The Development and Evaluation of a Low-Emission, Fuel-Flexible, Modular, and Interchangeable Solid Oxide Fuel Cell System Architecture for Combined Heat and Power Production: The SO-FREE Project
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminary Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Overall Objectives
- The development of a versatile system capable of operating with multiple SOFC technologies working at different temperatures.
- Fuel flexibility, allowing for the system to operate with pure hydrogen (H2), pure natural gas (CH4), or variable mixtures of methane and hydrogen in different proportions.
- Simplification of the SOFC system, enabling operation across a broad range of fuel compositions and temperatures with only a few essential components, including an autothermal reformer, an SOFC stack, a burner, a high-temperature blower, four heat exchangers, low-temperature compressors, and various splitters/mixers.
3.2. System Architecture and Aspen Plus Modeling
- The process operates under steady-state and isothermal conditions [48].
- The Peng–Robinson equation of state is used to model the gas phase.
- The gas phase includes N2, O2, H2, CO, CO2, CH4, and H2O as volatile species [49].
- The system operates slightly above atmospheric pressure, with an inlet pressure of 1.07 bar and an outlet pressure of 1.03 bar, resulting in a total pressure drop of 40 mbar.
- Two minimum stack temperatures are considered: 600 °C for low-temperature (LT) operation and 700 °C for high-temperature (HT) operation.
- The system is designed to deliver a constant power output of around 5 kWe, regardless of the fuel composition.
- The blower’s maximum operating temperature is 750 °C, as specified by the manufacturer.
- The burner’s maximum operating temperature is set at 950 °C.
3.2.1. Fuel Input and Anodic Recirculation
3.2.2. Autothermal Reformer
3.2.3. SOFC Stack
3.2.4. Burner and Heat Recovery System
3.2.5. Global System Considerations
3.3. System Control
3.3.1. Design Spec 1—Air to ATR: TAnode In Control
3.3.2. Design Spec 2—Air to Cathode: TCathode In Control
3.3.3. Design Spec 3—Air to Burner: TBurner Control
3.3.4. Design Spec 4—Input Fuel: Control of Stack Current Values
3.3.5. Design Spec 5—Fraction of Fuel Sent Directly to SOFC Stack: ΔTAnode Control
3.3.6. Design Spec 6—Duty of HEAIRCAT: ΔTCathode Control
3.3.7. Design Spec 7—The Fraction of the O2 Sent to the Anode: UFF Control
3.3.8. Design Spec 8 and 9: Duty of Anode and Cathode Fictious Heat Exchangers
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Assessment and Validation of SOFC Core Model
4.1.1. Output Composition Validation
4.1.2. Heat Distribution Validation
4.2. Performance Evaluation of Global SOFC Simulation
4.2.1. System Inputs
4.2.2. HEXFUEL and Recirculation
4.2.3. Autothermal Reformer
4.2.4. SOFC Stack
4.2.5. Burner and Heat Recovery System
4.2.6. Overall Analysis
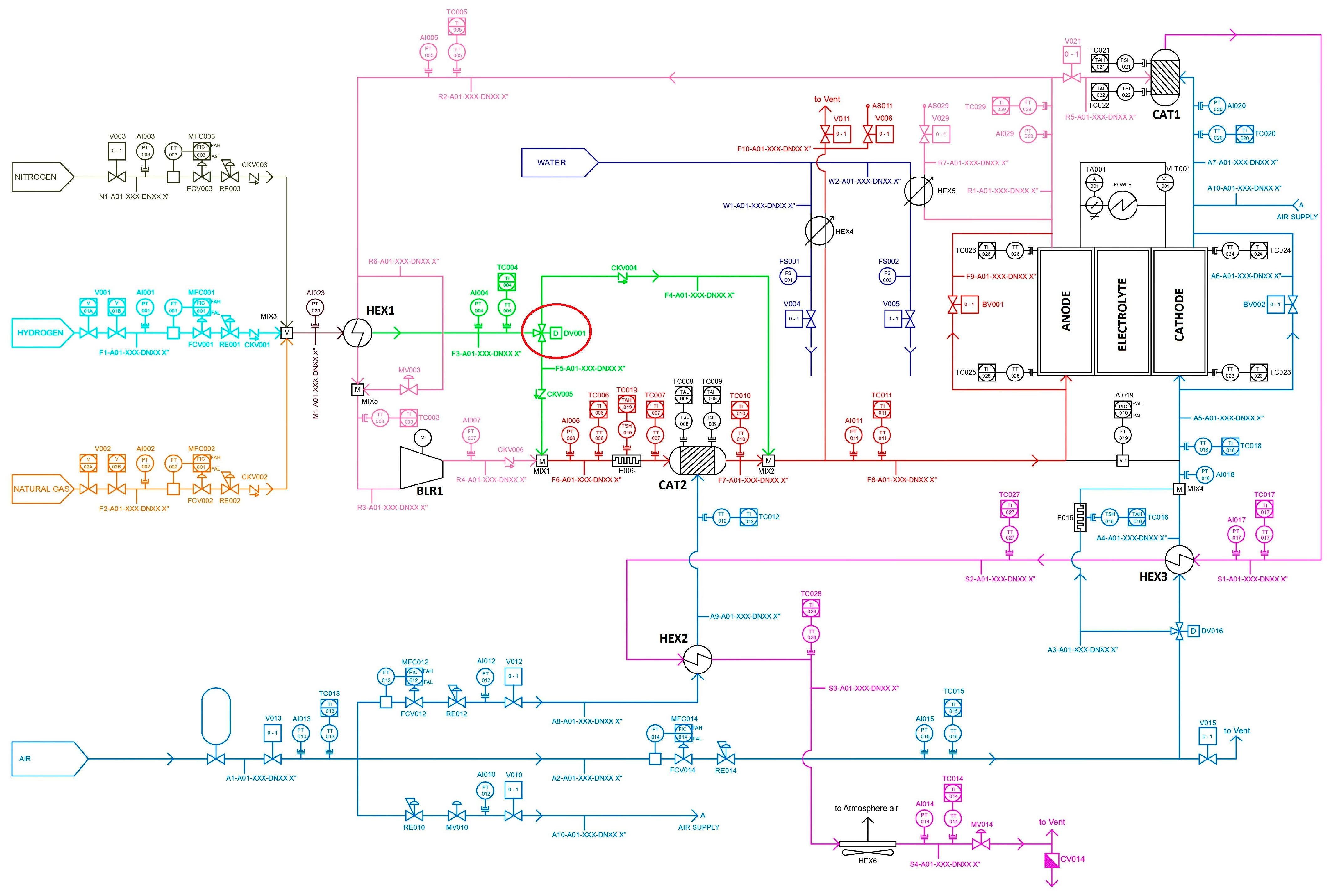
4.3. The PI&D of the Real System
- Fuel input: The amount of fuel entering the system and its composition can be varied to regulate the mixture at the SOFC anode inlet.
- Fuel split between ATR and stack: The proportion of fuel directed to the ATR versus the fraction sent directly to the SOFC stack can be adjusted to manage the temperature gradient between the anode input and output.
- Air supply to the ATR: The amount of air fed into the ATR can be regulated to control the pre-reforming process and the temperature increases before the anode inlet.
- Anodic recirculation: The fraction of anode exhaust gas that is recirculated can be varied to regulate heat absorption by the anode flow relative to the cathode, to ensure compliance with the steam-to-carbon ratio, and to improve overall system efficiency by reducing the fuel sent to the burner.
