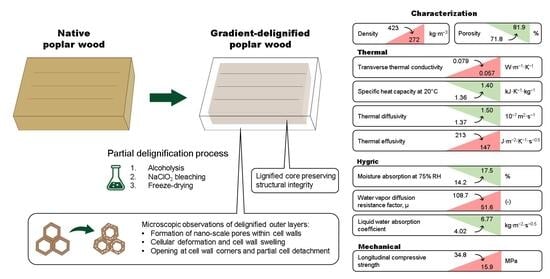
Gradient-Delignified Wood as a Sustainable Anisotropic Insulation Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Wood Delignification Technique
2.3. Sample Characterization
2.3.1. Microscopic Observation
2.3.2. Porosity
2.3.3. Thermal Property Characterization
- Specific heat capacity
- 2.
- Thermal conductivity
- 3.
- Thermal diffusivity and effusivity
2.3.4. Hygric Property Characterization
- Moisture storage function
- 2.
- Water vapor transmission properties—Dry cup method
- 3.
- Water absorption coefficient by partial immersion
2.3.5. Mechanical Property Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microscopic Observations
3.2. Thermal Properties
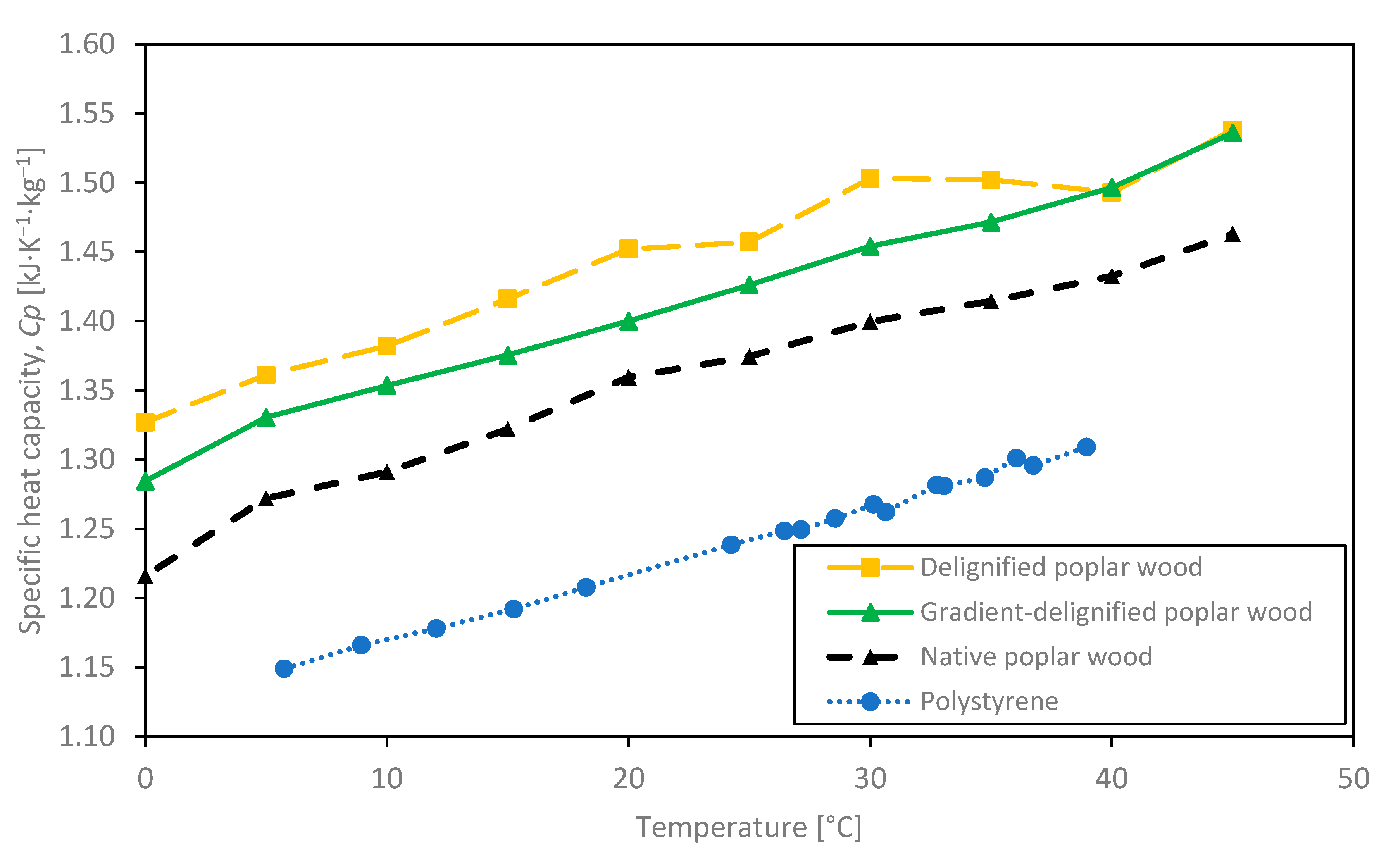
3.2.1. Specific Heat Capacity
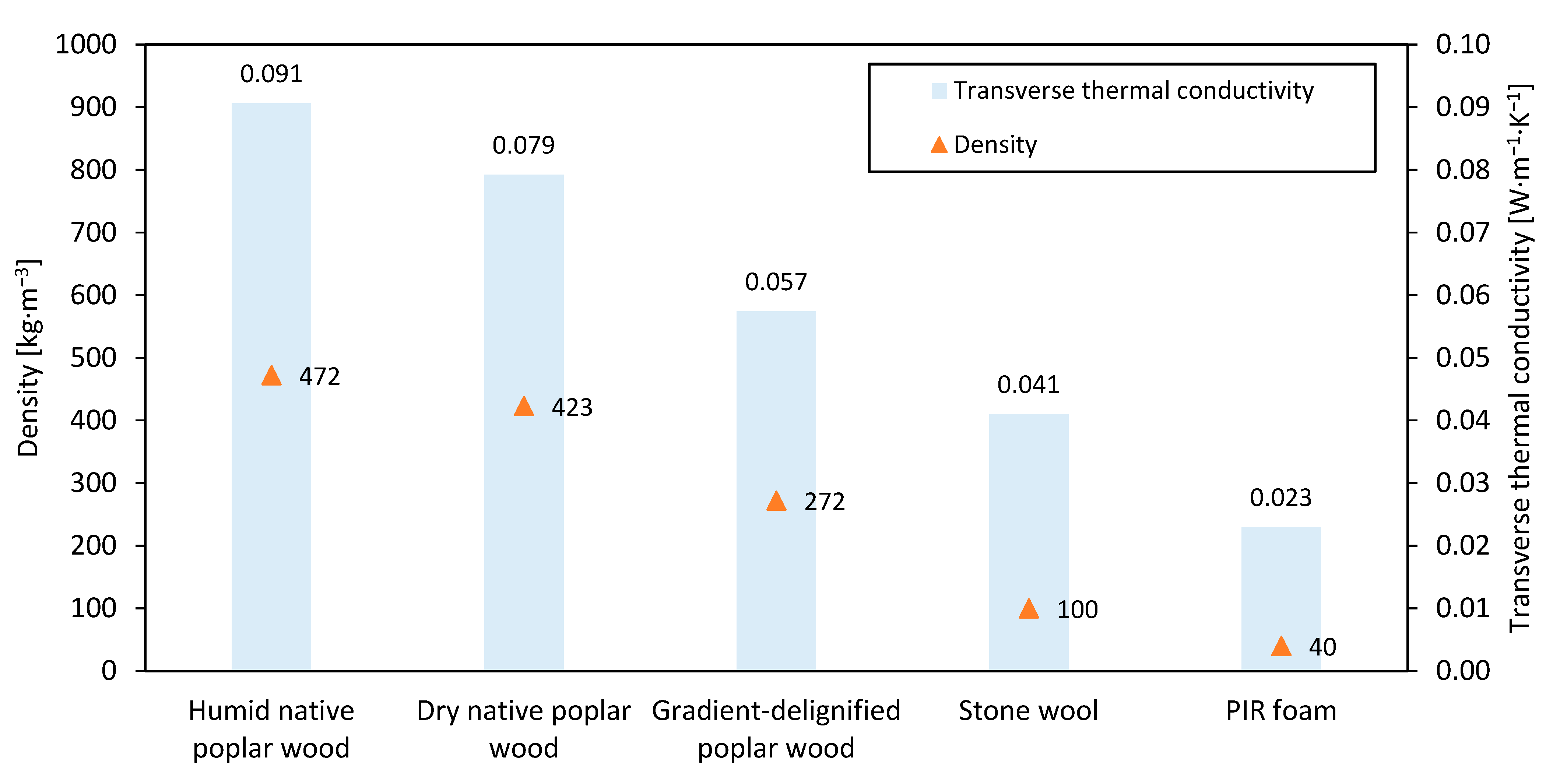
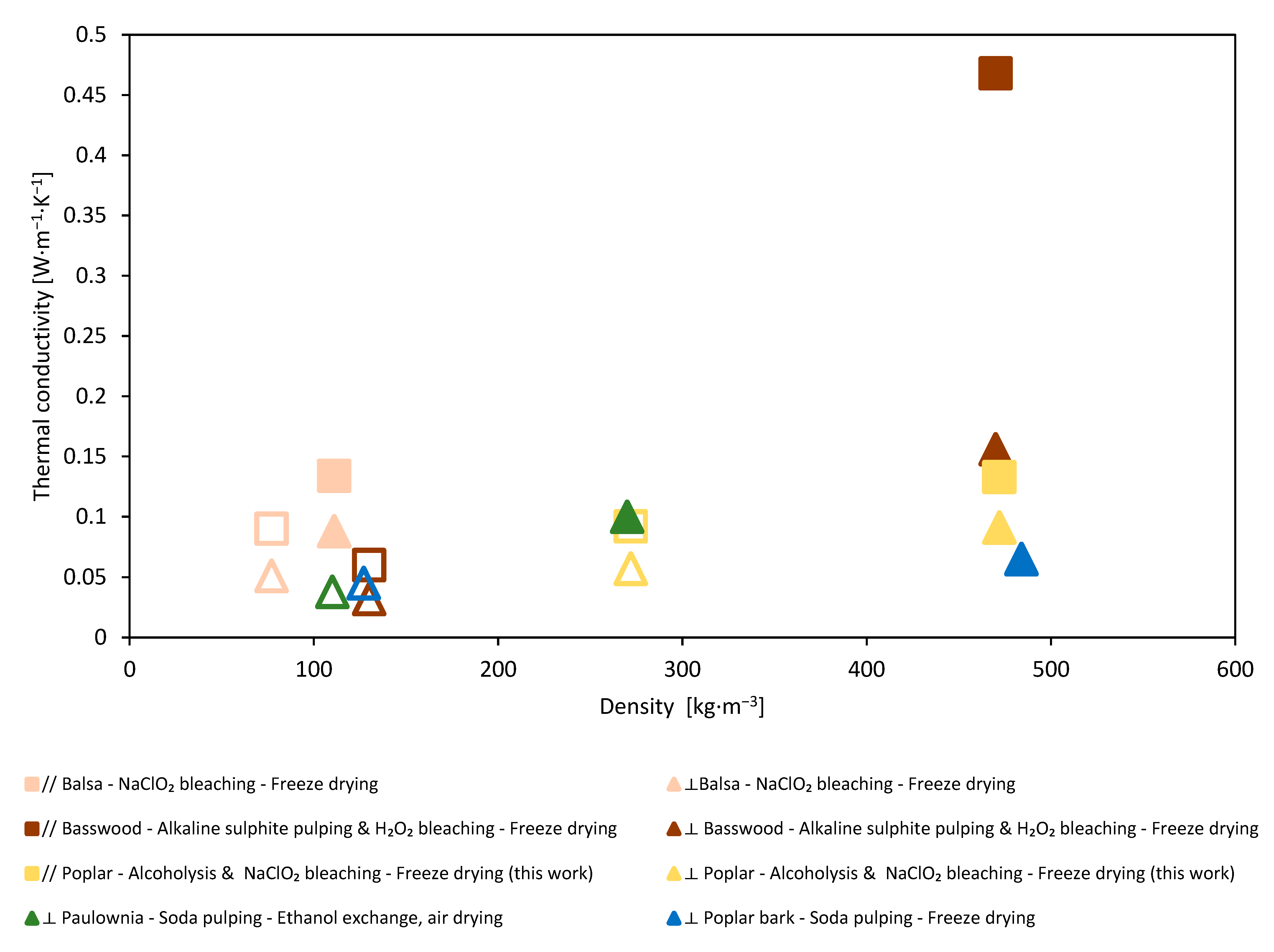
3.2.2. Thermal Conductivity
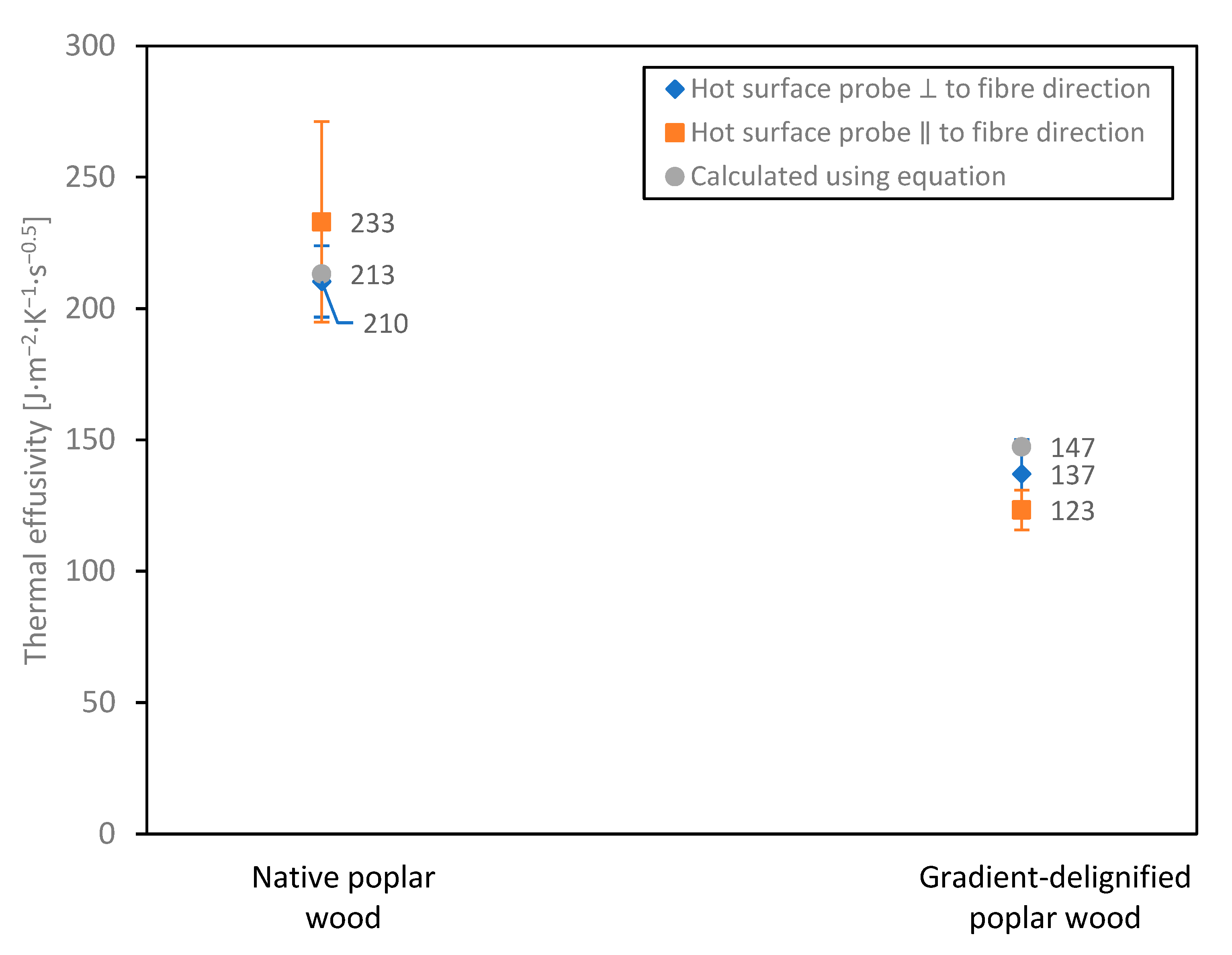
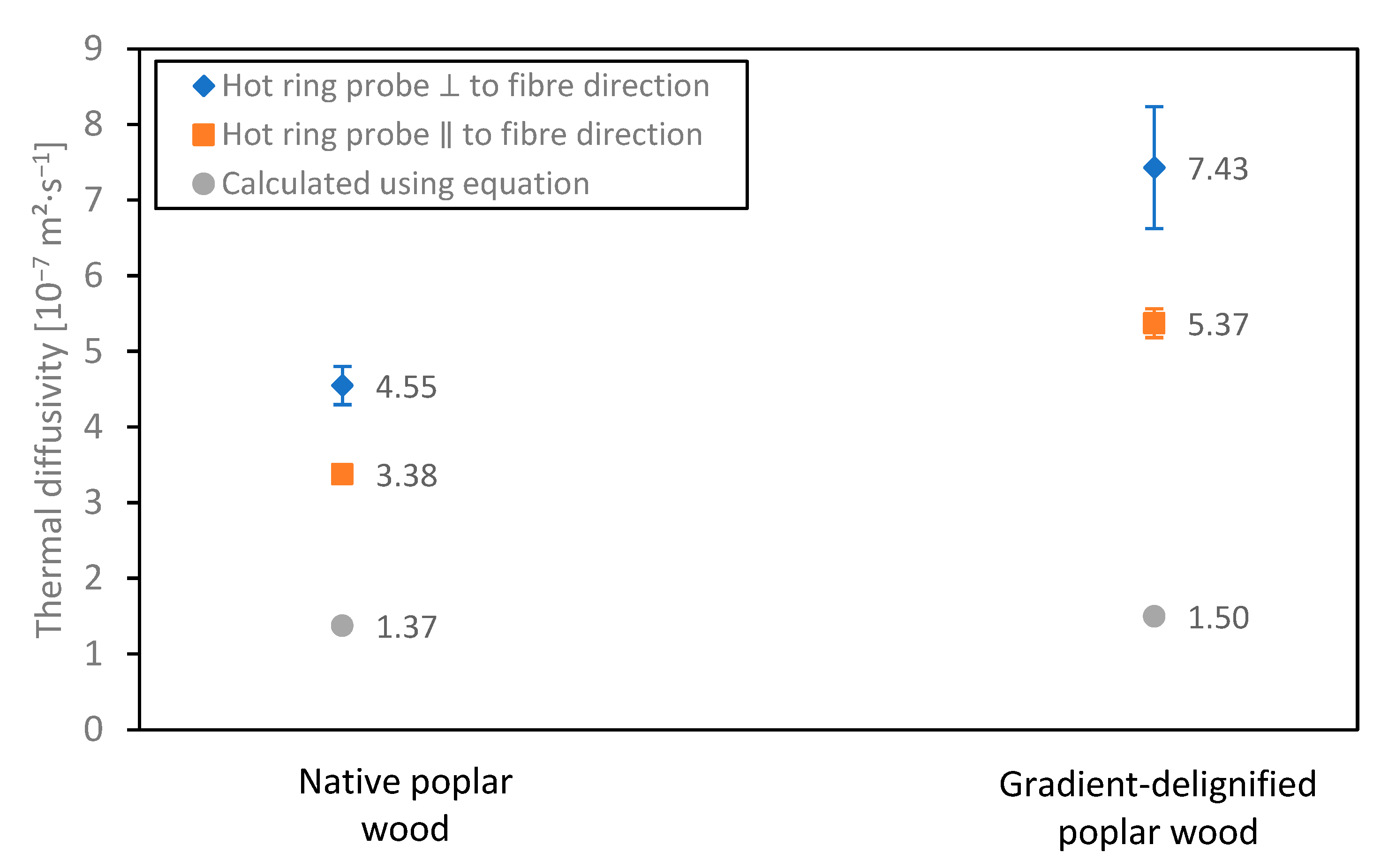
3.2.3. Heat Diffusivity and Effusivity
3.3. Hygric Properties
3.3.1. Moisture Storage Function
3.3.2. Water Vapor Transmission Properties
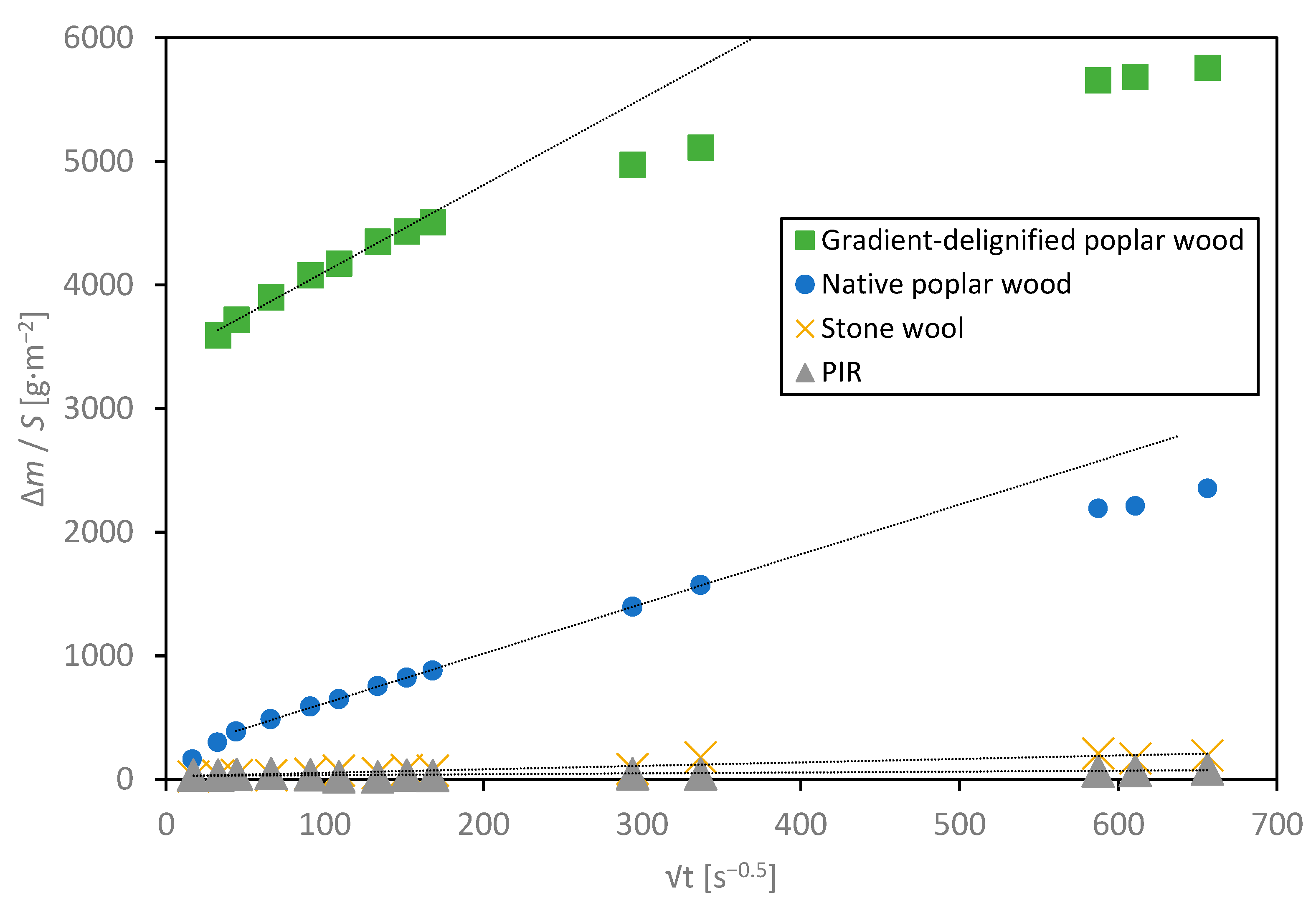
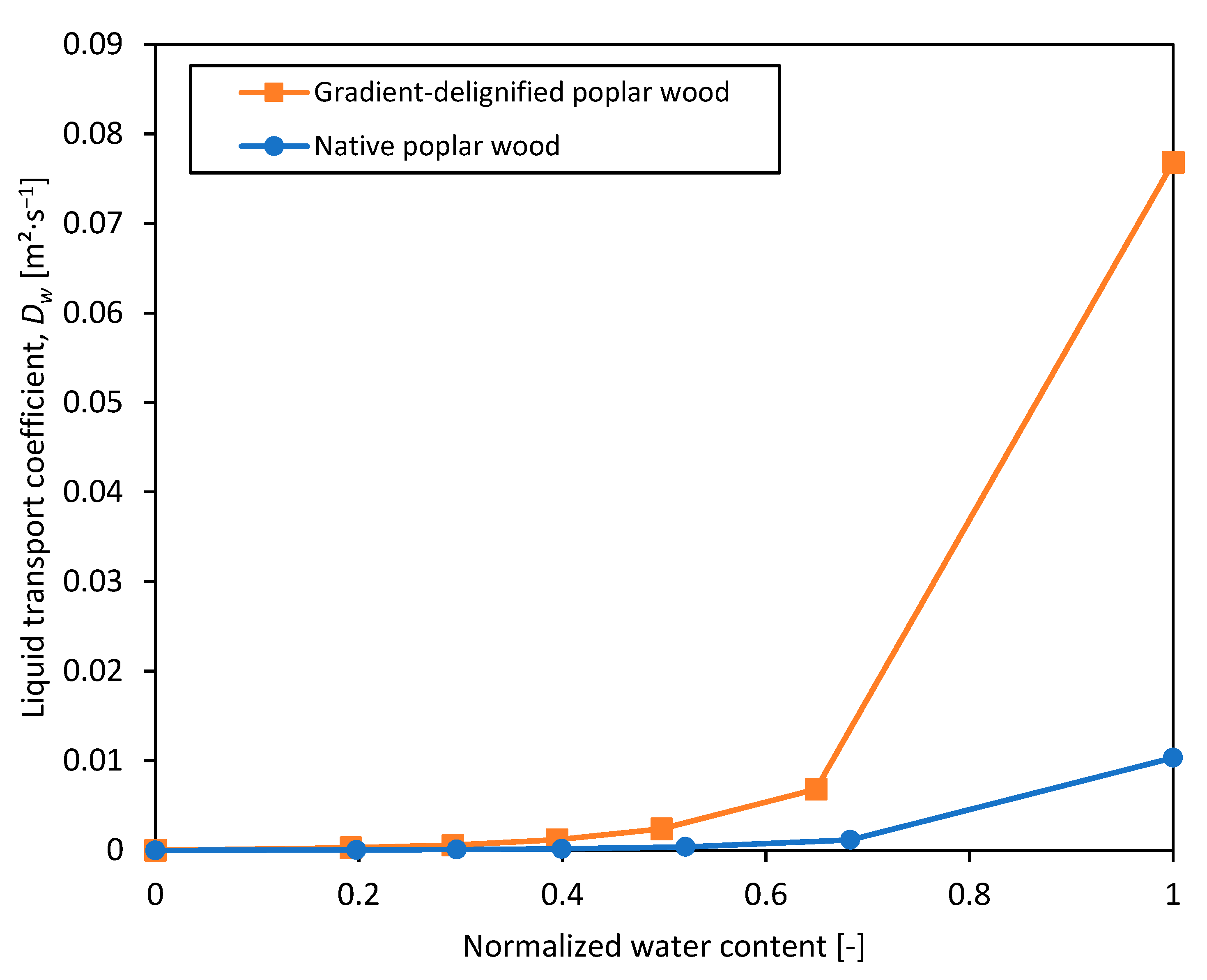
3.3.3. Water Absorption Coefficient
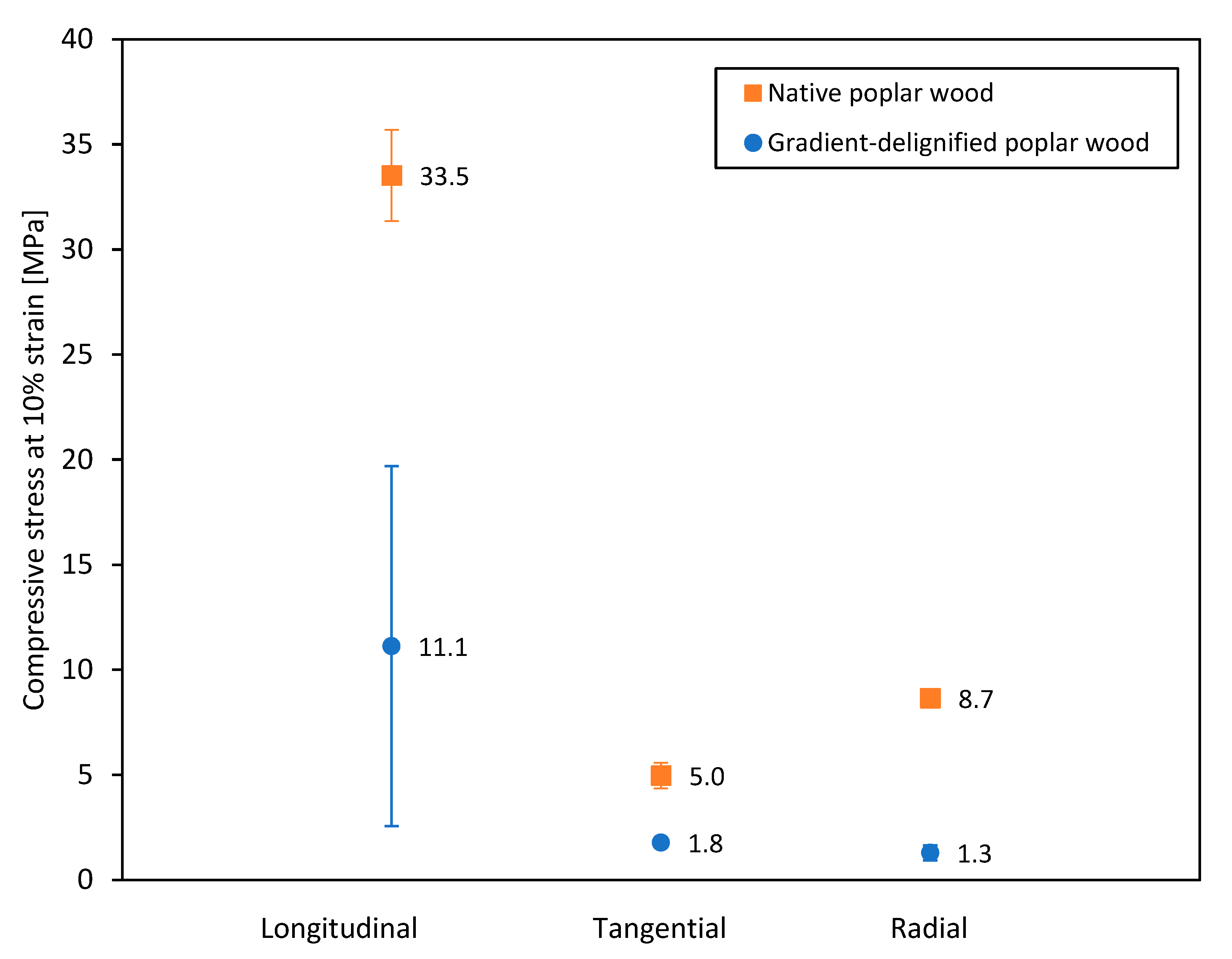
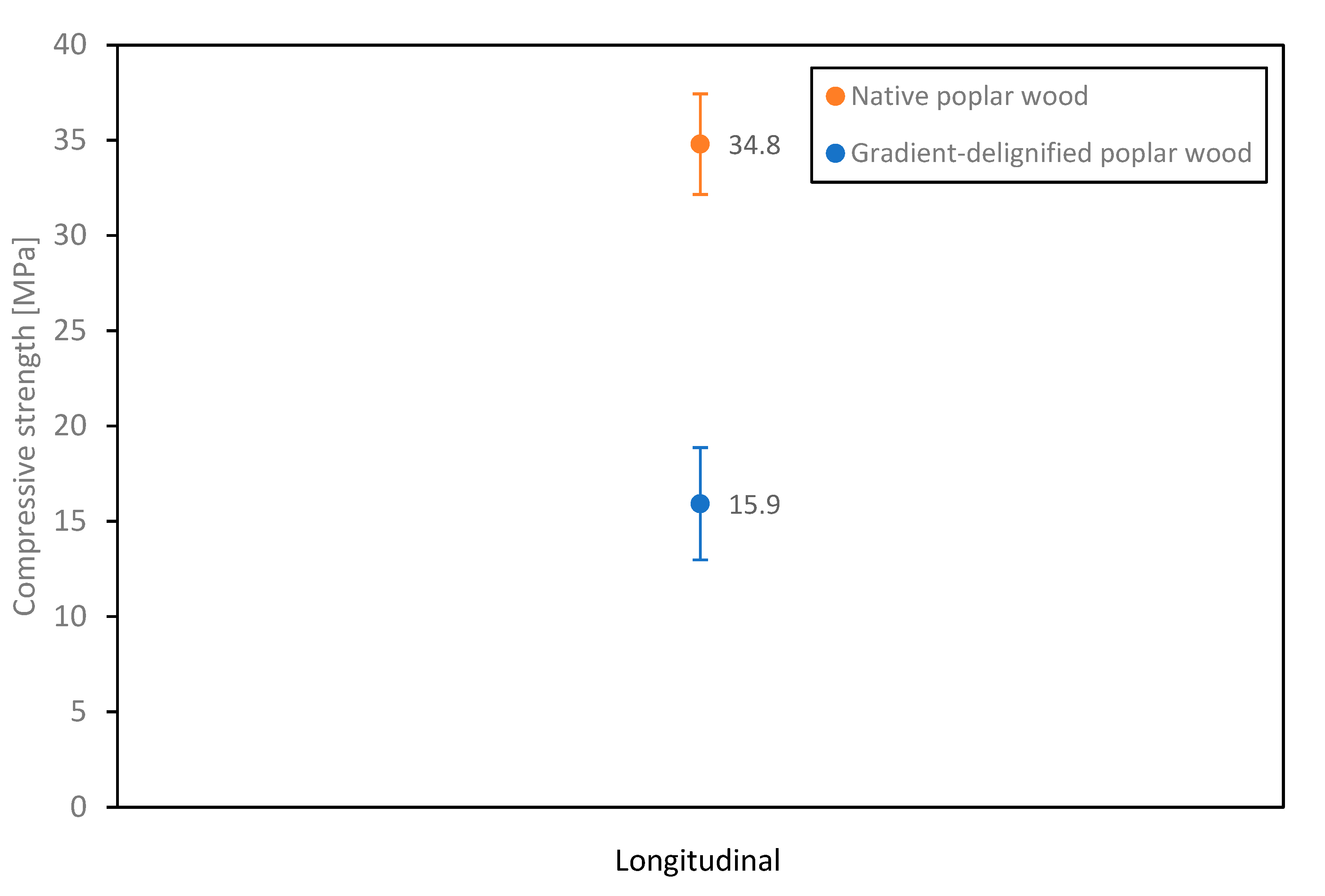
3.4. Mechanical Properties
4. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DVS | Dynamic vapor sorption |
| PIR | Polyisocyanurate |
| RH | Relative humidity |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
References
- Tlaiji, G.; Biwole, P.; Ouldboukhitine, S.; Pennec, F. A Mini-Review on Straw Bale Construction. Energies 2022, 15, 7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yazdkhasti, A.; Mao, Y.; Siciliano, A.P.; Dai, J.; Jing, S.; Xie, H.; Li, Z.; et al. A scalable high-porosity wood for sound absorption and thermal insulation. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, M.; Lewandowski, I.; Pude, R.; Wagner, M. Comparative life cycle assessment of bio-based insulation materials: Environmental and economic performances. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 979–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkour, A.; Ouldboukhitine, S.-E.; Biwole, P.; Amziane, S. A review of multi-scale hygrothermal characteristics of plant-based building materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Chen, C.; Li, T.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Kuang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Hitz, E.; Kong, W.; et al. An Energy-Efficient, Wood-Derived Structural Material Enabled by Pore Structure Engineering towards Building Efficiency. Small Methods 2020, 4, 1900747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, J.; Guibal, D.; Paradis, S.; Vernay, M.; Beauchêne, J.; Brancheriau, L.; Châlon, I.; Daigremont, C.; Détienne, P.; Fouquet, D.; et al. Tropix, version 7; CIRAD: Montpellier, France, 2011; 25 MB. [CrossRef]
- Forest Products Laboratory (Ed.) Wood Handbook: Wood as an Engineering Material, Centennial ed.; General technical report/United States Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory; Forest Products Laboratory, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Madison, WI, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4848-5970-4. [Google Scholar]
- Keplinger, T.; Wittel, F.K.; Rüggeberg, M.; Burgert, I. Wood Derived Cellulose Scaffolds—Processing and Mechanics. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2001375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segmehl, J.S. Wood and Wood-Derived Cellulose Scaffolds for the Preparation of Multi-Functional Materials. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2017; p. 190. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, H.; Hirose, A.; Collins, P.J.; Yazaki, Y. Effects of the removal of matrix substances as a pretreatment in the production of high strength resin impregnated wood based materials. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2001, 20, 1125–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jyske, T.; Petrič, M. Delignified Wood from Understanding the Hierarchically Aligned Cellulosic Structures to Creating Novel Functional Materials: A Review. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2000251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzopoulou, P.; Vouvoudi, E.C.; Achilias, D.S. Delignification as a Key Strategy for Advanced Wood-Based Materials: Chemistry, Delignification Parameters, and Emerging Applications. Forests 2025, 16, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, C.; Zhu, J.Y.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Hu, L. In Situ Wood Delignification toward Sustainable Applications. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 606–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelle, B.P. Traditional, state-of-the-art and future thermal building insulation materials and solutions—Properties, requirements and possibilities. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 2549–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Z.; Pastel, G.; Xu, S.; Jia, C.; Dai, J.; Chen, C.; Gong, A.; et al. Anisotropic, lightweight, strong, and super thermally insulating nanowood with naturally aligned nanocellulose. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Dang, B.; Luo, X.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, S.; Li, S. Deep Eutectic Solvent-Assisted In Situ Wood Delignification: A Promising Strategy To Enhance the Efficiency of Wood-Based Solar Steam Generation Devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 26032–26037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garemark, J.; Perea-Buceta, J.E.; Rico del Cerro, D.; Hall, S.; Berke, B.; Kilpeläinen, I.; Berglund, L.A.; Li, Y. Nanostructurally Controllable Strong Wood Aerogel toward Efficient Thermal Insulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 24697–24707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.; Zha, L.; Koskela, S.; Berglund, L.A.; Zhou, Q. Wood xerogel for fabrication of high-performance transparent wood. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, Y.; Tsushima, R.; Noguchi, K.; Nakaba, S.; Funada, R. Development of colorless wood via two-step delignification involving alcoholysis and bleaching with maintaining natural hierarchical structure. J. Wood Sci. 2020, 66, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Kierzewski, I.; Liu, B.; He, S.; et al. Highly Compressible, Anisotropic Aerogel with Aligned Cellulose Nanofibers. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Tian, F.; She, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhu, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, B.; Xu, X. Thermal Insulation Properties of Delignified Balsa and Paulownia Wood “Foams” with Polylactic Acid Coverings. Forests 2023, 14, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, K.T.; Cardoso, G.V.; Pereira Acosta, A.; Aramburu, A.B.; Delucis, R.D.A.; Gatto, D.A.; Labidi, J.; Beltrame, R. Unveiling the Potential of Brazilian Eucalyptus for Transparent Wood Manufacturing via the Kraft Pulping Process as a Future Building Material. Forests 2024, 15, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurei, T.; Tsushima, R.; Okahisa, Y.; Nakaba, S.; Funada, R.; Horikawa, Y. Creation and Structural Evaluation of the Three-Dimensional Cellulosic Material “White-Colored Bamboo”. Holzforschung 2021, 75, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.H.; Horikawa, Y.; Vial, C.; Gril, J.; Moutou Pitti, R.; Ouldboukhitine, S.-E.; Labonne, N.; Biwole, P. A scalable solvent-exchange strategy for the drying of colorless Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica). Dry. Technol. 