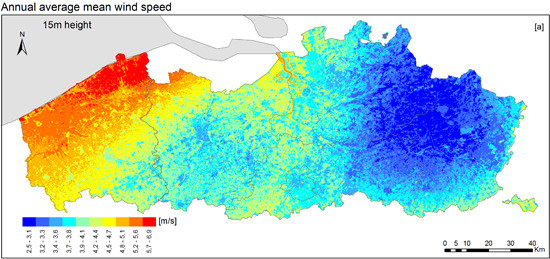
Wind Resource Mapping Using Landscape Roughness and Spatial Interpolation Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
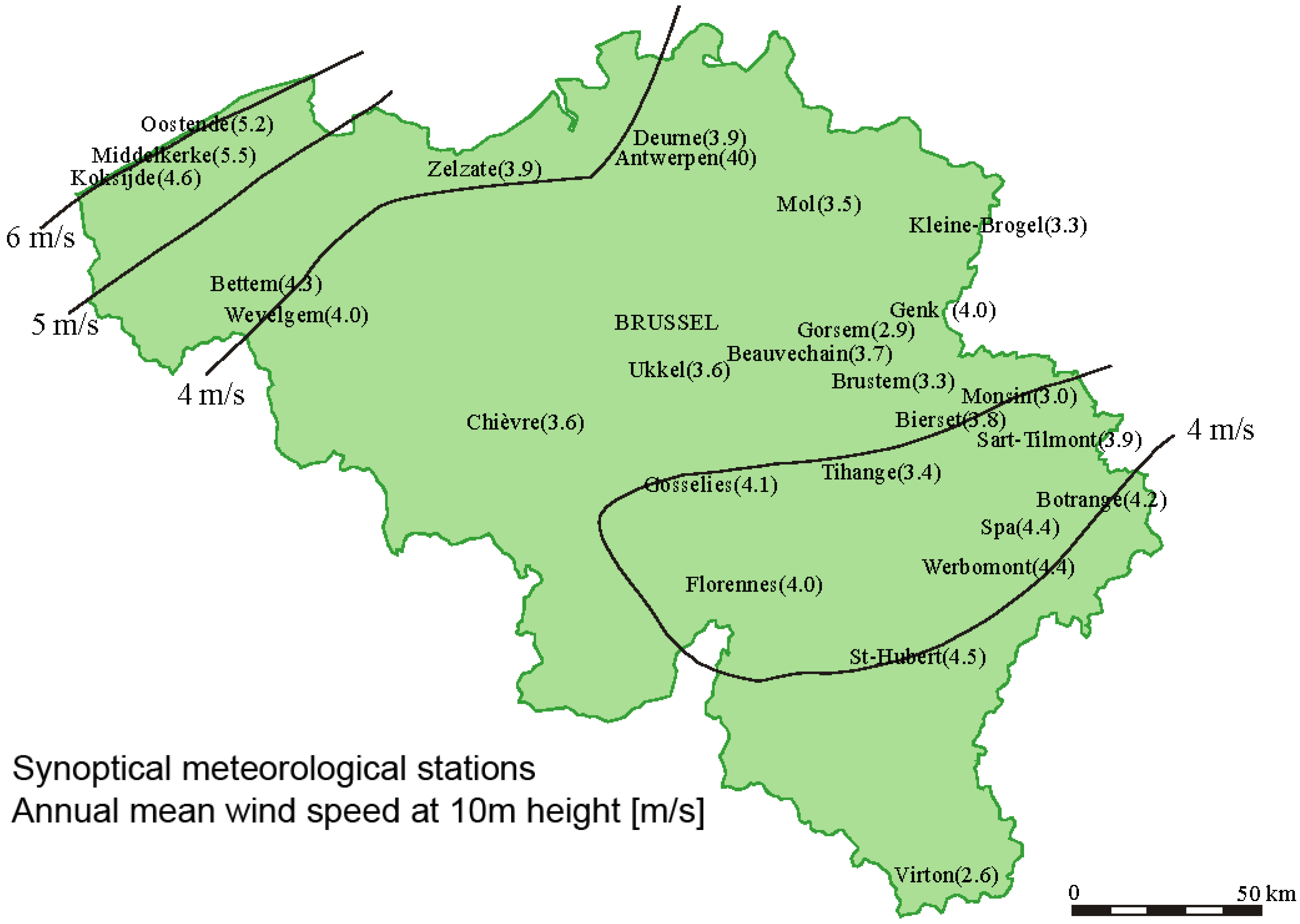
2. Data collection
2.1. Wind speed Measurements
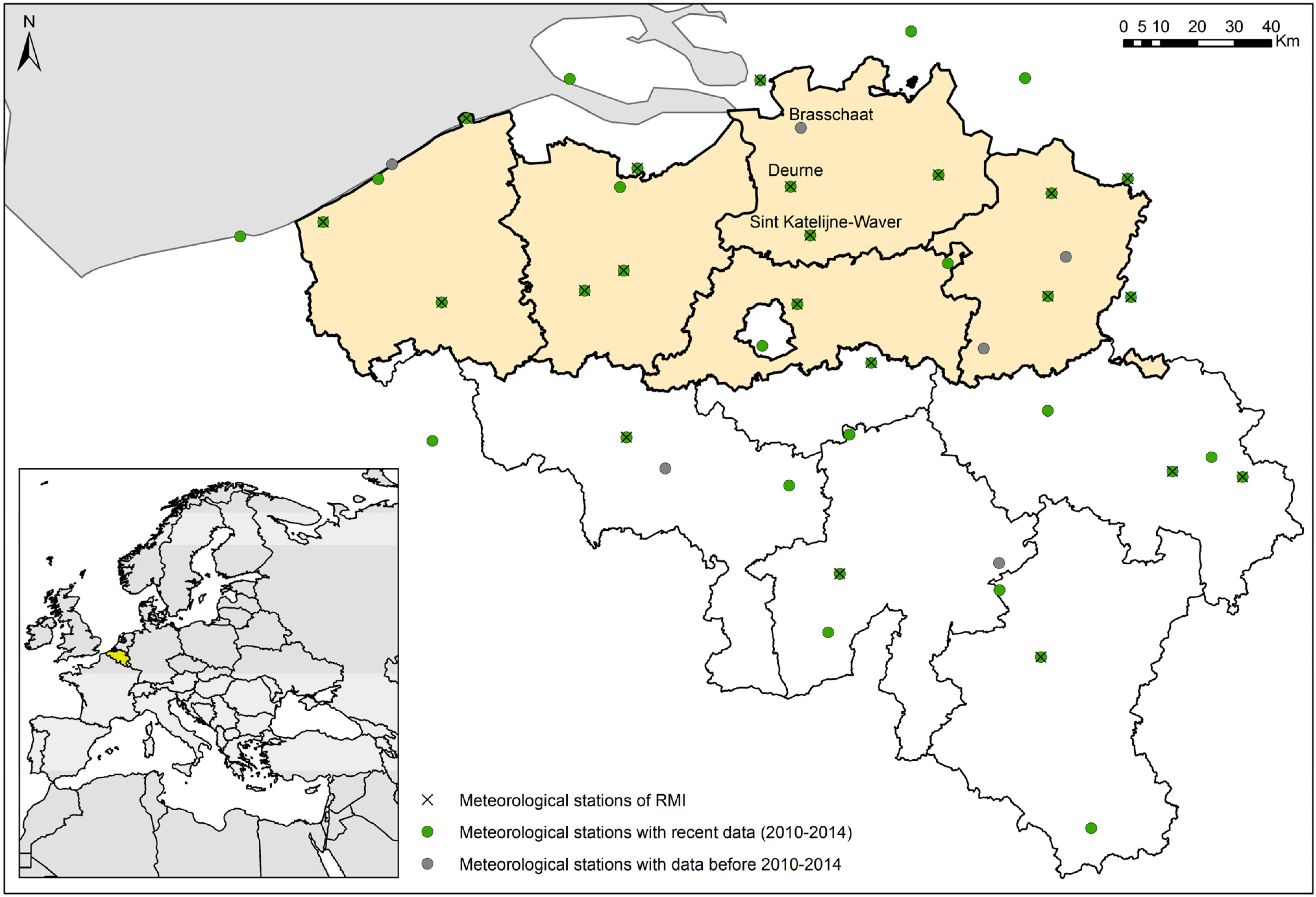
| Station | Roughness [m] | Latitude [°] | Longitude [°] | Begin Date | End Date | Mean Wind Speed [m/s] | Mean Wind Speed (2010–2014) [m/s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beauvechain | 0.03 | 50.758 | 4.768 | 1/01/1973 | 42.004 | 3.88 | 3.70 |
| Beitem | 0.469 | 50.900 | 3.116 | 1/02/2008 | 42.035 | 3.69 | 3.67 |
| Brasschaat | 0.14 | 51.333 | 4.500 | 1/02/1973 | 31/01/2006 | 3.26 | |
| Brussels NATL | 0.037 | 50.902 | 4.485 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.99 | 3.62 |
| Brussels South | 0.2 | 50.459 | 4.453 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.96 | 4.00 |
| Buzenol | 0.6 | 49.616 | 5.583 | 26/10/2009 | 25/10/2014 | 2.76 | 2.74 |
| Casteau/Heli | 0.8 | 50.500 | 3.980 | 1/01/2011 | 31/12/2014 | 2.18 | |
| Chievres | 0.1 | 50.575 | 3.831 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.73 | 3.75 |
| Deurne | 0.896 | 51.189 | 4.460 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.55 | 3.58 |
