Learning and Characterizing Chaotic Attractors of a Lean Premixed Combustor
Abstract
1. Introduction
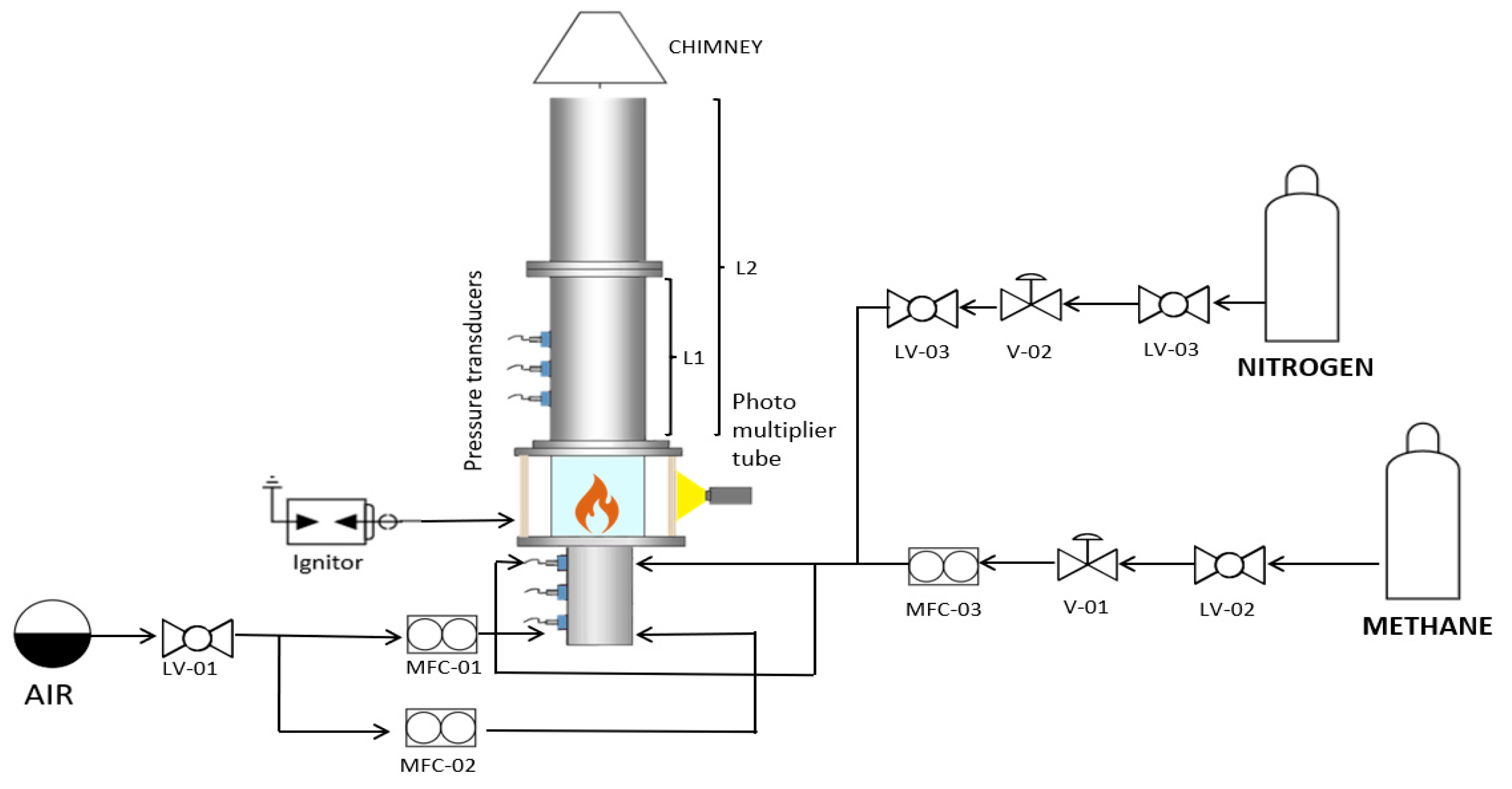
2. Methodology and Experimental Set up
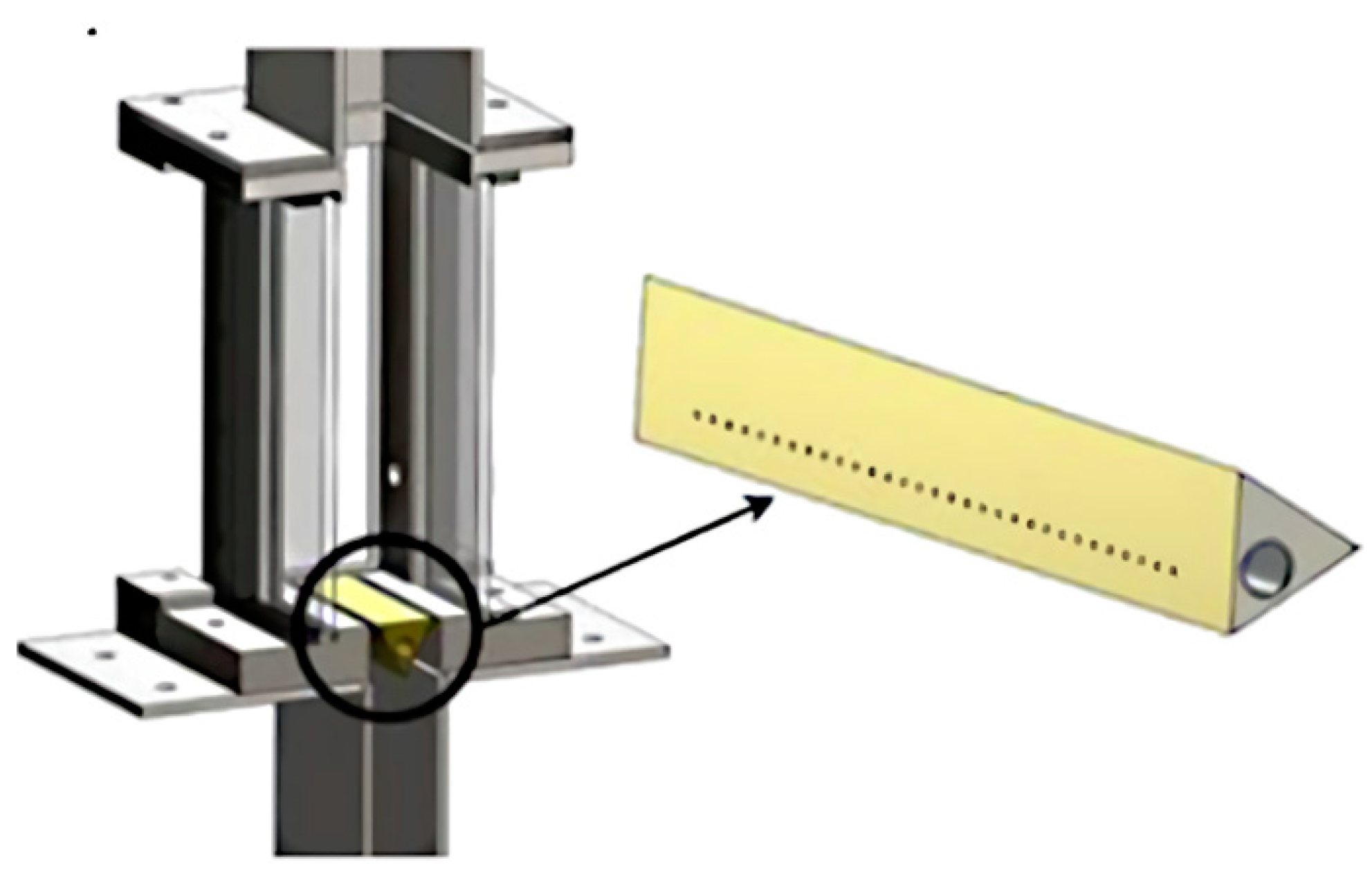
2.1. Experimental Set up
2.2. Instrumentation and Data Acquisition
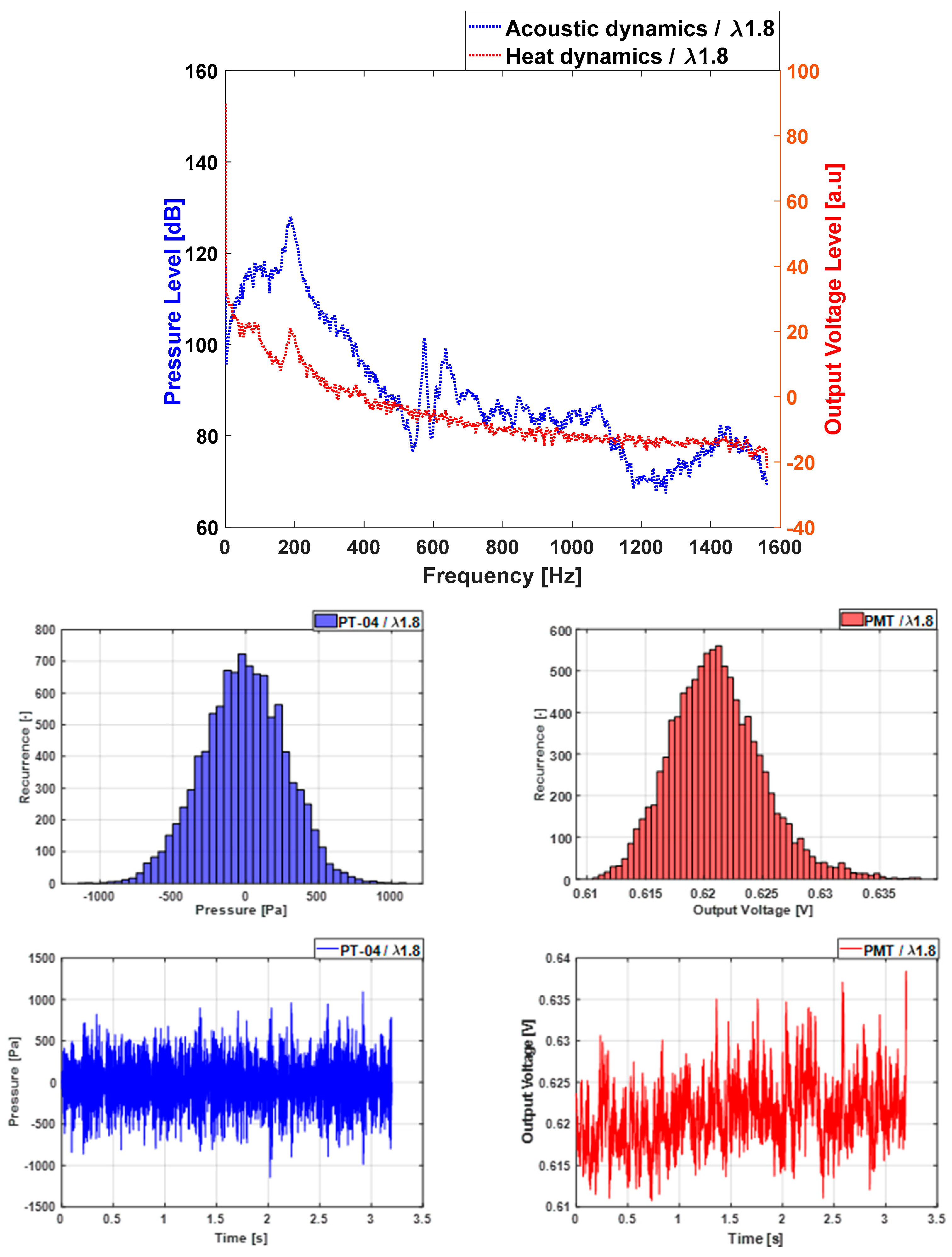
3. Analysis of Optics and Pressure Data
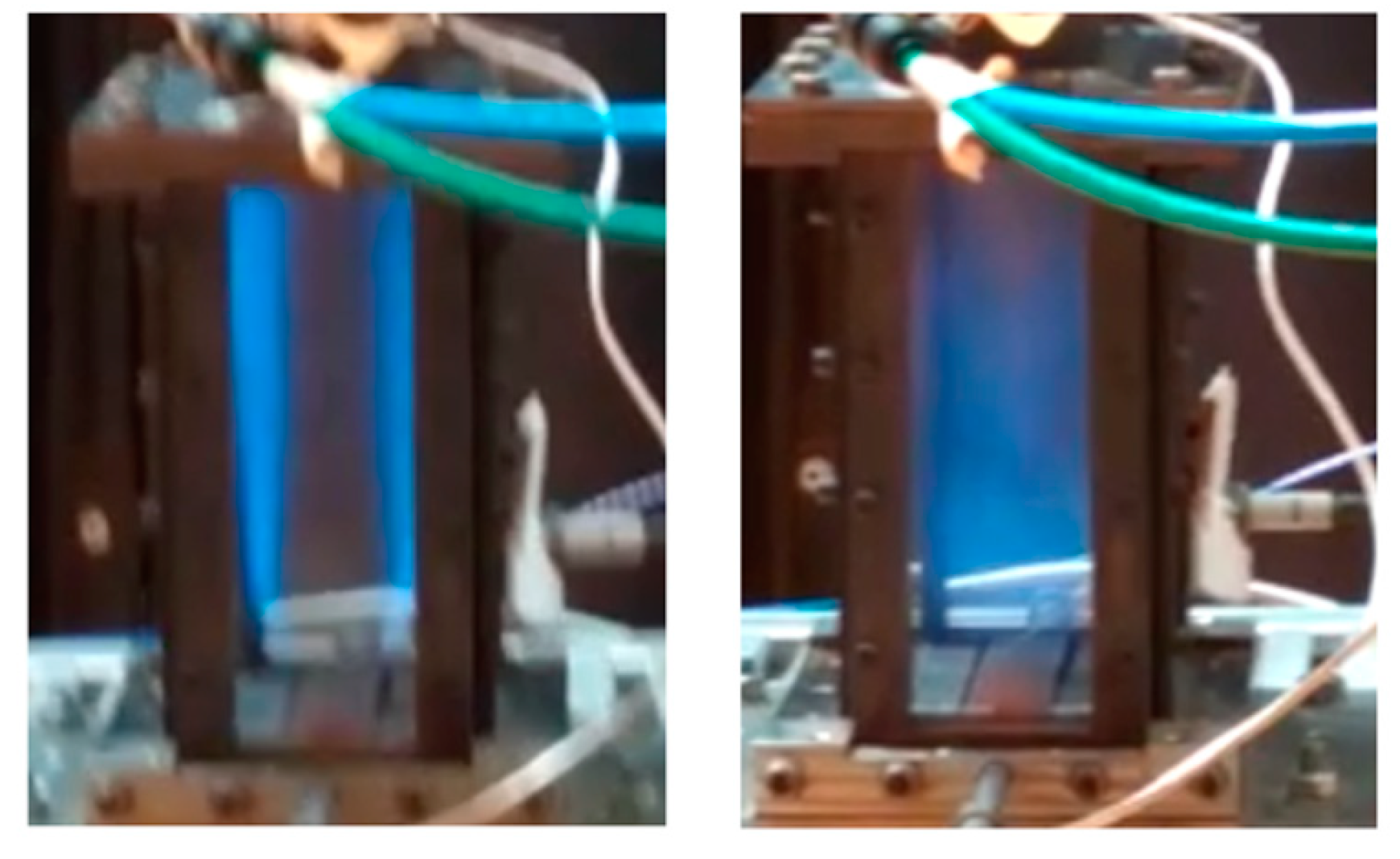
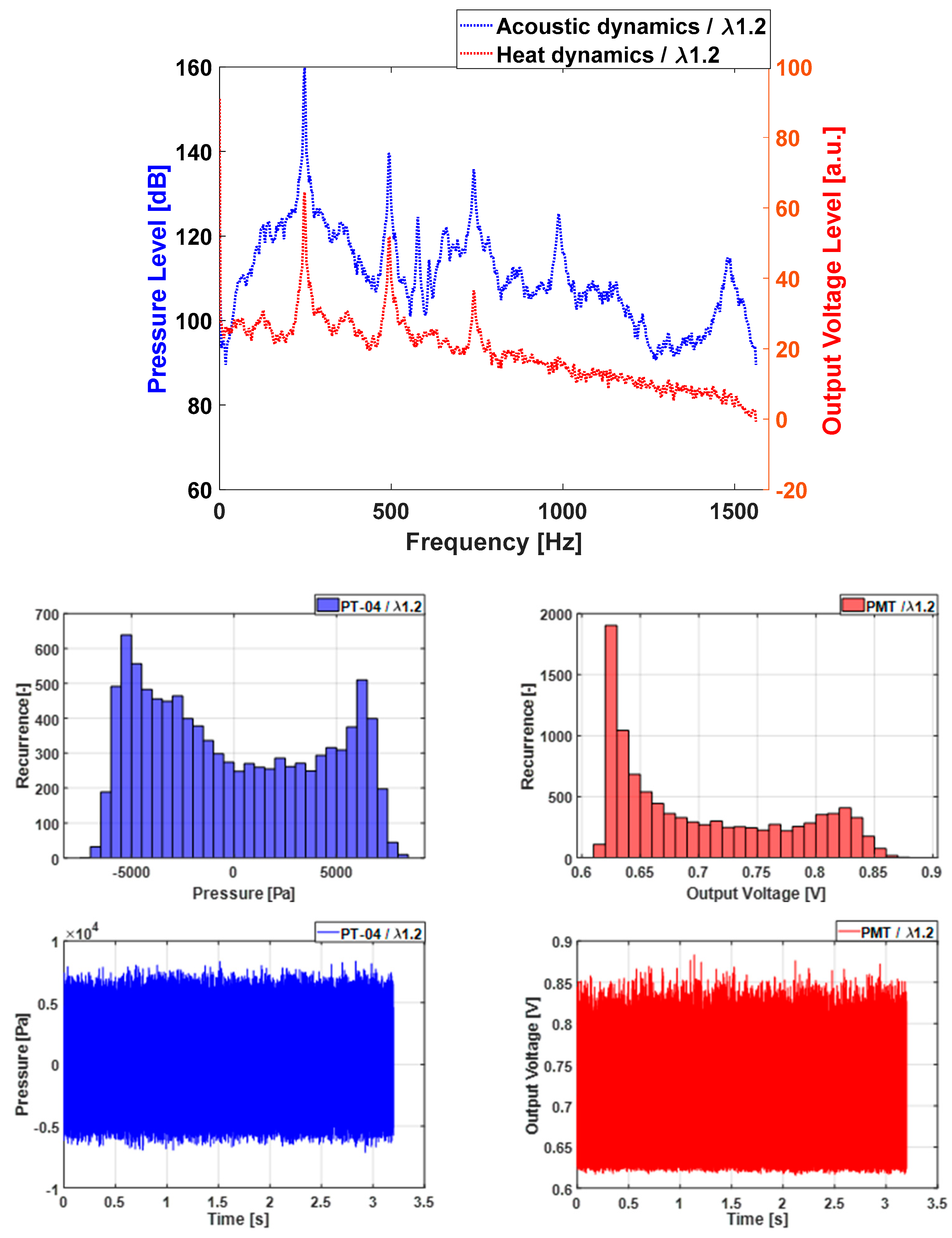
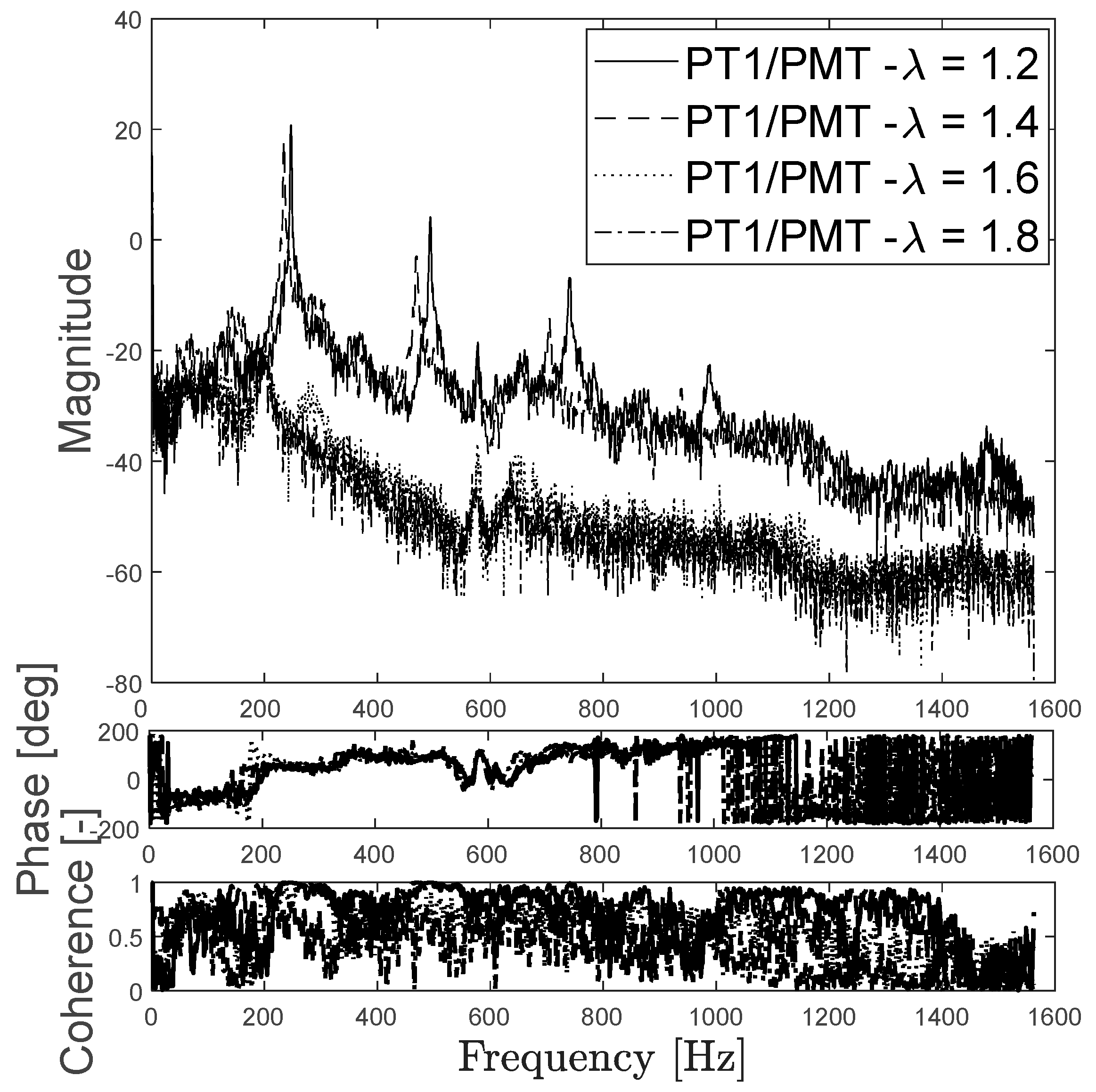
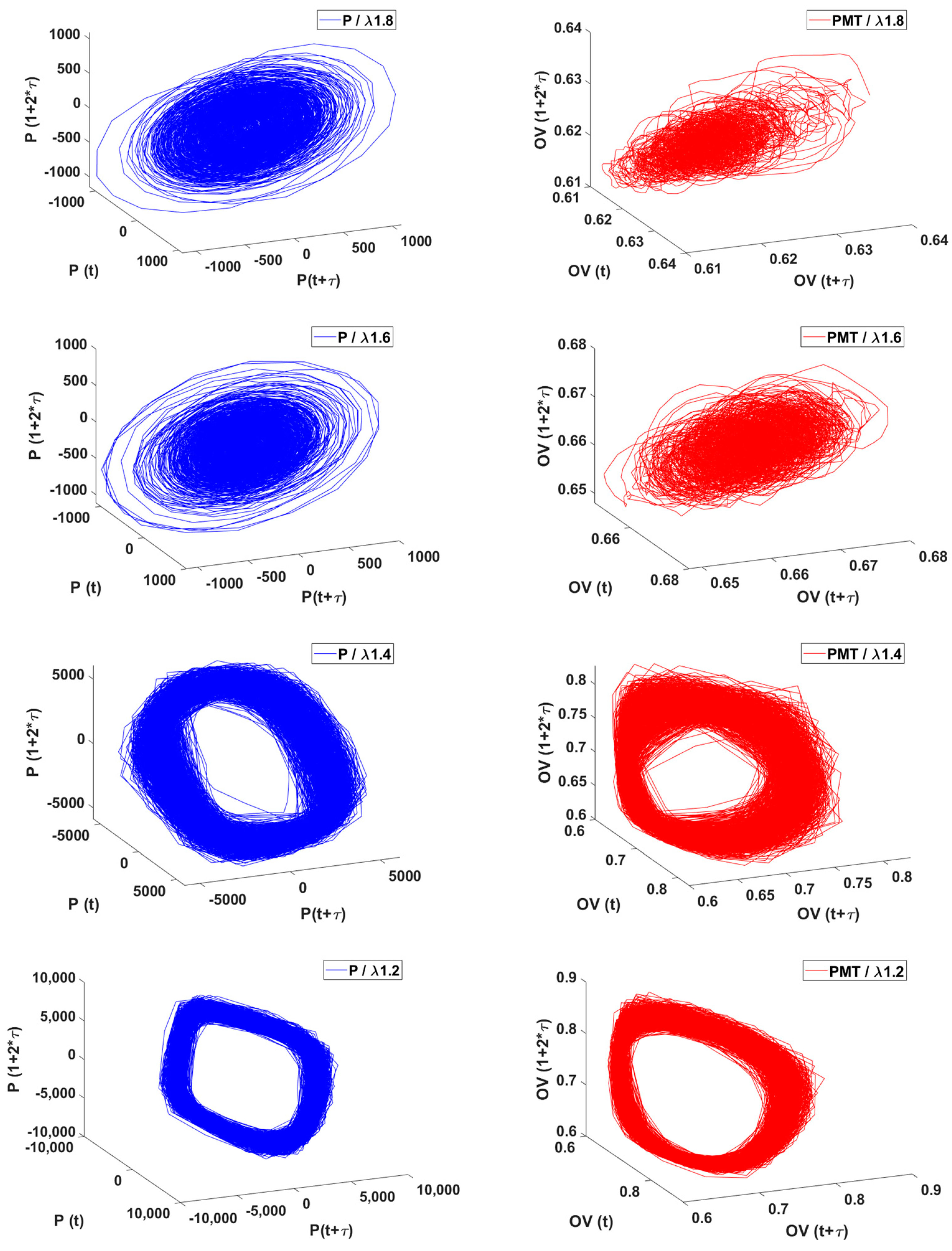
3.1. For the L1 Case (Original Length)
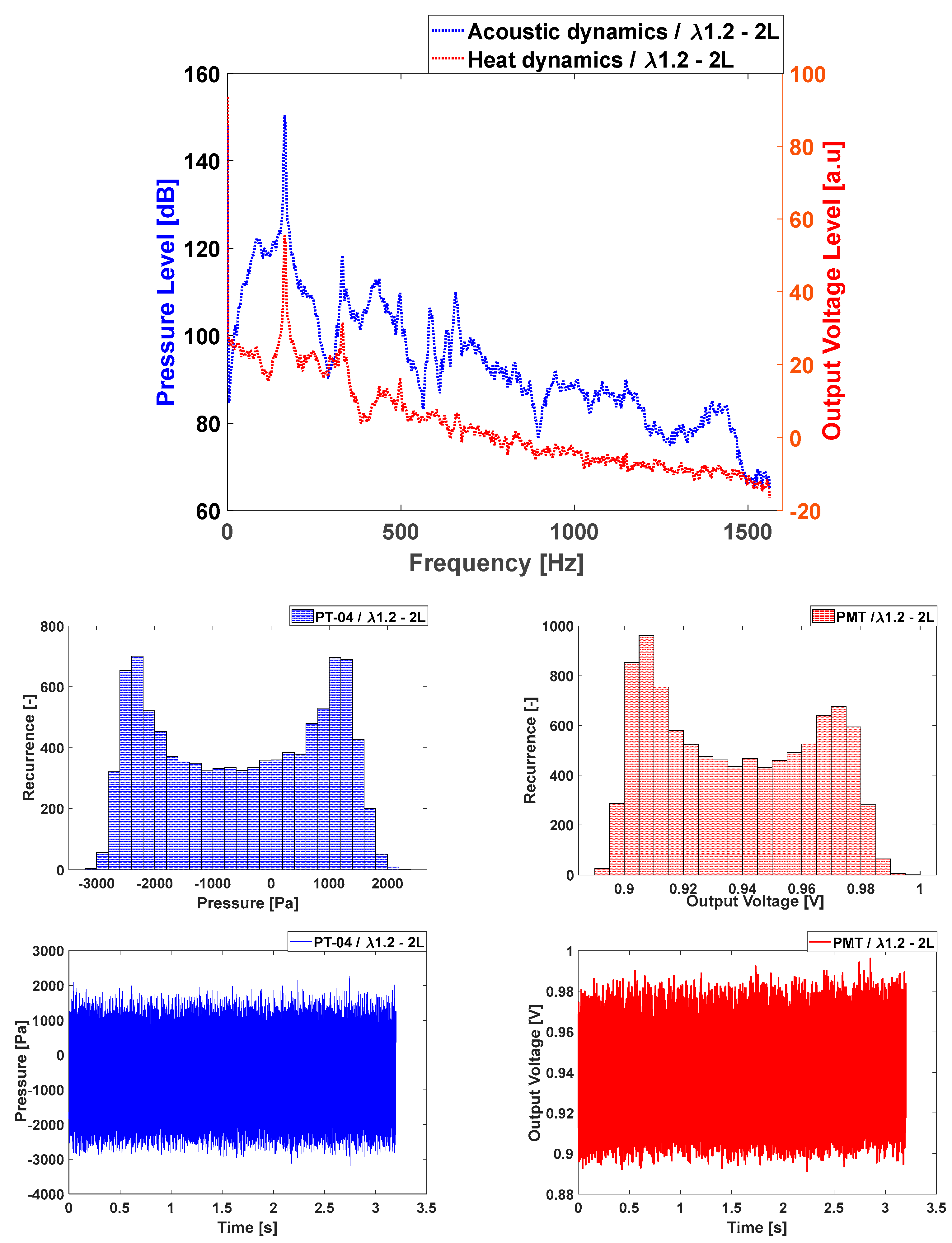
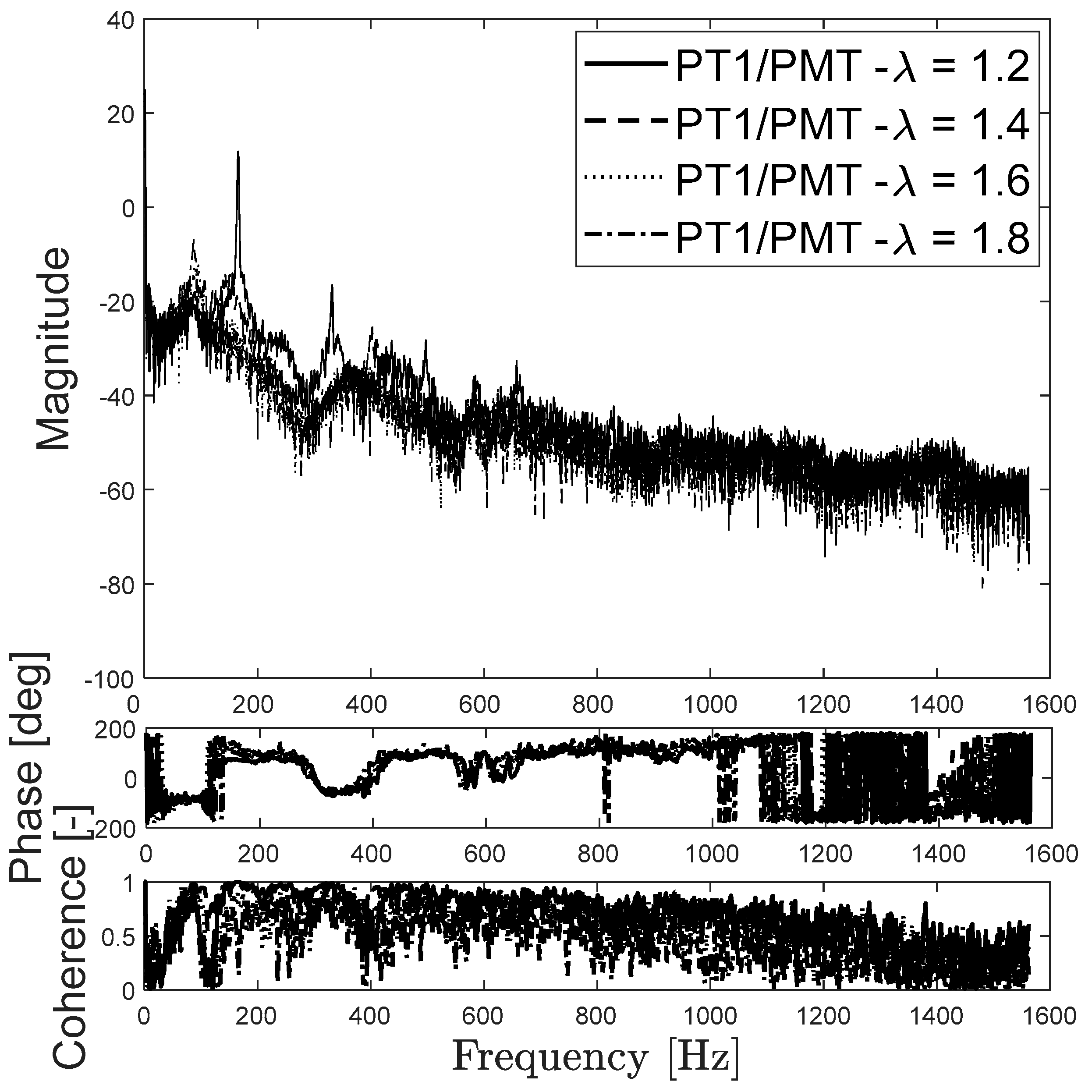
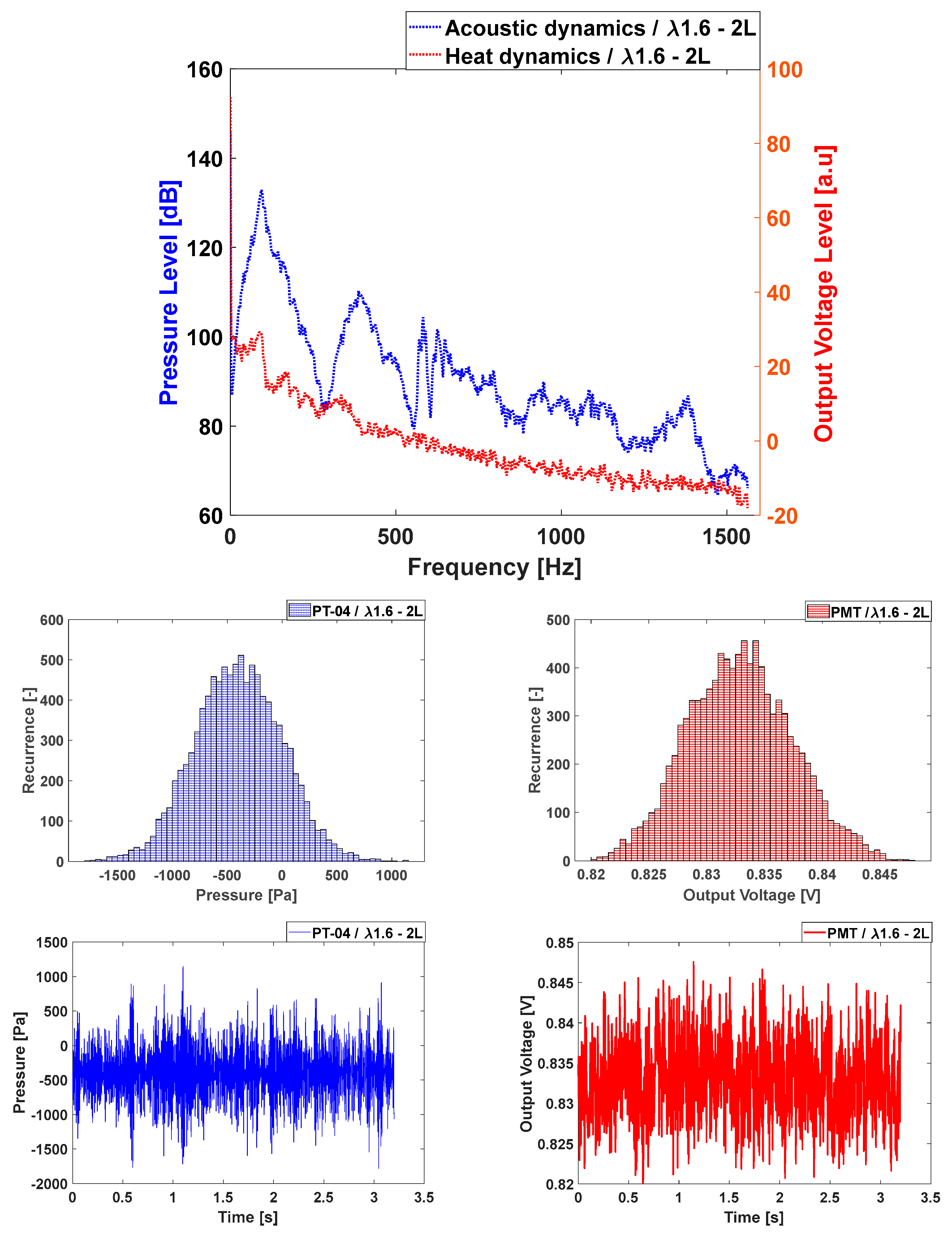
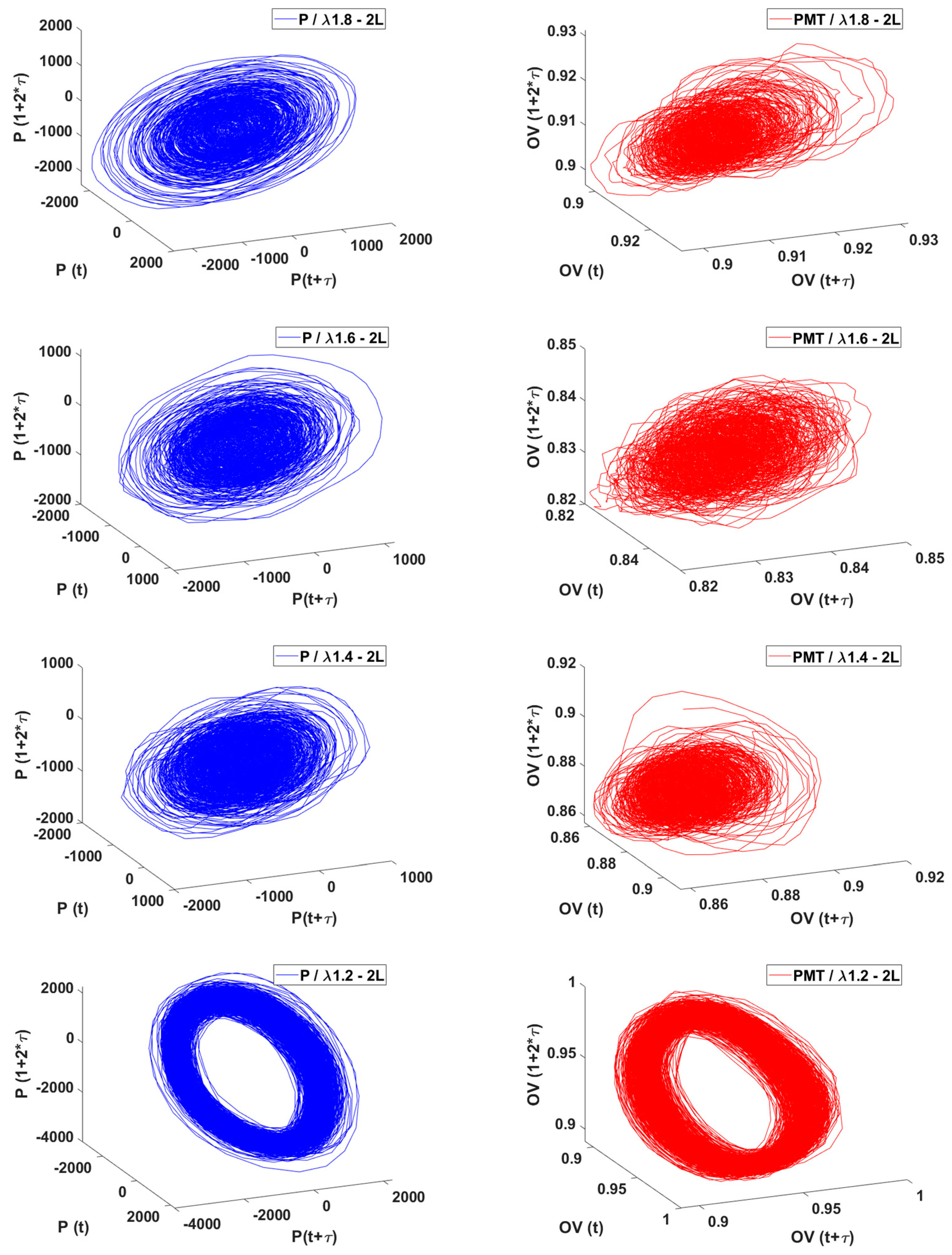
3.2. For the L2 Case (Double Length)
3.3. Intermittent Case for L2
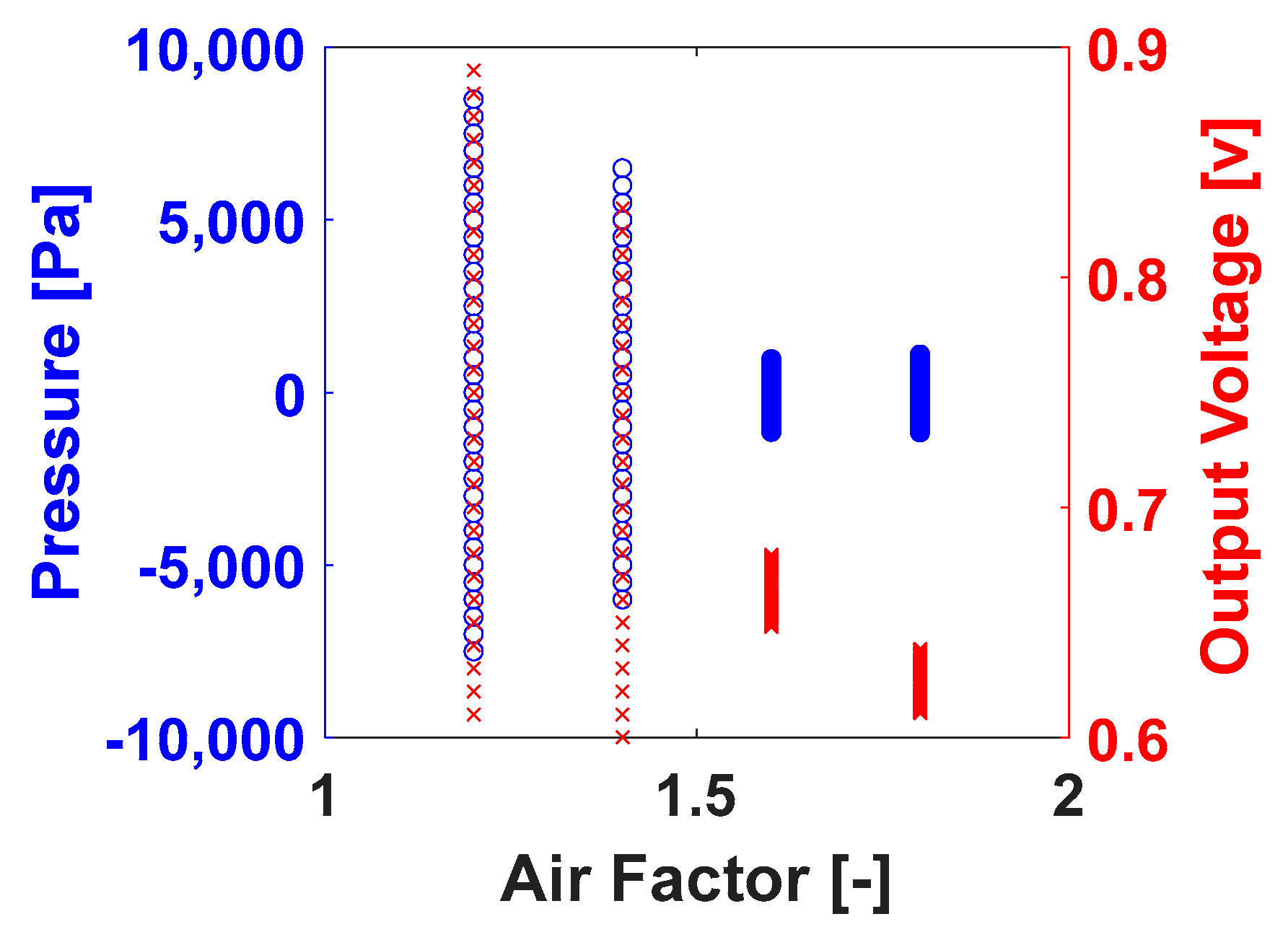
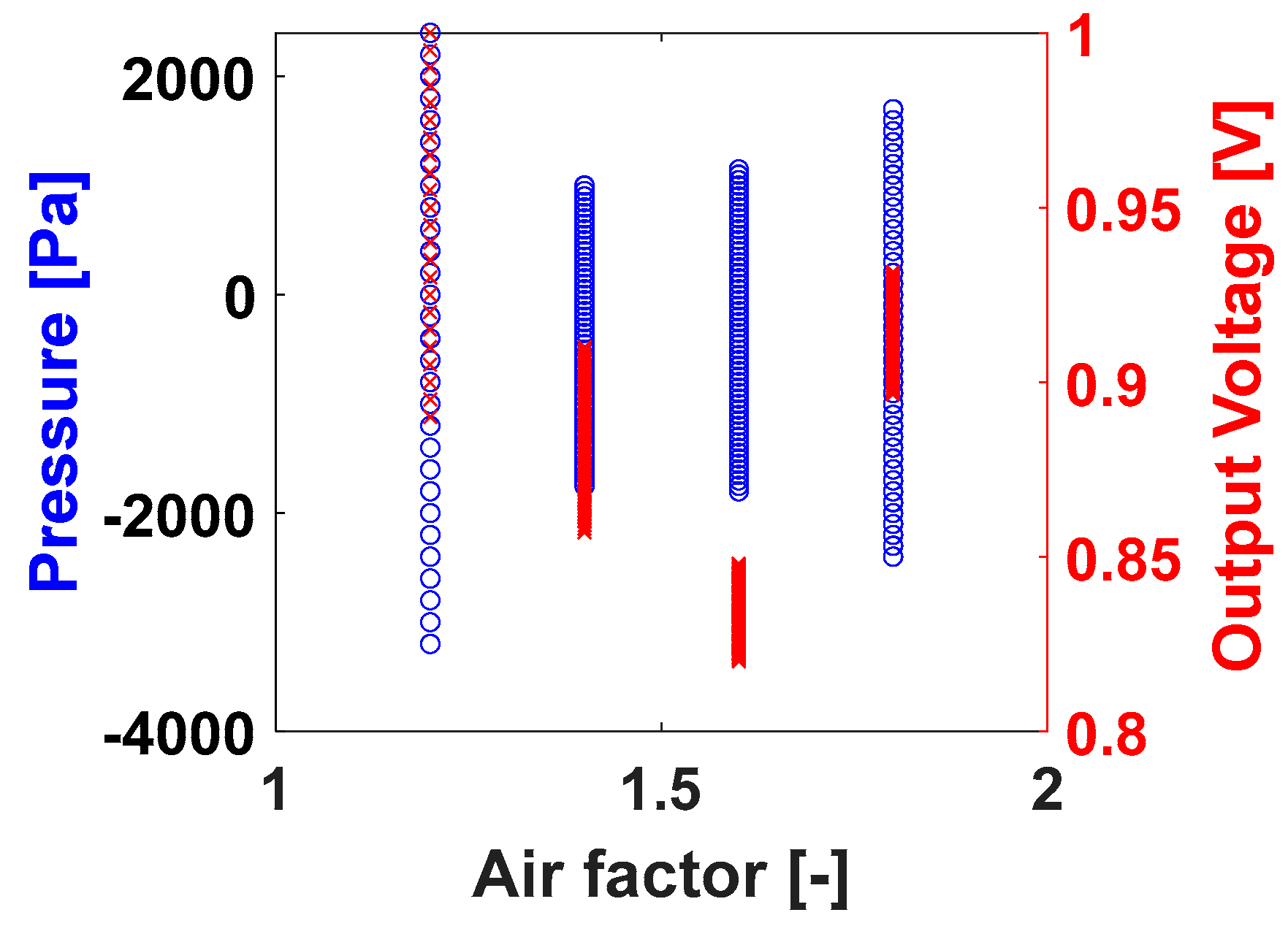
3.4. Bifurcation Diagrams
4. Nonlinear Analysis
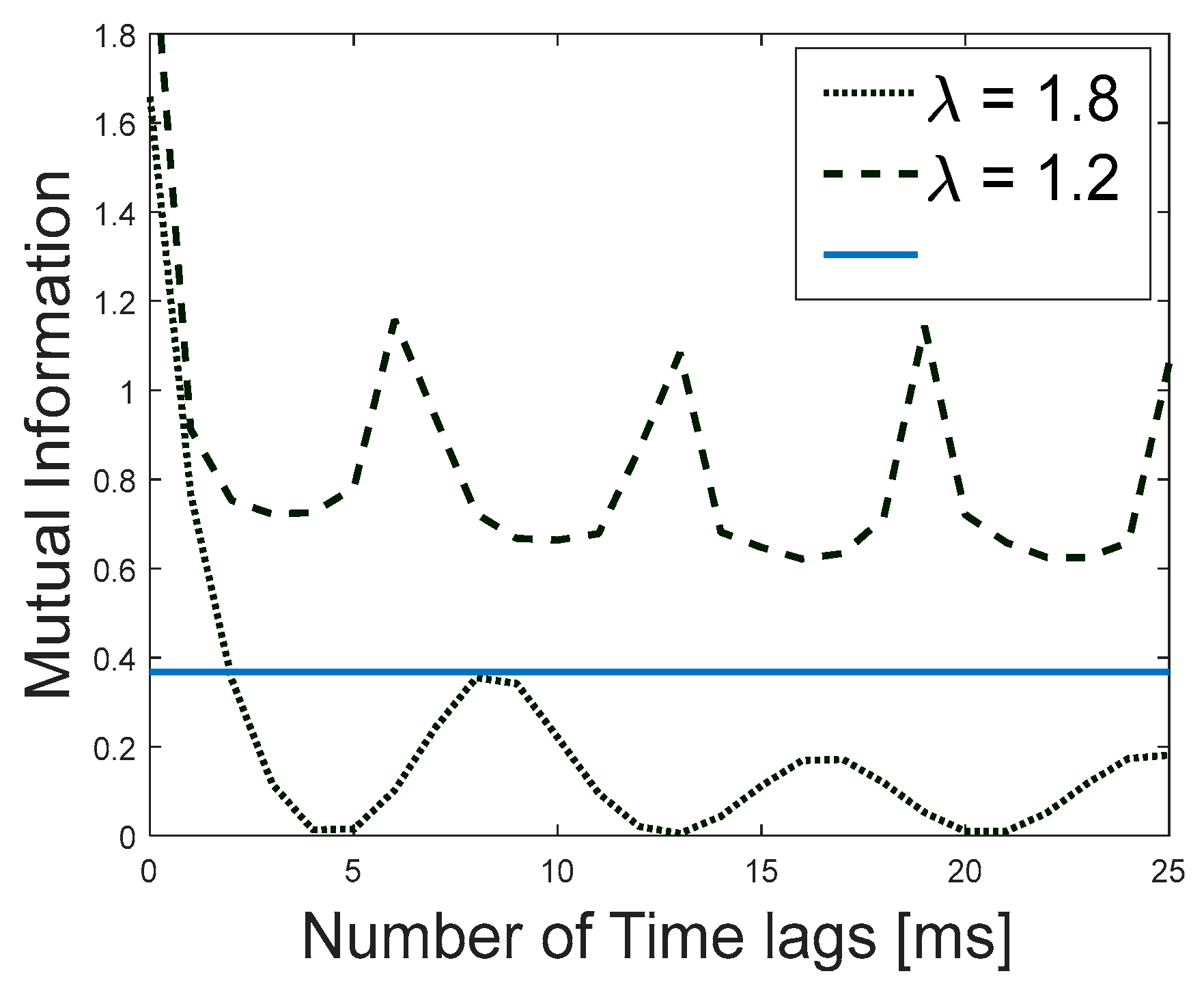
