Morphology, Thermal, Mechanical Properties and Rheological Behavior of Biodegradable Poly(butylene succinate)/poly(lactic acid) In-Situ Submicrofibrillar Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
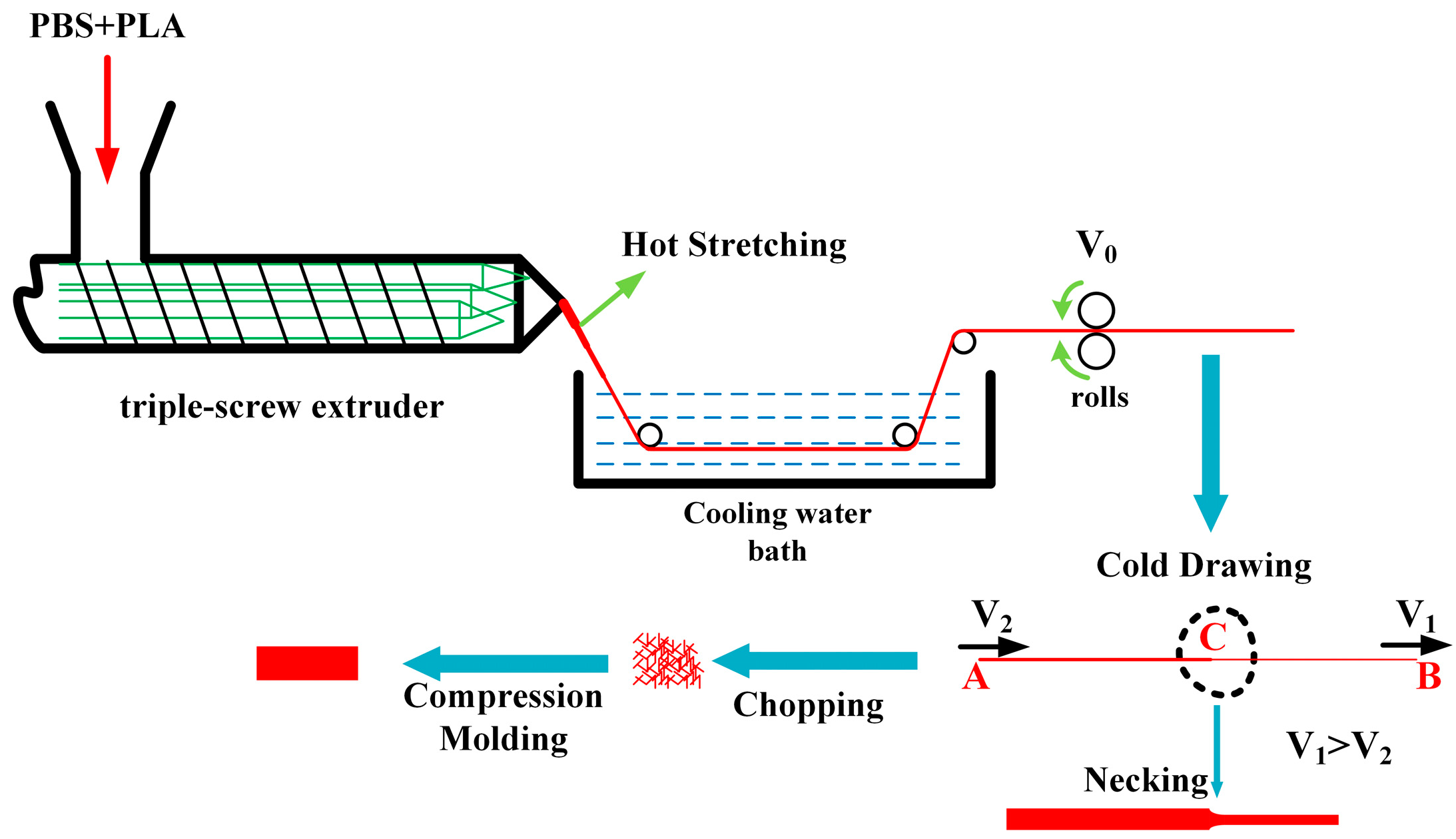
2.2. Preparation of PBS/PLA Composites
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4. Rheological Characterization Measurements
2.5. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA)
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Measurements
2.7. Wide-Angle X-ray Diffraction (WAXD)
2.8. Tensile Tests
3. Results and Discussions
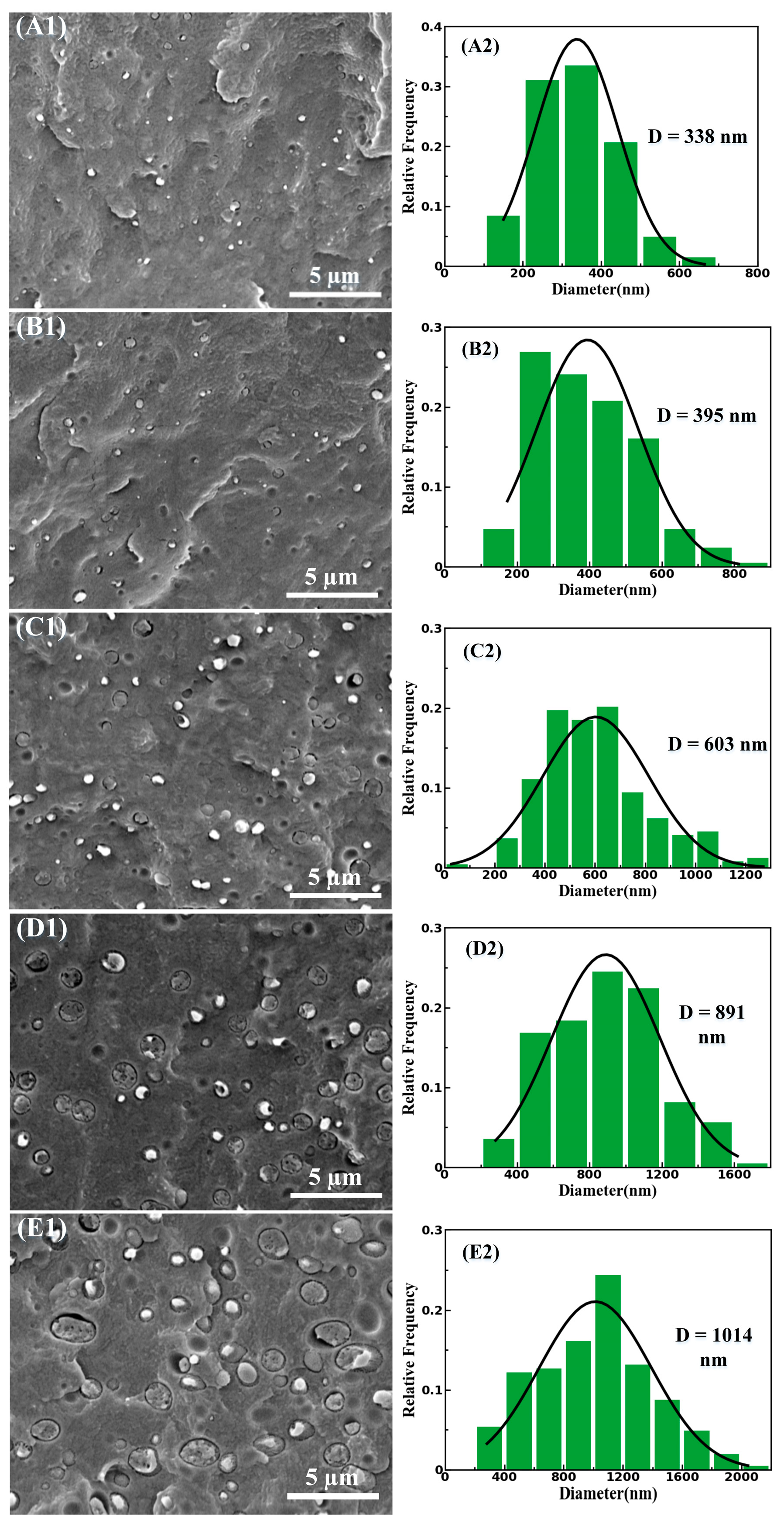
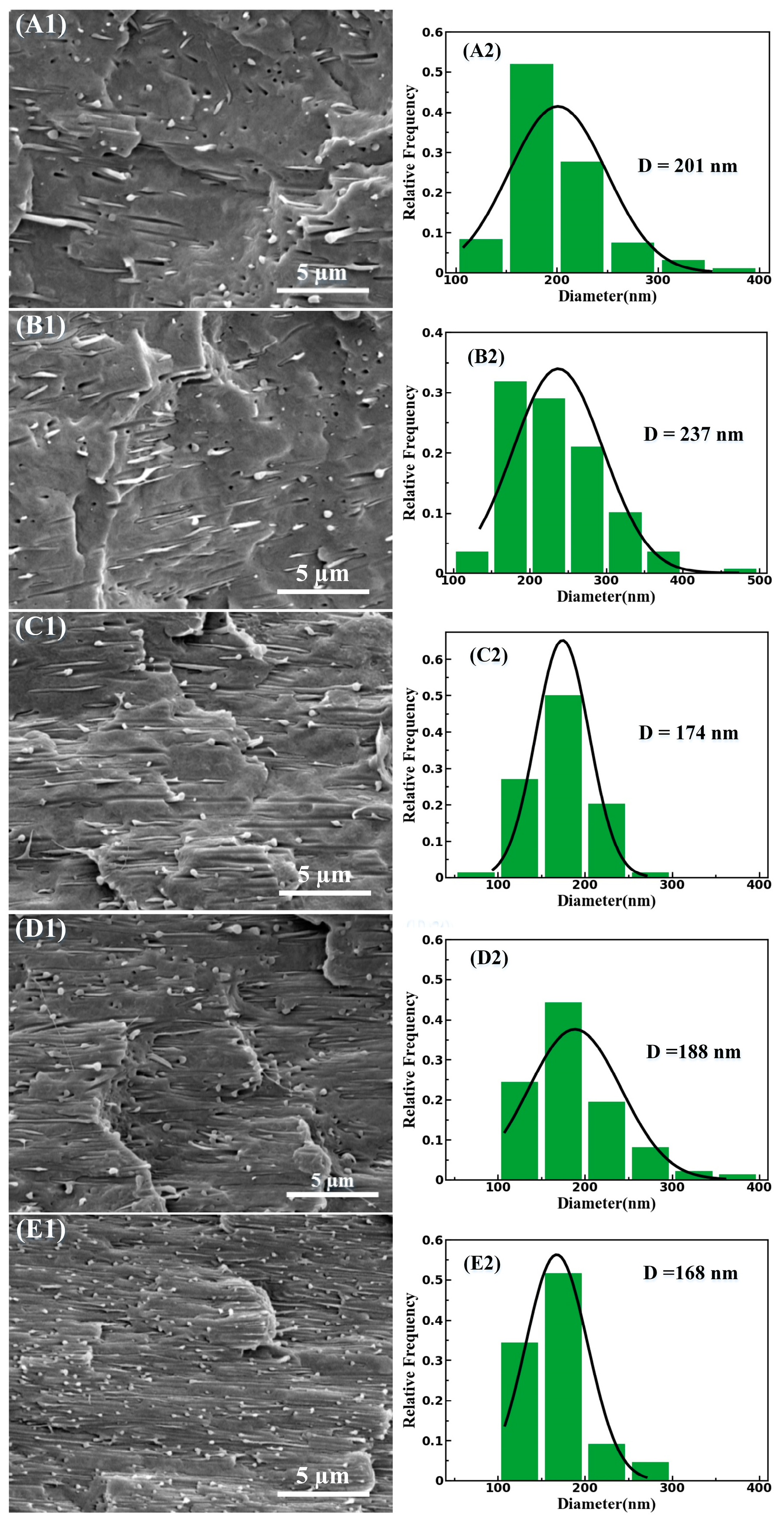
3.1. Phase Morphology of PBS/PLA Composites
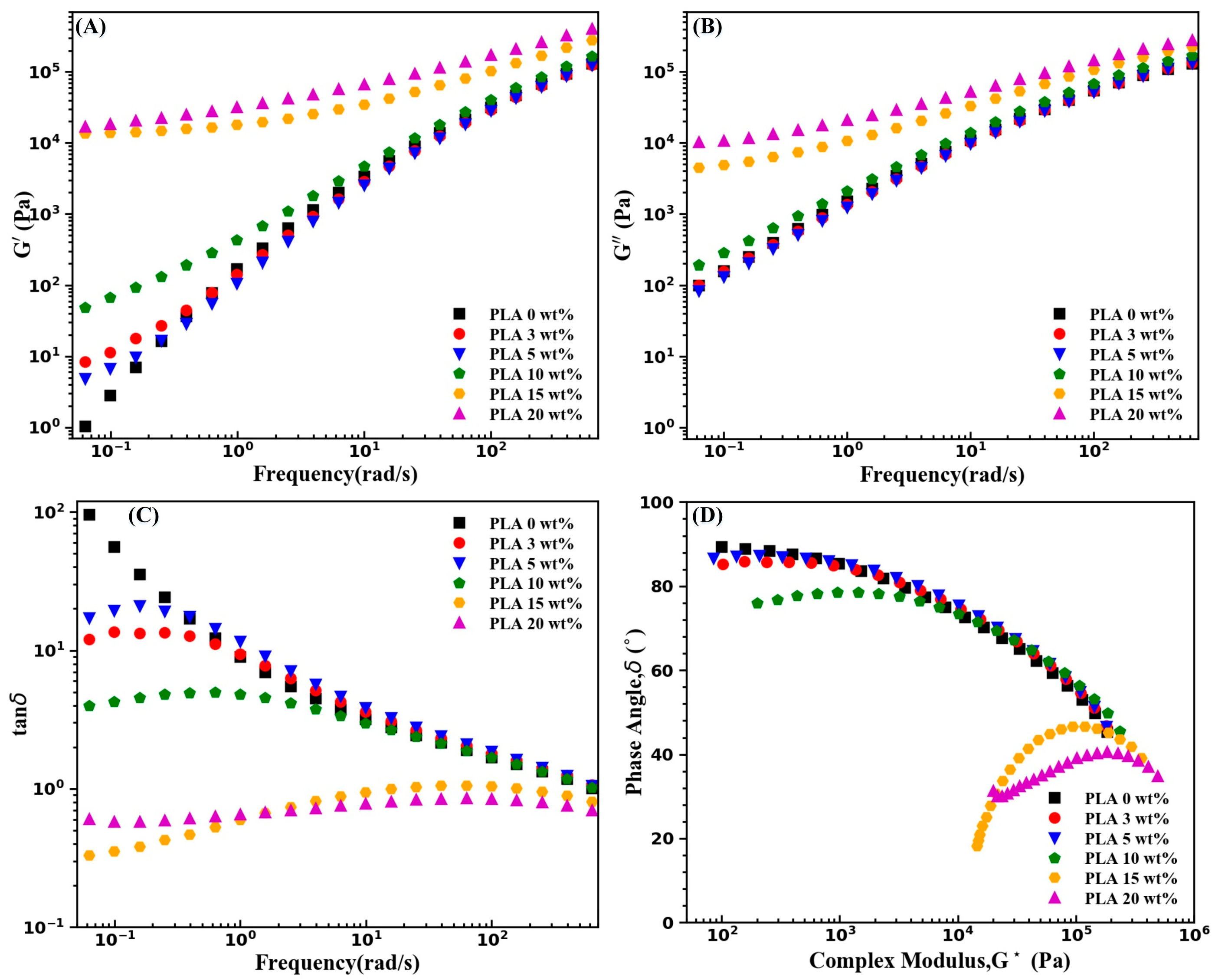
3.2. Rheological Behaviors
3.3. Thermal Properties
3.4. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calabia, B.; Ninomiya, F.; Yagi, H.; Oishi, A.; Taguchi, K.; Kunioka, M.; Funabashi, M. Biodegradable poly(butylene succinate) composites reinforced by cotton fiber with silane coupling agent. Polymers 2013, 5, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wu, C.; Peng, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhuang, J.; Cao, X.; Roy, V.A.L.; Li, R.K.Y. Effect of nitrogen-doped graphene on morphology and properties of immiscible poly(butylene succinate)/polylactide blends. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2017, 113, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yuan, L.; Laredo, E.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, W. Interfacial properties, viscoelasticity, and thermal behaviors of poly(butylene succinate)/polylactide blend. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, G.Z.; Bikiaris, D.N. Synthesis, cocrystallization, and enzymatic degradation of novel poly(butylene-co-propylene succinate) copolymers. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2437–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, Y.; Giang, N.T.T.; Ninomiya, F.; Funabashi, M.; Kunioka, M. Cellulose acetate butyrate as multifunctional additive for poly(butylene succinate) by melt blending: Mechanical properties, biomass carbon ratio, and control of biodegradability. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2010, 95, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Mincheva, R.; Xu, Y.; Raquez, J.M.; Dubois, P. High molecular weight poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene furandicarboxylate) copolyesters: From catalyzed polycondensation reaction to thermomechanical properties. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 2973–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Li, F.; Yu, J.; Cao, A. Synthesis of poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene terephthalate) (pbst) copolyesters with high molecular weights via direct esterification and polycondensation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jin, J. Synthesis and biodegradation of aliphatic polyesters from dicarboxylic acids and diols. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.M.; Wang, Y.Z.; Yang, K.K.; Wang, X.L.; Zhou, Q.; Ding, S.D. A new biodegradable copolyester poly(butylene succinate-co-ethylene succinate-co-ethylene terephthalate). Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 5871–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guo, B.H. Poly(butylene succinate) and its copolymers: Research, development and industrialization. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha Ray, S.; Okamoto, K.; Okamoto, M. Structure−property relationship in biodegradable poly(butylene succinate)/layered silicate nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 2355–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Song, L.; Hu, Y.; Xing, W.; Lu, H. Morphology, mechanical and thermal properties of graphene-reinforced poly(butylene succinate) nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 72, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosq, N.; Aht-Ong, D. Nonisothermal crystallization behavior of poly(butylene succinate)/nay zeolite nanocomposites. Macromol. Res. 2018, 26, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Cheng, L.; Qu, W. Mechanical properties of poly(butylene succinate) (pbs) biocomposites reinforced with surface modified jute fibre. Compos. Part A-Appl. S. 2009, 40, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.H.; Ogihara, S.; Tung, N.H.; Kobayashi, S. Effect of alkali treatment on interfacial and mechanical properties of coir fiber reinforced poly(butylene succinate) biodegradable composites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2011, 42, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lv, L.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q. Polymer-supported nanocomposites for environmental application: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakroodi, A.R.; Kazemi, Y.; Nofar, M.; Park, C.B. Tailoring poly(lactic acid) for packaging applications via the production of fully bio-based in situ microfibrillar composite films. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nampoothiri, K.M.; Nair, N.R.; John, R.P. An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (pla) research. Bioresource Technol. 2010, 101, 8493–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunati, E.; Puglia, D.; Iannoni, A.; Terenzi, A.; Kenny, J.M.; Torre, L. Processing conditions, thermal and mechanical responses of stretchable poly (lactic acid)/poly (butylene succinate) films. Materials 2017, 10, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.Y.; Gierke, T.D.; Molnar, C.J. Morphological effects on the physical properties of polymer composites. Macromolecules 1983, 16, 1945–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakroodi, A.R.; Kazemi, Y.; Ding, W.; Ameli, A.; Park, C.B. Poly(lactic acid)-based in situ microfibrillar composites with enhanced crystallization kinetics, mechanical properties, rheological behavior, and foaming ability. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3925–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, A.; Park, C.B.; Favis, B.D. Tuning viscoelastic and crystallization properties of polypropylene containing in-situ generated high aspect ratio polyethylene terephthalate fibrils. Polymer 2015, 68, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, A.; Park, C.B. Dispersed polypropylene fibrils improve the foaming ability of a polyethylene matrix. Polymer 2014, 55, 4199–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, A.; Tabatabaei, A.; Barzegari, M.R.; Mahmood, S.H.; Park, C.B. In situ fibrillation