Study on the Failure Causes and Improvement Measures of Arresters in 10 kV Distribution Transformer Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
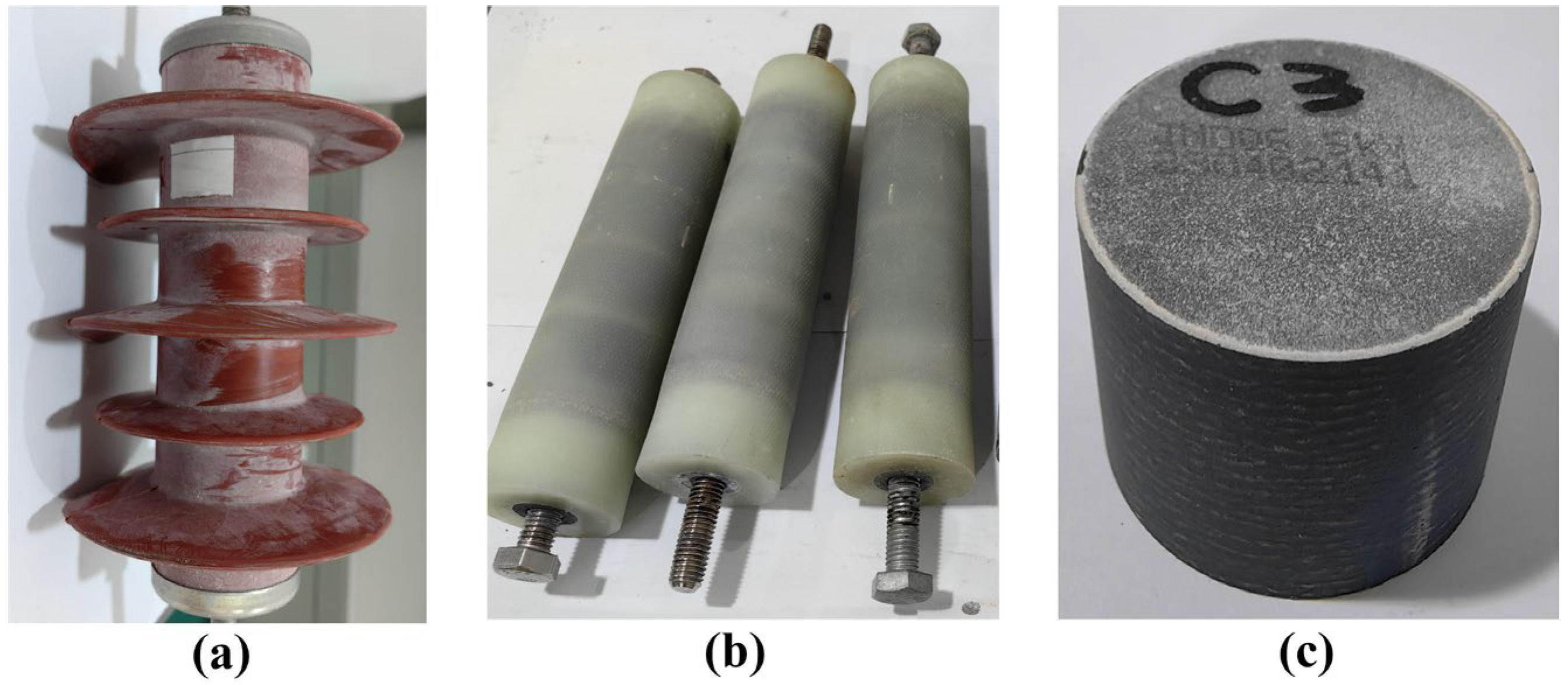
2.1. Test Samples
