Preparation and Characterization of Zeolite/TiO2 Cement-Based Composites with Excellent Photocatalytic Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Zeolite/TiO2 Composite (ZTC)
2.3. Preparation of Photocatalytic Cement-Based Material (PCM)
2.4. Physicochemical Properties Characterization
2.5. Evaluation of Photocatalytic-Degradation Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties
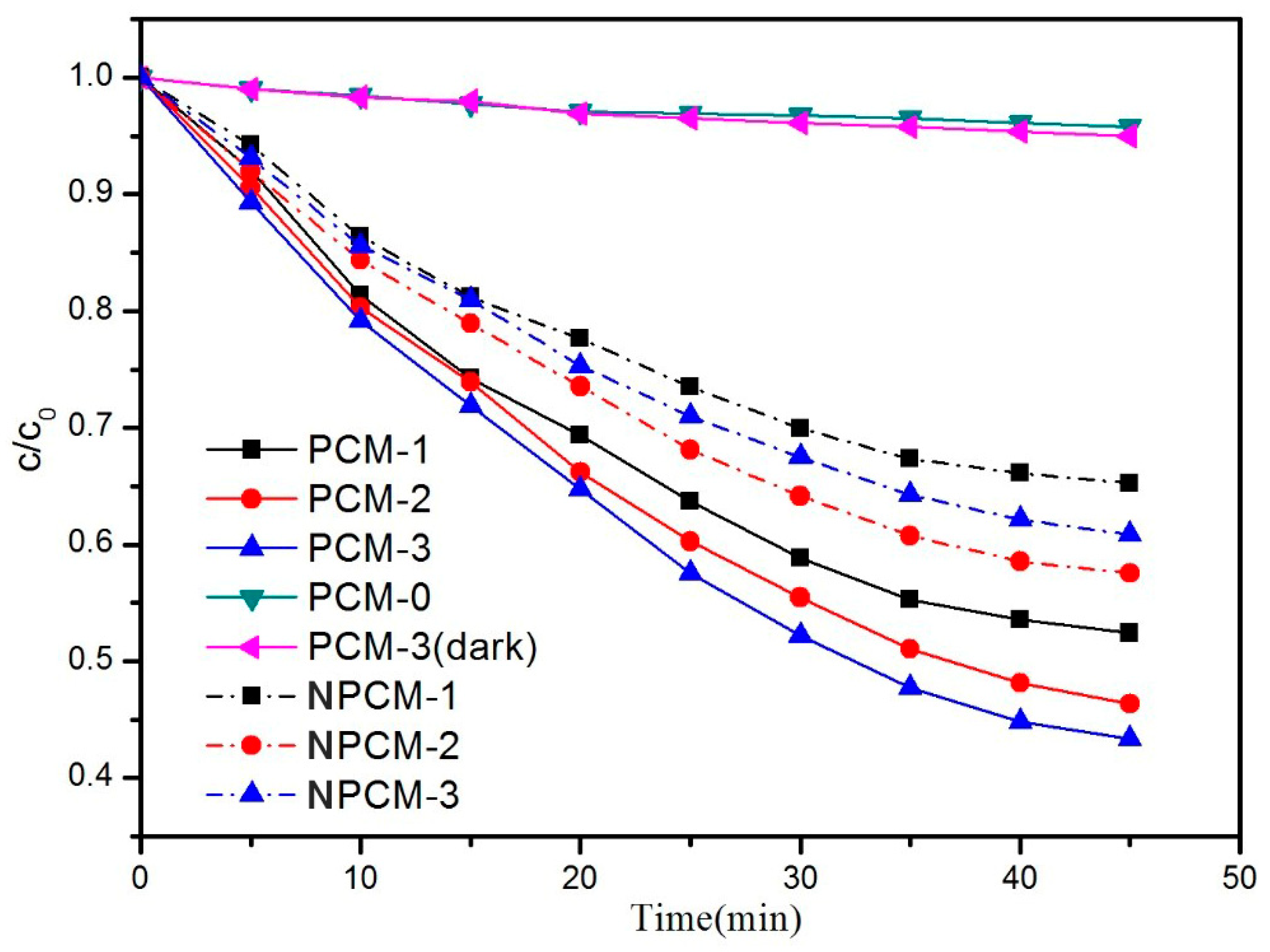
3.2. Evaluation of the Photocatalytic Efficiency
4. Conclusions
- (1)
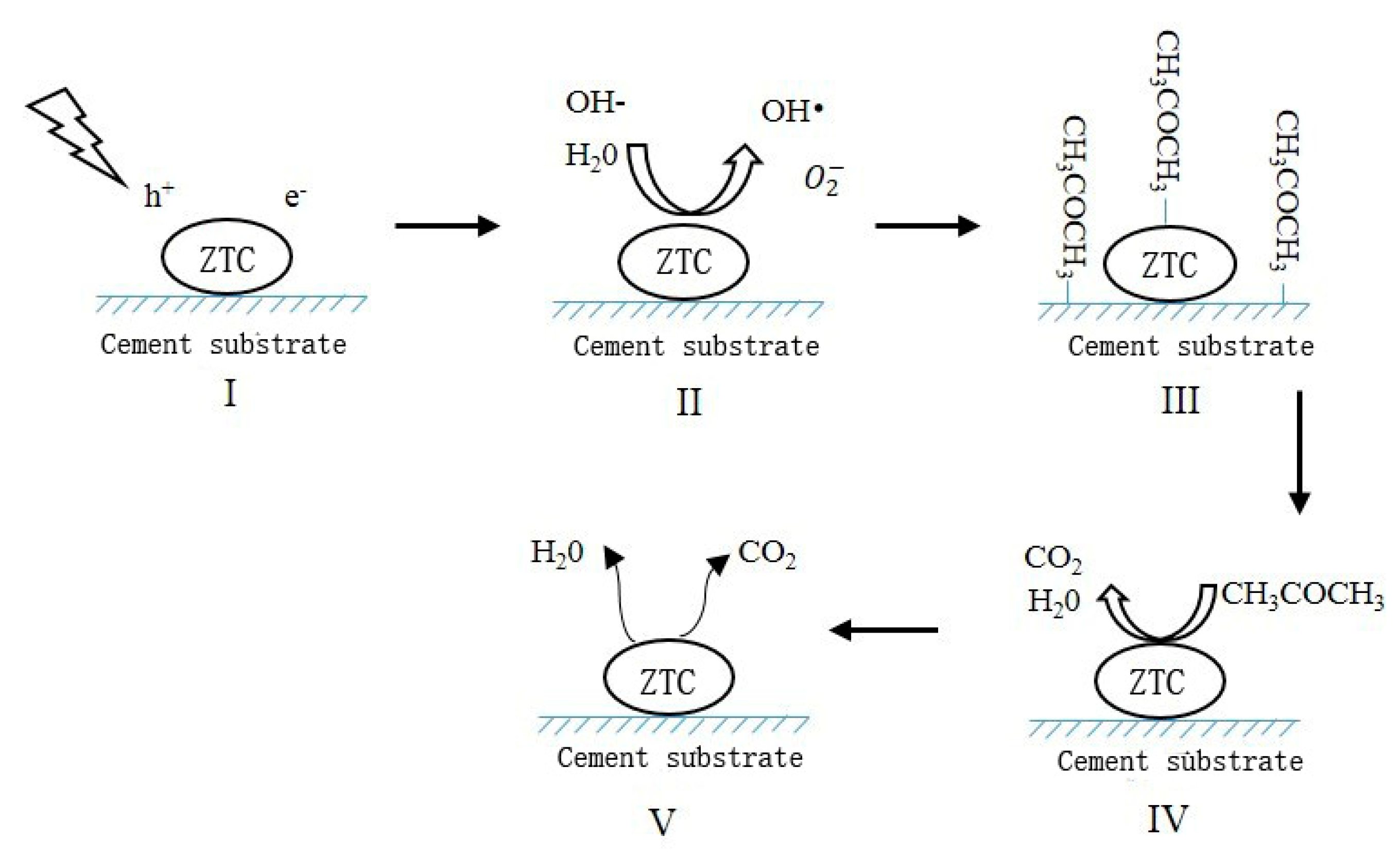
- Due to the large specific surface area, natural zeolite is an optimal carrier for TiO2. After alkali corrosion and calcination, the surface of the MZ was suitable for a TiO2 precipitation. The TiO2 particles were homogeneously dispersed on the surface of the MZ in nano-scale, thereby providing a mass of active sites to participate in the photocatalytic reaction, leading to a high reaction rate.
- (2)
- With the ZTC sprayed onto the surface of the cement matrix, the cement hydration products were not observed on TiO2 particles, indicating that the photocatalytic property of TiO2 particles would not be weakened by a cementitious system and the segregation protection of the ZTC was effective.
- (3)
- Under the same test conditions, the acetone removal rate of PCM-3 reached up to 56% and the reaction rate of PCM-3 was 1.7 times higher than NPCM-3, proving that the ZTC had a high photocatalytic performance and that the middle-carrier method applied in this work contributed to the enhancement of the photocatalytic performance of the PCM.
- (4)
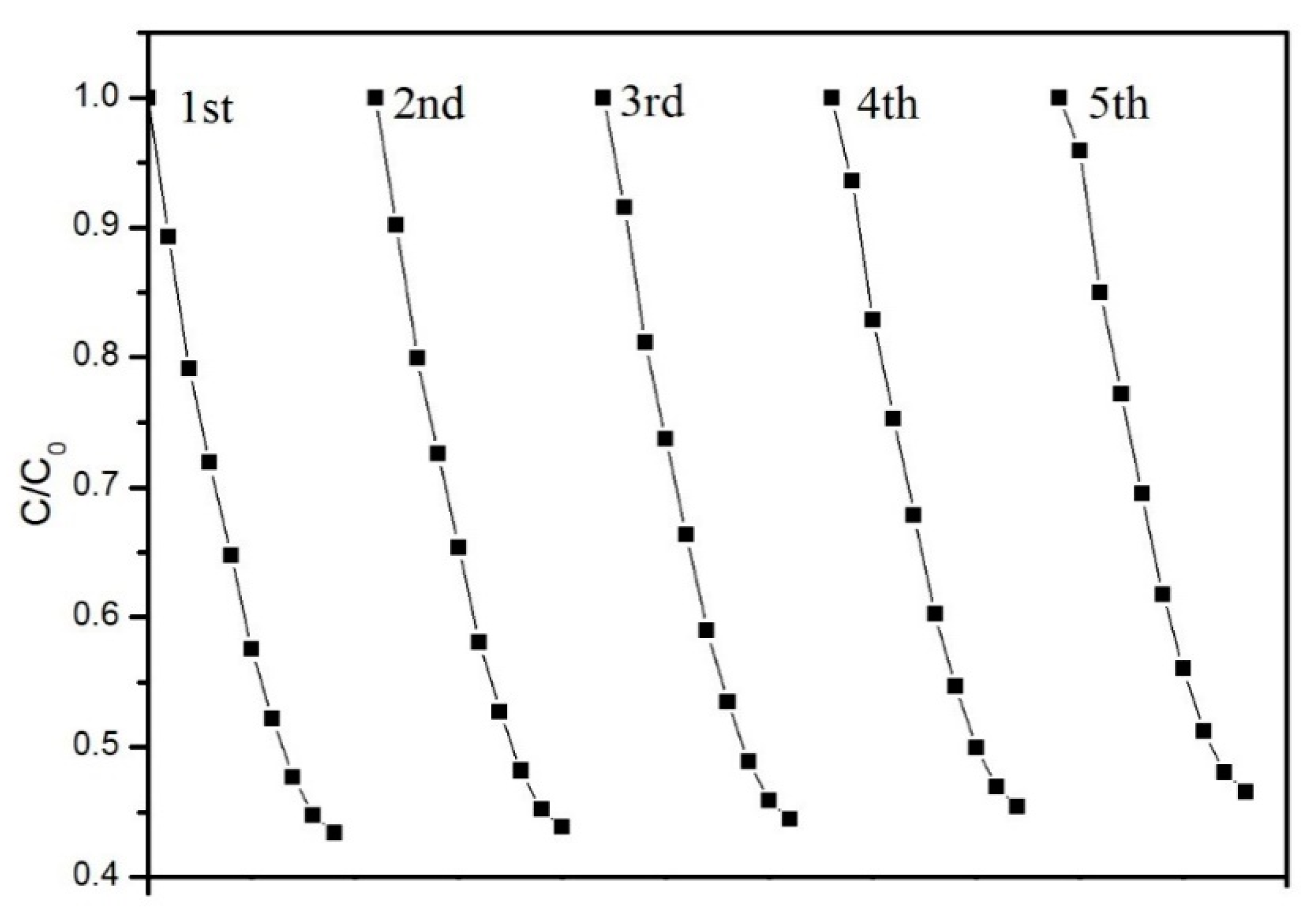
