Analysis of Key Risk Factors in the Thermal Coal Supply Chain
Abstract
1. Thermal Coal Supply Chain Overview and Identification of Risk Factors
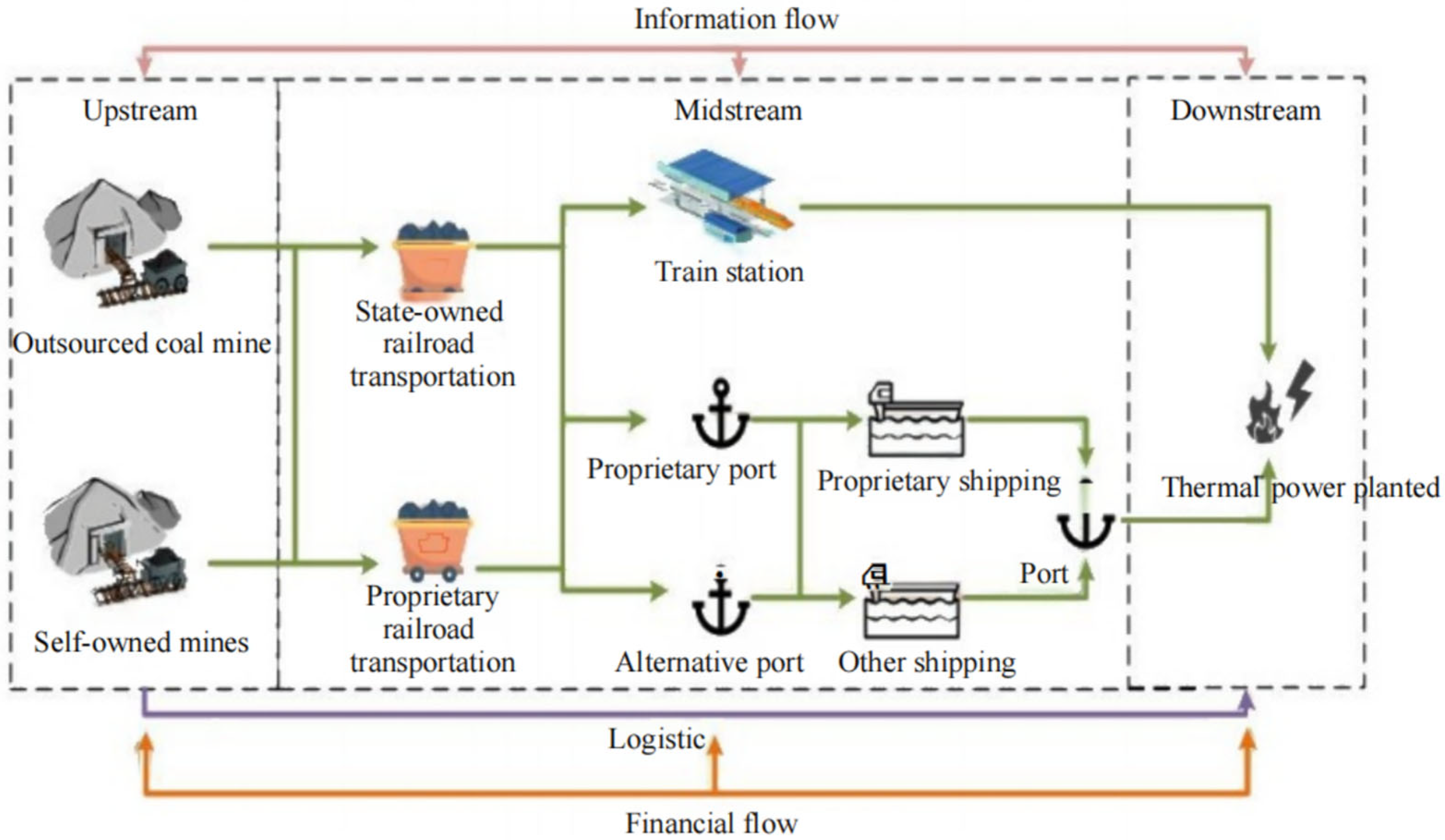
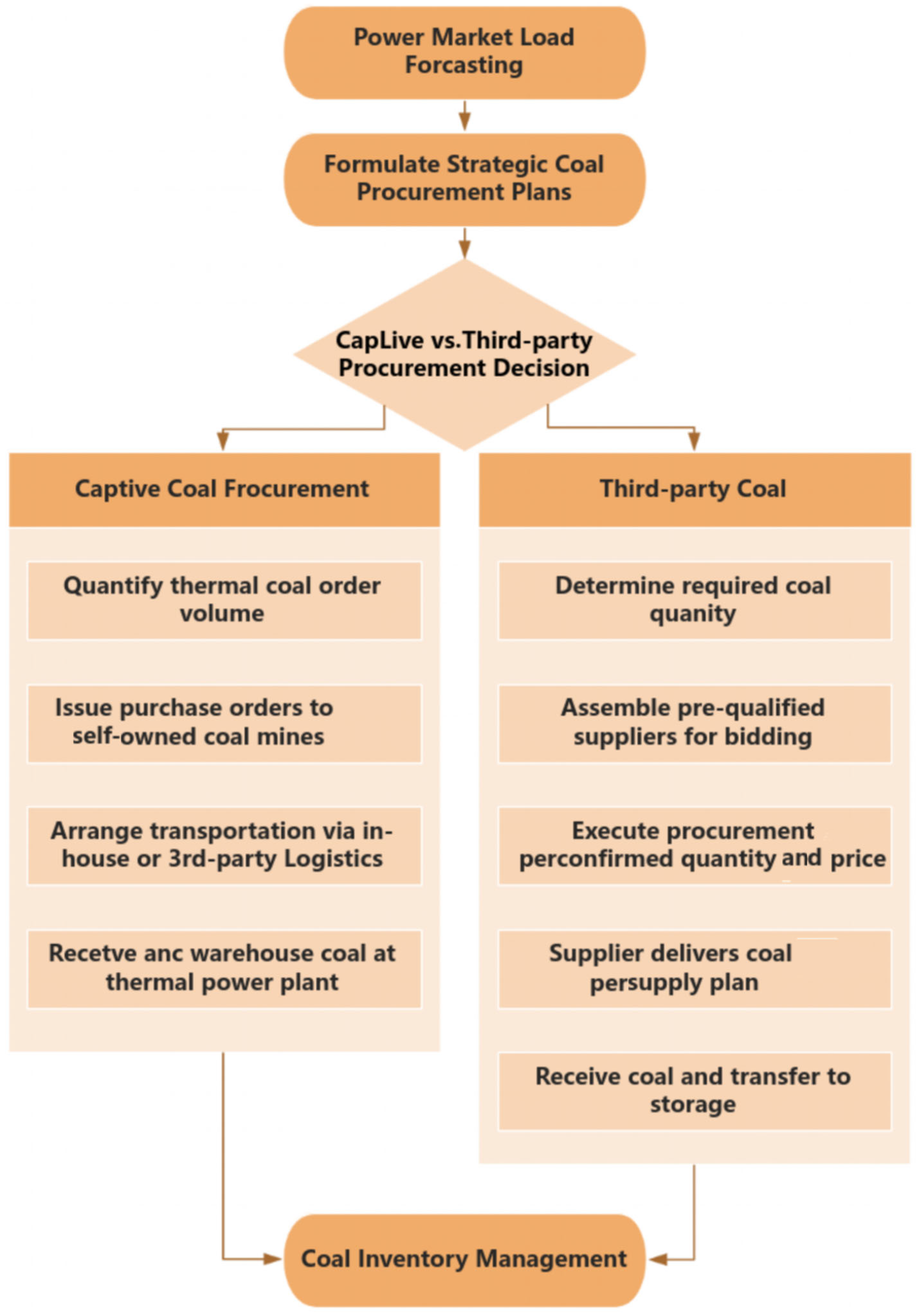
1.1. Analysis of Thermal Coal Supply Chain Operation Process
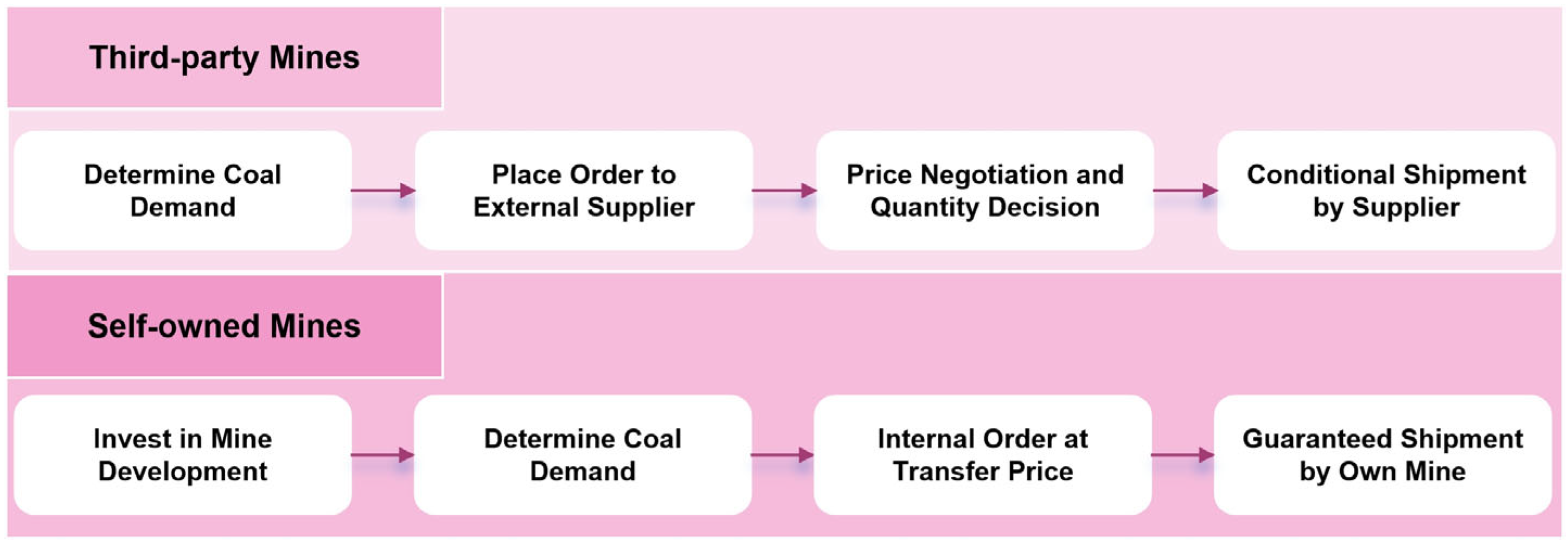
1.1.1. Upstream Overview of the Thermal Coal Supply Chain and Operation Process
- (1)
- Domestic coal supply
- (2)
- Imported coal supply
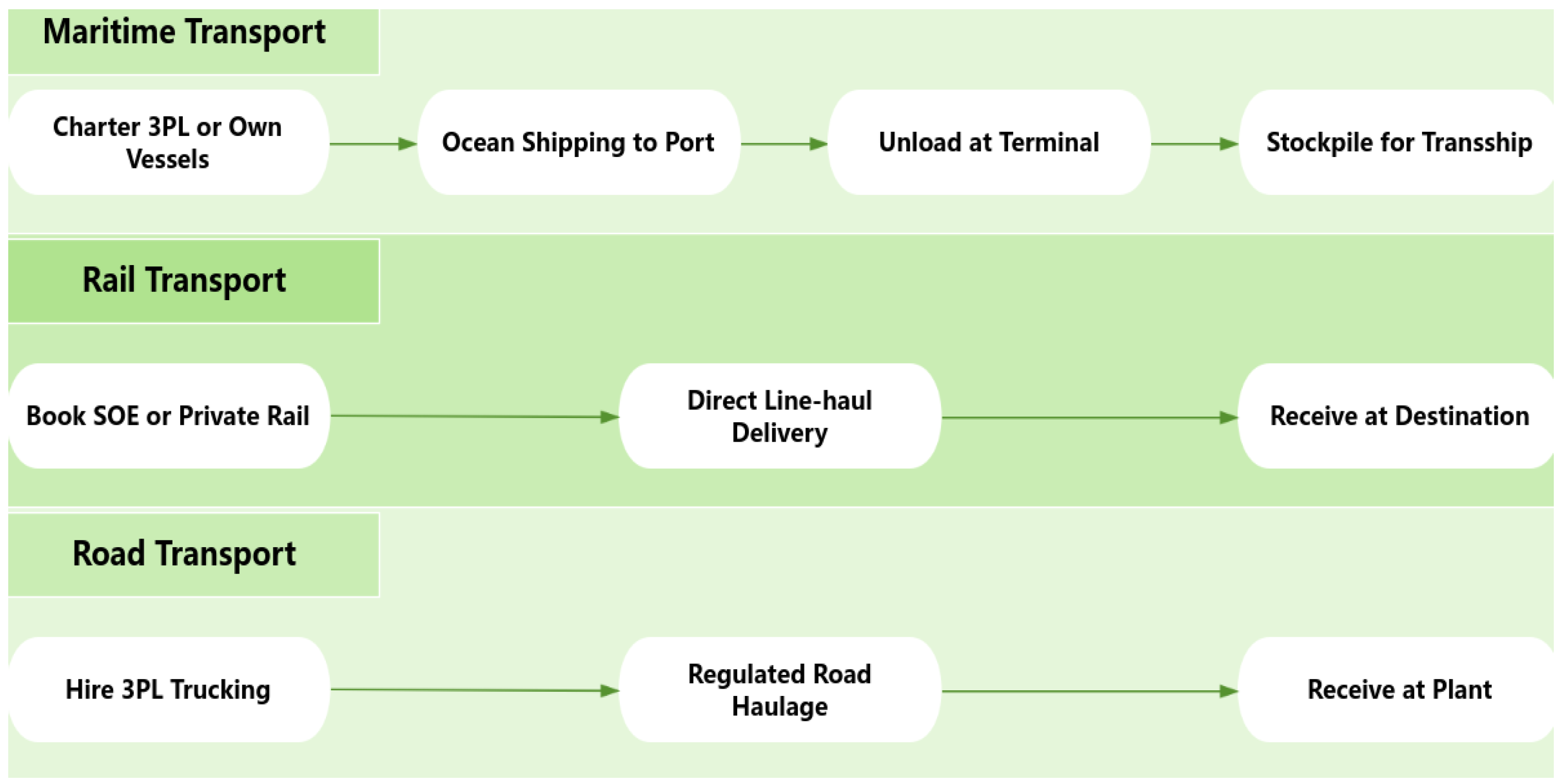
1.1.2. Overview of the Midstream of the Thermal Coal Supply Chain and Operation Process
- (1)
- Maritime Transportation
- (2)
- Railway Transportation
- (3)
- Roadway Transportation
1.1.3. Downstream Overview and Operation Process of Electricity and Coal Supply Chain
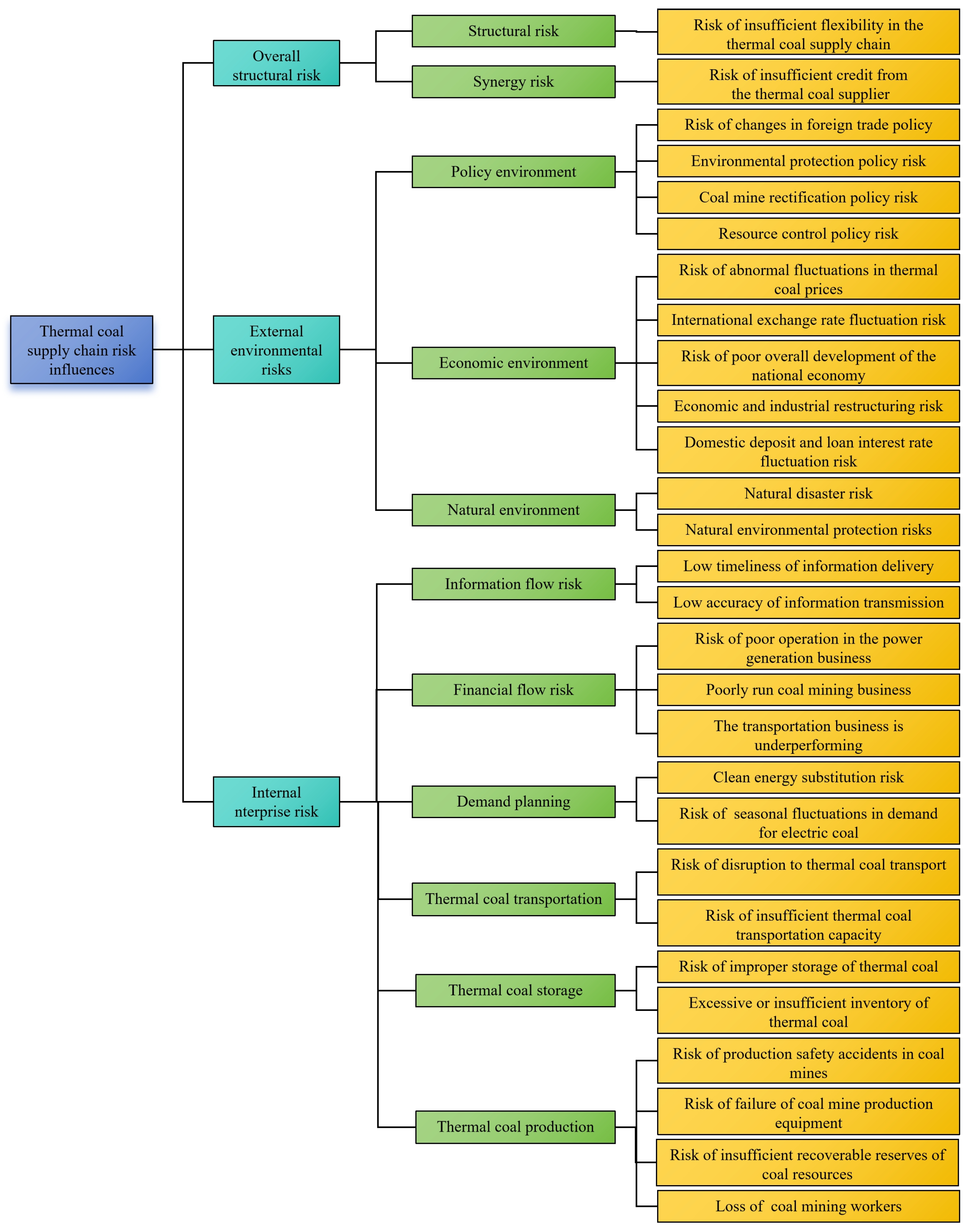
1.2. Thermal Coal Supply Chain Risk Factor Identification
2. Petri Net-Based Supply Chain Risk Modeling
2.1. Causality Analysis of Supply Chain Risk Factors
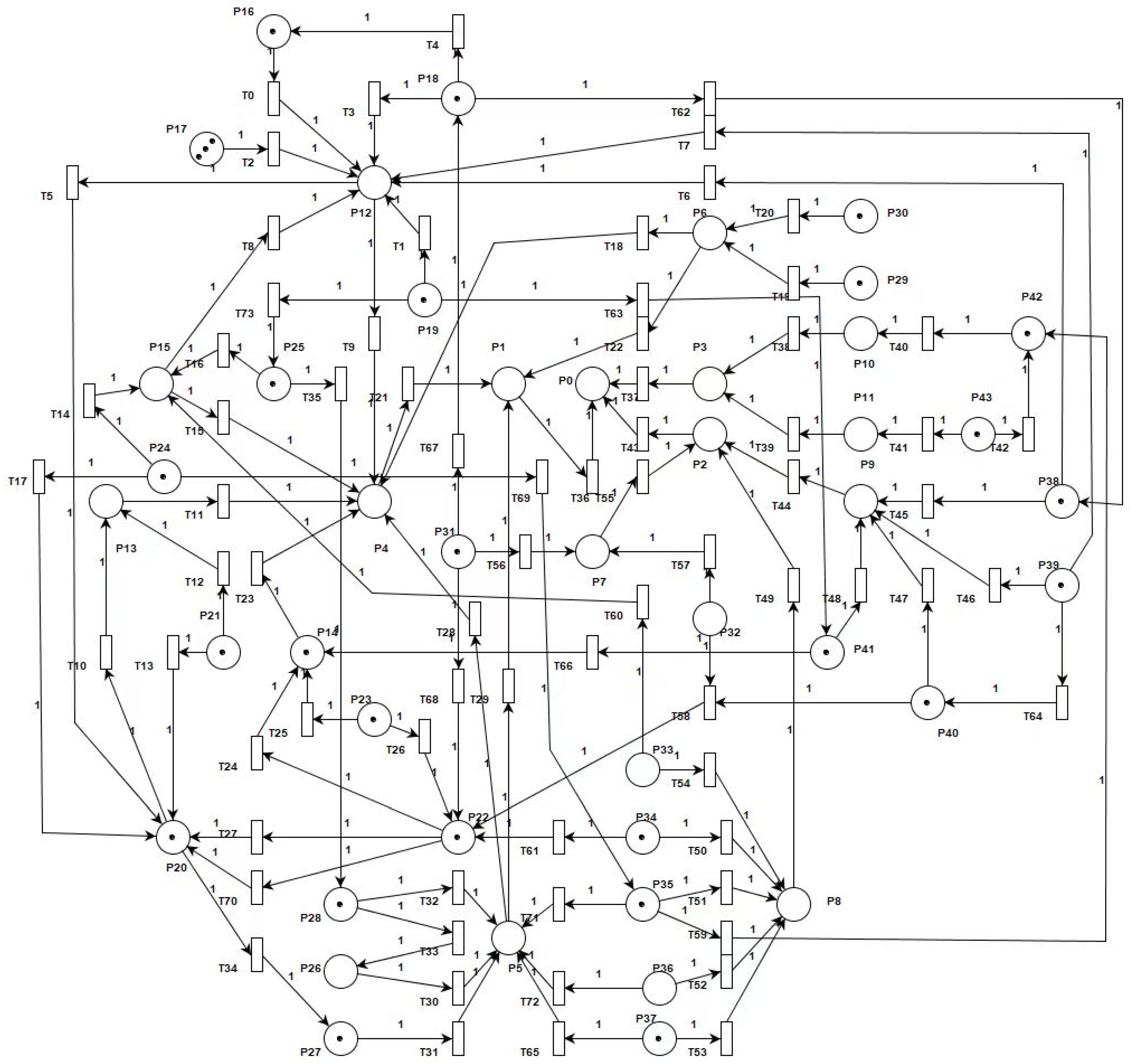
2.2. Petri Net-Based Supply Chain Risk Modeling
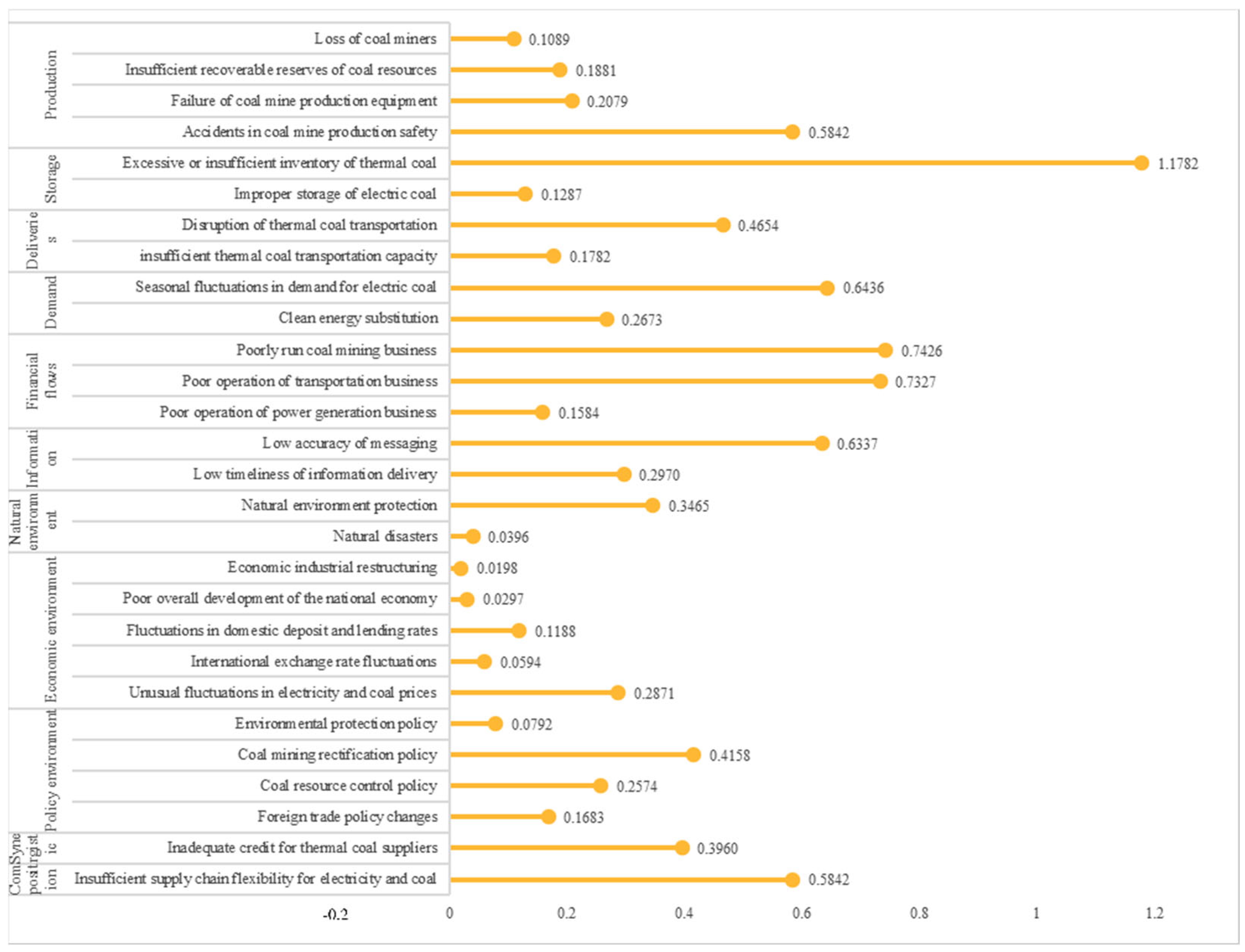
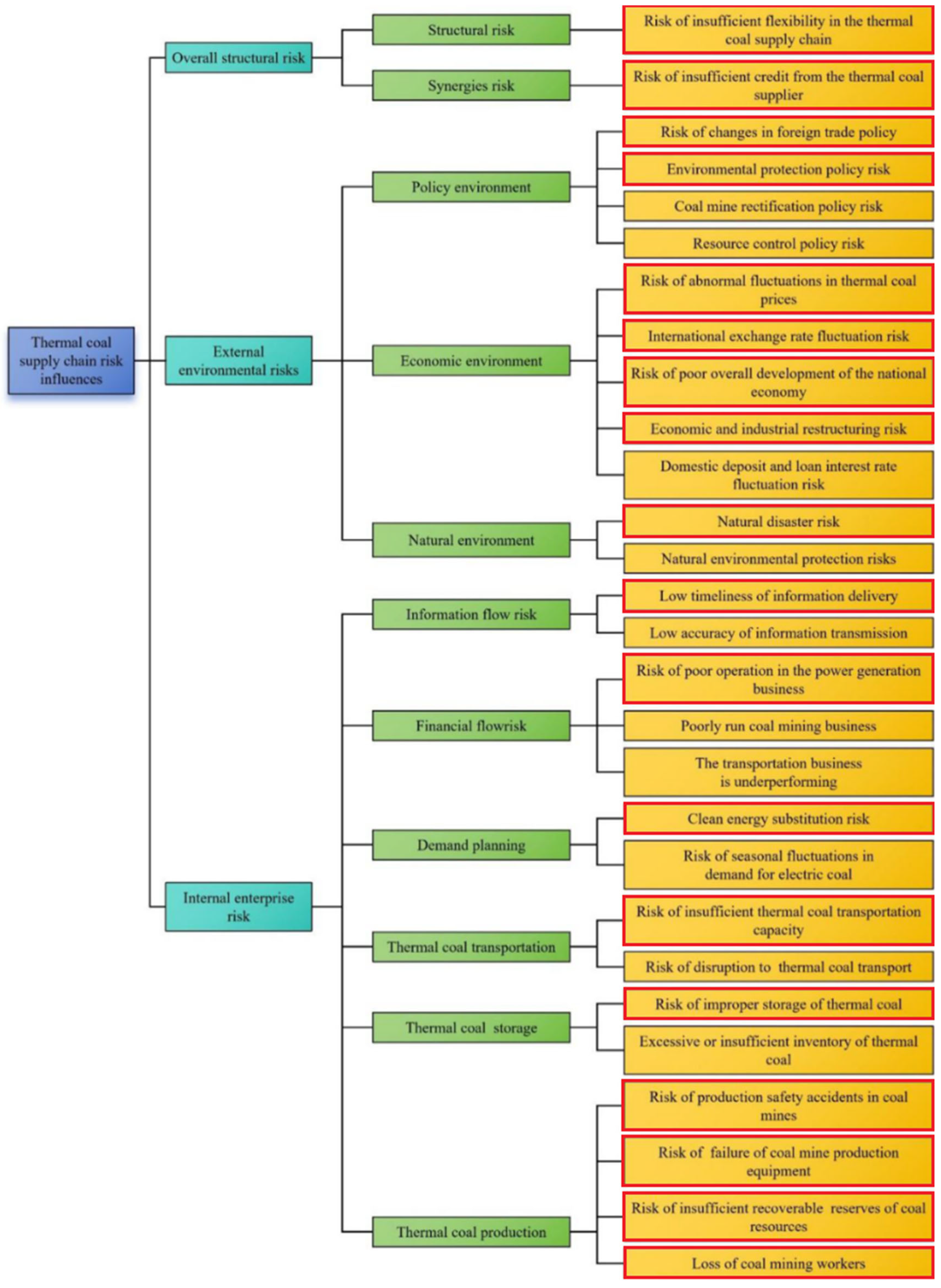
3. Analysis of Supply Chain Risk Factors Based on Petri Net
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Causal Relationship | Cause of Formation |
|---|---|
| Insufficient recoverable reserves of coal resources → Clean energy substitution risk | Insufficient coal resources will lead to a transformation of the energy mix and an increase in the use of cleaner energy sources |
| Insufficient recoverable reserves of coal resources → Coal resource control policy risk | Regional governments may ban local mining to protect local coal resources |
| Occurrence of production safety accidents in coal mines → Loss of coal mining employees | The perception of coal production as dirty and unkempt was causing the industry to lose personnel |
| Occurrence of coal mine production safety accidents → Coal mine rectification policy risk | Government departments introduced policies to govern the prevention of large-scale coal mine safety and production accidents |
