Physics-Informed Neural Networks in Grid-Connected Inverters: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
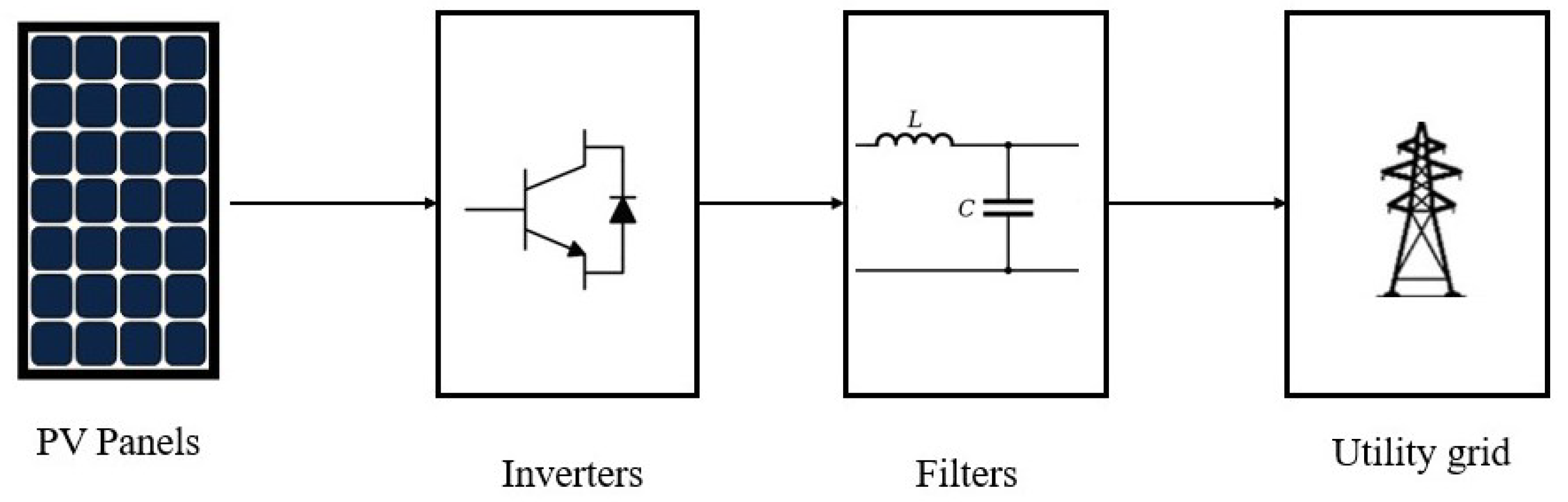
2. An Overview to Grid-Connected Inverters
3. Data-Driven Approaches for Grid-Connected Inverter Systems
4. Architecture and Applications of Physics-Informed Neural Networks in Grid-Connected Inverters
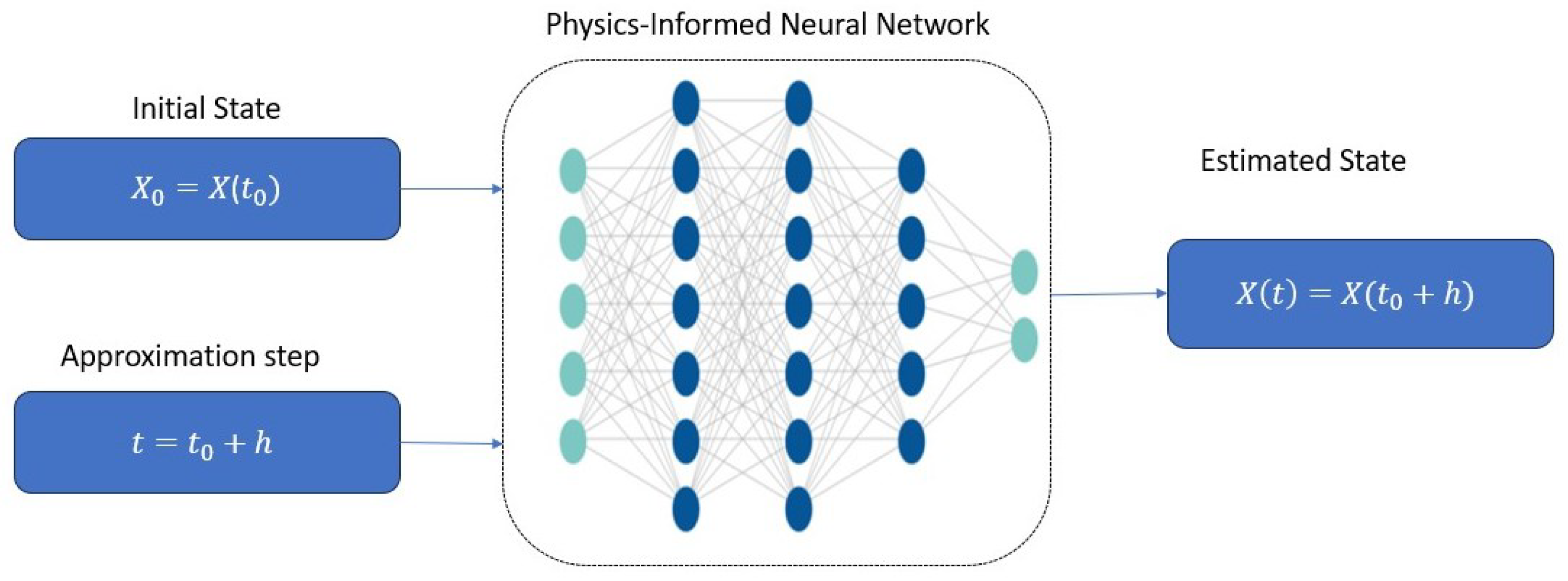
4.1. Architecture of PINN
- (i)
- a data loss: mean-squared error between predicted and measured values, if any
- (ii)
- PDE loss: MSE of the PDE residual at collocation points
- (iii)
- a boundary/initial-condition loss
4.2. Applications of PINN in GCISs
4.2.1. Parameter Estimation
4.2.2. State Estimation
4.2.3. Control Strategies
4.2.4. Fault Detection and Diagnosis
4.2.5. System Identification
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PINNs | Physics-Informed Neural Networks |
| GCISs | Grid-Connected Inverter Systems |
| DERs | Distributed Energy Resources |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| RESs | Renewable Energy Sources |
| EMT | Electromagnetic Transient |
| PDEs | Partial Differential Equations |
| ODEs | Ordinary Differential Equations |
| gPINNs | gradient-Enhanced Physics-Informed Neural Networks |
| BPINNs | Bayesian Physics-Informed Neural Networks |
| UPINN | Uniform Physics-Informed Neural Network |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| MSEs | Mean Square Errors |
| PINC | Physics-Informed Neural Control |
| CNNs | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| GCNNs | Graph Convolutional Neural Networks |
| GCPIs | Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Inverters |
| THDI | Total Harmonic Distortion |
| MLPNN | Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| ePINNs | Enhanced Physics-Informed Neural Networks |
| PIML | Physics-Informed Machine Learning |
| UKF | Unscented Kalman Filter |
| GNN-PINN | Graph-Based Physics-Informed Neural Network |
| ICRs | Inverter-Coupled Resources |
| MPC | Model Predictive Control |
| NMPC | Nonlinear Model Predictive Control |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| VSCs | Voltage Source Converters |
| NPC | Neutral Point Clamped |
| IBRs | Inverter-Based Resources |
| HIFs | High Impedance Faults |
| PICAE | Physics-Informed Convolutional Autoencoder |
| PMU | Phasor Measurement Unit |
| ISCF | Interturn Short Circuit Faults |
| SINDy | Sparse Identification of Nonlinear Dynamics |
| SELMs | Sparse Extreme Learning Machines |
References
- Nair, V.J. Enhanced Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) for High-Order Power Grid Dynamics. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.07527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, P.; Cui, C.; Lin, P.; Ghias, A.M.Y.M.; Niu, X.; Zhang, C. On Physics-Informed Neural Network Control for Power Electronics. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.15787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Jung, Y.; Kang, S.; Jang, G. Physics-Informed Neural Network-Based VSC Back-to-Back HVDC Impedance Model and Grid Stability Estimation. Electronics 2024, 13, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasimalla, S.R.; Park, K.; Hong, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, H. AI-Enhanced Inverter Fault and Anomaly Detection System for Distributed Energy Resources in Microgrids. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.08761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedula, S.; Olajube, A.; Anubi, O. Fault-Tolerant Decentralized Control for Large-scale Inverter-based Resources for Active Power Tracking. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.03444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics Informed Deep Learning (Part I): Data-Driven Solutions of Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, Z.K.; Yassin, H.; Lai, D.T.C.; Idris, A.C. Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN) Evolution and Beyond: A Systematic Literature Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2022, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, S.; Schiano Di Cola, V.; Giampaolo, F.; Rozza, G.; Raissi, M.; Piccialli, F. Scientific Machine Learning Through Physics–Informed Neural Networks: Where we are and What’s Next. J. Sci. Comput. 2022, 92, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Fan, F.; Sun, Q.; Jie, H.; Shu, Z.; Wang, W.; See, K.Y. Physics Informed Neural Network-based High-frequency Modeling of Induction Motors. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2022, 8, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misyris, G.S.; Venzke, A.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Power Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Montreal, QC, Canada, 2–6 August 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganga, S.; Uddin, Z. Exploring Physics-Informed Neural Networks: From Fundamentals to Applications in Complex Systems. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.00422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, D.; Pham, K.; Tran, T. MP-PINN: A Multi-Phase Physics-Informed Neural Network for Epidemic Forecasting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.06781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Zhou, D.; Wei, X.; Wang, H. A Physics-informed Neural Network Method for LC Parameter Estimation in Three-Phase Inverter. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 10th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC-ECCE Asia), Chengdu, China, 17–20 May 2024; pp. 3957–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, M.; Graichen, K. PINN-based Dynamical Modeling and State Estimation in Power Inverters. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications (CCTA), Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 21–23 August 2024; pp. 618–623. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, Q.H.; Nguyen, B.L.H.; Vu, T.V.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, T. Physics-informed graphical neural network for power system state estimation. Appl. Energy 2024, 358, 122602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misyris, G.; Stiasny, J.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Capturing Power System Dynamics by Physics-Informed Neural Networks and Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2021 60th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Austin, TX, USA, 14–17 December 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, D.; Lalic, B.; Petrić, M.; Nguyen, B.; Roantree, M. Adapting Physics-Informed Neural Networks to Improve ODE Optimization in Mosquito Population Dynamics. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0320342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, M.T. Theory-training deep neural networks for an alloy solidification benchmark problem. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2020, 180, 109687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasoudi, F. Enhancing Power Grid Resilience through Real-Time Fault Detection and Remediation Using Advanced Hybrid Machine Learning Models. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, P.; Maragliano, G.; Marchesoni, M.; Parodi, G. A New Fault Detection Method for NPC Converters. In Proceedings of the 2011 14th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Birmingham, UK, 30 August–1 September 2011; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Stiasny, J.; Misyris, G.S.