Electrospun Fabrication of 1–3-Type PVP/SbSI and PVP/SbSeI Nanocomposites with Excellent Piezoelectric Properties for Nanogenerators and Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials Preparation and Their Properties
2.1. Nanowires Preparation
2.2. Characterization of Synthesized Nanowires
2.3. Nanocomposites Preparation
2.4. Analysis of Morphology and Structure of the Fabricated Nanofibres
2.5. Sample Preparation
3. Experimental Methods and Measurement Setups
3.1. Diffuse Reflectance Spectroscopy
3.2. DC Conduction Measurements
3.3. Impedance Spectroscopy
3.4. Piezoelectric Measurements
4. Results
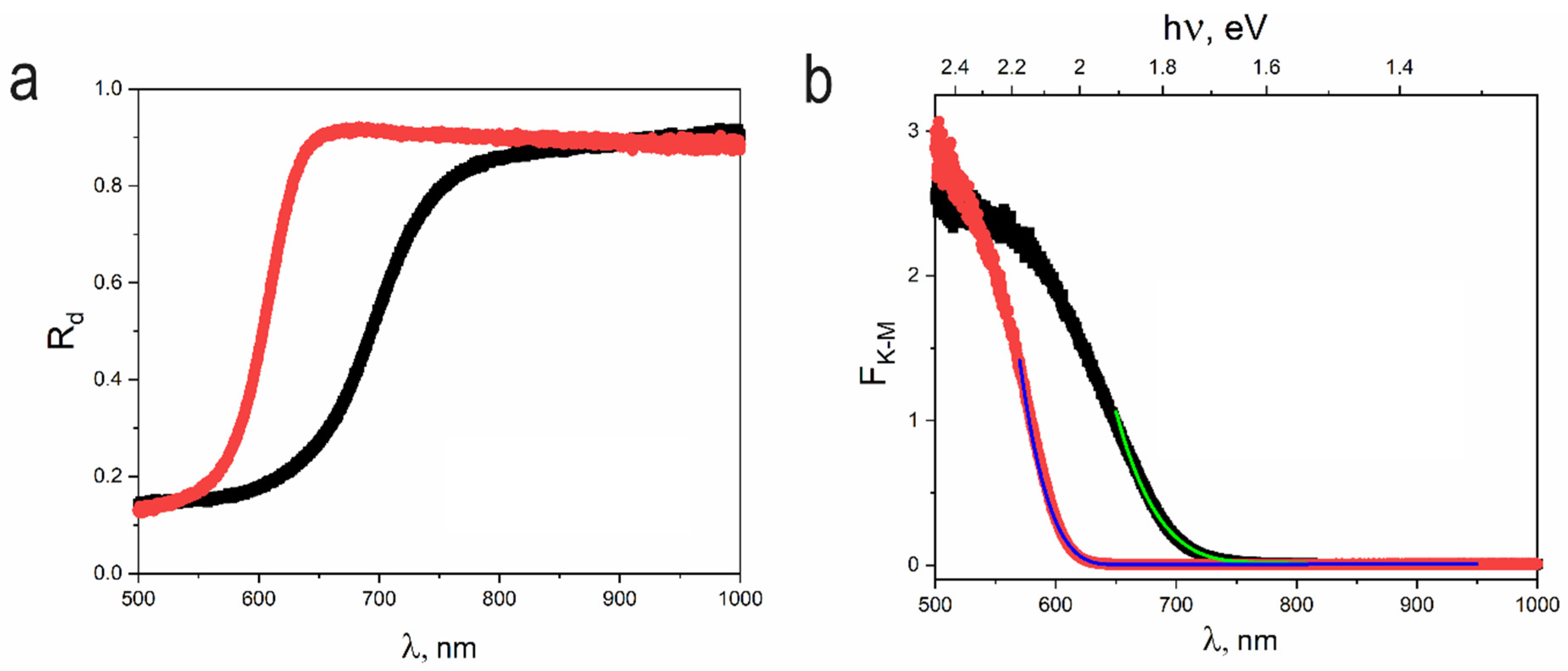
4.1. Light Absorption Properties and Kubelka-Munk Analysis
4.2. Temperature Dependence of DC Conductivity
4.3. Impedance Spectroscopy Results and Equivalent Circuits
4.4. Piezoelectric Properties
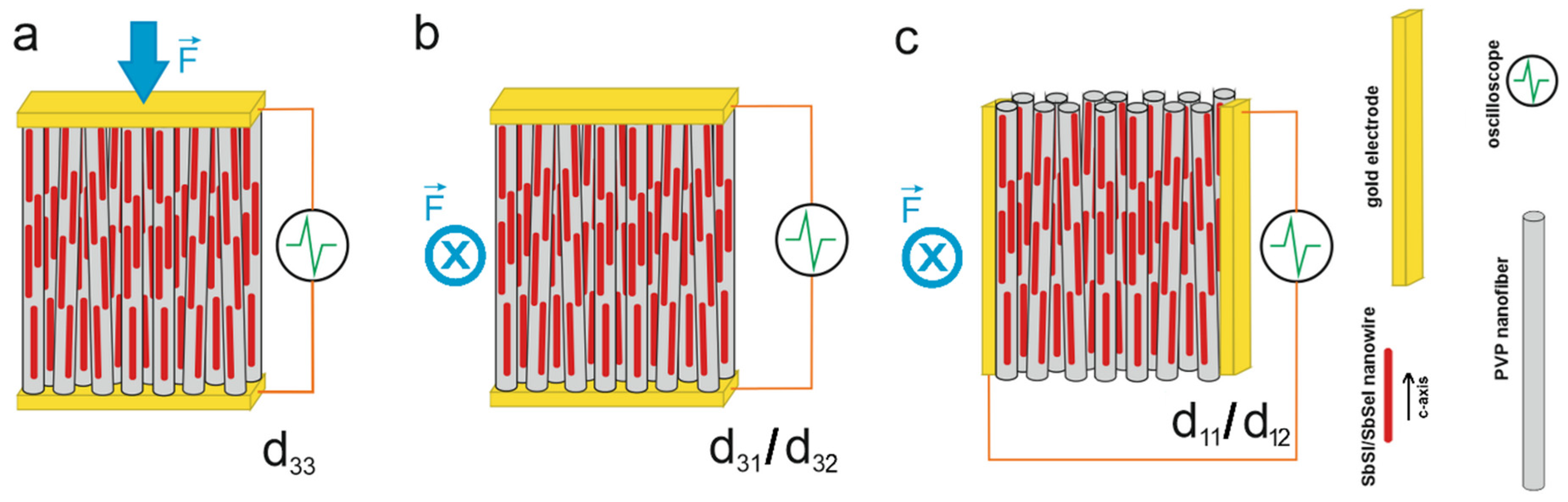
4.4.1. Calculation of d33 and d31/d32 Piezoelectric Coefficients
4.4.2. Determination of the d11/d12 Piezoelectric Coefficients
4.4.3. Influence of Temperature on Piezoelectric Properties
4.4.4. Comparison with Other PVP-Based Materials
| Sample Type | Umax [V] | d33 [pC/N] | Comment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVP/SbSeI | 1.564 | 64.4(73) | Voltage for sandwich structure at 17.03 bar | This work |
| PVP/SbSI | 2.092 | 98(20) | Voltage for sandwich structure at 17.03 bar | This work |
| PVP/(Ti + Zr) | 23.2 | For the composite with 1.25 PVP content. | [66] | |
| Glycine/PVP | 0.11–7.45 | Depending on the glycine-to-PVP ratio | [67] | |
| KNN–LN-PVP | 140 | 0.94KNN–0.06LN with PVP 55K | [68] | |
| PZT/MWCNT/PVP | 16 | Mechanical impact | [69] | |
| P(VDF-TrFE)/PVP/AIL | 6.5 | Finger tapping | [70] | |
| PVP/BaTiO3/MXene/PVDF-TrFE | 3.3 | Pressing with a force of 18 N | [71] | |
| PVP/ZnO | 45 | Finger tapping | [72] | |
| [PAN/BTO]@[PANI/PVP] | ~1 | Nanofibre membrane with 15% BTO contents | [73] |
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hong, H.-K. Preparation of Ag/PVP nanocomposites as a solid precursor for silver nanocolloids solution. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Matysiak, W.; Tański, T.; Zaborowska, M. Electrospinning process and characterization of PVP/hematite nanofibers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 461, 12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Park, D.W.; Shim, S.E. Electrospun PEDOT:PSS/carbon nanotubes/PVP nanofibers as chemiresistors for aromatic volatile organic compounds. Synth. Met. 2012, 162, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, P.; Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S. 2D MoSe2@PVP nanosheets with multi-enzyme activity alleviate the acute pancreatitis via scavenging the reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turky, A.O.; Barhoum, A.; MohamedRashad, M.; Bechlany, M. Enhanced the structure and optical properties for ZnO/PVP nanofibers fabricated via electrospinning technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 