| Too much or too little thermal coal stockpile → Poor operation of transportation business | Too much thermal coal stockpile increases inventory costs, too little leads to unavailability of goods for shipment and lower profit margins |
| Risk of insufficient thermal coal transportation capacity → Risk of disruption of thermal coal transportation | Insufficient capacity of open wagons and other means of transportation for thermal coal will lead to transportation disruptions |
| Risk of interruption of transportation of thermal coal → Excessive or low stocks of thermal coal | Disruptions in thermal coal transportation have led to low stocks of thermal coal at power plants |
| Production chain risk →Excessive or insufficient inventory of thermal coal | Disruption of coal mine production sources can lead to a reduction in thermal coal stockpiles |
| Risk of improper storage of thermal coal → Excessive or insufficient inventory of thermal coal | Deterioration of thermal coal while in storage can lead to a reduction in the amount of usable thermal coal in a power plant’s inventory. |
| Risk of improper storage of thermal coal → Risk of insufficient creditworthiness of thermal coal suppliers | Coal mines were unable to meet long-term contracts due to insufficient coal availability as a result of improper storage of coal |
| Risk of seasonal fluctuations in demand for thermal coal → Excessive or insufficient inventory of thermal coal | High demand for thermal coal in the summer and winter seasons leading to a decrease in thermal coal stockpiles |
| Clean energy substitution risk → Poor operation of power generation business | Substitution of thermal power by wind power, nuclear power, etc., will affect the operating level of thermal power business |
| Poor power generation business operations → Poor coal mining business operations | Poor operation of the power generation business will lead to lower demand for thermal coal, which will in turn affect the operating level of the coal mining business |
| Information flow risk → Logistics risk | Biases in the information dissemination process will lead to biases in logistics and transportation |
