A WGAN-GP Approach for Data Imputation in Photovoltaic Power Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Proposing the Concept of Data Imputation
- (2)
- Designing a PV Data Imputation Network
- (3)
- Validating the Generated Data
2. Related Work
2.1. Interpolation-Based Methods
2.2. Classical Machine Learning Methods
2.2.1. Regression-Based Methods
2.2.2. Other Machine Learning Methods
2.3. Deep Learning-Based Methods
2.3.1. Supervised Learning Methods
2.3.2. Semi-Supervised Learning Methods
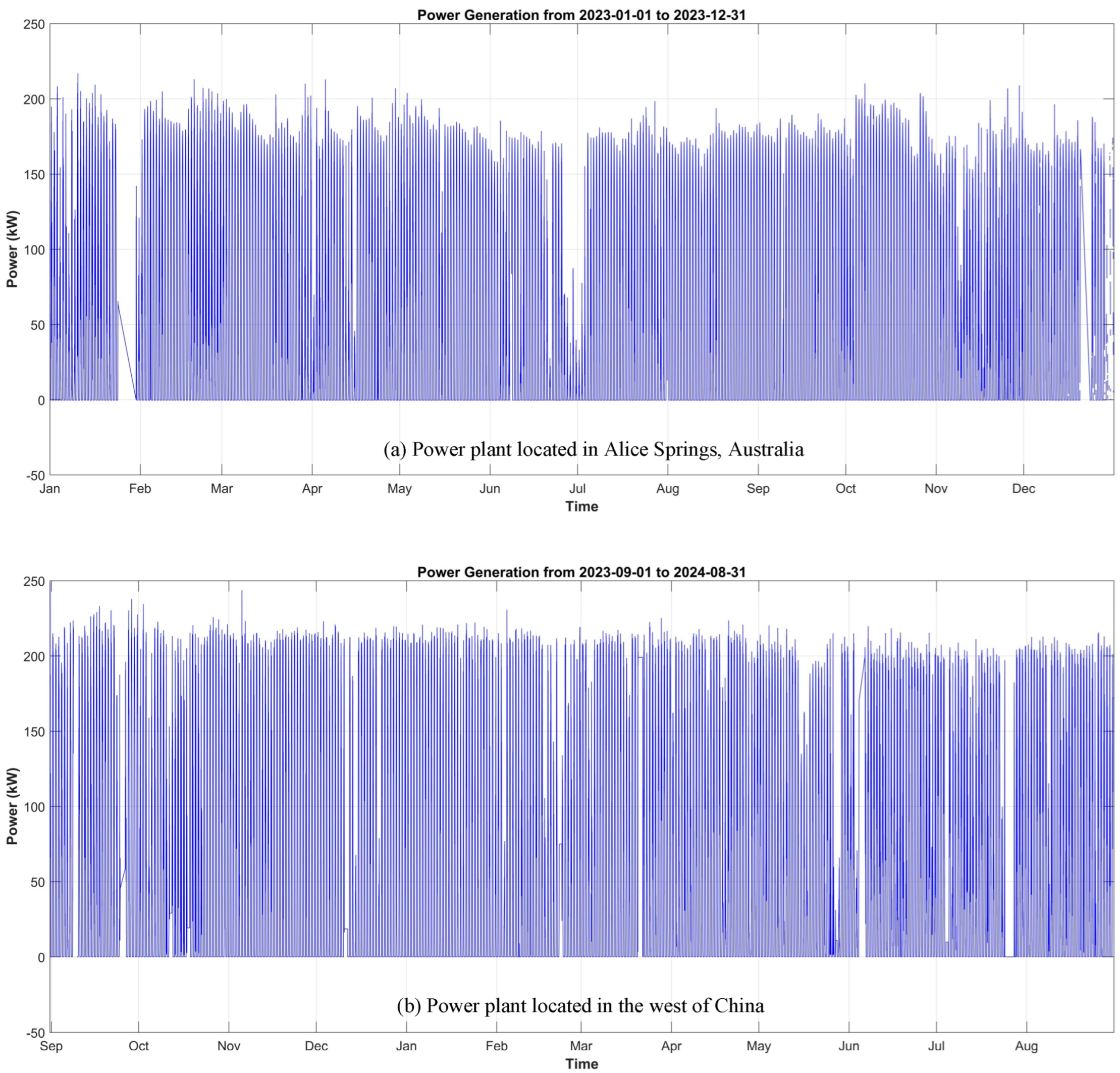
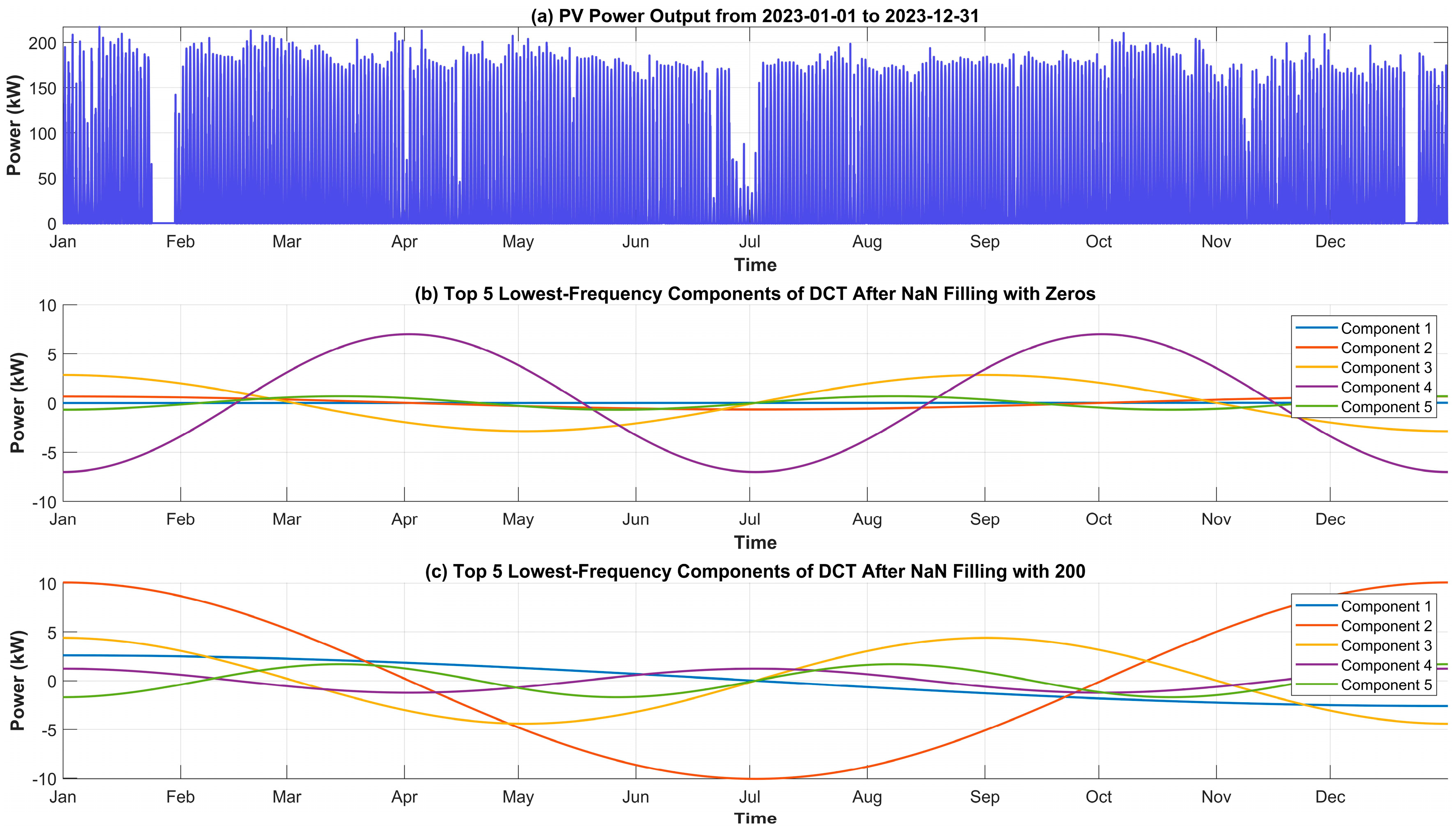
3. Data Continuity Analysis
4. Data Imputation
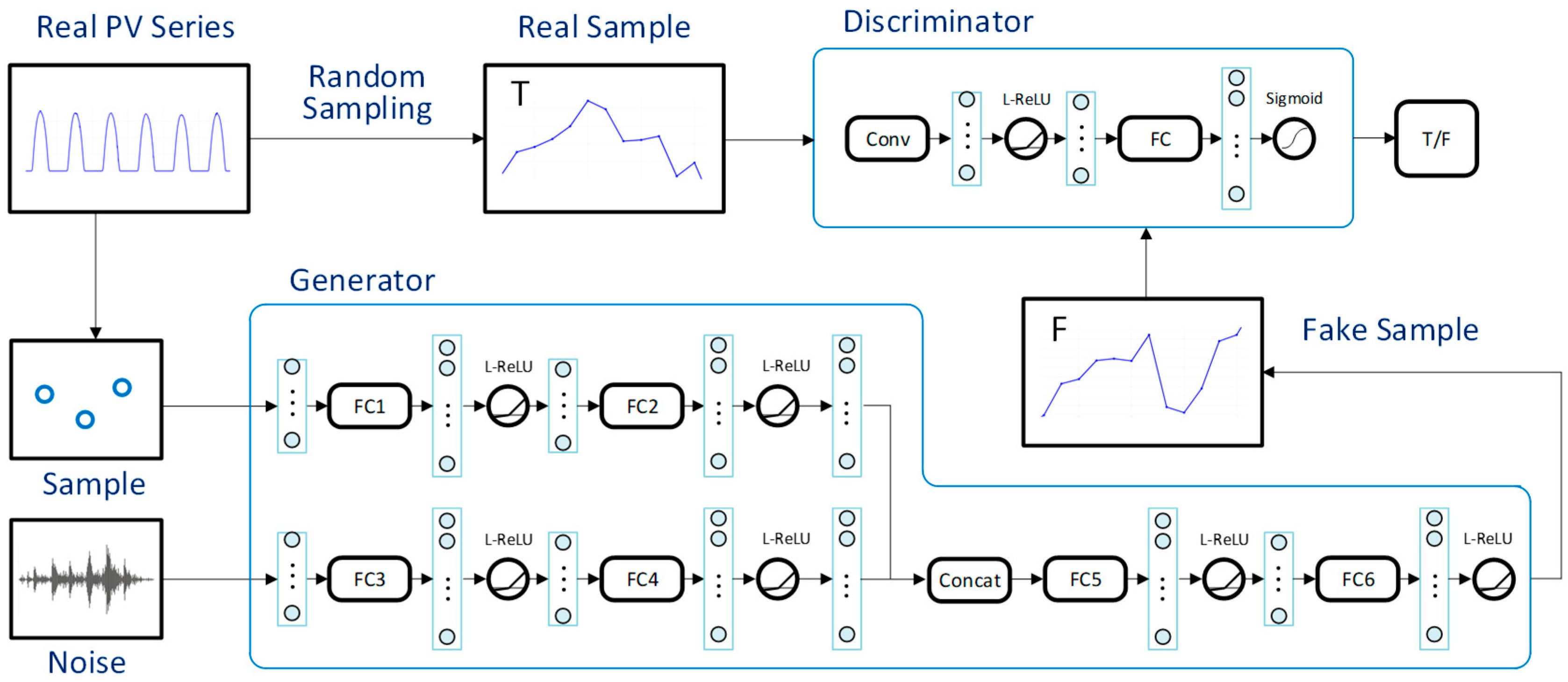
4.1. Generator
4.2. Discriminator
4.3. Loss Function
4.4. Hyperparameter Determination
5. Experiments
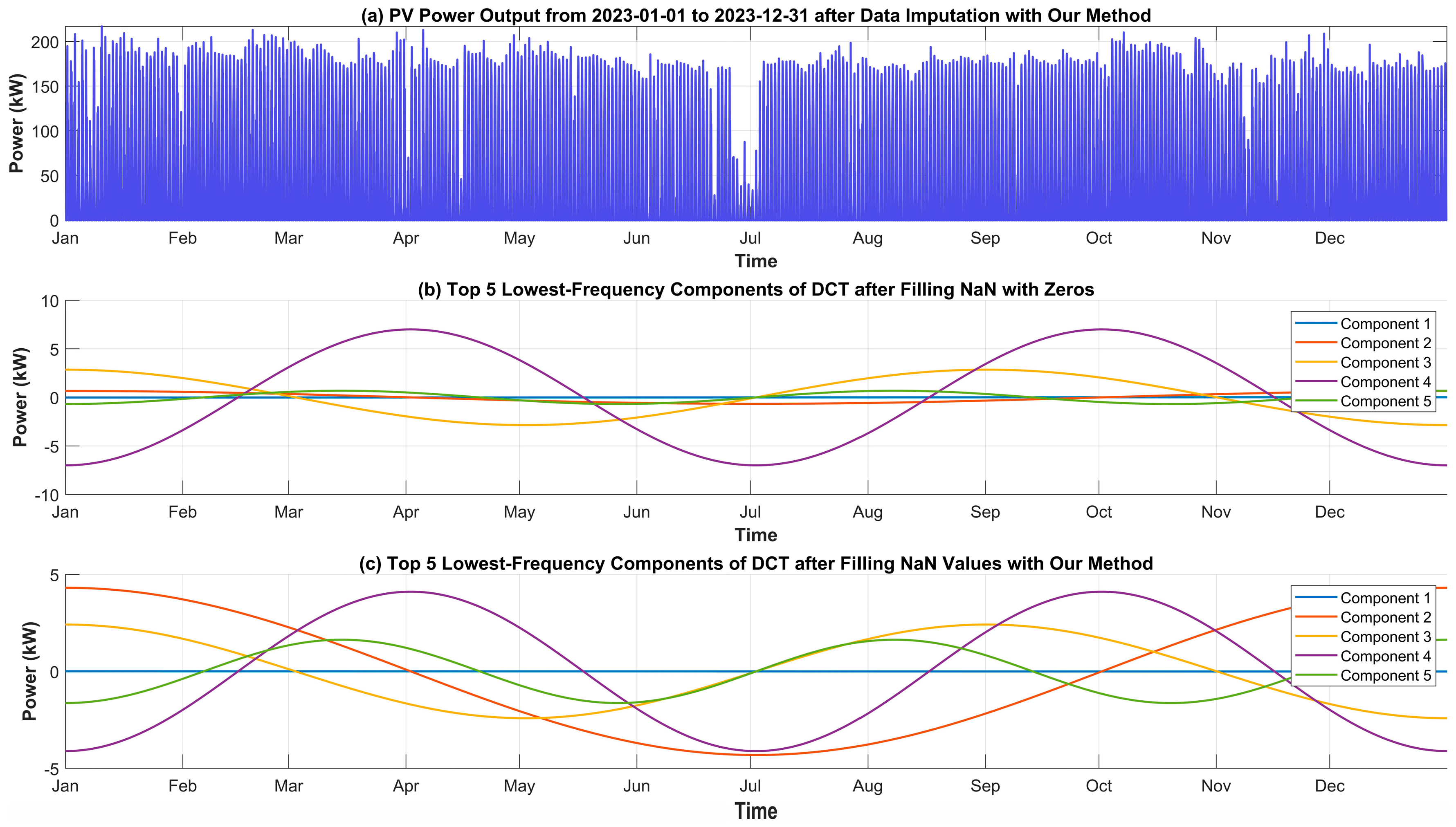
5.1. Validation Test
5.2. Effectiveness Test
5.2.1. Evaluation Metrics
- (1)
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
- (2)
- Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE)
- (3)
- R-squared (R2)
5.2.2. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demirhan, H.; Renwick, Z. Missing value imputation for short to mid-term horizontal solar irradiance data. Appl. Energy 2018, 225, 998–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Cheng, L.; Sun, G.; Wei, Z. Improving ultra-short-term photovoltaic power forecasting using a novel sky-image-based framework considering spatial-temporal feature interaction. Energy 2024, 293, 130538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Ali, M.M.; Lin, Y.; Liu, H. Ultra-short-term forecasting of large distributed solar PV fleets using sparse smart inverter data. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2024, 15, 1968–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhu, Q.; Wong, K.-c.; Wang, X.; Lin, Q. A complementary fused method using GRU and XGBoost models for long-term solar energy hourly forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 254, 124286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Liu, J. Enhanced photovoltaic power generation forecasting for newly-built plants via Physics-Infused transfer learning with domain adversarial neural networks. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 322, 119114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Mao, Z. Short-term photovoltaic power forecasting with feature extraction and attention mechanisms. Renew. Energy 2024, 226, 120437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Song, S.; Suo, L.; Wang, Y.; Nazir, M.S.; Zhang, C. Research and application of a novel graph convolutional RVFL and evolutionary equilibrium optimizer algorithm considering spatial factors in ultra-short-term solar power prediction. Energy 2024, 308, 132928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zheng, P.; Dong, J.; Liu, J.; Nakanishi, Y. Interpretable feature selection and deep learning for short-term probabilistic PV power forecasting in buildings using local monitoring data. Appl. Energy 2024, 376, 124271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos-Gómez, L.S.; Ruiz-Muñoz, J.F.; Ruiz-Mendoza, B.J. Short-term forecasting of global solar irradiance in tropical environments with incomplete data. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, K.; Pei, Y.; Huang, Z. Photovoltaic power missing data filling based on multiple matching and long- and short-term memory network. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2021, 31, 12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Suh, D. CC-GAIN: Clustering and classification-based generative adversarial imputation network for missing electricity consumption data imputation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 255, 124507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Gulrajani, I.; Ahmed, F.; Arjovsky, M.; Dumoulin, V.; Courville, A.C. Improved training of Wasserstein GANs. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Junninen, H.; Niska, H.; Tuppurainen, K.; Ruuskanen, J.; Kolehmainen, M. Methods for imputation of missing values in air quality data sets. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2895–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, M.J.; von Backström, T.W.; van Dyk, E.E. Performance characteristics of a perforated shadow band in the presence of cloud. Sol. Energy 2016, 139, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layanun, V.; Suksamosorn, S.; Songsiri, J. Missing-data imputation for solar irradiance forecasting in Thailand. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Conference of the Society of Instrument and Control Engineers (SICE), Kanazawa, Japan, 19–22 September 2017; pp. 1234–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Benitez, I.B.; Ibañez, J.A.; Lumabad, C.D.; Cañete, J.M.; De los Reyes, F.N.; Principe, J.A. A novel data gaps filling method for solar PV output forecasting. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2023, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-C.; Tsai, C.-F.; Lin, W.-C. Towards missing electric power data imputation for energy management systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 174, 114743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Comesaña, M.; Eguia-Oller, P.; Martinez-Torres, J.; Febrero-Garrido, L.; Granada-Álvarez, E. Optimisation of thermal comfort and indoor air quality estimations applied to in-use buildings combining NSGA-III and XGBoost. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinith, P.J.; Sam, K.N.; Vidya, T.; Kathiresan, A.C. Development and performance analysis of aquila algorithm optimized SPV power imputation and forecasting models. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2024, 15, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lei, M.; Saunier, N.; Sun, L. Low-rank autoregressive tensor completion for spatiotemporal traffic data imputation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 12301–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo Turrado, C.; Sánchez Lasheras, F.; Calvo-Rollé, J.L.; Piñón-Pazos, A.J.; de Cos Juez, F.J. A new missing data imputation algorithm applied to electrical data loggers. Sensors 2015, 15, 31069–31082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, T.; Falcão, B.; Mohamed, M.A.; Annuk, A.; Marinho, M. Employing machine learning for advanced gap imputation in solar power generation databases. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Bühlmann, P. MissForest—Non-parametric missing value imputation for mixed-type data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Park, S.; Lee, J.; Joo, Y.; Choi, J.K. Learning-based adaptive imputation method with kNN algorithm for missing power data. Energies 2017, 10, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Ramírez, E.-L.; Pino-Mejías, R.; López-Coello, M.; Cubiles-de-la-Vega, M.-D. Missing value imputation on missing completely at random data using multilayer perceptrons. Neural Netw. 2011, 24, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ren, C.; Xu, Y. PV generation forecasting with missing input data: A super-resolution perception approach. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 12, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Cheng, J.C.; Jiang, F.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Zhai, C. A bi-directional missing data imputation scheme based on LSTM and transfer learning for building energy data. Energy Build. 2020, 216, 109941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de-Paz-Centeno, I.; García-Ordás, M.T.; García-Olalla, Ó.; Alaiz-Moretón, H. Imputation of missing measurements in PV production data within constrained environments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 217, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, Y.; Xue, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. AdImpute: An imputation method for single-cell RNA-seq data based on semi-supervised autoencoders. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H. A novel GAN architecture reconstructed using Bi-LSTM and style transfer for PV temporal dynamics simulation. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2024, 15, 2826–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Srinivasan, D. SolarGAN: Multivariate solar data imputation using generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2020, 12, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Zhu, R.; Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Yu, W. CM-GAN: A cross-modal generative adversarial network for imputing completely missing data in digital industry. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 2917–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.; Xu, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wong, W.K. A robust spatiotemporal forecasting framework for photovoltaic generation. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid. 2020, 11, 5370–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouq, M.; El Fadili, H.; Zenkouar, K.; Lakhliai, Z.; Amouzg, M. Short term solar irradiance forecasting via a novel evolutionary multi-model framework and performance assessment for sites with no solar irradiance data. Renew. Energy 2020, 157, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhan, R.A.; Heatubun, Y.R.; Tan, S.F.; Lee, H. Comparison of physical and machine learning models for estimating solar irradiance and photovoltaic power. Renew. Energy 2021, 178, 1006–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, D. SolarNet: A hybrid reliable model based on convolutional neural network and variational mode decomposition for hourly photovoltaic power forecasting. Appl. Energy 2021, 300, 117410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z. Photovoltaic power forecasting: A hybrid deep learning model incorporating transfer learning strategy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 162, 112473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE). Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2014, 7, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, P.; Vig, L.; Shroff, G.; Agarwal, P. Long short term memory networks for anomaly detection in time series. In Proceedings of the European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 22–24 April 2015; Volume 2015, pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Venugopalan, S.; Xu, H.; Donahue, J.; Rohrbach, M.; Mooney, R.; Saenko, K. Translating videos to natural language using deep recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the ACL, Denver, CO, USA, 31 May–5 June 2015; pp. 1494–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1724–1734. [Google Scholar]

| MAE | RMSE | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.186196247 | 0.389140511 | 0.984074517 |
| LSTM_F | 0.184734812 | 0.387618016 | 0.985344046 |
| BiLSTM | 0.190740165 | 0.376485922 | 0.984697024 |
