Abstract
A numerical investigation of the double-effect adsorption refrigeration cycle is examined in this manuscript. The proposed cycle is based on the cascading adsorption cycle, where condensation heat that is produced in the top cycle is utilized as the driving heat source for the bottom cycle. The results show that the double-effect cycle produces a higher coefficient of performance (COP) as compared to that of the conventional single-stage cycle for driving temperatures between 100 °C and 150 °C in which the average cycle chilled water temperature is fixed at 9 °C. Moreover, the COP of the double-effect cycle is more than twice that of the single-stage cycle when the temperature reaches 130 °C. It is also observed that the adsorbent mass ratio of the high temperature cycle (HTC) to the low temperature cycle (LTC) affects the performance of the double-effect adsorption refrigeration cycle.
1. Introduction
In recent years, growing awareness of fossil fuel depletion has prompted a rapid increase in energy preservation efforts. National and international governmental energy policies will strongly affect the success of these efforts. The World Energy Outlook 2009 by the IEA reported that if current energy utilization is continued without any changes to existing policies, then dependence on fossil fuels will increase rapidly, resulting in energy scarcities. This will also raise issues regarding energy-generated CO2 emissions. To address these problems, current energy policies should be reconsidered in light of renewable energy, advanced, energy-saving technology, and clean energy sectors.
In the refrigeration field (which is a large contributor to environmental degradation), research focuses on developing more environmentally friendly, new systems that have high primary energy efficiencies and are able to utilize various forms of energy. The adsorption refrigeration system has attracted much interest because it can be driven by various types of thermal energy, such as waste heat that is generated by power plants and other industries. Unlike conventional equipment that uses hydrochlorofluorocarbons and chlorofluorocarbons, the adsorption refrigeration system employs safe and non-polluting refrigerants that do not negatively affect the environment. Furthermore, in comparison with the absorption system that is most often used in heat-driven refrigeration systems, the adsorption system has the advantages of having the capability to be powered by heat sources with wide temperature ranges and of lacking corrosion and crystallization problems.
Despite the advantages described above, it is known that the coefficient of performance (COP) of the adsorption system is low compared with that of other conventional equipment. There are several extensive investigations aimed at improving system performance; these investigations consider intensifying heat and mass transfer within the heat exchangers, improving adsorbent performance, employing various adsorbent/refrigerant combinations, and proposing advanced adsorption cycles.
Lambert [1] designed a new adsorber configuration for solar-powered adsorption heat pumps that possessed a magnified contact area between the heat exchangers and granular or powdered adsorbents. The COP for cooling was predicted to be approximately 1.6. Aristov et al. [2] studied the adsorbent performance. They reported that composite bases of various host micro- and mesoporous silica gel matrices were able to absorb water when they were impregnated with calcium chloride (CaCl2) and lithium bromide (LiBr) salts. For the same reason, various other adsorbent/refrigerant combinations have been investigated for their adsorption capabilities. The performance of silica gel/water [3,4,5], activated carbon/methanol [6,7,8], and zeolite/water [10,11] has been analyzed. However, silica gel/water is already widely used as an adsorbent/refrigerant combination in adsorption systems because silica gel can be regenerated at a relatively low temperature compared to that of other adsorbents, and it also has a high latent heat of evaporation. For example, Saha et al. [12,13] proposed and experimentally examined a three-stage adsorption chiller with the silica gel/water combination to utilize a low-temperature waste heat source between 40 and 60 °C. In a similar manner, Chua et al. [14,15] performed analytical studies on a two-bed silica gel/water adsorption chiller using a lumped parameter model.
Moreover, in order to improve system performance, many researchers have proposed various advanced adsorption cycles. Shelton et al. [16] proposed a thermal wave cycle for an adsorption heat pump using a zeolite/ammonia combination. Wang [17] studied the performance of vapor recovery cycles using activated carbon/methanol as the adsorbent/refrigerant pair and indicated that the mass recovery cycle is effective for low regenerative temperatures. Ng et al. [18] reported that when both heat and mass recovery cycles are employed at a rating point of maximum cooling capacity, the system COP could increase further to as much as 48%.
The high performance of advanced adsorption cycles is also presented by Douss and Meunier [19]. They proposed a cascading adsorption cycle that employed two different working pairs of zeolite/water and active carbon/methanol, three adsorbers, two condensers and two evaporators. Zeolite/water beds on the top cycle provide adsorption heat to active carbon/methanol beds on the bottom cycle, serving as the driving heat source when the desorption process occurs.
Liu and Leong [20] improved the new cascading adsorption cycle based on the proposed cycle of Douss. This new cycle is simpler because it uses only one type of refrigerant (water) and requires only one condenser and one evaporator. However, because zeolite was used as the adsorbent, the cascading cycles of Douss and Liu used high temperature sources (near 170 °C or higher) to generate the adsorbent. Because one of the advantages of the adsorption chiller is that it can be used at lower temperature as compared to that of the absorption chiller, this cascading cycle does not adequately utilize the chiller. Another improvement to the cascading cycle was developed by Uyun et al. [21]. The cycle combines the internal heat recovery and mass recovery cycles and uses only silica gel/water as a working pair. The results showed that the proposed cycle with mass recovery produced a COP as high as that produced by the conventional cascading cycle, even though it used a low temperature driving heat source.
The present study is also based on a cascading adsorption cycle that utilizes condensation heat produced in the top cycle and is called the double-effect adsorption cycle. The waste heat of a middle temperature range (90–150 °C) is used as a driving heat source. For simplification, the cycle uses only silica gel/water as the working pair for both the high temperature and low temperature stages and consists of six heat exchangers. In our previous study, the performance was investigated by using static analysis, which confirmed improvement in the COP [22]. However, it is important to evaluate the performance of the proposed cycle by using dynamic models that simulate the actual operation of the cycle. This manuscript presents the performance of the proposed cycle as determined from dynamic simulations, and the results are compared with conventional single-stage results to which the chilled outlet temperature is equivalent.
2. Working Principle
The conceptual Duhring diagram for the cycle is shown in Figure 1. The cycle is divided into two stages: a high temperature cycle (HTC) as the top cycle and a low temperature cycle (LTC) as the bottom cycle. The working principle of the bottom cycle is the same as that of the conventional single-stage cycle; the only difference is the heat source. In a single-stage cycle, the cycle is driven by external heat; however, in a double-effect cycle, the LTC is driven by condensation heat from the top cycle (the HTC). Because the top cycle operates at high temperatures, the waste heat from the desorption-condensation process can be re-used to generate the LTC. This relationship is the basic principle of the double-effect adsorption refrigeration cycle.
