Abstract
Water, energy, and food are lifelines for modern societies. The continuously rising world population, growing desires for higher living standards, and inextricable links among the three sectors make the water-energy-food (WEF) nexus a vibrant research pursuit. For the integrated delivery of WEF systems, quantifying WEF connections helps understand synergies and trade-offs across the water, energy, and food sectors, and thus is a critical initial step toward integrated WEF nexus modeling and management. However, current WEF interconnection quantifications encounter methodological hurdles. Also, existing calculation results are scattered across a wide collection of studies in multiple disciplines, which increases data collection and interpretation difficulties. To advance robust WEF nexus quantifications and further contribute to integrated WEF systems modeling and management, this study: (i) summarizes the estimate results to date on WEF interconnections; (ii) analyzes methodological and practical challenges associated with WEF interconnection calculations; and (iii) points out opportunities for enabling robust WEF nexus quantifications in the future.
1. Introduction
The energy and resource challenges in turning society to a more sustainable direction are tremendous and urgent. Water, energy, and food are lifeline sectors essential for human well-being and social and economic sustainability. The demand for sustainable development derives from the growing world population and its demand for increasing living standards, which generates a huge demand for water, energy, and food. The United Nations estimates that the world population will rise to approximately 10 billion by 2050 [1], of which approximately 4 billion will live in severely water-stressed basins [2]. The growth of global energy demand is comparatively modest because of widespread deployment of energy-efficient technologies and the transition of the world economy toward service and lighter industrial sectors, but a 37% increase in demand by 2040 is still predicted [3].
Water-energy-food (WEF) systems have inherent antagonisms, and the development of one sector usually depletes resources in the two other sectors. Due to existing institutional arrangements (e.g., separate government ministries), important decision making about water, energy, and food usually lacks coordination [4]. Too often, policy makers fail to consider sustainability challenges in a holistic way and ignore the interconnections among the WEF systems. Energy policies usually idealistically assume abundant water for potential energy solutions, but today’s interlinked and dynamic world leaves little room for such fragmented governances. For example, China is estimated to have the world largest shale gas reserves, and the shale gas development plan for 2011 to 2015 put forth by the Chinese government projects an annual shale gas production of 60 to 100 billion cubic meters (bcm) by 2020 [5]. This production target, however, was lowered to 30 bcm [6], one of the constraints being the lack of access to water and its transport cost [7], because water is consumed in substantial amounts by hydraulic fracturing activities.
The nexus of energy, water, and food sectors affects the extent to which WEF security can be simultaneously achieved [4]. The WEF nexus approach is a holistic vision of sustainability that tries to strike a balance among the different goals, interests, and needs of people and the environment (Figure 1). The tentative concept of addressing WEF issues in a systematic manner dates back to the Limits to Growth in the early 1970s [8]. That work established a prospective model based on the exponential growth of five variables—world population, industrialization, pollution, food production, and resource depletion—and presented a system analysis archetype for addressing sustainability challenges. In 2011, the World Economic Forum emphasized that the world’s food, water, and energy resources were already experiencing significant stress or shortfalls and would continue to experience them in the next 20 years. The highly interlinked nature of the three issues requires nexus solutions where water is central [9]. The Bonn Nexus conference predicted that world population growth and economic development would put pressure on water, energy, and food security, lead to resource depletion, degraded ecosystem services, and irreversible societal and environmental changes, and thereby threaten sustainable development [10]. They called for a nexus approach to addressing WEF challenges.
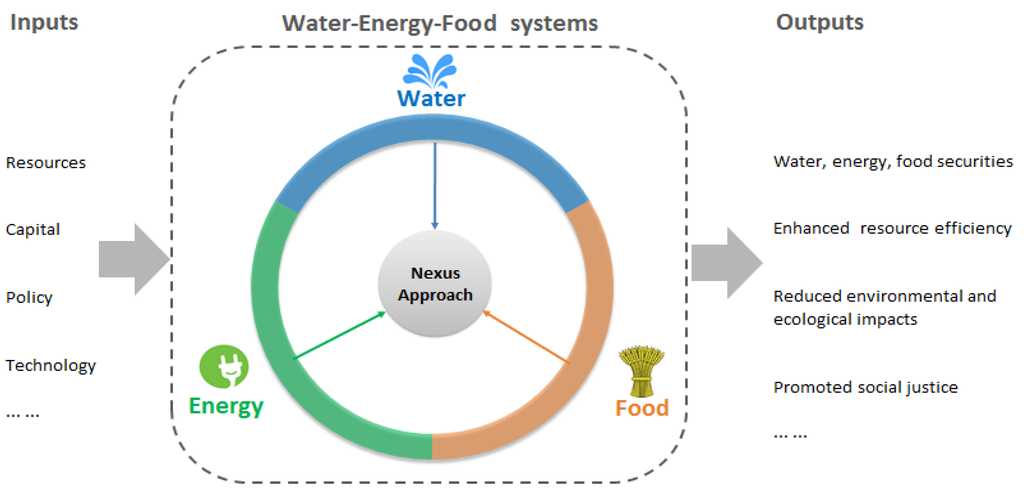
Figure 1.
Water-energy-food (WEF) nexus management concepts.
Quantifying the interconnections among energy, water, and food sectors is an initial step toward integrated WEF systems modeling, which will further contribute to robust WEF security management. Existing studies have calculated the impacts of various energy technologies (such as electric power generation technologies), water production and supply technologies, and food products (such as cereal, meat, and beverage) on the three sectors. The calculations were at multiple levels, ranging from global and national to local and urban, thus providing fundamental parameter inputs for comprehensive WEF nexus modeling. Detail analyses are presented in Section 2, Section 3 and Section 4. However, the quantifications of WEF interconnections are still immature, having inconsistent impact indicator selections, different system boundary definitions, and segmented uses of bottom-up and top-down approaches. In addition, existing calculation results of WEF interconnections are scattered across a wide collection of studies in multiple disciplines, which increases data collection and interpretation difficulties. Therefore, in this study we summarize and analyze WEF interconnection estimate results to date, point out the methodological and practical challenges associated with WEF interconnection calculations, and shed light on opportunities for advancing robust WEF nexus quantifications.
2. The Water-Energy Nexus
2.1. Water Usage in Energy Production
Water is indispensable for the production, distribution, and use of energy. In 2010, water withdrawal for energy production was estimated at 583 bcm, approximately 15% of the world’s total withdrawal, of which 66 bcm were consumed [11]. Existing studies of water-energy correlations primarily focus on calculating the water consumption of different energy productions.
