Production of Bioethanol from Carrot Pomace Using the Thermotolerant Yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Composition of the Hydrolysate from Carrot Pomace
2.2. SSF of Carrot Pomace Using Different Fermentation Strategies
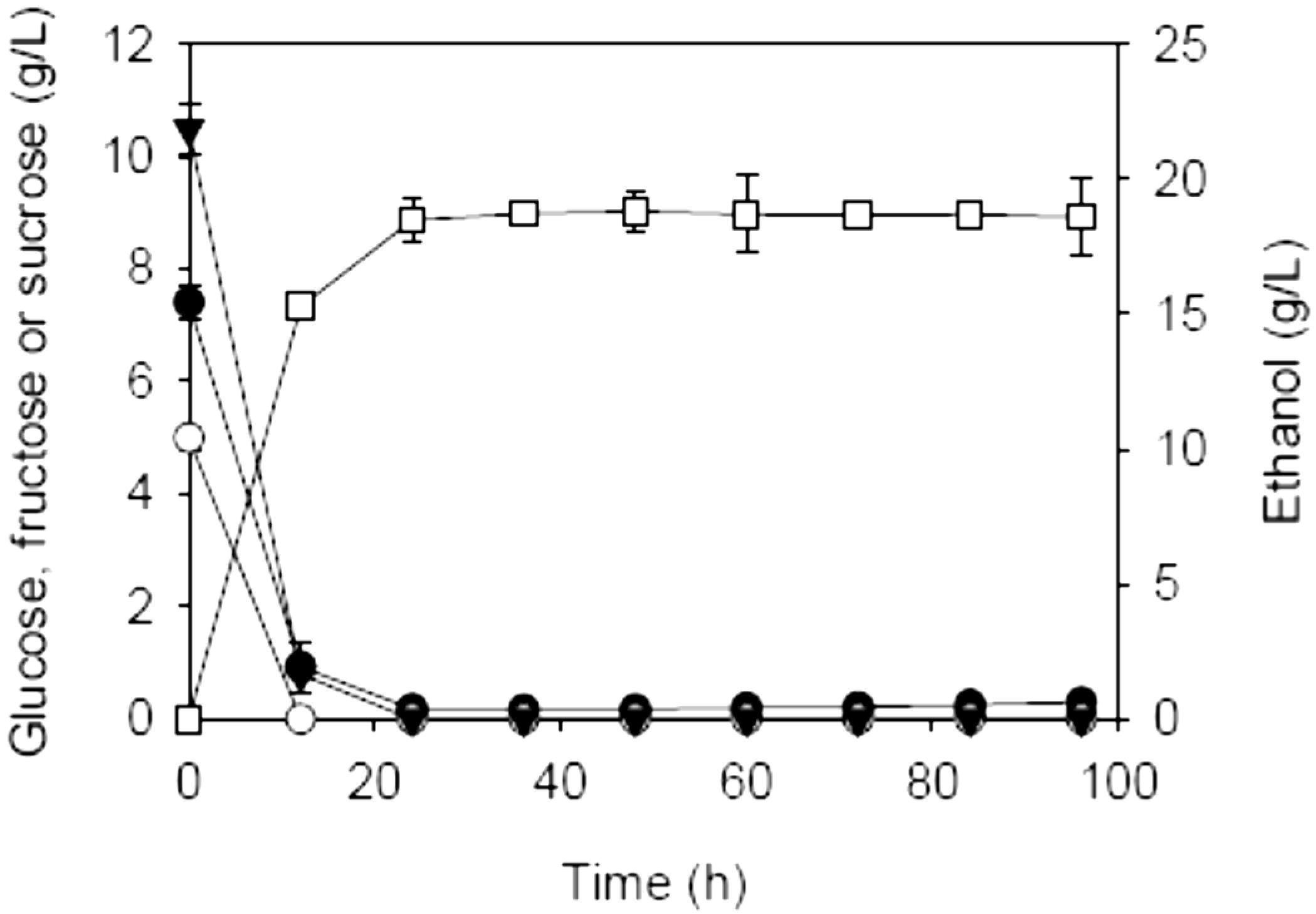
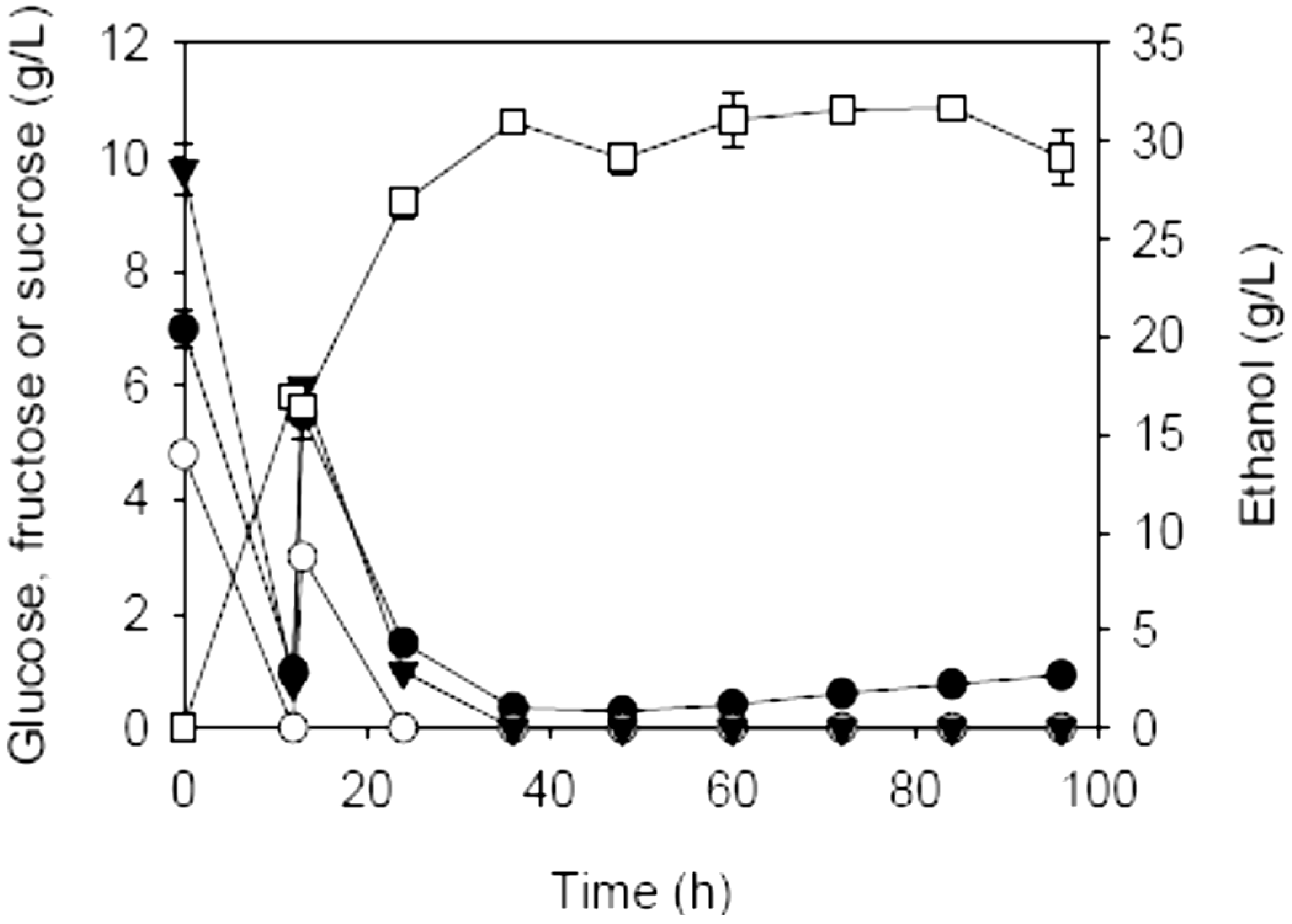
| Initial charge of carrot pomace (%, w/v) | Addition (%, w/v) | Prehydrolysis dosages of AccelleraseTM 1000 (FPU/g dry matter) & pectinase (U/g dry matter) | Max. EtOH (g/L) | Theoretical max. EtOH (g/L) a | YE/S (g/g) b | QE (g/L·h)c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t = 12 h | t = 18 h | ||||||
| 10 | - | 18 | 21.2 | 0.18 | 0.75 (24 h) | ||
| 10 | 5 | - | 30 | 32.2 | 0.2 | 0.83 (36 h) | |
| 10 | 5 | 5 | - | 32 | 42.8 | 0.16 | 0.89 (36 h) |
| 10 | 10 | - | 37 | 42.8 | 0.185 | 0.88 (42 h) | |
| 10 | 15 & 52.3 | 18 | 21.4 | 0.18 | 0.75 (24 h) | ||
| 10 | 10 | 7.5 & 26.2 | 30 | 42.8 | 0.15 | 0.83 (36 h) | |
| 20 | 15 & 52.3 | 15 | 42.8 | 0.075 | 0.21 (72 h) | ||
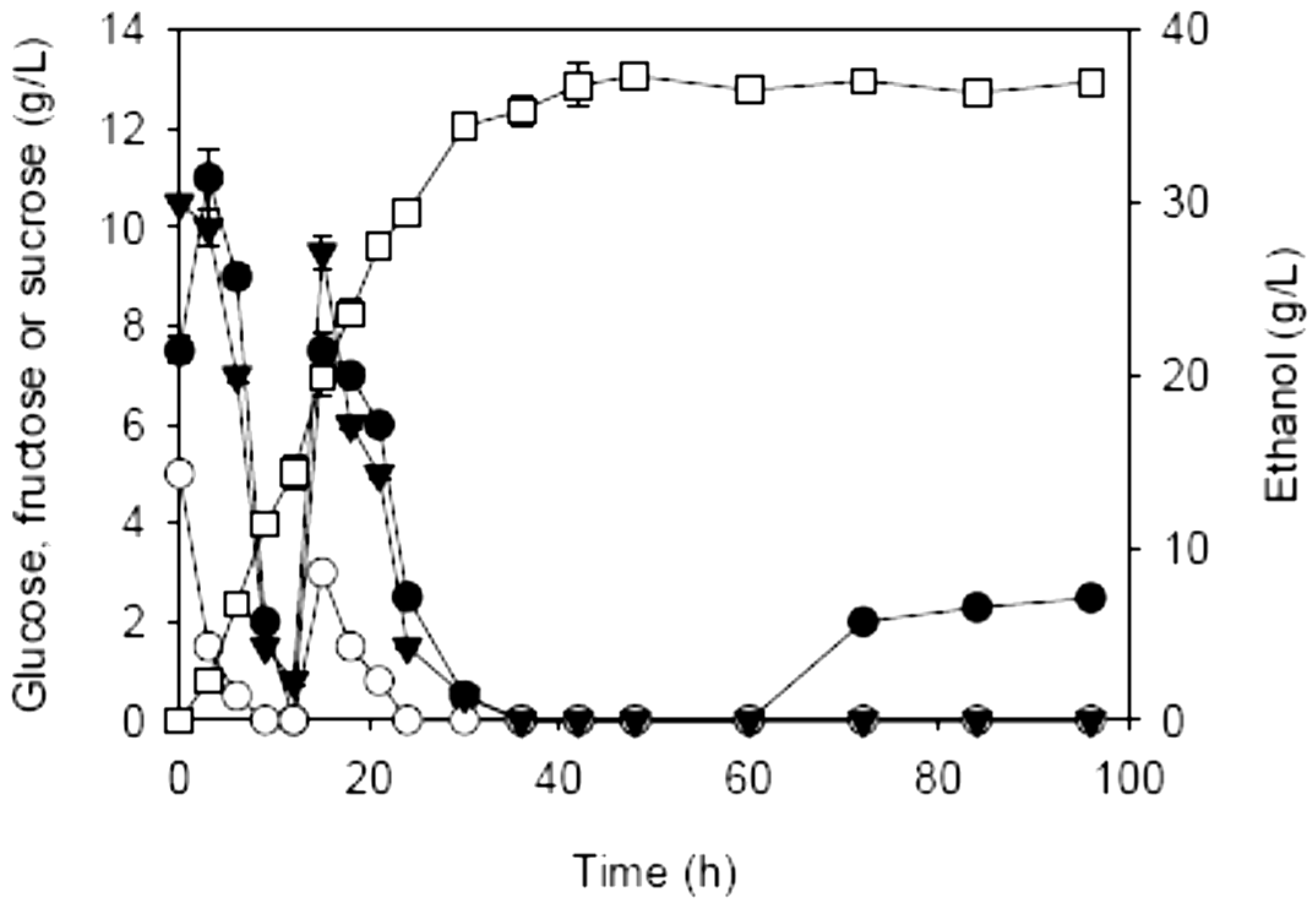