| Diepenbeek | 0.08 | 50.916 | 5.450 | 1/01/2010 | 31/12/2014 | 2.92 | 2.92 |
| Dourbes | 0.6 | 50.100 | 4.600 | 1/01/2010 | 31/12/2014 | 2.52 | 2.52 |
| Elsenborn | 0.6 | 50.466 | 6.183 | 1/01/1987 | 31/12/2014 | 3.11 | 3.12 |
| Ernage | 0.1 | 50.583 | 4.683 | 1/01/2008 | 31/12/2014 | 4.06 | 4.04 |
| Florennes | 0.15 | 50.243 | 4.645 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.75 | 3.69 |
| Genk/Zwartberg | 0.676 | 51.012 | 5.522 | 7/01/1973 | 6/01/2004 | 3.60 | |
| Gent/Industrie | 0.021 | 51.187 | 3.799 | 1/01/1985 | 31/12/2014 | 3.31 | 3.32 |
| Humain | 0.4 | 50.200 | 5.250 | 1/03/2010 | 28/02/2015 | 3.69 | 3.66 |
| Kleine Brogel | 0.054 | 51.168 | 5.470 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.01 | 3.01 |
| Koksijde | 0.06 | 51.090 | 2.652 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 4.68 | 4.57 |
| Liege | 0.15 | 50.637 | 5.443 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 4.07 | 4.11 |
| Melle | 0.2 | 50.983 | 3.816 | 1/01/2010 | 31/12/2014 | 3.42 | 3.42 |
| Mont-Rigi | 0.2 | 50.516 | 6.066 | 16/01/2008 | 15/01/2015 | 3.83 | 3.74 |
| Oostende | 0.64 | 51.198 | 2.862 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 5.22 | 4.75 |
| Oostende (Pier) | 0.98 | 51.235 | 2.914 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2005 | 6.91 | |