Because the condensation heat from the HTC is directly transferred to the LTC beds and is used to generate the desorption process of the LTC, the condensing pressure of the HTC side is influenced by latent heat on the LTC. As shown in the Duhring diagram, the condensing pressure of the LTC remains equal to that of the condenser pressure; however, the condensing pressure of the HTC is not fixed and is assumed to increase linearly with the LTC bed pressure.
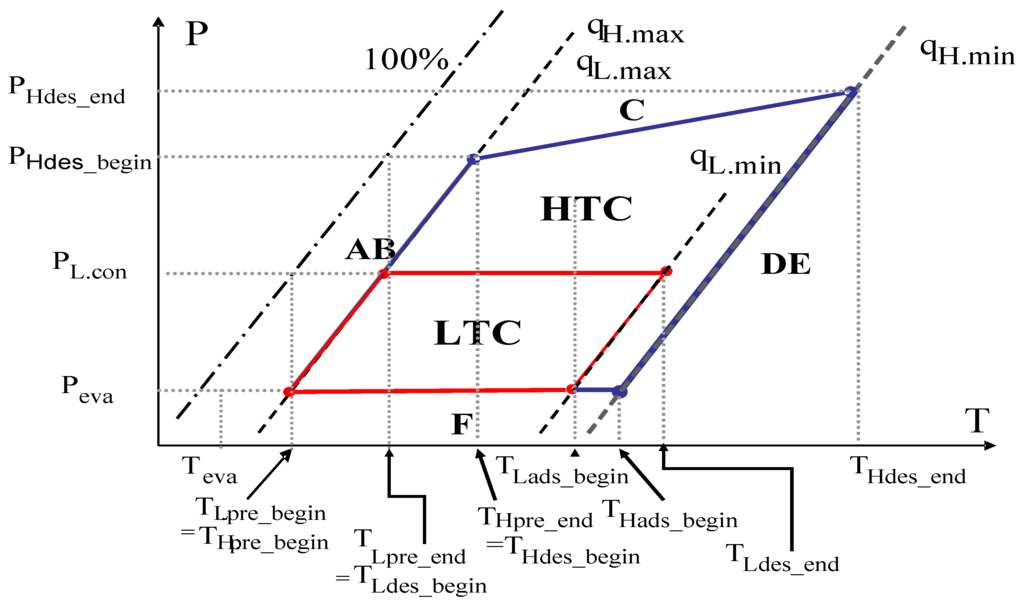
Figure 1.
Conceptual Duhring diagram of the double-effect cycle that utilizes condensation heat.
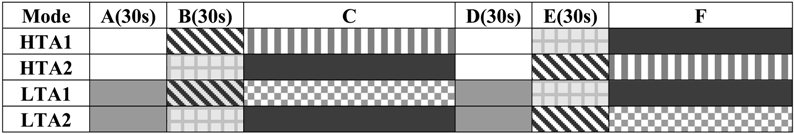
The schematic diagram and time allocation of a four-bed double-effect adsorption chiller are shown in Figure 2 and Table 1, respectively. The chiller consists of six heat exchangers: a condenser, an evaporator, one pair of adsorber/desorber heat exchangers for the HTC, and one combination of adsorber/desorber that establishes the condenser as an annex for the LTC, as shown in Figure 2. Two beds (HTA1 and HTA2) are designed for use in the HTC, while the other two beds (LTA1 and LTA2) are designed for use in the LTC. To complete a full cycle, the chiller requires six modes (A–F), as shown in Table 1.
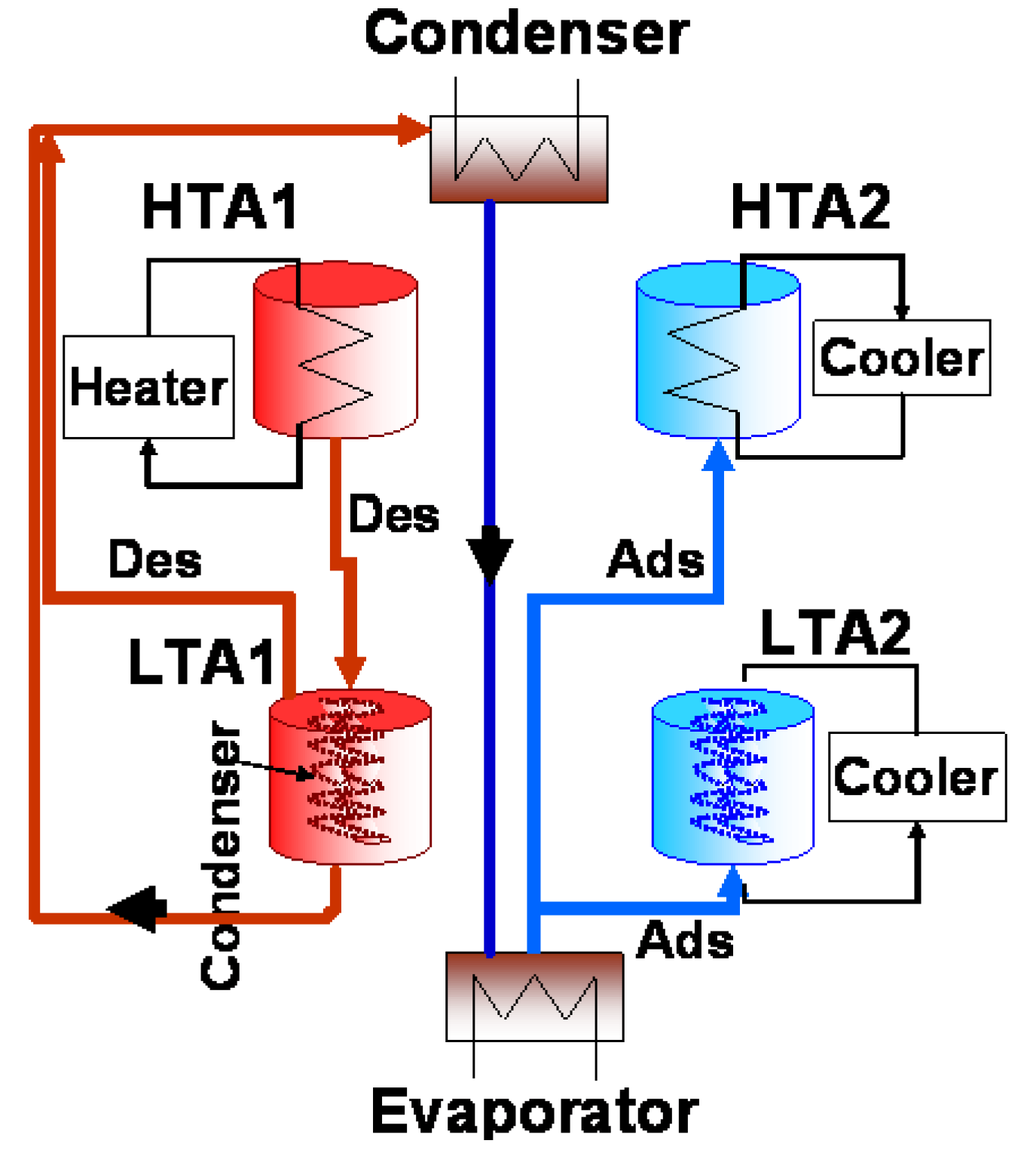
Figure 2.
