Abstract
Given the growing need for high-performance operation of 4WID-UGVs, coordinated optimization of trajectory tracking, vehicle stability, and energy efficiency poses a challenge. Existing control strategies often fail to effectively balance these multiple objectives, particularly in integrating energy-saving goals while ensuring precise trajectory following and stable vehicle motion. Thus, a hierarchical control architecture based on Model Predictive Control (MPC) is proposed. The upper-level controller focuses on trajectory tracking accuracy and computes the optimal longitudinal acceleration and additional yaw moment using a receding horizon optimization scheme. The lower-level controller formulates a multi-objective allocation model that integrates vehicle stability, energy consumption, and wheel utilization, translating the upper-level outputs into precise steering angles and torque commands for each wheel. This work innovatively integrates multi-objective optimization more comprehensively within the intelligent vehicle context. To validate the proposed approach, simulation experiments were conducted on S-shaped and circular paths. The results show that the proposed method can keep the average lateral and longitudinal tracking errors at about 0.2 m, while keeping the average efficiency of the wheel hub motor above 85%. This study provides a feasible and effective control strategy for achieving high-performance, energy-saving autonomous driving of distributed drive vehicles.
1. Introduction
With the rapid advancement of intelligent transportation systems and vehicle electrification technologies, electric vehicles (EVs) have become a pivotal component in autonomous driving systems [1]. Conventional centralized electric drivetrains—typically employing a central motor or integrated axle architecture—are inherently limited in torque distribution flexibility due to their structural centralization. In complex driving scenarios such as emergency obstacle avoidance, off-road navigation, or high-speed cornering, these architectures often fail to deliver rapid and precise torque allocation, resulting in increased risks of steering instability and degraded maneuverability.
To address these limitations, the four-wheel independently driven in-wheel motor (4WID-IWM) configuration has attracted significant attention [2]. This architecture enables each wheel to be controlled independently in both torque and steering, thereby enhancing vehicular agility and terrain adaptability, particularly under unstructured and dynamically evolving environments. Baras and Dasygenis [3] proposed an energy-efficient path planning approach that significantly improves adaptability in heterogeneous environments, while Lin et al. [4] developed an optimized torque allocation strategy to improve overall system efficiency and dynamic response.
Despite notable progress, most existing control strategies primarily focus on optimizing a single objective, such as path tracking or energy consumption, without achieving coordinated scheduling and system-level control under diverse task demands. Traditional approaches, including rule-based control, fuzzy logic control, and centralized optimization, may perform adequately under specific conditions but often struggle to balance stability and efficiency in unstructured and complex road environments. For instance, Song et al. [5] proposed a robust tracking control strategy that improves trajectory accuracy but remains insufficient in addressing global energy optimization.
Recent studies have thus begun to explore the multi-degree-of-freedom control potential of the in-wheel motor architecture. Zhang et al. [6] highlighted that this structure inherently supports multi-objective coordination—encompassing trajectory tracking, attitude control, and energy management. Hua et al. [7] aimed at the problem of limited energy storage in distributed drive electric vehicles with four-wheel motors and proposed a hierarchical control method, which effectively improved the tracking performance and reduced the total power consumption compared with the fixed torque ratio distribution method. Liu et al. [8] established a joint optimization model integrating trajectory tracking and energy efficiency, validating the feasibility of dual-objective control in distributed-drive vehicles. Jafari et al. [9] proposed a dual-layer torque distribution framework that improves driving responsiveness while balancing energy efficiency and stability. Jing et al. [10] emphasized the intrinsic conflicts between energy efficiency and dynamic performance in multi-objective control, advocating for a hierarchical architecture to decouple competing objectives.