| BiLSTM_F | 0.189486873 | 0.373610254 | 0.985937555 |
| SLSTM | 0.17901024 | 0.411963163 | 0.982579983 |
| SLSTM_F | 0.177306056 | 0.410760062 | 0.982265822 |
| CNN_LSTM | 0.175097703 | 0.401689078 | 0.983706477 |
| CNN_LSTM_F | 0.174056652 | 0.40113345 | 0.984127151 |
| GRU | 0.183788996 | 0.398229391 | 0.984124486 |
| GRU_F | 0.184477308 | 0.397778235 | 0.984984212 |
| BiGRU | 0.191201229 | 0.412379908 | 0.982185075 |
| BiGRU_F | 0.191340529 | 0.410100013 | 0.983502992 |
| MAE | RMSE | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.186821839 | 0.387610254 | 0.98446909 |
| LSTM_F | 0.185143555 | 0.387304998 | 0.984418894 |
| BiLSTM | 0.191263683 | 0.376392603 | 0.984692799 |
| BiLSTM_F | 0.190849318 | 0.374420885 | 0.98653103 |
| SLSTM | 0.179179386 | 0.412062082 | 0.982844343 |
| SLSTM_F | 0.178519265 | 0.409987307 | 0.983222614 |
| CNN_LSTM | 0.175921877 | 0.401576963 | 0.982665936 |
| CNN_LSTM_F | 0.173947251 | 0.399999232 | 0.983597441 |
| GRU | 0.185331267 | 0.398246292 | 0.982768998 |
| GRU_F | 0.184967549 | 0.397475245 | 0.984630677 |
| BiGRU | 0.191617142 | 0.411262155 | 0.982123923 |
| BiGRU_F | 0.191232847 | 0.410126485 | 0.982937645 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Xuan, L.; Gong, D.; Xie, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, D. A WGAN-GP Approach for Data Imputation in Photovoltaic Power Prediction. Energies 2025, 18, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051042
Liu Z, Xuan L, Gong D, Xie X, Liang Z, Zhou D. A WGAN-GP Approach for Data Imputation in Photovoltaic Power Prediction. Energies. 2025; 18(5):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051042
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhu, Lingfeng Xuan, Dehuang Gong, Xinlin Xie, Zhongwen Liang, and Dongguo Zhou. 2025. "A WGAN-GP Approach for Data Imputation in Photovoltaic Power Prediction" Energies 18, no. 5: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051042
APA StyleLiu, Z., Xuan, L., Gong, D., Xie, X., Liang, Z., & Zhou, D. (2025). A WGAN-GP Approach for Data Imputation in Photovoltaic Power Prediction. Energies, 18(5), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18051042





