A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management Based on Liquid Cooling and Its Evaluation Method
Abstract
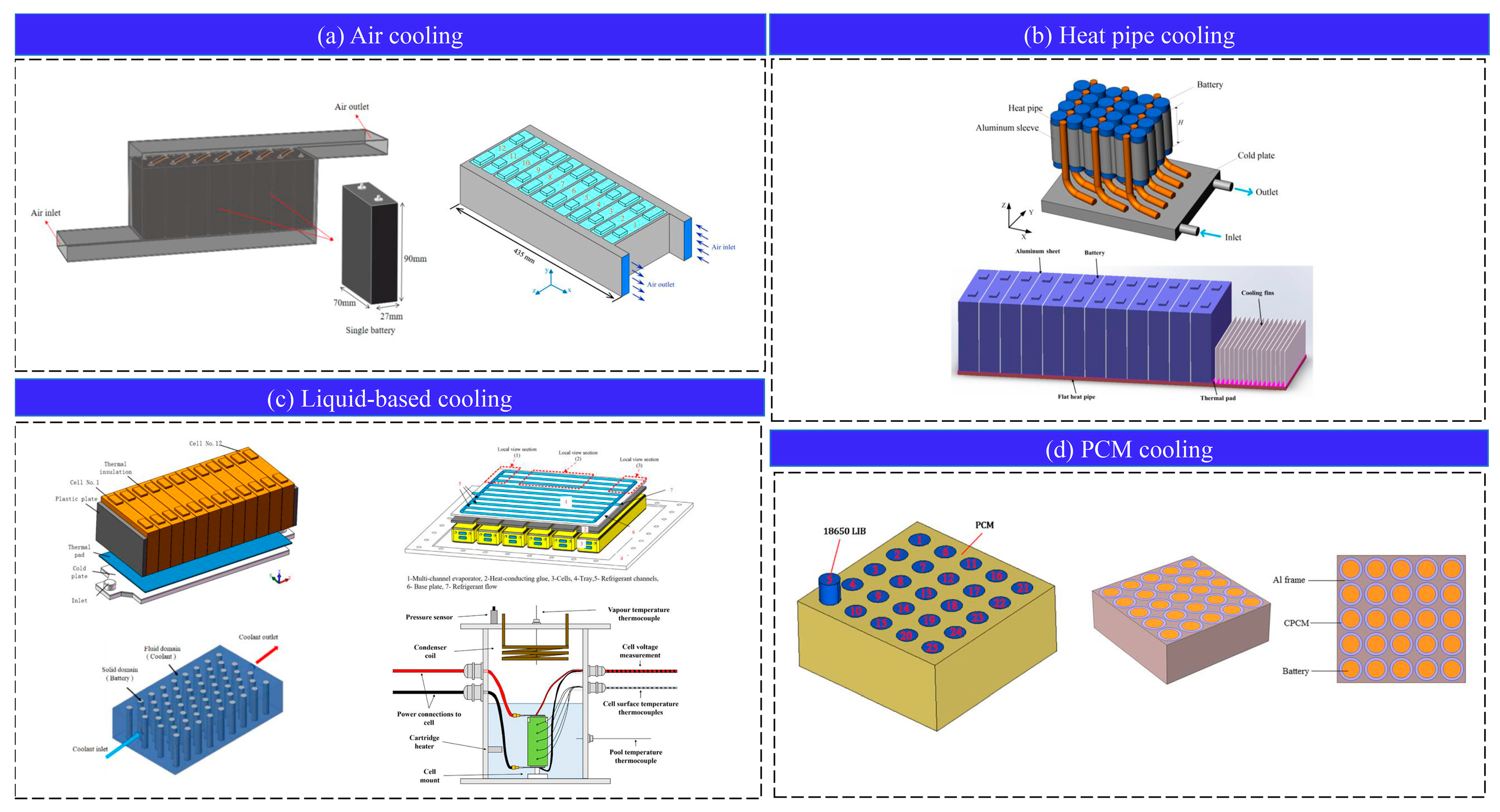
1. Introduction
2. BTMS
3. Method of Liquid-Based BTMS
3.1. Indirect-Contact Liquid Cooling
3.1.1. Single-Phase Liquid Indirect Cooling
3.1.2. Two-Phase Liquid Indirect Cooling
3.2. Direct-Contact Liquid Cooling
3.2.1. Single-Phase Liquid Direct Cooling
- (1)
- Safety characteristics: Non-flammable, low pour point, and high flash point.
- (2)
- Thermal performance: High thermal conductivity, high specific heat capacity, and good thermal stability.
- (3)
- Flow properties: Low density and low kinematic viscosity.
- (4)
- Stability: Good material compatibility and long service life.
- (5)
- Environmental factors: Low global warming potential (GWP), good degradability, and recyclability.