- The removal efficiency of PCM-3 to the acetone was still 52% after cycling five times, thus confirming the durability and stability of the PCM.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demeestere, K.; Dewulf, J.; de Witte, B.; Beeldens, A.; van Langenhove, H. Heterogeneous photocatalytic removal of toluene from air on building materials enriched with TiO2. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, W.K.; Park, J.H.; Chun, H.D. Photocatalytic destruction of VOCs for in-vehicle air cleaning. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2002, 148, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, F.L.; Bertrand, G.; Klein, D.; Coddet, C. Photocatalytic removal of nitrogen oxides via titanium dioxide. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2004, 2, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüsken, G.; Hunger, M.; Brouwers, H.J. Comparative Study on Cementitious Products Containing Titanium Dioxide as Photo-Catalyst. In Proceedings of the International RILEM Symposium on Photocatalysis, Environment and Construction Materials—TDP, Florence, Italy, 8–9 October 2007; pp. 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Dalton, J.S.; Janes, P.A.; Jones, N.G.; Nicholson, J.A.; Hallam, K.R.; Allen, G.C. Photocatalytic oxidation of NOx gases using TiO2: A surface spectroscopic approach. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 120, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, C.H.; Lee, S.C. Enhancement effect of TiO2 immobilized on activated carbon filter for the photodegradation of pollutants at typical indoor air level. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 44, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.S.; Cheung, E. NO removal efficiency of photocatalytic paving blocks prepared with recycled materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1746–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, X.D. Photocatalytic oxidation for indoor air purification: A literature review. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devahasdin, S.; Fan, C., Jr.; Li, K.; Chen, D.H. TiO2 photocatalytic oxidation of nitric oxide: Transient behavior and reaction kinetics. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2003, 156, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Stefanakos, E.K.; Goswami, D.Y. Effect of photocatalytic surface roughness on reactors effectiveness for indoor air cleaning. Build. Environ. 2013, 61, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugrañez, R.; Álvarez, J.I.; Cruz-Yusta, M.; Mármol, I.; Morales, J.; Vila, J.; Sánchez, L. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of NOx gases by regulating the microstructure of mortar cement modified with titanium dioxide. Build. Environ. 2013, 69, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horgnies, M.; Dubois-Brugger, I.; Gartner, E.M. NOx de-pollution by hardened concrete and the influence of activated charcoal additions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Poon, C.-S. Photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide modified concrete materials—Influence of utilizing recycled glass cullets as aggregates. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3436–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, L.; Sun, G.; Guan, L.; Hu, S. The hierarchical porous structure of substrate enhanced photocatalytic activity of TiO2/cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 64, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S.; Tanaka, S.; Tsukamoto, H. Kinetic studies of oxidation of ethylene over a TiO2 photocatalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1999, 121, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folli, A.; Pochard, I.; Nonat, A.; Jakobsen, U.H.; Shepherd, A.M.; Macphee, D.E. Engineering Photocatalytic Cements: Understanding TiO2 Surface Chemistry to Control and Modulate Photocatalytic Performances. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 3360–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackhoff, M.; Prieto, X.; Nestle, N.; Dehn, F.; Niessner, R. Photocatalytic activity of semiconductor-modified cement-influence of semiconductor type and cement ageing. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 43, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kou, S.; Poon, C. Photocatalytic cement-based materials: Comparison of nitrogen oxides and toluene removal potentials and evaluation of self-cleaning performance. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neppolian, B.; Kanel, S.R.; Choi, H.C.; Shankar, M.V.; Arabindoo, B.; Murugesan, V. Photocatalytic degradation of reactive yellow 17 dye in aqueous solution in the presence of TiO2 with cement binder. Int. J. Photoenergy 2003, 5, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, F.; Ruot, B.; Bonafous, L.; Guillot, L.; Pimpinelli, N.; Cassar, L.; Strini, A.; Mapelli, E.; Schiavi, L.; Gobin, C.; et al. Innovative Self-Cleaning and De-Polluting Facade Surfaces. Presented at the CIB World Building Congress 2004, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2–7 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.Y.; Jayapalan, A.R.; Bergin, M.H.; Kurtis, K.E. Photocatalytic cement exposed to nitrogen oxides: Effect of oxidation and binding. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 60, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Burton, M.; Jobson, B.; Haselbach, L. Pervious concrete with titanium dioxide as a photocatalyst compound for a greener urban road environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafabadi, A.T.; Taghipour, F. Physicochemical impact of zeolites as the support for photocatalytic hydrogen production using solar-activated TiO2-based nanoparticles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 82, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, E.P.; Davydov, L.; Smirniotis, P. TiO2-loaded zeolites and mesoporous materials in the sonophotocatalytic decomposition of aqueous organic pollutants: The role of the support. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2003, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, I.; Suárez, S.; Garcia-Garcia, F.J.; Sánchez, B. Zeolite-TiO2 hybrid composites for pollutant degradation in gas phase. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 178, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, X.; Zheng, S.; Sun, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, H. Influence of calcination temperature on the structural, adsorption and photocatalytic properties of TiO2 nanoparticles supported on natural zeolite. Powder Technol. 2015, 274, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, P.; Hu, S. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of cementitious material with TiO2@Ag modified fly ash micro-aggregates. Cuihua Xuebao/Chin. J. Catal. 2017, 38, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, B.; Su, Y. Hydrothermal preparation and photocatalytic activity of hierarchically sponge-like macro-/mesoporous Titania. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 10582–10589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Jiang, A.; Shen, C.; Yan, T. Seasonal choice of factors defining the ultraviolet radiation intensity levels. Sci. Meteorol. Sin. 2010, 30, 516–521. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, Y.; Tseng, K.Y.; Wang, W.Y. Decomposition of gaseous acetone in an annular photoreactor coated with TiO2 thin film. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2005, 168, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Man, A.J.M.; Sauer, J. Coordination, Structure, and Vibrational Spectra of Titanium in Silicates and Zeolites in Comparison with Related Molecules. An ab Initio Study. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.Z.; Li, C.L.; Lu, L.N.; Bing, L.W. A facile and low-cost synthesis of granulated blast furnace slag-based cementitious material coupled with Fe2O3 catalyst for treatment of dye wastewater. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 138–139, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, D. Bibliography of Work on Photocatalytic Removal of Hazardous Compounds from Water and Air. Sol. Energy 2001, 30, 845–856. [Google Scholar]
- Jenny, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Zhang, J.; Horiuchi, Y.; Anpo, M.; Bahnemann, D. Understanding TiO2 photocatalysis: Mechanisms and materials. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9919–9986. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, G.; Marquaire, P.M.; Zahraa, O. Abatement of volatile organic compounds using an annular photocatalytic reactor: Study of gaseous acetone. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2008, 197, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H. Zeolite-based photocatalysts. Chem. Commun. 2004, 35, 1443–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, S. Zeolite photochemistry: Impact of zeolites on photochemistry and feedback from photochemistry to zeolite science. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2003, 4, 19–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M.; Anpo, M. Local structures, excited states, and photocatalytic reactivities of highly dispersed catalysts constructed within zeolites. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2003, 3, 225–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Pehkonen, S.O.; Ray, M.B. Kinetics and mechanisms of UV-photodegradation of chlorinated organics in the gas phase. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4203–4214. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.W.; Ray, M.B. Application of ultraviolet photooxidation to remove organic pollutants in the gas phase. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2000, 19, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, K.; Tonegawa, Y.; Ishitani, O. Destruction of Indoor Air Pollutants in TiO2-Wall Coated Cylindrical Flow Reactor Under 254 nm UV Irradiation. J. Adv. Oxid. Technol. 1999, 4, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Guan, B. Photocatalytic oxidation of nitrogen oxides using TiO2 loading on woven glass fabric. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, J.M.; Kataoka, S.; Tejedor-Tejedor, I.; Anderson, M.A. Dynamic phenomena during the photocatalytic oxidation of ethanol and acetone over nanocrystalline TiO2: Simultaneous FTIR analysis of gas and surface species. J. Catal. 2003, 219, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zi, G.; Suib, S.L.; Obee, T.N.; Hay, S.O.; Freihaut, J.D. Photocatalytic Oxidation of Toluene on Nanoscale TiO2 Catalysts: Studies of Deactivation and Regeneration. J. Catal. 2000, 196, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

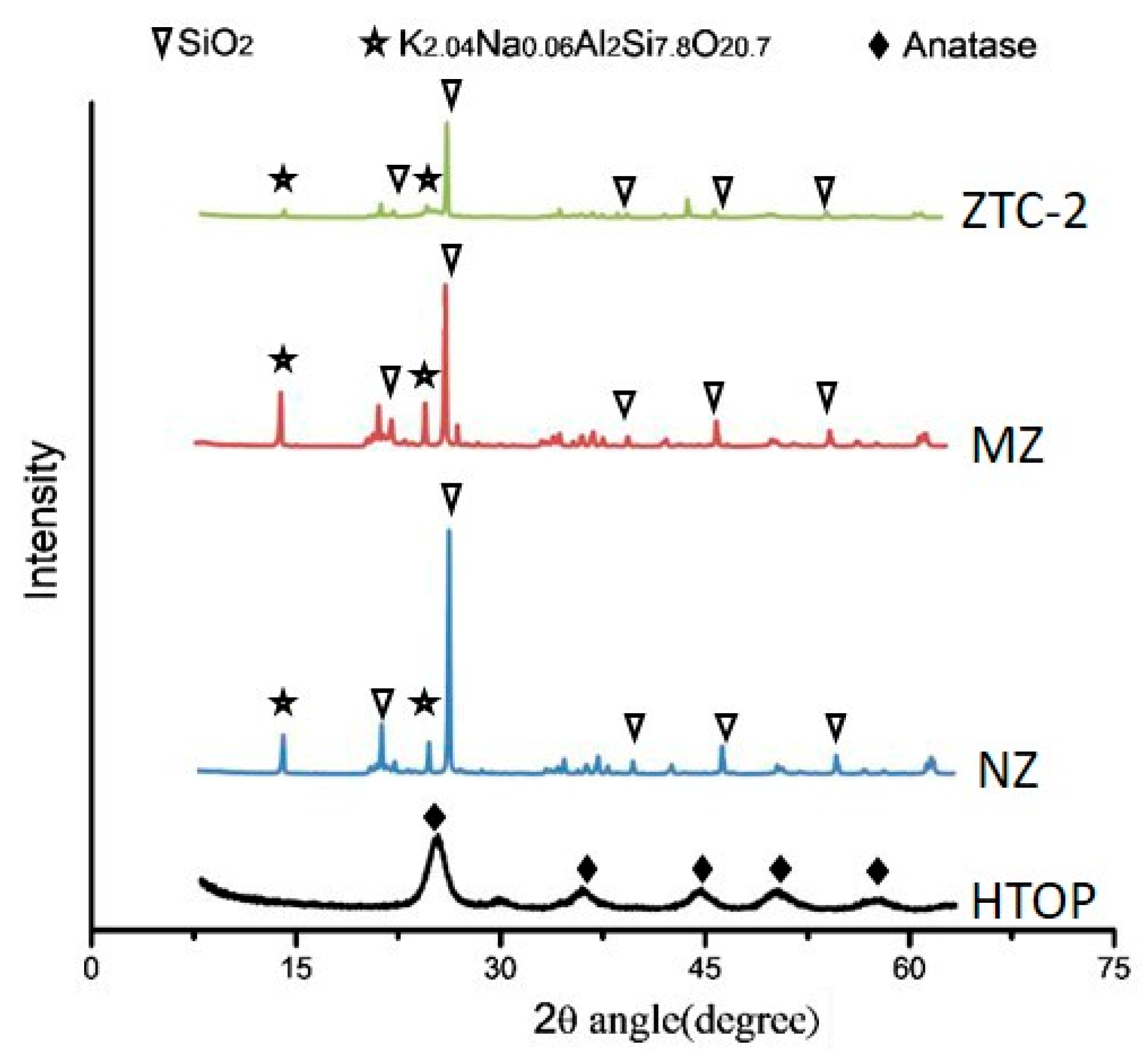
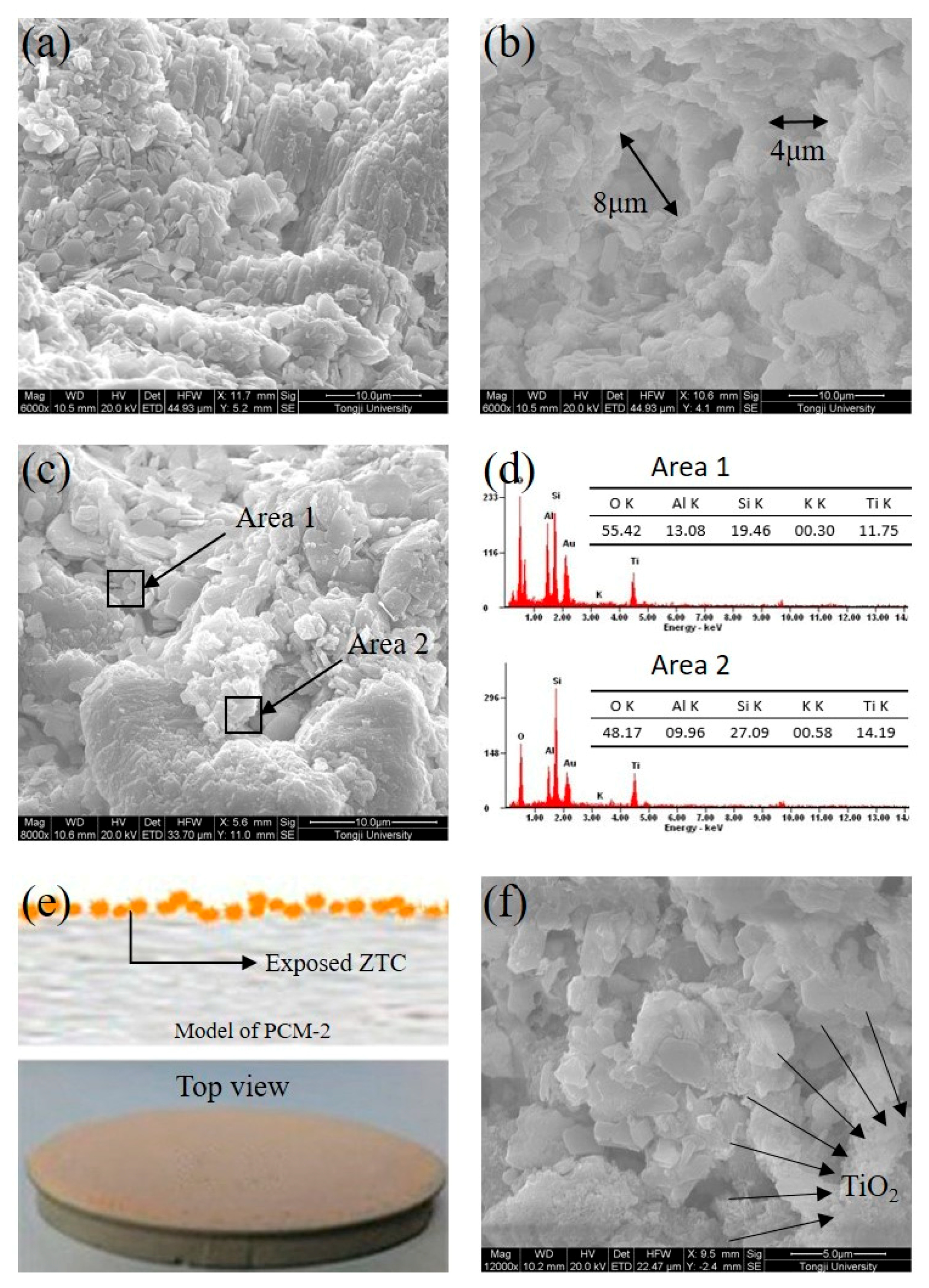
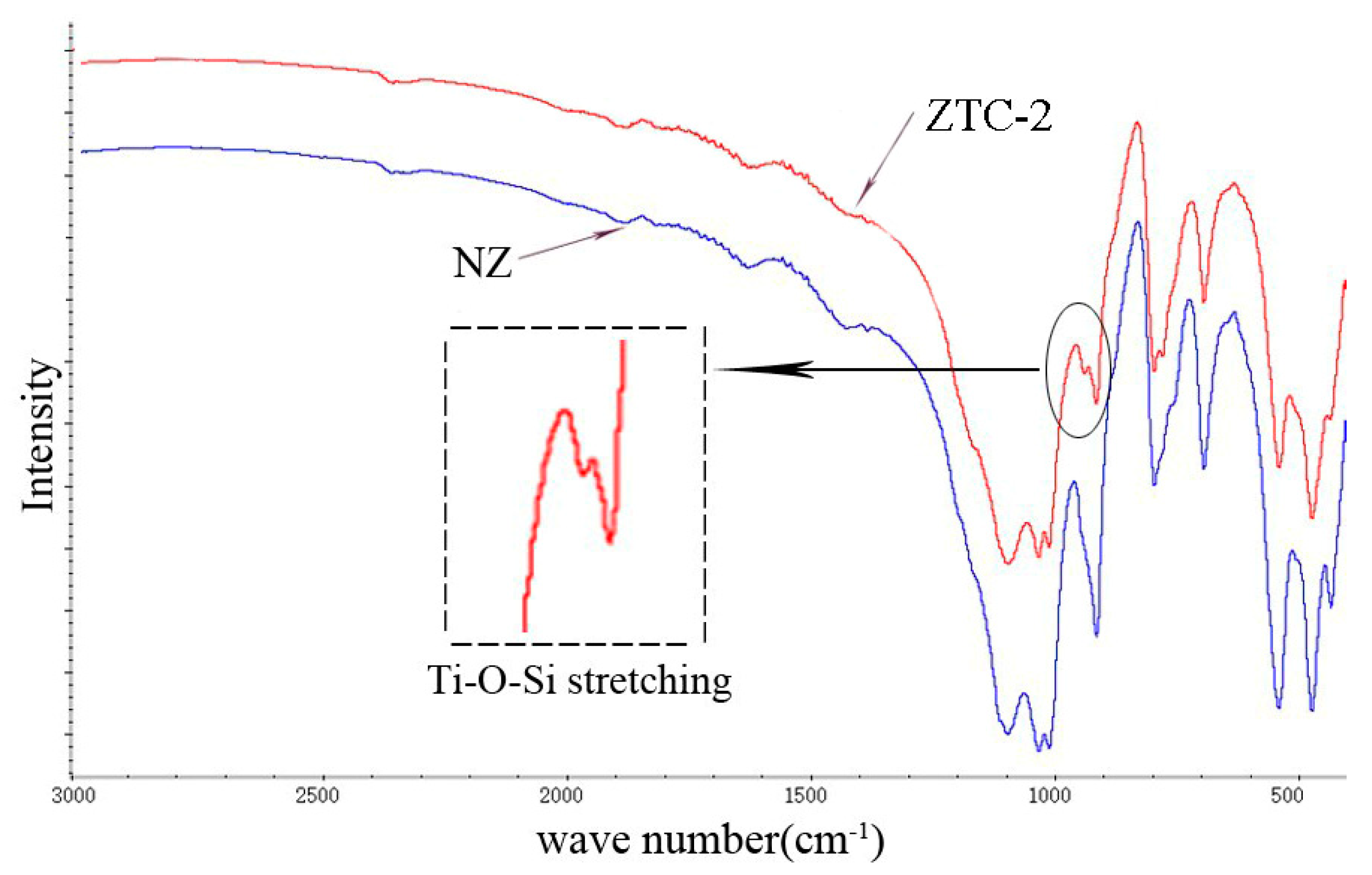

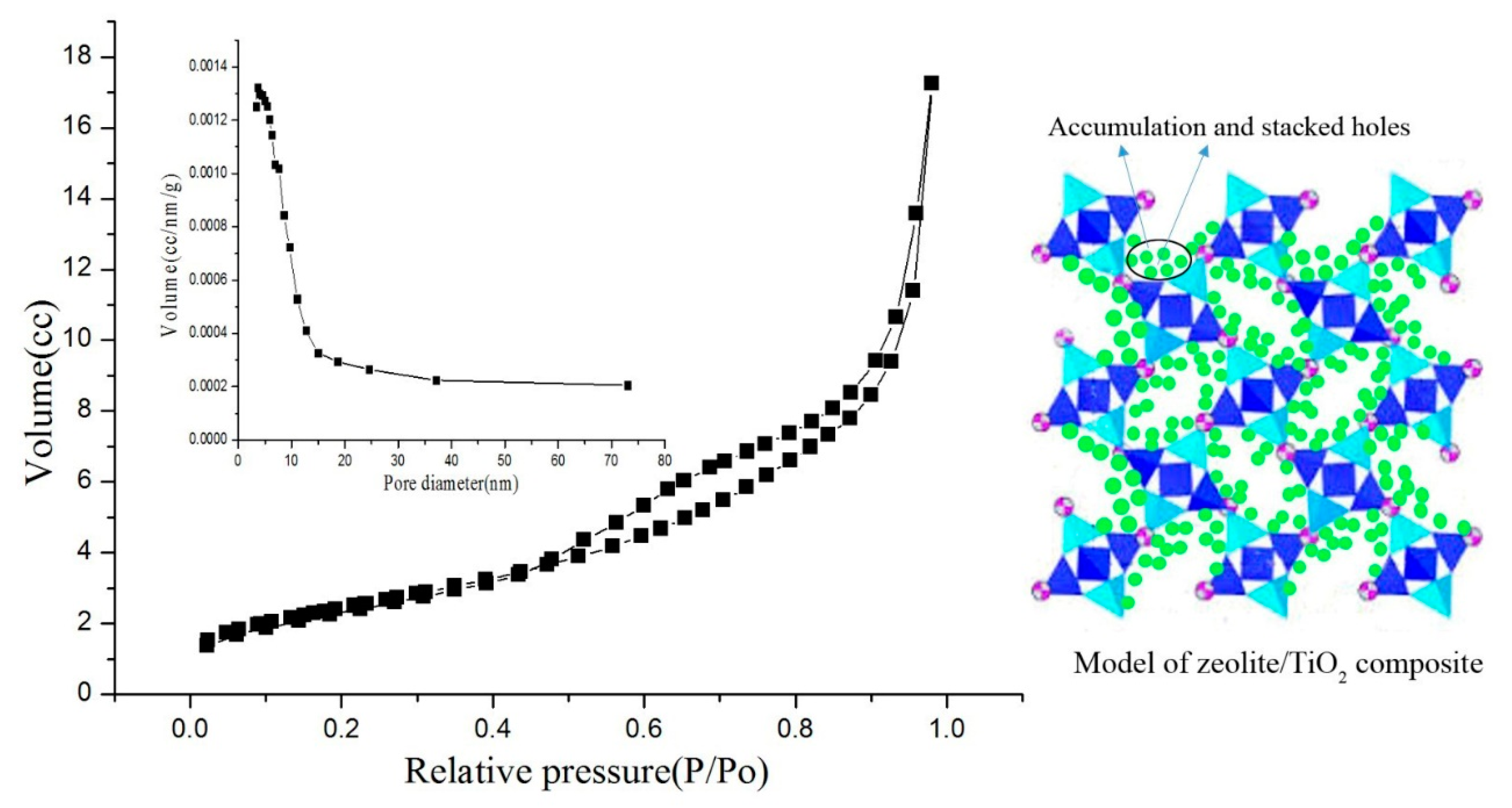

| Density (g/cm3) | Wear Rate | Pore Size (mm) | Water Absorption | Volume Weight (T/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.55 | <0.03% | 0.125~0.425 | 0.3% | 1.70 |
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Na2O | CaO | K2O | MgO | Fe2O3 | FeO | TiO2 | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60~70 | 17.8 | 4.2 | 2.6 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.26 |
| Specimen | TiO2-sol/MZ Ratio | TiO2 Content (wt%) |
|---|---|---|
| ZTC-1 | 0.47 | 0.99 |
| ZTC-2 | 2.36 | 4.76 |
| ZTC-3 | 4.72 | 9.10 |
