Characteristics of Wind Profiles for Airborne Wind Energy Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources and Methodology
3. Wind Speed Profiles
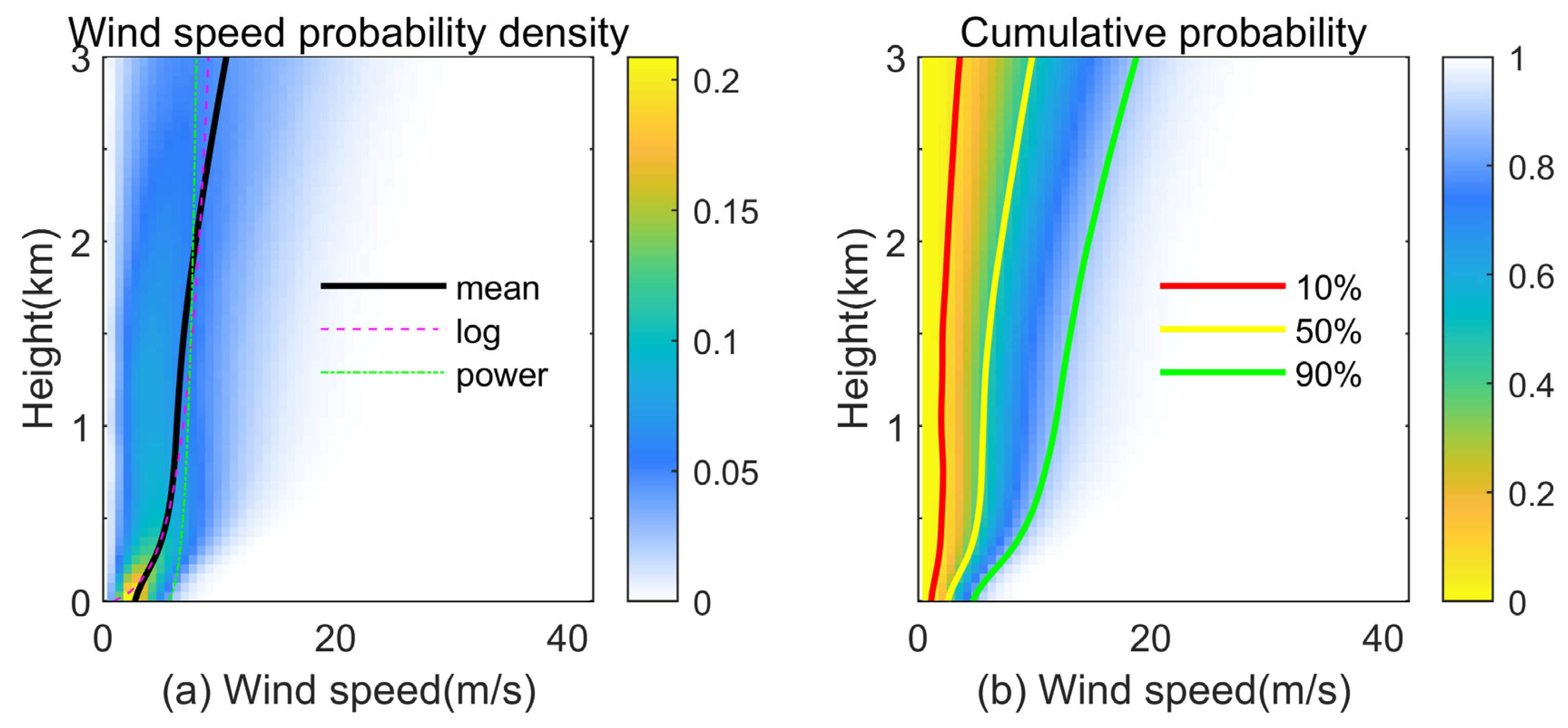
3.1. Long-Term Averaged Wind Profiles
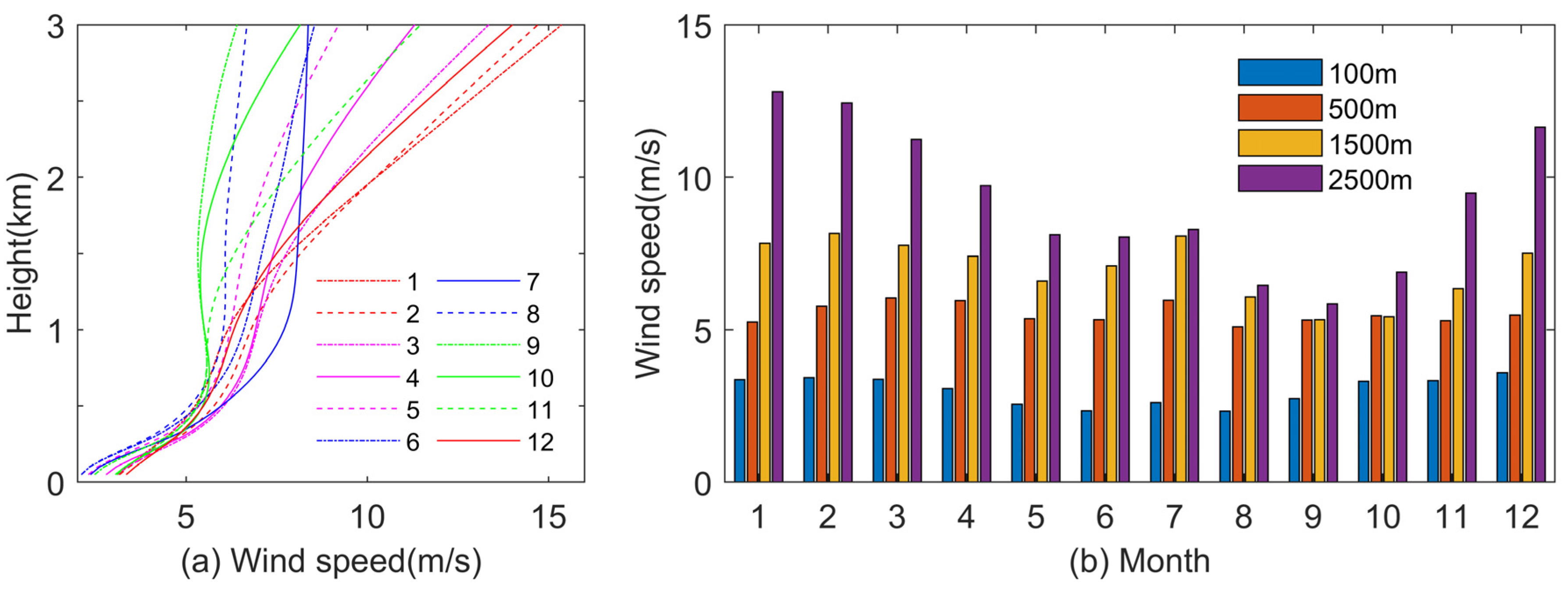
3.2. Monthly Variation in Wind Profiles
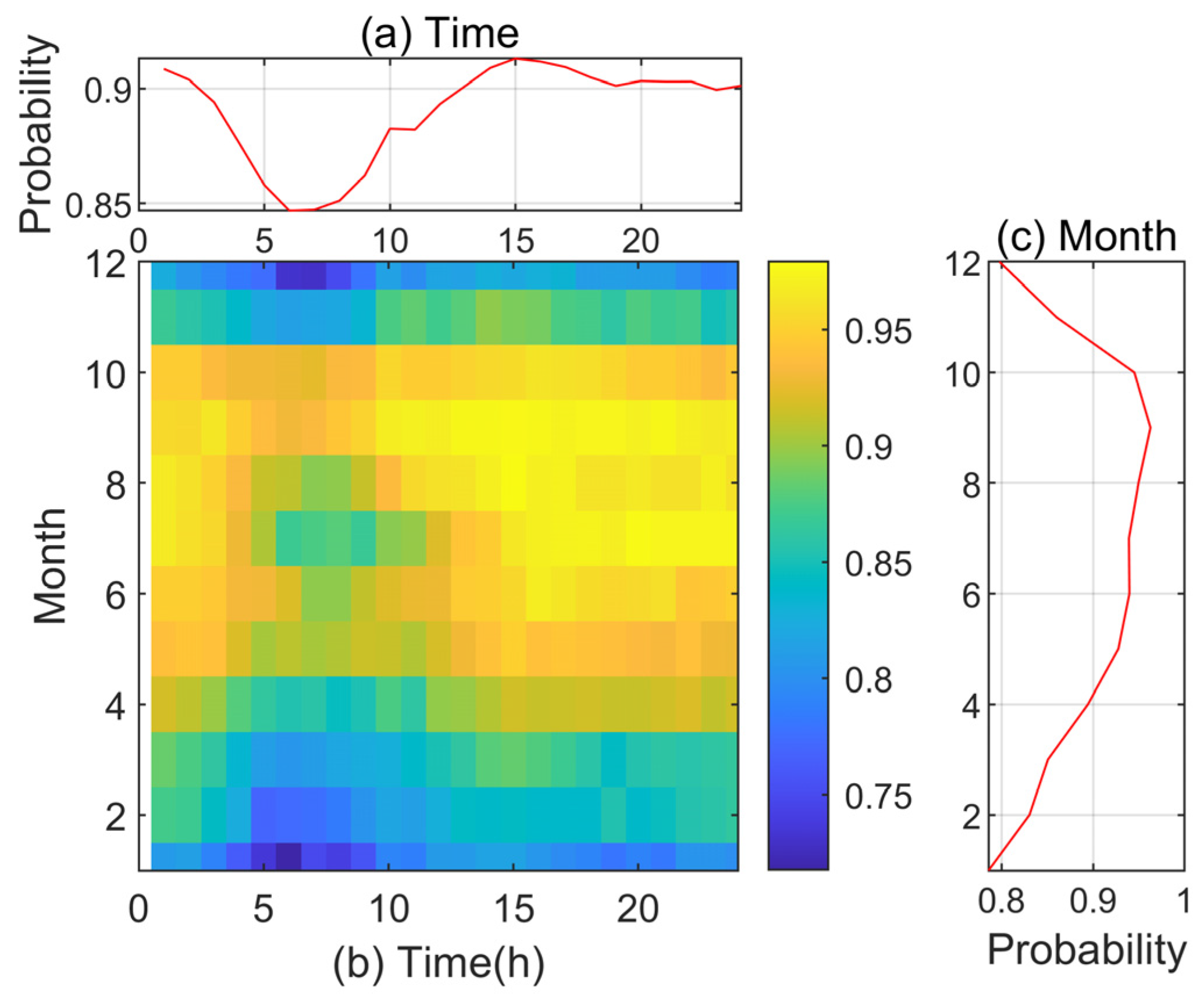
3.3. Occurrence Probability of Negative Wind Shear
4. Fluctuations in Wind Speed and Direction
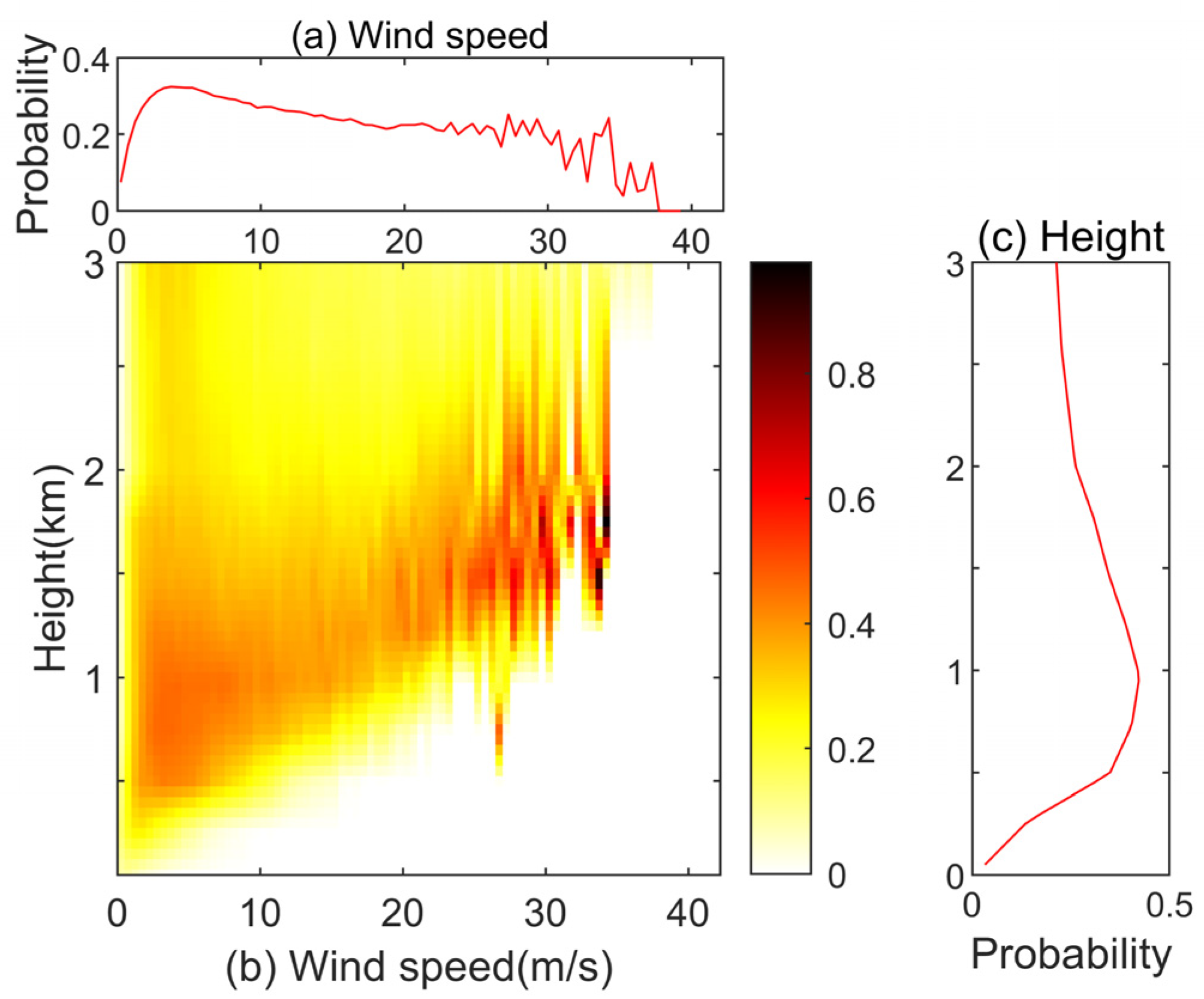
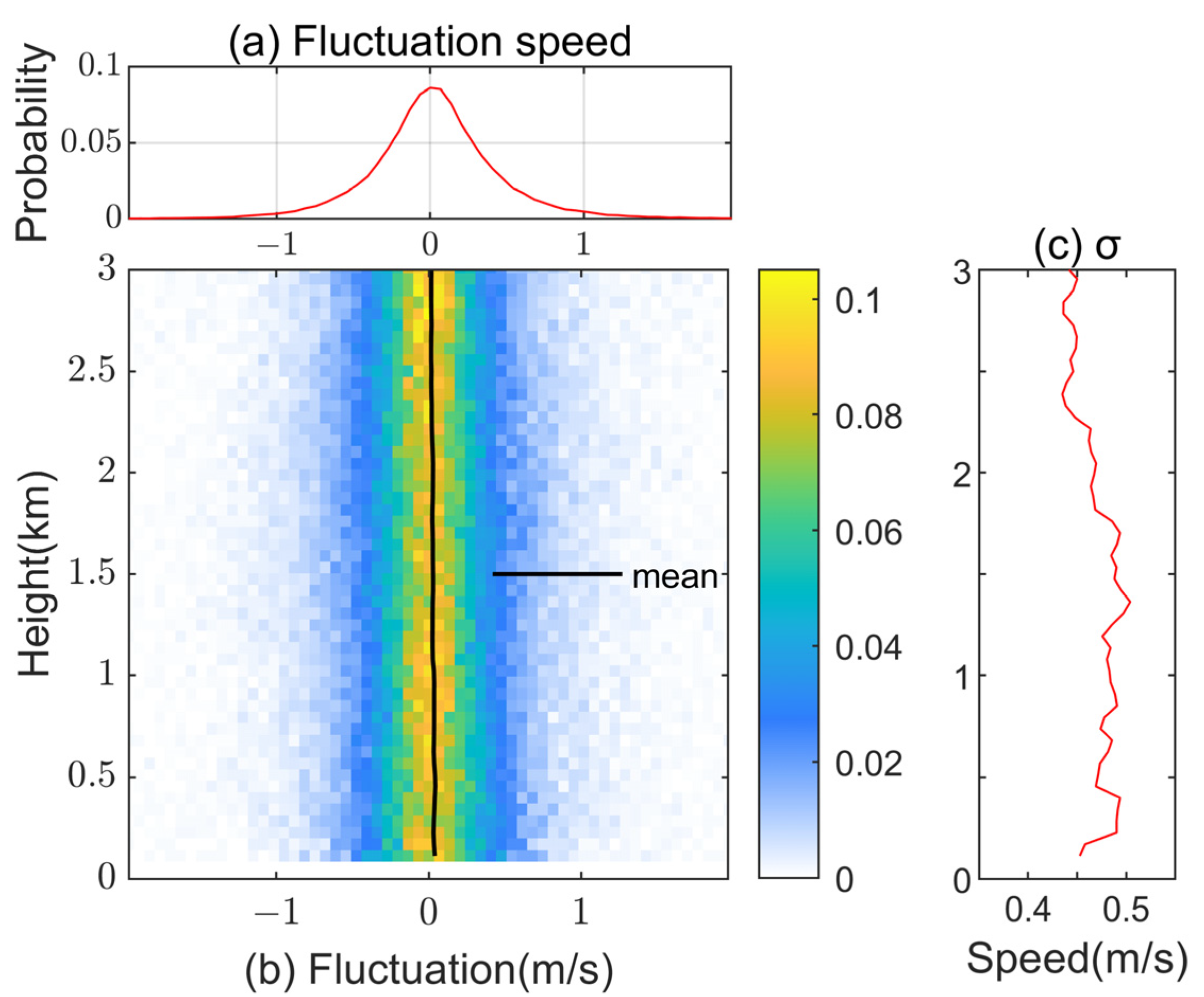
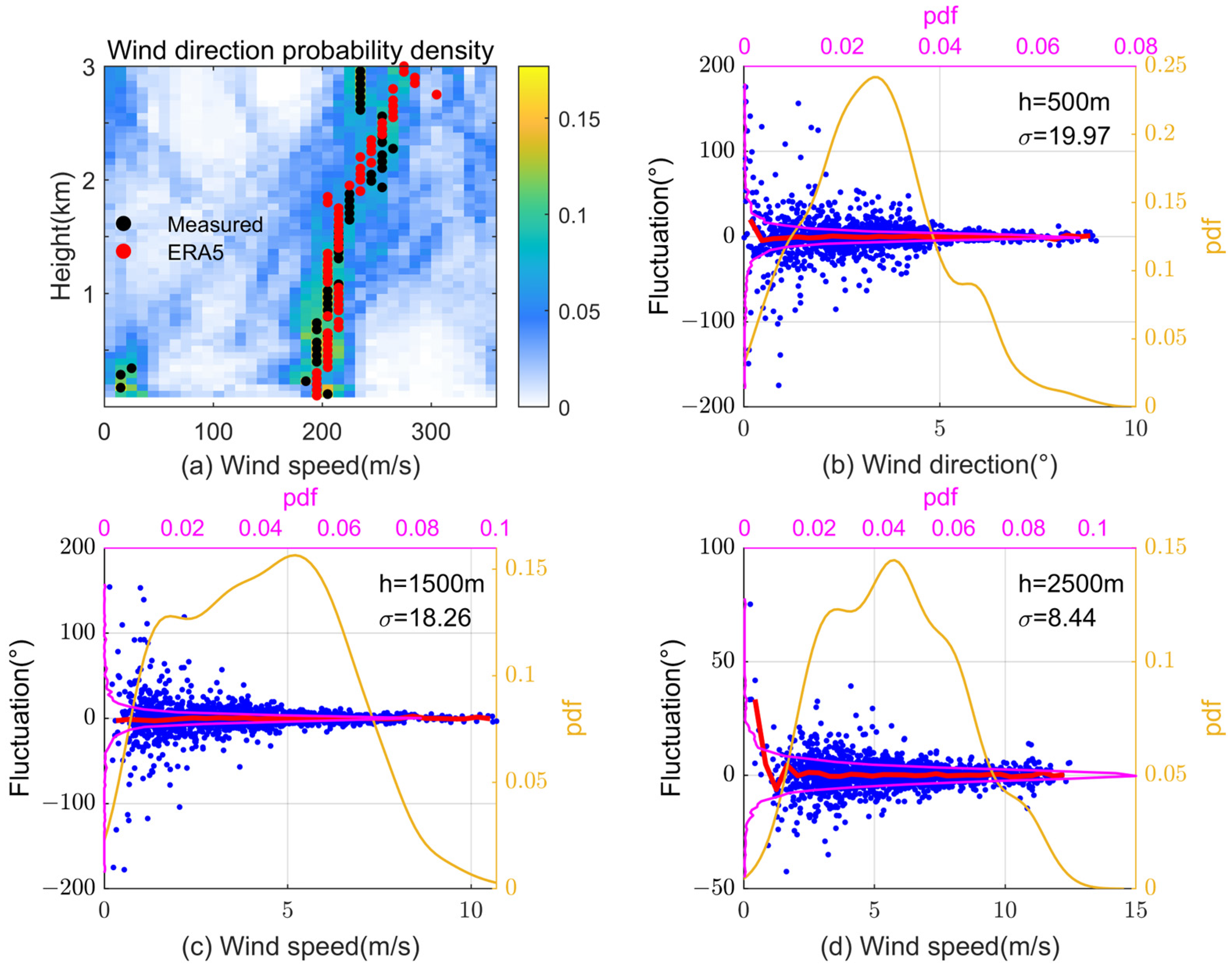
4.1. Characteristics of Fluctuations in Wind Speed
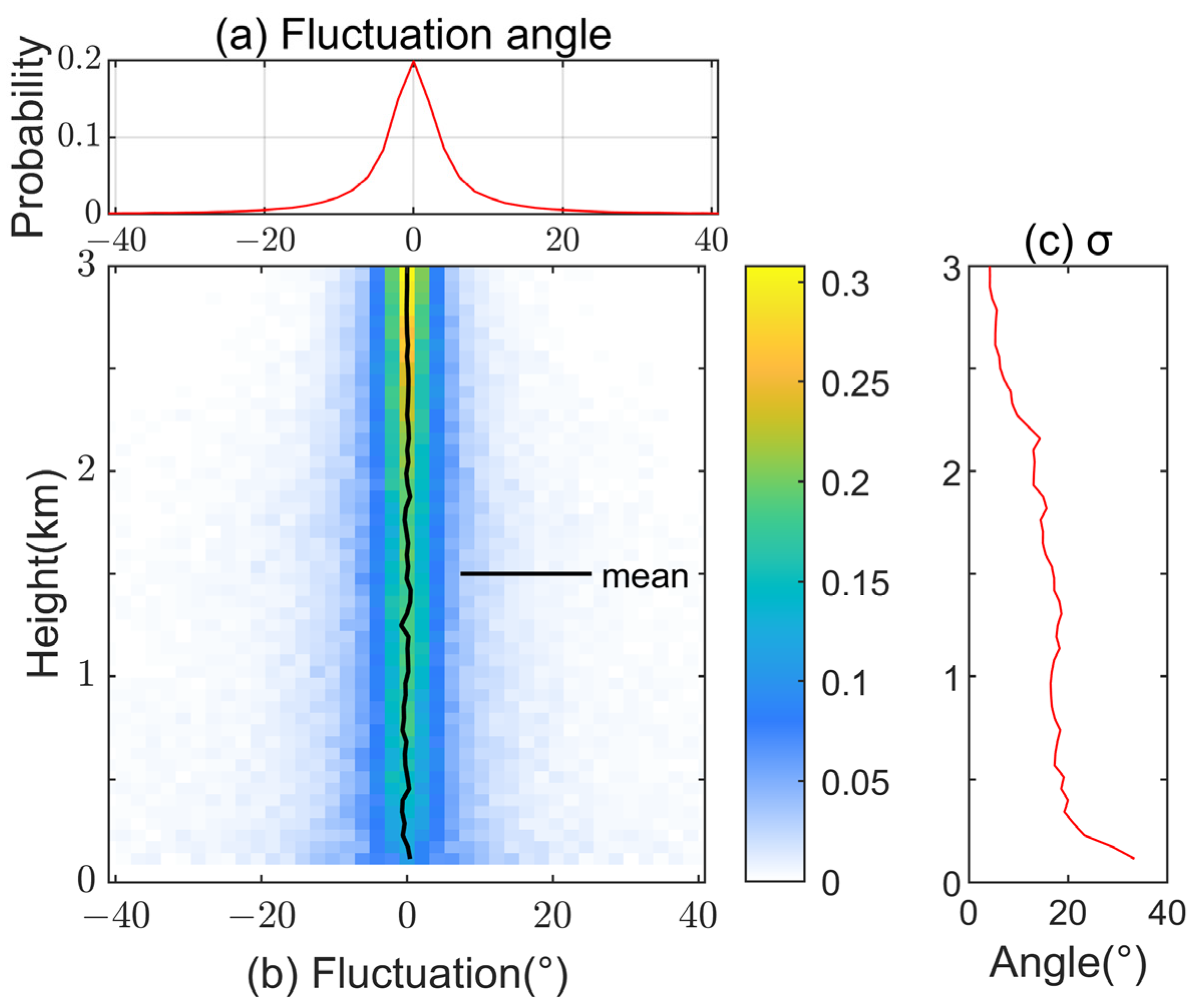
4.2. Characteristics of Fluctuations in Wind Direction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Archer, C.; Caldeira, K. Global assessment of high-altitude wind power. Energies 2009, 2, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IRENA. Future of Wind: Deployment, Investment, Technology, Grid Integration and Socio-Economic Aspects (A Global Energy Transformation Paper); International Renewable Energy Agency: Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2019; Available online: https://www.irena.org/publications/2019/Oct/Future-of-wind (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- Bechtle, P.; Schelbergen, M.; Schmehl, R.; Zillmann, U.; Watson, S. Airborne wind energy resource analysis. Renew. Energy 2019, 141, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPO and IRENA. Patent Insight Report: Offshore Wind Energy; EPO: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.irena.org/Publications/2023/Nov/IRENA-EPO-Offshore-Wind-Energy-Patent-Insight-Report (accessed on 11 December 2024).