- Cathodic air management: The total amount of air supplied to the cathode can be adjusted, including the fraction bypassing the HEX3 heat exchanger. This is the main parameter used to control heat absorption within the stack.
- Additional air input to the burner: The quantity of extra air entering the burner can be varied to regulate the maximum temperature rise inside the burner.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATR | Autothermal Reformer |
| DS | Design Specification |
| FC | Fuel Cells |
| GT | Gas Turbine |
| HT | High Temperature |
| ICE | Internal Combustion Engine |
| LHV | Lower Heating Value |
| LT | Low Temperature |
| P&ID | Piping and Instrumentation Diagram |
| R-WGS | Reverse Water–Gas Shift |
| SMR | Steam Methane Reforming |
| SOFC | Solid Oxide Fuel Cell |
| SR-SOFC | External Steam Reforming SOFC |
| UFF | Fuel Utilization Factor |
| Vop | Stack Operating Voltage |
| WGS | Water–Gas Shift |
References
- Johnsson, F.; Kjärstad, J.; Rootzén, J. The threat to climate change mitigation posed by the abundance of fossil fuels. Clim. Policy 2019, 19, 258–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulin, N.; Le Billon, P. Climate change and fossil fuel production cuts: Assessing global supply-side constraints and policy implications. Clim. Policy 2020, 20, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, M.A.; Koohi-Fayegh, S. The prospects for hydrogen as an energy carrier: An overview of hydrogen energy and hydrogen energy systems. Energy Ecol. Environ. 2016, 1, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeyi, M.J.B.; Olanrewaju, O.A. Biogas Production and Applications in the Sustainable Energy Transition. J. Energy 2022, 2022, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Kumar, M.; Bolan, N.S.; Kapley, A.; Kumar, R.; Singh, L. Multidimensional approaches of biogas production and up-gradation: Opportunities and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 338, 125514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balat, H.; Kirtay, E. Hydrogen from biomass—Present scenario and future prospects. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 7416–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasajja, H.; Lindeboom, R.E.F.; van Lier, J.B.; Aravind, P.V. Techno-economic review of biogas cleaning technologies for small scale off-grid solid oxide fuel cell applications. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 197, 106215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, F.H.; Monroy, C.R.; Pérez, J.L.H. Critical analysis on hydrogen as an alternative to fossil fuels and biofuels for vehicles in Europe. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Han, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Jin, H. Assessment of a combined cooling, heating and power system by synthetic use of biogas and solar energy. Appl. Energy 2018, 229, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, R.; Marcantonio, V.; Cioccolanti, L.; Bocci, E. Integrating biomass gasification with a steam-injected micro gas turbine and an Organic Rankine Cycle unit for combined heat and power production. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 205, 112464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadabadi, S.A.; Thallam Thattai, A.; Fan, L.; Lindeboom, R.E.F.; Spanjers, H.; Aravind, P.V. Solid Oxide Fuel Cells fuelled with biogas: Potential and constraints. Renew. Energy 2019, 134, 194–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcantonio, V.; Monarca, D.; Villarini, M.; Di Carlo, A.; Del Zotto, L.; Bocci, E. Biomass Steam Gasification, High-Temperature Gas Cleaning, and SOFC Model: A Parametric Analysis. Energies 2020, 13, 5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcantonio, V.; Del Zotto, L.; Ouweltjes, J.P.; Bocci, E. Main issues of the impact of tar, H2S, HCl and alkali metal from biomass-gasification derived syngas on the SOFC anode and the related gas cleaning technologies for feeding a SOFC system: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 517–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ando, Y.; Kishizawa, H.; Tomida, K.; Matake, N. Recent Progress of SOFC-GT Combined System with Tubular Type Cell Stack at MHI. ECS Trans. 