4.1. Average Mutual Information Function
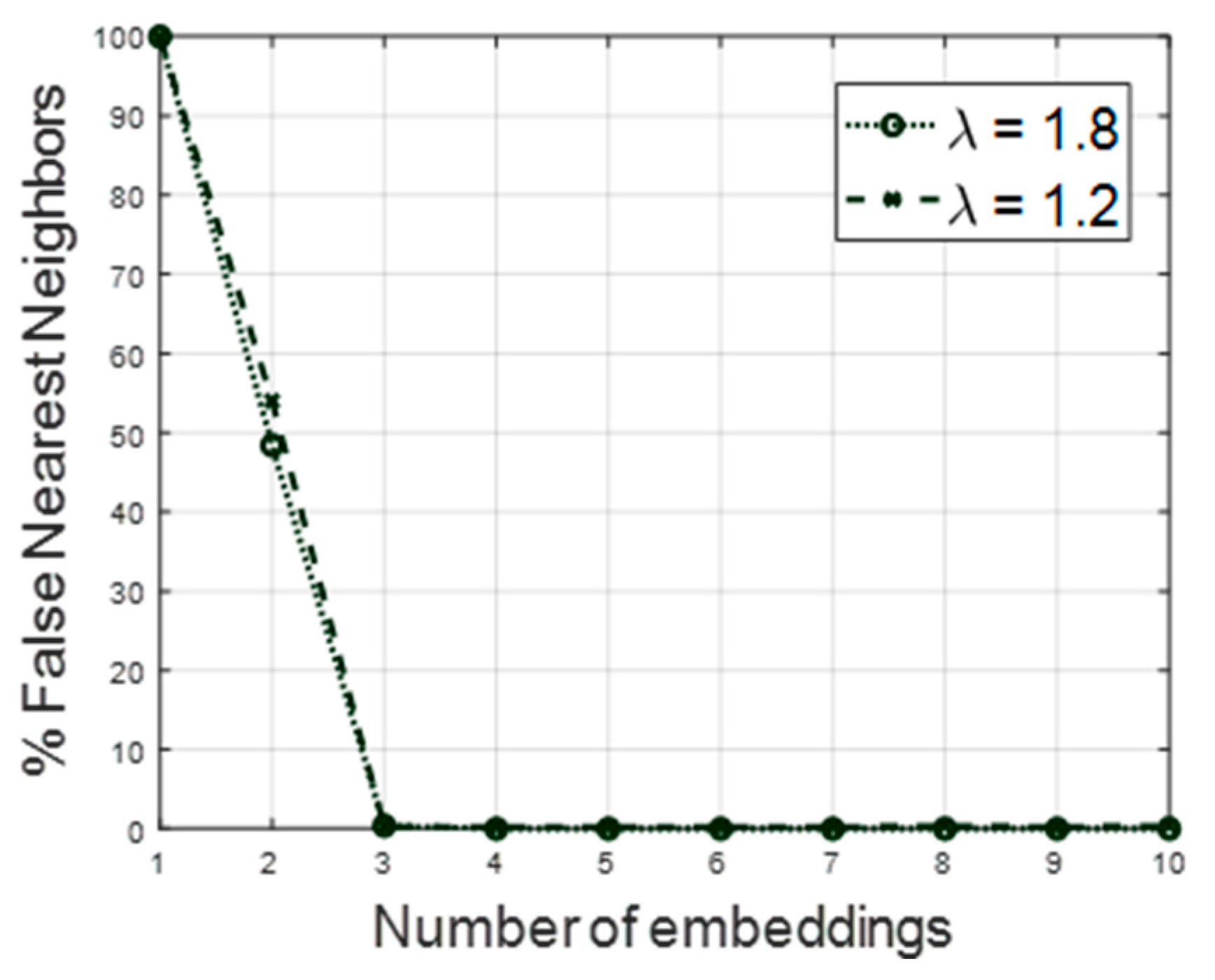
4.2. False Nearest Neighbors Function
4.3. Intermittent Case
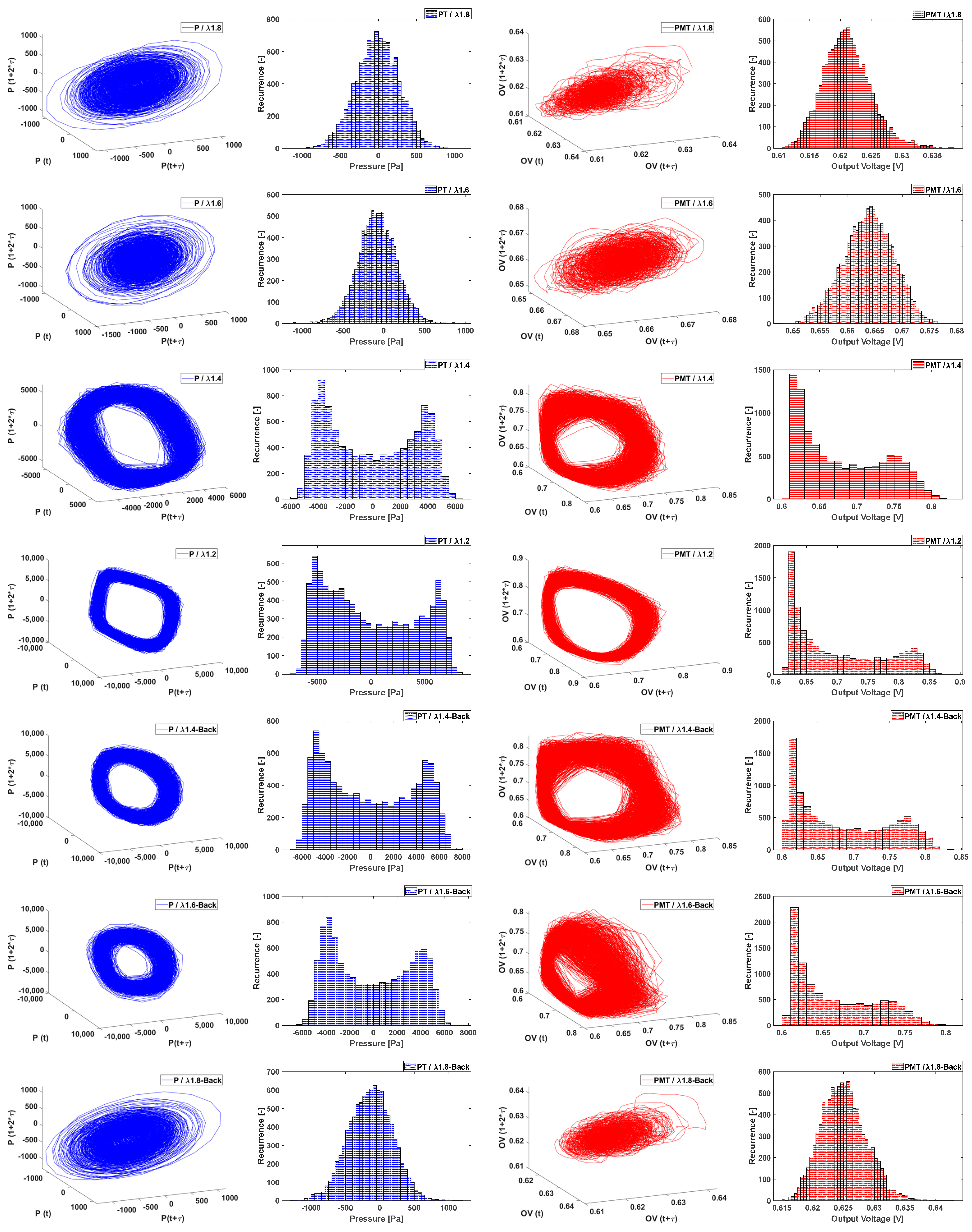
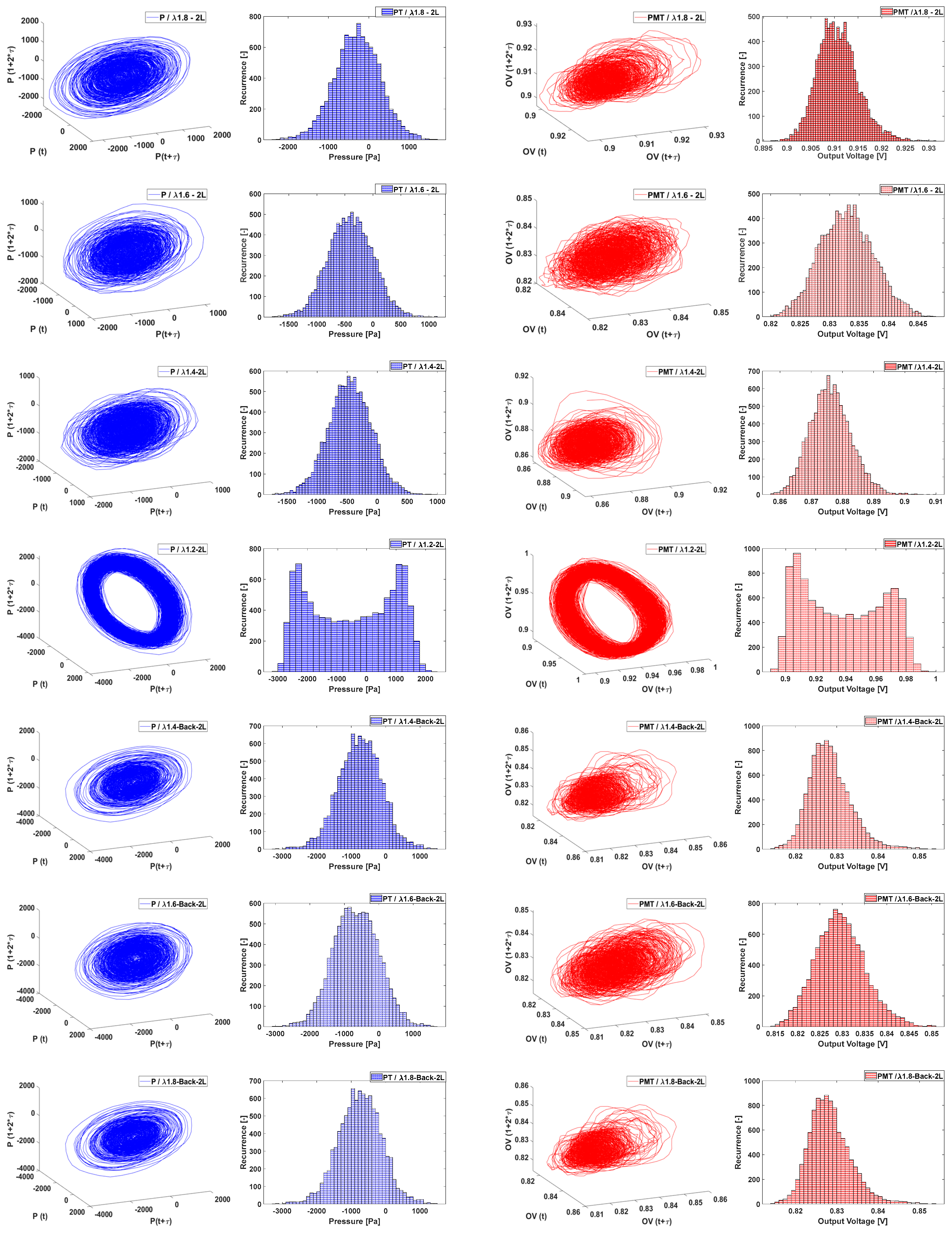
4.4. Hysteresis Effects: Histogram and Phase Portraits Approach
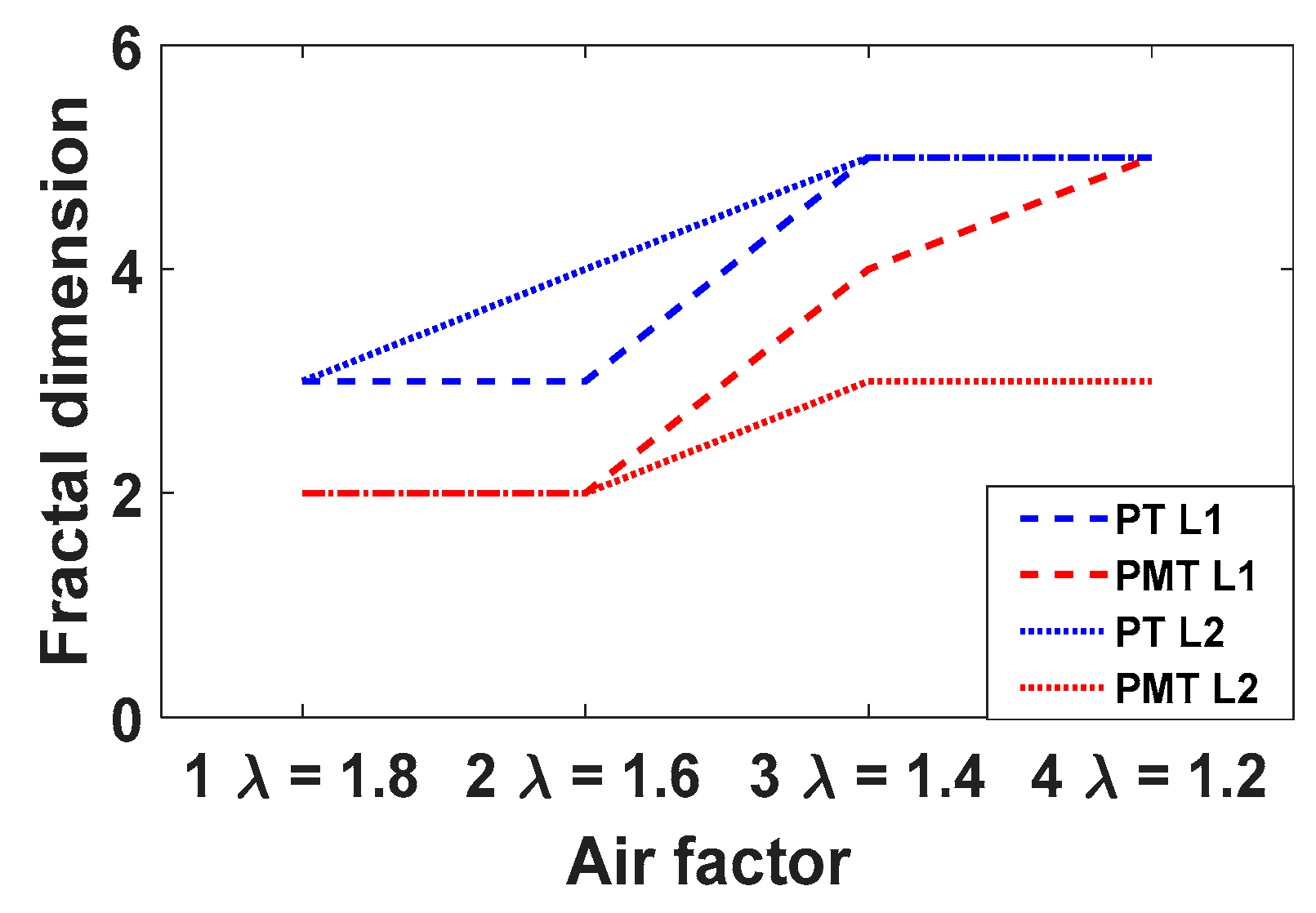
4.5. Fractal Dimension
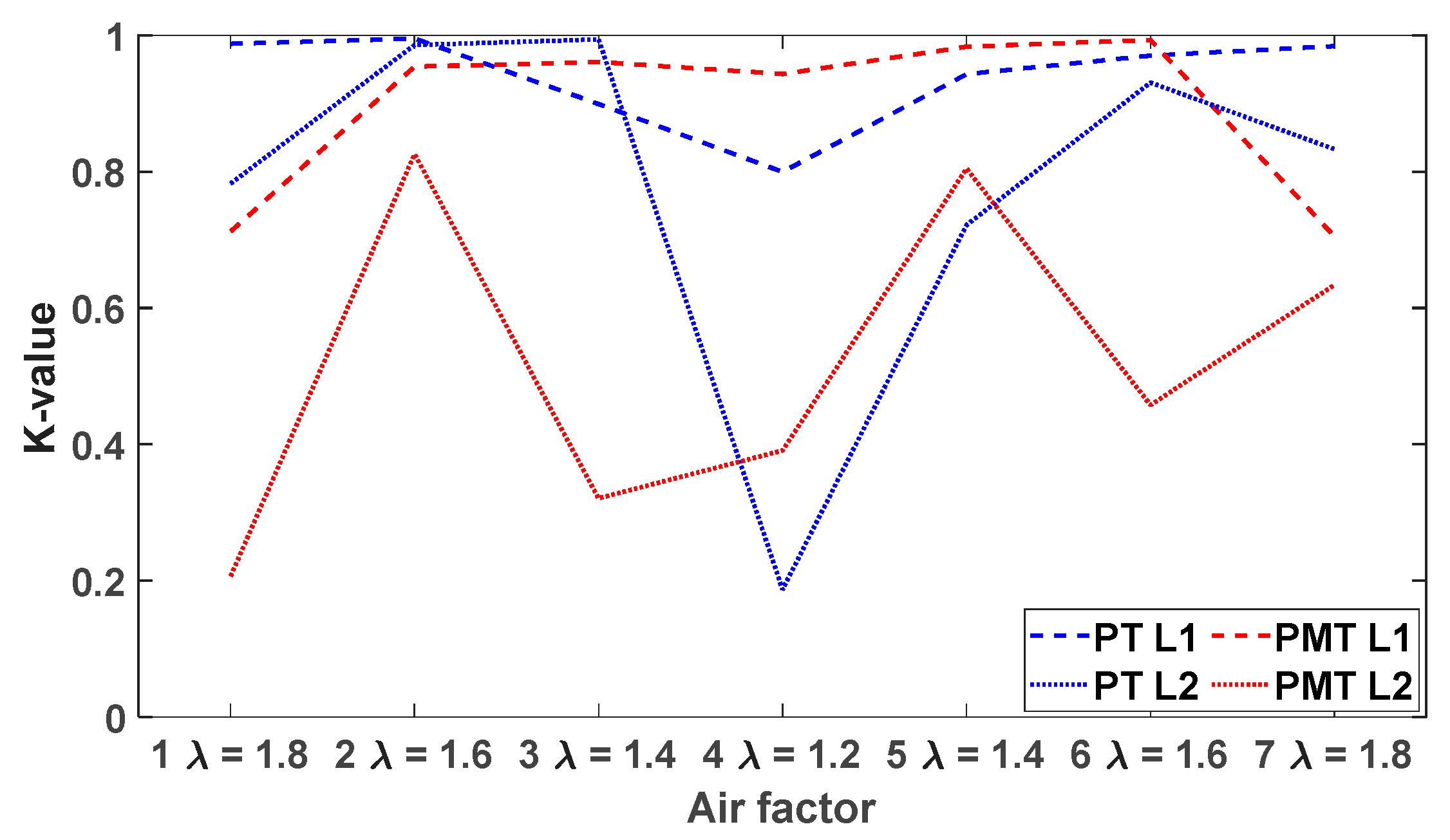
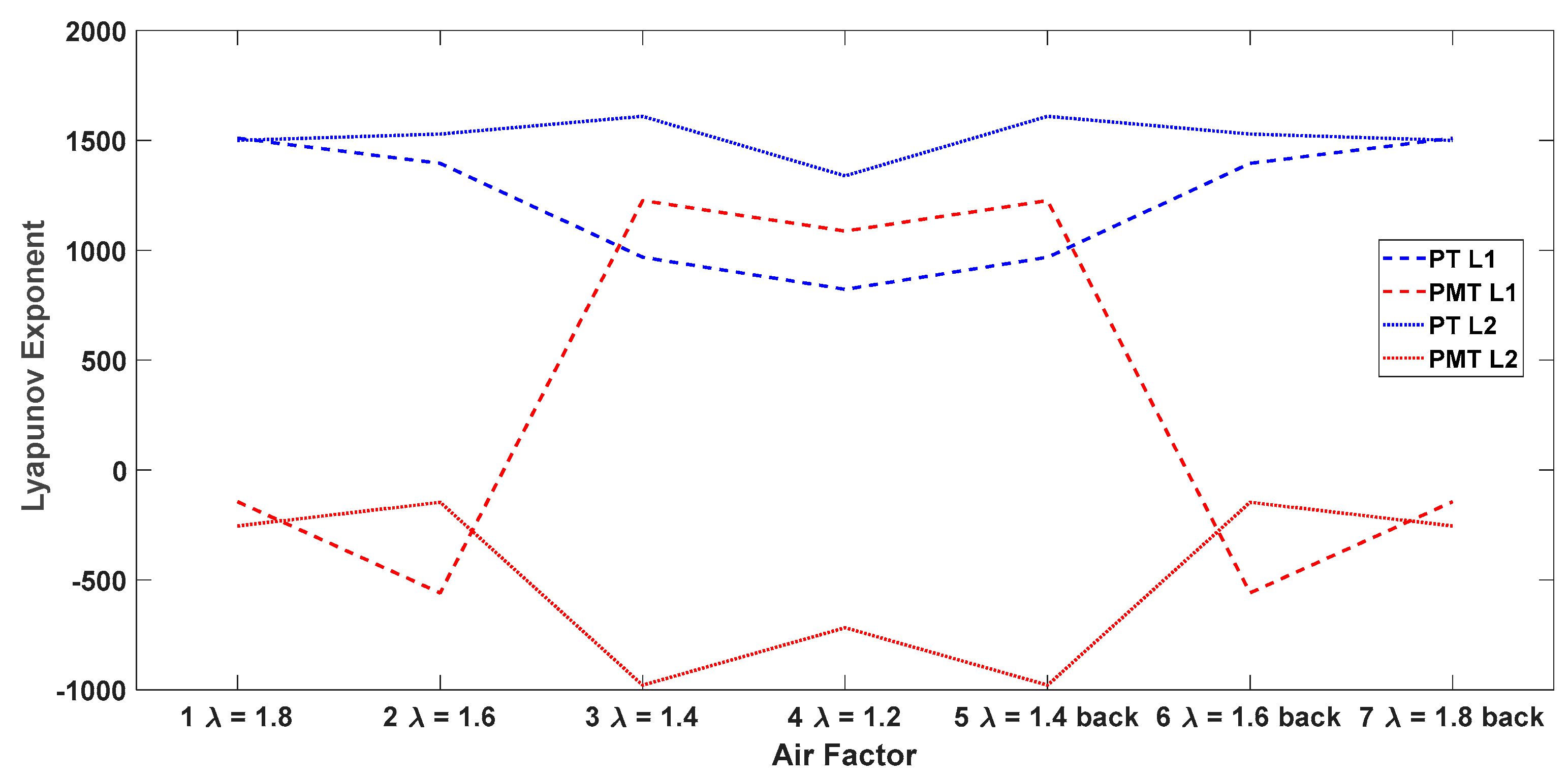
5. The 0-1 Test for Chaos
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ourbak, T.; Tubiana, L. Changing the game: The Paris Agreement and the role of scientific communities. Clim. Policy 2017, 17, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashchenko, D. Hydrogen-rich gas as a fuel for the gas turbines: A pathway to lower CO2 emission. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 173, 113117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinsot, T. Prediction and control of combustion instabilities in real engines. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, P. A review of active control approaches in stabilizing combustion systems in aerospace industry. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2018, 97, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoda, H.; Nikimoto, H.; Miyano, T.; Tachibana, S. Dynamic properties of combustion instability in a lean premixed gas-turbine combustor. Chaos 2011, 21, 013124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabiraj, L.; Sujith, R.I.; Wahi, P. Bifurcations of self-excited ducted laminar premixed flames. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2012, 134, 031502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Premchand, C.P.; Raghunathan, M.; Krishnan, A.; Nair, V.; Sujith, R.I. Critical region in the spatiotemporal dynamics of a turbulent thermoacoustic system and smart passive control. Combust. Flame 2021, 226, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Sujith, R.I. Multifractality in combustion noise: Predicting an impending combustion instability. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 747, 635–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unni, V.R.; Yogesh Prasaad, M.S.; Ravi, N.T.; Iqbal, S.M.; Pesala, B.; Sujith, R.I. Experimental investigation of bifurcations in a thermoacoustic engine. Int. J. Spray Combust. Dyn. 2015, 7, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlis, E.; Liu, Y.; Hardalupas, Y.; Taylor, A.M.K.P. H2 enrichment of CH4 blends in lean premixed gas turbine combustion: An experimental study on effects on flame shape and thermoacoustic oscillation dynamics. Fuel 2019, 254, 115524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palies, P.; Durox, D.; Schuller, T.; Candel, S. Nonlinear combustion instability analysis based on the flame describing function applied to turbulent premixed swirling flames. Combust. Flame 2011, 158, 