2.1.1. Thermoelectric Power Generation
Electric power systems underpin prosperous modern societies. Over the past few decades, global electricity generation increased dramatically from 6129 TWh in 1973 to 22,668 TWh in 2012 [12], and is expected to grow rapidly with rising demands for electricity-based products and services [13]. Despite the share of renewable power in global power supply increases in recent years, nearly 70% of today’s electricity is still generated by thermoelectric power plants, resulting in tremendous dependency on water resources. The water footprint (WF) of power plants is determined by their thermal efficiency, their heat sink accessibility, and the cooling systems they adopt [11]. Generally, there are two cooling system options for thermal power plants, once-through and closed-loop. The once-through cooling system has higher water withdrawal but lower water consumption, while the closed-loop cooling system has the reverse [14]. Alternative technologies include dry cooling, which uses air instead of water to cool process water, and hybrid cooling, which combines both dry and wet cooling technologies to enable less water use compared to wet systems while improving hot-weather performance compared to dry systems [15]. However, since air is less effective than water for cooling, a dry cooling system implies decreased thermal efficiency, reducing power generation by 1% to 7% on average [16,17]. Additionally, the initial and operational costs of a dry cooling system are significantly higher (3–4 times) than wet systems [11,18]. Therefore, selecting a cooling system for thermoelectric power generation needs to involve the trade-offs of water consumption, energy yield, and economic cost. Economically developed regions with high water-resource stress should give priority to a dry cooling technology. The closed-loop system should be selected by regions with limited water resource accessibility, while the once-through system is more suitable for water-abundant areas.
2.1.2. Energy Resource Extraction and Processing
The extraction of fossil energy (such as coal, crude oil, and natural gas) and nuclear energy involves water consumption, which varies by geographical features, reserve conditions, and extraction technologies. A coal layer could be close to the Earth’s crust or deep underground, resulting in different water consumption for cooling drilling equipment, lubricating cutting machines to suppress dust, and removing impurities such as limestone slurry and scrubber sludge from the coal [19]. Crude oil production consists of three stages, which are primary, secondary, and tertiary (or enhanced) recovery. An oil well’s initial production derives from natural pressure bringing oil to the surface, extracting only approximately 10% of the oil in the oil field. Using water or gas injection, secondary recovery techniques maintain the well’s production and extract 20% to 40% of the original oil reserve [20]. Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) is ultimately employed to stimulate the oil well, with a potential extraction of 30% to 60% of the oil reserve. It should be noted that oil production processes also produce large quantities of water, and US experience indicates that the ratio of produced water to oil ranges from 6.3:1 to 9.5:1 [21]. Most of the produced water is treated and then re-injected into the oil reservoir for pressure maintenance and recovery improvement [22]. Apart from the intensive water consumption, the large quantity of brine produced by EOR is a potential contaminator of water resources if not properly handled [23]. Compared to coal and crude oil production, the WF of natural gas extraction is not significant except for shale gas production, which relies on hydraulic fracturing to release natural gas from low-permeable shale rock formations by propagating fractures in the rock layer. For a typical shale gas well, the water consumption of hydraulic fracturing is estimated at 14,300 metric ton in the United States [24], but much higher (23,650 metric ton) in China [25] because of the differences in geological conditions [26], fracturing technology maturity, and flowback-water management.
2.1.3. Bioenergy Production
Bioenergy is energy derived from biological sources (biomass), and biomass is all organic material originating from plants [27]. Since irrigation is essential for plant cultivation, the WF of biomass such as sugarcane, maize, and soybean is significantly higher than that of fossil energy, and substantially varies by biomass type and region. For example, two biodiesel feedstocks—soybean and rapeseed—have obviously different water consumption per unit energy in Brazil, 61 m3/GJ and 214 m3/GJ respectively. The WF of maize is 9 m3/GJ in the Netherlands, but is doubled in the United Sates, around 18 m3/GJ [28]. Given that biomass holds great promise for greenhouse gas (GHG) mitigation, the world has begun to move toward bioenergy to advance the transition to a low-carbon society. In 2008, global biomass energy supply was 50.3 EJ (approximately 10% of the annual world primary energy supply), and this number is projected to increase to 100–300 EJ by 2050 [29]. But the deployment of biomass energy is affected by various factors, such as feedstock plant selection, soil and climate condition, irrigation facilities, mechanization level, and water resource availability [30,31,32]. Bioenergy utilization is primarily a response to climate change, and biomass deployment is not cost-effective in terms of energy and water inputs. The energy used for crop cultivation outweighs the energy harvested, and the WF of crops specifically grown for energy is larger than that of crops grown for food [28]. One additional concern about bioenergy is that its land use requirement impinges on cropland, resulting in increased competition between energy and food, see Section 4.3.
To enable a more complete understanding of the WF associated with different energy production options and create a more robust decision-making environment for government authorities, life cycle assessment (LCA) modeling approaches are widely used because of their strength in systematic thinking and quantitative analysis. For example, shale gas production is usually regarded as water intensive because of hydraulic fracturing activities, but shale gas energy has a smaller WF than coal for power generation if the extraction-to-wire effects are considered. Therefore, the shift from coal to shale gas for power generation is an important transition pathway to a less water-dependent electricity grid [33]. Table 1 summarizes the cradle-to-use water consumption of different energy technologies, including conventional thermal power options such as coal, natural gas, oil, and nuclear, and much cleaner renewables, such as wind, solar, and geothermal energy. Two energy carriers are adopted, electricity and liquid fuel. It can be seen that the cradle-to-wire water consumption of conventional thermal power generation technologies is generally higher than that of renewable technologies, and is dominated by the operational water consumption of power generation. In addition, existing studies have also revealed that nuclear and renewable power could substantially reduce air pollutant emissions, such as SO2 and GHG, as compared to coal-fired technologies [13,29]. This means that from water resource consumption and climate change mitigation perspectives, a shift from coal to renewable energy such as solar, wind, and ocean for electric power generation is the optimal strategy for a transition to green power. But current limitations of renewable electric power technologies such as intermittency, dependence on regions with large energy resource reserves, and energy storage barriers inhibit a massive-scale deployment in the near term [33]. In the interim, nuclear electricity may serve as a transitional player, offering a lower carbon and water pathway to reducing coal dependence until renewables become more viable. For different biofuel feedstocks, maize and sugar beets have a smaller WF than rapeseed and soybean, prioritizing the former as a better selection for the increasing penetration of biofuel in the transport fuel market.

Table 1.