Schematic of four-bed double-effect adsorption refrigeration cycle (mode C).
In mode A, HTA1 (at the end of the adsorption-evaporation process) and HTA2 (at the end of the desorption-condensation process) are connected to each other. HTA1 is subsequently heated by energy transported from HTA2 via a heat transfer fluid. This is classified as the heat recovery process. Simultaneously, LTA1 and LTA2 are connected to each other, establishing another heat recovery process. Via heat transfer fluid (water), LTA1 is heated by energy transported from LTA2. Once the pressure of both HTA1 and HTA2 becomes nearly equal, the warming process (mode B, pre-heating or pre-cooling) begins. In mode B, HTA1 is heated by hot fluid, and HTA2 is cooled by cooling fluid. Simultaneously, LTA1 is heated by hot water, and LTA2 is cooled by cooling water. In mode C, HTA1 enters the desorption-condensation process while being heated to temperature TH,des by hot fluid. When HTA1 is connected to LTA1, the high pressure water vapor from HTA1 is transferred to LTA1. During this process, LTA1 is heated by the energy from HTA1, and once the pressure of LTA1 becomes nearly equal to that of the condenser, LTA1 is connected to the condenser. The higher temperature water vapor from HTA1 flows through LTA1 to the condenser. Simultaneously, once the pressure of HTA2 and LTA2 reaches that of the evaporator, then HTA2 and LTA2 are connected to the evaporator, and the adsorption-evaporation process begins. The ensuing modes D, E, and F correspond to modes A, B, and C, respectively. Upon completion of mode F, mode A begins anew.

Table 1.
Operational stages of the double-effect cycle.
The baseline parameter values used in the present simulation and standard operating conditions are presented in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively. Because the HTC needs an external heat resource of 100 °C or warmer, heat transfer fluid is used. On the other hand, the LTC uses water as the heat transfer fluid. For simplification, this chiller employed the silica gel/water working pair for both the HTC and the LTC.

Table 2.
Baseline parameters [23].
| Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cs | 924 | Jkg−1K−1 |
| Cpw | 4.18E + 3 | Jkg−1K−1 |
| Cp,cu | 386 | Jkg−1K−1 |
| Cp,al | 905 | Jkg−1K−1 |
| Cpf | 2,090 | Jkg−1K−1 |
| Lw | 2.50E + 6 | Jkg−1 |
| Dso | 2.54E − 4 | m2s−1 |
| Qst | 2.8E + 6 | kJkg−1 |
| WH, WL | 28 | kg |
| Wcond,w | 5 | kg |
| Weva,w | 25 | kg |
| UhexAhex,ads | 2,663 | Wm−2K−1 |
| UhexAhex,des | 2,972 | Wm−2K−1 |
| UcondAcond | 4,061 | Wm−2K−1 |
| UevaAeva | 2,360 | Wm−2K−1 |

Table 3.
Standard operating conditions.
| Temperature [°C] | Flow Rate [kg/s] | |
|---|---|---|
| Hot fluid | 90–150 | 1.0 |
| Cooling fluid | 30 | 1.0 |
| Hot water | 55–95 | 0.4 |
| Cooling water | 30 | 0.74 (= 0.4ads + 0.34cond) |
| Chilled water | 14 | controlled |
| Cycle time | 1200s = (540(ads/des) + 30(ph/pc) + 30(hr))s × 2 (double-effect) 1200s = (570(ads/des) + 30(ph/pc))s × 2 (single-stage) | |
3. Numerical Modeling
3.1. Energy Balance for the Adsorber/Desorber Heat Exchanger
Adsorption and desorption heat balances are described by identical equations in which heat transfer fluid (oil) temperature terms Tf,in and Tf,out denote hot fluid for the desorption process and cooling fluid for the adsorption process, respectively. TH denotes the HTC bed temperature. The equations model is defined by a modified form of Uyun`s model [21]. The heat transfer and energy balance for the HTA adsorbent bed can be described as follows:
where is either 0 or 1, depending on whether the HTC bed is functioning as a desorber or an adsorber. Equation (1) expresses the importance of the heat transfer parameters, namely the heat transfer area and the heat transfer coefficient . The left-hand side of the adsorber/desorber energy balance equation [Equation (2)] provides the amount of sensible heat required to cool or heat the HTC adsorbent (silica gel) and the water (w) content in the bed and in the metallic parts of the heat exchanger during adsorption or desorption. This term accounts for the input/output of sensible heat required by the batched-cycle operation. The first term on the right-hand side of Equation (2) represents the release of adsorption heat or the input of desorption heat, while the second term represents the sensible heat of the adsorbed vapor. The last term on the right-hand side of Equation (2) indicates the total amount of heat that is released to the cooling fluid during the adsorption process or that provided by the hot fluid for desorption.
Next, the energy balance equations for the LTC can be described as follows:
where is either 0 or 1, depending whether the LTC bed is functioning as a desorber or an adsorber. and denote cooling water temperatures at the inlet and outlet during adsorption. denotes the LTC bed temperature. The last term on the right-hand side of Equation (4) represents the heat of the high temperature vapor from the HTC for desorption and the latent heat of vaporization.
3.2. Energy Balance for Condenser
The energy balance equation for the condenser can be expressed as:
where the suffixes “cool” and “cond” indicate cooling water and condenser, respectively. The left-hand side of Equation (6) represents the sensible heat that is required by refrigerant condensate and by metallic parts of the heat exchanger tubes due to the temperature change in the condenser. On the right-hand side, the first, second, and third terms represent the latent heat of vaporization (Lw) for the amount of refrigerant desorbed, the sensible heat required to cool the incoming vapor from the HTC and LTC desorber at temperature Tdes,L to the condenser temperature of Tcond, and the total amount of heat released to the cooling water, respectively.