| Financial flow risk → Logistics risk | Inadequate liquidity among business entities will affect thermal coal transportation |
| Risk of natural disasters → Occurrence of production safety accidents in coal mines | Natural disasters such as earthquakes can easily lead to production safety accidents in coal mines |
| Natural disaster risk → Risk of disruption of thermal coal transportation | Natural disasters such as blizzards can affect coal transportation |
| Poor overall development of the national economy → Program link risk | National economic development affects the country’s overall demand for electricity |
| Economic and industrial restructuring risk → Program link risk | Substitution of the secondary sector by the tertiary sector will lead to a reduction in electricity demand |
| Planning process risk → Production process risk | Coal mines need to reduce their mining capacity in line with the planned reduction in demand for coal |
| Risk of seasonal fluctuations in thermal coal demand → Risk of fluctuations in thermal coal prices | Price fluctuations occur when there was an “oversupply” or “undersupply” of coal in the marketplace |
| Risk of changes in foreign trade policies → Risk of fluctuations in thermal coal prices | The tightening of foreign trade policies will affect the supply and demand of imported coal, which in turn will affect the supply and demand of domestic coal, leading to fluctuations in the price of thermal coal |
| Thermal coal price fluctuation risk → Capital flow risk | Soaring thermal coal prices can lead to higher costs for corporate coal mining purchases |
| Risk of fluctuation in thermal coal prices → Risk of insufficient credit from thermal coal suppliers | High demand for thermal coal in summer and winter seasons and high market coal prices, thermal coal suppliers will choose to sell coal at market prices rather than long-term contract prices |
| Domestic deposit and loan interest rate fluctuation risk → Funding flow risk | Fluctuations in domestic interest rates on deposits and loans affect the enterprise’s capital operating policy, leading to changes in the enterprise’s capital flows |