| Retie | 0.118 | 51.216 | 5.033 | 26/10/2009 | 25/10/2014 | 2.64 | 2.63 |
| Saint Hubert Mil | 0.2 | 50.035 | 5.404 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.88 | 3.29 |
| Schffen | 0.03 | 51.000 | 5.066 | 2/01/1973 | 1/01/2015 | 3.93 | 3.21 |
| Semmerzake | 0.231 | 50.933 | 3.666 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.70 | 3.26 |
| Sinsin | 0.3 | 50.266 | 5.250 | 20/09/1984 | 19/09/1995 | 3.49 | |
| Sint Katelijne-waver | 0.278 | 51.070 | 4.535 | 1/10/2012 | 30/09/2014 | 3.02 | 3.05 |
| Sint Truiden | 0.03 | 50.791 | 5.201 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/1991 | 3.62 | |
| Spa/La Sauveniere | 0.1 | 50.483 | 5.916 | 1/01/1974 | 31/12/2014 | 3.87 | 3.74 |
| Uccle | 0.621 | 50.800 | 4.350 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.48 | 3.44 |
| Zeebrugge | 0.001 | 51.350 | 3.200 | 26/10/2009 | 25/10/2014 | 6.05 | 6.02 |
| Dunkerque | 0.01 | 51.050 | 2.333 | 2/01/1973 | 1/01/2015 | 6.20 | 5.26 |
| Lesquin | 0.1 | 50.561 | 3.089 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 4.37 | 4.09 |
| Eindhoven | 0.1 | 51.450 | 5.374 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.94 | 3.64 |
| Ell AWS | 0.15 | 51.200 | 5.766 | 1/01/2002 | 31/12/2014 | 3.53 | 3.46 |
| Gilze Rijen | 0.05 | 51.567 | 4.931 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 3.81 | 3.53 |