- He, H.; Niu, X.J. Spatial distribution of high-altitude wind energy resources in China. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2025, 44, 28–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnja, J.; Schmehl, R.; De Breuker, R.; Jensen, K.; Vander Lind, D. Aeroelastic analysis of a large airborne wind turbine. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2018, 41, 2374–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Marquis, M.; Cooperman, A.; Draxl, C.; Hammond, R.; Jonkman, J.; Lemke, A.; Lopez, A.; Mudafort, R.; Optis, M.; et al. Airborne Wind Energy; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Thresher, R.; Robinson, M.; Veers, P. To capture the wind. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2007, 5, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.; Lansdorp, B.; Ockels, W. Optimal cross-wind towing and power generation with tethered kites. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2008, 31, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubini, A.; Papini, A.; Vertechy, R.; Fontana, M. Airborne wind energy systems: A review of the technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 51, 1461–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malz, E.C.; Walter, V.; Göransson, L.; Gros, S.M. The value of airborne wind energy to the electricity system. Wind. Energy 2022, 25, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Fagiano, L.; Milanese, M. KiteGen: A revolution in wind energy generation. Energy 2009, 34, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Fagiano, L.; Milanese, M. High altitude wind energy generation using controlled power kites. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2010, 18, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhard, M.; Strauch, H. Control of towing kites for seagoing vessels. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2013, 21, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhard, M.; Strauch, H. Flight control of tethered kites in autonomous pumping cycles for airborne wind energy. Control. Eng. Pract. 2015, 40, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehle, C.; Schmehl, R. Applied tracking control for kite power systems. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2014, 37, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmehl, R.; Noom, M.; van der Vlugt, R. Traction power generation with tethered wings. In Airborne Wind Energy; Ahrens, U., Diehl, M., Schmehl, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Li, X.Y. High-Altitude Wind Field Observation of Airborne Wind Energy System. South. Energy Constr. 2024, 11, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneberg, M.; Wölfle, D.; Bormann, A.; Rohde, P.; Breipohl, F.; Bastigkeit, I. Fast Power Curve and Yield Estimation of Pumping Airborne Wind Energy Systems. In Airborne Wind Energy; Green Energy and Technology; Schmehl, R., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanon, M.; Gros, S.; Andersson, J.; Diehl, M. Airborne Wind Energy Based on Dual Airfoils. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2013, 21, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuthold, R.; De Schutter, J.; Malz, E.; Licitra, G.; Gros, S.; Diehl, M. Operational Regions of a Multi-Kite AWE System. In Proceedings of the 2018 European Control Conference (ECC), Limassol, Cyprus, 12–15 June 2018; pp. 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Koenemann, J.; Bürger, A.; Williams, P.; Ruiterkamp, R.; Diehl, M. Performance assessment of a rigid wing Airborne Wind Energy pumping system. Energy 2019, 173, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmehl, R.; Rodriguez, M.; Ouroumova, L.; Gaunaa, M. Airborne Wind Energy for Martian Habitats. In Adaptive On- and Off-Earth Environments; Cervone, A., Bier, H., Makaya, A., Eds.; Springer Series in Adaptive Environments; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryning, S.E.; Batchvarova, E.; Floors, R.; Peña, A.; Brümmer, B.; Hahmann, A.; Mikkelsen, T. Long-Term Profiles of Wind and Weibull Distribution Parameters up to 600 m in a Rural Coastal and an Inland Suburban Area. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2013, 150, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Bai, Z.; Zha, X.Q.D.; Yang, F.L.; Yuan, C.H. Research on Wind Field Characteristics of High-Altitude Area in Tibet. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 170, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Prakash, O. Wind energy potential and its current status in India. Wind. Eng. 2023, 47, 1067–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, M.; Crawford, C.; Monahan, A.; Bastigkeit, I. LiDAR-based characterization of mid-altitude wind conditions for airborne wind energy systems. Wind. Energy 2019, 22, 1101–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelbergen, M.; Kalverla, P.C.; Schmehl, R.; Watson, S.J. Clustering wind profile shapes to estimate airborne wind energy production. Wind Energ. Sci. 2020, 5, 1097–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, M.; Dörenkämper, M.; De Schutter, J.; Crawford, C. Impact of wind profiles on ground-generation airborne wind energy system performance. Wind Energ. Sci. 2023, 8, 1153–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagiano, L.; Milanese, M. Airborne Wind Energy: An overview. In Proceedings of the 2012 American Control Conference (ACC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–29 June 2012; pp. 3132–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertovec, N.; Ober-Blöbaum, S.; Margellos, K. Safety-Aware Hybrid Control of Airborne Wind Energy Systems. J. Guid. Control. Dyn. 2024, 47, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, C.; Nahon, M.; Chalmers, D. Implementation of an Aerostat Positioning System With Cable Control. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2007, 12, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molebny, V.; McManamon, P.; Steinvall, O.; Kobayashi, T.; Chen, W.B. Laser radar: Historical prospective—From the East to the West. Ove 2016, 56, 031220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulli, D.; Avolio, E.; Calidonna, C.; Lo Feudo, T.; Torcasio, R.C.; Sempreviva, A.M. Two years of wind-lidar measurements at an Italian Mediterranean Coastal Site. Energy Procedia 2017, 125, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, M.; Dörenkämper, M.; Steinfeld, G.; Crawford, C. Improving mesoscale wind speed forecasts using lidar-based observation nudging for airborne wind energy systems. Wind. Energy Sci. 2019, 4, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graßl, S.; Ritter, C.; Schulz, A. The Nature of the Ny-Ålesund Wind Field Analysed by High-Resolution Windlidar Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Rozum, I.; et al. ERA5 Hourly Data on Pressure Levels from 1940 to Present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS), 2023. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-era5-pressure-levels?tab=overview (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Olauson, J. ERA5: The new champion of wind power modelling? Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Abdullah, M.; Kanwal, A.; Tahir, Z.U.R.; Saeed, U.B.; Manzoor, F.; Atif, M.; Abbas, S. Offshore wind resource assessment using reanalysis data. Wind. Eng. 2022, 46, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, A.G. Rationale for determining design wind velocities. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1961, 126, 184–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, A.; Obukhov, A. Basic Laws of Turbulent Mixing in the Atmosphere Near the Ground. Tr. Geofiz. Instituta Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1954, 24, 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- Bartholy, J.; Radics, K. Wind profile analyses and atmospheric stability over a complex terrain in southwestern part of Hungary. Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 30, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucevic, N.; Djurisic, Z. Vertical wind speed profiles estimation recognizing atmospheric stability. In Proceedings of the 2011 10th International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering, Rome, Italy, 8–11 May 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
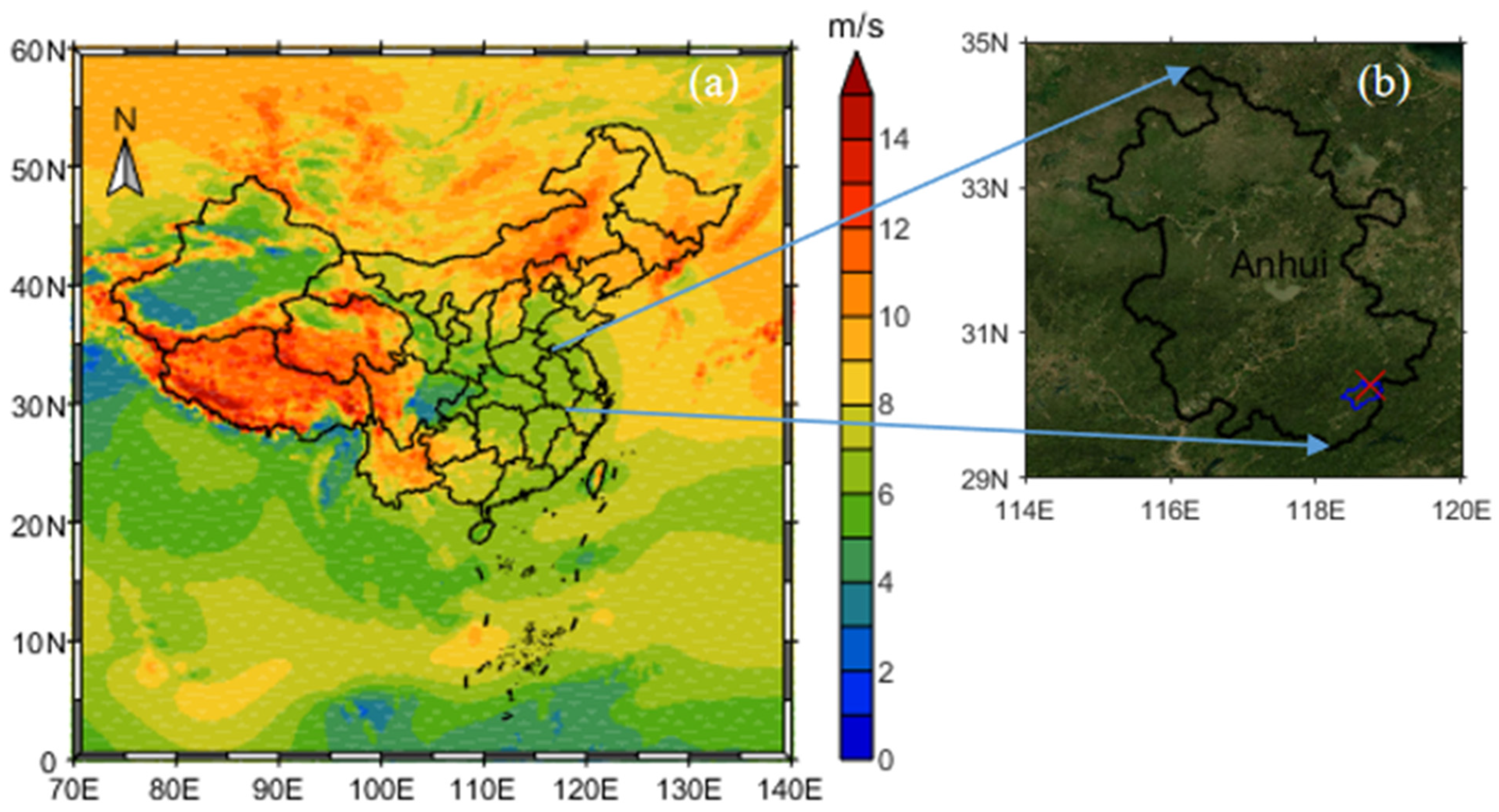


| Data Sources | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Coverage | Intervals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERA5 | 0.25° | 1 h | 1000~600 hPa | 25/50 hPa |
| LiDAR | \ | 10 min | 113~3020 m | 57 m |
| Height/m | 5% | 10% | 25% | 50% | 75% | 90% | 95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.46 | 0.53 | 0.68 | 0.92 | 1.25 | 1.57 | 1.79 |
| 200 | 0.46 | 0.54 | 0.69 | 0.94 | 1.25 | 1.55 | 1.73 |
| 300 | 0.45 | 0.53 | 0.69 | 0.94 | 1.25 | 1.55 | 1.75 |
| 400 | 0.44 | 0.52 | 0.68 | 0.94 | 1.26 | 1.57 | 1.78 |
| 500 | 0.43 | 0.50 | 0.67 | 0.93 | 1.26 | 1.59 | 1.81 |