3.3. Energy Balance for Evaporator
The energy balance equation for the evaporator can be expressed as:
where the suffixes “chill” and “eva” indicate chilled water and evaporator, respectively. The left-hand side of Equation (8) represents the sensible heat required by the liquid refrigerant (w) and the metal of the heat exchanger tubes in the evaporator. On the right-hand side, the first term gives the latent heat of evaporation (Lw) for the amount of refrigerant adsorbed, the second term represents the sensible heat required to cool the incoming condensate from the condensation temperature Tcond to the evaporation temperature Teva, and the last term represents the total amount of heat given off by the chilled water.
3.4. Adsorption Rate
The adsorption rate is expressed as:
where is the overall mass transfer coefficient for adsorption and is given by:
The adsorption rate is assumed to be controlled by the surface diffusion within a silica gel particle. The surface diffusivity () is expressed by Sakoda and Suzuki [24] as a function of temperature by:
where is the amount adsorbed at an equilibrium pressure of and is derived from the manufacturer property data by the following equation:
where and are the saturation vapor pressures at temperatures (water vapor) and (silica gel), respectively. The saturation vapor pressure and temperature are correlated by Antoine’s equation, which can be written as:
3.5. Mass Balance
The mass balance for the refrigerant in the evaporator can be defined as follows:
where subscripts “des-cond” and “eva-ads” stand for the vapor flow from the desorber to the condenser and from the evaporator to the adsorber, respectively.
3.6. Adsorption Mass Ratio
According to Hamamoto et al. [25], adsorbent mass allocation between upper and lower beds in a two-stage adsorption refrigeration cycle influences the cooling capacity. Therefore, it is important to calculate the effect of the mass ratio between the HTC and the LTC for a double-effect cycle. The adsorbent mass ratio r is defined as the ratio of adsorbent mass between the HTC and the LTC. It can be expressed as:
3.7. System Perfzormance
The system performance of this double-effect adsorption cycle can be characterized by the COP, which is defined as:
where the numerator is the total heat released by the evaporator (cooling effect). The denominator is the total heat input for the HTC and the LTC during one cycle. Heat input for the LTC is from hot water that is used for the pre-heating process of the LTC. In fact, little heat is required to pre-heat the LTC bed because the desorber is already heated during the heat recovery process. The heat source (hot water) temperature range is 55–90 °C and increases linearly with the HTC heat source (hot fluid) inlet temperature. The relation between inlet temperatures of the HTC and the LTC can be expressed as:
Specific cooling power (SCP) can be calculated from the following expression:
where Wtot denotes the total adsorbent weight within the chiller.
4. Results and Discussion
A double-effect adsorption refrigeration cycle that utilizes condensation heat is proposed, and a cycle simulation computer program is developed to analyze its performance. Our primary interest is to improve the COP, but because one of the advantages of the adsorption chiller is that it can be used at low temperature (compared to that of an absorption chiller), it is important to operate the chiller with waste heat at a middle temperature range (below 150 °C). In this context, the hot fluid temperature range is taken between 90 and 150 °C.
4.1. Effect of Hot Fluid Temperature
Figure 3 and Figure 4 show the influence of the hot fluid temperature on the COP and SCP. Simulation results from the proposed cycle are compared with the two-bed single-stage scheme. For both analyses, all conditions, such as mass flow rates of the hot fluid and cool water, are set equal (refer to Table 3). When the performance of one cycle is compared with that of the other cycle, it is important to consider the outlet temperature of the chilled water because performance is strongly dependent on the evaporation temperature. Therefore, the average cycle outlet temperature of the chilled water is fixed at 9 °C for comparison.
Figure 3 illustrates the effect of the hot fluid temperature on the COP. It also compares the COP values of the single-stage and double-effect cycles. The results show that the COP of the proposed cycle is higher than that of the conventional two-bed single-stage chiller when the hot fluid temperature is above 100 °C. Moreover, the COP of the proposed cycle is more than twice that of the conventional chiller once the temperature reaches 130 °C. When the hot fluid temperature increases, the desorption process at the HTC is prompted, and refrigerant vapor is produced at a higher temperature. Because condensation heat from the HTC refrigerant vapor is utilized for the LTC desorption process, the incremental heat input causes an increase in the cooling effect. Also, because no heat is inputted at the LTC from externally driven heat, then the COP of the proposed cycle is enhanced. On the other hand, the single-stage cycle produces a higher COP than that of the double-effect cycle when the heat source temperature is 90 °C (even though it decreases slowly as temperature increases). Figure 4 shows that when the temperature level is above 90 °C, the SCP of the single-stage cycle increases slightly, meaning that the cooling effect also increases only slightly. However, because the total heat input is relatively high, the COP of the single-stage cycle decreases. According to these results, the double-effect cycle that utilizes the HTC condensation heat improves the COP more than does the single-stage cycle when the heat source temperature is above 100 °C.
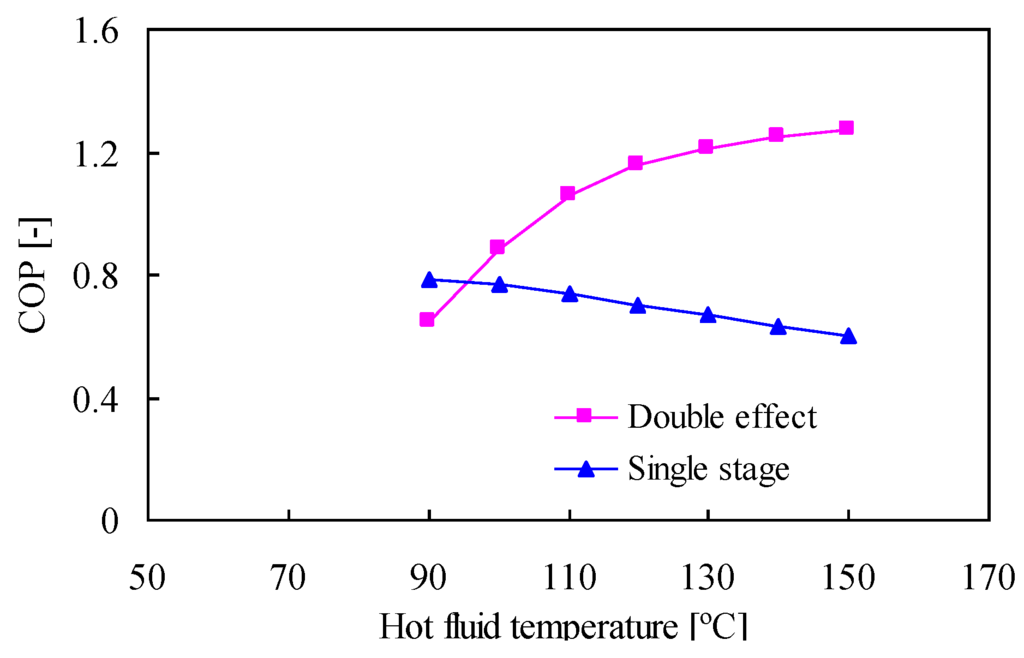
Figure 3.