While these efforts have expanded the design space for control strategies in 4WID Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs), challenges remain due to high system coupling, redundant torque management, and increased computational complexity [11]. These factors pose significant demands on the real-time performance, robustness, and coordination capability of control frameworks. To overcome these challenges, Model Predictive Control (MPC) has emerged as a promising solution owing to its real-time optimization capability and constraint handling. Zhu et al. [12] introduced a dynamically constrained NMPC framework that performs well in multi-variable coupled systems. Weißmann et al. [13] developed an MPC-based longitudinal controller that balances energy consumption and speed planning. Falcone et al. [14] were among the first to apply MPC to active steering control, significantly improving cornering stability. Jeong et al. [15] further proposed an integrated control algorithm based on MPC to enhance the coordination of path tracking. Nguyen et al. [16] incorporated stability constraints into MPC, boosting control robustness under extreme conditions.
Other contributions include Tian and Yang [17], who examined the impact of wheel-end coordination on overall vehicle stability, and Han et al. [18], who applied MPC to cornering control for improved performance in boundary scenarios. Liang et al. [19] proposed an energy-driven torque vectoring strategy to minimize energy consumption across multiple motors. Nevertheless, Grymin et al. [20] pointed out that centralized MPC architectures often face limitations in real-time execution due to high computational costs and inadequate scalability under actuator constraints and dynamic tasks.
To enhance modularity and responsiveness, Li et al. [21] introduced a multi-layer control framework for electric vehicles; however, the effective decoupling and coordination between trajectory planning and torque execution still need to be further explored and improved. Moreover, Chen et al. [22] applied a deep reinforcement learning (DRL)-based multi-objective control method to jointly optimize path adaptability, fuel consumption, and stability. Yet, most DRL approaches suffer from extensive training data requirements, long convergence times, and sensitivity to observational uncertainty, limiting their practical applicability in dynamic and uncertain environments.
To overcome the above limitations, this paper proposes a hierarchical MPC-based control architecture tailored for 4WID-IWM UGVs operating in complex paths and multi-objective task scenarios. Compared to existing studies that often tackle trajectory tracking and torque allocation in a monolithic, computationally burdensome manner, our hierarchical framework introduces a distinctive decoupling strategy. At the upper layer, a trajectory-oriented dynamic optimization model is developed to generate desired longitudinal acceleration and additional yaw moment references. This separates the high-level planning focus on path-following precision from the low-level actuation demands, directly addressing the computational complexity challenge inherent in 4WID-UGV systems—by avoiding simultaneous solving of all control objectives in a single optimization loop.
At the lower layer, a wheel-level torque allocation model is designed to optimize vehicle stability, load balancing, and energy efficiency. For actuator constraints (e.g., motor torque limits, tire-road friction boundaries), the hierarchical structure enforces constraint handling in two stages: the upper layer preconditions feasible acceleration/yaw commands within physical limits, while the lower layer refines torque distribution to respect individual in-wheel motor capabilities. This structure enables a decoupled and executable mapping from high-level planning to low-level actuation, thus enhancing both modularity and control precision. By isolating trajectory tracking (upper) and torque allocation (lower) logics, we mitigate the “one-size-fits-all” optimization shortfalls of centralized methods, specifically reducing computational redundancy and improving constraint adherence for 4WID-UGVs navigating complex paths.
The key contributions of this study are summarized as follows:
- (1)
- A decoupled hierarchical MPC framework is proposed, enabling separate optimization of trajectory accuracy and wheel-end actuation to ensure control modularity and task adaptability.
- (2)
- A multi-objective wheel-level optimization model is developed, integrating stability, actuation efficiency, and energy consumption to enhance control synergy.
- (3)
- Comprehensive simulations under representative S-shaped and circular path scenarios are conducted to evaluate the proposed strategy’s tracking accuracy, energy-saving performance, and robustness under complex driving conditions.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the vehicle dynamics modeling, including the coordinate transformation and the four-wheel independently driven vehicle dynamics formulation. Section 3 describes the model predictive control (MPC) method employed to achieve accurate trajectory tracking and robust control performance. Section 4 presents the adaptive energy-saving torque distribution strategy designed to optimize power efficiency while ensuring vehicle stability. Section 5 provides experimental evaluations of the proposed adaptive energy-saving control strategies under both S-shaped and circular road conditions. Finally, Section 6 concludes the paper and outlines future research directions. The overall flow chart is shown in Figure 1.