of CO2-philic polymers: Sustainable route to polymer foams in a continuous process. Polymer 2013, 54, 4645–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakirov, S. Nano-/microfibrillar polymer–polymer and single polymer composites: The converting instead of adding concept. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 89, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanarayanan, K.; Jose, T.; Thomas, S.; Joseph, K. Effect of draw ratio on the microstructure, thermal, tensile and dynamic rheological properties of insitu microfibrillar composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.J.; Li, L.; Mendes, E.; Byelov, D.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.M. Suppression of skin−core structure in injection-molded polymer parts by in situ incorporation of a microfibrillar network. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6771–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, K.; Evstatiev, M.; Fakirov, S.; Evstatiev, O.; Ishii, M.; Harrass, M. Microfibrillar reinforced composites from pet/pp blends: Processing, morphology and mechanical properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Huang, H.D.; Xu, L.; Yan, Z.; Zhong, G.J.; Hsiao, B.S.; Li, Z.M. In situ nanofibrillar networks composed of densely oriented polylactide crystals as efficient reinforcement and promising barrier wall for fully biodegradable poly(butylene succinate) composite films. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2887–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Li, L.-B.; Shen, K.Z.; Yang, M.B.; Huang, R. In-situ microfibrillar pet/ipp blend via slit die extrusion, hot stretching, and quenching: Influence of hot stretch ratio on morphology, crystallization, and crystal structure of ipp at a fixed pet concentration. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys. 2004, 42, 4095–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xu, H.; Niu, B.; Ji, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.M.; Hsiao, B.S.; Zhong, G.-J. Unprecedented access to strong and ductile poly(lactic acid) by introducing in situ nanofibrillar poly(butylene succinate) for green packaging. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 4054–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, H.; Zhong, G.J.; Li, Z.M.; Yang, M.B.; Xie, B.H.; Yang, S.Y. Morphology and mechanical properties of poly (phenylene sulfide)/isotactic polypropylene in situ microfibrillar blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kröger, M.; Liu, W.K. Nanoparticle geometrical effect on structure, dynamics and anisotropic viscosity of polyethylene nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambon, F.; Winter, H.H. Linear viscoelasticity at the gel point of a crosslinking pdms with imbalanced stoichiometry. J. Rheol. 1987, 31, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y. Thermal, crystallographic, and mechanical properties of poly(butylene succinate)/magnesium hydroxide sulfate hydrate whisker composites modified by in situ polymerization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 3516–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.M.; Tang, Y.R.; Xu, J.; Guo, B.H. Role of poly(butylene fumarate) on crystallization behavior of poly(butylene succinate). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 10682–10689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizundia, E.; Larrañaga, A.; Vilas, J.L.; León, L.M. Three-dimensional orientation of poly(l-lactide) crystals under uniaxial drawing. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 11943–11951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

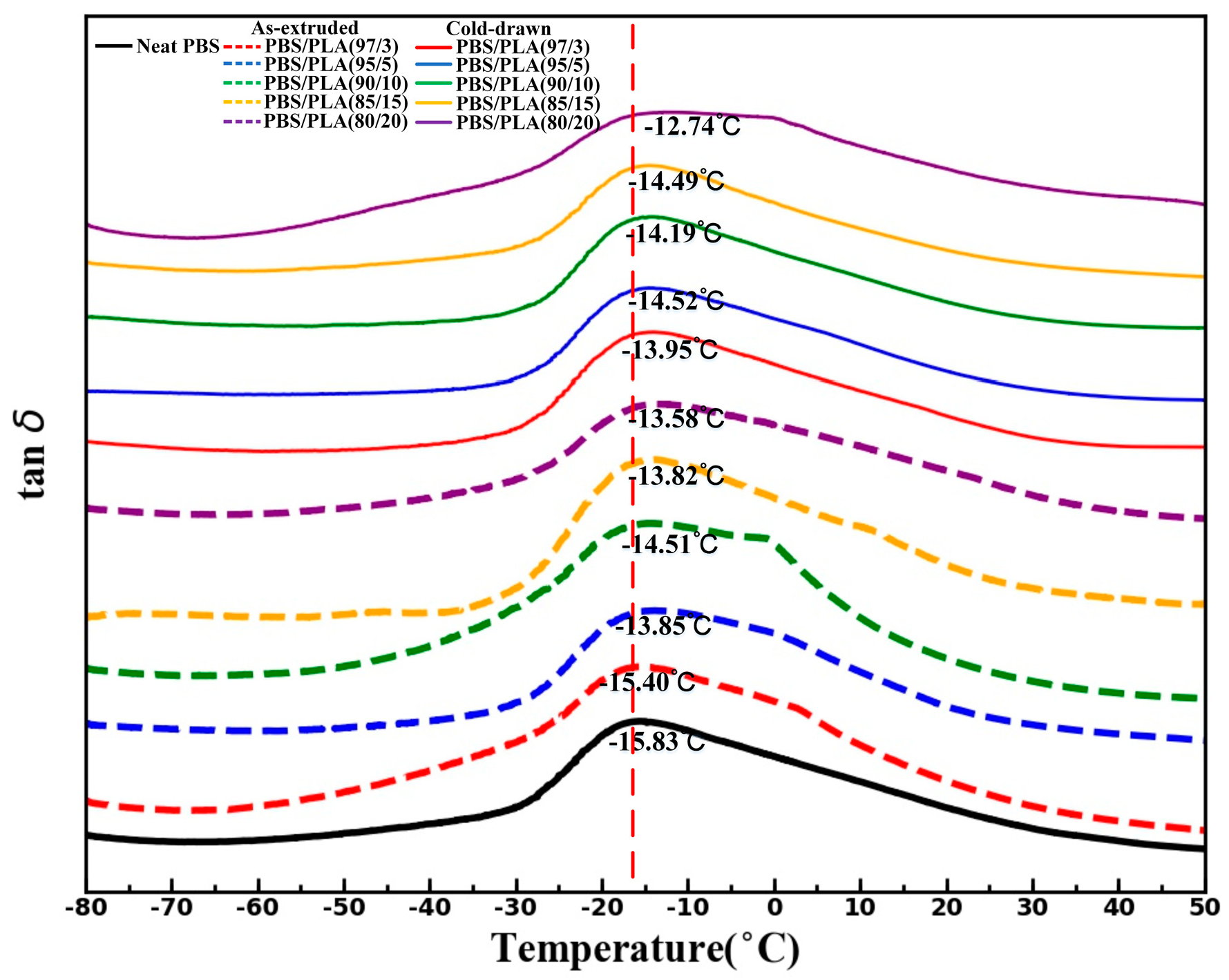

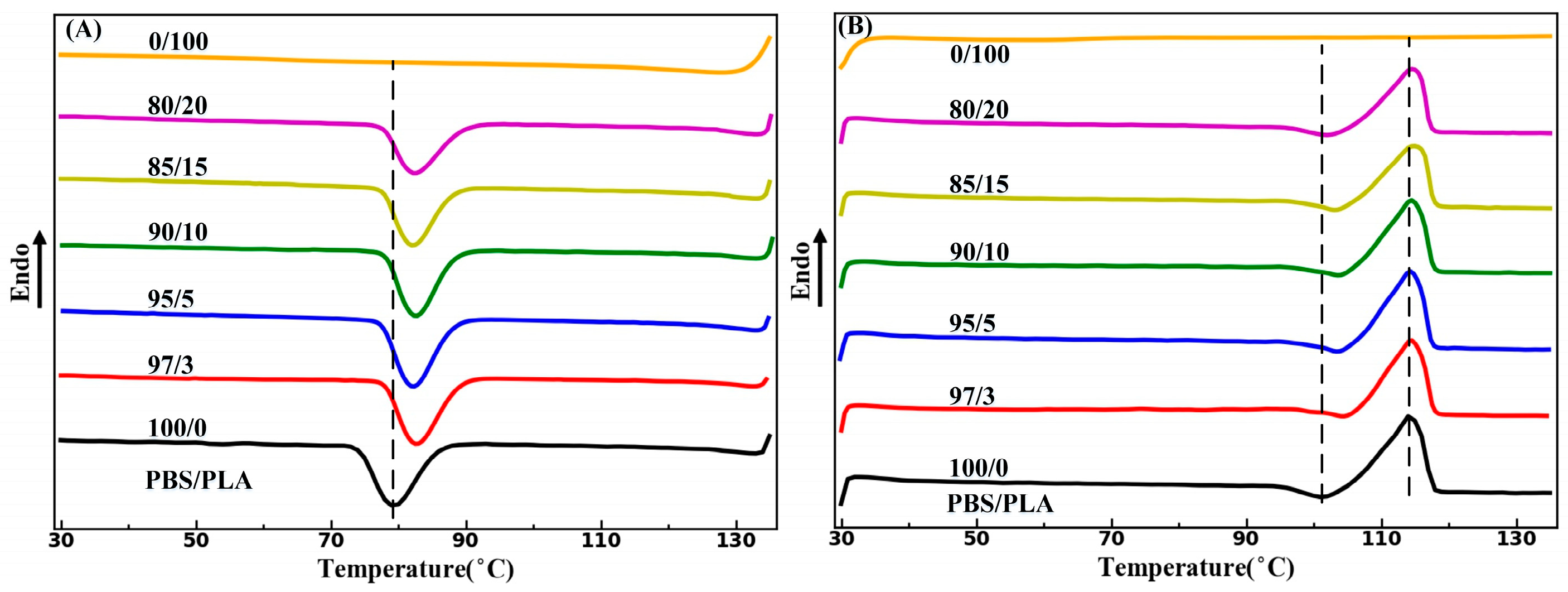
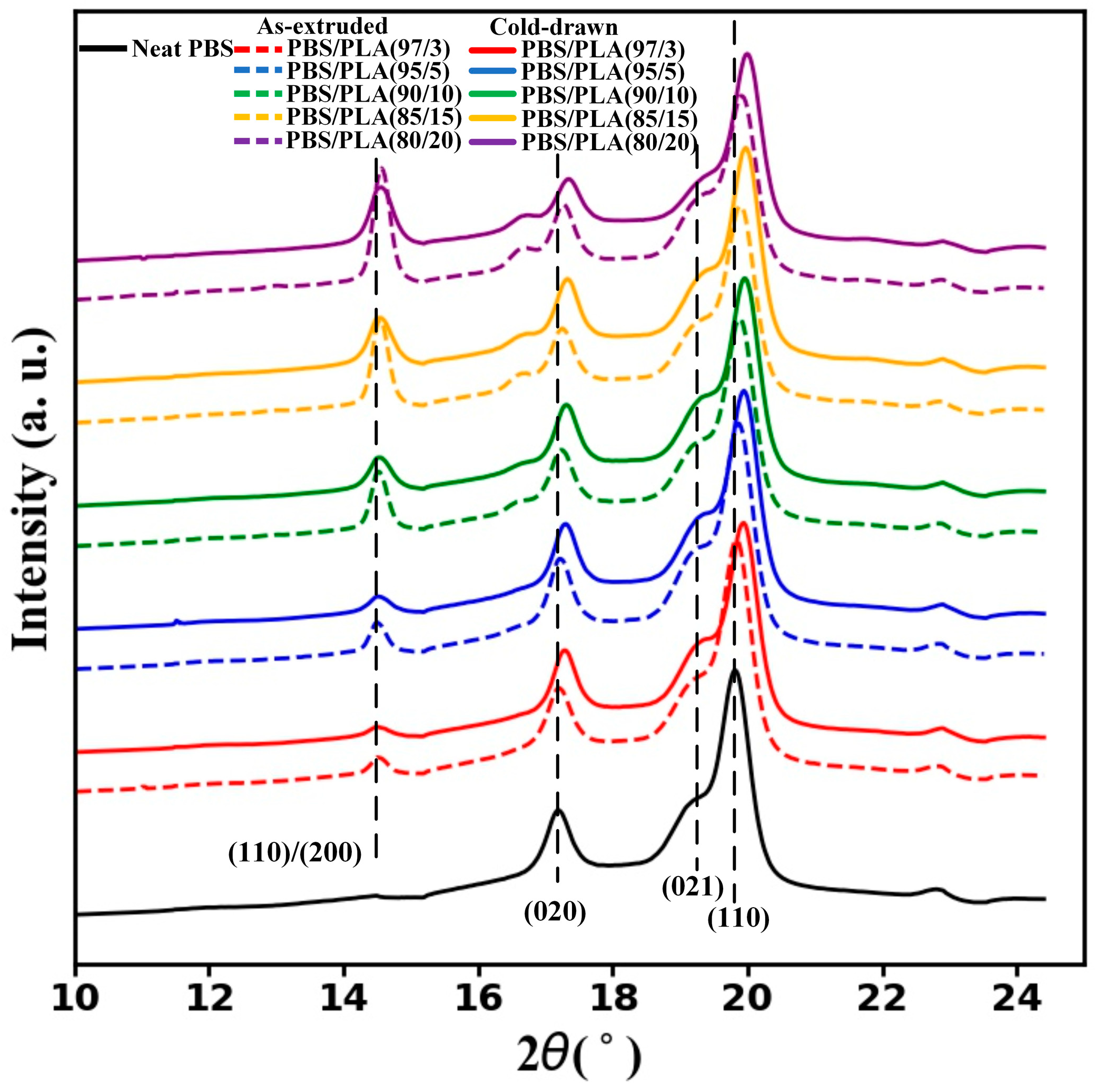
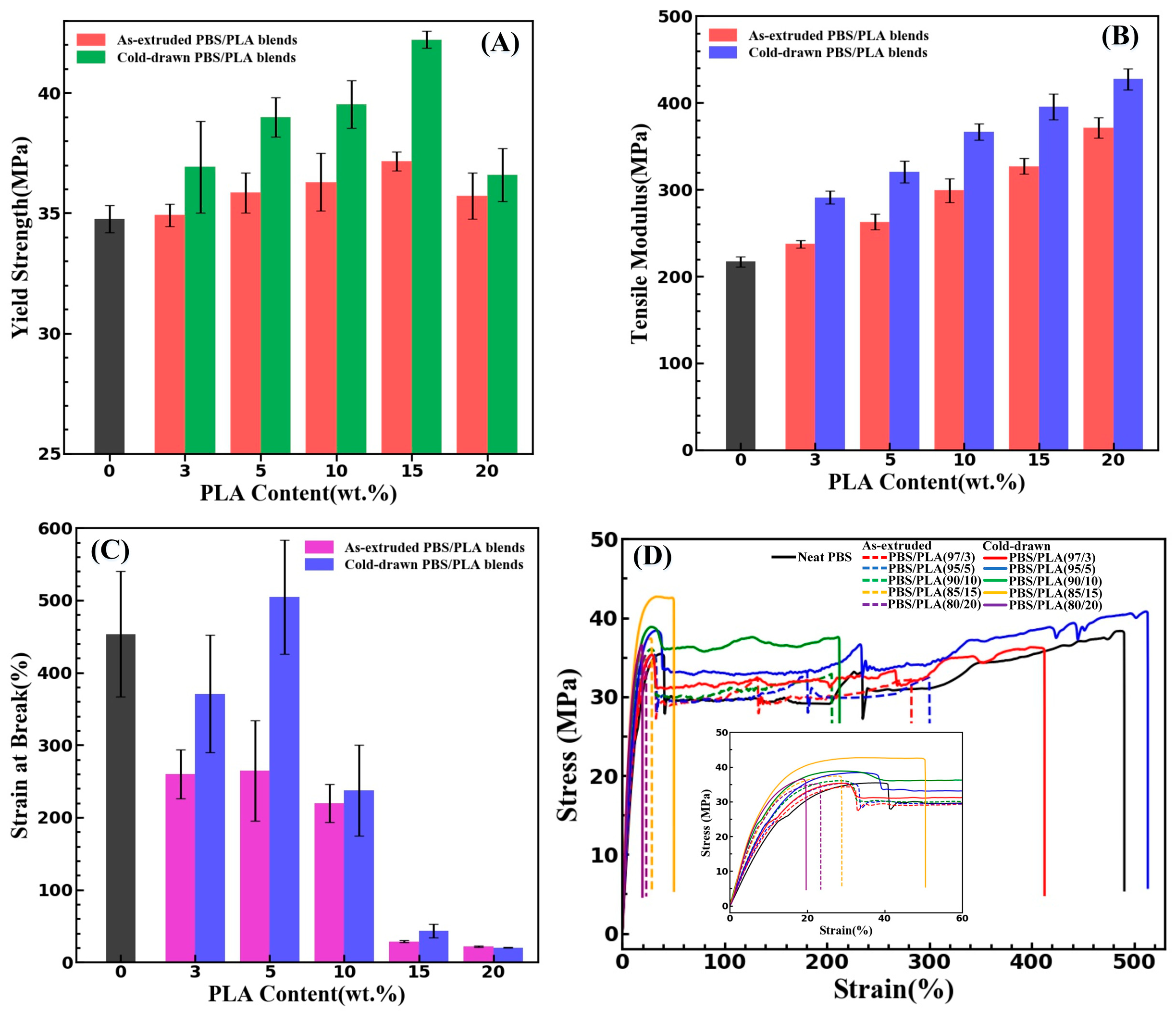
| Samples | TC (°C) | TCC (°C) | Tm (°C) | ΔHCC (J/g) | ΔHm (J/g) | XC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | 79.5 ± 0.3 | 101.2 ± 0.1 | 114.2 ± 0.1 | 6.04 ± 0.36 | 66.84 ± 0.44 | 50.7 ± 0.6 |
| PBS/PLA (97/3) | 78.0 ± 0.5 | 100.1 ± 0.2 | 114.4 ± 0.1 | 7.07 ± 0.51 | 66.80 ± 1.85 | 51.3 ± 1.1 |
| PBS/PLA (95/5) | 78.3 ± 0.4 | 99.9 ± 0.2 | 114.4 ± 0.1 | 6.61 ± 0.55 | 63.91 ± 1.21 | 50.3 ± 0.6 |
| PBS/PLA (90/10) | 78.1 ± 0.3 | 99.8 ± 0.2 | 144.3 ± 0.2 | 6.49 ± 0.55 | 59.20 ± 0.79 | 48.8 ± 0.7 |
| PBS/PLA (85/15) | 77.2 ± 0.4 | 99.4 ± 0.2 | 114.3 ± 0.1 | 6.72 ± 0.30 | 56.87 ± 0.75 | 49.2 ± 1.0 |
| PBS/PLA (80/20) | 77.0 ± 0.9 | 99.4 ± 0.5 | 114.2 ± 0.1 | 5.69 ± 0.67 | 52.47 ± 0.77 | 48.7 ± 0.9 |
| Samples | TC (°C) | TCC (°C) | Tm (°C) | ΔHCC (J/g) | ΔHm (J/g) | XC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | 79.5 ± 0.3 | 101.2 ± 0.1 | 114.2 ± 0.1 | 6.04 ± 0.36 | 66.84 ± 0.44 | 50.7 ± 0.6 |
| PBS/PLA (97/3) | 82.7 ± 0.1 | 103.9 ± 0.3 | 114.3 ± 0.1 | 2.95 ± 0.29 | 63.47 ± 1.17 | 52.0 ± 0.8 |
| PBS/PLA (95/5) | 82.3 ± 0.1 | 103.5 ± 0.3 | 114.2 ± 0.1 | 4.38 ± 0.66 | 63.32 ± 1.08 | 51.7 ± 1.2 |