Effect of the hot fluid temperature on the COP.
The effect of the hot fluid temperature on the SCP is shown in Figure 4; the SCP of the proposed cycle is much less than that of the single-stage cycle. However, the value increases as the temperature increases incrementally. This occurs because the condensation heat is the only heat source at the LTC. Although the heat source temperature of the HTC is high, the condensation heat is smaller, which produces a low level of cooling power per adsorbent mass.
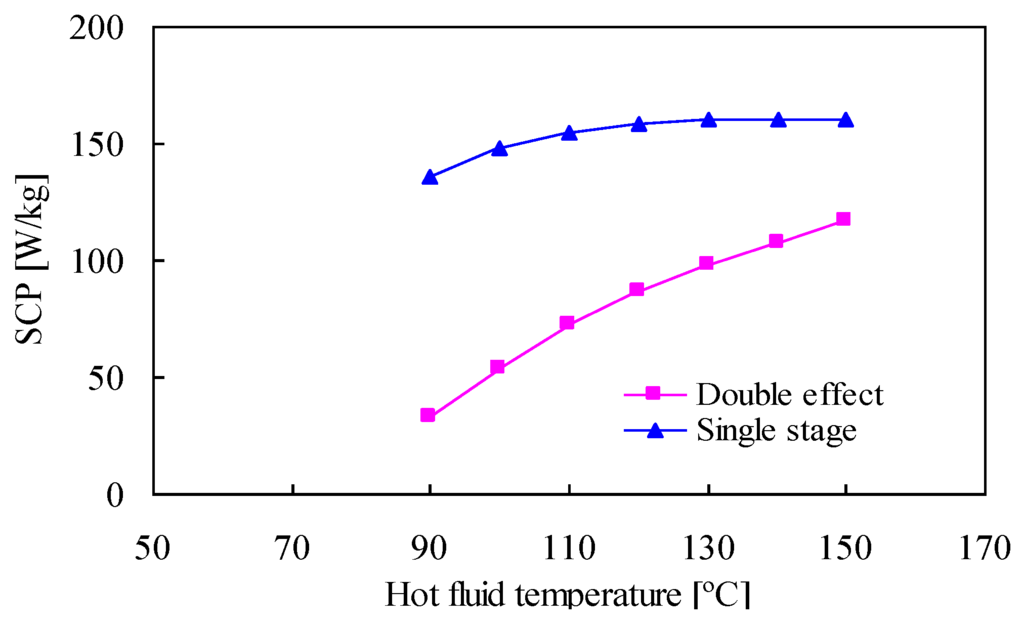
Figure 4.
Effect of the hot fluid temperature on the SCP.
4.2. Effect of Cycle Time
COP and SCP variations as a function of cycle time are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively. Heat recovery and pre-heating/pre-cooling times are maintained constant at 30 s. As a result, the COP increases linearly with cycle time. It is well known that the COP increases with cycle time because the adsorption/desorption process is enhanced by lengthening the cycle time. Longer cycle times yield a higher cooling effect for a given heat input.
On the other hand, Figure 6 shows that the SCP does not vary much with cycle time (although the SCP does decrease slightly when the cycle time increases). This occurs because adsorbent becomes more saturated and loses its adsorption capability when the adsorption process lasts for an extended period of time. We see from Equation (18) that because the cooling effect is not much different, because the SCP depends on the cooling effect and cycle time, the SCP value decreases when the adsorption time increases.
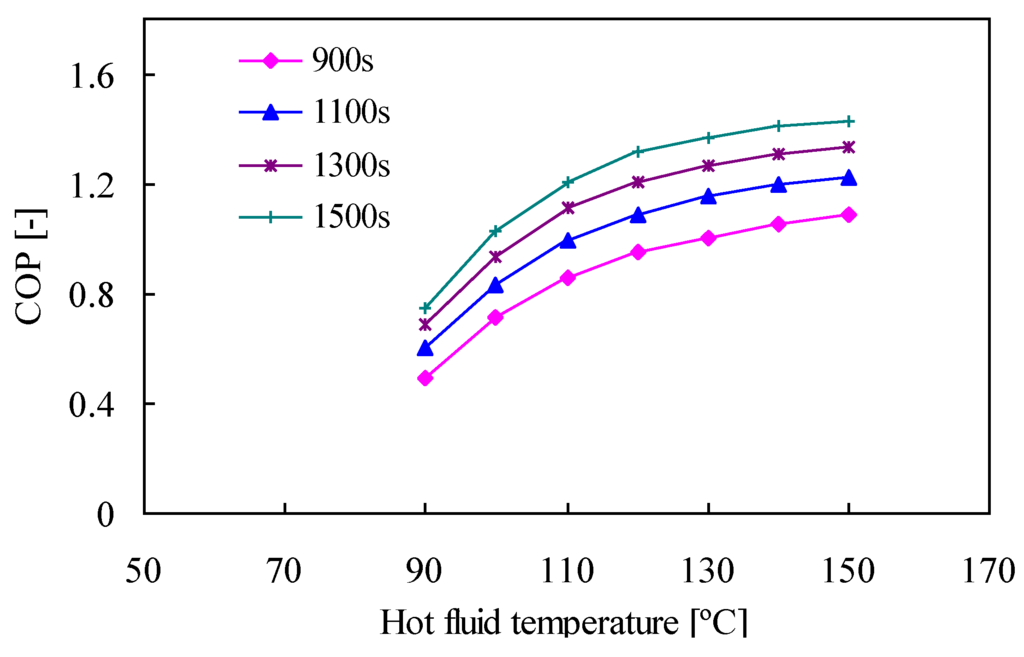
Figure 5.
Effect of cycle time on COP.