Water consumption of different energy technologies.
| Energy Type | Extraction and Processing | Cradle-to-wire | Cradle-to-liquid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m3/GWh | m3/GWh | m3/GJ | ||
| Coal | Surface mining | 23–220 | 160–5160 | 0.12–0.29 |
| Underground mining | 64–870 | 200–5800 | ||
| Natural gas | Conventional natural gas | 4–100 | 4–4530 | 0–0.01 |
| Shale gas | 8–800 | 8–5230 | 0.04–0.06 | |
| Nuclear (Uranium) | 50–1250 | 430–4450 | 0.03–0.05 | |
| Solar | Photovoltaic | 20–800 | 20–810 | - |
| Concentrated solar power | 300–640 | 400–4800 | ||
| Wind | Onshore | ∼0–35 | 4–42 | - |
| Offshore | ∼0–35 | ∼0–38 | ||
| Hydropower | 1–60 | 5400–68,200 | - | |
| Geothermal | 8–7600 | 26–2730 | ||
| Ocean | 60–220 | 60–220 | ||
| Oil | Conventional oil | - | - | 0.01–0.02 |
| Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) | 0.02–2.52 | |||
| Biofuel | Sugarcane (ethanol) | - | - | 25–108 |
| Maize (ethanol) | 9–200 | |||
| Sugar beets (ethanol) | 13–23 | |||
| Rapeseed (biodiesel) | 400–574 | |||
| Soybean (biodiesel) | 50–394 | |||
Note: Data sources include [13,19,28,34,35].
2.2. Energy Consumption of Water Supply and Management
Energy consumption is inevitable for water services, including water withdrawal, treatment, and distribution, and the energy footprint of water provision significantly varies among different water sources. To provide one cubic meter of water, the embodied energy is 2–3 MJ for surface water, 3–17 MJ for recycled water (consisting of 1.4–1.8 MJ consumption in wastewater treatment plants), 24–42 MJ for desalinated water, and 5–18 MJ for imported water [36,37]. The wide ranges of quantifications in different studies are caused by factors such as research boundaries, energy mixes, and technology adoptions. Additionally, water end uses require energy consumption and tend to be more energy intensive [38]. The US experience is that water heating consumes more energy than water supply and treatment. In California, 14% of electricity and 31% of natural gas consumption are associated with hot water, which is primarily used by the residential sector [39]. The energy consumption of urban residential hot water in China, driven by rapid urbanization and continuously rising living standards, has increased dramatically from 1.6 million metric ton of coal equivalent (MTCE) in 1996 to 14.5 million MTCE in 2011—approximately 10% of the nation’s total building operational energy use [40,41]. Therefore, enhancing the water efficiency of household water-consuming fixtures and fittings, such as toilets, showerheads, faucets, and water heaters, contributes to wastewater reduction, and more importantly, wastewater treatment energy and water embodied energy. Such initiatives have been widely encouraged by current green building rating systems, such as leadership in energy and environmental design (LEED) and building research establishment environmental assessment methodology (BREEAM).
Furthermore, considerations of water provision and management have spread to ecological domains. Their proponents advocate the construction of green water infrastructures, such as wetlands, healthy soil and forest ecosystems, and snowpack, which are more flexible, cost effective, and ecologically friendly than conventional man-made management approaches. Those approaches to water supply, flooding regulation, erosion control, and water storage for hydropower and irrigation include building dams, piping water, and constructing protective barriers [42]. A case in point is the ongoing “sponge city” program in China’s urbanization construction [43]. The sponge city is a type of low-impact development focusing on strengthening rainfall water collection, storage, and use to mitigate urban flooding risk and to reduce urban water end uses, such as landscaping irrigation, street cleaning, and firefighting.
3. The Water-Food Nexus
The water-food nexus mainly refers to the WF of agricultural products (e.g., cereals and vegetables), animal products (e.g., meat, eggs, and fish), and food and beverage production (e.g., soft drinks and tea), see Table 2 for details. The continuously growing world population drives increasing food demand. Given that the world population is projected to grow by 30% from 2015 to 2050, demand for food production will increase by 70% globally and nearly 100% in developing countries [44]. Furthermore, the rising living standard of residents in developing countries such as China and India leads to changes in food consumption patterns and expands the share of animal products in residents’ daily food consumption, significantly increasing the WF of residential consumption. For example, the water requirement for food in China has increased from 255 m3/cap/y in 1961 to 860 m3/cap/y in 2003 [45].

Table 2.
Water footprint (WF) of main food products.
| Food Items | WF per Food Product | WF per Food Energy Provision | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (m3/kg) | (L/kcal) | ||
| Cereal | Rice | 1.7 | 0.5 |
| Wheat | 1.8 | 0.7 | |
| Maize | 1.2 | 0.4 | |
| Animal products | Beef | 3.8–23.8 | 1.9–11.8 |
| Pork | 4.4–12.1 | 1.3–3.5 | |
| Chicken meat | 1.7–6.7 | 0.9–3.7 | |
| Sheep meat | 5.8–11.3 | 2.9–5.6 | |
| Goat meat | 1.6–8.5 | 0.8–4.2 | |
| Eggs | 1.3–6.0 | 0.9–4.1 | |
| Milk | 0.5–1.3 | 0.7–1.9 | |
| Vegetables | 0.2–0.3 | 1.1–1.6 | |
| Fruits | 0.5–1 | 1.2–2.4 | |
| Groundnuts | 3.1 | 1.0 | |
| Beverage products | Wine | 1 | 1.4 |
| Tea | 0.12 | - | |
| Soft drinks | 0.3–0.6 | 0.7–1.4 | |
Note: Data resources include [45,46,47,48,49]. The WF consists of green, blue, and gray water consumption. Single estimates are global average values. The energy content of tea is almost zero. The soft drink estimate derives from a case study [50].