| PBS/PLA (90/10) | 82.6 ± 0.1 | 103.5 ± 0.4 | 144.3 ± 0.2 | 4.10 ± 0.44 | 59.09 ± 1.30 | 50.9 ± 1.1 |
| PBS/PLA (85/15) | 82.1 ± 0.3 | 102.8 ± 0.2 | 114.8 ± 0.4 | 4.28 ± 0.11 | 54.91 ± 1.39 | 49.6 ± 1.4 |
| PBS/PLA (80/20) | 82.4 ± 0.1 | 102.0 ± 0.1 | 114.8 ± 0.3 | 4.16 ± 0.24 | 52.47 ± 0.90 | 50.3 ± 0.8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.; He, H.; Xue, B.; Zhan, Z.; Wang, G.; Chen, M. Morphology, Thermal, Mechanical Properties and Rheological Behavior of Biodegradable Poly(butylene succinate)/poly(lactic acid) In-Situ Submicrofibrillar Composites. Materials 2018, 11, 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122422
Zhu Z, He H, Xue B, Zhan Z, Wang G, Chen M. Morphology, Thermal, Mechanical Properties and Rheological Behavior of Biodegradable Poly(butylene succinate)/poly(lactic acid) In-Situ Submicrofibrillar Composites. Materials. 2018; 11(12):2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122422
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zhiwen, Hezhi He, Bin Xue, Zhiming Zhan, Guozhen Wang, and Ming Chen. 2018. "Morphology, Thermal, Mechanical Properties and Rheological Behavior of Biodegradable Poly(butylene succinate)/poly(lactic acid) In-Situ Submicrofibrillar Composites" Materials 11, no. 12: 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122422
APA StyleZhu, Z., He, H., Xue, B., Zhan, Z., Wang, G., & Chen, M. (2018). Morphology, Thermal, Mechanical Properties and Rheological Behavior of Biodegradable Poly(butylene succinate)/poly(lactic acid) In-Situ Submicrofibrillar Composites. Materials, 11(12), 2422. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11122422