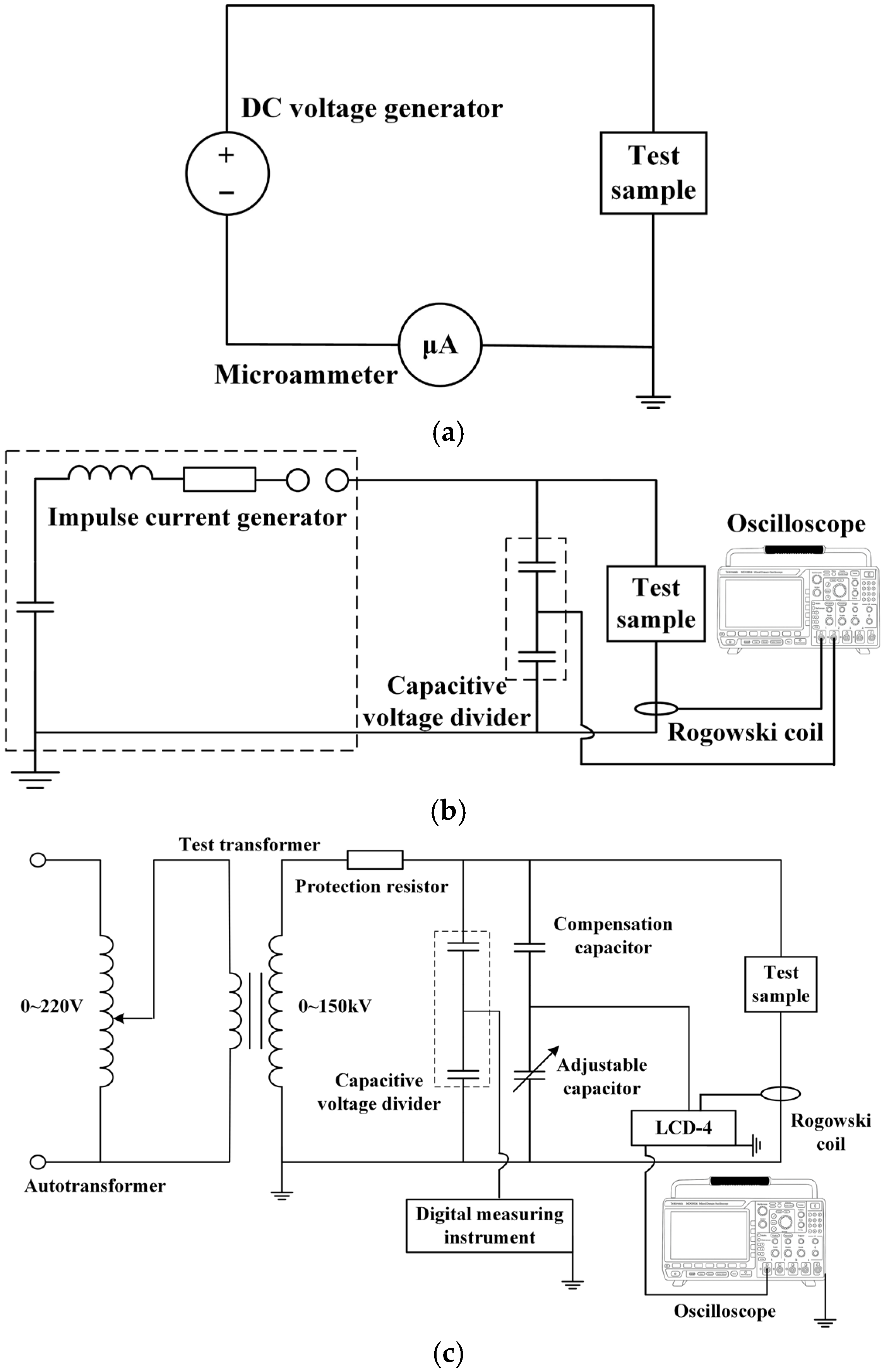
2.2. Test Methods
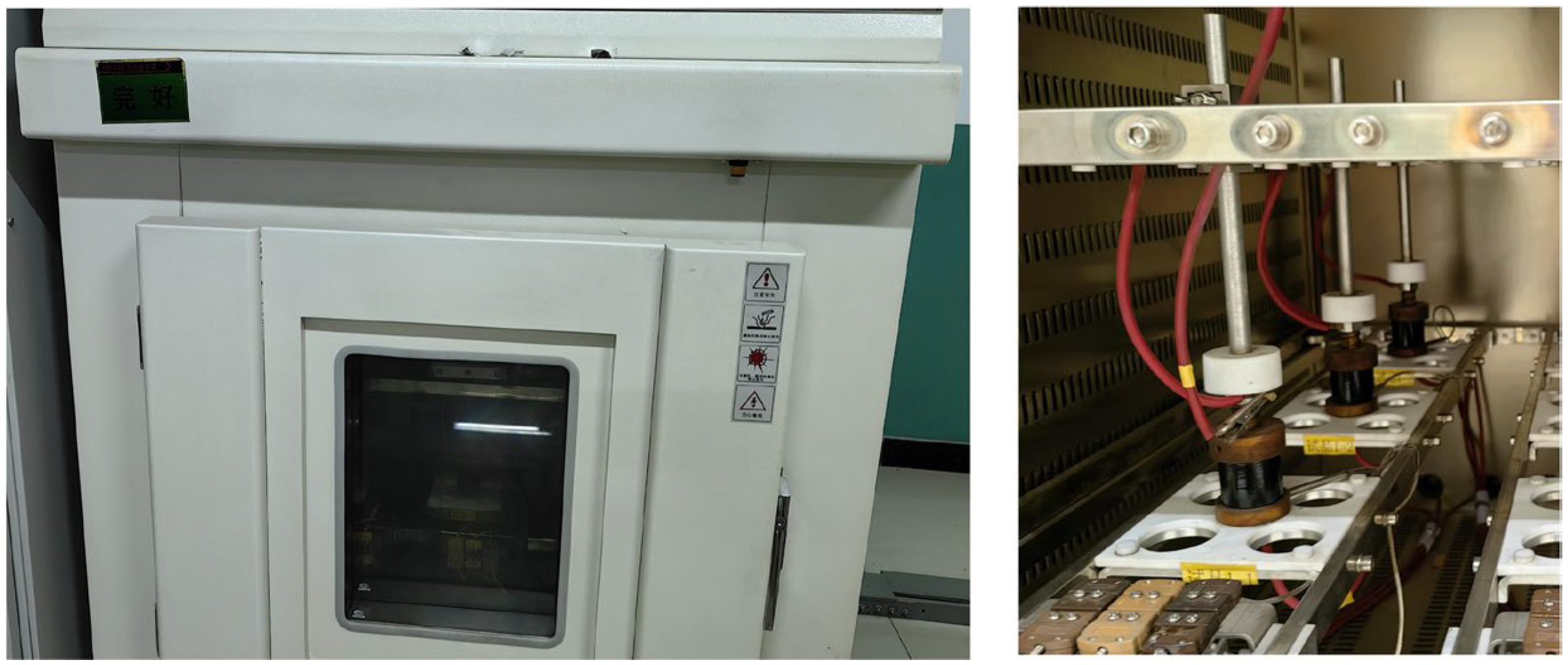
2.3. Electrical Performance Measurement Methods
3. Results
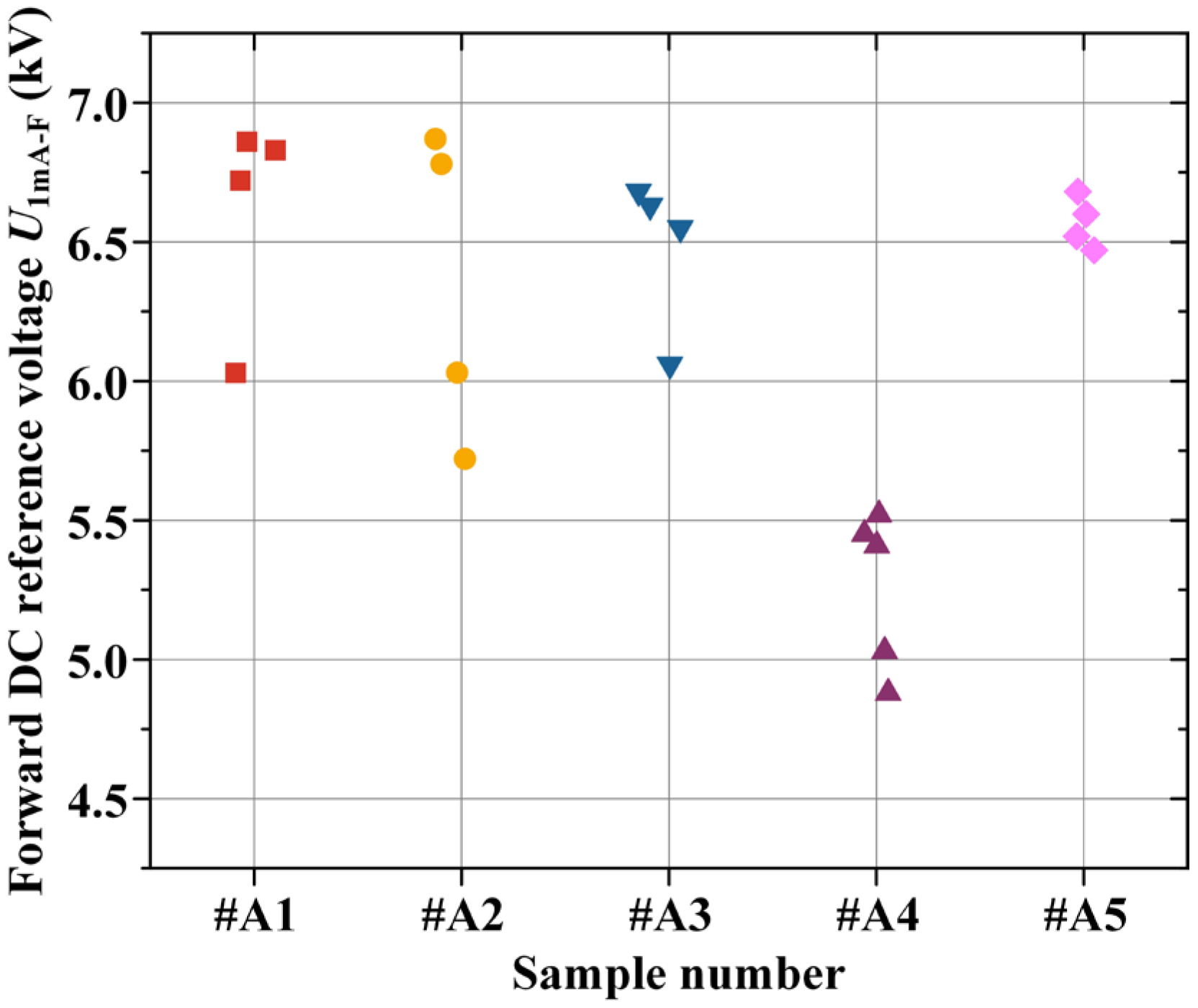
