friction composites. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2014, 10, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Gao, C.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, K. Effect of PVC-coated bamboo fiber on tribological performance of its reinforced brake composites. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2015, 3, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, G.; Zheng, D.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Effect of rare-earth addition on morphotropic phase boundary and relaxation behavior of the PNN-PZT ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Wang, S.X.; Huang, Z.H. A kinetic analysis of thermal decomposition of polyaniline and its composites with rare earth oxides. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 119, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, D.D.; Cheng, X.H. Tribological behavior of polytetrafluroethylene composites filled with rare earths treated carbon fiber under dry friction condition. Tribology 2006, 26, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K.; Gao, C.; He, F.; Lin, Y.; Lin, J. Effect of rare earth solution on mechanical and tribological properties of bamboo fiber reinforced brake material. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K. Surface Modifications of Bamboo Fibers and the Effects on Tribological Performance of Automotive Brake Pads. Master’s Thesis, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties; ISO 527-4; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Composites—Determination of Flexural Properties; ISO 14125; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998.
- Fiber-Reinforced Plastics Composites—Determination of Charpy Impact Properties; GB/T 1451-2005; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2005.
- Standard Test Method for Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness of Metallic Materials; GB 4161-1984; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1984.
- Chen, X.; Ashcroft, I.A.; Wildman, R.D.; Tuck, C.J. A combined inverse finite element—Elastoplastic modelling method to simulate the size-effect in nanoindentation and characterise materials from the nano to micro-scale. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2017, 104–105, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.S.; Zhu, X.D.; Lu, S.; He, G.Y.; Xu, K.W. Quantitative evaluation of bonding strength for hard coating by interfacial fatigue strength under cyclic indentation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 315, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazaria, A.M.; Miri, A.K.; Shinozaki, D.M. Mechanical characterization of nanoclay-filled PDMS thin films. Polym. Test. 2016, 52, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jiang, Y.; Cen, Q.; Yan, J. Effect of complex modification of RE-Mg on structure and mechanical properties of high boron iron-based alloys. China Foundry 2013, 62, 641–645. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, D.; Chen, L.; Zhang, D. Tribological properties of PA1010 composites filled with rare earth compounds. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2001, 30, 476–479. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.Z.; Pan, G.W.; Xu, H.L.; Huang, Y.L.; Yang, Y.Q. Cellulosic fibers with high aspect ratio from cornhusks via controlled swelling and alkaline penetration. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 124, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Cheng, H.; Tian, G.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, Q.F.; Zhou, X.; Han, X.; Gao, X. Structures of Bamboo Fiber for Textiles. Text. Res. J. 2010, 80, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Effects of chemical treatments on hemp fibre structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 276, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Takagi, H.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Katoh, M.; Ueki, T.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Li, Y. Influence of alkali treatment on internal microstructure and tensile properties of abaca fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 65, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiha, H.; Sain, M.; Mei, L.H. Modification and characterization of hemp and sisal fibers. J. Nat. Fibers 2014, 11, 144–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.L.; Huang, A.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Liu, J.L. Natural bamboo (Neosinocalamus affinis Keng) fiber identification using FT-IR and 2D-IR correlation spectroscopy. J. Nat. Fibers 2015, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.H.; Fleming, I. Spectroscopic Methods in Organic Chemistry, 6th ed.; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 30–34. ISBN 7-301-04865-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, J. Natural Fiber Reinforced Plastics, 1st ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 27–35. ISBN 7-5025-7603-7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y. Rare Earth Elements and Its Analytical Chemistry, 1st ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 156–166. ISBN 978-7-122-06186-7. [Google Scholar]



| Physical Properties | Mechanical Properties | Chemical Composition (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g·cm−3) | Diameter (µm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (GPa) | Cellulose | Hemicellulose | Lignin | Others |
| 1.34 | 10–25 | 750 | 35 | 58.5 | 18 | 22 | 1.5 |
| Sieve Analysis Test 160-Mesh Sieve (%) | Curing Time 150 °C (s) | Flow Distance 125 °C (mm) | Viscosity (mPa·s) | Molecular Weight | PH | Free Phenol (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤5 | 50~100 | 40~80 | 3~4 | 600~700 | >7 | ≤5 |
| Bamboo Fiber | Resin | Alumina | Barium Sulfate | Copper | Rubber Powder | Graphite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 25 | 25 | 20 | 15 | 5 | 3 |
| Properties | Untreated Composites | Alkali-Treated Composites | RES-Treated Composites | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | Standard Deviation | Average | Standard Deviation | Average | Standard Deviation | |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 40.24 | 1.41 | 42.85 | 0.66 | 43.56 | 0.49 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 68.05 | 0.72 | 70.22 | 0.66 | 72.33 | 0.65 |
| Fracture toughness () | 1.46 | 0.01 | 1.57 | 0.09 | 1.78 | 0.07 |
| Impact strength (kJ/m2) | 6.33 | 0.29 | 6.85 | 0.08 | 7.13 | 0.06 |
| Wave Number (cm−1) | Functional Group Assignment | |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated BF | RES-Treated BF | |
| 3416 | 3424 | O–H, stretching vibration |
| 2922 | 2921 | C–H, stretching vibration |
| 1625 | 1628 | C=O, stretching vibration |
| 1371 | 1372 | C–H, deformation |
| 1032 | 1034 | C–O, stretching vibration |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, K.; Gao, C.; He, F.; Lin, Y.; Liu, M.; Lin, J. Study on the Interfacial Functionary Mechanism of Rare-Earth-Solution-Modified Bamboo-Fiber-Reinforced Resin Matrix Composites. Materials 2018, 11, 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071190
Zheng K, Gao C, He F, Lin Y, Liu M, Lin J. Study on the Interfacial Functionary Mechanism of Rare-Earth-Solution-Modified Bamboo-Fiber-Reinforced Resin Matrix Composites. Materials. 2018; 11(7):1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071190
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Kaikui, Chenghui Gao, Fushan He, Youxi Lin, Ming Liu, and Jiao Lin. 2018. "Study on the Interfacial Functionary Mechanism of Rare-Earth-Solution-Modified Bamboo-Fiber-Reinforced Resin Matrix Composites" Materials 11, no. 7: 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071190
APA StyleZheng, K., Gao, C., He, F., Lin, Y., Liu, M., & Lin, J. (2018). Study on the Interfacial Functionary Mechanism of Rare-Earth-Solution-Modified Bamboo-Fiber-Reinforced Resin Matrix Composites. Materials, 11(7), 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071190