17526–17532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divyasree, M.C.; Shiju, E.; Francis, J.; Anusha, P.T.; Rao, S.V.; Chandrasekharan, K. ZnSe/PVP nanocomposites: Synthesis, structural and nonlinear optical analysis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 197, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tański, T.; Matysiak, W.; Krzemiński, Ł.; Jarka, P.; Gołombek, K. Optical properties of thin fibrous PVP/SiO2 composite mats prepared via the sol-gel and electrospinning methods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 424, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, A.H.; Alshammari, K.; Alshammari, M.; Taha, T.A.M. Structural and Optical Characterization of g-C3N4 Nanosheet Integrated PVC/PVP Polymer Nanocomposites. Polymers 2023, 15, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Szperlich, P.; Bober, Ł.; Szala, J.; Moskal, G.; Stróż, D. Sonochemical preparation of SbSI gel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2008, 15, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Kauch, B.; Szperlich, P.; Jesionek, M.; Kepińska, M.; Bober, Ł.; Szala, J.; Moskal, G.; Rzychoń, T.; Stróz, D. Sonochemical preparation of SbSeI gel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooser, E.; Pearson, W.B. The crystal structure and properties of the group VB to VIIB elements and of compounds formed between them. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1958, 7, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, R.; Merz, W.J. Photoconduction in ternary V-VI-VII compounds. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1960, 13, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatuzzo, E.; Harbeke, G.; Merz, W.J.; Nitsche, R.; Roetschi, H.; Ruppel, W. Ferroelectricity in SbSI. Phys. Rev. 1962, 127, 2036–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumi, H.; Terutaro, N.; Yoshihiro, I.; Takako, O. Piezoelectric Property of SbSl Single Crystal. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 20, 1886–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumi, H.; Toshio, S. Electrostriction, Piezoelectricity and Elasticity in Ferroelectric SbSI. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1972, 33, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toroń, B.; Mistewicz, K.; Jesionek, M.; Kozioł, M.; Stróż, D.; Zubko, M. Nanogenerator for dynamic stimuli detection and mechanical energy harvesting based on compressed SbSeI nanowires. Energy 2020, 212, 118717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistewicz, K.; Jesionek, M.; Nowak, M.; Kozioł, M. SbSeI pyroelectric nanogenerator for a low temperature waste heat recovery. Nano Energy 2019, 64, 103906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Kauch, B.; Szperlich, P.; Stróz, D.; Szala, J.; Rzychoń, T.; Bober, Ł.; Toroń, B.; Nowrot, A. Sonochemical preparation of SbS1−xSexI nanowires. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010, 17, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerzanich, E.I.; Lyakhovitskaya, L.A.; Fridkin, V.M.; Popovkin, B.A.; Kaldis, E. Current Topics in Materials Science; North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1982; pp. 141–155. [Google Scholar]