| Risk of international exchange rate fluctuations → Risk of financial flows | The risk of international exchange rate fluctuations can affect the price of thermal coal imports, leading to changes in the cost of purchasing imported coal and an impact on capital flows |
| Coal mine rectification policy risk → Production Segment Risk | Coal mines ordered to improve may cause their production to be affected |
| Environmental protection policy risk → Production chain risk | The introduction of environmental protection policies has made it necessary to consider the impact of coal mine production on the natural environment, which may lead to production disruptions |
| Risk of changes in foreign trade policy → Risk of interruption of thermal coal transportation | The tightening of the takeaway policy will affect the purchase of imported coal, leading to the disruption of imported coal transportation |
| Environmental protection policy risk → Natural environmental protection risk | National environmental protection policies have led to the need to consider natural environmental protection in the operation of the coal supply chain |
| Coal mine control policy risk → Transportation link risk | Local authorities’ ban on coal shipments into or out of the country has led to disruptions in the transportation of thermal coal |
| Insufficient credit risk of thermal coal suppliers → Insufficient flexibility risk of thermal coal supply chain | Insufficient credit for thermal coal suppliers has led to excessive dependence on some thermal coal suppliers and insufficient supply chain flexibility |
Appendix B
| Places | Token | Factors | Places | Token | Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0 | 0 | Thermal coal supply chain operational risk factors | P22 | 1 | Risk of interruption in the transportation of thermal coal |
| P1 | 0 | Internal operational risk | P23 | 1 | Risk of insufficient thermal coal transportation capacity |
| P2 | 0 | External environmental risk | P24 | 1 | Risk of seasonal fluctuations in demand for thermal coal |
