Synergizing Metaheuristic Optimization and Model Predictive Control: A Comprehensive Review for Advanced Motor Drives
Abstract
1. Introduction
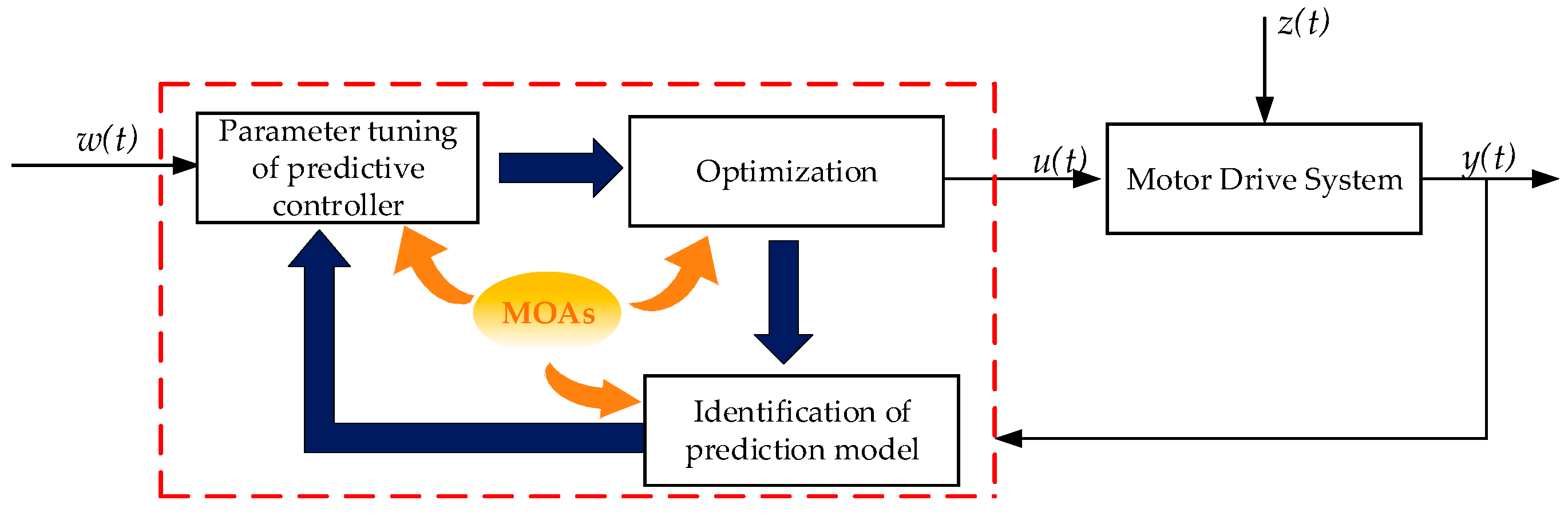
2. Principles of Model Predictive Control
- (1)
- Model inaccuracies and stochastic disturbances degrading prediction efficacy;
- (2)
- Empirical parameter tuning struggling to balance performance against computational efficiency;
- (3)
- Traditional gradient-based or enumerative solvers often fail in high-dimensional, non-convex constrained spaces. They struggle to simultaneously achieve real-time feasibility and global optimality.
3. Applications of MOA in MPC
3.1. Dynamic Models
3.1.1. Studies Discussion
3.1.2. Research Comparison and Prospects
3.2. Parameter Tuning
3.2.1. Studies Discussion
3.2.2. Research Comparison and Prospects
3.3. Optimization Algorithms
3.3.1. Studies Discussion
3.3.2. Research Comparison and Prospects
4. Conclusions
- 1.
- Lightweight Swarm Intelligence Operators and Hierarchical Optimization Strategies: Breakthroughs in computational efficiency for embedded platforms
- Operator Simplification: Designing adaptive MOAs variants (e.g., “adaptive PSO” with dynamically adjusted inertia weights and crossover probabilities) or incorporating “pruning mechanisms” (e.g., early termination of ineffective particle searches) to reduce per-iteration computation while preserving global exploration capabilities.
- Hierarchical Optimization: Decomposing the optimization process into “global coarse-tuning” and “local fine-tuning” stages. The global stage uses low-complexity MOAs (e.g., simplified PSO) to rapidly locate feasible solution regions, while the local stage employs gradient-based methods (e.g., fast gradient descent in MPC) for precise adjustments, balancing search efficiency and solution quality.