3.1. Performance Testing Results of Failed Arresters
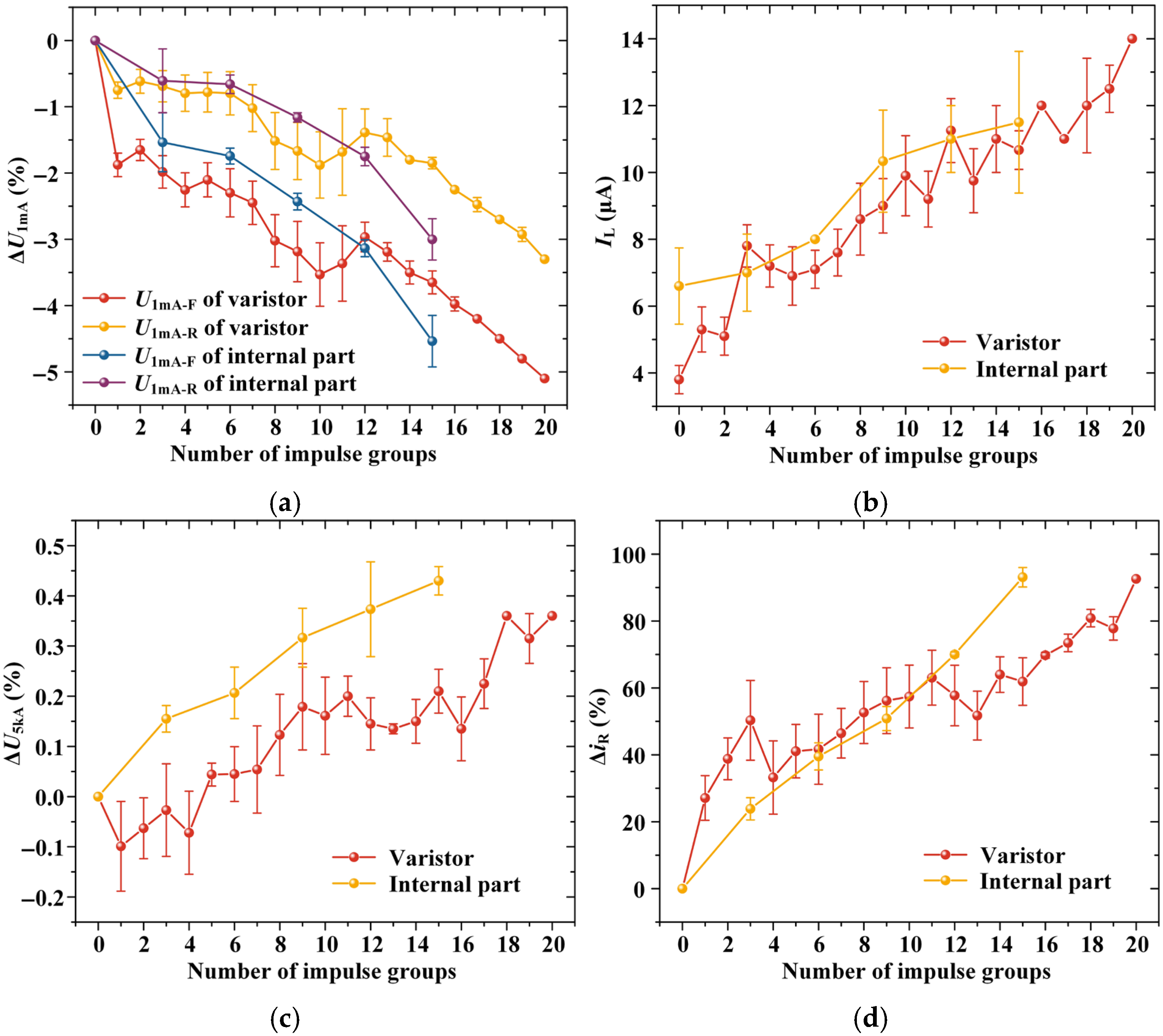
3.2. Lightning Impulse Test Results
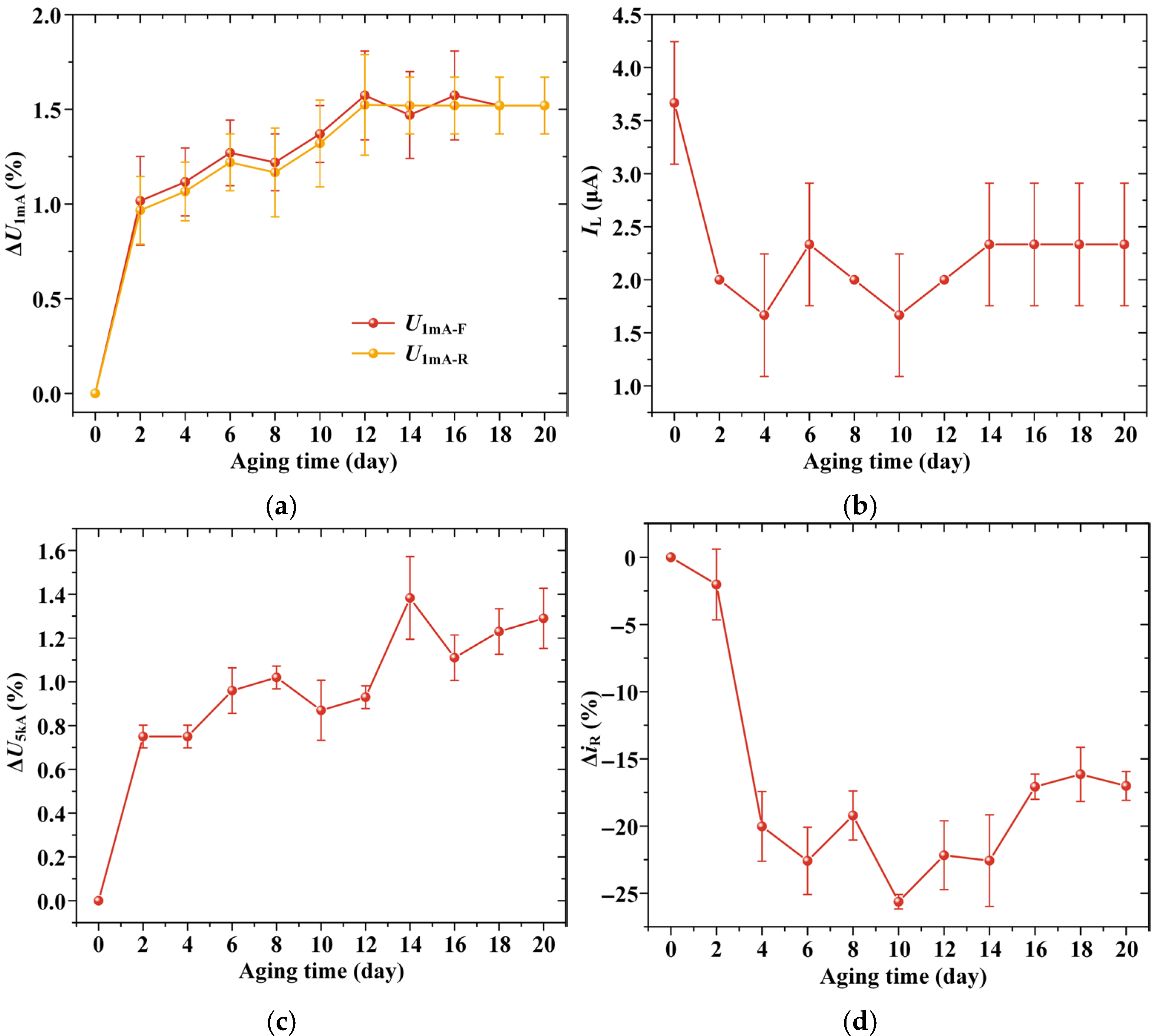
3.3. AC Aging Test Results