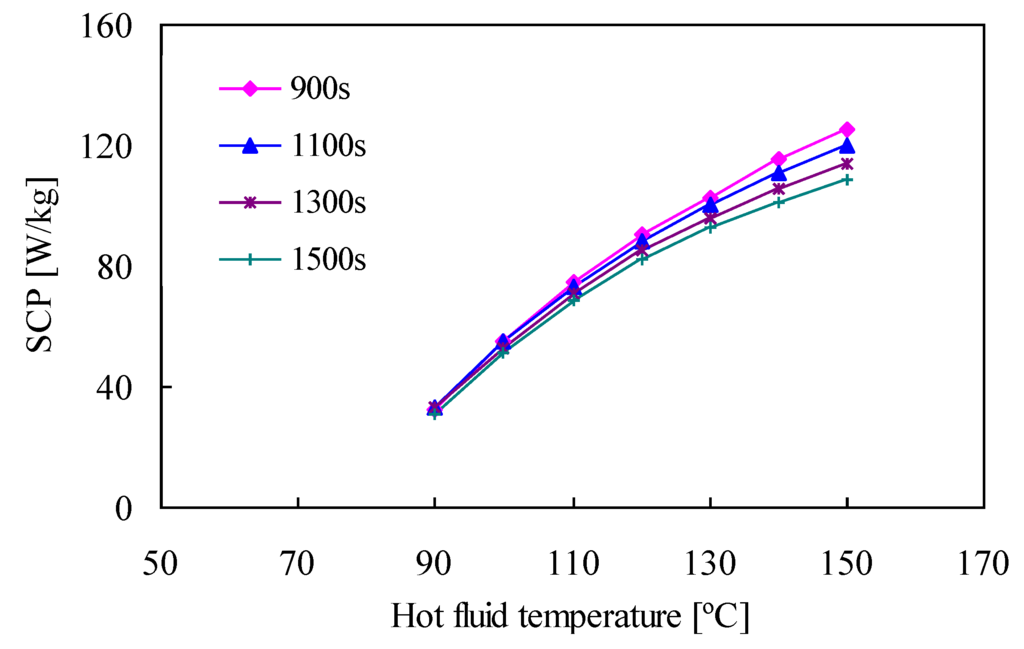
Figure 6.
Effect of cycle time on SCP.
4.3. Effect of Adsorbent Mass Ratio
The effects of the adsorbent mass ratio of the HTC to the LTC are presented in Figure 7 and Figure 8. Because condensation heat from the HTC directly influences the LTC desorption process, the optimal combination of adsorbent mass between the HTC and the LTC should be investigated to obtain the best performance. It should be noted here that the total amount of adsorbent mass in the chiller is the same. Figure 7 shows that the adsorbent mass ratio affects the COP value significantly. For each temperature Tf,in the COP increases until it reaches its maximum value, at which the adsorbent mass ratio is in the range of 1.0–1.25. Above this range, the COP decreases due to the increase in the adsorbent mass ratio. When the HTC adsorbent mass increases, the amount of condensation heat produced by the HTC is higher. However, because the LTC adsorbent mass is less, the total amount of cooling power increases only slightly and is not proportional to the heat input that is required to increase the adsorbent mass at the HTC. Hence, the COP value decreases when the adsorbent mass ratio increases. Figure 7 also shows that for each temperature, there is an adsorbent mass distribution that produces an optimal COP value. When Tf,in = 110 °C, the optimal COP value is produced if the adsorbent mass ratio is 1.0. Meanwhile, when Tf,in is 130 °C and 150 °C, the optimal adsorbent mass ratio is 1.15 and 1.25, respectively.
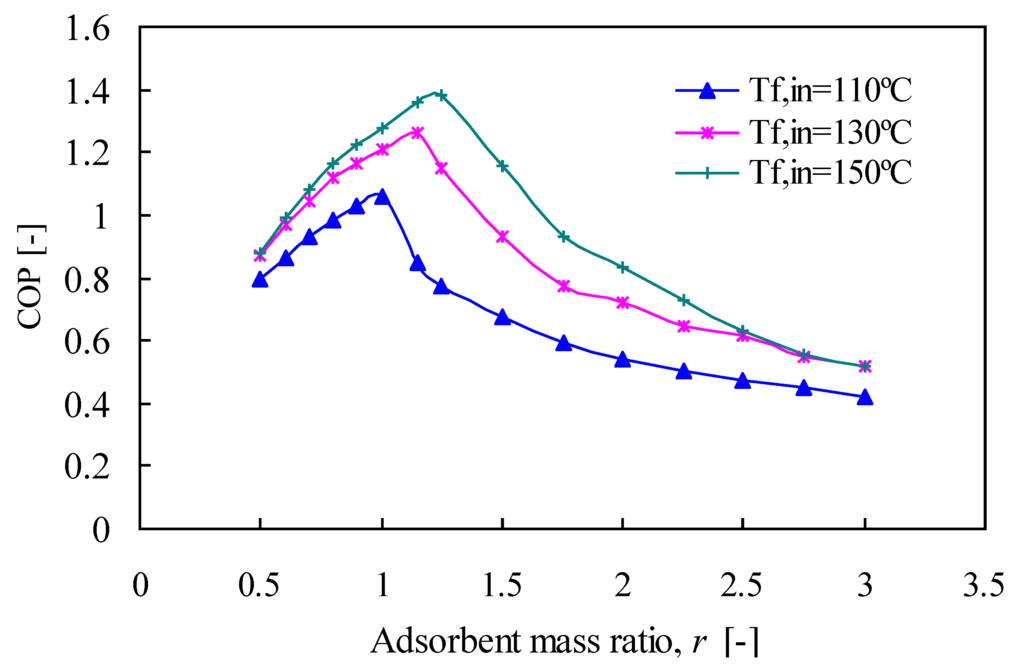
Figure 7.
Effect of adsorbent mass ratio on COP.
Figure 8 shows the Duhring diagrams that express the adsorption and desorption behavior when the adsorbent mass ratio is r = 1, 1.25, and 1.5 for temperature Tf,in = 150 °C. It should be noted that the highest value of the COP for Tf,in = 150 °C is achieved when r = 1.25, as presented in Figure 7. The adsorption concentration line (thin red line) in Figure 8 (b) shows that both the HTC and the LTC release much refrigerant when the desorption process occurs and adsorb much refrigerant when adsorption process occurs. Hence, it can be assumed that the cooling effect produces the maximum value when r = 1.25, which leads to the highest COP. On the other hand, Figure 8 (a) shows that the LTC releases much refrigerant, but that the HTC does not. Conversely, Figure 8 (c) shows that the HTC releases much refrigerant, but that the LTC does not.
The effect of the adsorbent mass ratio on the SCP value is less significant, as shown in Figure 9. For a relatively low heat source temperature (110 °C), the SCP value is fairly stable. When the heat source temperature becomes higher than 110 °C, the SCP increases incrementally to its maximum value as the adsorbent mass ratio increases. For each temperature, the maximum is attained when the ratio r is in the range of 1.15–1.25.