| Maastricht | 0.05 | 50.911 | 5.770 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 4.25 | 4.06 |
| Vlissingen | 0.25 | 51.450 | 3.600 | 1/01/1973 | 31/12/2014 | 6.07 | 6.10 |
| Westdorpe | 0.25 | 51.233 | 3.866 | 1/01/1995 | 31/12/2014 | 4.02 | 4.00 |
| Woensdrecht | 0.3 | 51.449 | 4.342 | 1/01/1996 | 31/12/2014 | 3.45 | 3.48 |
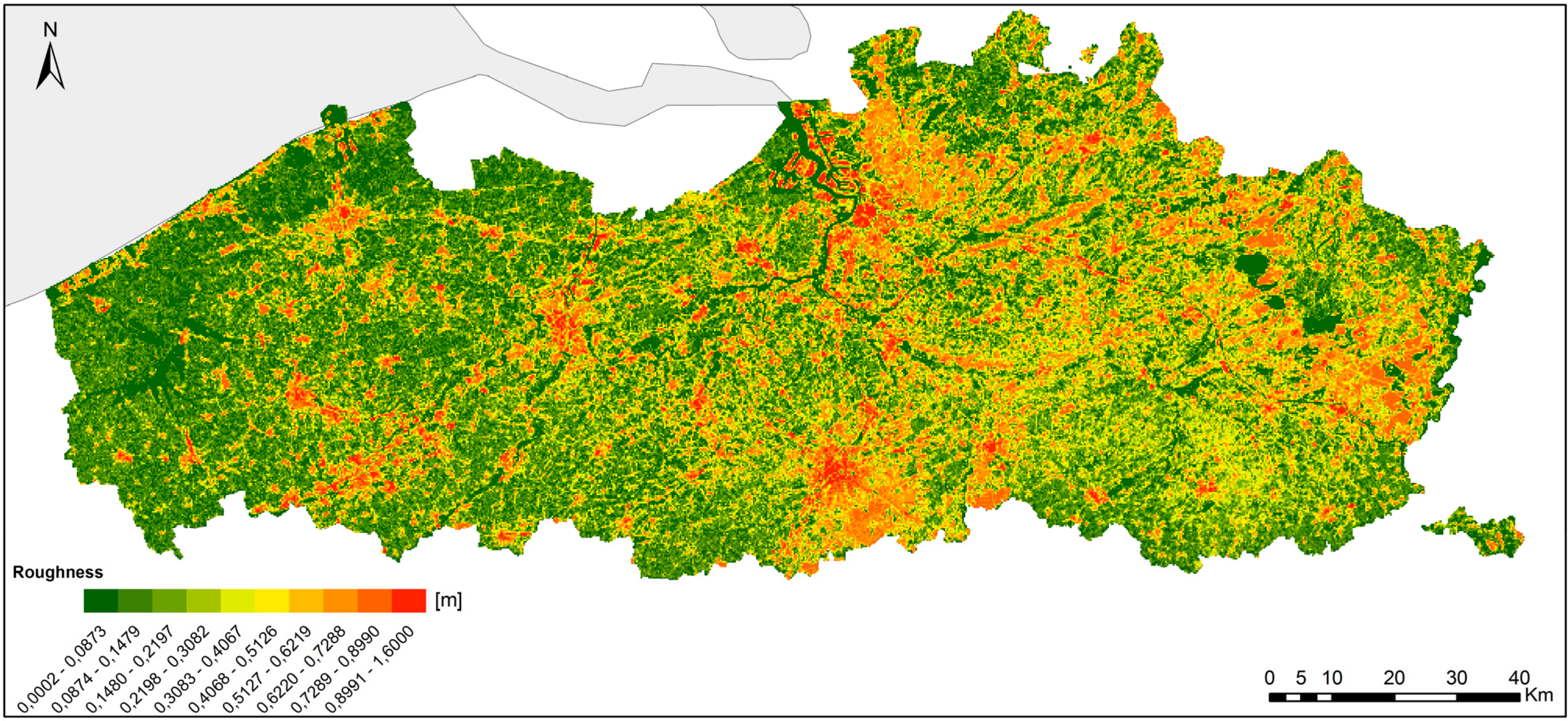
2.1.1. Roughness Map Flanders
3. Methodology
3.1. The PBL Two Layer Model
3.1.1. Mesowind
3.1.2. Macrowind
3.2. Spatial Interpolation Methods
3.2.1. Deterministic methods
Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW)
Global Polynomial Interpolation (GPI)
Local Polynomial Interpolation (LPI)
Radial Basic Functions (RBF)
3.2.2. Geostatistical Methods
3.3. Validation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Exposure Correction
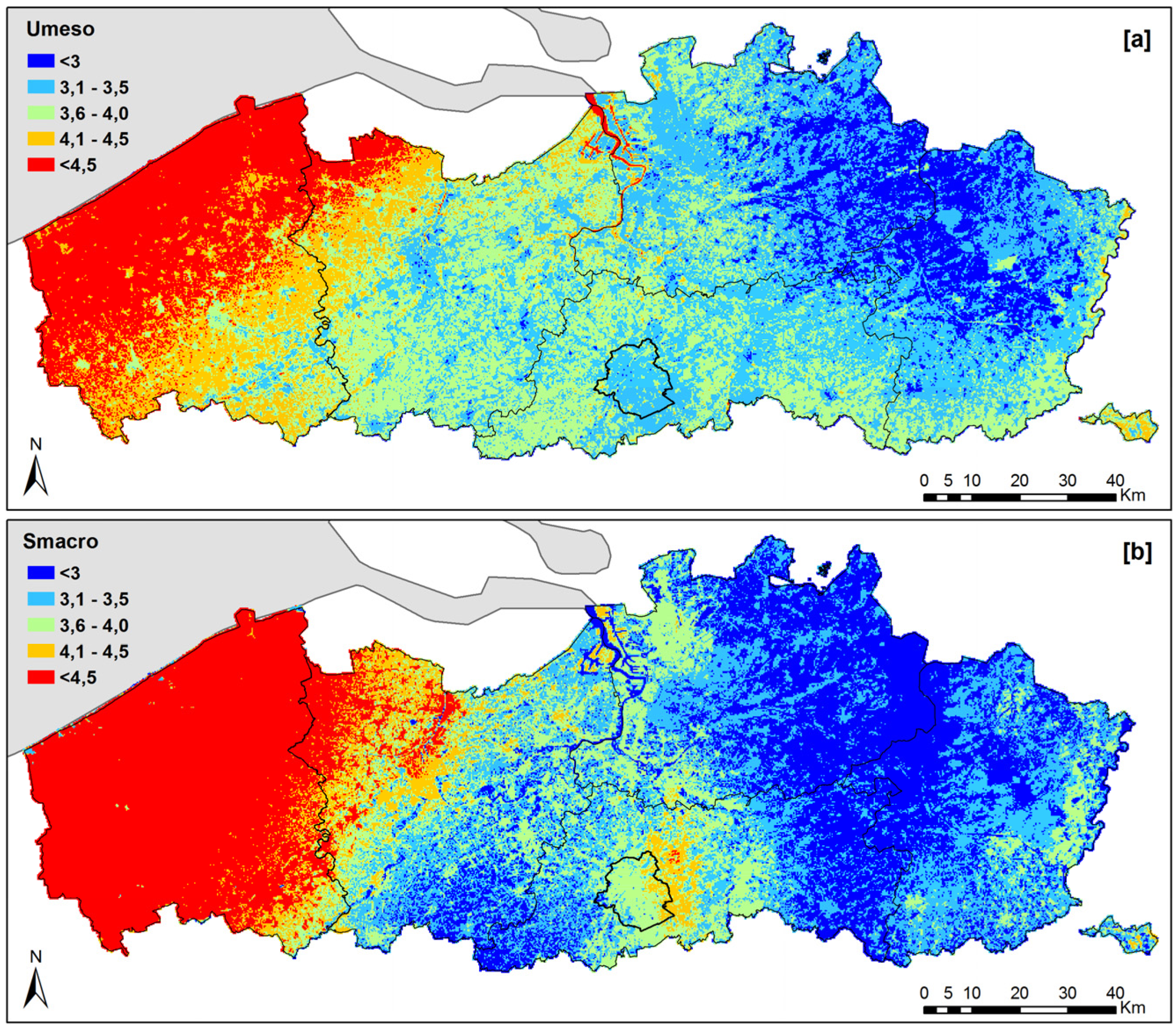
| Method | ME [m/s] | MAPE [%] | RMSE [m/s] | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Umeso | −0.069 | 13.82 | 0.596 | 0.68 |
| Smacro | 0.035 | 19.42 | 0.945 | 0.56 |
4.2. Spatial Interpolation Methods Comparison
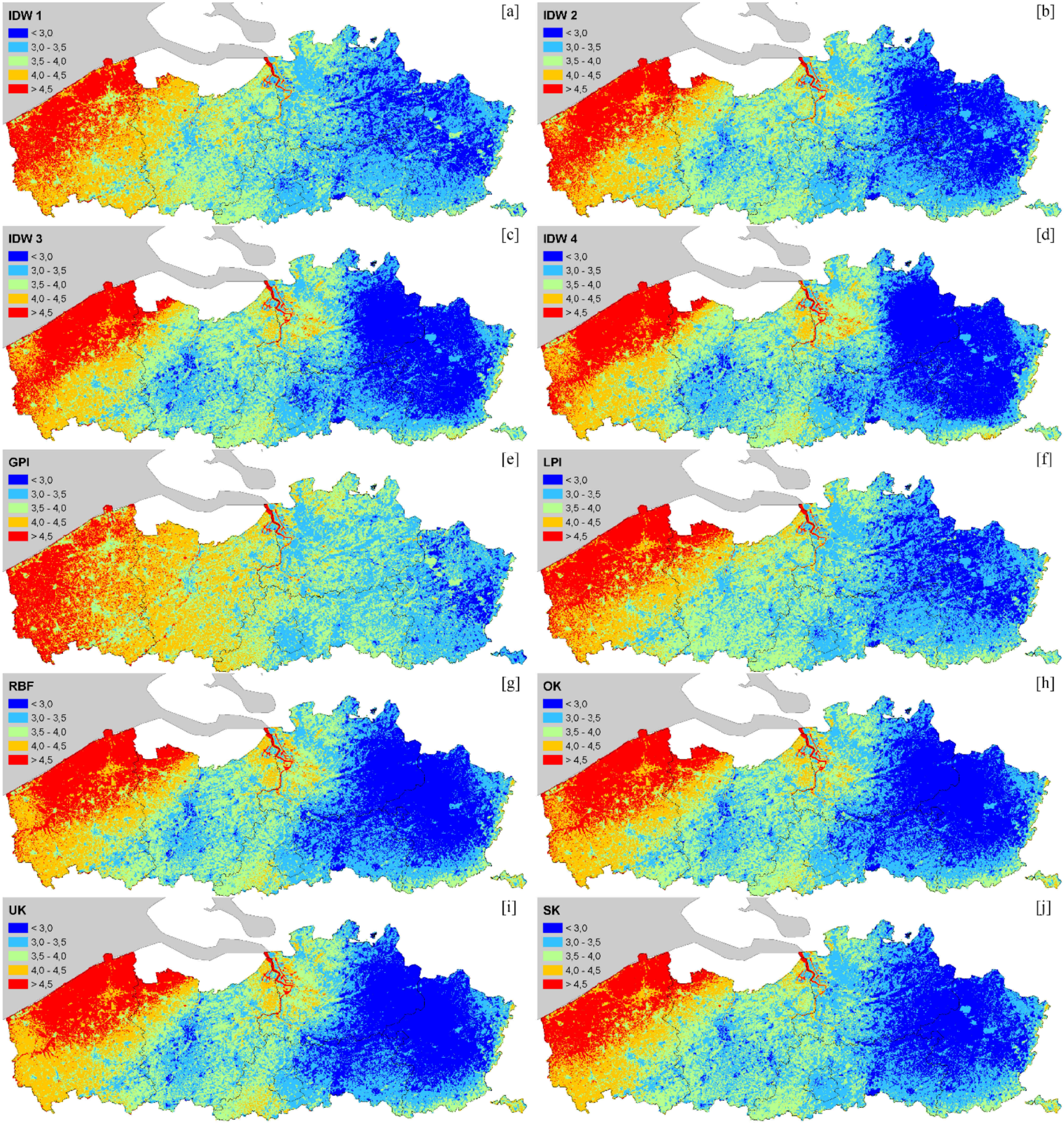
| Method | ME [m/s] | MAPE [%] | RMSE [m/s] | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDW 1 | −0.143 | 14.58 | 0.577 | 0.56 |