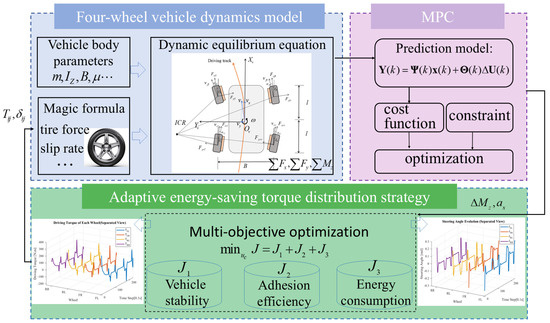
Figure 1.
Overall Flow Chart of MPC Hierarchical Control for Multi-objective Energy-Efficient Driving of UGVs.
2. Vehicle Dynamics Modeling
When investigating the motion characteristics of four-wheel independently driven in-wheel motor systems, the first and foremost step is to establish an appropriate coordinate transformation framework. This is essential for constructing a corresponding vehicle dynamics model, which can subsequently be formulated into a suitable state-space representation.
2.1. Coordinate Transformation
To characterize vehicle motion in three-dimensional space, two coordinate systems are defined: the vehicle body coordinate system and the inertial coordinate system. The body-fixed coordinate system is established at the vehicle’s center of mass, with the -axis pointing forward, to the left, and upward. This frame is directly tied to the vehicle’s dynamic states and is commonly used in tire force analysis and moment computations.
In contrast, the inertial coordinate system is fixed to the ground and represents the vehicle’s absolute motion, including displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Its axes are aligned with the global reference frame, providing an objective basis for kinematics and dynamics analysis.
To relate the vehicle’s body-frame velocities to the inertial frame, a coordinate transformation is performed using sequential Euler angle rotations. The longitudinal, lateral, and vertical velocities in the inertial frame are expressed as:
where , , and represent the yaw angle, pitch angle, and roll angle, respectively, while , , and denote the rotation matrices about the corresponding axes.
In this study, the vehicle model is assumed to operate in a two-dimensional plane, and the effects of suspension on the vehicle body are neglected. Therefore, the above transformation model can be further simplified, as illustrated in Figure 2.
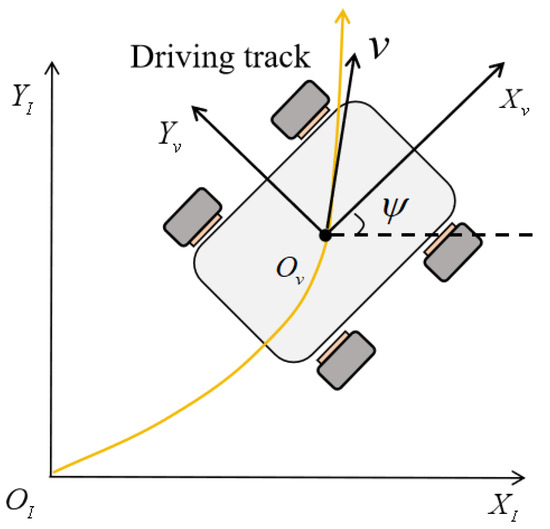
Figure 2.
Planar inertial coordinate system.
The simplified formulation is expressed as:
where and represent the longitudinal and lateral velocities in the inertial coordinate system, respectively. Similarly, and denote the longitudinal and lateral velocities in the vehicle body coordinate system. The parameter refers to the yaw angle, which defines the orientation of the vehicle body coordinate system’s -axis relative to the -axis of the inertial coordinate system.
2.2. Vehicle Dynamics Model
To capture the motion characteristics of a four-wheel independently driven unmanned ground platform during composite steering maneuvers, a seven-degree-of-freedom dynamics model is established, as illustrated in Figure 3. This model comprehensively considers lateral, longitudinal, and yaw motions, as well as the rotational dynamics of each wheel.