3.1. Water Consumption of Agriculture
The world’s largest water consumer, agriculture, is globally responsible for 70% of the fresh water withdrawn from aquifers, streams, and lakes [51]. The WF of humanity is estimated at 9087 km3/y, of which agriculture accounts for 92% [52]. Water resources are critical for agriculture, and 280 million hectares of land were irrigated worldwide, approximately 18% of the total cropland [53]. However, the agriculture sector also presents obvious water saving potential as more water-efficient irrigation techniques such as sprinkler irrigation, micro-irrigation, and low-pressure pipe irrigation become cost-effective and available [54]. Drought is a threat to crop yields, and operates at different temporal and spatial scales depending on multiple factors such as the climate cycle, the hydroenvironment, and the species of crops planted [55]. The effects of drought ripple through economic sectors, people’s health and safety, and environmental systems. Strategies that contribute to reducing drought vulnerability include planting drought-resilient crops, expanding water infrastructure investment, using voluntary water reallocation, strengthening drought planning, and diversifying off-farm income [56]. Organic agriculture, as a counterpart of traditional agriculture, adopts ecosystem management approaches and techniques (e.g., crop rotation, green manure, and biological pest control) to grow crops and rear animals, instead of using chemical inputs such as synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and additives [57]. The energy footprint of organic food is typically regarded as 20%–70% smaller than that of conventional food [58,59,60], although there are studies with opposite conclusions [61,62], because of different calculation boundaries (whether the energy of manure is considered in organic farming). However, it is clear that organic agriculture could effectively decrease the fossil energy used for operating machinery and producing synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
3.2. Water Consumption of Animal Products
Compared to crops, animal products usually have a larger water requirement per unit of nutritional energy [46]. For example, the global average WF of beef (10.2 L/kcal) is 20 times as large as that of cereals (0.51 L/kcal) [47]. The WF of various meat categories significantly varies: global average WF estimates are 4.3 m3/kg for chicken meat, 5.5 m3/kg for goat meat, 6 m3/kg for pork, 10.4 m3/kg for sheep meat, and 15.4 m3/kg for beef [47]. Moreover, quantification based on US practice reveals that the environmental cost per consumed calorie of beef is much higher than that of dairy, poultry, pork, and eggs, requiring 28, 11, 5, and 6 times more land, irrigation water, GHG, and reactive nitrogen (Nr), respectively [63]. Therefore, a dietary shift from red meat to chicken, fish, and eggs contributes to the transition toward more sustainable living [64].
3.3. Water Consumption of Beverage Products
The WF of beverage products typically derives from their supply-chain consumption. For example, soft drinks require the main ingredients of sugar, water, and carbon dioxide, and for packaging they require bottles, caps, and labeling film. The WF of a 0.5 L carbonated beverage is estimated at 169–309 L, depending on sugar sources, and the supply-chain footprint accounts for 99.7% of that water [50]. For a 250 mL cup of tea, the WF is estimated at 30 L, and an additional 22 L of water is involved if one brews his tea in the British fashion, including 10 L for a small dash of milk and 12 L for two teaspoons of sugar [65]. Thus, in addition to current product carbon labeling programs, such as Carbon Trust and CarbonCounted, footprint labeling programs with more impact categories are needed to help consumers realize the total footprints (both direct and indirect) associated with their consumption behaviors, thereby cultivating an awareness of extended consumer responsibility.
Apart from water resource consumption, arable land availability is another challenge to the food security of countries with large populations. Fertilizers help boost crop yields, but their excessive use leads to air and soil pollution [66]. Thus, scientists are trying to maximize crop yields at the lowest economic and environmental costs [67]. On the other hand, reducing food loss and waste along the entire supply chain contributes to strengthening food security and reducing resource and environmental footprints. In China, grain loss during storage, processing, and distribution is estimated at approximately 35 million ton, or 14% of the nation’s total annual output [68]. An additional 2.5% of food waste (approximately 5.5 million ton) is generated in household consumption, calling for public awareness of food preservation to build a sustainable society.
4. The Food-Energy Nexus
4.1. Energy Consumption of Agriculture
Agriculture is energy intensive, consisting of direct consumption of farm on-site energy and indirect energy consumption embodied in machinery, farm equipment, fertilizers, and pesticides. Food systems currently consume 30% of the world’s available energy [69], of which the primary production of crops, livestock, and fisheries account for 6.6% [70]. Modern farms are typically mechanized, and farming operations, such as tillage, sowing, irrigation, and harvesting, are efficiently completed by agricultural equipment and thus rely on fuel and electricity consumption. The case of Belgium shows that the energy consumption per hectare of winter wheat cultivation is approximately 3400 MJ, and is dominated by ploughing (800 MJ) and combine harvesting (650 MJ). The consumption of field preparation and sowing, manure injection, manure spreading, and sowing forage crops is close (approximately 400–500 MJ), while the footprints of spraying, on-site wheat transport, and baling straw are insignificant [71]. In terms of on-farm energy end uses, the main consumers are motors (irrigation being the largest motor application), machinery, and on-site transportation [72]. On the other hand, the production of various farming inputs involves energy consumption. The energy consumption of one kilogram of nitrogen, phosphate, and potash fertilizer production is 34 MJ, 8 MJ, and 6 MJ, respectively [73]. The energy used for producing synthetic fertilizers and chemical pesticides and herbicides to boost crop yields is estimated at 30% to 50% of total agriculture energy consumption [74]. Therefore, the transition to sustainable agriculture requires greening both on-farm production and supply chains, which heavily depend on the energy reduction of various industrial end uses, such as boilers, motors, compressors, and pumps [75].
Studies on agriculture energy efficiency are relatively rare compared to those on industry, transport, and buildings. Because energy consumption and GHG emissions are closely linked, current energy consumption patterns for food production are unsustainable if climate change targets are to be met. As a result, the global community has begun to launch initiatives, such as the energy efficiency in agriculture (AGREE) project of the European Union and the energy smart food for people and climate (ESF) programme of the united nations food and agriculture organization (FAO). Their aim is to improve energy efficiency in agrifood systems, enable energy saving potentials through technical and managerial approaches, diversify energy use, and integrate food and energy production. The energy saving potential for the US agriculture sector is approximately 10%, or 98 trillion btu [76] (Figure 2). Enhanced energy efficiency also helps reduce the energy costs of agriculture production, increase farmers’ income, and stabilize the food supply, and thus contributes to strengthening the food security of a country.

Figure 2.
Energy saving potentials associated with US food sectors. Data source is [76].
4.2. Energy Consumption of Meat Products
Of all the meat products, beef has the highest cradle-to-fork energy inputs (up to 75 MJ/kg) and chicken has the lowest, only 35 MJ/kg. The energy footprints of pork and lamb are 40 MJ/kg and 43 MJ/kg respectively [77], reconfirming that a dietary shift from red meat to chicken contributes to a sustainable society. Notably, energy efficiency, as measured by energy use per ton of physical product output, of meat sectors in Europe has gradually decreased [78]. The deterioration in France, Germany, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom from 1990 to 2001 was primarily caused by more stringent hygiene regulations for food security, e.g., the temperature of water used for cleaning and sterilization in slaughterhouses was required to increase from 60 °C to 82 °C, requiring more energy for meat processing [79]. In terms of food processing and production, existing studies calculated the energy consumption and identified energy saving potentials for a wide range of product categories, including tomato pastes and purees [80], dairy products [81,82], bakery products [83], seafood [84], and fruits and vegetables [85], providing government authorities and residents more references for green decision making. One example is the cap-and-trade regulation in California [86], where policy makers use estimates on the energy and carbon intensity of individual products to determine the number of free allowances California facilities are eligible to receive to advance the GHG emissions mitigations in the state.