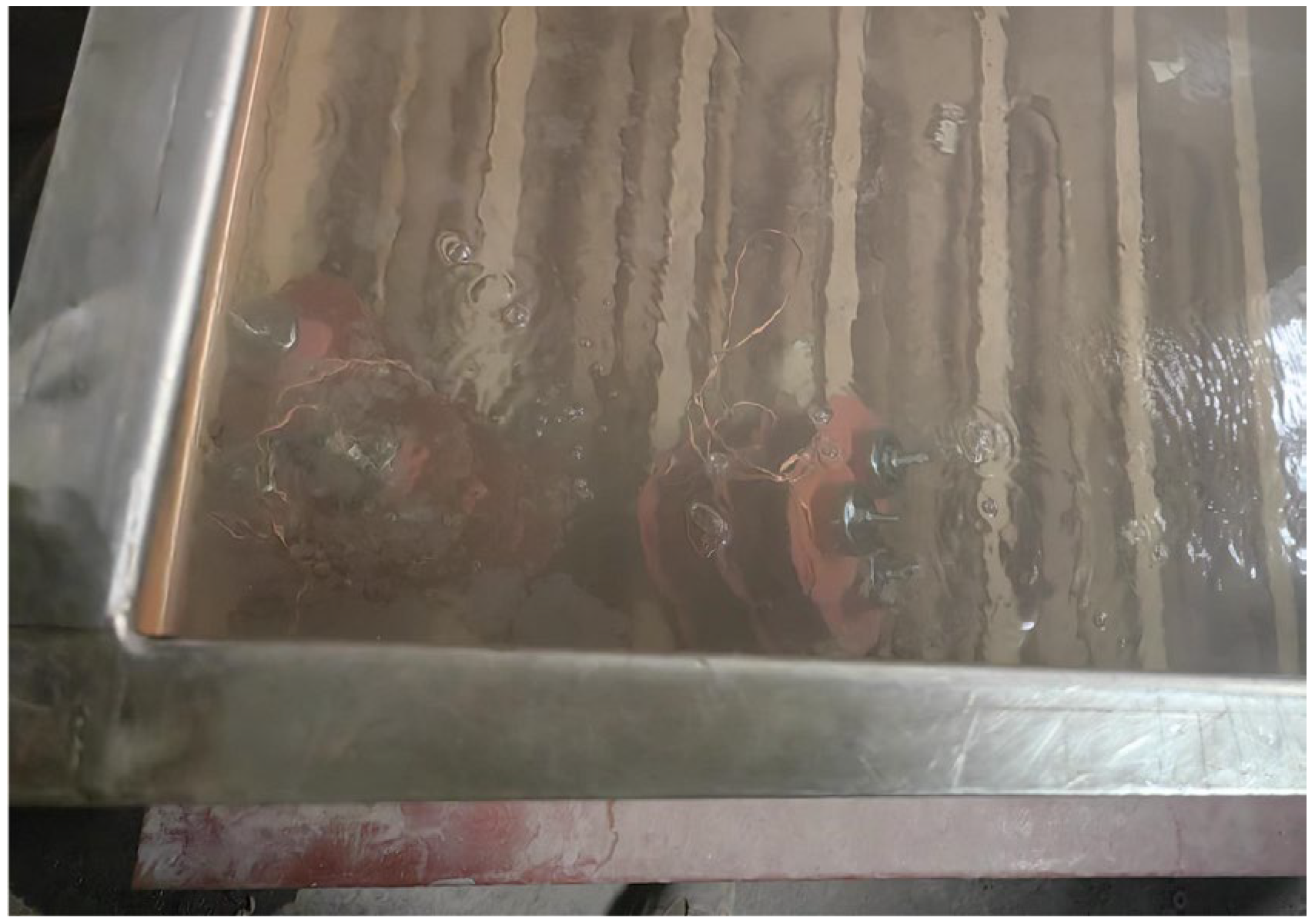
3.4. Water Immersion Test Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Failure Cause Analysis
4.2. Improvement Measures
5. Conclusions
- (1)
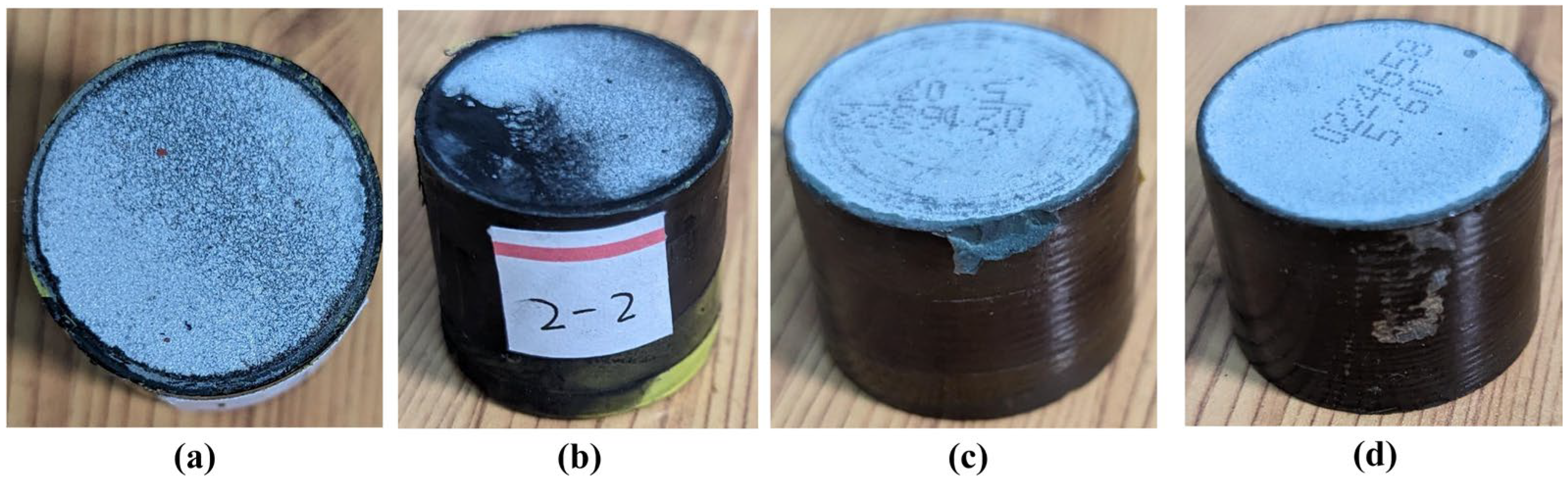
