A High-Throughput Search for Composition–Phase–Property Relations of Cu–Ni/Ti–Al Elastic Copper Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Approach
3. Results and Discussion
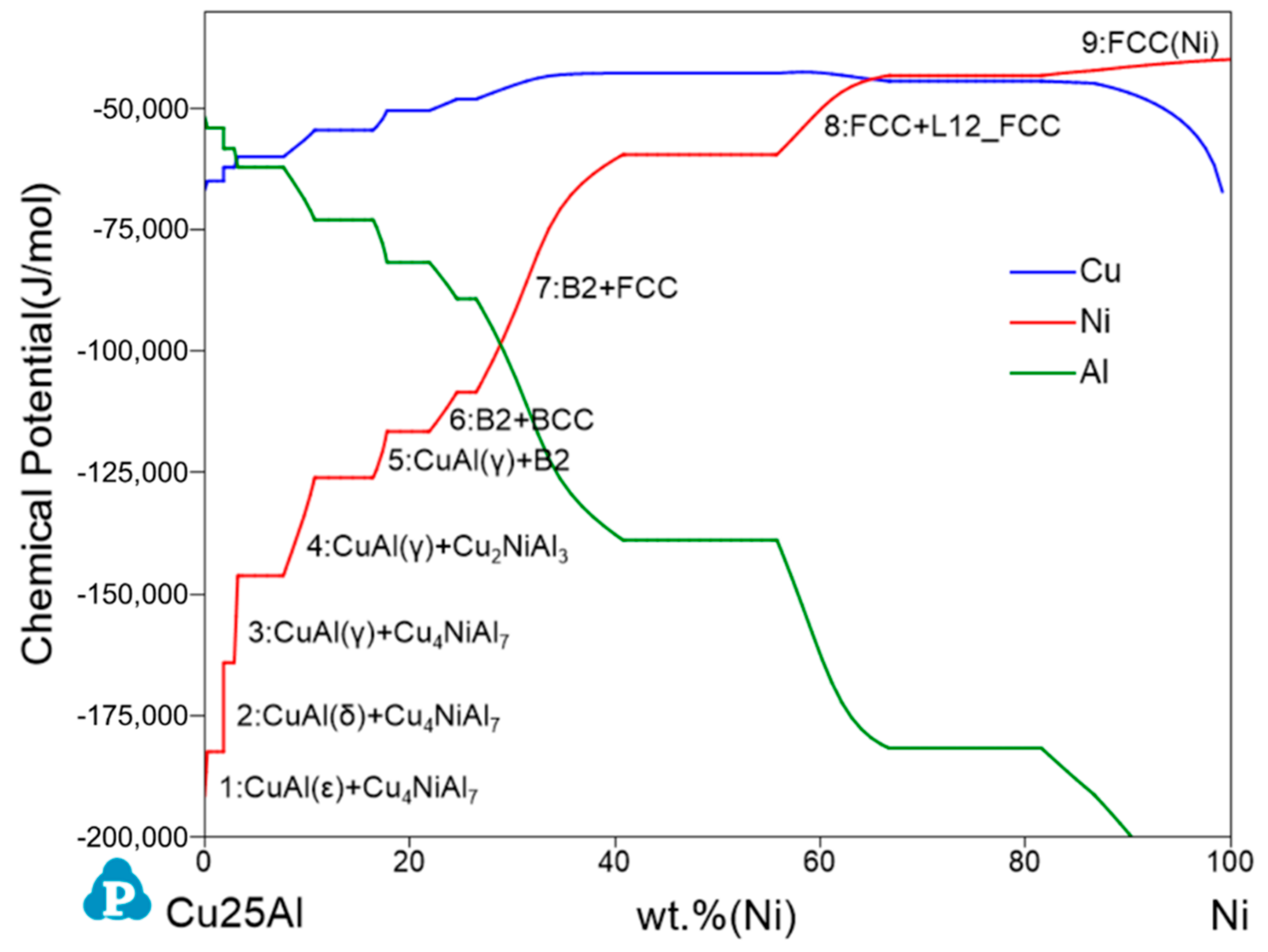
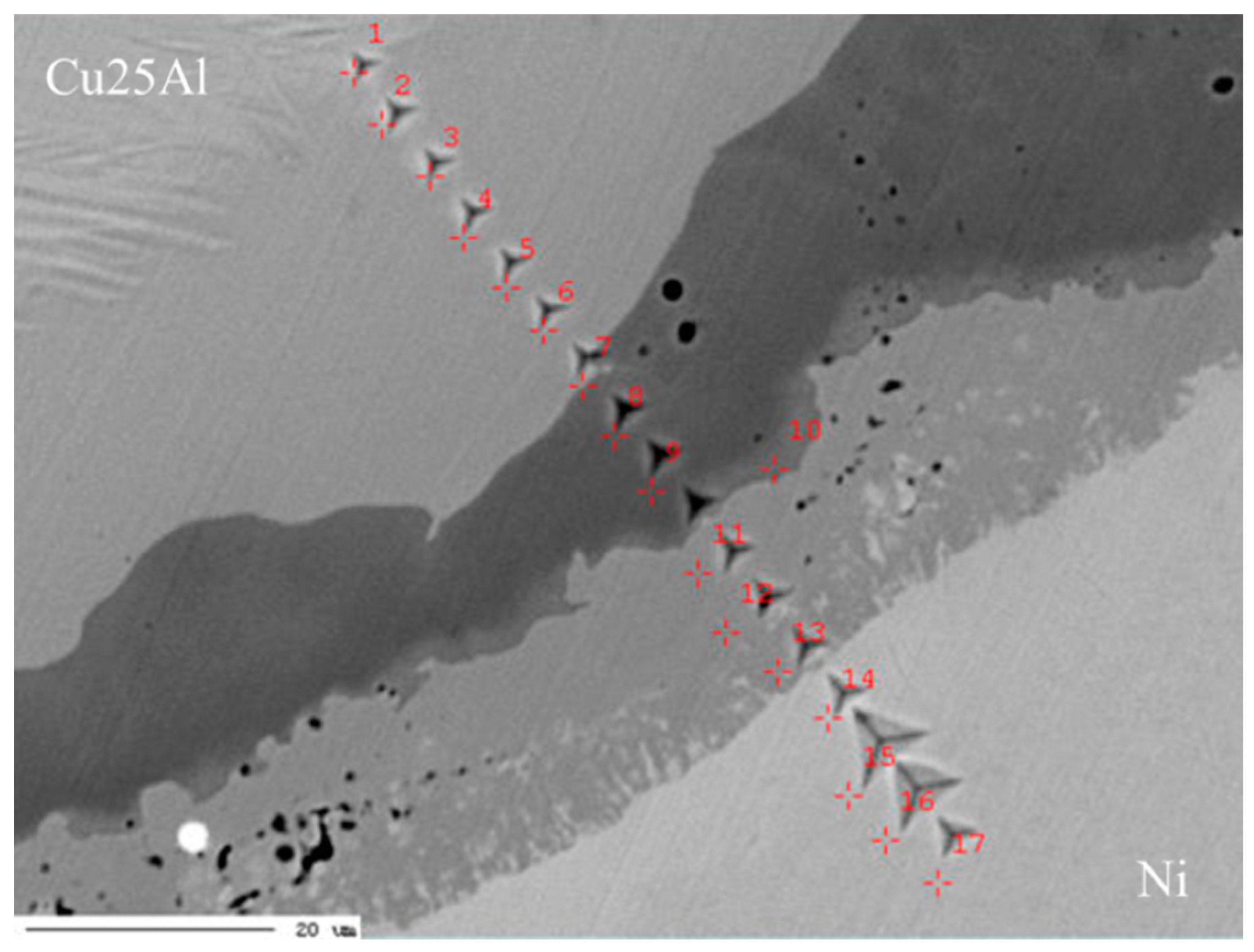
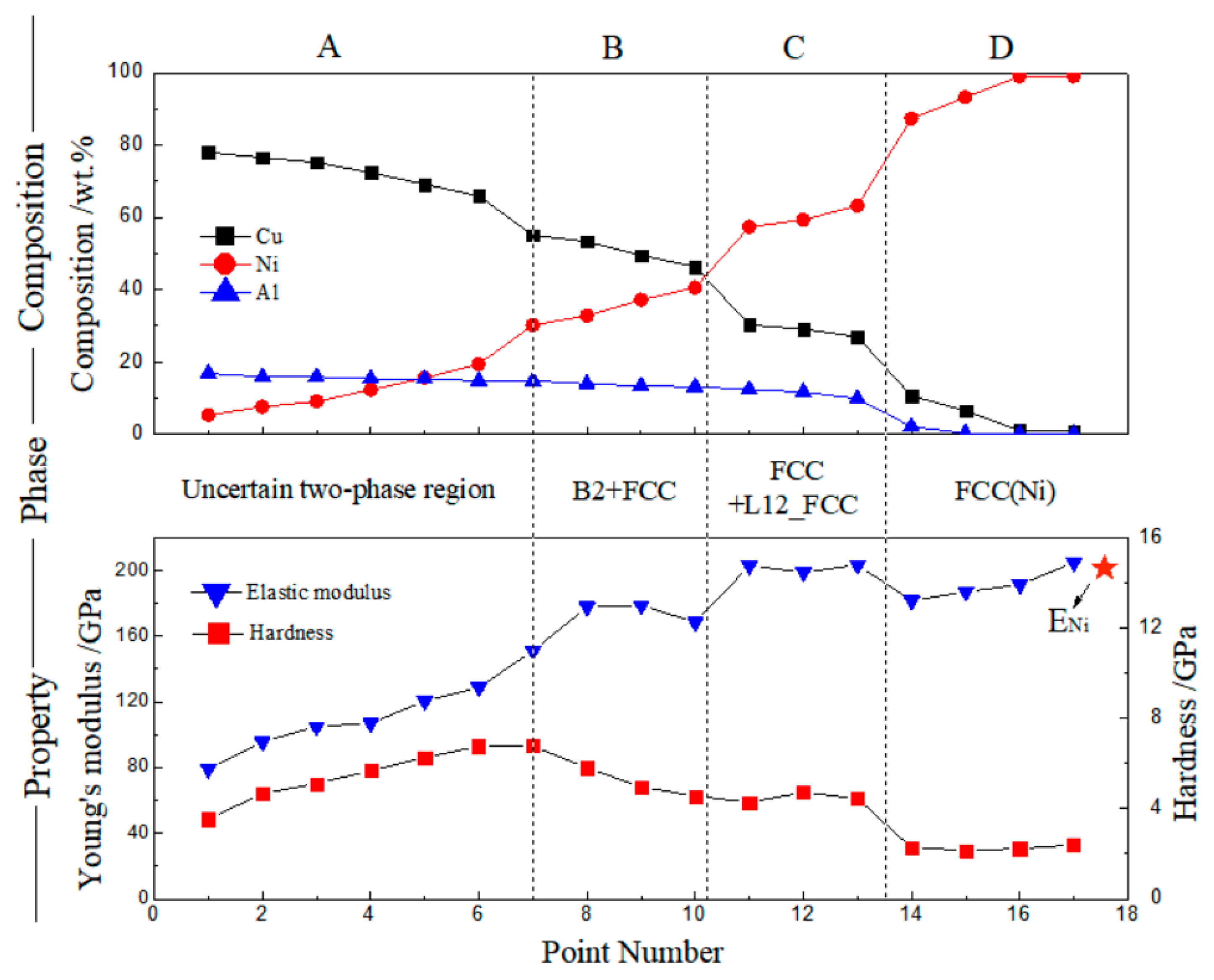
3.1. Cu–Ni–Al System
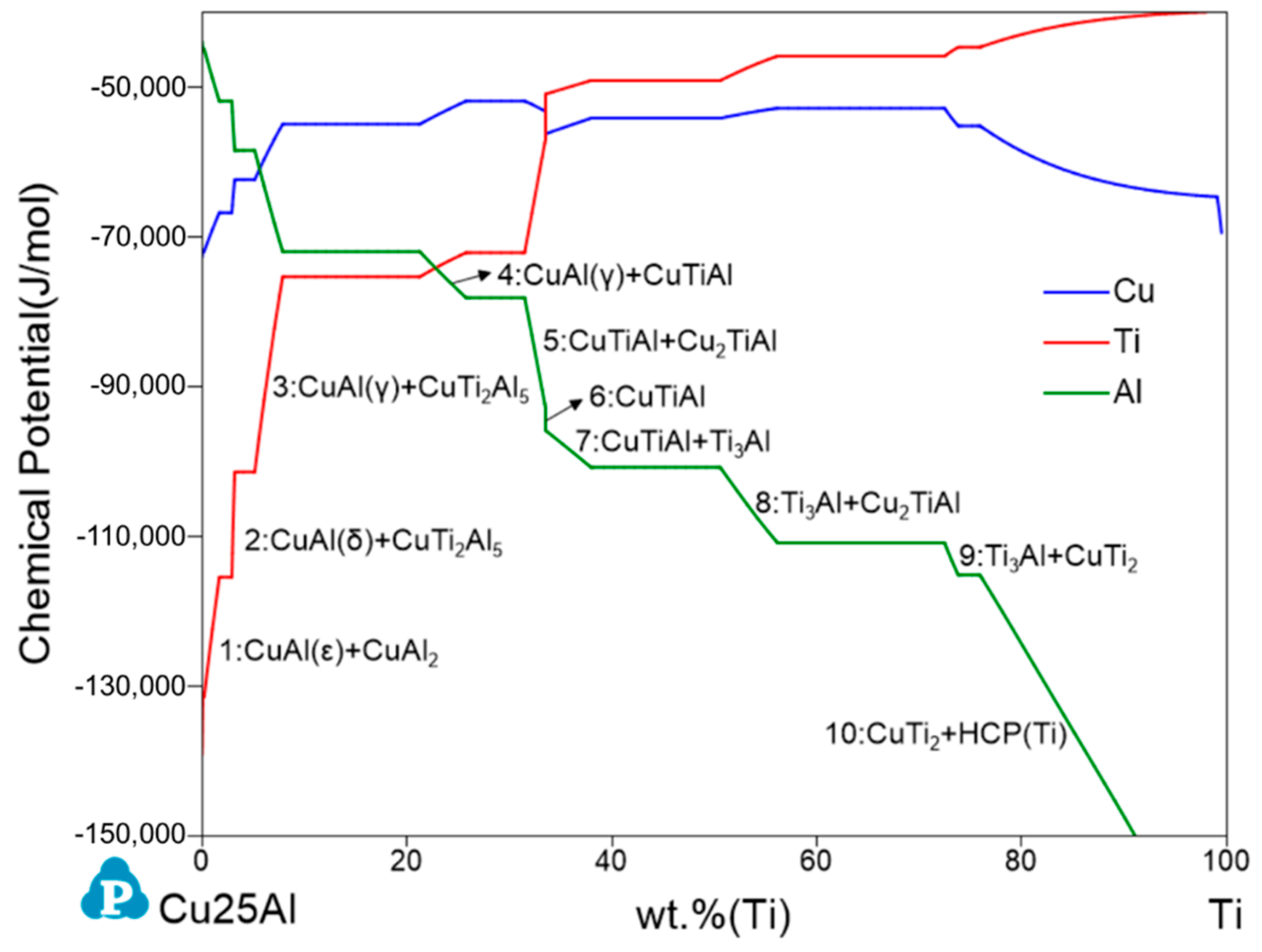
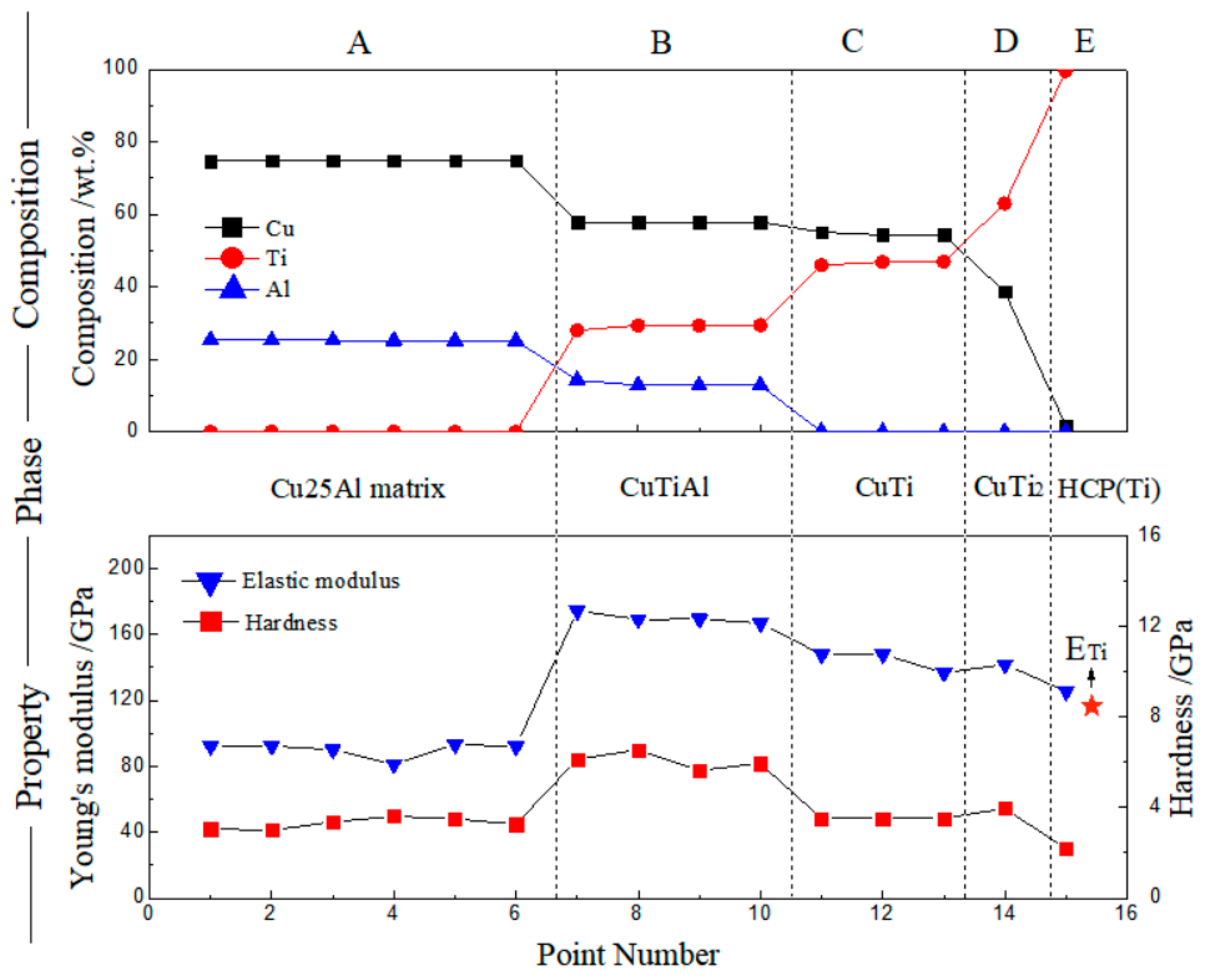
3.2. Cu–Ti–Al System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kukareko, V.A. Role of the structural state of a copper–beryllium alloy in the formation of its tribotechnical properties. Phys. Met. Met. 2017, 118, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouda, P.A.; Azeez, A.; Hydershah, S.J. Sliding Wear Behavior of Cryogenic Treated Copper Beryllium Alloy. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2016, 852, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Yamabe, J.; Matsunaga, H.; Matsuoka, S. Material performance of age-hardened beryllium–copper alloy, CDA-C17200, in a high-pressure, gaseous hydrogen environment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 16887–16900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, N. Beryllium and copper-beryllium alloys. Chembioeng. Rev. 2017, 5, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianez, M.J.; Donoso, E.; Sayagues, M.J.; Perejón, A.; Sánchez-Jiménez, P.E.