| Specimen | Water (g) | Cement (g) | Photocatalyst Type | Photocatalyst (g) | TiO2 (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCM-0 | 9.9 | 22 | - | - | - |
| PCM-1 | 9.9 | 22 | ZTC-1 | 0.220 | 0.002 |
| PCM-2 | 9.9 | 22 | ZTC-2 | 0.220 | 0.010 |
| PCM-3 | 9.9 | 22 | ZTC-3 | 0.220 | 0.020 |
| NPCM-1 | 9.9 | 22 | HTOP | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| NPCM-2 | 9.9 | 22 | HTOP | 0.010 | 0.010 |
| NPCM-3 | 9.9 | 22 | HTOP | 0.020 | 0.020 |
| Sample | S (m2g−1) a | V (cm3g−1) b | D (nm) c |
|---|---|---|---|
| MZ | 412 | 0.32 | 11.15 |
| ZTC-2 | 319 | 0.24 | 10.87 |
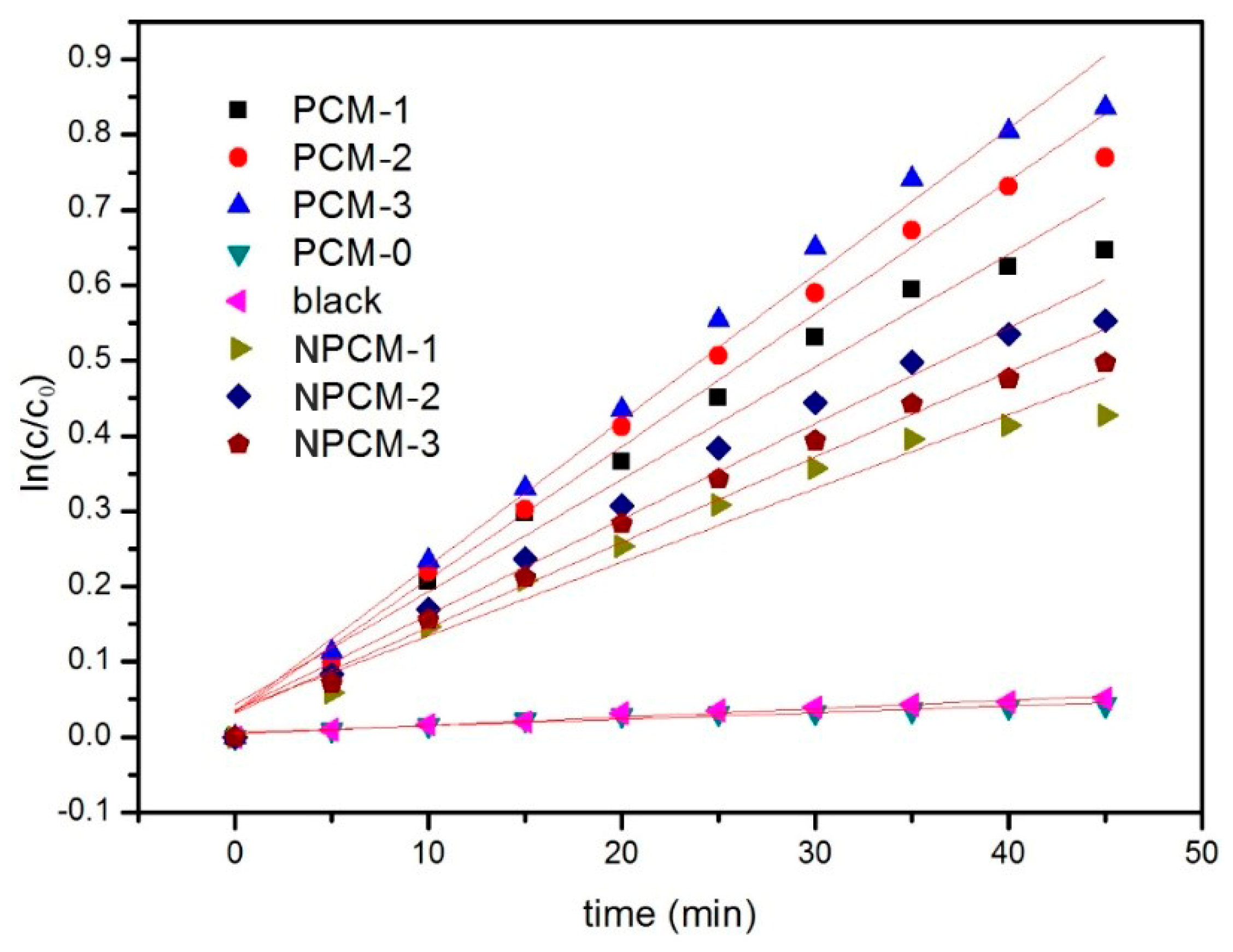
| Specimen | Reaction Rates (k/min−1) | Relativity (R2) |
|---|---|---|
| blank | 0.0011 | 0.9678 |
| PCM-0 | 0.0008 | 0.9273 |
| PCM-1 | 0.0140 | 0.9684 |
| PCM-2 | 0.0177 | 0.9860 |
| PCM-3 | 0.0194 | 0.9856 |
| NPCM-1 | 0.0097 | 0.9581 |
| NPCM-2 | 0.0120 | 0.9767 |
| NPCM-3 | 0.0113 | 0.9766 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, G.; Yao, W.; Zuo, J. Preparation and Characterization of Zeolite/TiO2 Cement-Based Composites with Excellent Photocatalytic Performance. Materials 2018, 11, 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122485
Liao G, Yao W, Zuo J. Preparation and Characterization of Zeolite/TiO2 Cement-Based Composites with Excellent Photocatalytic Performance. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122485
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Gang, Wu Yao, and Junqing Zuo. 2018. "Preparation and Characterization of Zeolite/TiO2 Cement-Based Composites with Excellent Photocatalytic Performance" Materials 11, no. 12: 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122485
APA StyleLiao, G., Yao, W., & Zuo, J. (2018). Preparation and Characterization of Zeolite/TiO2 Cement-Based Composites with Excellent Photocatalytic Performance. Materials, 11(12), 2485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122485