| IDW 2 | −0.127 | 13.06 | 0.520 | 0.64 |
| IDW 3 | −0.121 | 12.10 | 0.509 | 0.67 |
| IDW 4 | −0.125 | 11.93 | 0.521 | 0.68 |
| IDW 5 | −0.132 | 12.29 | 0.540 | 0.68 |
| GPI | −0.258 | 17.43 | 0.688 | 0.43 |
| LPI | −0.257 | 13.15 | 0.504 | 0.77 |
| RBF | −0.125 | 10.88 | 0.479 | 0.74 |
| SK | −0.030 | 10.82 | 0.484 | 0.67 |
| OK | −0.133 | 11.37 | 0.487 | 0.72 |
| UK | −0.144 | 11.38 | 0.477 | 0.72 |
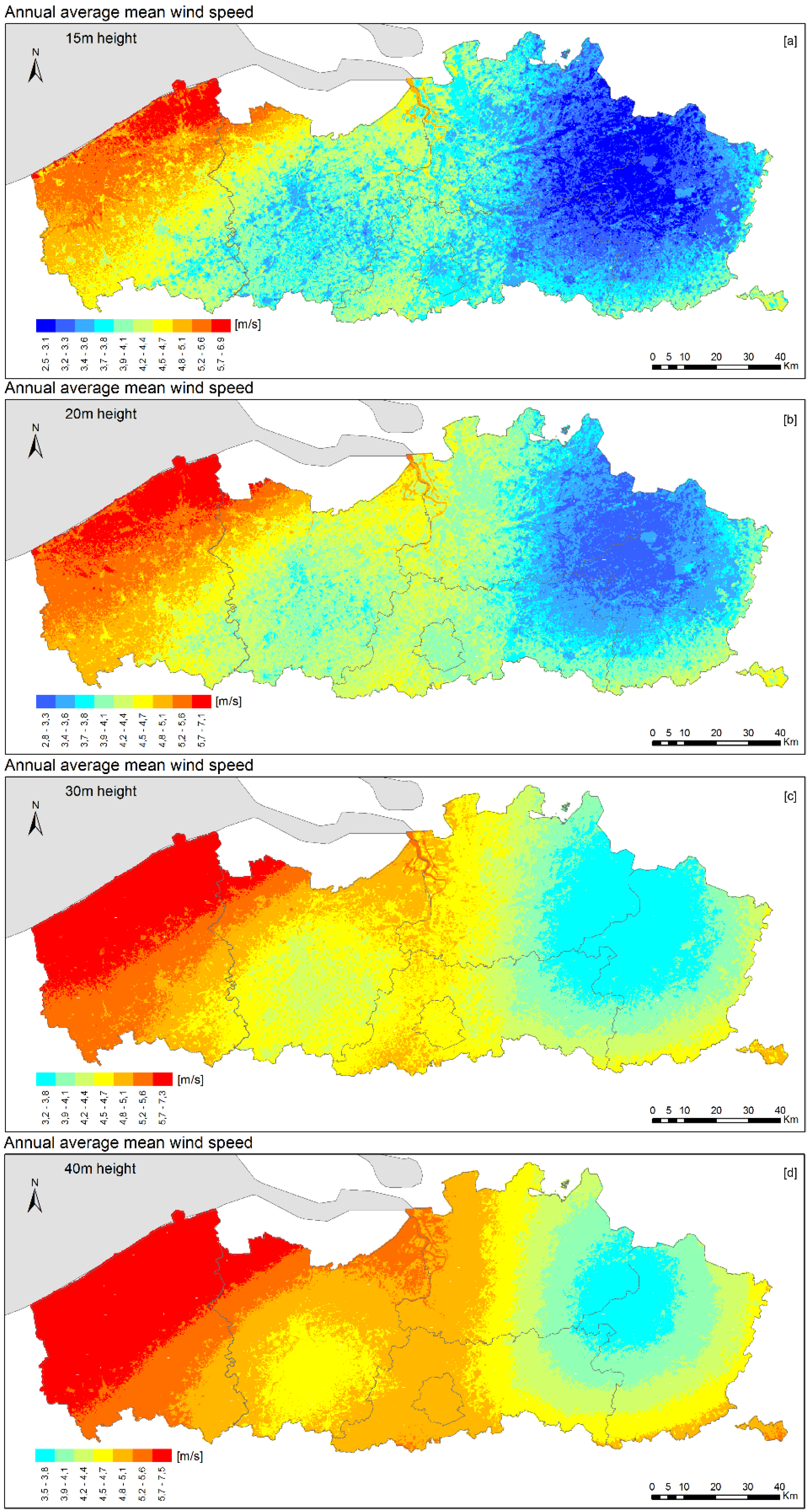
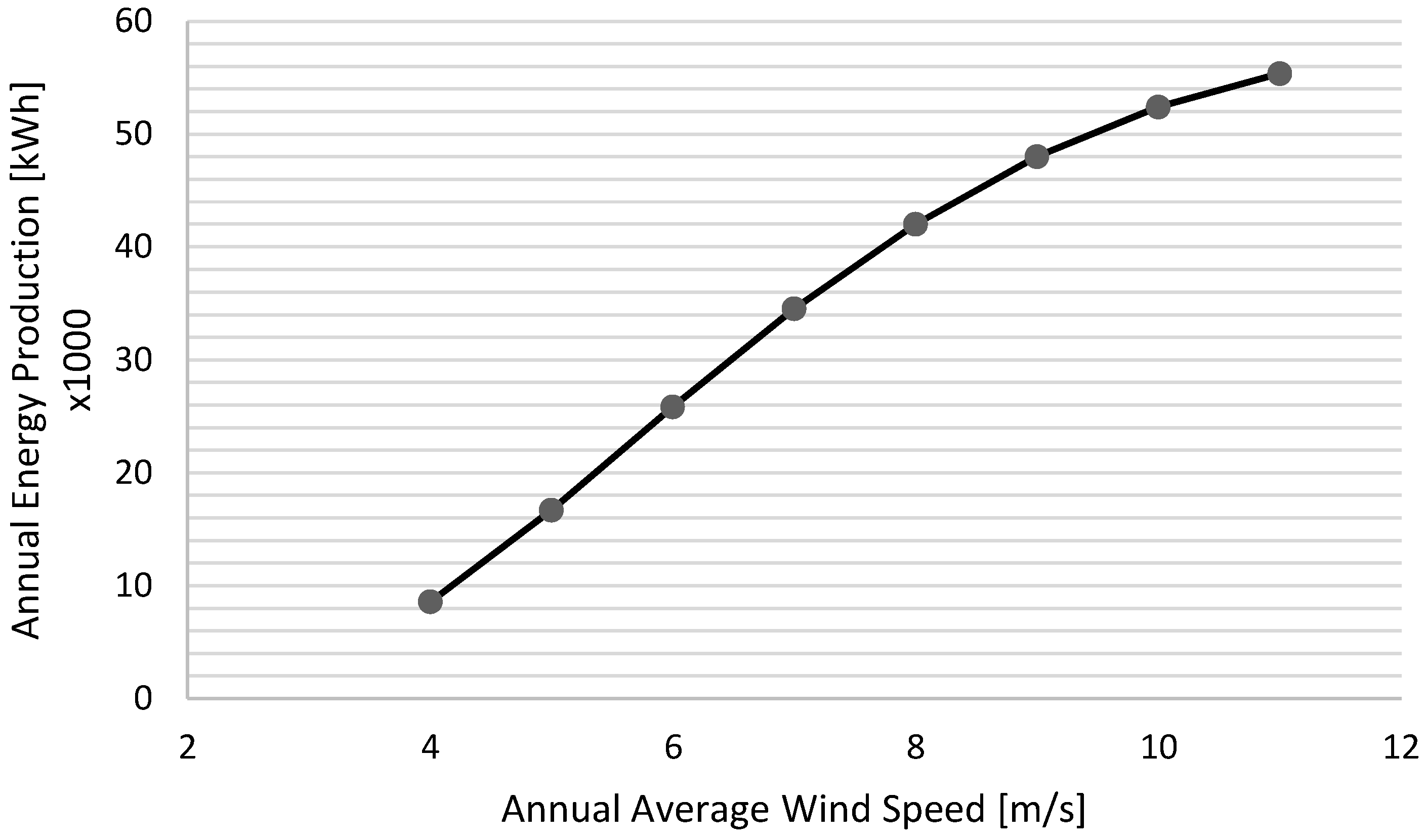
5. Energy Resource Mapping
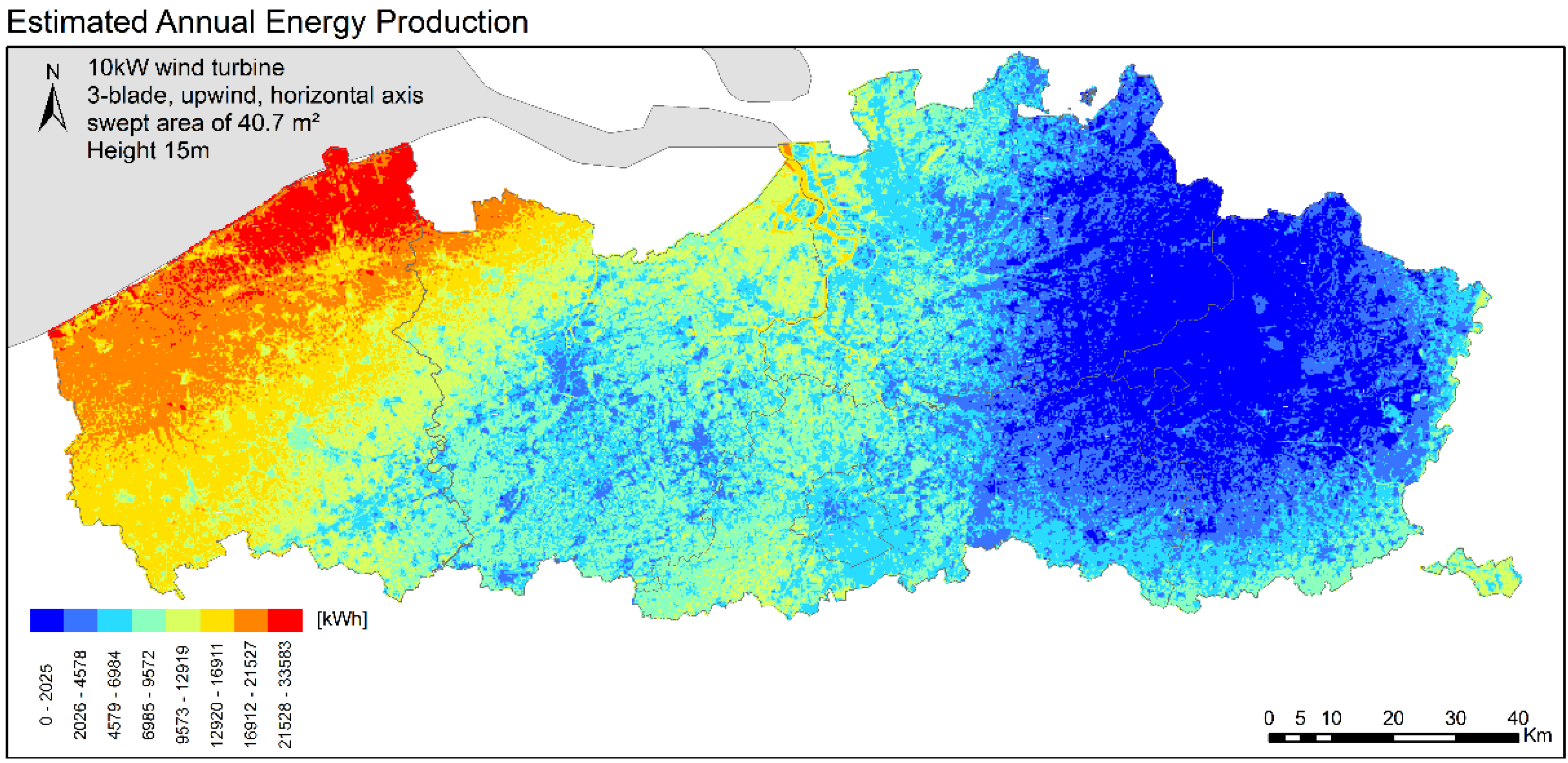
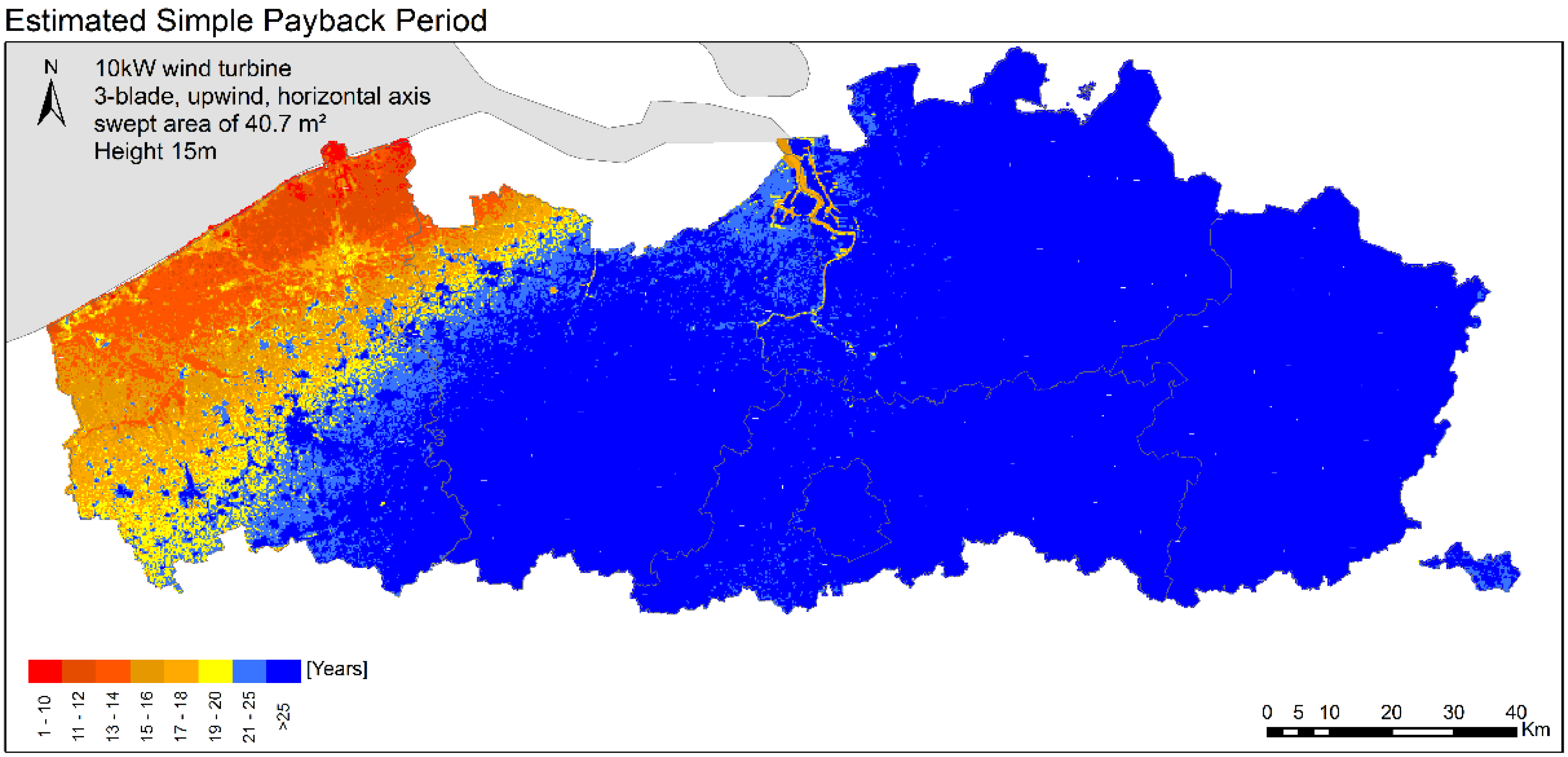
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giacomarra, M.; Bono, F. European Union commitment towards RES market penetration: From the first legislative acts to the publication of the recent guidelines on State aid 2014/2020. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 47, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanslian, D.; Hošek, J. Combining the VAS 3D interpolation method and Wind Atlas methodology to produce a high-resolution wind resource map for the Czech Republic. Renew. Energy 2015, 77, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempels, B.; Pisman, A. Open Ruimte in Verstedelijkt Vlaanderen: Een Vergelijkende Studie Naar Vier Onderschatte Ruimtegebruiken. Ruimte Maatsch. 2013, 5, 33–58. [Google Scholar]