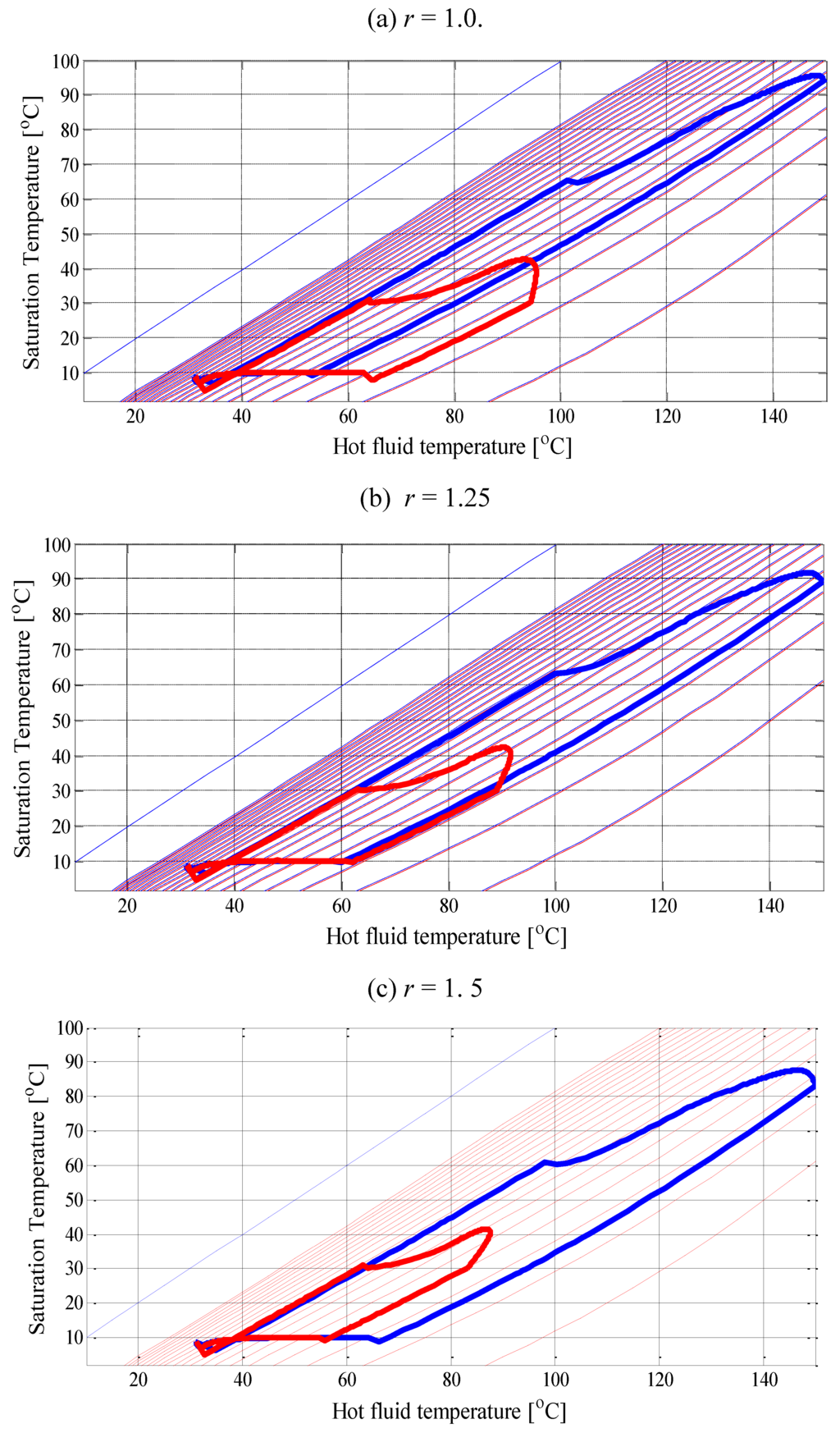
Figure 8.
Duhring diagram of the double-effect cycle for Tf,in = 150 °C with varying adsorbent mass ratio r.
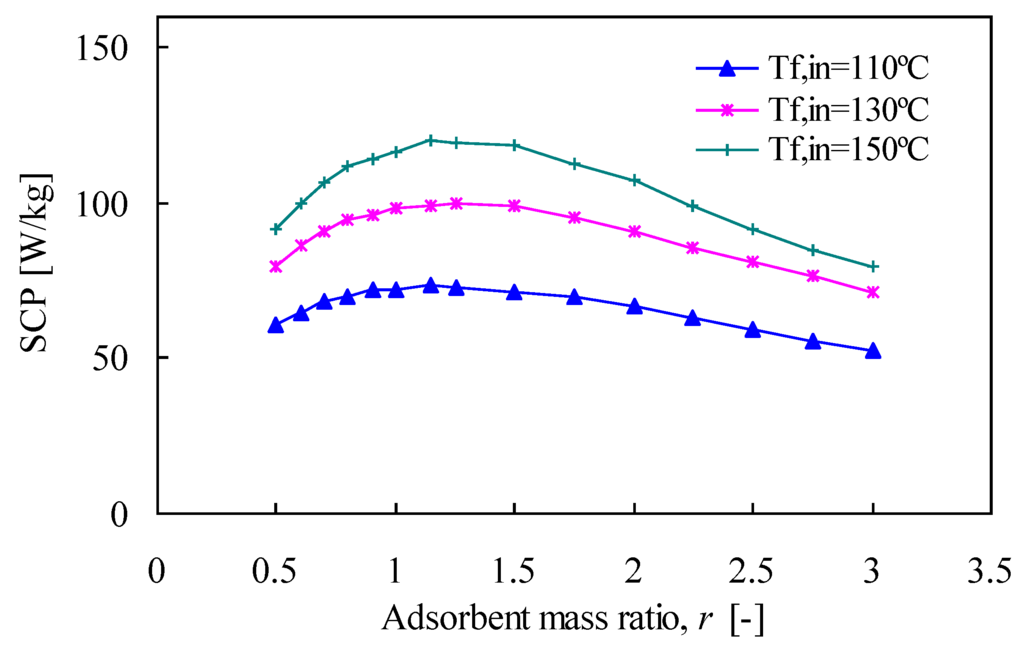
Figure 9.
Effect of adsorbent mass ratio on SCP.
5. Conclusions
The double-effect adsorption refrigeration cycle that utilizes condensation heat is introduced, and the performance is evaluated with numerical analyses in this manuscript. The results can be summarized as follows:
- (1)
- When the average cycle chilled water temperature is fixed at 9 °C, the double-effect cycle produces a higher COP than does the conventional single-stage cycle for driven temperatures between 100 and 150 °C. Although the SCP of the double-effect cycle is much smaller, it can be enhanced if the cycle is operated at a higher heat resource temperature.