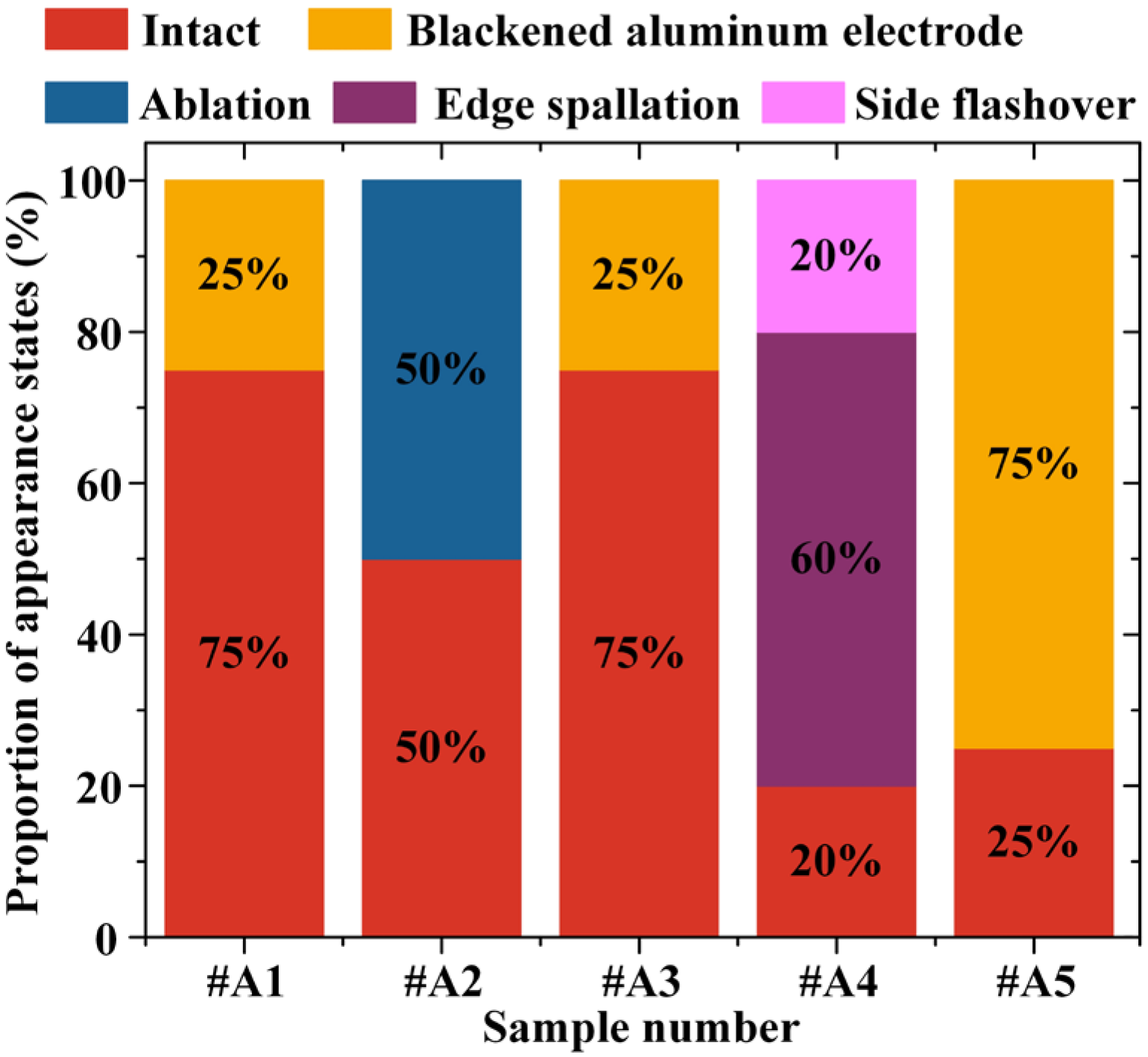
- Most failed arresters exhibit significant external deterioration, including corrosion on metal components, contamination buildup on the housing, and contamination accompanied by visible traces of side flashover. Internal inspection reveals that some varistors display typical damage modes, such as blackened aluminum electrodes, ablation, edge spallation, and side flashover.