- VMM. Luchtkwaliteit in het Vlaamse Gewest—Jaarverslag Immissiemeetnetten; Vlaamse Milieumaatschappij: Erembodegem, Belgium, 2014. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar]
- Ministerie van de Vlaamse Gemeenschap, afdeling Natuurlijke Rijkdommen en Energie. Windenergie Winstgevend; Ministerie van de Vlaamse Gemeenschap, afdeling Natuurlijke Rijkdommen en Energie: Brussel, Belgium, 1998; p. 16. Available online: http://stro.vub.ac.be/wind/windenergie_winstgevend.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2015). (In Dutch)
- National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). U.S. Daily Observational Data. NOAA: Washington, DC, USA. Available online: http://gis.ncdc.noaa.gov/map/viewer/#app=cdo (accessed on 12 August 2015).
- Pryor, S.; Barthelmie, R. Climate change impacts on wind energy: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antrop, M. Landscape change and the urbanization process in Europe. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 67, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Ribeiro, C.; Guedes, R. Roughness length classification of Corine Land Cover classes. In Proceedings of the European Wind Energy Conference, Milan, Italy, 7–10 May 2007; pp. 1–10.
- NGI. De eenheid beeldverwerking van het NGI. Available online: http://www.ngi.be/Common/articles/CA_Td/artikel_td.htm (accessed on 12 August 2015). (In Dutch)
- Stepek, A.; Wijnant, I.L. Interpolating Wind Speed Normals from the Sparse Dutch Network to a High Resolution Grid Using Local Roughness from Land Use Maps; Koninklijk Nederlands Meteorologisch Instituut: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa, J. Roughness-dependent geographical interpolation of surface wind speed averages. Quart. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1986, 112, 867–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkaik, J. Evaluation of two gustiness models for exposure correction calculations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1613–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkaik, J. A Method for the Geographical Interpolation of Wind Speed over Heterogeneous Terrain; Koninklijk Nederlands Meteorologisch Instituut: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Verkaik, J.; Smits, A. Interpretation and estimation of the local wind climate. In Proceedings of the 3rd European & African Conference on Wind Engineering, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2–6 July 2001; pp. 2–6.