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.; Criado, J.M. The calorimetric analysis as a tool for studying the aging hardening mechanism of a Cu-10wt%Ni-5.5wt%Sn alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianez, M.J.; Donoso, E.; Criado, J.M.; Sayagués, M.J.; Diaz, G.; Olivares, L. Study by DSC and HRTEM of the aging strengthening of Cu–Ni–Zn–Al alloys. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torra, V.; Martorell, F.; Lovey, F.C.; Sade, M. Remarks on the Particular Behavior in Martensitic Phase Transition in Cu-Based and Ni–Ti Shape Memory Alloys. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 2018, 4, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, J.D.; Sánchez, M.; Ureña, A. Wettability study of a Cu-Ti alloy on tungsten and EUROFER substrates for brazing components of DEMO fusion reactor. Mater. Des. 2016, 99, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Hou, L.F.; Cui, Y.C.; Wei, Y.H. Effect of Ti content on corrosion behavior of Cu-Ti alloys in 3.5% NaCl solution. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gan, X.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, Y.X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, K.C. Effect of applied load on transition behavior of wear mechanism in Cu−15Ni−8Sn alloy under oil lubrication. J. Cent. South Univ. 2017, 24, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J. Effect of Ni Content on Microstructure and Characterization of Cu-Ni-Sn Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi Chieu, L.; Thang, S.M.; Nam, N.D.; Khanh, P.M. The Effect of Deformation on Microstructure of Cu-Ni-Sn Aging Alloys. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 682, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goll, D.; Loeffler, R.; Herbst, J.; Karimi, R.; Pflanz, U.; Stein, R.; Schneider, G. Novel Permanent Magnets by High-Throughput Experiments. JOM 2015, 67, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottman, M.; Zhang, S.; Mcguffin-Cawley, J.; Denney, P.; Narayanan, B.K. Laser Hot Wire Process: A Novel Process for Near-Net Shape Fabrication for High-Throughput Applications. JOM 2015, 67, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, M.J.; Voorhees, P.W. A graphical method for constructing coherent phase diagrams. Acta Met. Mater. 1991, 39, 2001–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, A.; Bernardini, F.; Massidda, S.S. The phase diagrams of iron-based superconductors: Theory and experiments. C. R. Phys. 2016, 17, 5–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, R.J.; Pártay, L.B.; Bartók, A.P.; Payne, M.C.; Csányi, G. Determining pressure-temperature phase diagrams of materials. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 174108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Hirakura, Y.; Yuda, M.; Teramura, T.; Terada, K. Detection of Cocrystal Formation Based on Binary Phase Diagrams Using Thermal Analysis. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.C. A Combinatorial Approach for Efficient Mapping of Phase Diagrams and Properties. J. Mater. Res. 2001, 16, 1565–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Shen, B.; Zhai, J.; Chen, H. Phase Diagrams and Electromechanical Strains in Lead-Free BNT-Based Ternary Perovskite Compounds. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 3510–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Zhao, J.C. Application of dual-anneal diffusion multiples to the effective study of phase diagrams and phase transformations in the Fe–Cr–Ni system. Acta Mater. 2015, 88, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Sim, K.J. General equations of CALPHAD-type thermodynamic description for metallic nanoparticle systems. Calphad 2014, 44, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ales, K. Modelling of phase diagrams and thermodynamic properties using Calphad method—Development of thermodynamic databases. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2013, 66, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Xu, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Du, Y.; Zhang, L.; Kong, D.; Zhang, Z. Application of CALPHAD approach in simulation of liquid phase migration of cellular cemented carbide. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 42, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Stratmann, M.; Du, Y.; Sundman, B.; Steinbach, I. Incorporating the CALPHAD sublattice approach of ordering into the phase-field model with finite interface dissipation. Acta Mater. 