1980–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Shahsavari, M.; Rao, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, B. Thermoacoustic instability drivers and mode transitions in a lean premixed methane-air combustor at various swirl intensities. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2021, 38, 6115–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, R.; Schouten, J.C.; Giles, C.L.; Takens, F.; Bleek, C.M. van den Learning Chaotic Attractors by Neural Networks. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2355–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, J.D.; Sidorowich, J.J. Predicting chaotic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abarbanel, H.D.I. Analysis of Observed Chaotic Data; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0-387-98372-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T.; Murayama, S.; Hachijo, T.; Gotoda, H. Early Detection of Thermoacoustic Combustion Instability Using a Methodology Combining Complex Networks and Machine Learning. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo, S.N.; Kok, J. A model to study spontaneous oscillations in a lean premixed combustor using non linear analysis. In Proceedings of the 26th International Congress on Sound and Vibration, ICSV 2019—Hotel Bonaventure, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–11 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Takens, F. Detecting Strange Attractors in Turbulence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981; pp. 366–381. [Google Scholar]
- Wallot, S.; Mønster, D. Calculation of Average Mutual Information (AMI) and false-nearest neighbors (FNN) for the estimation of embedding parameters of multidimensional time series in matlab. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, A.K.; Koyama, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Fujita, O. Effect of geometrical parameters on thermo-acoustic instability of downward propagating flames in tubes. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KERSTEIN, A.R. Fractal Dimension of Turbulent Premixed Flames. Combust. Sci. Technol. 1988, 60, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Hagiwara, Y.; Hitomi, S.; Kuwana, K. Flame Propagation and Fractal Dimension in a Concentric Double Cylinders Apparatus. J. Jpn. Soc. Exp. Mech. 2014, 14, s101–s104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Gupta, V.; Li, L.K.B. Intermittency route to self-excited chaotic thermoacoustic oscillations. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 894, R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwald, G.A.; Melbourne, I. A new test for chaos in deterministic systems. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 460, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstein, M.T.; Collins, J.J.; De Luca, C.J. A practical method for calculating largest Lyapunov exponents from small data sets. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 1993, 65, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navarro-Arredondo, S.; Kok, J.B.W. Learning and Characterizing Chaotic Attractors of a Lean Premixed Combustor. Energies 2025, 18, 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071852
Navarro-Arredondo S, Kok JBW. Learning and Characterizing Chaotic Attractors of a Lean Premixed Combustor. Energies. 2025; 18(7):1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071852
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavarro-Arredondo, Sara, and Jim B. W. Kok. 2025. "Learning and Characterizing Chaotic Attractors of a Lean Premixed Combustor" Energies 18, no. 7: 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071852
APA StyleNavarro-Arredondo, S., & Kok, J. B. W. (2025). Learning and Characterizing Chaotic Attractors of a Lean Premixed Combustor. Energies, 18(7), 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18071852