2.3. Effects of Enzymatic Prehydrolysis
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Preparation of Carrot Pomace
3.2. Hydrolysis of Carrot Pomace
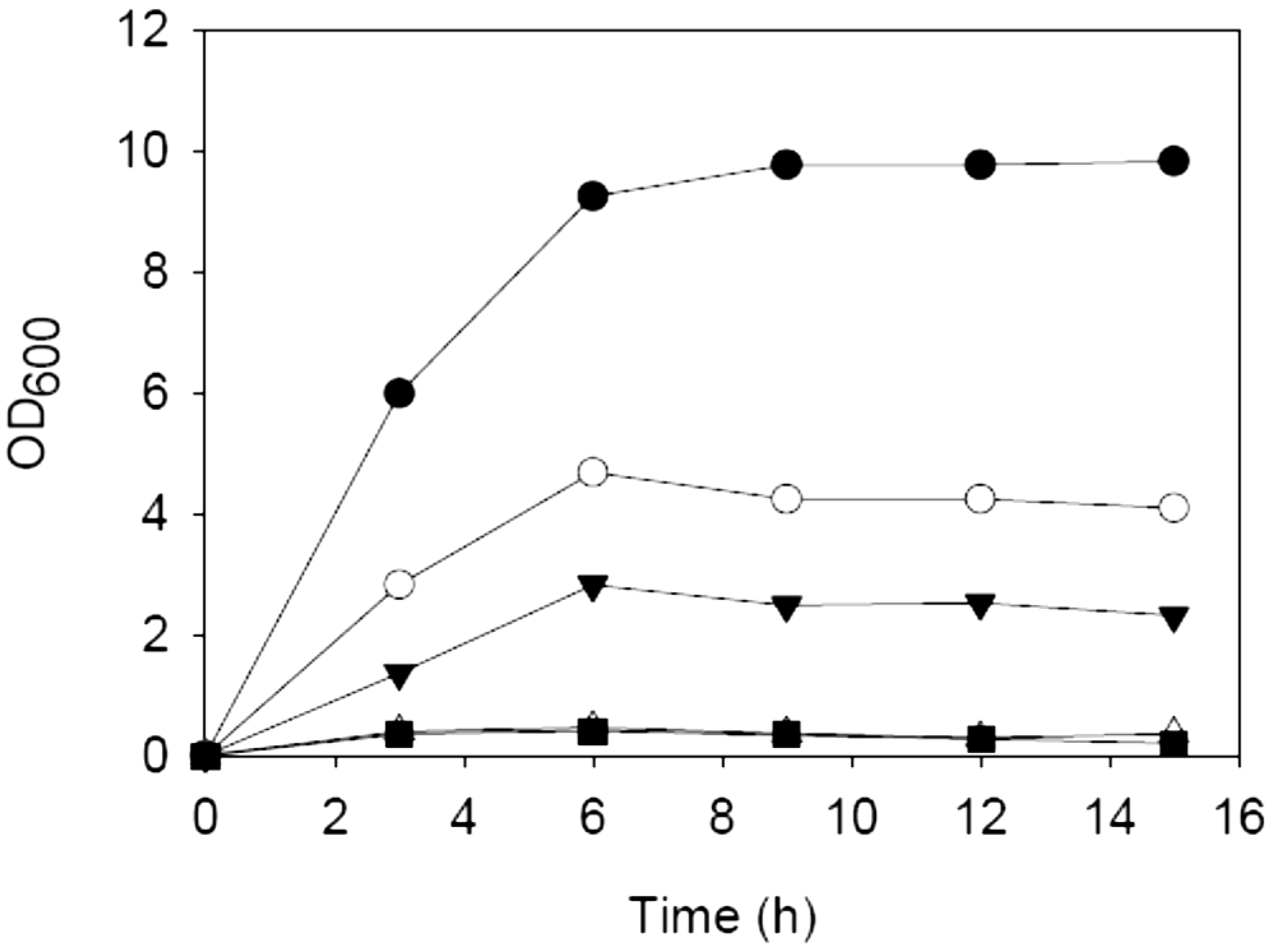
3.3. Microorganism and Growth Conditions
3.4. SSF of Carrot Pomace
3.5. Analytical Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Margeot, A.; Hahn-Hagerdal, B.; Edlund, M.; Slade, R.; Monot, F. New improvements for lignocellulosic ethanol. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2009, 20, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balat, M. Production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials via the biochemical pathway: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 858–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.Y.; Cha, M.; Shin, S.R.; Kim, K.S. Enzymatic production of a soluble-fibre hydrolyzate from carrot pomace and its sugar composition. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawirska, A.; Kwaśniewska, M. Dietary fibre fractions from fruit and vegetable processing waste. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patle, S.; Lal, B. Ethanol production from hydrolysed agricultural wastes using mixed culture of Zymomonas mobilis and Candida tropicalis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 29, 1839–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfani, F.; Gallifuoco, A.; Saporosi, A.; Spera, A.; Cantarella, M. Comparison of SHF and SSF processes for the bioconversion of steam-exploded wheat straw. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 25, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás-Pejó, E.; García-Aparicio, M.; Negro, M.J.; Oliva, J.M.; Ballesteros, M. Effect of different cellulase dosages on cell viability and ethanol production by Kluyveromyces marxianus in SSF processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sá-Correia, I.; Uden, N. Effects of ethanol on thermal death and on the maximum temperature for growth of the yeast Kluyveromyces fragilis. Biotechnol. Lett. 1982, 4, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, C.; Nakagawa, A.; Koyanagi, T.; Tanaka, K.; Minami, H.; Tamaki, H.; Katayama, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kumagai, H. Kluyveromyces marxianus-based platform for direct ethanol fermentation and recovery from cellulosic materials under air-ventilated conditions. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 113, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Xia, L. Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of alkaline-pretreated corn stover to ethanol using a recombinant yeast strain. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayani, R.S.; Saxena, S.; Gupta, R. Microbial pectinolytic enzymes: A review. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2931–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Lau, M.; Balan, V.; Dale, B.; Yuan, Y.-J. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis and ethanol fermentation from AFEX-treated rice straw. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.-Y.; Jiang, B.-H.; Duan, K.-J. Production of Bioethanol from Carrot Pomace Using the Thermotolerant Yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Energies 2013, 6, 1794-1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6031794
Yu C-Y, Jiang B-H, Duan K-J. Production of Bioethanol from Carrot Pomace Using the Thermotolerant Yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Energies. 2013; 6(3):1794-1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6031794
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Chi-Yang, Bo-Hong Jiang, and Kow-Jen Duan. 2013. "Production of Bioethanol from Carrot Pomace Using the Thermotolerant Yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus" Energies 6, no. 3: 1794-1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6031794
APA StyleYu, C.-Y., Jiang, B.-H., & Duan, K.-J. (2013). Production of Bioethanol from Carrot Pomace Using the Thermotolerant Yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Energies, 6(3), 1794-1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6031794