2015, 88, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Du, Y. Phase-Field Model of Finite Interface Dissipation: A Novel Way to Directly Couple with calphad Databases. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2016, 37, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Chen, S.L.; Zhang, F.; Wu, K.; Yang, Y.; Chang, Y.A.; Schmid-Fetzer, R.; Oates, W.A. PANDAT software with PanEngine, PanOptimizer and PanPrecipitation for multi-component phase diagram calculation and materials property simulation. Calphad 2009, 33, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Peng, P.; Chen, S.; Wang, P.; Yu, J. Summary of CALPHAD Methods Based on Pandat Software. Hot Work. Technol. 2014, 12, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, P.; Li, W.; Liu, X. Thermodynamic Calculation and Assessment of Ti-Al System Based on Pandat. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 35, 368–373. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, A.; Kumar, K.H. Light Metal Systems. Part 2; Al–Cu–Ni (Aluminium–Copper–Nickel); Effenberg, G., Ilyenko, S., Eds.; Landolt-Börnstein—Group IV Physical Chemistry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 104–126. [Google Scholar]
- Farraro, R.; Mclellan, R.B. Temperature dependence of the Young’s modulus and shear modulus of pure nickel, platinum, and molybdenum. Met. Trans. A 1977, 8, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid-Fetzer, R. Light Metal Systems. Part 2; Al–Cu–Ti (Aluminium–Copper–Titanium); Effenberg, G., Ilyenko, S., Eds.; Landolt-Börnstein—Group IV Physical Chemistry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 156–173. [Google Scholar]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jianwei, W.; Wei, X.; Chuan, Z.; Lu, S.; Guojie, H.; Jingmin, S.; Ligen, W. A High-Throughput Search for Composition–Phase–Property Relations of Cu–Ni/Ti–Al Elastic Copper Alloys. Materials 2018, 11, 2513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122513
Jianwei W, Wei X, Chuan Z, Lu S, Guojie H, Jingmin S, Ligen W. A High-Throughput Search for Composition–Phase–Property Relations of Cu–Ni/Ti–Al Elastic Copper Alloys. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122513
Chicago/Turabian StyleJianwei, Wang, Xiao Wei, Zhang Chuan, Sun Lu, Huang Guojie, Shi Jingmin, and Wang Ligen. 2018. "A High-Throughput Search for Composition–Phase–Property Relations of Cu–Ni/Ti–Al Elastic Copper Alloys" Materials 11, no. 12: 2513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122513
APA StyleJianwei, W., Wei, X., Chuan, Z., Lu, S., Guojie, H., Jingmin, S., & Ligen, W. (2018). A High-Throughput Search for Composition–Phase–Property Relations of Cu–Ni/Ti–Al Elastic Copper Alloys. Materials, 11(12), 2513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122513