- Starczewska, A.; Nowak, M.; Szperlich, P.; Toroń, B.; Mistewicz, K.; Stróz, D.; Szala, J. Influence of humidity on impedance of SbSI gel. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 183, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.; Yun, H.; Paik, M.-J.; Mehta, A.; Park, B.; Choi, Y.C.; Seok, S.I. Efficient Solar Cells Based on Light-Harvesting Antimony Sulfoiodide. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1701901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, R.; Hu, M.; Risqi, A.M.; Li, Z.; Seok, S.I. Efficient and Stable Antimony Selenoiodide Solar Cells. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, A.C.; Malliakas, C.D.; Liu, Z.; Peters, J.A.; Sebastian, M.; Chung, D.Y.; Wessels, B.W.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Photoconductivity in the Chalcohalide Semiconductor, SbSeI: A New Candidate for Hard Radiation Detection. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 7045–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grekov, A.A.; Danilova, S.P.; Zaks, P.L.; Kulieva, V.V.; Rubanov, L.A.; Syrkin, L.N.; Chekhunova, N.P.; Elgard, A.M. Piezoelectric elements made from antimony sulfoiodide crystals. Sov. Phys. Acoust. 1974, 19, 393–394. [Google Scholar]
- Kozioł, M.; Toroń, B.; Szperlich, P.; Jesionek, M. Fabrication of a piezoelectric strain sensor based on SbSI nanowires as a structural element of a FRP laminate. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 157, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szperlich, P.; Toroń, B. An ultrasonic fabrication method for epoxy resin/SbSI nanowire composites, and their application in nanosensors and nanogenerators. Polymers 2019, 11, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toroń, B.; Szperlich, P.; Nowak, M.; Stróż, D.; Rzychoń, T. Novel piezoelectric paper based on SbSI nanowires. Cellulose 2018, 25, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesionek, M.; Toroń, B.; Szperlich, P.; Biniaś, W.; Biniaś, D.; Rabiej, S.; Starczewska, A.; Nowak, M.; Kępińska, M.; Dec, J. Fabrication of a new PVDF/SbSI nanowire composite for smart wearable textile. Polymer 2019, 180, 121729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purusothaman, Y.; Alluri, N.R.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Kim, S.-J. Photoactive piezoelectric energy harvester driven by antimony sulfoiodide (SbSI): A AVBVICVII class ferroelectric-semiconductor compound. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Tański, T.; Szperlich, P.; Matysiak, W.; Kępińska, M.; Stróż, D.; Bober, Ł.; Toroń, B. Using of sonochemically prepared SbSI for electrospun nanofibers. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, C.-W.; Jia, Q. Obtaining ultimate functionalities in nanocomposites: Design, control, and fabrication. MRS Bull. 2015, 40, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnithan, A.R.; Arathyram, R.S.; Kim, C.S. Electrospinning of Polymers for Tissue Engineering. In Nanotechnology Applications for Tissue Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.K. Ceramic Nanofibers by Electrospinning Technique—A Review. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2007, 66, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.P.F.; da Silva, A.B.; Arjmand, M.; Sundararaj, U.; Bretas, R.E.S. Nanofibers of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/copper nanowire: Microstructural analysis and dielectric behavior. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 101, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rianjanu, A.; Marpaung, K.D.P.; Melati, E.K.A.; Aflaha, R.; Wibowo, Y.G.; Mahendra, I.P.; Yulianto, N.; Widakdo, J.; Triyana, K.; Wasisto, H.S.; et al. Integrated adsorption and photocatalytic removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by hierarchical Nb2O5@PAN/PVDF/ANO composite nanofibers. Nano Mater. Sci. 2024, 6, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Huang, Y.; Kang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Yin, K.; Nie, M.; Sun, L. SnO2 induced electrostatic polarization PVDF composite nanofibers for efficient energy harvesting and self-powered wireless monitoring/motion recognition systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, B.; Ghosh, S.K.; Prasad, G.; Shanmugasundaram, A.; Lee, D. Giant Energy Harvesting via Maxwell Displacement Current Enhancement Using Metal Sheet Interspaced Hetero-Layer Structured Piezo-Composite Nanofiber Device. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2307723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.; Fang, K.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Liang, Y. Green preparation of water-stable coptidis-dyeing composite nanofiber filters with ultraviolet shielding and antibacterial activity and biodegradability. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 336, 126289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Qu, Q.; Ma, W.; Li, F.; Du, W.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Q.; He, S.; Huang, C. Free-standing porous carbon nanofiber membranes obtained by one-step carbonization and activation for high-performance supercapacitors. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 329, 111545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zhong, L. Advanced separators based on aramid nanofiber (ANF) membranes for lithium-ion batteries: A review of recent progress. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 12923–12946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat Bayan, M.A.; Afshar Taromi, F.; Lanzi, M.; Pierini, F. Enhanced efficiency in hollow core electrospun nanofiber-based organic solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tressler, J.F.; Alkoy, S.; Dogan, A.; Newnham, R.E. Functional composites for sensors, actuators and transducers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1999, 30, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlincourt, D.; Jaffe, H.; Merz, W.J.; Nitsche, R. Piezoelectric Effect in the Ferroelectric Range in SbSI. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1964, 4, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiding, C.; Schmidt, G. Piezoelectricity and electrostriction of SbSJ single crystals. Phys. Status Solidi 1972, 9, K77–K80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, A.S.; Newnham, R.E.; Shrout, T.R.; Cross, L.E. Piezoelectric SbSI: Polymer composites. Ferroelectrics 1982, 41, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toroń, B.; Szperlich, P.; Nowak, M.; Starczewska, A. A novel method for measuring piezoelectric coefficients. Measurement 2023, 206, 112274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Kauch, B.; Szperlich, P. Determination of energy band gap of nanocrystalline SbSI using diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2009, 80, 46107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, K.; Siddaiah, T.; Gopal, N.O.; Madhava Kumar, Y.; Ramu, C. Optical and electrical conductivity studies of VO2+ doped polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) polymer electrolytes. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S. Study of Optical properties of Polymer PVP thin films grafted by Fluorescence dyes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1879, 32111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toroń, B.; Nowak, M.; Kępińska, M.; Szperlich, P. Mobility of ferroelectric domains in antimony sulfoiodide. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2014, 126, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szperlich, P.; Nowak, M.; Bober, Ł.; Szala, J.; Stróż, D. Ferroelectric properties of ultrasonochemically prepared SbSI ethanogel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahenoor Basha, S.; Sunita Sundari, G.; Vijay Kumar, K.; Veera Bhadra Reddy, K.; Rao, M.C. Electrical conduction behaviour of PVP based composite polymer electrolytes. Rasayan J. Chem. 2017, 10, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, K.; Siddaiah, T.; Gopal, N.O.; Jyothi, N.K.; Kumar, K.V.; Ramu, C. Thermal, Structural, Optical and Electrical Conductivity studies of pure and Mn2+ doped PVP films. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 36, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengwa, R.J.; Choudhary, S.; Dhatarwal, P. Nonlinear optical and dielectric properties of TiO2 nanoparticles incorporated PEO/PVP blend matrix based multifunctional polymer nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 12275–12294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahalyani, J.; Rahangdale, K.K.; K, B. The dielectric properties and charge transport mechanism of π-conjugated segments decorated with intrinsic conducting polymer. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 69733–69742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonscher, A.K. Dielectric relaxation in solids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, R57–R70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.R. Complex Nonlinear Least Squares Immitance Fitting Program LEVM. (n.d.). Available online: https://www.jrossmacdonald.com/levmlevmw/ (accessed on 17 October 2025).