- Hardware Adaptation: Optimizing the parallel computing architecture of MOAs (e.g., grouped parallel evaluation of particles) to align with edge computing hardware (e.g., low-power DSPs, specialized AI chips), enabling online optimization within 100 μs time windows to meet the high-frequency control requirements of motors (e.g., switching frequencies above 10 kHz).
- 2.
- Online Hyperparameter Adaptation: Data-driven dynamic tuning and robustness enhancement
- Meta-Learning-Driven Parameter Tuning: Training meta-learning models (e.g., MAML) on historical operational data (e.g., optimal prediction horizons and weight configurations under different loads) to enable rapid adaptation to new operating conditions, mitigating the lag of offline tuning.
- Bayesian Optimization for Online Tuning: Treating MPC performance (e.g., tracking error, switching losses) as the objective function, gaussian process regression models can map parameter-performance relationships to online select optimal parameter combinations, balancing exploration and exploitation.
- Reinforcement Learning for Robustness: Designing reinforcement learning agents with hyperparameter adjustments as the action space and “minimizing long-term control costs” as the reward function to online learn robust parameter configurations adaptable to extreme disturbances (e.g., ±20% load abrupt changes).
- 3.
- Dynamic Multi-Objective Strategies: Online weight reconstruction and rapid pareto frontier updates
- Operating Condition-Aware Weight Adjustment: Using real-time monitoring of load torque, speed fluctuations, and other features, fuzzy rules or neural networks can dynamically allocate objective weights (e.g., prioritizing response speed during acceleration, efficiency at steady-state).
- Rapid Pareto Frontier Updates: Adopting incremental multi-objective optimization algorithms (e.g., dynamic MOEA/D) allows retaining only current non-dominated solutions, thereby reducing Pareto update time from seconds to milliseconds.
- Disturbance-Integrated Decision-Making: Incorporating load disturbance predictions into multi-objective optimization to generate “disturbance-resilient” pareto frontiers, ensuring control strategies remain optimal during disturbances.
- 4.
- Objective-Structure-Guided Optimization: Intelligent search scope limitation based on problem characteristics
- Feature-Driven Search Space Reduction: Online identification of key motor parameters (e.g., inductance, flux linkage) and combining them with control objectives (e.g., torque tracking) to dynamically define feasible regions for optimization variables (e.g., limiting inductance variations to ±10%), avoiding unstructured global searches.
- Structure-Adaptive MOAs Design: Automatically selecting MOA types based on problem structure (e.g., continuous/discrete control variables, convex/non-convex objectives)—e.g., improved PSO for continuous variables, ant colony optimization (ACO) for discrete voltage vector selection, and simulated annealing (SA) for non-convex objectives to enhance global escape.
- Constraint-Aware Heuristic Search: Translating hard constraints (e.g., current limits) into penalty functions or boundary constraints, and combining them with MOA heuristic rules (e.g., particle “obstacle avoidance”), can guide the search toward feasible regions and improve optimization efficiency.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mensah Akwasi, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Duku, O.-A. Hybrid Adaptive Learning-Based Control for Grid-Forming Inverters: Real-Time Adaptive Voltage Regulation, Multi-Level Disturbance Rejection, and Lyapunov-Based Stability. Energies 2025, 18, 4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, X. A Double Vector Model Predictive Torque Control Method Based on Geometrical Solution for SPMSM Drive in Full Modulation Range. Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 5558–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Xiang, X.; Li, Y.; Tao, T. Simplified Model Predictive Current Control for Dual Three-Phase PMSM with Low Computation Burden and Switching Frequency. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2024, 8, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Garcia, C.; Mora, A.; Alireza, S. Latest Advances of Model Predictive Control in Electrical Drives—Part II: Applications and Benchmarking with Classical Control Methods. Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 5047–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, A.A.; Cho, H.M.; Mahmud, M.I. Essential Features and Torque Minimization Techniques for Brushless Direct Current Motor Controllers in Electric Vehicles. Energies 2024, 17, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, H.; Zeng, P.; Xiong, W.; Wen, M.; Su, M.; Rivera, M. Model Predictive Control-Based Direct Torque Control for Matrix Converter-Fed Induction Motor with Reduced Torque Ripple. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2021, 5, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Yan, Y.; Shi, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Xia, C. A Novel SVPWM Scheme for Field-Oriented Vector-Controlled PMSM Drive System Fed by Cascaded H-Bridge Inverter. Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 8988–9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shinshi, T. Torque Regulation Theory and Sensorless Control Technology for Unipolar Salient Synchronous Permanent Magnet Motor Based on Unified Models. Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 5672–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafqolian, M.A.; Alipour, K.; Mousavifard, R.; Tarvirdizadeh, B. Control of Aerial Robots Using Convex QP LMPC and Learning-Based Explicit-MPC. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 10883–10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hua, W.; Fan, Q. Performance Analysis and Comparison of Two Fault-Tolerant Model Predictive Control Methods for Five-Phase PMSM Drives. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2021, 5, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yan, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hussain, F. Model Predictive Control System Based on Direct Yaw Moment Control for 4WID Self-Steering Agriculture Vehicle. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavuş, B.; Aktaş, M. MPC-Based Flux Weakening Control for Induction Motor Drive with DTC for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 4430–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, C. Virtual-Vector-Based Robust Predictive Current Control for Dual Three-Phase PMSM. Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; He, J. Dual-Mode Laguerre MPC and Its Application in Inertia-Frequency Regulation of Power Systems. Energies 2025, 18, 4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanelli, J.; Kullick, H.M.; Eldeeb, G.; Frison, C.; Hackl, C.M.; Diehl, M. Continuous Control Set Nonlinear Model Predictive Control of Reluctance Synchronous Machines. Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2022, 30, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, G. Adaptive Model Predictive Current Control for PMSM Drives Based on Bayesian Inference. Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 8490–8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Chai, F. Model Predictive Direct Speed Control of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors with Voltage Error Compensation. Energies 2023, 16, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konuhova, M. Modeling of Induction Motor Direct Starting with and without Considering Current Displacement in Slot. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shen, T.; Sun, X.; Xu, H.; Pan, W. Model Predictive Control of Robot Flexible Joint Motor Based on Lyapunov Prediction Model. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2025, 40, 10783–10792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerdali, E.; Rivera, M.; Wheeler, P. A Review on Weighting Factor Design of Finite Control Set Model Predictive Control Strategies for AC Electric Drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 9967–9981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanyam, S.A.; Ghaemi, S.; Golmohamadi, H.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A.; Bak-Jensen, B. Leveraging Dynamic Pricing and Real-Time Grid Analysis: A Danish Perspective on Flexible Industry Optimization. Energies 2025, 18, 4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaswal, A.; Abu-Ayyad, M.; Lad, Y.; Attaluri, A. Stepper motor position control using PD and MPC algorithms embedded in programmable logic controller. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 39096–39106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Ke, D.; Qi, H.; Wang, F.; Rodríguez, J. Multistep Predictive Current Control for Electrical Drives with Adaptive Horizons. Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkar, S.G.; Eshwar, K.; Thippiripati, V.K. A Modified Model Predictive Current Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drive. Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Xiong, S.; Sun, B.; Chen, P.; Chen, H.; Zhu, S. Research on Energy-Saving Control of Automotive PEMFC Thermal Management System Based on Optimal Operating Temperature Tracking. Energies 2025, 18, 4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nori, A.M.; Abdulabbas, A.K.; Aljohani, T.M. Coordinated Sliding Mode and Model Predictive Control for Enhanced Fault Ride-Through in DFIG Wind Turbines. Energies 2025, 18, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E.; Xue, J.; Chen, T.; Jiang, S. Robust Trajectory Tracking Control of an Autonomous Tractor-Trailer Considering Model Parameter Uncertainties and Disturbances. Agriculture 2023, 13, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Meng, Q.; Shi, T. A Review on Model Predictive Control Strategies for AC Motor Drives. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2024, 18, 1584–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukili, Y.; Ayiad, M.M.; Moayyed, H.; Aguiar, A.P.; Vale, Z. Robust state estimation model for low voltage distribution networks in the presence of multiple gross errors. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 42403–42415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deraz, S.A.; Alharbi, F. An interior point algorithm for parameter estimation of a geared PMDC motor using current and speed step responses. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 121892–121901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Braatz, R.D. A direct optimization algorithm for input-constrained MPC. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2025, 70, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Wang, A.X.; Taghia, J.; Katupitiya, J. Force Control of Two-Wheel-Steer Four-Wheel-Drive Vehicles Using Model Predictive Control and Sequential Quadratic Programming for Improved Path Tracking. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 4614–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Ye, Y.; Xiong, X.; Chai, J.; Cui, H.; Li, H. Low Carbon Economic Dispatch of Power System Based on Multi-Region Distributed Multi-Gradient Whale Optimization Algorithm. Energies 2025, 18, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.; Chowdhury, M.M.-U.-T.; Kamalasadan, S. Sequential quadratic programming (SQP) based optimal power flow methodologies for electric distribution system with high penetration of DERs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 4810–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Harley, R.G.; Habetler, T.G. Performance Evaluation and Comparison of Multi-Objective Optimization Algorithms for the Analytical Design of Switched Reluctance Machines. Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2017, 1, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.-J.; Chen, R.-W.; Wang, Q.-A.; Lu, W.-L. Shuffled Puma Optimizer for Parameter Extraction and Sensitivity Analysis in Photovoltaic Models. Energies 2025, 18, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, I.A.T.; Alaba, F.A.; Jumare, M.H.; Ibrahim, A.O.; Abulfaraj, A.W. Adaptive stochastic conjugate gradient optimization for backpropagation neural networks. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 33757–33768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomdapu, S.T.; Vardhan, H.; Rajawat, K. Stochastic compositional gradient descent under compositional constraints. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2023, 71, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elaziz, M.; Dahou, A.; Abualigah, L.; Yu, L.; Alshinwan, M.; Khasawneh, A.M.; Lu, S. Advanced Metaheuristic Optimization Techniques in Applications of Deep Neural Networks: A Review. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 14079–14099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Adria, N.; Dusabe, K.D.; Zhong, Y.; Guverinoma, A. Rapid and Nondestructive Watermelon Seed Viability Detection Based on Visible Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging and Machine Learning. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 4403–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Yang, Q.; Niu, K.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, Y. Discrete Element-Based Optimization Parameters of an Experimental Corn Silage Crushing and Throwing Device. Trans. ASABE 2021, 64, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Yao, M.; Zhang, T.; Shi, J. Design and Working Parameter Optimization of Pneumatic Reciprocating Seedling-Picking Device of Automatic Transplanter. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y.; Pan, X.; Zou, W.; Wei, Y.; Zhai, C.; Chen, L. Optimization of a Boom Height Ultrasonic Detecting Model for the Whole Growth Cycle of Wheat: Affected by the Oscillation of the Three-Section Boom of the Sprayer. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Jayan, H.; Cai, J.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Guo, Z.; Zou, X. Spoilage Monitoring and Early Warning for Apples in Storage Using Gas Sensors and Chemometrics. Foods 2023, 12, 2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosch, A.; Hanke, S.; Wallscheid, O.; Böcker, J. Data-Driven Recursive Least Squares for Model Predictive Current Control. Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mesery, H.S.; Qenawy, M.; Li, J.; El-Sharkawy, M.; Du, D. Predictive modeling of garlic quality in hybrid infrared-convective drying using artificial neural networks. Food Bioprod. Process. 2024, 145, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonah, E.; Huang, X.; Yu, H.; Aheto, J.H.; Yi, R.; Yu, S.; Tu, H. Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium Contamination Levels in Fresh Pork Samples Using Electronic Nose Smellprints in Tandem with Support Vector Machine Regression and Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithms. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 3861–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, H.; Vayssettes, J.; Mercère, G. A robust and regularized algorithm for recursive total least squares estimation. IEEE Control Syst. Lett. 2024, 8, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ou, J.; Yan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, G. Path Tracking Control of Automated Vehicles Based on Adaptive MPC in Variable Scenarios. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 18, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khulal, U.; Zhao, J.; Hu, W.; Chen, Q. Nondestructive quantifying total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) content in chicken using hyperspectral imaging (HSI) technique combined with different data dimension reduction algorithms. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Tang, X.; Tang, H. Speed Control of PMSM Based on Neural Network Model Predictive Control. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2022, 44, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.; Sarma, R.; Guha, D. Performance Analysis of Advanced Metaheuristics for Optimal Design of Multi-Objective Model Predictive Control of Doubly Fed Induction Generator. Processes 2025, 13, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Gao, S.; Lang, B. Adaptive Fault-Tolerant Control of Five-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Current Using Chaotic-Particle Swarm Optimization. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Liu, X.; Zou, Y.; Huang, C.; Liang, J. Design and Optimization of a Mechanical Variable-Leakage-Flux Interior Permanent Magnet Machine with Auxiliary Rotatable Magnetic Poles. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2021, 5, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Xi, J.; Hu, H.; Xiong, L.; Lu, G.; Xiao, T. Neural ODE-Based Dynamic Modeling and Predictive Control for Power Regulation in Distribution Networks. Energies 2025, 18, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Pei, W.; Zhang, Q. Research on Intelligent Vehicle Tracking Control and Energy Consumption Optimization Based on Dilated Convolutional Model Predictive Control. Energies 2025, 18, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Chung, I.-Y.; Cartes, D.A. Real-Time Particle Swarm Optimization-Based Parameter Identification Applied to Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlet, P.G.; Favato, A.; Bolognani, S.; Dörfler, F. Data-driven continuous-set predictive current control for synchronous motor drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 6637–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorshedy, M.F.; Xu, W.; El-Sousy, F.F.M.; Islam, M.R.; Ahmed, A.A. Recent achievements in model predictive control techniques for industrial motor: A comprehensive state-of-the-art. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 58170–58191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Eull, M.; Preindl, M. Derivation and Review of Optimization-Based Estimation for Motor Drives and Power Electronics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2024, 60, 6593–6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H. Model-free predictive control of motor drives: A review. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2025, 9, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeva, G.; Mo, Y. Model predictive control for industrial drive applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 7897–7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Sun, K.; Huang, S.; Hu, Y.; Liang, D.; Fang, Y. A review on multimotor synchronous control methods. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, J.; Xia, Y.; Tian, X.; Guo, Z.; Huang, W. Long-Term Evaluation of Soluble Solids Content of Apples with Biological Variability by Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Calibration Transfer Method. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 151, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, M.; Zou, X.; Tahir, H.E.; Hu, X.; Rakha, A.; Basheer, S.; Zhao, H. Near-infrared spectroscopy coupled chemometric algorithms for prediction of antioxidant activity of black goji berries. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 2366–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H. An Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm Based on Variable Neighborhood Search. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, J.J.; Castoldi, M.F.; Goedtel, A.; Agulhari, C.M.; Sanches, D.S. Parameters Estimation of Three-Phase Induction Motors Using Differential Evolution. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 154, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.A.; Fateh, M.M.; Keighobadi, J. Grey wolf optimization algorithm-based robust neural learning control of passive torque simulators with predetermined performance. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2024, 32, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, R.; Men, B.; Khan, N.H. c Meta-Heuristic Optimization Approach of GWO Optimizer for Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch Problems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 202596–202610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Hu, C.; Lei, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J. State Feedback Control for a PM Hub Motor Based on Gray Wolf Optimization Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhu, Z.Q. Quantum genetic algorithm-based parameter estimation of PMSM under variable speed control accounting for system identifiability and VSI nonlinearity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 62, 2363–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonah, E.; Huang, X.; Yi, R.; Aheto, J.H.; Osae, R.; Golly, M. Electronic Nose Classification and Differentiation of Bacterial Foodborne Pathogens Based on Support Vector Machine Optimized with Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Nirere, A.; Tian, Y.; Wu, X. Nondestructive Detection for Egg Freshness Grade Based on Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, W. Thermal Error Modeling of Electrical Spindle Based on Optimized ELM with Marine Predator Algorithm. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 38, 102326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunekpeku, X.; Zhang, W.; Gao, J.; Adade, S.Y.-S.S.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Gel Strength Prediction in Ultrasonicated Chicken Mince: Fusing Near-Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy Coupled with Deep Learning LSTM Algorithm. Food Control 2025, 168, 110916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Sun, J.; Mao, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X. Non-destructive detection for mold colonies in rice based on hyperspectra and GWO-SVR. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Nirere, A.; Wu, X.; Dai, R. Classification detection of saccharin jujube based on hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazelan, A.M.; Osman, M.K.; Salim, N.A.; Samat, A.A.A.; Ahmad, K.A. PSO-Based Neural Network Controller for Speed Sensorless Control of PMSM. In Proceedings of the 2017 7th IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering (ICCSCE), Penang, Malaysia, 24–26 November 2017; pp. 366–371. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Huang, D. Structure optimization of radial basis probabilistic neural networks by the maximum absolute error combined with the micro-genetic algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–17 May 2002. [Google Scholar]
- hou, S.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Parameter identification of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on modified-fuzzy particle swarm optimization. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 873–879. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.X.; Chen, L.; Huang, C.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C. A Dynamic Tire Model Based on HPSO-SVM. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. Frequency Scanning-Based Dynamic Model Parameter Estimation: Case Study on STATCOM. Energies 2025, 18, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Cong, S.L.; Mao, H.P.