- (2)
- Under lightning impulse stress, the varistor samples predominantly exhibit pinhole-type damage, whereas the internal part samples show damage to the injection molded structure as well as internal varistors. The electrical performance parameters of both types of samples deteriorate significantly. Although the varistor samples deteriorate more rapidly, their structural stability is superior to that of the internal part samples. In contrast, AC aging does not cause visible damage to the varistor samples. After initial fluctuations, the electrical performance of the varistor samples stabilizes, with deterioration primarily reflected in the increase in residual voltage. Water immersion induces minor, reversible degradation in arrester and internal part samples, but causes severe and irreversible degradation in varistor samples, characterized by blackening of aluminum electrodes and a sharp decline in electrical performance.
- (3)
- A critical internal cause of arrester failure is the widespread occurrence of moisture ingress into the internal varistors. Under the influence of AC voltage, lightning impulses, or the combined effect of both, the presence of moisture significantly exacerbates varistor damage and accelerates electrical performance degradation, ultimately manifesting as a decline in the arrester’s overall electrical characteristics. Externally, contamination buildup on the silicone rubber housing, particularly under harsh outdoor conditions, emerges as a major concern. In humid environments, this contamination is prone to triggering pollution flashovers, serving as a key external factor contributing to the failure of certain arrester samples. The findings provide a scientific basis for the optimization of the design, evaluation, and maintenance of arresters in distribution transformer areas.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ZnO | Zinc oxide |
| Nomenclature | |
| IL | Leakage current at the DC voltage of 0.75 × U1mA–F |
| iR | Resistive current at the continuous operating voltage |
| U1mA | DC reference voltage at the DC current of 1 mA |
| U1mA–F | Forward DC reference voltage at the DC current of 1 mA |
| U1mA–R | Reverse DC reference voltage at the DC current of 1 mA |
| U5kA | Residual voltage at the amplitude of 5 kA and the waveform of 8/20 μs |
References
- Li, D.J.; Sun, W.X.; Song, K.Y.; Zhu, R.F.; Zhong, Z.X.; Ding, T.S.; Gao, J.C. Research on Differentiated Lightning Protection of Overhead Distribution Lines under Continuous Lightning Strikes. Energies 2024, 17, 4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazim, M.; Khawaja, A.H.; Zabit, U.; Huang, Q. Fault Detection and Localization for Overhead 11-kV Distribution Lines with Magnetic Measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 2028–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas, R.P.d.S.; Rocha, G.V.S.; Muniz, J.R.S.; Bezerra, U.H.; Nunes, M.V.A.; Silva, J.S.E. Methodology for Analysis of Electric Distribution Network Criticality Due to Direct Lightning Discharges. Energies 2020, 13, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Xu, C.F.; Wang, J.G.; Chu, W.X.; Zhou, M.; Fan, Y.D.; Cao, J.X. Three-Phase Overvoltage Induced on Overhead Distribution Line 40 m from Rocket-Triggered Lightning. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2023, 38, 3782–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodworth, J. Lightning Protection of Distribution Power Systems: Arrester Development and Application Over the Years. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2023, 21, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.X.; Du, Y.P.; Ding, Y.X.; Qi, R.H.; Chen, M.L.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.E.; Andreotti, A. Lightning Protection with a Differentiated Configuration of Arresters in a Distribution Network. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2023, 38, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, N.; Proto, D.; Andreotti, A. Surge arrester optimal placement in distribution networks: A decision theory-based approach. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2024, 234, 110744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.Q.; Xu, Z.R.; Tang, J.; Liang, Z.Y.; Chen, D.Z. Present Situation and Problems Analysis for Lightning Protection of 10 kV Power Distribution Line Based on Historical Trip Records. Insul. Surge Arrester 2012, 2, 40–45+50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sabiha, N.A. Limiting surge arrester failure under direct lightning strokes for attaining service continuity of distribution networks. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2020, 14, 4796–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.X.; Du, Y.P.; Ding, Y.X.; Qi, R.H.; Li, B.H.; Chen, M.L.; Li, Z. Practical Schemes on Lightning Energy Suppression in Arresters for Transformers on 10 kV Overhead Distribution Lines. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2022, 37, 4272–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Huang, J.R.; Chen, L.; Wan, K.; Zuo, Z.Q. Influencing Factors of High Current Impulse Withstand Capability of 10 kV Distribution Arrester. Insul. Surge Arrester 2022, 5, 59–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto, N.; Ishii, M. Repetitive Impulse Withstand Performance of Metal-Oxide Varistors. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2017, 32, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, T.A.; de Salles, C.; Neto, E.T.W.; Pinheiro, F.F. Short duration current impulse waveform effects on the degradation and energy absorption capability of zinc oxide varistors. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2023, 220, 109336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, B.; Darvishi, A.; Dashti, R.; Shaker, H.R. A Survey of Diagnostic and Condition Monitoring of Metal Oxide Surge Arrester in the Power Distribution Network. Energies 2022, 15, 8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.P.; Wang, Q.; He, J.; Li, X.; Ding, L.J. TSC characteristics of AC aged ZnO varistors. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2013, 56, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Tan, J.Y.; Wu, X.G.; Wang, D.S.; Chen, X.X. Study on Accelerated Electrical Aging Frequency Domain Feature of ZnO Valve Based on Extended Debye Model. High Volt. Eng. 2020, 46, 1759–1767. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Neto, E.T.W.; da Costa, E.G.; Maia, M.J.A. Artificial Neural Networks Used for ZnO Arresters Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2009, 24, 1390–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahti, K.; Kannus, K.; Nousiainen, K. Diagnostic methods in revealing internal moisture in polymer housed metal oxide surge arresters. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2002, 17, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC 60099-4; Surge Arresters—Part 4: Metal Oxide Surge Arresters Without Gaps for a.c. Systems. IEC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Tu, Y.P.; Zheng, Z.H.; Li, X. AC ageing characteristics of Co-doped ZnO varistors. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2013, 56, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, C.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Accelerated aging test of domestic and Hitachi zinc oxide valve sheets and operation load test after aging. Insul. Surge Arrester 1989, 4, 22–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, J.L.; Liu, J.; Hu, J.; Zeng, R.; Long, W.C. Non-uniform ageing behavior of individual grain boundaries in ZnO varistor ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tian, J.L. Study of the Effect of Ca on the Electrical Properties of SnO2 Varistor Based on the Voronoi Model. J. Electron. Mater. 2024, 53, 5433–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Ren, X.; Zhou, Q.B.; Li, Z.Y.; Yang, H.X.; Jiang, H.B.; Yan, Y.; Ruan, X.J.; Yu, W.Q.; Jin, L.J.; et al. High improvement of degradation behavior of ZnO varistors under high current surges by appropriate Sb2O3 doping. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, Y.X.; Yu, F.; Huang, W.T.; Li, L.C.; Luo, X.; Meng, Y.C.; Sun, Q. Study on Improving the Operating Lifespan of AC Filter Arresters in Converter Station Based on the Degradation Characteristics of ZnO Varistor Under Unipolar and Bipolar Polarity Impulse Currents. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2024, 39, 3039–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, C.A.; Vita, V.; Mladenov, V.; Ekonomou, L. On the Computation of the Voltage Distribution along the Non-Linear Resistor of Gapless Metal Oxide Surge Arresters. Energies 2018, 11, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Mogaveera, V. Voltage distribution studies on ZnO arresters. IEE Proc. Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2002, 149, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Dalai, S.; Chatterjee, B. A Novel Approach to Estimate the Quantity of Ingressed Moisture Content Inside Metal Oxide Surge Arrester Using Dielectric Modulus Technique. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2021, 28, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, C.; Huang, L.; Wang, D.Y.; Ma, Y.T. Effect of Moisture on the Multiple Lightning Strike Resistance of ZnO Valve Discs. High Volt. Eng. 2024, 50, 5368–5377. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]







| Type | Rated Voltage (kV) | DC Reference Voltage at 1 mA (kV) | Residual Voltage at 5 kA, 8/20 μs (kV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YH5WS-17/50 | 17 | ≥25 | ≤50 |
| Sample Number | U1mA-F (kV) | U1mA-R (kV) | IL (μA) | U5kA (kV) | iR (μA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #A1 | 27.03 | 27.03 | 4 | 51.90 | 36.56 |
| #A2 | 26.24 | 26.20 | 3 | 52.26 | 46.17 |
| #A3 | 26.48 | 27.05 | 3 | 49.90 | 34.31 |
| #A4 | 26.74 | 27.12 | 24 | 47.89 | 58.68 |
| #A5 | 26.72 | 27.08 | 17 | 47.77 | 55.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, T.; Wu, Y.; Liao, Z.; Liu, G.; Hu, S.; Han, Y.; Qu, L.; Li, L. Study on the Failure Causes and Improvement Measures of Arresters in 10 kV Distribution Transformer Areas. Energies 2025, 18, 4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174501
Hu T, Wu Y, Liao Z, Liu G, Hu S, Han Y, Qu L, Li L. Study on the Failure Causes and Improvement Measures of Arresters in 10 kV Distribution Transformer Areas. Energies. 2025; 18(17):4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174501
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Taishan, Yuanzhi Wu, Zhiming Liao, Gang Liu, Shangmao Hu, Yongxia Han, Lu Qu, and Licheng Li. 2025. "Study on the Failure Causes and Improvement Measures of Arresters in 10 kV Distribution Transformer Areas" Energies 18, no. 17: 4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174501
APA StyleHu, T., Wu, Y., Liao, Z., Liu, G., Hu, S., Han, Y., Qu, L., & Li, L. (2025). Study on the Failure Causes and Improvement Measures of Arresters in 10 kV Distribution Transformer Areas. Energies, 18(17), 4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18174501