2013, 51, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Seyama, T.; Sobue, T.; Yamashita, S. Development of Residential SOFC CHP System with Flatten Tubular Segmented-In-Series Cells Stack. ECS Trans. 2011, 35, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J. Modeling and Model-based Analysis of a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Thermal-Electrical Management System with an Air Bypass Valve. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 177, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shen, T.; Deng, Z.; Fu, X.; Li, J.; Li, X. High efficiency thermoelectric cooperative control of a stand-alone solid oxide fuel cell system with an air bypass valve. Energy 2018, 152, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papurello, D.; Iafrate, C.; Lanzini, A.; Santarelli, M. Trace compounds impact on SOFC performance: Experimental and modelling approach. Appl. Energy 2017, 208, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, X.; Deng, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Control-oriented dynamic model optimization of steam reformer with an improved optimization algorithm. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 11288–11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrečko, D.; Nerat, M.; Vrančić, D.; Dolanc, G.; Dolenc, B.; Pregelj, B.; Meyer, F.; Siu, F.A.; Makkus, R.; Juričić, Đ. Feedforward-feedback control of a solid oxide fuel cell power system. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 6352–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorce, A.; Greco, A.; Magistri, L.; Costamagna, P. FDI oriented modeling of an experimental SOFC system, model validation and simulation of faulty states. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, X.; Deng, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. Thermal management of an independent steam reformer for a solid oxide fuel cell with constrained generalized predictive control. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 12317–12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joneydi Shariatzadeh, O.; Refahi, A.H.; Rahmani, M.; Abolhassani, S.S. Economic optimisation and thermodynamic modelling of SOFC tri-generation system fed by biogas. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barelli, L.; Bidini, G.; Ottaviano, A. Part load operation of a SOFC/GT hybrid system: Dynamic analysis. Appl. Energy 2013, 110, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oryshchyn, D.; Harun, N.F.; Tucker, D.; Bryden, K.M.; Shadle, L. Fuel utilization effects on system efficiency in solid oxide fuel cell gas turbine hybrid systems. Appl. Energy 2018, 228, 1953–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun, N.F.; Tucker, D.; Adams, T.A. Technical challenges in operating an SOFC in fuel flexible gas turbine hybrid systems: Coupling effects of cathode air mass flow. Appl. Energy 2017, 190, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Zaccaria, V.; Tucker, D. Fuel composition effect on cathode airflow control in fuel cell gas turbine hybrid systems. J. Power Sources 2018, 384, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuneo, A.; Zaccaria, V.; Tucker, D.; Source, A. Gas turbine size optimization in a hybrid system considering SOFC degradation. Appl. Energy 2018, 230, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, H.; Weng, S. Control strategy design for a SOFC-GT hybrid system equipped with anode and cathode recirculation ejectors. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 132, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccaria, V.; Tucker, D.; Traverso, A. Transfer function development for SOFC/GT hybrid systems control using cold air bypass. Appl. Energy 2016, 165, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.A.; Brouwer, J. Progress in solid oxide fuel cell-gas turbine hybrid power systems: System design and analysis, transient operation, controls and optimization. Appl. Energy 2018, 215, 237–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, M. Addressing fuel recycling in solid oxide fuel cell systems fed by alternative fuels. Energy 2017, 137, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papurello, D.; Borchiellini, R.; Bareschino, P.; Chiodo, V.; Freni, S.; Lanzini, A.; Pepe, F.; Ortigoza, G.A.; Santarelli, M. Performance of a Solid Oxide Fuel Cell short-stack with biogas feeding. Appl. Energy 2014, 125, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandiglio, M.; Lanzini, A.; Santarelli, M.; Acri, M.; Hakala, T.; Rautanen, M. Results from an industrial size biogas-fed SOFC plant (the DEMOSOFC project). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 5449–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, R.; Lombardi, L.; Tribioli, L. Use of biogas from biowaste in a solid oxide fuel cell stack: Application to an off-grid power plant. Renew. Energy 2017, 111, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, G.; Gandiglio, M.; Lanzini, A.; Santarelli, M. Dynamic model with experimental validation of a biogas-fed SOFC plant. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 135, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjaden, B.; Gandiglio, M.; Lanzini, A.; Santarelli, M.; Järvinen, M. Small scale biogas-SOFC plant: Technical analysis and assessment of the European potential. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 4216–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, W.; Reynolds, A.; Kennedy, D. Modelling and Simulation of a Biomass Gasification-Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Combined Heat and Power Plant Using Aspen Plus; Technical Report; Technological University Dublin: Dublin, Ireland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, P.; Lanzini, A.; Santarelli, M.; Calì, M.; Sagnelli, F.; Boulanger, A.; Scaletta, A.; Zitella, P. Methane-free biogas for direct feeding of solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Licata, B.; Sagnelli, F.; Boulanger, A.; Lanzini, A.; Leone, P.; Zitella, P.; Santarelli, M. Bio-hydrogen production from organic wastes in a pilot plant reactor and its use in a SOFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 7861–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laycock, C.J.; Panagi, K.; Reed, J.P.; Guwy, A.J. The importance of fuel variability on the performance of solid oxide cells operating on H2/CO2 mixtures from biohydrogen processes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 8972–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Bian, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, N.; Zhao, H.; Li, F.; Chou, K.C. Effect of hydrogen and carbon dioxide on the performance of methane fueled solid oxide fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 7453–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikooyeh, K.; Clemmer, R.; Alzate-Restrepo, V. Hill JM. Effect of hydrogen on carbon formation on Ni/YSZ composites exposed to methane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 347, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, G.; Bidini, G.; Hemmes, K. Comparison of the solid oxide fuel cell system for micro CHP using natural gas with a system using a mixture of natural gas and hydrogen. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, G.; Dhir, A.; Bujalski, W. Direct Operation of IP-Solid Oxide Fuel Cell with Hydrogen and Methane Fuel Mixtures under Current Load Cycle Operating Condition. Fuel Cells 2014, 14, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagi, K.; Laycock, C.J.; Reed, J.P.; Guwy, A.J. Highly efficient coproduction of electrical power and synthesis gas from biohythane using solid oxide fuel cell technology. Appl. Energy 2019, 255, 113854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluswamy, G.K.; Laycock, C.J.; Shah, K.; Ball, A.S.; Guwy, A.J.; Dinsdale, R.M. Biohythane as an energy feedstock for solid oxide fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 27896–27906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Croiset, E.; Douglas, P.L.; Fowler, M.W.; Entchev, E. Simulation of a tubular solid oxide fuel cell stack using AspenPlusTM unit operation models. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianko-Oprych, P.; Palus, M. Simulation of SOFCs based power generation system using Aspen. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2017, 19, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, A.; Bocci, E.; Naso, V. Process simulation of a SOFC and double bubbling fluidized bed gasifier power plant. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcantonio, V.; Bocci, E.; Ouweltjes, J.P.; Del Zotto, L.; Monarca, D. Evaluation of sorbents for high temperature removal of tars, hydrogen sulphide, hydrogen chloride and ammonia from biomass-derived syngas by using Aspen Plus. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 6651–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhukhan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Leach, M.; Brandon, N.P.; Shah, N. Energy integration and analysis of solid oxide fuel cell based microcombined heat and power systems and other renewable systems using biomass waste derived syngas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 11506–11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudra, S.; Kim, H.T. A simulation study of Solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) for IGFC power generation using Aspen Plus. J. Energy Clim. Change 2010, 5, 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ameri, M.; Mohammadi, R. Simulation of an atmospheric SOFC and gas turbine hybrid system using Aspen Plus software. Int. J. Energy Res. 2013, 37, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, C.H.; Kazempoor, P.; Braun, R.J. A thermodynamic approach for selecting operating conditions in the design of reversible solid oxide cell energy systems. J. Power Sources 2016, 301, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calise, F.; Palombo, A.; Vanoli, L. Design and partial load exergy analysis of hybrid SOFC–GT power plant. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, L.; Packbier, U.; Vinke, I.C.; de Haart, L.G.J. Long-Term Testing of SOFC Stacks at Forschungszentrum Jülich. Fuel Cells 2013, 13, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| ASPEN Plus Name | Block ID | Description |
|---|---|---|
| COMPR | COMPFUEL | Compressor—increases the pressure of the fuel inlet stream up to 1.07 bar |
| COMPCAT | Compressor—increases the pressure of the cathode air inlet stream up to 1.07 bar | |
| COMPAIR | Compressor—increases the pressure of the ATR air inlet stream up to 1.07 bar | |
| COMPBURN | Compressor—increases the pressure of the additional air inlet stream up to 1.07 bar | |
| BLOWER | Compressor—compensates for the pressure drop related to RECYCLE stream, restoring the pressure of the system (1.07 bar) | |
| FSPLIT | SPLITFUE | Splitter—splits the fuel inlet stream into the stream FUELPATR and the stream FUELPHAN |
| SPLITAN | Splitter—splits the stream out of the anode into two sub-streams, one led to the afterburner (FUELBURN) and the other led to the recirculation part of the system (RECHOT) | |