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.H.; Zhang, X.D. Identification of eggs from different production systems based on hyperspectra and CS-SVM. Br. Poult. Sci. 2017, 58, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.; Yao, K.; Cao, Y.; Tang, N. Identification of maize seed varieties based on stacked sparse autoencoder and near-infrared hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Process. Eng. 2022, 45, e14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, Q. Determination of tea polyphenols in green tea by homemade color sensitive sensor combined with multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2020, 319, e12658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Tao, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Ouyang, Q.; Shi, J.; Zou, X. Quantitative assessment of zearalenone in maize using multivariate algorithms coupled to Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, B.; Sahu, S. Parameter estimation of DC motor through whale optimization algorithm. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2019, 10, 813–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q. SSC prediction of cherry tomatoes based on IRIV-CS-SVR model and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J. Food Process. Eng. 2018, 41, e12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Sun, J.; Yao, K.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Cao, Y.; Fu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Identification of Lycium barbarum varieties based on hyperspectral imaging technique and competitive adaptive reweighted sampling-whale optimization algorithm-support vector machine. J. Food Process. Eng. 2021, 44, e13603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Jiao, T.; Wang, Z.; Adade, S.Y.-S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; et al. On-line detecting soluble sugar, total acids, and bacterial concentration during kombucha fermentation based on the visible/near infrared combined meta-heuristic algorithm. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, e10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Dai, C.; Cao, Y.; et al. A knee point-driven many-objective evolutionary algorithm with adaptive switching mechanism. J. Appl. Math. 2024, 2024, e37604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.J.; Sun, Y.S.; Liu, J.X. An integrated parameter identification method of asynchronous motor combined with adaptive load characteristics. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2023, 18, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Chen, Q.; Lu, B.; Dai, C. Detection of viability of soybean seed based on fluorescence hyperspectra and CARS-SVM-AdaBoost model. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cai, Y. Improved Weighting Factor Selection Method of Predictive Torque Control for High Speed Surface-mounted PMSM based on RBFNN. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Su, T.J.; Chiu, Y.H.; Yang, T.W. Torque ripple reduction of induction motor based on a hybrid method of model predictive torque control and particle swarm optimization. Meas. Control 2016, 49, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, T.; He, P.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Q. Rapid measurement of fatty acid content during flour storage using a color-sensitive gas sensor array: Comparing the effects of swarm intelligence optimization algorithms on sensor features. Food Chem. 2021, 338, e27828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsanedzie, F.Y.H.; Chen, Q.; Hassan, M.M.; Yang, M.; Sun, H.; Rahman, M.H. Near infrared system coupled chemometric algorithms for enumeration of total fungi count in cocoa beans neat solution. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.H.; Abido, M.A.; Salem, A.; Alolah, A.I. Weighting Factors Optimization of Model Predictive Torque Control of Induction Motor Using NSGA-II with TOPSIS Decision Making. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 177595–177606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; He, J.; Yao, W.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Determination of aflatoxin B1 value in corn based on Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy: Comparison of optimization effect of characteristic wavelengths. LWT 2022, 164, 113657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.Q.; Li, B.; Ma, J. MOPSO Based Predictive Control Strategy for Efficient Operation of Sensorless Vector Control Induction Motor Drives. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2017, 25, 3012–3025. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, F. Research on Load Spectrum Reconstruction Method of Exhaust System Mounting Bracket of a Hybrid Tractor Based on MOPSO-Wavelet Decomposition Technique. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1919–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, M. Optimization of Model Predictive Control Weights for Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by Using the Multi Objective Bees Algorithm. Model-Based Control Eng. 2022, 17, e18810. [Google Scholar]
- Bjelonic, M.; Grandia, R.; Geilinger, M.; Harvey, O.; Tsounis, V.; Lee, J.; Hutter, M. Offline motion libraries and online MPC for advanced mobility skills. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2022, 41, 903–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Zheng, R.; Liu, M.; Li, M. Robust Control of PMSM Using Geometric Model Reduction and μ-Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Kawai, F.; Nakazawa, C.; Takahashi, N.; Azuma, T.; Fujikawa, T.; Kondo, N. Parameter Optimization of Model Predictive Control by PSO. IEEJ Trans. Electron. Inf. Syst. 2009, 129, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Jin, M.; Lu, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, N.; Chen, T. Reinforcement-learning-based parameter adaptation method for particle swarm optimization. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 9, 5585–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H. Auto Tuning Controller Using MLPSO with K means Clustering and Adaptive Learning Strategy for PMSM Drives. ISA Trans. 2022, 120, 338–349. [Google Scholar]