4.3. Food and Energy Co-Production
Approximately 11% of the World’s land surface is used for crop production [51], and the land competition between bioenergy and agriculture is also an important issue for the food-energy nexus. In the face of a growing world energy demand and deteriorating climate conditions, bioenergy holds the promise of increasing the energy supply and mitigating GHG emissions. But the land use change caused by bioenergy development might threaten biodiversity and food security [87]. As a result, certification initiatives for bioenergy have been globally launched to guide the sustainable direction for bioenergy/biofuel deployment, such as the renewable energy directive (RED) 2009/28/EC in the European Union (EU), the renewable fuel standard (RFS) in the US, and the renewable transport fuel obligation (RTFO) in the UK. However, different initiatives should be further harmonized in terms of assessment frameworks, definitions, approaches, and methodologies [88]. As for land competition between food and energy, the FAO has estimated that the land area used for biofuels would increase from 4 Mha in 2000 to 35 Mha in 2020, accounting for more than 6% of the total area of wheat, maize, sugar cane, and oilseeds [89]. It has been suggested that bioenergy production should be constrained to land of marginal productivity to minimize land competition with food [90,91], but market mechanisms might prove this solution unfeasible given that the economic incentives for bioenergy enable owners of productive land to out-compete the more costly bioenergy production on low-yielding land [92]. Therefore, cultivating biomass adapted to non-arable land and local climate and soil conditions contributes to mitigating land competition, minimizing agricultural resource inputs, reducing fossil energy use, and lowering the economic costs of energy production. For example, Salix, as a biomass feedstock for electricity generation, is cultivated in sandy land without fertilizer or pesticide use, and the natural conditions of an aquifer could sustain its growth [93]. As for the solar and wind energy, their distributed nature offers opportunities for multipurpose land use, enabling co-production of energy and food [4] that expands energy access without impairing crop yields.
5. Challenges and Trends for Water-Energy-Food Nexus Quantification
5.1. Concept Perception and Affecting Factors Identification
Since it was conceived by the Bonn Nexus Conference in 2011, the concept of WEF nexus continues to brew with expanding boundaries. Because of the inextricable linkages among the WEF systems and their external resource and ecological environments, the sustainability triangle evolves to embrace more dimensions, such as water-energy-land-food [94], water-energy-climate-food [95], and ecosystem-water-food-energy nexuses [96], to promote an understanding of opportunities, challenges, and trade-offs of sustainability transitions in a more complete system context.
Technological innovations and advances are undoubtedly critical for breaking the bottlenecks of the WEF nexus, but WEF sustainability also goes beyond the technosphere and is anthropogenically imprinted. Therefore, completely analyzing the societal and economic context of WEF systems helps to create a more supportive environment for strategy implementation. Regarded as important factors affecting sustainable WEF systems delivery are climate change, urbanization, globalization, political and economic change, regional and economic development, demographics, and infrastructures and facilities [10,97]. The related cross-sector synergies and quantifications with considerations of technology shift and risk adaption are emerging research agendas.
5.2. Synthesis of Bottom-Up and Top-Down Approaches
For WEF footprint accounting, two main approaches are widely adopted: bottom-up and top-down approach respectively [98]. The bottom-up method quantifies the resource footprints of individual products and analyzes key processes and technologies crucial to reducing the products’ footprints. In contrast, the top-down approach starts from the “big picture” of sector performance by modeling the resource stocks and flows of the WEF systems in an economy, and then breaks down the footprint reduction potentials of individual sectors and end uses. Thus, applications of the two approaches tend to diverge, as the top-down model is typically used for macro studies, usually at a national or sector level, while the bottom-up model is more suitable for micro studies for individual products and discrete technologies.
Bottom-up and top-down approaches have their own strengths and limitations, yielding different study estimates. For example, for total WFs of nations, the gap between the two models’ results could be as high as 48%, and the variation is even more obvious for sector estimates [99]. The bottom-up method presents detailed product- or technology-specific analyses, and facilitates the identification of green strategies and engineered solutions. However, due to time and cost constraints, the method fails to consider products’ entire supply chains [100,101], and such inter-sectoral cutoff might introduce one-sidedness to policy making. In addition, subjective system boundaries and diverse indicator selections among different bottom-up studies make model results difficult to compare with one another, and harmonization is needed to adjust the study estimates to a consistent set of methods and assumptions [102]. Using macroeconomic data, the top-down approach yields complete product supply-chain calculations, but the model results are of high uncertainty, mainly attributable to the scarcity of product-level data needed for model development. Therefore, the computational structure of the two methods offers complementary opportunities. Results of the bottom-up model fill the data gap encountered by top-down model development, while conclusions of top-down analyses pilot system boundary determination in bottom-up studies. The synthesis of the two approaches contributes to quantifying the WEF nexus in a more complete, specific, and precise manner.
5.3. Integrated and Flexible Analytical Framework
Robust analytical framework development is a vital step toward sustainable WEF systems. Appropriate conceptual models, reasonable algorithms, and complete datasets help to accurately quantify the WEF nexus and address the associated trade-offs [103]. Existing literature makes considerable progress in WEF nexus quantifications using various sustainability approaches, including national footprint accounts (NFA), global footprint network (GFN), LCA, material flow analysis (MFA), environmentally extended economic input-output analysis (EEIOA), emergy analysis, and exergy analysis [104]. However, applications of study results to government policy making are hampered due to differences in study focus, indicators, system boundaries, and datasets. Moreover, recent studies mostly focus on analyzing the two-sector linkages within the WEF systems, and thereby capture only a limited range of the complex WEF interconnections. It should be noted that the climate, land, energy, and water (CLEW) tool presents a framework for integrated modeling and quantifications for multiple sustainable systems, and was applied for assessing resource interlinkages in developing economies [105,106]. The CLEW tracks resources and technologies required for achieving certain development goals, and overcomes the inherent limits of single-sector modeling tools, such as the long-range energy alternatives planning system (LEAP) for energy policy analysis and the water evaluation and planning system (WEAP) for water resource assessment [107]. However, the structural scope of the CLEW model could be further extended to couple with societal and economic simulations, such as population, gross domestic product (GDP), urbanization, and international trade, to achieve fully integrated WEF nexus quantifications.