| P3 | 0 | Overall structural risk | P25 | 1 | Clean energy substitution risk |
| P4 | 0 | Logistics risk | P26 | 1 | Risk of poor coal mine segment operations |
| P5 | 0 | Financial flow risk | P27 | 1 | Risk of poor operation of transportation business |
| P6 | 0 | Information flow risk | P28 | 1 | Risk of poor operation in the power generation business |
| P7 | 0 | Natural environment risk | P29 | 1 | Risk of low timeliness of information delivery |
| P8 | 0 | Economic environment risk | P30 | 1 | Low risk of messaging accuracy |
| P9 | 0 | Policy environment risk | P31 | 1 | Natural disaster risk |
| P10 | 0 | Supply chain structure risk | P32 | 1 | Risks to the protection of the natural environment |
| P11 | 0 | Supply chain synergy risk | P33 | 0 | Risk of poor overall development of the national economy |
| P12 | 0 | Production chain risk | P34 | 1 | Economic and industrial restructuring risk |
| P13 | 0 | Storage chain risk | P35 | 1 | Risk of abnormal fluctuation of electric coal price |
| P14 | 0 | Transportation segment risk | P36 | 1 | Exposure to fluctuations in domestic deposit and lending rates |
| P15 | 0 | Program segment risk | P37 | 1 | Exposure to international exchange rate fluctuations |
| P16 | 1 | Insufficient storable coal resources | P38 | 1 | Coal mine rectification policy risk |
| P17 | 3 | Risk of failure of coal mine production equipment | P39 | 1 | Environmental protection policy risk |
| P18 | 1 | Risk of coal mine production safety accidents | P40 | 1 | Foreign trade policy change risk |
| P19 | 1 | Risk of loss of coal mining employees | P41 | 1 | Coal resource control policy risk |
| P20 | 1 | Risk of too much or too little thermal coal stockpiles | P42 | 1 | Risk of insufficient supply chain flexibility for thermal coal |
| P21 | 1 | Risk of improper storage of thermal coal | P43 | 1 | Risk of insufficient credit from thermal coal suppliers |
Appendix C
References