- (2)
- The COP increases as the adsorption/desorption cycle time increases, while the SCP remains fairly stable.
- (3)
- The adsorbent mass ratio of the HTC to the LTC also affects the performance. At Tf,in = 150 °C, the COP gives the highest value when mass ratio r = 1.25.
Nomenclature
| A | area (m2) |
| C | specific heat (J kg−1 K−1) |
| Dso | surface specific heat (m2 s−1) |
| Ea | activation energy (J kg−1) |
| Lw | latent heat of vaporization (J kg−1) |
mass flow rate (kg s−1) | |
| Ps | saturated vapor pressure (Pa) |
| q | concentration (kg refrigerant/kg adsorbent) |
| q* | concentration at equilibrium (kg refrigerant/kg adsorbent) |
| T | temperature (K) |
| T | time (s) |
| U | heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K−1) |
| W | weight (kg) |
Subscripts
| ads | adsorber or adsorption |
| cond | condenser |
| chill | chilled water |
| coolw | cooling water |
| des | desorber or desorption |
| eva | evaporator |
| f | heat transfer fluid (oil) |
| H | HTC |
| Qst | isosteric heat of adsorption (J kg−1) |
| r | adsorbent mass ratio |
| R | gas constant (J kg−1K−1) |
| hex | heat exchanger |
| hotf | hot fluid |
| hotw | hot water |
| in | inlet |
| L | LTC |
| out | outlet |
| s | silica gel |
| w | water |
References
- Lambert, M.A. Design of solar powered adsorption heat pump with ice storage. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 1612–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristov, Y.I.; Restuccia, G.; Cacciola, G.; Parmon, V.N. A family of new working materials for solid sorption air conditioning system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2002, 22, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.Q.; Wang, R.Z.; Wu, J.Y.; Huang, X.H.; Huangfu, Y.; Wu, D.W.; Xu, Y.X. Experimental investigation of a micro-combined cooling, heating and power system driven by a gas engine. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.C.A.; Akahira, A.; Hamamoto, Y.; Akisawa, A.; Kashiwagi, T. A four-bed mass recovery adsorption refrigeration cycle driven by low temperature waste/renewable heat source. Renewable Energy 2004, 29, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.C.; Chua, H.T.; Chung, C.Y.; Loke, C.Y.; Kashiwagi, T.; Akisawa, T.; Saha, B.B. Experimental investigation of the silica gel-water adsorption isotherm characteristics. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2001, 21, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Wang, R.Z.; Xu, Y.X. Influence of adsorption and desorption capacity on operating process for adsorption heat pump. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2002, 22, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechang, W.; Jingyi, W.; Honggang, S.; Ruzhu, W. Experimental study on the dynamic characteristics of adsorption heat pumps driven by intermittent heat source at heating mode. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2005, 25, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.B.; Wang, R.Z.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.Y.; Xu, Y.X. Performance modeling and testing on a heat-regenerative adsorptive reversible heat pump. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2002, 22, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, M.; Szarzynski, S. Accounting for the real properties of the heat transfer fluid in heat-regenerative adsorption cycles for refrigeration. Int. J. Refrig. 2000, 23, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, D.; Tan, Y. Heat transfer enhancement of the adsorber of an adsorption heat pump. Adsorption 1999, 5, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restruccia, G.; Freni, A.; Maggio, G. A zeolite-coated bed for air conditioning adsorption systems: Parametric study of heat and mass transfer by dynamic simulation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2002, 22, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.B.; Boelman, E.C.; Kashiwagi, T. Computational analysis of an advanced adsorption-refrigeration cycle. Energy 1995, 20, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.B.; Akisawa, A.; Kashiwagi, T. Silica gel water advanced adsorption refrigeration cycle. Energy 1997, 22, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, H.T.; Ng, K.C.; Malek, A.; Kashiwagi, T.; Akisawa, A.; Saha, B.B. Modeling the performance of two-bed, silica gel–water adsorption chillers. Int. J. Refrig. 1999, 22, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, H.T.; Ng, K.C.; Wang, W.; Yap, C.; Wang, X.L. Transient modeling of a two-bed silica gel-water adsorption chiller. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2004, 47, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, S.V.; Wepfer, J.W.; Miles, D.J. Ramp wave analysis of the solid/vapor heat pump. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 1990, 112, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z. Performance improvement of adsorption cooling by heat and mass recovery operation. Int. J. Refrig. 2001, 24, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.C.; Wang, X.; Lim, Y.S.; Saha, B.B.; Chakarborty, A.; Koyama, S.; Akisawa, A.; Kashiwagi, T. Experimental study on performance improvement of a four-bed adsorption chiller by using heat and mass recovery. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2006, 49, 3343–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douss, N.; Meunier, F. Experimental study of cascading adsorption cycles. Chemical Eng. Sci. 1989, 44, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Leong, K.C. Numerical study of a novel cascading adsorption cycle. Int. J. Refrig. 2006, 29, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyun, A.S.; Miyazaki, T.; Akisawa, A.; Kashiwagi, T. High performance cascading adsorption refrigeration cycle with internal heat recovery driven by a low grade heat source temperature. Energies 2009, 2, 1170–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlinda; Miyazaki, T.; Ueda, Y.; Akisawa, A. Static analysis of double-effect adsorption refrigeration cycle using silica gel/water pair. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Refrig. Air Condit. Eng. 2010, 27, 57–65. (in Japanese). [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.Z.I.; Alam, K.C.A.; Saha, B.B.; Hamamoto, Y.; Akisawa, A.; Kashiwagi, T. Parametric study of a two stage adsorption chiller using re-heat—The effect of overall thermal conductance and adsorbent mass on system performance. Int. J. Thermal. Sci. 2006, 45, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoda, A.; Suzuki, M. Fundamental study on solar powered adsorption cooling system. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1984, 17, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamoto, Y.; Alam, K.C.A.; Akisawa, A.; Kashiwagi, T. Performance evaluation of a two-stage adsorption refrigeration cycle with different mass ratio. Int. J. Refrig. 2005, 28, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyun, A.S.; Miyazaki, T.; Akisawa, A.; Kashiwagi, T. Performance comparison of double-effect adsorption refrigeration cycles. In Proceedings of the Asian Thermophysical Properties Conference, Fukuoka, Japan, 21–24 August 2007.
- Saha, B.B.; Boelman, E.C.; Kashiwagi, T. Computational analysis of an advanced adsorption-refrigeration cycle. Energy 1995, 20, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).