Energy-Saving Lipid Extraction from Wet Euglena gracilis by the Low-Boiling-Point Solvent Dimethyl Ether
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
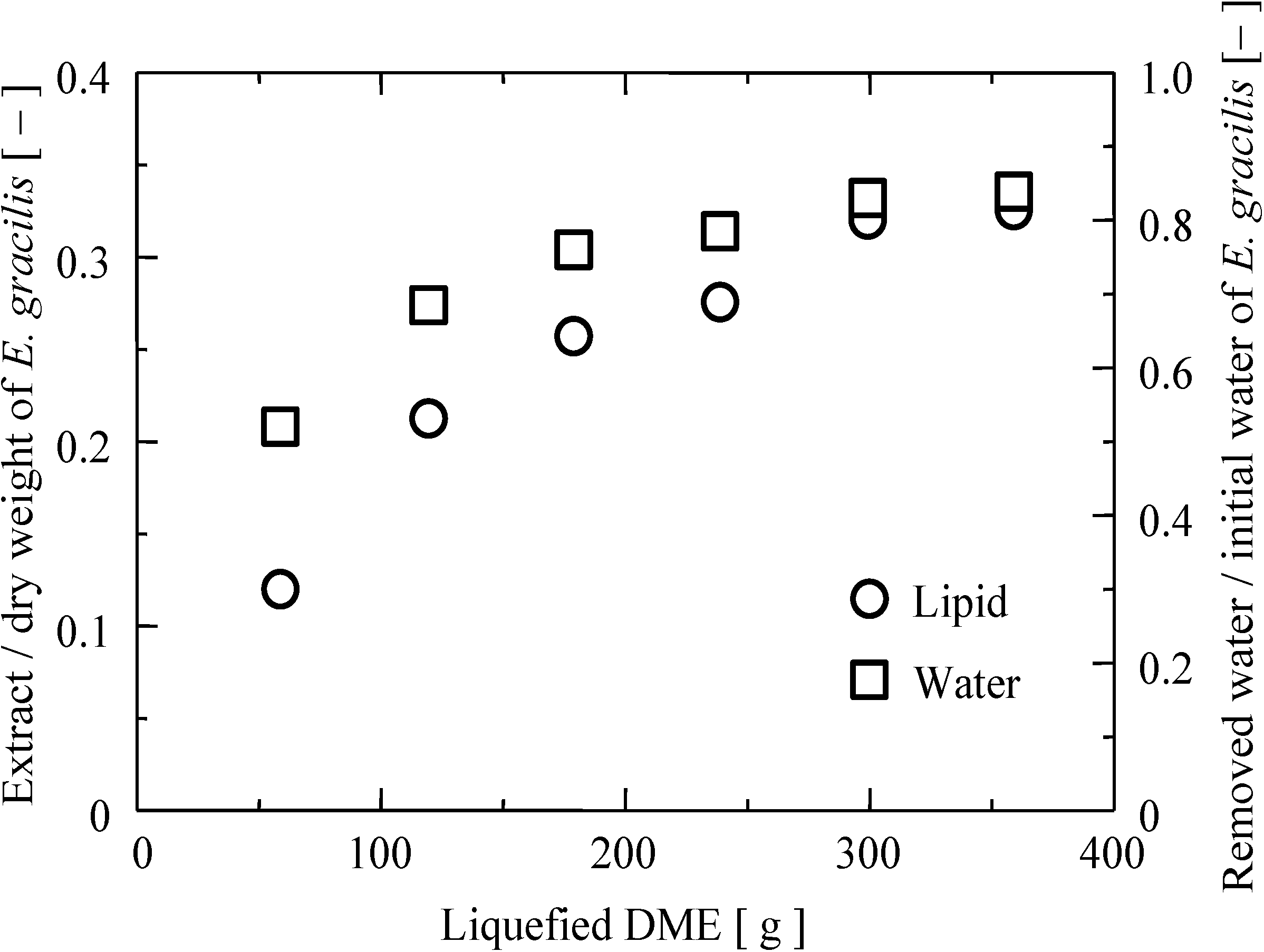
2.1. Extraction Yield, Elemental Analysis, and Higher Heating Value of the Extract
| Analysis | E. gracilis | Liquefied DME | Hexane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residue | Lipid | Residue | Lipid | ||
| Proximate analysis (wt.% dry basis) | |||||
| Ash yield | 6.2 | 8.2 | 1.2 | 8.1 | 1.4 |
| Volatile matter | 83.2 | 75.2 | ‐ | 76.2 | ‐ |
| Fixed carbon | 10.6 | 16.6 | ‐ | 15.7 | ‐ |
| Higher heating value (MJ/kg) | 34.5 | 29.3 | 40.8 | 29.5 | 40.7 |
| Main elements (wt.% dry basis) | |||||
| C | 55.5 | 45.2 | 76.5 | 46.9 | 76.3 |
| H | 8.7 | 6.4 | 12.4 | 6.6 | 12.3 |
| N | 6.8 | 9.8 | 2.4 | 9.5 | 2.2 |
| O * | 21.9 | 29.2 | 7.4 | 27.7 | 7.7 |
| S | 0.87 | 1.23 | 0.02 | 1.21 | 0.01 |
| (Non-combustible S) | <0.01 | <0.01 | ‐ | <0.01 | ‐ |
| Minor elements (ppm) | |||||
| Na | ‐ | ‐ | 320 | ‐ | 30 |
| K | ‐ | ‐ | 4500 | ‐ | 680 |
| Mg | ‐ | ‐ | 1900 | ‐ | 250 |
| Ca | ‐ | ‐ | 150 | ‐ | 170 |
| Al | 3 | <1 | |||
| Zn | ‐ | ‐ | 34 | ‐ | 10 |
| Fe | ‐ | ‐ | 38 | ‐ | 43 |
| P | ‐ | ‐ | 6000 | ‐ | 1400 |
2.2. Molecular Weight Distribution
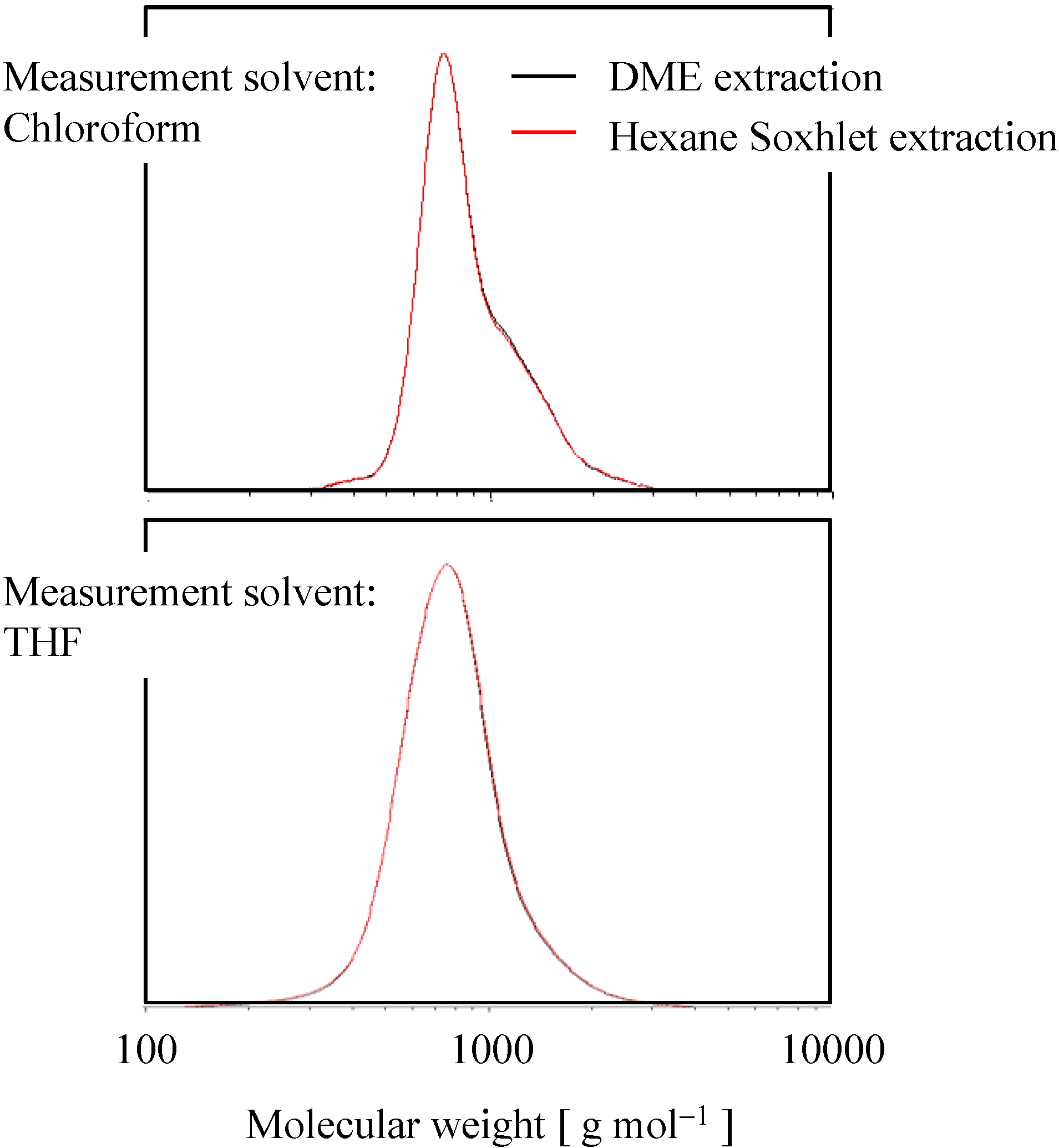
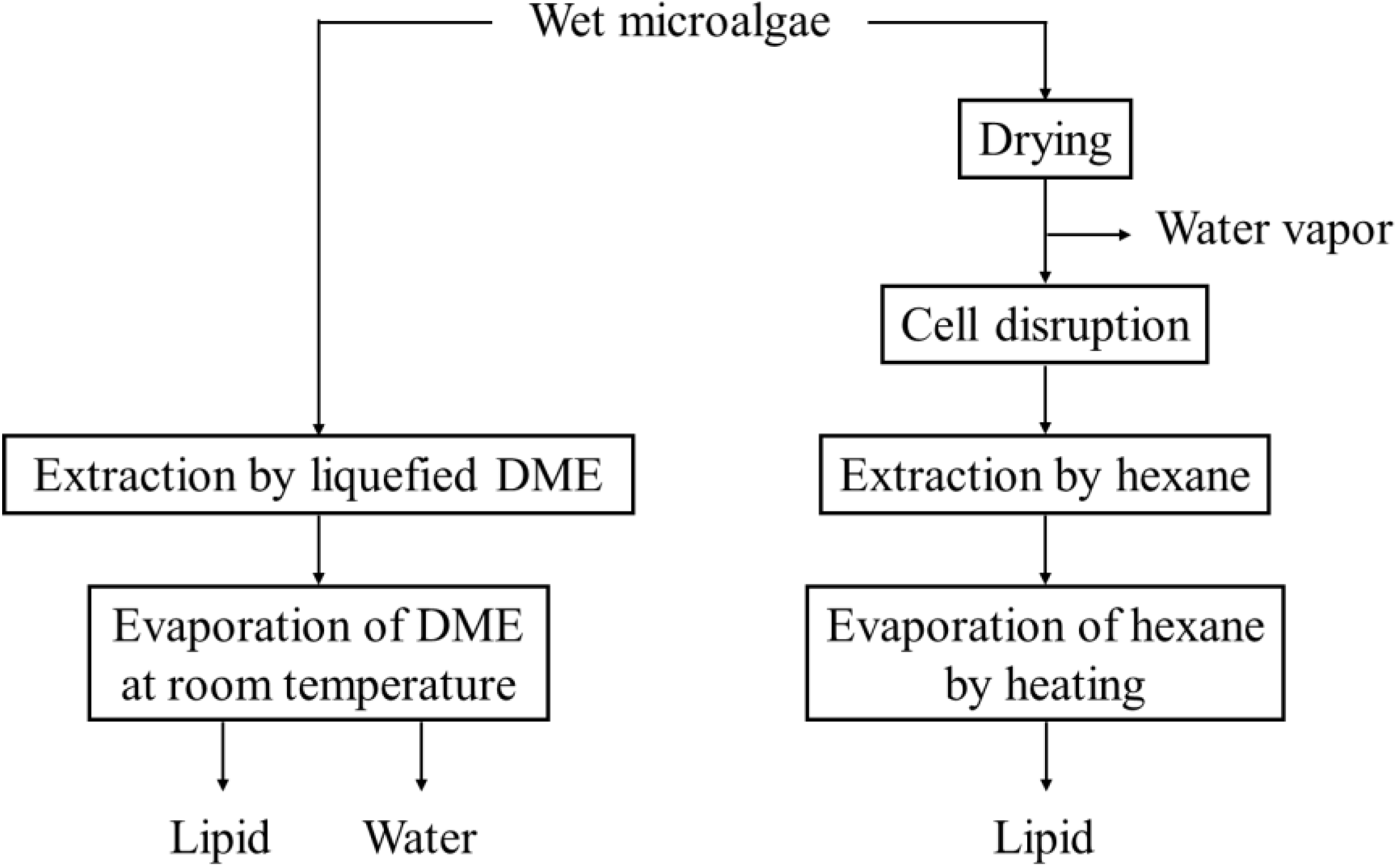
2.3. Procedure Comparison of Proposed and Conventional Methods

3. Experimental Section
3.1. DME and Hexane Soxhlet Extraction

3.2. Compositional Analyses
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chisti, Y. Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, K.; Murthy, G.S. Life cycle analysis of algae biodiesel. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2010, 15, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, K.L. Environmental implications of power generation via coal-microalgae cofiring. Energy 2002, 27, 905–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, A.L.; Kazamia, E.; Dennis, J.S.; Howe, C.J.; Scott, S.A.; Smith, A.G. Life-cycle assessment of potential algal biodiesel production in the United Kingdom: A comparison of raceways and air-lift tubular bioreactors. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 4062–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, R.; Rupasinghe, T.; Tull, D.L.; Webley, P.A. Mechanical cell disruption for lipid extraction from microalgal biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reijnders, L. Do biofuels from microalgae beat biofuels from terrestrial plants? Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lardon, L.; Hélias, A.; Sialve, B.; Steyer, J.-P.; Bernard, O. Life-cycle assessment of biodiesel production from microalgae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6475–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrich, G.; Zinnai, A.; Nesti, U.; Venturi, F.; Fiorentini, R. Supercritical fluid extraction of oil from microalga Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis. Acta Alimentaria 2006, 35, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahena, F.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Jinap, S.; Karim, A.A.; Abbas, K.A.; Norulaini, N.A.N.; Omar, A.K.M. Application of supercritical CO2 in lipid extraction—A review. J. Food Eng. 2009, 95, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Goto, M.; Hirose, T. Fractional extraction with supercritical carbon dioxide for the removal of terpenes from citrus oil. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1995, 34, 3941–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Lenucci, M.S.; D’Amico, L.; Piro, G.; Mita, G. Effect of drying and co-matrix addition on the yield and quality of supercritical CO2 extracted pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch.) oil. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machmudah, S.; Kawahito, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Goto, M. Supercritical CO2 extraction of rosehip seed oil: Fatty acids composition and process optimization. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2007, 41, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, J.O.; Perrut, M.; Majewski, W. Extraction of astaxantine and phycocyanine from microalgae with supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2003, 48, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, H.; Li, P. Simple extraction method of green crude from natural blue-green microalgae by dimethyl ether. Fuel 2011, 90, 1264–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, H.; Kanda, H.; Morita, M.; Kinura, T.; Yoshikoshi, A. Yuukibutsu no tyuusyutsu houhou, yuukibutsu no seizou houhou, yuukibutsu tyuusyutsu souchi kumitatetai, sitsujyunzairyou no syorihouhou. JP 5328547, 31 July 2009. (In Japanese)[Google Scholar]
- Catchpole, O.J.; Grey, J.B.; Mackenzie, A.D.; Tallon, S.J. Energy efficient method and apparatus for the extraction of biomolecules from dilute aqueous solution. WO 2014039638, 5 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fast, G.; Kuhn, D.; Class, A.G.; Maas, U. Auto-ignition during in stationary jet evolution of dimethyl ether (DME) in a high-pressure atmosphere. Combust. Flame 2009, 156, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.C.; Seo, S.B.; Chung, J.H.; Joo, Y.J.; Ahn, D.H. Industrial gas turbine combustion performance test of DME to use as an alternative fuel for power generation. Fuel 2009, 88, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.; Song, T.; Mitsos, A.; McKinnon, J.T.; Ko, G.H.; Tolsma, J.E.; Denholm, D.; Park, T. Optimal design and operation of a natural gas tri-reforming reactor for DME synthesis. Catal. Today 2009, 139, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lemmon, E.W. An equation of state for the thermodynamic properties of dimethyl ether. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2011, 40, 023104:1–023104:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holldorff, H.; Knapp, H. Binary vapor-liquid-liquid equilibrium of dimethyl ether-water and mutual solubilities of methyl chloride and water—Experimental results and data reduction. Fluid Phase Equilib. 1988, 44, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific opinion of the panel on food contact materials, enzymes, flavourings and processing aids (CEF) on dimethyl ether as an extraction solvent. EFSA J. 2009, 984, 1–13.
- Varlet, V.; Smith, F.; Augsburger, M. New trends in the kitchen: Propellants assessment of edible food aerosol sprays used on food. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, M.; Radcliffe, C.; Wada, Y.; Hoshino, T.; Liu, X.; Arai, M.; Tamura, M. A comparative study on the autoxidation of dimethyl ether (DME) comparison with diethyl ether (DEE) and diisopropyl ether (DIPE). J. Loss Prevent. Proc. 2005, 18, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeyama, H.; Kanamaru, A.; Yoshino, Y.; Kakuta, H.; Kawamura, Y.; Matsunaga, T. Production of antioxidant vitamins, β-carotene, vitamin C, and vitamin E, by two-step culture of Euglena gracilis Z. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1997, 53, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Zavala, J.S.; Ortiz-Cruz, M.A.; Mendoza-Hernández, G.; Moreno-Sánchez, R. Increased synthesis of α-tocopherol, paramylon and tyrosine by Euglena gracilis under conditions of high biomass production. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 2160–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications—A review. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, A. A comparison of lipid patterns in photosynthesizing and nonphotosynthesizing cells of Euglena Gracilis. Biochemistry 1963, 2, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Mercer, P.; Armenta, R.E. Developments in oil extraction from microalgae. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2011, 113, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, H.; Makino, H. Energy-efficient coal dewatering using liquefied dimethyl ether. Fuel 2010, 89, 2104–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kanda, H.; Li, P.; Goto, M.; Makino, H. Energy-Saving Lipid Extraction from Wet Euglena gracilis by the Low-Boiling-Point Solvent Dimethyl Ether. Energies 2015, 8, 610-620. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8010610
Kanda H, Li P, Goto M, Makino H. Energy-Saving Lipid Extraction from Wet Euglena gracilis by the Low-Boiling-Point Solvent Dimethyl Ether. Energies. 2015; 8(1):610-620. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8010610
Chicago/Turabian StyleKanda, Hideki, Peng Li, Motonobu Goto, and Hisao Makino. 2015. "Energy-Saving Lipid Extraction from Wet Euglena gracilis by the Low-Boiling-Point Solvent Dimethyl Ether" Energies 8, no. 1: 610-620. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8010610
APA StyleKanda, H., Li, P., Goto, M., & Makino, H. (2015). Energy-Saving Lipid Extraction from Wet Euglena gracilis by the Low-Boiling-Point Solvent Dimethyl Ether. Energies, 8(1), 610-620. https://doi.org/10.3390/en8010610