Decision and policy making for transitioning to sustainable WEF systems usually adopt bottom-up approaches for data acquisition to estimate the intra- and inter-flows of materials and resources and to identify relevant resource saving opportunities. Therefore, flexibility is an essential and inherent attribute for a WEF nexus assessment framework, which should be developed in a temporal- and spatial-specific manner. Decisions and policies should be made based on the parameters of mainstream technologies in recent social and economic contexts with considerations for their sustainability potentials in the future to avoid misdirection caused by out-of-date information. For example, the advances in thermal power generation systems in China during the past decade significantly reduced the water consumption per kWh of electricity generation from 4.1 kg in 2000 to 2 kg in 2013 [108]. Additionally, world food prices doubled from 2003 to 2014, with significant fluctuations from 2007 to 2012 [109]. On the other hand, because different regions and countries might have substantial variations in resource availability, climate conditions, energy systems and evolution, geographical features, population, and market structures and demand, one-size-fits-all analytic solutions to sustainable WEF nexus are lacking in the real world. The trade-offs of the WEF systems should be highlighted and addressed in a spatially specific manner with prioritized technology deployment and policy management. For example, existing literature advocates adopting a spatially varying water stress index for weighting water consumption to reflect resource scarcity in different regions, and to support more robust decision making for the deployment of bioenergy technologies [110,111]. Therefore, joint efforts of governmental authorities, organizations, research agencies, and institutes to establish datasets specific to local resource conditions and conflicts are crucial for achieving robust WEF nexus quantifications.
6. Conclusions
Population growth and economic development rely on a reliable supply of water, energy, and food. However, the interconnections and trade-offs among these resources challenge the simultaneous achievement of water, food, and energy security objectives. Thus, quantifications of the WEF nexus has become, and will continue to be, a vibrant research pursuit that advances integrated WEF modeling and management to provide important strategies for sustainable development in today’s dynamic and complex world. Figure 3 summarized the methodological supports, challenges, and opportunities associated with robust WEF footprint quantification. The inherent correlation of the three sectors requires stakeholders in both public and private sectors to model and manage the sustainability issue in a systematic and holistic manner. As discussed in Section 2, Section 3 and Section 4, previous literature has presented relatively complete calculations for the two-sector (water-energy, water-food, and food-energy) linkages. The existing estimates at various scales (global, national, regional, and technical) for a broad range of impact categories such as energy, water, land use, and environmental pollutant and GHG emissions, pave the way for integrated WEF nexus modeling and assessment. But the comparability of different study results needs to be further improved by harmonizing system boundaries, definitions, approaches, and methodologies adopted for quantification. For example, applying the harmonization approach to existing WF estimates of electricity generation technologies such as coal, conventional natural gas, shale gas, nuclear, and renewables to yield robust results that include complete life cycle stages, important production activities, and cost-effective technology adoptions for decision makings.

Figure 3.
Methodological supports, challenges, and opportunities associated with robust WEF nexus quantification.
To achieve robust WEF nexus quantifications, the directions for future research endeavors include key indicator identification and comprehensive sustainability scope definition, establishing multi-level and technology-specific WEF footprints database, synthesizing bottom-up and top-down approaches, and developing an integrated and flexible analytical framework with spatial- and temporal-specific constraints consideration.
Acknowledgments
The work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 71473285) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author Contributions
Yuan Chang designed the research; all authors conducted literature view and wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Population Prospects: The 2015 Revision; United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Mountford, H. Water: The Environmental Outlook to 2050. In Proceeding of the OECD Global Forum on Environment: Making Water Reform Happen, Paris, France, 25–26 October 2011.
- World Energy Outlook 2014; International Energy Agency (IEA): Paris, France, 2014.
- Renewable Energy in the Water, Energy & Food Nexus; Food Nexus; International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA): Abu Dhabi, UAE, 2015.
- Shale Gas Development Plan (2011–2015); National Energy Administration (NEA): Beijing, China, 2012.
- Energy Development Strategy Action Plan (2014–2020); State Council of the People’s Republic of China (SCC): Beijing, China, 2014.
- Chang, Y.; Liu, X.; Christie, P. Emerging shale gas revolution in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12281–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meadows, D.H.; Meadows, D.L.; Randers, J.; Behrens, W.W. The Limits to Growth; Universe Books: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Waughray, D. Water Security: The Water-Food-Energy-Climate Nexus; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hoff, H. Understanding the Nexus Background Paper for the Bonn2011 Conference: The Water, Energy and Food Security Nexus; Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Swenden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- World Energy Outlook 2012; International Energy Agency (IEA): Paris, France, 2012.
- 2014 Key World Energy Statistics; International Energy Agency (IEA): Paris, France, 2014.
- Masanet, E.; Chang, Y.; Gopal, A.R.; Larsen, P.; Morrow, W.R.; Sathre, R.; Shehabi, A.; Zhai, P. Life-cycle assessment of electric power systems. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2013, 38, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.E.; Theregowda, R.B.; Safari, I.; Abbasian, J.; Arastoopour, H.; Dzombak, D.A.; Hsieh, M.-K.; Miller, D.C. Utilization of municipal wastewater for cooling in thermoelectric power plants: Evaluation of the combined cost of makeup water treatment and increased condenser fouling. Energy 2013, 60, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power Plant Cooling and Associated Impacts: The Need to Modernize U.S. Power Plants and Protect Our Water Resources and Aquatic Ecosystems; Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC): New York, NY, USA, 2014.
- Clean Water Act—Section 316b Chapter 3; US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Qin, Y.; Curmi, E.; Kopec, G.M.; Allwood, J.M.; Richards, K.S. China’s energy-water nexus—Assessment of the energy sector’s compliance with the “3 red lines” industrial water policy. Energy Policy 2015, 82, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulbetsch, J.S. Comparison of Alternate Cooling Technologies for California Power Plants: Economic, Environmental and Other Tradeoffs; California Energy Commission: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- McMahon, J.E.; Price, S.K. Water and energy interactions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2011, 36, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Energy (DOE). Enhanced Oil Recovery. Available online: http://energy.gov/fe/science-innovation/oil-gas-research/enhanced-oil-recovery (accessed on 18 June 2015).