| MIXER | MIXER | Mixer—combines the incoming fuel stream directed to the ATR (FUELPATR) with the recirculated stream from the blower (RECPRESS) |
| MIXFUEL | Mixer—combines the ATR output (FUELREF) with the portion of fuel that is sent directly to the SOFC stack (FUELPHAN) | |
| HEATER | AN-HEAT | Heat Exchanger—it is a fictious exchanger that heats the temperature of the stream ANOUT in order to consider anode outlet temperature increase owing to SOFC exothermic reactions |
| CAT-HEAT | Heat Exchanger—it is a fictious exchanger that heats the CATOUT stream in order to consider cathode outlet temperature increase owing to SOFC exothermic reactions | |
| QSENS | Heat Exchanger—simulates the residual energy available downstream of preheating the system’s inlet air streams, which can be recovered for low-temperature cogeneration | |
| HEATX | HEXFUEL | Heat Exchanger—used to heat up the inlet fuel stream and to cool down the recycle stream before compression—heats the feed FUELPRES by means of the heat contained in the stream RECHOT |
| HEAIRATR | Heat Exchanger—used to heat up the air sent to the ATR—heats the inlet stream of air AIRREFPR by means of the heat contained in the exhausted stream BURNEDMT | |
| HEAIRCAT | Heat Exchanger—used to heat up the air sent to the cathode—heats the inlet stream of air AIRCATPR using the stream from the afterburner BURNEDHT | |
| RGIBBS | ATR | RGibbs reactor—simulates the autothermal reformer reactor. |
| ANODE | RGibbs reactor—simulates the SOFC anode | |
| RSTOIC | BURNER | RStoic reactor—simulates the burner downstream of the SOFC stack |
| SEPARATOR | CATH | Separator—simulates the SOFC cathode and splits the inlet stream AIRCATH into oxygen O2SUPP sent to the ANODE and cathode exhaust gas CATOUT |
| Number | Reaction | Description |
|---|---|---|
| R1 | CH4 + H2O → 3H2 + CO | Steam Methane Reforming |
| R2 | CO + H2O → H2 + CO2 | Water–Gas Shift |
| R3 | CH4 + 3/2 O2 → CO + 2H2O | CH4 Partial Combustion |
| R4 | CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2H2O | CH4 Full Combustion |
| R5 | CO + 1/2 O2 → CO2 | CO Combustion |
| R6 | H2 + 1/2O2 → H2O | H2 Combustion |
| 67% H2 and 33% CH4—Input = 4.24 × 10−3 mol/s | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT | EXP_OUT | SIM_OUT | Δ (EXP-SIM) | |
| CH4 | 15.70% | 0.50% | 0% | 0.50% |
| CO | 1.70% | 2.87% | 3.30% | −0.43% |
| CO2 | 9.50% | 17.34% | 17.20% | 0.14% |
| H2 | 33.80% | 14.10% | 15.43% | −1.33% |
| H2O | 39.10% | 65.18% | 64.07% | 1.11% |
| T [°C] | 763 | 817 | 817 | 0 |
| 100% CH4—Input = 2.45 × 10−3 mol/s | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT | EXP_OUT | SIM_OUT | Δ (EXP-SIM) | |
| CH4 | 8.00% | 0.83% | 0% | 0.83% |
| CO | 3.20% | 2.81% | 3.62% | −0.81% |
| CO2 | 28.00% | 30.80% | 30.26% | 0.54% |
| H2 | 21.60% | 6.37% | 8.65% | −2.28% |
| H2O | 38.90% | 59.19% | 57.47% | 1.72% |
| T [°C] | 767 | 814 | 814 | 0 |
| 100% H2—Input = 4.25 × 10−3 mol/s | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT | EXP_OUT | SIM_OUT | Δ (EXP-SIM) | |
| H2 | 57.50% | 14.70% | 14.10% | 0.60% |
| H2O | 42.50% | 85.30% | 85.90% | −0.60% |
| T [°C] | 758 | 819 | 819 | 0 |
| System Inputs | HT | LT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | |
| Input Fuel [kg/h] | 0.49 | 0.57 | 0.22 | 0.58 | 0.64 | 0.28 |
| Input Fuel [kmol/h] | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.14 |
| H2 [%mol] | 50% | 0% | 100% | 50% | 0% | 100% |
| CH4 [%mol] | 50% | 100% | 0% | 50% | 100% | 0% |
| Input air ATR [kmol/h] | 0.013 | 0.033 | 0.005 | 0.024 | 0.028 | 0 |
| Input air Cathode [kmol/h] | 1.32 | 1.32 | 1.40 | 1.61 | 1.58 | 1.69 |
| HT | LT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | |
| Recirculation Rate | 70% | 70% | 80% | 70% | 70% | 80% |
| Input Fuel [kg/h] | 0.49 | 0.57 | 0.22 | 0.58 | 0.64 | 0.28 |
| T In Fuel [°C] | 32 | 32 | 33 | 32 | 32 | 28 |
| T Out Fuel [°C] | 753 | 730 | 767 | 663 | 655 | 714 |