- (6)
- Availability: Capable of large-scale production.
3.2.2. Two-Phase Liquid Direct Cooling
4. Evaluation Indicator
5. Challenges and Outlooks
5.1. Coolant Selection
5.2. Cold Plate Design and Optimization
5.3. Coolant Leakage and Long-Term Reliability
5.4. Intelligent Control Strategy
5.5. Localized Hot Spots Reduced by PCM Combined Cooling
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saber, N.; Richter, C.P.; Unnthorsson, R. Review of Thermal Management Techniques for Prismatic Li-Ion Batteries. Energies 2025, 18, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afia, S.E.; Cano, A.; Arévalo, P.; Jurado, F. Energy Sources and Battery Thermal Energy Management Technologies for Electrical Vehicles: A Technical Comprehensive Review. Energies 2024, 17, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, S.; Xi, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, J. A Review of Thermal Management and Heat Transfer of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energies 2024, 17, 3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. Automobile Industry under China’s Carbon Peaking and Carbon Neutrality Goals: Challenges, Opportunities, and Coping Strategies. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, 5834707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection. EU Member States Pave Way for Zero-Emission Cars from 2035. Available online: https://www.bmuv.de/PM10536-1 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Boero, A.; Mercier, A.; Mounaïm-Rousselle, C.; Valera-Medina, A.; Ramirez, A.D. Environmental assessment of road transport fueled by ammonia from a life cycle perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 390, 136150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.; Eskandari, H.; Saadatmand, H.; Sahraei, M.A. An interpretable multi-stage forecasting framework for energy consumption and CO2 emissions for the transportation sector. Energy 2024, 286, 129499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togun, H.; Basem, A.; Mohammed, H.I.; Sadeq, A.M.; Biswas, N.; Abdulrazzaq, T.; Hasan, H.A.; Homod, R.Z.; Talebizadehsardari, P. A comprehensive review of battery thermal management systems for electric vehicles: Enhancing performance, sustainability, and future trends. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 97, 1077–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernagozzi, M.; Georgoulas, A.; Miché, N.; Marengo, M. Heat pipes in battery thermal management systems for electric vehicles: A critical review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 219, 119495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Prospects for Electric Vehicle Deployment. 2023. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2023/prospects-for-electric-vehicle-deployment (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Hong, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Shan, T. Collision-Caused thermal runaway investigation of li-ion battery in Real-World electric vehicles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 236, 121901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, C.; Awasthi, A.; Kumar, B.; Im, S.K.; Jeon, Y. Advances in battery thermal management for electric vehicles: A comprehensive review of hybrid PCM-metal foam and immersion cooling technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 208, 115021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Chen, Q.; Tang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, F.; Guo, Y.; Bhagat, R.; Zheng, Y. Critical review of life cycle assessment of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles: A lifespan perspective. Etransportation 2022, 12, 100169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, N.; Gao, X.; Yang, H.; Guo, Z.; Hu, G.; Cheng, H.M.; Li, F. Challenges and development of lithium-ion batteries for low temperature environments. Etransportation 2022, 11, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuch, R.; Wagner, R.; Hörpel, G.; Placke, T.; Winter, M. Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Cruden, A.; Peng, Q.; Liu, K. Enabling extreme fast charging. Joule 2023, 7, 2660–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisha; Tiwari, S.; Sahdev, R.K.; Chhabra, D.; Kumari, M.; Ali, A.; Sehrawat, R.; Tiwari, P. Advancements and challenges in battery thermal management for electric vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 209, 115089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, T.; Tang, Q.; Wang, X. Experimental investigation on thermal runaway propagation in the lithium ion battery modules under charging condition. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 211, 118522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, S.; Yang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Cao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Interface optimization and fast ion exchange route construction in CoS2 electrode by decorated with dielectric Al2O3 nanoparticles for high temperature primary lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 2021, 511, 230424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, X. A review of power battery cooling technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 213, 115494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.L.; He, C.X.; Wu, M.C.; Zhao, T.S. Advances in thermal management systems for next-generation power batteries. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 181, 121853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ju, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, L.; Cao, B. A comprehensive study on the impact of heating position on thermal runaway of prismatic lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2022, 520, 230919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Bae, S.J.; Jang, M. A study on effect of lithium ion battery design variables upon features of thermal-runaway using mathematical model and simulation. J. Power Sources 2015, 293, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, J.; Doose, S.; Weber, S.; Münch, S.; Haselrieder, W.; Kwade, A. Development of a New Procedure for Nail Penetration of Lithium-Ion Cells to Obtain Meaningful and Reproducible Results. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 090504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zichen, W.; Changqing, D. A comprehensive review on thermal management systems for power lithium-ion batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Xu, C.; He, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Ouyang, M. Mechanisms for the evolution of cell variations within a LiNixCoyMnzO2/graphite lithium-ion battery pack caused by temperature non-uniformity. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Jiaqiang, E.; Zhang, B.; Zuo, H.; Wei, K.; Chen, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, H.; Deng, Y. Effects analysis on heat dissipation characteristics of lithium-ion battery thermal management system under the synergism of phase change material and liquid cooling method. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 472–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wei, K. Experimental and numerical study of a passive thermal management system using flat heat pipes for lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 166, 114660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.X.; Yue, Q.L.; Wan, S.B.; Guo, Z.X.; Sun, J.; Zhao, T.S. Experimental and numerical investigations of liquid cooling plates for pouch lithium-ion batteries considering non-uniform heat generation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 258, 124777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, C.; Feng, X.; White, G.; Li, R.; Wang, H.; Rui, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, F.; Null, V.; Parkes, M.; et al. Immersion cooling for lithium-ion batteries—A review. J. Power Sources 2022, 525, 231094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behi, H.; Karimi, D.; Jaguemont, J.; Gandoman, F.H.; Kalogiannis, T.; Berecibar, M.; Van Mierlo, J. Novel thermal management methods to improve the performance of the Li-ion batteries in high discharge current applications. Energy 2021, 224, 120165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, F.S.; Confrey, T.; Reidy, C.; Picovici, D.; Callaghan, D.; Culliton, D.; Nolan, C. Review of battery thermal management systems in electric vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 192, 114171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorino, A.; Cilenti, C.; Petruzziello, F.; Aprea, C. A review on thermal management of battery packs for electric vehicles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 238, 122035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Teng, S.; Xi, H.; Li, Y. Cooling performance optimization of air-cooled battery thermal management system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 195, 117242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, M.; Kalogiannis, T.; Jaguemont, J.; Jin, L.; Behi, H.; Karimi, D.; Beheshti, H.; Van Mierlo, J.; Berecibar, M. A comparative study between air cooling and liquid cooling thermal management systems for a high-energy lithium-ion battery module. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 198, 117503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; He, L.; Liang, J.; Tan, M.; Xiong, T.; Li, Y. A numerical study on the performance of a thermal management system for a battery pack with cylindrical cells based on heat pipes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 179, 115740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Panchal, S.; Fowler, M.; Li, W.; Tran, M.K.; Xie, Y. A novel heat dissipation structure based on flat heat pipe for battery thermal management system. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 15961–15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tong, G.; Li, R. Numerical study and optimizing on cold plate splitter for lithium battery thermal management system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 167, 114787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Ding, G.; Li, G.; Wang, Y. A distributed parameter model of refrigerant-cooled multi-channel evaporator for battery thermal management. Energy 2024, 304, 132170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Ren, X.; Yang, J.; Guo, H.; Han, X.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y. Theoretical and experimental investigations on liquid immersion cooling battery packs for electric vehicles based on analysis of battery heat generation characteristics. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 310, 118478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.P.; Trimble, D.; O’Shaughnessy, S.M. Liquid immersion thermal management of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles: An experimental study. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Li, Z.; Hong, W.; Wu, Q.; Yu, X. Experimental and numerical study of PCM thermophysical parameters on lithium-ion battery thermal management. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Xiao, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, H.; Long, X. Thermal management of lithium-ion batteries under high ambient temperature and rapid discharging using composite PCM and liquid cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 210, 118230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, X.; Negnevitsky, M.; Zhang, H. A review of air-cooling battery thermal management systems for electric and hybrid electric vehicles. J. Power Sources 2021, 501, 230001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, A.; Ljung, A.L.; Lundström, T.S. A study on the effect of cell spacing in large-scale air-cooled battery thermal management systems using a novel modeling approach. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarshenas, B.; Aghaei, A.; Zamani, A.H.; Yuan, Y. Comparison of different cooling techniques for a lithium-ion battery at various discharge rates using electrochemical thermal modeling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 258, 124596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilali, E.; Soltani, M.; Hatefi, M.; Shafiei, S.; Salimi, M.; Amidpour, M. Passive thermal management systems with phase change material-based methods for lithium-ion batteries: A state-of-the-art review. J. Power Sources 2025, 632, 236345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zou, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, L. Battery thermal management systems (BTMs) based on phase change material (PCM): A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Shashidhara, S.; Rakshit, D. A comparative study on battery thermal management using phase change material (PCM). Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2019, 11, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Feng, C.; Zhu, H.; Chen, J.; Wen, M.; Yin, H. Effects of different coolants and cooling strategies on the cooling performance of the power lithium ion battery system: A review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 142, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathoni, A.M.; Putra, N.; Mahlia, T.M.I. A systematic review of battery thermal management systems based on heat pipes. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 109081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Khan, S.Y.; Liu, S.; Zaidi, A.A.; Shaoliang, Z.; Sohrabi, A.; Rashidov, J. Scientific mapping and review of the research landscape in battery thermal management strategies using heat pipe. J. Energy Storage 2024, 103, 114147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaqiang, E.; Xu, S.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zuo, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, Z. Investigation on thermal performance and pressure loss of the fluid cold-plate used in thermal management system of the battery pack. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 145, 552–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, S.; Gudlanarva, K.; Tran, M.K.; Herdem, M.S.; Panchal, K.; Fraser, R.; Fowler, M. Numerical Simulation of Cooling Plate Using K-Epsilon Turbulence Model to Cool Down Large-Sized Graphite/LiFePO4 Battery at High C-Rates. World Electr. Veh. J. 2022, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zang, M.; Wang, S. Experimental and theoretical study of an immersion battery thermal management system based on synthetic ester fluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 250, 127332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, W.T.; Lv, J.; Gao, L.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, Y. Experimental investigations of liquid immersion cooling for 18650 lithium-ion battery pack under fast charging conditions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 227, 120287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, K.; Wang, S.; Xin, C. A compact and lightweight liquid-cooled thermal management solution for cylindrical lithium-ion power battery pack. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 144, 118581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaidi, J.; Chitta, S.D.; Akkaldevi, C.; Panchal, S.; Fowler, M.; Fraser, R. Performance Study on the Effect of Coolant Inlet Conditions for a 20 Ah LiFePO4 Prismatic Battery with Commercial Mini Channel Cold Plates. Electrochem 2022, 3, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Ren, F.; Feng, Y. A manifold channel liquid cooling system with low-cost and high temperature uniformity for lithium-ion battery pack thermal management. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2023, 41, 101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, M.; Jaguemont, J.; Kalogiannis, T.; Karimi, D.; He, J.; Jin, L.; Xie, P.; Van Mierlo, J.; Berecibar, M. A novel liquid cooling plate concept for thermal management of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 231, 113862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhou, L. Thermal performance of rectangular serpentine mini-channel cooling system on lithium battery. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Su, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, K.; Fang, Y.; Ye, W. Effect analysis on thermal profile management of a cylindrical lithium-ion battery utilizing a cellular liquid cooling jacket. Energy 2021, 220, 119725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Saikia, T.; Saikia, P.; Rakshit, D.; Ugalde-Loo, C.E. Thermal performance analysis and experimental verification of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicle applications through optimized inclined mini-channels. Appl. Energy 2023, 335, 120743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, F.C.; Kannaiyan, S.; Boobalan, C. Intensification of heat transfer rate using alumina-silica nanocoolant. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 149, 119127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Su, L.; Zhang, Z. Lightweight liquid cooling based thermal management to a prismatic hard-cased lithium-ion battery. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 170, 120998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fu, L.; Sheng, L.; Ye, W.; Sun, Y. Method of liquid-cooled thermal control for a large-scale pouch lithium-ion battery. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 211, 118417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.; Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F. A review on soft computing and nanofluid applications for battery thermal management. J. Energy Storage 2022, 53, 105214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, T.; Ni, M. Investigation of battery thermal management system with considering effect of battery aging and nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 202, 123685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Leng, E. Thermal performance of lithium-ion battery thermal management system based on nanofluid. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 216, 118997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Yang, X. A simple cooling structure with precisely-tailored liquid cooling plate for thermal management of large battery module. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 212, 118575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, D. Heat dissipation optimization for a serpentine liquid cooling battery thermal management system: An application of surrogate assisted approach. J. Energy Storage 2021, 40, 102771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Y.; You, J.; Jiang, Y. Battery temperature performance of external cooling method for electric vehicles under different working conditions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 269, 126010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monika, K.; Chakraborty, C.; Roy, S.; Dinda, S.; Singh, S.A.; Datta, S.P. Parametric investigation to optimize the thermal management of pouch type lithium-ion batteries with mini-channel cold plates. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 164, 120568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.; Feng, X.; Wei, X.; Ouyang, M.; Dai, H. Multi-objective optimization design and experimental investigation for a parallel liquid cooling-based Lithium-ion battery module under fast charging. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 211, 118503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, L. Heat dissipation analysis and optimization of lithium-ion batteries with a novel parallel-spiral serpentine channel liquid cooling plate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 189, 122706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Lei, Z.; An, C. Research on battery thermal management system based on liquid cooling plate with honeycomb-like flow channel. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 218, 119324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, W.; Bei, S.; Quan, Z. Analysis of Heat Dissipation Performance of Battery Liquid Cooling Plate Based on Bionic Structure. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Qin, W.; Li, J. Optimal design of liquid cooling structure with bionic leaf vein branch channel for power battery. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 218, 119283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Guo, J.; Li, Y. Multi-objective optimization of heat transfer performance of power battery cold plate based on bionic spider web flow channel. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 72, 106410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Meng, C.; Yang, Y.; Lin, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, S.; Jiang, C. Numerical optimization of the cooling effect of a bionic fishbone channel liquid cooling plate for a large prismatic lithium-ion battery pack with high discharge rate. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monika, K.; Datta, S.P. Comparative assessment among several channel designs with constant volume for cooling of pouch-type battery module. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 251, 114936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ji, H.; Wei, M.; Liu, R. Effect of liquid cooling system structure on lithium-ion battery pack temperature fields. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 183, 122178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhao, J.; Rao, Z. Heat transfer performance enhancement of liquid cold plate based on mini V-shaped rib for battery thermal management. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 189, 116729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffal, H.M.; Mahmoud, N.S.; Imran, A.A.; Hasan, A. Performance enhancement of a novel serpentine channel cooled plate used for cooling of Li-ion battery module. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 184, 107955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Garg, A.; Gao, L.; Zhou, Q. Multi-objective design optimization of battery thermal management system for electric vehicles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 196, 117235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Eze, C.; Dong, K.; Shahid, A.R.; Patil, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Hussain, I.; Zhao, J. Design of a new optimized U-shaped lightweight liquid-cooled battery thermal management system for electric vehicles: A machine learning approach. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 136, 106209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, S.; Jin, H.; Wang, R.; Jiang, Y. Performance analysis of liquid cooling battery thermal management system in different cooling cases. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkan, O.; Celen, A.; Bakirci, K.; Dalkilic, A.S. Experimental investigation of thermal performance of novel cold plate design used in a Li-ion pouch-type battery. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 191, 116885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Cheng, J. A lightweight liquid cooling thermal management structure for prismatic batteries. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 103078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Zhu, J.; Mao, J. Thermal performance analysis and burning questions of refrigerant direct cooling for electric vehicle battery. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 232, 121055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; Xiao, J.; Sun, W.; Min, Z. Numerical investigation and structural optimization of a battery thermal management system based on refrigerant evaporation. J. Energy Storage 2024, 104, 114438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Su, L. Experimental investigation on flow boiling instability of R1233zd(E) in a parallel mini-channel heat sink for the application of battery thermal management. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 188, 122585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Gao, Q. Structural design and multi-criteria evaluation of refrigerant-based cold plate for battery thermal management system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 273, 126481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Yang, J.; Yang, P.; Zhang, H.; Cai, T. Optimization and working performance analysis of liquid cooling plates in refrigerant direct cooling power battery systems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 231, 125899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X. Study on battery direct-cooling coupled with air conditioner novel system and control method. J. Energy Storage 2023, 70, 108032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Ling, H.; Song, G.; Ma, Q.; He, B. Experimental investigation on a heating-and-cooling difunctional battery thermal management system based on refrigerant. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 225, 120138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ruan, L. Performance investigation of integrated thermal management system based on a pumped two-phase cooling system for electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 107922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamodharan, P.; Salman, M.; Prabakaran, R.; Choi, G.S.; Kim, S.C. Revolutionizing electric vehicle cooling: Optimal performance of R1234yf two-phase refrigerant cooling for EV battery thermal management system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 260, 125070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Luo, X.; Yu, F.; Li, T.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Fan, Y. Effects of inlet subcooling on the flow boiling heat transfer performance of bi-porous mini-channels. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 229, 120577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zareer, M.; Dincer, I.; Rosen, M.A. Development and evaluation of a new ammonia boiling based battery thermal management system. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 280, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zareer, M.; Dincer, I.; Rosen, M.A. A novel phase change based cooling system for prismatic lithium ion batteries. Int. J. Refrig. 2018, 86, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, H.; Peng, W. Parametric investigation on the performance of a direct evaporation cooling battery thermal management system. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 189, 122685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Jang, D.S.; Park, S.; Yun, S.; Kim, Y. Thermal performance of direct two-phase refrigerant cooling for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 173, 115213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Gao, Q. Structure design and effect analysis on refrigerant cooling enhancement of battery thermal management system for electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2020, 32, 101940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Ling, H.; Song, G.; Gong, K.; Fan, C.; Wang, F.; He, B. Optimization and thermal performance analysis of direct cooling plates with multi-splitting-merging channels for electric-vehicle battery thermal management. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2025, 214, 109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Yu, P.; Cheng, J. Investigation on the thermal management performance of a non-contact flow boiling cooling system for prismatic batteries. J. Energy Storage 2023, 66, 107499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Yin, L.; Dang, C.; Liu, R.; Jia, L.; Ding, Y. Phase-change cooling of lithium-ion battery using parallel mini-channels cold plate with varying flow rate. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 45, 102960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, T. Simulation of battery simultaneous cooling based on the dual fluid medium system. J. Energy Storage 2023, 61, 106732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.; Tang, W.; Yao, W.; Wu, Z. A review of thermal management of batteries with a focus on immersion cooling. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 217, 115751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, A.; Najmi, A.U.H.; Senobar, H.; Amjady, N.; Kemper, H.; Khayyam, H. Immersion cooling innovations and critical hurdles in Li-ion battery cooling for future electric vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 211, 115268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, T.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. A review of flow boiling heat transfer: Theories, new methods and emerging applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 215, 115615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadar, A.; Amir, M.; Mohammad, N. An optimal design of battery thermal management system with advanced heating and cooling control mechanism for lithium-ion storage packs in electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2024, 99, 113421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.S.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, M.Y. A novel dielectric fluid immersion cooling technology for Li-ion battery thermal management. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 229, 113715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, S. Dynamic-static composite immersion cooling for improving thermal equalization behavior in lithium-ion battery packs. Energy 2025, 330, 136774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jithin, K.V.; Rajesh, P.K. Numerical analysis of single-phase liquid immersion cooling for lithium-ion battery thermal management using different dielectric fluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 188, 122608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Cheng, J. Multi-objective optimization of parallel flow immersion cooling battery thermal management system with flow guide plates based on artificial neural network. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2025, 274, 126833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.M.; Marconnet, A.M. Effect of immersion cooling parameters on thermal and electrochemical response of a Li-ion cell. J. Power Sources 2025, 632, 236285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wu, J.; Liu, X.; Jiao, X.; Zheng, N.; Sun, Z. A novel water-based direct contact cooling system for thermal management of lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Storage 2025, 107, 114973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febriyanto, R.; Ariyadi, H.M.; Pranoto, I.; Rahman, M.A. Experimental study of serpentine channels immersion cooling for lithium-ion battery thermal management using single-phase dielectric fluid. J. Energy Storage 2024, 97, 112799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, A.; Cifterler, N.; Amjady, N.; Date, A.; Kemper, H.; Khayyam, H. Enhancing energy and thermal efficiency of single-phase liquid immersion cooling systems for lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2025, 131, 117365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Huang, J.; Xia, Y.; Li, R. Improve immersion cooling of cylindrical batteries in channel flows using the Tesla valve principle. J. Energy Storage 2025, 112, 115546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, W.; Xiong, S.; Luo, Z.; Ahmed, M. Single-phase static immersion-cooled battery thermal management system with finned heat pipes. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 254, 123931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousi, M.; Sarchami, A.; Najafi, M.; Bellur, K. Investigating the efficiency of a novel combined Direct/Indirect thermal management system in optimizing the thermal performance of a new generation 46800-type LIB pack. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 235, 121402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borujerd, S.V.N.; Soleimani, A.; Esfandyari, M.J.; Masih-Tehrani, M.; Esfahanian, M.; Nehzati, H.; Dolatkhah, M. Fuzzy logic approach for failure analysis of Li-ion battery pack in electric vehicles. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 149, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, R.K.; Langeh, H.; Kumar, V.; Chouhan, S.S.; Prabhakar, A. Faulty cell prediction accuracy comparison of machine learning algorithms using temperature sensor placement optimization approach in immersion cooled Li-ion battery modules. Appl. Energy 2024, 367, 123299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donmez, M.; Tekin, M.; Karamangil, M.I. Artificial neural network predictions for temperature: Utilizing numerical analysis in immersion cooling systems using mineral oil and an engineered fluid for 32700 LiFePO4. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2025, 211, 109742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.P.; Trimble, D.; O’Shaughnessy, S.M. Electrochemical-thermal numerical model of a lithium-ion battery under natural convection liquid immersion cooling conditions. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2025, 27, 101062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Wang, C.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, J. Experimental study of a novel guided sequential immersion cooling system for battery thermal management. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 257, 124337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.P.; Trimble, D.; O’Shaughnessy, S.M. An experimental investigation of liquid immersion cooling of a four cell lithium-ion battery module. J. Energy Storage 2024, 86, 111289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, L.; Bai, M.; Gao, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Song, Y. Experimental studies of liquid immersion cooling for 18650 lithium-ion battery under different discharging conditions. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 34, 102034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, M.; Zhou, Z.; Lv, J.; Hu, C.; Gao, L.; Peng, C.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, Y. Experimental study of liquid immersion cooling for different cylindrical lithium-ion batteries under rapid charging conditions. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2023, 37, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Wen, X.; Cai, W.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Yu, H.; Zhu, H.; et al. Experimental studies on two-phase immersion liquid cooling for Li-ion battery thermal management. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Lyu, P.; Liu, X.; Wen, C.; Rao, Z. Evaluation of thermal performance of immersion flow boiling thermal management in large-scale battery packs with simplified model. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 162, 108656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, W.T.; Wei, L.; Hu, C.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Song, Y. Numerical simulation for comparison of cold plate cooling and HFE-7000 immersion cooling in lithium-ion battery thermal management. J. Energy Storage 2024, 101, 113938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.W.; Zhou, Z.F.; Yin, J.; Zhu, X.G.; Shi, M.Y.; Chen, B. A comparative investigation of two-phase immersion thermal management system for lithium-ion battery pack. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 140472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.; Jannesari, H.; Ameri, M. Experimental study of Li-ion battery thermal management based on the liquid-vapor phase change in direct contact with the cells. J. Energy Storage 2023, 62, 106834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.; Kong, D.; Kang, M.; Park, J.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, J.; In, J.B.; Oh, K.Y.; Lee, H. Enhanced immersion cooling using laser-induced graphene for Li-ion battery thermal management. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 155, 107558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Ye, X.; Yao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Yu, B. Efficient thermal management of the large-format pouch lithium-ion cell via the boiling-cooling system operated with intermittent flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 170, 121018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Li, L.; Xu, Q.; Ling, L.; Xie, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, L.; Bei, S. Numerical investigation of a compact and lightweight thermal management system with axially mounted cooling tubes for cylindrical lithium-ion battery module. Energy 2023, 274, 127410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Liu, C.; Li, N.; Yang, L.; Yang, X.G.; Dou, B.; Hou, S.; Feng, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; et al. Wireless transmission of internal hazard signals in Li-ion batteries. Nature 2025, 641, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.P.; He, Y.B.; Wang, B.C.; Li, H.X. Physics-Dominated Neural Network for Spatiotemporal Modeling of Battery Thermal Process. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broatch, A.; Pla, B.; Bares, P.; Agizza, L. Single value decomposition for sparse temperature sensing and state observation in multicell battery packs. J. Energy Storage 2024, 97, 112888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Duan, J.; Panchal, S.; Yuan, J.; Fraser, R.; Fowler, M.; Chen, M. Simulation of cooling plate effect on a battery module with different channel arrangement. J. Energy Storage 2022, 49, 104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Ma, C.; Hu, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. The performance investigation and optimization of reciprocating flow applied for liquid-cooling-based battery thermal management system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 292, 117378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, A.; Prosser, R.; Diaz, L.B.; White, G.; Patel, Y.; Offer, G. The Cell Cooling Coefficient as a design tool to optimise thermal management of lithium-ion cells in battery packs. Etransportation 2020, 6, 100089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.M.; Salem, M.S.; Kannan, A.M.; Hamed, A.M.; Shouman, M.A. Exploratory study on electric batteries thermal performance metrics and thermal management systems evaluation. J. Energy Storage 2025, 110, 115282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anqi, A.E. Numerical investigation of heat transfer and entropy generation in serpentine microchannel on the battery cooling plate using hydrophobic wall and nanofluid. J. Energy Storage 2023, 66, 106548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zheng, J.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Kou, G.; Wen, X.; Sun, J.; Mu, M. Thermal performance of thermal management system combining bionic fern-vein liquid channel with phase change materials for prismatic Lithium-ion battery. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2025, 214, 109844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Qin, J.; Minqiang, P. A lightweight and low-cost liquid-cooled thermal management solution for high energy density prismatic lithium-ion battery packs. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 203, 117871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Yu, X.; Wei, L.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Meng, X.; Jin, L. Parametric study of forced air cooling strategy for lithium-ion battery pack with staggered arrangement. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 136, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Lyu, P.; Fan, Y.; Rao, J.; Ouyang, K. Numerical investigation of the direct liquid cooling of a fast-charging lithium-ion battery pack in hydrofluoroether. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 196, 117279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausthubharam; Koorata, P.K.; Panchal, S.; Fraser, R.; Fowler, M. Investigation of the thermal performance of biomimetic minichannel-based liquid-cooled large format pouch battery pack. J. Energy Storage 2024, 84, 110928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.S.; Kumar, R. Techno-economic analysis of cooling technologies used in electric vehicle battery thermal management: A review. J. Energy Storage 2024, 103, 114135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, L.; Kallitsis, E.; Hales, A.; Edge, J.S.; Korre, A.; Offer, G. Cost and carbon footprint reduction of electric vehicle lithium-ion batteries through efficient thermal management. Appl. Energy 2021, 289, 116737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y. SOH prediction of lithium battery based on IC curve feature and BP neural network. Energy 2022, 261, 125234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, K.