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Physics-informed neural networks for non-linear system identification for power system dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Madrid PowerTech, Madrid, Spain, 28 June–2 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, S.; Babazadeh, D.; Becker, C.; Chatzivasileiadis, S. Bayesian Physics-informed Neural Networks for System Identification of Inverter-Dominated Power Systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 235, 110860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, S.; Hadi, A.A.; Challoo, R. Novel Neural Control of Single-Phase Grid-Tied Multilevel Inverters for Better Harmonics Reduction. Electronics 2018, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Yang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Q.; Yu, H. Data-driven Optimal Power Flow: A Physics-Informed Machine Learning Approach. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.00544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. A Convolutional Neural Network-Based Method of Inverter Fault Diagnosis in a Ship’s DC Electrical System. Pol. Marit. Res. 2022, 29, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Fan, J. Adaptive Feature Extraction and Fault Diagnosis for Three-Phase Inverter Based on Hybrid-CNN Models Under Variable Operating Conditions. Complex Intell. Syst. 2021, 8, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Gama, F.; Lavaei, J.; Sojoudi, S. Distributed Power System State Estimation Using Graph Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elattar, Y.; Stovall, F.A.; Lipo, T.A. Harmonic Distortion Prediction Model of a Grid-Tie Photovoltaic Inverter Using an Artificial Neural Network. Energies 2019, 12, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothala, D.G.; Vasi, L.; Pagadam, N.K. Recurrent Neural Network Based Fault Identification System For PV System Interfaced Three Phase Multimachine Grid System. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Recent Innovation in Smart and Sustainable Technology (ICRISST), Bengaluru, India, 15–16 March 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shamash, Y.A.; Sharma, R.; Chen, B. Physics-Informed AI Inverter. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.17661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelo, E.; Camponogara, E.; Seman, L.; Jordanou, J.; Souza, E.; Hübner, J. Physics-Informed Neural Nets for Control of Dynamical Systems. Neurocomputing 2024, 579, 127419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayana, S.; Sthapit, S.; Maple, C. Application of Physics-Informed Machine Learning Techniques for Power Grid Parameter Estimation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.H.; Tsai, J.T.; Lian, K.L. A Non-Invasive Method for Estimating Circuit and Control Parameters of Voltage Source Converters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 4911–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, F.; Dana, N.H.; Sarker, S.K.; Li, L.; Muyeen, S.M.; Ali, F.M.; Tasneem, Z.; Hasan, M.M.; Abhi, S.H.; Islam, M.R.; et al. Data-driven next-generation smart grid towards sustainable energy evolution: Techniques and technology review. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2023, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassi, Y.; Heiries, V.; Boutet, J.; Boisseau, S. Toward Physics-Informed Machine-Learning-Based Predictive Maintenance for Power Converters—A Review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 2692–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, B.; Harrison, G. Physics-Informed Neural Network for Microgrid Forward/Inverse Ordinary Differential Equations. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Seattle, WA, USA, 21–25 July 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Sahoo, S.; Sangwongwanich, A.; Blaabjerg, F.; Hassanifar, M.; Votava, M.; Langwasser, M.; Liserre, M. Physics-Informed Neural Network for Parameter Identification: A Buck Converter Case Study. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.20528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbomwan, O.E.; Liu, S.; Chaoui, H. Physics-Informed Neural Network for Inertia Estimation of Power System with Inverter-Based Distributed Generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems (ICPS), St. Louis, MO, USA, 12–15 May 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S. Physics-informed Neural Network-Based Control of Power Electronic Converters. In Control of Power Electronic Converters and Systems; Blaabjerg, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; Volume 4, pp. 309–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oner, M.U.; İlker, Ş.; Keysan, O. Neural Networks Detect Inter-Turn Short Circuit Faults Using Inverter Switching Statistics for a Closed-Loop Controlled Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 2387–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Subhan, F.E.; Khan, W.; Faheem, M.; Wang, J.; Bhutta, M.S. Uniform Physics Informed Neural Network Framework for Microgrid and Its Application in Voltage Stability Analysis. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 4576–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, R.; Babazadeh, D.; Stock, S.; Becker, C. Real-time inertia estimation in an inverter-dominated distribution grid using a physics-informed recurrent neural network. In Proceedings of the CIRED Porto Workshop 2022: E-Mobility and Power Distribution Systems, Porto, Portugal, 2–3 June 2022; Volume 2022, pp. 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falas, S.; Asprou, M.; Konstantinou, C.; Michael, M.K. Physics-Informed Neural Networks for Accelerating Power System State Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE PES Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Europe (ISGT EUROPE), Grenoble, France, 23–26 October 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhong, M.; Xu, K.; Sánchez-Cortés, L.G.; Guerra, I.d.C. PINNs-Based Uncertainty Quantification for Transient Stability Analysis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.12947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Deka, D. Physics-Informed Learning for High Impedance Faults Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Madrid PowerTech, Madrid, Spain, 28 June–2 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Y. Inverse physics–informed neural networks for digital twin–based bearing fault diagnosis under imbalanced samples. Knowl. Based Syst. 2024, 292, 111641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Physical-Information-Based Neural Network Grid-Connected Inverter Impedance Model. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 2nd International Power Electronics and Application Symposium (PEAS), Guangzhou, China, 10–13 November 2023; pp. 2559–2562. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Sun, W.; Jiang, D.; Li, D.; Qu, R. An Inverter Nonlinearity Identification Method Based on Physics-Informed Network for Different Working Conditions. Res. Sq. 2024. preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood-Alexander, M.; Arcieri, G.; Kamariotis, A.; Chatzi, E. Response Estimation and System Identification of Dynamical Systems via Physics-Informed Neural Networks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.01340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, C.; Zhang, P.; Shamash, Y.A. Physics-Informed, Safety and Stability Certified Neural Control for Uncertain Networked Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2023, 15, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Aspects | SELM | CNN | MLP | RNN | GCNN | PINN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small datasets | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Dynamic estimation | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| System physics integration | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Scalability for large systems | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ |
| Robustness to noise/cyber-attacks | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Ref. | Application | Task | Efficiency | Data Required | Validation | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [50] | Power Systems (Nonlinear Dynamics) | System Identification | Captured nonlinear dynamics; good qualitative match | Small time-domain datasets | Simulation | No hardware validation; model simplifications |
| [21] | Power System Dynamics | System Identification | Accurate dynamic reconstruction | Voltage/angle data | Simulation | Sensitive to complexity of equations |
| [30] | Grid-Connected Inverter (EMT) | System Identification | × faster than PSCAD | Moderate | Simulation | Needs real-world validation |
| [22] | Inverter-Dominated Grids | System Identification | Orders-of-magnitude error reduction vs. SINDy | Synthetic | IEEE Test Cases | Sensitive to priors; high cost |
| [13] | 3-Phase Inverter (LC) | Parameter Estimation | (C), (L) | 360 samples/phase | Simulation and Hardware | ADC quantization/sync issues |
| [10] | Buck Converter | Parameter Estimation | Median errors <5% | Moderate | Simulation | Accuracy-speed trade-off |
| [15] | Power Grid | State Estimation | lower MSE vs. baseline | Bus-wise data | IEEE Test Cases | Not inverter-level states |
| [1] | High-Order Inverter | State Estimation | All states recovered; no labels | Initial/ boundary vals | Simulation | Ill-conditioning in stiff systems |
| [3] | HVDC Back-to-Back VSC | System Identification/ State Estimation | Accurate grid stability estimation | Simulation data | Simulation | No real-world validation |
| [37] | Power System Operation | Control Support | Improved convergence | Partial + boundary | Simulation | Not real-time ready |
| [2] | Buck Inverter | Control | Settling time 1.5–2.1 ms; < 1.2 V overshoot | Live measurements | Hardware | Needs manual tuning |
| [31] | General Nonlinear | Control | Long-horizon accuracy | Low | Standard simulation models | Not yet applied to switching systems |
| [40] | High-Impedance Faults | Fault Detection | Unlabeled fault detection | Unlabeled data | Simulation | Focused on distribution lines |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahdouri, E.A.; Al-Abri, S.; Yousef, H.; Al-Naimi, I.; Obeid, H. Physics-Informed Neural Networks in Grid-Connected Inverters: A Review. Energies 2025, 18, 5441. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205441
Mahdouri EA, Al-Abri S, Yousef H, Al-Naimi I, Obeid H. Physics-Informed Neural Networks in Grid-Connected Inverters: A Review. Energies. 2025; 18(20):5441. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205441
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahdouri, Ekram Al, Said Al-Abri, Hassan Yousef, Ibrahim Al-Naimi, and Hussein Obeid. 2025. "Physics-Informed Neural Networks in Grid-Connected Inverters: A Review" Energies 18, no. 20: 5441. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205441
APA StyleMahdouri, E. A., Al-Abri, S., Yousef, H., Al-Naimi, I., & Obeid, H. (2025). Physics-Informed Neural Networks in Grid-Connected Inverters: A Review. Energies, 18(20), 5441. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18205441