- Verkaik, J.W. On Wind and Roughness over Land; Wageningen Universiteit: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Verkaik, J.W. Windmodellering in het KNMI-hydra project—Opties en Knelpunten; Koninklijk Nederlands Meteorologisch Instituut: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wever, N.; Groen, G. Improving Potential Wind for Extreme Wind Statistics; Koninklijk Nederlands Meteorologisch Instituut: De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, A.S.; Palma, J.M.L.M.; Piomelli, U. On the Determination of Effective Aerodynamic Roughness of Surfaces with Vegetation Patches. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2015, 156, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente-Plazas, R.; Montávez, J.P.; Jimenez, P.A.; Jerez, S.; Gómez-Navarro, J.J.; García-Valero, J.A.; Jimenez-Guerrero, P. Characterization of surface winds over the Iberian Peninsula. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 35, 1007–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, P.; Bosveld, F.C.; Burgers, G. The impact of atmospheric stability on the near-surface wind over sea in storm conditions. Wind Energy 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreibich, H.; Bubeck, P.; Kunz, M.; Mahlke, H.; Parolai, S.; Khazai, B.; Daniell, J.; Lakes, T.; Schröter, K. A review of multiple natural hazards and risks in Germany. Nat. Hazards 2014, 74, 2279–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieringa, J. An objective exposure correction method for average wind speeds measured at a sheltered location. Quart. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1976, 102, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manwell, J.F.; McGowan, J.G.; Rogers, A.L. Wind Energy Explained: Theory, Design and Application; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa, J. Representative roughness parameters for homogeneous terrain. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1993, 63, 323–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukhov, A. Turbulence in an atmosphere with a non-uniform temperature. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1971, 2, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Businger, J.; Yaglom, A. Introduction to Obukhov’s paper on ‘turbulence in an atmosphere with a non-uniform temperature’. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1971, 2, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennekes, H. The logarithmic wind profile. J. Atmos. Sci. 1973, 30, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högström, U. Von Karman’s constant in atmospheric boundary layer flow: Reevaluated. J. Atmos. Sci. 1985, 42, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzen, P.; Vogel, C.A. A further note “on the magnitude and apparent range of variation of the von karman constant”. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1995, 75, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garratt, J.R.; Hess, G.D.; Physick, W.L.; Bougeault, P. The atmospheric boundary layer—Advances in knowledge and application. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1996, 78, 9–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tieleman, H.W. Strong wind observations in the atmospheric surface layer. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 41–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S. Suggested revisions to certain boundary layer parameterization schemes used in atmospheric circulation models. Mon. Weather Rev. 1977, 105, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.F.; Klein, P.M. The impacts of atmospheric stability on the accuracy of wind speed extrapolation methods. Resources 2014, 3, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, J.D. A Modelling Study of PBL Heights. 2010. Available online: http://www.meteor.iastate.edu/~jdduda/portfolio/605_paper.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2015).
- Apaydin, H.; Sonmez, F.K.; Yildirim, Y.E. Spatial interpolation techniques for climate data in the GAP region in Turkey. Clim. Res. 2004, 28, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellura, M.; Cirrincione, G.; Marvuglia, A.; Miraoui, A. Wind speed spatial estimation for energy planning in Sicily: Introduction and statistical analysis. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinta, S. A Comparison of Spatial Interpolation Methods in Wind Speed Estimation across Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh. J. Earth Sci. Res. 2014, 2, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Taylor, M.; Parker, S. A comparison of spatial interpolation methods to estimate continuous wind speed surfaces using irregularly distributed data from England and Wales. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, S.U.; Uddin Qazi, M.; Siddiqui, I.; Shah, N.H.S. Comparing Geostatistical and Non-geostatistical Techniques for the Estimation of Wind Potential in Un-sampled Area of Sindh, Pakistan. Eur. Acad. Res. 2013, I, 1770–1792. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y. Spatial Variation and Interpolation of Wind Speed Statistics and Its Implication in Design Wind Load. Postdoctoral Thesis, The University of Western Ontario, London, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dobesch, H.; Dumolard, P.; Dyras, I. Spatial Interpolation for Climate Data: The Use of GIS in Climatology and Meteorology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen, J. Cross-validation in statistical climate forecast models. J. Clim. Appl. Meteorol. 1987, 26, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keckler, D. The Surfer Manual; Golden Software, Inc.: Golden, CO, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; DePinto, J.V. A GIS-based Data Quer y System. In Proceedings of the International Association for Great Lakes Research (IAGLR) Conference, Windsor, ON, Canada, 10–14 January 1995.
- Johnston, K.; ver Hoef, J.M.; Krivoruchko, K.; Lucas, N. Using ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst; ESRI: Redlands, CA, USA, 2001; p. 300. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.M.; Mahdi, A.S.; Shaban, A.H. Wind Speed Estimation for Iraq using several Spatial Interpolation Methods. Br. J. Sci. 2012, 7, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, C.-Y.; de Mesnard, L. Types of Interpolation Methods. Available online: http://www.gisresources.com/types-interpolation-methods_3/ (accessed on 3 July 2015).
- Shi, G. Chapter 8—Kriging Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery for Geoscientists; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 238–274. [Google Scholar]
- Eberly, S.; Swall, J.; Holland, D.; Cox, B.; Baldridge, E. Developing Spatially Interpolated Surfaces and Estimating Uncertainty; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Alodat, M.T.; Anagreh, Y.N. Durations distribution of Rayleigh process with application to wind turbines. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2011, 99, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaofe, Z.O.; Folly, K.A. Statistical Analysis of Wind Resources at Darling for Energy Production. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2012, 2, 250–261. [Google Scholar]
- Olaofe, Z.O.; Folly, K.A. Wind energy analysis based on turbine and developed site power curves: A case-study of Darling city. Renew. Energy 2013, 53, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmmad, M.R. Statistical Analysis of the Wind Resources at the Importance for Energy Production in Bangladesh. Int. J. U- & E-Service Sci. Technol. 2014, 7, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- IEC. International Standard IEC 61400-12-1. Available online: ftp://ftp.ee.polyu.edu.hk/wclo/Ext/OAP/IEC61400part12_1_WindMeasurement.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2015).
- AWEA Small Wind Turbine Performance and Safety Standard; American Wind Energy Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Van Ackere, S.; van Wyngene, K. Windkracht 13. Available online: http://www.windkracht13.be/ (accessed on 3 July 2015).
- Van Eetvelde, G.; van Zwam, B.; Maes, T.; Vollaard, P.; De Vries, I.; Tavernier, P.; D’Hooge, E.; Geenens, D.; Verdonck, L.; Leynse, L. Praktijkboek duurzaam bedrijventerreinmanagement; POM West-Vlaanderen: Sint-Andries, Belgium, 2008; p. 117. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Ackere, S.; Van Eetvelde, G.; Schillebeeckx, D.; Papa, E.; Van Wyngene, K.; Vandevelde, L. Wind Resource Mapping Using Landscape Roughness and Spatial Interpolation Methods. Energies 2015, 8, 8682-8703. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8088682
Van Ackere S, Van Eetvelde G, Schillebeeckx D, Papa E, Van Wyngene K, Vandevelde L. Wind Resource Mapping Using Landscape Roughness and Spatial Interpolation Methods. Energies. 2015; 8(8):8682-8703. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8088682
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Ackere, Samuel, Greet Van Eetvelde, David Schillebeeckx, Enrica Papa, Karel Van Wyngene, and Lieven Vandevelde. 2015. "Wind Resource Mapping Using Landscape Roughness and Spatial Interpolation Methods" Energies 8, no. 8: 8682-8703. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8088682
APA StyleVan Ackere, S., Van Eetvelde, G., Schillebeeckx, D., Papa, E., Van Wyngene, K., & Vandevelde, L. (2015). Wind Resource Mapping Using Landscape Roughness and Spatial Interpolation Methods. Energies, 8(8), 8682-8703. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8088682