2024, 43, 510–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmann, F.F.P.; Côté, W.A. Principles of Wood Science and Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1968; ISBN 978-3-642-87930-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jannot, Y.; Degiovanni, A.; Félix, V.; Bal, H. Measurement of the thermal conductivity of thin insulating anisotropic material with a stationary hot strip method. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 035705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adl-Zarrabi, B.; Boström, L.; Wickström, U. Using the TPS method for determining the thermal properties of concrete and wood at elevated temperature. Fire Mater. 2006, 30, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NF EN ISO 12572; Hygrothermal Performance of Building Materials and Products—Determination of Water Vapour Transmission Properties—Cup Method. AFNOR: Saint-Denis, France, 2016.
- NF EN 12086; Thermal Insulating Products for Building Applications—Determination of Water Vapour Transmission Properties. AFNOR: Saint-Denis, France, 2013.
- NF EN ISO 15148; Hygrothermal Performance of Building Materials and Products—Determination of Water Absorption Coefficient by Partial Immersion. AFNOR: Saint-Denis, France, 2003.
- NF EN 826; Thermal Insulating Products for Building Applications—Determination of Compression Behaviour. AFNOR: Saint-Denis, France, 2013.
- Fu, Q.; Medina, L.; Li, Y.; Carosio, F.; Hajian, A.; Berglund, L.A. Nanostructured Wood Hybrids for Fire-Retardancy Prepared by Clay Impregnation into the Cell Wall. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 36154–36163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fu, Q.; Yu, S.; Yan, M.; Berglund, L. Optically Transparent Wood from a Nanoporous Cellulosic Template: Combining Functional and Structural Performance. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 1358–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurei, T.; Sakai, S.; Nakaba, S.; Funada, R.; Horikawa, Y. Structural and mechanical roles of wood polymer assemblies in softwood revealed by gradual removal of polysaccharides or lignin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, Y.; Tariku, F. Thermal Conductivity and Specific Heat Capacity of Insulation materials at Different Mean Temperatures. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2069, 012090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocentini, K. Comportement Thermo-Hygrique de Blankets Aérogels de Silice et Applications à L’isolation des Bâtiments. Matériaux. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris Sciences et Lettres, Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hemingway, B.S.; Robie, R.A. Heat Capacity of Polystyrene from 275 to 315 K; UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR, U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY: Reston, VA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, J.; Gu, H. Finite Element Analyses of Two Dimensional, Anisotropic Heat Transfer in Wood. In Proceedings of the 2004 International ANSYS Conference, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 24–26 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Busquets-Ferrer, M.; Czabany, I.; Vay, O.; Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Hansmann, C. Alkali-extracted tree bark for efficient bio-based thermal insulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Li, T.; He, S.; Song, J.; Chen, C. Delignified Wood Materials, and Methods for Fabricating and Use Thereof. U.S. Patent US20200238565A1, 30 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Grönquist, P.; Frey, M.; Keplinger, T.; Burgert, I. Mesoporosity of Delignified Wood Investigated by Water Vapor Sorption. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12425–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, C.; Olsén, P.; Berglund, L.A. Interface tailoring by a versatile functionalization platform for nanostructured wood biocomposites. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 8012–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, G.H.; McLean, R.C.; Guo, J. Moisture permeability data presented as a mathematical function applicable to heat and moisture transport models. Build. Simul. 1997, 5, 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Ansari, F.; Zhou, Q.; Berglund, L.A. Wood Nanotechnology for Strong, Mesoporous, and Hydrophobic Biocomposites for Selective Separation of Oil/Water Mixtures. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2222–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastantuoni, G.G.; Tran, V.C.; Garemark, J.; Dreimol, C.H.; Engquist, I.; Berglund, L.A.; Zhou, Q. Rationally designed conductive wood with mechanoresponsive electrical resistance. Compos. Part Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 178, 107970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglund, L.A.; Burgert, I. Bioinspired Wood Nanotechnology for Functional Materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


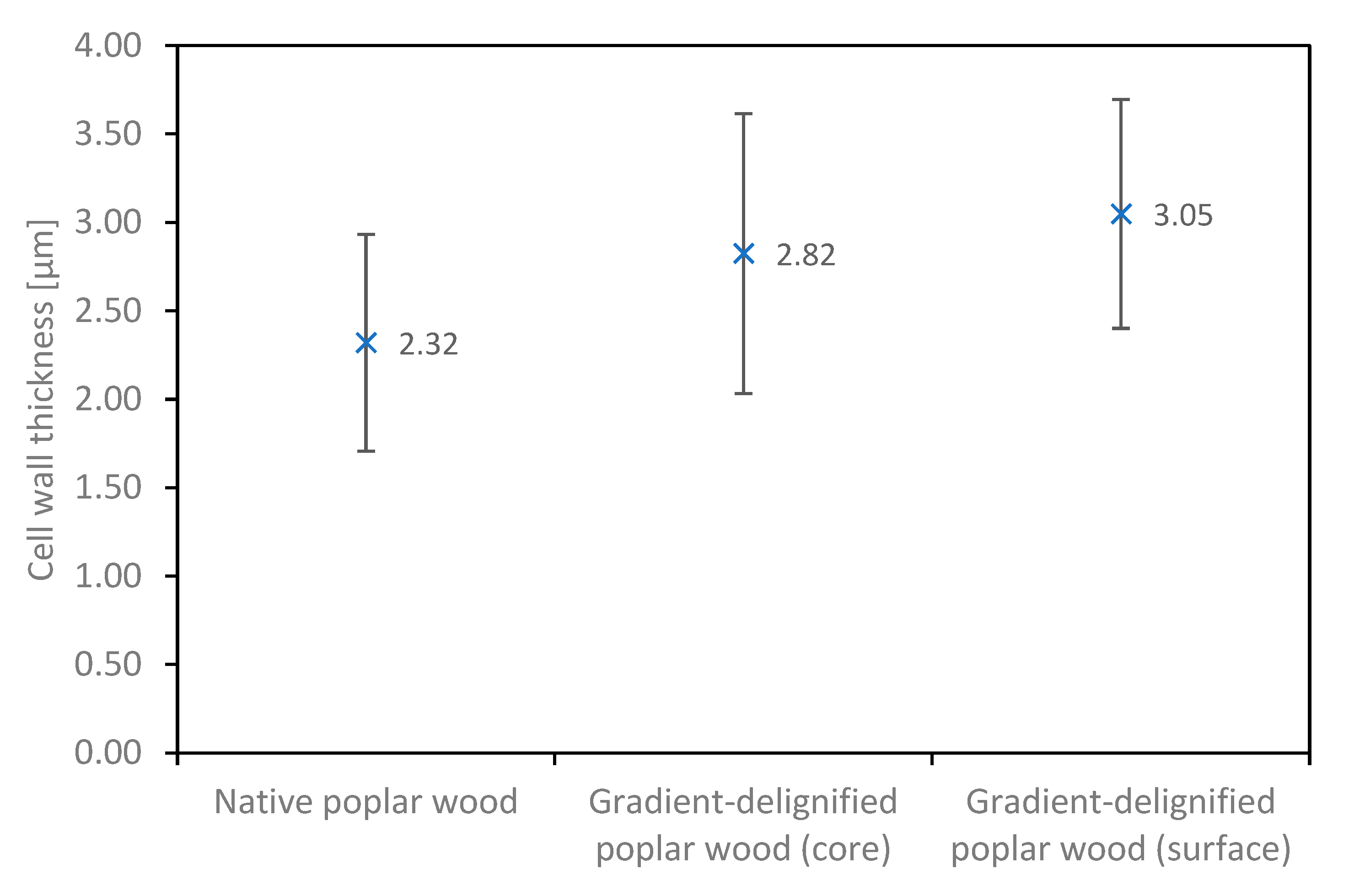



| Type of Poplar Wood | Cell Wall Thickness [µm] |
|---|---|
| Native | 1.46–3.78 |
| Gradient-delignified (core) | 1.77–3.58 |
| Gradient-delignified (surface) | 2.17–3.98 |
| Properties | Native Poplar Wood | Gradient-Delignified Poplar Wood |
|---|---|---|
| Density, ρ [kg·m−3] | 423 | 272 |
| Porosity [%] | 71.8 | 81.9 |
| Specific heat capacity at 20 °C, Cp [kJ·K−1·kg−1] | 1.36 | 1.40 |
| Transverse thermal conductivity, k [W·m−1·K−1] | 0.079 | 0.057 |
| Transverse thermal effusivity, e [J·m−2·K−1·s−0.5] | 213.18 | 147.32 |
| Transverse thermal diffusivity, α [10−7 m2·s−1] | 1.37 | 1.50 |
| Water Vapor Transmission Properties | Stone Wool | PIR | Native Poplar Wood | Gradient-Delignified Poplar Wood |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water vapor permeance, W [10−10 kg·Pa−1·m−2·s−1] | 17.159 | 2.507 | 1.832 | 3.602 |