- Song, S.-H.; Xiao, P. An impedance spectroscopy study of oxide films formed during high temperature oxidation of an austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audzijonis, A.; Žigas, L.; Sereika, R.; Žaltauskas, R. Electronic Structure and Piezoelectric Properties of SbSI Crystals. In Piezoelectric Materials; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Briscoe, J.; Dunn, S. Piezoelectric nanogenerators—A review of nanostructured piezoelectric energy harvesters. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasipour, M.; Khajavi, R.; Akbarzadeh, A.H. A Comprehensive Review on Piezoelectric Polymeric and Ceramic Nanogenerators. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2101312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuo Shoji, K.S.; Yasuo Uehara, Y.U. Grain Orientation of SbSI Ceramics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 30, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbarz-Glos, B.; Grigas, J. Modified SbSI Electroceramics. Ferroelectrics 2009, 393, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, R.; Amaral, H.; Levelut, A.; Ziolkiewicz, S.; Balkanski, M.; Teng, M.K.; Vittori, J.F.; Stone, H. Tricritical Point Induced by Atomic Substitution in SbSexS1−xI. Phys. Status Solidi 1982, 73, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.S.; Park, C.K.; Cho, J.H.; Paik, J.-H.; Jeong, Y.H.; Nam, J.-H.; Hwang, K.-R. The effect of PVP contents on the fiber morphology and piezoelectric characteristics of PZT nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2014, 137, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Liao, J.; Peng, Z.; Li, P.; Yang, X.; Yan, X.; Hong, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. One-step high-speed thermal-electric aerosol printing of piezoelectric bio-organic films for wirelessly powering bioelectronics. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadq3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.K.I.; Yao, K.; Goh, P.C.; Ma, J. 0.94(K0.5Na0.5)NbO3–0.06LiNbO3 piezoelectric ceramics prepared from the solid state reaction modified with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) of different molecular weights. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 2513–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanish Babu, T.; Madhuri, W. A hybrid microwave sintered PZT composite as a flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 34454–34462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, V.; Khanduri, P.; Ansari, M.U.; Anoop, G.; Park, S. P(VDF-TrFE)/PVP/ionic liquid-based piezo-ionic polymer blend for touch sensing applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 362, 114680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, C.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z. Flexible piezoelectric sensor based on PVP-modified BaTiO3/MXene/PVDF-TrFE composite film for wearable applications. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2025, 36, 095102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, S.; Hassan, G.; Shuja, A. Fabrication and Characterization of Piezoelectric Nanogenerator Based on ZnO and PVP for Harvesting Energy System Applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2025, 36, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Jiang, W.; Hu, K.; Lyu, Z. Synchronous Construction of Piezoelectric Elements and Nanoresistance Networks for Pressure Sensing Based on the Wheatstone Bridge Principle. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2021, 3, 3936–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| PVP/SbSI Nanofibres | PVP/SbSeI Nanofibres | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element-Line | Wt% | At% | Element-Line | Wt% | At% |
| C-K | 72.6 | 86.85 | C-K | 61.86 | 82.81 |
| O-K | 3.28 | 2.95 | O-K | 2.98 | 2.99 |
| Al-K | 17.8 | 9.48 | Al-K | 17.77 | 11.84 |