| Recirculation [kg/h] | 6.41 | 7.90 | 7.92 | 8.10 | 8.35 | 9.61 |
| T In Rec [°C] | 768 | 745 | 782 | 678 | 670 | 729 |
| T Out Rec [°C] | 625 | 638 | 652 | 559 | 572 | 603 |
| HT | LT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4-H2 | CH4 | CH4-H2 | CH4 | |
| ATR Fuel [kg/h] | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.19 |
| Bypass Fuel [kg/h] | 0.44 | 0.4 | 0.41 | 0.45 |
| ATR Fuel [%] | 10.20% | 29.82% | 29.31% | 29.69% |
| Bypass Fuel [%] | 89.80% | 70.18% | 70.69% | 70.31% |
| HT | LT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | |
| ATR Air Input [kg/h] | 0.38 | 0.94 | 0.16 | 0.69 | 0.80 | 0 |
| ATR Fuel Input [kg/h] | 6.46 | 8.07 | 7.96 | 8.28 | 8.55 | 9.67 |
| ATR Output [kg/h] | 6.84 | 9.01 | 8.12 | 8.97 | 9.34 | 9.67 |
| TATR AIR INPUT [°C] | 259 | 236 | 232 | 248 | 243 | - |
| TATR FUEL INPUT [°C] | 635 | 650 | 664 | 572 | 584 | 615 |
| TATR FUEL OUTPUT [°C] | 689 | 696 | 690 | 591 | 593 | 615 |
| LHV(MIXEDFUEL) [kW] | 2.59 | 4.31 | 3.64 | 4.83 | 5.10 | 3.99 |
| LHV(FUELREF) [kW] | 2.36 | 3.97 | 3.48 | 4.64 | 4.94 | 3.99 |
| O2/O2-Stoich | 14% | 19% | 4% | 13% | 14% | 0% |
| HT | LT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | |
| ATR Fuel Input [kmol/h] | 0.2806 | 0.3203 | 0.4804 | 0.3628 | 0.3435 | 0.5898 |
| H2 | 8.6% | 6.5% | 11.3% | 9.9% | 8.4% | 10.1% |
| H2O | 59.4% | 45.4% | 85.1% | 54.7% | 46.0% | 89.9% |
| CO | 1.6% | 2.1% | 0.0% | 1.0% | 1.7% | 0.0% |
| CO2 | 20.8% | 23.9% | 0.0% | 19.7% | 25.5% | 0.0% |
| CH4 | 1.0% | 3.3% | 0.0% | 2.7% | 3.5% | 0.0% |
| N2 | 8.6% | 18.8% | 3.6% | 12.1% | 14.8% | 0.0% |
| ATR Fuel Output [kmol/h] | 0.2963 | 0.3674 | 0.4847 | 0.4007 | 0.3889 | 0.5898 |
| H2 | 9.5% | 11.6% | 10.7% | 14.7% | 14.9% | 10.1% |
| H2O | 56.7% | 39.5% | 84.8% | 48.4% | 39.3% | 89.9% |
| CO | 2.0% | 3.8% | 0.0% | 2.0% | 3.2% | 0.0% |
| CO2 | 20.1% | 21.7% | 0.0% | 19.0% | 23.9% | 0.0% |
| CH4 | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.1% | 0.0% |
| N2 | 11.6% | 23.4% | 4.5% | 15.7% | 18.7% | 0.0% |
| HT | LT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | |
| Stack UF | 76% | 75% | 71% | 76% | 73% | 80% |
| TINPUT ANODE [°C] | 700 | 700 | 700 | 600 | 600 | 627 |
| TOUTPUT ANODE [°C] | 768 | 745 | 782 | 678 | 670 | 729 |
| TINPUT CATHODE [°C] | 700 | 700 | 700 | 586 | 598 | 590 |
| TOUTPUT CATHODE [°C] | 815 | 784 | 810 | 701 | 696 | 726 |
| Anode Fuel Input [kg/h] | 7.28 | 9.41 | 8.30 | 9.37 | 9.79 | 9.89 |
| Anode Fuel Input [kmol/h] | 0.3931 | 0.4422 | 0.5742 | 0.4908 | 0.4736 | 0.6955 |
| H2 [% mol] | 15.2% | 10.8% | 24.6% | 18.3% | 13.9% | 23.7% |
| H2O [% mol] | 48.7% | 37.0% | 71.6% | 43.6% | 36.6% | 76.3% |
| CO [% mol] | 1.7% | 3.6% | 0.0% | 1.8% | 3.0% | 0.0% |
| CO2 [% mol] | 17.3% | 20.3% | 0.0% | 17.1% | 22.2% | 0.0% |
| CH4 [% mol] | 7.0% | 6.4% | 0.0% | 5.1% | 6.8% | 0.0% |
| N2 [% mol] | 10.0% | 21.9% | 3.8% | 14.1% | 17.5% | 0.0% |
| Anode Fuel Output [kg/h] | 9.16 | 11.28 | 9.90 | 11.58 | 11.93 | 12.01 |
| Anode Fuel Output [kmol/h] | 0.3931 | 0.4422 | 0.5742 | 0.4455 | 0.4169 | 0.6955 |
| H2 [% mol] | 7.8% | 6.7% | 7.2% | 7.6% | 8.8% | 4.7% |
| H2O [% mol] | 60.5% | 47.0% | 89.0% | 57.7% | 47.7% | 95.3% |
| CO [% mol] | 1.7% | 2.2% | 0.0% | 1.0% | 1.8% | 0.0% |
| CO2 [% mol] | 21.2% | 24.7% | 0.0% | 20.8% | 26.4% | 0.0% |
| CH4 [% mol] | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| N2 [% mol] | 8.8% | 19.4% | 3.8% | 12.8% | 15.4% | 0.0% |
| Cathode Air Input [kmol/h] | 1.3217 | 1.3217 | 1.3950 | 1.6141 | 1.5778 | 1.6915 |
| Cathode Air Output [kmol/h] | 1.2628 | 1.2632 | 1.3451 | 1.5452 | 1.5109 | 1.6252 |
| Air-to-Fuel Ratio [%] | 3.36 | 2.99 | 2.43 | 3.29 | 3.33 | 2.43 |
| HT | LT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | |
| PTOT STACK | 6.79 | 6.77 | 6.71 | 8.25 | 7.73 | 8.91 |
| Stack current [A] | 35 | 35 | 30 | 31 | 30 | 30 |
| Stack voltage [V] | 135 | 149 | 153 | 186 | 186 | 186 |