- CEC Statistics and Data Center. 2024–2025 National Electricity Supply and Demand Situation Analysis and Forecast Report. Available online: https://www.cec.org.cn/detail/index.html?3-341403 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Zhang, F.; Tan, H.; Li, W. Evolutionary game analysis of effective competition among thermal coal supply chain partners. Res. Coal Econ. 2017, 37, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Xie, H.; Ren, S.; Chen, P.; Jiao, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Qin, R. Research on the development strategy of China’s coal industry under the background of global industrial chain and energy supply chain reconstruction. China Eng. Sci. 2022, 24, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Z. An order acceptance decision-making method considering risk transfer scenarios. China Eng. Sci. 2019, 34, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roozbeh Nia, A.; Awasthi, A.; Bhuiyan, N. Assessment of coal supply chain under carbon trade policy by extended exergy accounting method. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2024, 36, 599–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sivageerthi, T.; Bathrinath, S.; Uthayakumar, M.; Bhalaji, R.K.A. A SWARA method to analyze the risks in coal supply chain management. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 5, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y. A Company Imported Iron Ore Supply Chain Risk Identification and Prevention. Master’s Thesis, Guilin University of Electronic Science and Technology, Guilin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D. Supply chain reliability diagnosis model constructed with intuitionistic fuzzy Petri net. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2017, 53, 260–265+270. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Zhao, L.T.; Li, F.R.; Yang, K.X. The coordination strategies of coal supply chain considering carbon emissions reduction. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 62, 6649–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, B. Research on the Co-Evolution Mechanism of Electricity Market Entities Enabled by Shared Energy Storage: A Tripartite Game Perspective Incorporating Dynamic Incentives/Penalties and Stochastic Disturbances. Systems 2025, 13, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics. Statistical Bulletin of National Economic and Social Development in 2024. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202501/t20250117_1958326.html (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Central People’s Government of the People’s Republic of China. Statistical Bulletin of Transportation Sector Development in 2024. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/yaowen/liebiao/202501/content_6997337.htm (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- National Bureau of Statistics. Report on Energy Production in 2024. Available online: https://www.stats.gov.cn/zwfwck/sjfb/202502/t20250228_1958817.html (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Kuang, Y. Research on Optimization Strategy of Thermal Coal Supply Chain of H Power Plant Under the Background of Energy Dual Control. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Research on Risk Management of Coal Supply Chain Based on System Dynamics. Master’s Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Bejing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D. Risk Analysis of Coal Supply Chain Under the Influence of Commodity Price Index. Master’s Thesis, North China Electric Power University, Bejing, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G. Research on Risk Management of Coal Supply Chain in S Company. Master’s Thesis, Donghua University, Shanghai, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, C. Research on Risk Identification and Evaluation of Coal Supply Chain Based On CSCOR_RS. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H. Research on risk evaluation of thermal coal supply chain. Mod. Commer. Ind. 2019, 40, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallikas, J.; Virolainen, V.; Tuominen, M. Risk analysis and assessment in network environments: A dyadic case study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2002, 78, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. Analysis of Supply Chain Risk Identification in China’s Iron and Steel Enterprises Based on Petri Network. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]