- Huan, J.; Cao, W.; Liu, X. A Dissolved Oxygen Prediction Method Based on K-Means Clustering and the ELM Neural Network: A Case Study of the Changdang Lake. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2017, 33, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Wheat Lodging Direction Detection for Combine Harvesters Based on Improved K-Means and Bag of Visual Words. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; He, X.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, T.; Qiao, X. Detection of Key Organs in Tomato Based on Deep Migration Learning in a Complex Background. Agriculture 2018, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, C.; Meng, L.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, Q. Early warning of rice mildew based on gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry technology and chemometrics. Food Meas. 2021, 15, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, M.; Ferreau, H.J.; Haverbeke, N. Efficient Numerical Methods for Nonlinear MPC and Moving Horizon Estimation. Nonlinear Model Predict. Control 2009, 384, 391–417. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, J.; Yoo, J.; Cui, S.; Lee, K.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Sul, S. Model Predictive Control for Six-Step Operation of PMSM Based on Adapted Fast Gradient Method. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 5952–5967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, P.; Alvarado, I.; Limon, D.; Grosso, J.M.; de la Peña, D.M. Implementation of Model Predictive Control for Tracking in Embedded Systems Using a Sparse Extended ADMM Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2022, 30, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Figueiredo, M.; Goldstein, T. Adaptive ADMM with Spectral Penalty Parameter Selection. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 20–22 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Figueiredo, M.A.T.; Yuan, X.; Yin, W.; Studer, C. Adaptive Relaxed ADMM: Convergence Theory and Practical Implementation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7234–7243. [Google Scholar]
- Lantos, B. Analysis of the explicit model predictive control for semi-active suspension. Period. Polytech. Electr. Eng. 2010, 1, 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, C.; Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, K. Robust Current Controller for IPMSM Drives Based on Explicit Model Predictive Control With Online Disturbance Observer. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 45898–45910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Qian, Y.; El-Mesery, H.S.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, X. Rapid detection of rice disease using microscopy image identification based on the synergistic judgment of texture and shape features and decision tree-confusion matrix method. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 6589–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Y.; Chen, J.; Guan, Z.H.; Wu, K.; Chen, D.; Li, Y. Development of a monitoring system for grain loss of paddy rice based on a decision tree algorithm. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masti, D.; Pippia, T.; Bemporad, A.; Sarda, R.; De Schutter, B. Learning approximate semi explicit hybrid MPC with an application to microgrids. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 5173–5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, G.; Allgwer, F. Semi-explicit MPC based on subspace clustering. Automatica 2017, 83, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mate, S.; Jaju, P.; Bhartiya, S.; Nataraj, P.S.V. Semi-Explicit Model Predictive Control of Quasi Linear Parameter Varying Systems. Eur. J. Control 2023, 69, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Missile fixed-structure μ controller design based on constrained PSO algorithm. Automatika 2017, 58, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallscheid, O.; Ammann, U.; Boecker, J. Real-Time Capable Model Predictive Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Using Particle Swarm Optimisation. In Proceedings of the International Exhibition and Conference for Power Electronics, Intelligent Motion, Renewable Energy and Energy Management, Nuremberg, Germany, 10–12 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Yang, Y.; Qin, W.; Wheeler, P. Switching State Selection for Model Predictive Control Based on Genetic Algorithm Solution in an Indirect Matrix Converter. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 8, 4496–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, K.B.; Sahu, A.; Mishra, R.N. Development of MPC-ACO based Direct Torque Controller for Induction Motor Drive. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th Biennial International Conference on Nascent Technologies in Engineering (ICNTE), Navi Mumbai, India, 15–16 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Aggelogiannaki, E.; Sarimveis, H. A Simulated Annealing Algorithm for Prioritized Multi-objective Optimization—Implementation in an Adaptive Model Predictive Control Configuration. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 2007, 37, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareh, M.R.; Marzband, M.; Nejad, S.M.S. Finding Optimum Parameters for Vector Control of Salient Pole Synchronous Motor Using Fuzzy-Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Taormina, Italy, 23–26 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Azab, M.; Serrano-Fontova, A. Optimal Tuning of Fractional Order Controllers for Dual Active Bridge-Based DC Microgrid Including Voltage Stability Assessment. Electronics 2021, 10, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wu, T.; Weir, J.D. An Adaptive Particle Swarm Optimization with Multiple Adaptive Methods. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2013, 17, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, C.S.; Lim, M.H.; Leong, M.S. Self-Tune Linear Adaptive-Genetic Algorithm for Feature Selection. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 138211–138232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancar, N.; Onakpojeruo, E.P.; Inan, D.; Uzun Ozsahin, D. Adaptive Elastic Net Based on Modified PSO for Variable Selection in Cox Model with High-Dimensional Data: A Comprehensive Simulation Study. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 127302–127316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, P.; Kuruoglu, E.E. Optimized Parameter-Efficient Deep Learning Systems via Reversible Jump Simulated Annealing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2024, 18, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yi, G.; Detao, M.; Zhicheng, L.; Tao, C. Research on diving control of underactuated UUV based on model predictive control with artificial bee colony algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hangzhou, China, 28–30 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. An optimization algorithm used in PMSM model predictive control. IEICE Electron. Express 2024, 21, e10444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chernogor, L.F.; Garmash, K.P.; Rozumenko, V.T. The parameters of the infrasonic waves generated by the Chelyabinsk meteoroid: System Statistic Analysis Results. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 2nd Ukraine Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (UKRCON), Lviv, Ukraine, 2–6 July 2019; pp. 1094–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, K.; Onoue, Y.; Wachi, A.; Yoshimura, T. Learning-Based Event-Triggered MPC with Gaussian Processes Under Terminal Constraints. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2025, 55, 1512–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.; Kötting, P.; Soloperto, R.; Allgöwer, F.; Müller, M.A. A robust adaptive model predictive control framework for nonlinear uncertain systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2020, 31, 8725–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Type | Algorithms | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White-box | PSO, DE, GWO | High interpretability | Slow convergence | [64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71] |
| Black-box | PSO, GA, GWO-LSTM | Capable of capturing complex nonlinearities | Poorly interpretable | [73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80] |
| Gray-box | GA-PSO, CS, WOA | Balances interpretability and adaptability | High computational costs | [90,91,92,93] |
| Type | Algorithms | Advantages | Limitations | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Offline single-objective | PSO, GA, GA-PSO | Strong global search capability | Limited to simple conditions | [95,96,97,98] |
| Offline multi-objective | NSGA-II, MOPSO, ABC | Multi-objective parallel optimization | Poor generalization and robustness | [99,101,103] |
| Online adaptive | Q-learning, K-means | Rapid response, high robustness | High computational cost | [104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111] |
| Category | Advantages | Disadvantages | Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gradient-based | Low computational cost | Prone to local optima | Simple | [112,113] |
| Operator splitting | Good parallelism | High iteration cost | High sampling-rate | [114,115,116] |
| Explicit MPC | Extremely low latency | Large memory requirement | Few variables and constraints | [120,121,122,123,124] |
| MOAs | Strong global search capability | Sensitive to hyperparameters | High-dimensional, multi-objective | [125,126,127,128,129] |
| Category | Common Ranges or Strategies | Key Notes and Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Population Size (N) | Small-scale: 20–50 Medium-scale: 50–100 Large-scale: 100–200+ | Population size affects exploration ability. Larger sizes enhance global search but increase cost [135]. |
| Iterations (T) | Typical range: 500–5000+ T = (Max function evaluations FEₘₐₓ)/(N) | Jointly determined with population size. In CEC2017 benchmarks, FEₘₐₓ = 10,000 × dimension. |
| Adaptive Mechanisms | Dynamically adjust parameters | Enhances robustness, reduces manual tuning [136]. |
| Termination Criteria | Max iterations or evaluations Stagnation threshold Target solution quality | Often combined. Stagnation-based thresholds avoid wasted computation [135]. |
| Algorithm-Specific Parameters | GA: Crossover rate Pc = 0.6–0.9, Mutation rate Pm = 0.001–0.1 PSO: Inertia weight ω = 0.4–0.9, Cognitive factor c1 = c2 = 1.5–2.0 SA: Initial temperature T0, Cooling rate α = 0.8–0.99 | Each algorithm has unique core parameters [137,138,139]. Strong impact on performance, usually tuned experimentally or via auto-configuration. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Shi, H.; Ye, C.; Zhou, H. Synergizing Metaheuristic Optimization and Model Predictive Control: A Comprehensive Review for Advanced Motor Drives. Energies 2025, 18, 4831. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18184831
Wang Q, Shi H, Ye C, Zhou H. Synergizing Metaheuristic Optimization and Model Predictive Control: A Comprehensive Review for Advanced Motor Drives. Energies. 2025; 18(18):4831. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18184831
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qicuan, Hai Shi, Chen Ye, and Huawei Zhou. 2025. "Synergizing Metaheuristic Optimization and Model Predictive Control: A Comprehensive Review for Advanced Motor Drives" Energies 18, no. 18: 4831. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18184831
APA StyleWang, Q., Shi, H., Ye, C., & Zhou, H. (2025). Synergizing Metaheuristic Optimization and Model Predictive Control: A Comprehensive Review for Advanced Motor Drives. Energies, 18(18), 4831. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18184831