| Pelectrical [kW] | 4.74 | 5.21 | 4.55 | 5.76 | 5.59 | 5.54 |
| Pthermal [kW] | 2.08 | 1.57 | 2.32 | 2.53 | 2.14 | 3.74 |
| Pelectrical/PTOT STACK [%] | 69% | 77% | 66% | 69% | 72% | 60% |
| Pthermal/PTOT STACK [%] | 31% | 23% | 34% | 31% | 28% | 40% |
| Panode/PTOT STACK [%] | 5% | 3% | 8% | 5% | 5% | 11% |
| Pcathode/PTOT STACK [%] | 20% | 14% | 20% | 19% | 17% | 22% |
| Pthermal-losses/PTOT [%] | 6% | 5% | 6% | 6% | 5% | 8% |
| Panode/Pthermal [%] | 15% | 15% | 23% | 17% | 18% | 27% |
| Pcathode/Pthermal [%] | 64% | 62% | 59% | 64% | 63% | 53% |
| Pthermal-losses/Pthermal [%] | 21% | 23% | 18% | 19% | 20% | 20% |
| HT | LT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | |
| HAIR BURNER INPUT [kW] | 9.26 | 8.87 | 9.80 | 9.53 | 9.24 | 10.43 |
| HFUEL BURNER INPUT [kW] | 1.04 | 1.12 | 0.98 | 1.11 | 1.06 | 1.11 |
| LHV FUEL BURNER INPUT [kW] | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.56 | 0.87 | 1.04 | 0.44 |
| HBURNER OUTPUT [kW] | 11.08 | 10.82 | 11.34 | 11.51 | 11.34 | 11.98 |
| QHEAIRCAT [kW] | 7.60 | 7.68 | 7.85 | 7.54 | 7.60 | 7.73 |
| QHEAIRCAT/HBURNER OUTPUT | 69% | 71% | 69% | 66% | 67% | 65% |
| QHEAIRATR [kW] | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0 |
| QHEAIRATR/HBURNER OUTPUT | 0.36% | 0.55% | 0.18% | 0.35% | 0.53% | 0.00% |
| QSENS [kW] | 2.47 | 2.21 | 2.30 | 2.87 | 2.77 | 2.91 |
| QSENS/HBURNER OUTPUT | 22% | 20% | 20% | 25% | 24% | 24% |
| HT | LT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | |
| [kW] | 7.80 | 7.94 | 7.43 | 9.31 | 8.93 | 9.35 |
| [kW] | 0.23 | 0.34 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.00 |
| [kW] | 6.79 | 6.77 | 6.71 | 8.25 | 7.73 | 8.91 |
| [kW] | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.56 | 0.87 | 1.04 | 0.44 |
| %ATR/FUEL | 3% | 4% | 2% | 2% | 2% | 0% |
| %SOFC/FUEL | 87% | 85% | 90% | 89% | 87% | 95% |
| %BURNER/FUEL | 10% | 10% | 7% | 9% | 12% | 5% |
| HT | LT | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | CH4-H2 | CH4 | H2 | |
| System ηelectrical | 61% | 66% | 61% | 62% | 63% | 59% |
| System ηThermal | 32% | 28% | 31% | 31% | 31% | 31% |
| Total System η | 92% | 93% | 92% | 93% | 94% | 90% |
| System UFF | 92% | 92% | 93% | 92% | 91% | 95% |
| Emissions [kg/h]CO2 | 1.19 | 1.57 | 0.00 | 1.41 | 1.76 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bocci, E.; Dell’Era, A.; Tregambe, C.; Tamburrano, G.; Marcantonio, V.; Santoni, F. The Development and Evaluation of a Low-Emission, Fuel-Flexible, Modular, and Interchangeable Solid Oxide Fuel Cell System Architecture for Combined Heat and Power Production: The SO-FREE Project. Energies 2025, 18, 2273. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092273
Bocci E, Dell’Era A, Tregambe C, Tamburrano G, Marcantonio V, Santoni F. The Development and Evaluation of a Low-Emission, Fuel-Flexible, Modular, and Interchangeable Solid Oxide Fuel Cell System Architecture for Combined Heat and Power Production: The SO-FREE Project. Energies. 2025; 18(9):2273. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092273
Chicago/Turabian StyleBocci, Enrico, Alessandro Dell’Era, Carlo Tregambe, Giacomo Tamburrano, Vera Marcantonio, and Francesca Santoni. 2025. "The Development and Evaluation of a Low-Emission, Fuel-Flexible, Modular, and Interchangeable Solid Oxide Fuel Cell System Architecture for Combined Heat and Power Production: The SO-FREE Project" Energies 18, no. 9: 2273. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092273
APA StyleBocci, E., Dell’Era, A., Tregambe, C., Tamburrano, G., Marcantonio, V., & Santoni, F. (2025). The Development and Evaluation of a Low-Emission, Fuel-Flexible, Modular, and Interchangeable Solid Oxide Fuel Cell System Architecture for Combined Heat and Power Production: The SO-FREE Project. Energies, 18(9), 2273. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18092273