| Author | Thermal Coal Supply Chain Risk Factors |
|---|---|
| Kuang Yang [14] | Policy change risk, inventory management risk, financial security risk, lower degree of informationization risk, demand fluctuation risk |
| Wang Qianqian [15] | Natural environment risk, economic environment risk, national policy risk, thermal coal production risk, thermal coal transportation risk, thermal coal inventory risk, capital operation risk |
| Liu Dongliang [16] | Price fluctuation risk, inventory risk, supply and demand side risk, transportation risk, policy risk, market environment risk, environmental risk |
| Yu Guoliang [17] | Planning process risk, raw material procurement risk, thermal coal production risk, thermal coal transportation process risk, return process risk |
| Mo Congying [18] | Mining process risk, processing risk, transportation process risk, storage risk, thermal coal sales risk |
| Tan Haiyan [19] | Produced electricity sales risk, thermal coal transportation risk, supply security risk, government regulation risk, economic and natural environment risk |
| Hallikas [20] | Demand-related risk, financial-related risk, pricing risk, delivery fulfillment capability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, S.; Chen, J.; Ning, R. Analysis of Key Risk Factors in the Thermal Coal Supply Chain. Energies 2025, 18, 5800. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215800
Zhong S, Chen J, Ning R. Analysis of Key Risk Factors in the Thermal Coal Supply Chain. Energies. 2025; 18(21):5800. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215800
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Shuheng, Jingwei Chen, and Ruoyun Ning. 2025. "Analysis of Key Risk Factors in the Thermal Coal Supply Chain" Energies 18, no. 21: 5800. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215800
APA StyleZhong, S., Chen, J., & Ning, R. (2025). Analysis of Key Risk Factors in the Thermal Coal Supply Chain. Energies, 18(21), 5800. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18215800