| 1000 | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.61 | 0.89 | 1.29 | 1.73 | 2.00 |
| 1500 | 0.33 | 0.40 | 0.58 | 0.88 | 1.31 | 1.77 | 2.05 |
| 2000 | 0.31 | 0.40 | 0.58 | 0.91 | 1.32 | 1.75 | 2.00 |
| 2500 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.59 | 0.93 | 1.33 | 1.72 | 1.95 |
| 3000 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.60 | 0.94 | 1.34 | 1.69 | 1.91 |
| Average | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.64 | 0.92 | 1.29 | 1.65 | 1.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, H.; Niu, X.; Li, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, L.; Ye, X.; Wang, J. Characteristics of Wind Profiles for Airborne Wind Energy Systems. Energies 2025, 18, 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092373
He H, Niu X, Li X, Cai Y, Li L, Ye X, Wang J. Characteristics of Wind Profiles for Airborne Wind Energy Systems. Energies. 2025; 18(9):2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092373
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Hao, Xiaojing Niu, Xiaoyu Li, Yanfeng Cai, Leming Li, Xinwei Ye, and Junhao Wang. 2025. "Characteristics of Wind Profiles for Airborne Wind Energy Systems" Energies 18, no. 9: 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092373
APA StyleHe, H., Niu, X., Li, X., Cai, Y., Li, L., Ye, X., & Wang, J. (2025). Characteristics of Wind Profiles for Airborne Wind Energy Systems. Energies, 18(9), 2373. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092373