| Au-M | 3.19 | 0.23 | Au-M | 2.75 | 0.22 |
| S-K | 0.39 | 0.17 | Se-L | 3.66 | 0.74 |
| Sb-L | 1.23 | 0.15 | Sb-L | 5.36 | 0.71 |
| I-L | 1.51 | 0.17 | I-L | 5.62 | 0.69 |
| Sample Type | Thickness; d [mm] | The Area Between Electrodes; A [mm2] |
|---|---|---|
| PVP/SbSI sandwich | 0.5 | 5.1 |
| PVP/SbSI planar | 0.1 | 1.9 × 18.3 |
| PVP/SbSeI sandwich | 0.5 | 5.1 |
| PVP/SbSeI planar | 0.1 | 1.9 × 19.2 |
| PVP/SbSI | PVP/SbSeI | |
|---|---|---|
| A0 [m−1] | 0.5382(42)·10−2 | 0.5398(80)·10−2 |
| A1 [m−1eV−3] | 77.4(43) | 34.09(57) |
| EgIf [eV] | 1.9091(20) | 1.6142(13) |
| A2 [m−1] | - | 0.34(12)·10−8 |
| EU [eV] | - | 0.1067(25) |
| PVP/SbSI | PVP/SbSeI | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| T < TC | T > TC | ||
| a [K] | −6845(34) | −528.4(16) | −366.5(15) |
| b | 7.51(12) | −14.3112(51) | −16.4360(50) |
| Ea [meV] | 589.9(29) | 45.53(14) | 31.58(13) |
| Sample Type | Umax [V] | t1 [ms] | A [mm2] | dij [pC/N] | η [mV/bar] | E [nJ] | PS [µW/cm2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVP/SbSeI planar | 0.526 | 2.5 | 5.34 | d31 = 35.0(45) | 84(22) | 0.065 | 0.49 |
| 0.806 | 0.115 | 0.86 | |||||
| 1.000 | 0.170 | 1.28 | |||||
| PVP/SbSeI sandwich | 0.910 | 4.0 | 5.10 | d33 = 64.4(73) | 130(35) | 0.289 | 1.42 |
| 1.272 | 0.378 | 1.85 | |||||
| 1.564 | 0.468 | 2.29 | |||||
| PVP/SbSI planar | 0.495 | 4.3 | 5.34 | d31 = 37.2(34) | 73(17) | 0.155 | 0.67 |
| 0.687 | 0.276 | 1.20 | |||||
| 1.116 | 1.080 | 4.71 | |||||
| PVP/SbSI sandwich | 1.564 | 5.7 | 5.10 | d33 = 98(20) | 202(73) | 1.465 | 5.04 |
| 1.868 | 3.468 | 11.93 | |||||
| 2.092 | 3.499 | 12.04 |
| Sample | Nanowires and Electrodes Alignment | Umax [V] | t1 [ms] | A [mm2] | dij [pC/N] | η [mV/bar] | E [nJ] | PS [µW/cm2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVP/SbSeI planar | parallel | 0.212 | 2.5 | 5.34 | d11 = 7.1 | 12.4 | 0.019 | 0.14 |
| perpendicular | 1.000 | 2.5 | 5.34 | d31 = 33.3 | 58.8 | 0.170 | 1.28 | |
| PVP/SbSI planar | parallel | 0.720 | 4.3 | 5.34 | d11 = 24.0 | 42.3 | 0.284 | 1.24 |
| perpendicular | 1.116 | 4.3 | 5.34 | d31 = 37.1 | 65.5 | 1.080 | 4.71 |
| Sample | T [K] | Umax [V] | t1 [ms] | A [mm2] | d31 [pC/N] | η [mV/bar] | E [nJ] | PS [µW/cm2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVP/SbSeI planar | 278 | 1.140 | 0.8 | 5.34 | 38.0 | 66.9 | 0.242 | 5.67 |
| 298 | 1.000 | 2.5 | 5.34 | 33.3 | 58.7 | 0.170 | 1.28 | |
| PVP/SbSI planar | 278 | 2.105 | 4.3 | 5.34 | 70.2 | 123.6 | 4.780 | 20.82 |
| 298 | 1.116 | 4.3 | 5.34 | 37.2 | 65.5 | 1.080 | 4.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toroń, B.; Matysiak, W.; Starczewska, A.; Dec, J.; Szperlich, P.; Nowak, M. Electrospun Fabrication of 1–3-Type PVP/SbSI and PVP/SbSeI Nanocomposites with Excellent Piezoelectric Properties for Nanogenerators and Sensors. Energies 2025, 18, 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205506
Toroń B, Matysiak W, Starczewska A, Dec J, Szperlich P, Nowak M. Electrospun Fabrication of 1–3-Type PVP/SbSI and PVP/SbSeI Nanocomposites with Excellent Piezoelectric Properties for Nanogenerators and Sensors. Energies. 2025; 18(20):5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205506
Chicago/Turabian StyleToroń, Bartłomiej, Wiktor Matysiak, Anna Starczewska, Jan Dec, Piotr Szperlich, and Marian Nowak. 2025. "Electrospun Fabrication of 1–3-Type PVP/SbSI and PVP/SbSeI Nanocomposites with Excellent Piezoelectric Properties for Nanogenerators and Sensors" Energies 18, no. 20: 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205506
APA StyleToroń, B., Matysiak, W., Starczewska, A., Dec, J., Szperlich, P., & Nowak, M. (2025). Electrospun Fabrication of 1–3-Type PVP/SbSI and PVP/SbSeI Nanocomposites with Excellent Piezoelectric Properties for Nanogenerators and Sensors. Energies, 18(20), 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205506