- Wu, M.; Mintz, M.; Wang, M.; Arora, S. Consumptive Water Use in the Production of Bioethanol and Petroleum Gasoline; Argonne National Laboratory: Lemont, IL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, S.; Kuuskraa, V.; O’Donnell, J. Enhanced Oil Recovery Scoping Study; TR-113836; Electric Power Research Institute: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore, D.O. Geochemical differentiation of oil and gas brine from other saltwater sources contaminating water resources: Case studies from Kansas and Oklahoma. Environ. Geosci. 1995, 2, 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, C.E.; Han, J.; Burnham, A.; Dunn, J.B.; Wang, M. Life-Cycle Analysis of Shale Gas and Natural Gas; Argonne National Laboratory: Argonne, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Huang, R.; Ries, J.R.; Masanet, E. Shale-to-well energy use and air pollutant emissions of shale gas production in China. Appl. Energy 2014, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Flower, R.J.; Thompson, J.R. Shale-gas plans threaten China’s water resources. Science 2013, 340, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKendry, P. Energy production from biomass (part 1): Overview of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbens-Leenes, P.W.; Hoekstra, A.Y.; Van Der Meer, T. The water footprint of energy from biomass: A quantitative assessment and consequences of an increasing share of bio-energy in energy supply. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Special Report on Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, D.R.; Leach, J.E. Translational genomics for bioenergy production: There’s room for more than one model. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2971–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Karp, A.; Shield, I. Bioenergy from plants and the sustainable yield challenge. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berndes, G. Bioenergy and water—The implications of large-scale bioenergy production for water use and supply. Glob. Environ. Change 2002, 12, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Huang, R.; Ries, R.J.; Masanet, E. Life-cycle comparison of greenhouse gas emissions and water consumption for coal and shale gas fired power generation in China. Energy 2015, 86, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, J.; Nettles-Anderson, S.; Heath, G.; Macknick, J. Life cycle water use for electricity generation: A review and harmonization of literature estimates. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macknick, J.; Newmark, R.; Heath, G.; Hallett, K. Operational water consumption and withdrawal factors for electricity generating technologies: A review of existing literature. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Zhang, Q.; Mihelcic, J.R.; Hokanson, D.R. Embodied energy comparison of surface water and groundwater supply options. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5577–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Dong, Y.-N.; Wang, H.; Keller, A.; Xu, J.; Chiramba, T.; Li, F. Quantification of the water, energy and carbon footprints of wastewater treatment plants in China considering a water–energy nexus perspective. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.; Nelson, B.; Wolff, G. Energy Down the Drain: The Hidden Costs of California’s Water Supply; Natural Resources Defense Council: Oakland, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Energy Demands on Water Resources; U.S. Department of Energy (DOE): Washington, DC, USA, 2006.
- Building Energy Efficiency Research Center of Tsinghua University. 2013 China Building Energy Efficiency Development Report; China Building Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Ries, R.J.; Wang, Y. Life-cycle energy of residential buildings in China. Energy Policy 2013, 62, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Liu, J.; Matthews, J.H.; Mumba, M.; D’Odorico, P. Manage water in a green way. Science 2015, 349, 584–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sponge City Construction Technology Guide; Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China (MHURDC): Beijing, China, 2014.
- The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture; The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011.
- Liu, J.; Savenije, H.H.G. Food consumption patterns and their effect on water requirement in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbens-Leenes, P.W.; Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The water footprint of poultry, pork and beef: A comparative study in different countries and production systems. Water Resour. Ind. 2013, 1, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. A global assessment of the water footprint of farm animal products. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The Green, Blue and Grey Water Footprint of Crops and Derived Crop Products; UNESCO-IHE Institute for Water Education: Delft, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, A.Y. The Water Footprint of Food. Available online: http://waterfootprint.org/media/downloads/Hoekstra-2008-WaterfootprintFood.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2015).
- Ercin, A.E.; Aldaya, M.; Hoekstra, A. Corporate water footprint accounting and impact assessment: The case of the water footprint of a sugar-containing carbonated beverage. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Water Uses Database. Available online: http://www.fao.org/nr/water/aquastat/water_use/index.stm (accessed on 18 August 2015).
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Mekonnen, M.M. The water footprint of humanity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Water: A Shared Responsibility; World Water Assessment Programme: Paris, France, 2006.
- Zou, X.; Li, Y.E.; Cremades, R.; Gao, Q.; Wan, Y.; Qin, X. Cost-effectiveness analysis of water-saving irrigation technologies based on climate change response: A case study of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 129, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhite, D.A. Drought as a natural hazard: Concepts and definitions. In Drought: A Global Assessment; Routledge: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgos, K. Droughts. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2008, 33, 85–118. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). What is Organic Agriculture? Available online: http://www.fao.org/organicag/oa-faq/oa-faq1/en/ (accessed on 1 July 2015).
- Pimentel, D.; Berardi, G.; Fast, S. Energy efficiency of farming systems: Organic and conventional agriculture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1983, 9, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Patzek, T.W. Ethanol production using corn, switchgrass, and wood; biodiesel production using soybean and sunflower. Nat. Resour. Res. 2005, 14, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flessa, H.; Ruser, R.; Dörsch, P.; Kamp, T.; Jimenez, M.A.; Munch, J.C.; Beese, F. Integrated evaluation of greenhouse gas emissions (CO2, CH4, N2O) from two farming systems in southern germany. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Langer, V.; Høgh-Jensen, H.; Egelyng, H. Energy use in organic, green and conventional pear producing systems—Cases from China. J. Sustain. Agric. 2010, 34, 630–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-W.; Feike, T.; Holst, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Doluschitz, R. Comparison of energy consumption and economic performance of organic and conventional soybean production—A case study from Jilin province, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshel, G.; Shepon, A.; Makov, T.; Milo, R. Land, irrigation water, greenhouse gas, and reactive nitrogen burdens of meat, eggs, and dairy production in the united states. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11996–12001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.L.; Matthews, H.S. Food-miles and the relative climate impacts of food choices in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3508–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazer, J. How Much Water Does It Take to Make A Cup of Tea? Available online: http://www.carbontrust.com/news/2015/07/how-much-water-does-it-take-to-make-a-cup-of-tea/ (accessed on 5 August 2015).
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, A.; Shen, J.; Cui, Z.; Vitousek, P.; Erisman, J.W.; Goulding, K.; Christie, P.; et al. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, X.; Vitousek, P. Chinese agriculture: An experiment for the world. Nature 2013, 497, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Cheng, S. Food security: Curb China’s rising food wastage. Nature 2013, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Energy-Smart Food at FAO: An Overview; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012.
- Vanham, D. Does the water footprint concept provide relevant information to address the water-food-energy-ecosystem nexus? Ecosyst. Serv. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van linden, V.; Herman, L. A fuel consumption model for off-road use of mobile machinery in agriculture. Energy 2014, 77, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Elliott, R.N. On-Farm Energy Use Characterizations; American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gellings, C.W.; Parmenter, K.E. Energy Efficiency in Fertilizer Production and Use. In Efficient Use and Conservation of Energy, Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems; Eolss Publishers: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Agriculture & Energy Efficiency (AGREE) Project Deliverable 3.1. Economic and Environmental Analysis of Energy Efficiency Measures in Agriculture: Case Studies and Trade Offs. Available online: http://www.agree.aua.gr/Files/Publications/D3.1_Econ+enviro_analysis_of_EE_measures_in_Agr.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2015).