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, C.; Zhang, Y. Thermal management requirements in battery packs: An analysis of the effects of battery degradation. Energy 2025, 331, 137067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, J.; Qiu, S.; Liu, X.; Lyu, K.; Chen, S.; Xing, S.; Guo, Y. Phased control reciprocating airflow cooling strategy for a battery module considering stage of charge and state of health inconsistency. J. Energy Storage 2023, 61, 106752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Q. Application of Refrigerant Cooling in a Battery Thermal Management System under High Temperature Conditions: A Review. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 25591–25609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Q.; Zhang, C.; Shi, J.; Chen, J. Machine learning based refrigerant leak diagnosis for a vehicle heat pump system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 215, 118524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Type of BTMS | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Air-cooling system | Simple structure Low cost Low energy consumption Lightweight | Poor temperature uniformity Not suitable for high-power batteries |
| Liquid-based cooling system | High-temperature control accuracy High-heat-transfer efficiency | Complex structure High weight |
| PCM cooling system | Temperature uniformity High heat storage capacity | Heavy Large volume High cost |
| Heat pipe cooling system | Long lifespan High compactness Flexible in various shapes High-heat-transfer efficiency | High cost Heavy |
| Coolant | Density, kg/m3 | Specific Heat Capacity, J/(kg·K) | Thermal Conductivity, W/(m·K) | Dynamic Viscosity, kg/(m·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water [60] | 998.2 | 4182 | 0.6 | 0.0010003 |
| Ethylene glycol [61] | 1111.4 | 2415 | 0.252 | 0.0157 |
| 50% glycol aqueous solution [62] | 1069 | 3319 | 0.373 | 0.002940 |
| Reference | Number of Batteries | Dielectric Fluid | Charge/Discharge C-Rate | Initial Temperature | Max Temperature | Max Temperature Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donmez et al. [126] | 16S1P | Engineered fluid | 4C discharge | 27 °C | 307.28 K | <6 K |
| Williams et al. [127] | 1 | Novec 7000 (3M, Maplewood, MN, USA) | 4C charge 4C discharge | \ | 294.6 K 300 K | 2.5 K 6.8 K |
| Zhong et al. [128] | 4S1P | EBC160 (The Karamay Petrochemical Company of China National Petroleum Corporation, Karamay, China) | 4C discharge 5C discharge | 25 °C | 40.682 °C 43.476 °C | 1.87 °C 2.25 °C |
| Patil et al. [113] | 14S1P | mineral oil | 5C discharge | 25 °C | <40°C | \ |
| Tripathi et al. [117] | 1 | deionized water mineral oil | 5C discharge | 25 °C | 32 °C 39 °C | \ \ |
| Wahab et al. [120] | 16S1P | MIVOLT DF7 (MIDEL & MIVOLT Fluids Ltd, Manchester, UK) | 8C discharge | 20 °C | 306.41 K | 4.13 K |
| Evaluation Indicator | Suitable System Type | Function | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum temperature | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Reflects the maximum temperature; Directly related to thermal safety | Cannot reflect the temporal and spatial characteristics of local hotspots |
| Average temperature | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Reflects the overall heat-transfer performance of the system | |
| Maximum temperature difference | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Evaluates the impact of thermal management on consistency of battery performance | |
| Temperature standard deviation | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Evaluates the impact of thermal management on consistency of battery performance | |
| Z-score of the factor [143] | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Retains the original distribution shape of battery temperatures; suitable for detecting abnormal temperature values | \ |
| The temperature distribution coefficient [144] | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Evaluates the temporal and spatial distribution of the hottest spot | Not suitable as an objective function for optimization design |
| Cell cooling coefficient [145] | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Evaluates the heat-transfer capability along the heat-transfer path | Heat transfer between adjacent batteries can affect the assessment results |
| Thermal entropy and viscous entropy [147] | Indirect-contact cooling | Evaluates the entropy generation of the fluid flowing through the cold plate | \ |
| j/f factor [148] | Indirect-contact cooling | Comprehensively evaluates heat-transfer performance and energy consumption | \ |
| Cooling efficiency factor [149,150] | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Evaluates BTMS cooling efficiency | \ |
| Energy density [151] | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Evaluates lightweighting of the BTMS | \ |
| Total average system cost [153] | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Economic evaluation based on investment, operation, and maintenance | \ |
| SOH [155] | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Evaluates battery SOH and performance consistency | \ |
| SOC [157] | Indirect-contact cooling/Direct-contact cooling | Evaluates battery SOC and charging/discharging consistency | \ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Shi, C.; Liu, C.; Chang, W. A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management Based on Liquid Cooling and Its Evaluation Method. Energies 2025, 18, 4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174569
Liu H, Shi C, Liu C, Chang W. A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management Based on Liquid Cooling and Its Evaluation Method. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174569
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongkai, Chentong Shi, Chenghao Liu, and Wei Chang. 2025. "A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management Based on Liquid Cooling and Its Evaluation Method" Energies 18, no. 17: 4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174569
APA StyleLiu, H., Shi, C., Liu, C., & Chang, W. (2025). A Review of Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management Based on Liquid Cooling and Its Evaluation Method. Energies, 18(17), 4569. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174569