| Corrected water vapor permeance (without air layer resistance), Wc [10−10 kg·Pa−1·m−2·s−1] | 19.784 | - | - | - |
| Water vapor resistance, Z [109 Pa·m2·s·kg−1] | 0.506 | 3.989 | 5.457 | 2.776 |
| Water vapor permeability, δ [10−12 kg·Pa−1·m−1·s−1] | 22.844 | 3.049 | 1.788 | 3.768 |
| Water vapor diffusion resistance factor, µ [-] | 8.490 | 63.760 | 108.713 | 51.575 |
| Water vapor diffusion-equivalent air layer thickness, Sd [m] | 0.098 | 0.776 | 1.061 | 0.539 |
| Materials | Linear Equation | Coefficient of Determination, R2 | Water Absorption Coefficient, Aw [kg·m−2·s−0.5] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stone wool | + 26 | 0.8947 | 0.203 |
| PIR | + 29 | 0.7273 | 0.064 |
| Native poplar wood (transverse direction) | + 216 | 0.9998 | 4.018 |
| Gradient-delignified poplar wood (transverse direction) | + 3408 | 0.9908 | 6.769 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chin, Y.H.; Ouldboukhitine, S.-E.; Vial, C.; Gril, J.; Moutou Pitti, R.; Labonne, N.; Biwole, P. Gradient-Delignified Wood as a Sustainable Anisotropic Insulation Material. Energies 2025, 18, 5519. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205519
Chin YH, Ouldboukhitine S-E, Vial C, Gril J, Moutou Pitti R, Labonne N, Biwole P. Gradient-Delignified Wood as a Sustainable Anisotropic Insulation Material. Energies. 2025; 18(20):5519. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205519
Chicago/Turabian StyleChin, Yi Hien, Salah-Eddine Ouldboukhitine, Christophe Vial, Joseph Gril, Rostand Moutou Pitti, Nicolas Labonne, and Pascal Biwole. 2025. "Gradient-Delignified Wood as a Sustainable Anisotropic Insulation Material" Energies 18, no. 20: 5519. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205519
APA StyleChin, Y. H., Ouldboukhitine, S.-E., Vial, C., Gril, J., Moutou Pitti, R., Labonne, N., & Biwole, P. (2025). Gradient-Delignified Wood as a Sustainable Anisotropic Insulation Material. Energies, 18(20), 5519. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205519