- Sathaye, J.; Lecocq, F.; Masanet, E.; Najam, A.; Schaeffer, R.; Swart, R.; Winkler, H. Opportunities to change development pathways toward lower greenhouse gas emissions through energy efficiency. Energy Effic. 2009, 2, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.; Elliott, R.N. Potential Energy Efficiency Savings in the Agriculture Sector; American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson-Kanyama, A.; Ekström, M.P.; Shanahan, H. Food and life cycle energy inputs: Consequences of diet and ways to increase efficiency. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 44, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florax, R.J.; De Groot, H.L.; Mulder, P. Improving Energy Efficiency Through Technology: Trends, Investment Behaviour and Policy Design; Edward Elgar Publishing: Northampton, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, C.A.; Patel, M.; Blok, K. How much energy to process one pound of meat? A comparison of energy use and specific energy consumption in the meat industry of four European countries. Energy 2006, 31, 2047–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.E.; Arnold, C.S.; Lettieri, D.J.; Hutchins, M.J.; Masanet, E. Improved product energy intensity benchmarking metrics for thermally concentrated food products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12370–12377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briam, R.; Walker, M.E.; Masanet, E. A comparison of product-based energy intensity metrics for cheese and whey processing. J. Food Eng. 2015, 151, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masanet, E.; Brush, A.; Worrell, E. Energy efficiency opportunities in the US Dairy processing industry. Energy Eng. 2014, 111, 7–34. [Google Scholar]
- Therkelsen, P.; Masanet, E.; Worrell, E. Energy efficiency opportunities in the US commercial baking industry. J. Food Eng. 2014, 130, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther, U.; Ziegler, F.; Hognes, E.S.; Emanuelsson, A.; Sund, V.; Ellingsen, H. Carbon Footprint and Energy Use of Norwegian Seafood Products; SINTEF Fisheries and Aquaculture: Trondheim, Norway, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Masanet, E.; Worrell, E.; Graus, W.; Galitsky, C. Energy Efficiency Improvement and Cost Saving Opportunities for the Fruit and Vegetable Processing Industry: An Energy Star® Guide for Energy and Plant Managers; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- California Environmental Protection Agency. Cap-and-Trade Program. Available online: http://www.arb.ca.gov/cc/capandtrade/capandtrade.htm (accessed on 11 October 2015).
- Scarlat, N.; Dallemand, J.-F.O.; Banja, M. Possible impact of 2020 bioenergy targets on european union land use. A scenario-based assessment from national renewable energy action plans proposals. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 18, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlat, N.; Dallemand, J.-F. Recent developments of biofuels/bioenergy sustainability certification: A global overview. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 1630–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2007–2016; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2007.
- Campbell, J.E.; Lobell, D.B.; Genova, R.C.; Field, C.B. The global potential of bioenergy on abandoned agriculture lands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5791–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, D.; Jiang, D.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y. Assessment of bioenergy potential on marginal land in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryngelsson, D.K.; Lindgren, K. Why large-scale bioenergy production on marginal land is unfeasible: A conceptual partial equilibrium analysis. Energy Policy 2013, 55, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Chang, Y.; Pang, M. Biomass direct-fired power generation system in China: An integrated energy, GHG emissions, and economic evaluation for Salix. Energy Policy 2015, 84, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringler, C.; Bhaduri, A.; Lawford, R. The nexus across water, energy, land and food (WELF): Potential for improved resource use efficiency? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.B.; Walker, R.V. On water security, sustainability, and the water-food-energy-climate nexus. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabulut, A.; Egoh, B.N.; Lanzanova, D.; Grizzetti, B.; Bidoglio, G.; Pagliero, L.; Bouraoui, F.; Aloe, A.; Reynaud, A.; Maes, J.; et al. Mapping water provisioning services to support the ecosystem-water-food-energy nexus in the Danube river basin. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawford, R.; Bogardi, J.; Marx, S.; Jain, S.; Wostl, C.P.; Knüppe, K.; Ringler, C.; Lansigan, F.; Meza, F. Basin perspectives on the water-energy-food security nexus. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhringer, C.; Rutherford, T.F. Combining bottom-up and top-down. Energy Econ. 2008, 30, 574–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Chapagain, A.; Suh, S.; Pfister, S.; Hubacek, K. Comparison of bottom-up and top-down approaches to calculating the water footprints of nations. Econ. Syst. Res. 2011, 23, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, T.J.; Pakarinen, S.; Sokka, L. Quantifying the total environmental impacts of an industrial symbiosis—A comparison of process-, hybrid and input-output life cycle assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4309–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, C.T.; Lave, L.B.; Matthews, H.S. Environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Goods and Services: An Input-Output Approach; Resources for the Future Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). Life Cycle Assessment Harmonization Methodology. Available online: http://www.nrel.gov/analysis/sustain_lca_method.html (accessed on 22 September 2015).
- Bazilian, M.; Rogner, H.; Howells, M.; Hermann, S.; Arent, D.; Gielen, D.; Steduto, P.; Mueller, A.; Komor, P.; Tol, R.S.J.; et al. Considering the energy, water and food nexus: Towards an integrated modelling approach. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 7896–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Heijungs, R.; De Snoo, G.R. Theoretical exploration for the combination of the ecological, energy, carbon, and water footprints: Overview of a footprint family. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, S.; Welsch, M.; Segerstrom, R.E.; Howells, M.I.; Young, C.; Alfstad, T.; Rogner, H.-H.; Steduto, P. Climate, land, energy and water (CLEW) interlinkages in Burkina Faso: An analysis of agricultural intensification and bioenergy production. Nat. Resour. Forum 2012, 36, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howells, M.; Hermann, S.; Welsch, M.; Bazilian, M.; Segerstrom, R.; Alfstad, T.; Gielen, D.; Rogner, H.; Fischer, G.; Van Velthuizen, H.; et al. Integrated analysis of climate change, land-use, energy and water strategies. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annex VI: Seeking Sustainable Climate Land Energy and Water (CLEW) Strategies; Nuclear Technology Review; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2009.
- Editorial Board of China Power Yearbook. 2014 China Electric Power Yearbook; China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). FAO Food Price Index. Available online: http://www.fao.org/worldfoodsituation/foodpricesindex/en/ (accessed on 12 July 2015).
- Pfister, S.; Hellweg, S. The water “shoesize” vs. footprint of bioenergy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, E93–E94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, S.; Koehler, A.; Hellweg, S. Assessing the environmental impacts of freshwater consumption in LCA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4098–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).