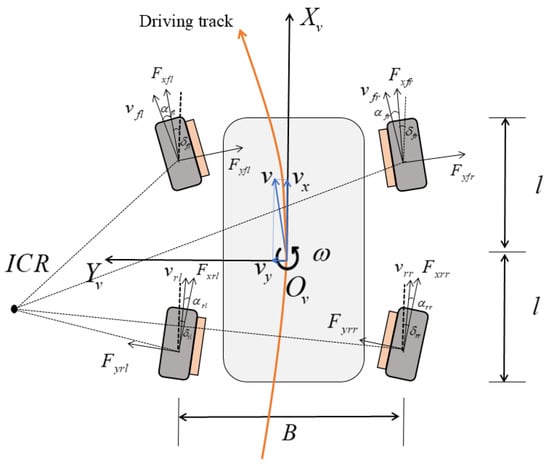
Figure 3.
Four-wheel independent steering vehicle dynamics model.
To focus on core trajectory tracking and torque allocation challenges in 4WID-UGVs, this study adopts a 2D plane assumption, simplifying the analysis by isolating lateral-longitudinal dynamics—critical for path-following and torque optimization. The exclusion of suspension effects is a deliberate simplification to prioritize computational feasibility in multi-objective optimization. While suspension dynamics can influence tire-road interaction and torque demands in real-world scenarios (especially during high-speed cornering or rough-road operations), integrating such complexities would significantly increase model dimensionality and computational burden.
The longitudinal motion equilibrium equation of the vehicle is expressed as follows:
The lateral motion equilibrium equation of the vehicle is expressed as follows:
The yaw motion equilibrium equation of the vehicle is expressed as follows:
The dynamic equilibrium equation for the wheels is expressed as follows:
where , , , and represent the front left, front right, rear left, and rear right wheels of the vehicle, respectively. denotes the driving torque applied to the wheel, refers to the longitudinal force acting on the wheel, and represents the vertical load on the wheel. is the wheel rotational speed, is the wheel radius, denotes the wheel’s rotational inertia, and is the rolling resistance coefficient. In this study, an unmanned ground vehicle is selected as the research subject, and its primary parameters are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Vehicle parameters.
To ensure the robustness of the MPC controller under extreme conditions, such as high-speed cornering, the “Magic Formula” tire model is employed to calculate the tire forces. This model utilizes a combination of trigonometric functions to fit experimental tire data, thereby obtaining a mathematical representation of the tire force [19]:
In the above formula, represent the front left, front right, rear left, and rear right wheels, respectively. denotes the longitudinal force of each wheel, while refers to the lateral force of each wheel. The parameters , , and are fitting coefficients for the longitudinal force formula, whereas , , and are fitting coefficients for the lateral force formula. These coefficients are obtained through curve fitting based on experimental tire test data and are used to adjust the formulas to match the actual force characteristics of different tires. In addition, represents the vertical load on the wheel, and denotes the longitudinal slip ratio of the tire. The lateral slip ratio is defined as follows:
where denotes the longitudinal velocity of each wheel hub, is the rolling radius of the wheel, and represents the angular velocity of each wheel. The longitudinal velocity of each wheel hub can be expressed as:
where and represent the longitudinal and lateral velocities of the vehicle’s center of mass, respectively. denotes the yaw angular velocity, and refers to the track width. The sideslip angle of each wheel can be expressed as:
Considering the axle load transfer caused by longitudinal and lateral accelerations during vehicle motion, the vertical load on each tire can be expressed as:
In the above expressions, , , , and represent the vertical loads on the front left, front right, rear left, and rear right wheels, respectively. denotes the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle, while represents the lateral acceleration. Additionally, is the height of the vehicle’s center of gravity above the ground.
In summary, the vehicle dynamics model can be simplified as follows:
3. Model Predictive Control Method
This section outlines the fundamental framework of Model Predictive Control (MPC), which involves linearizing and discretizing the nonlinear vehicle dynamics to construct a discrete-time state-space model. This transformation ensures compatibility with the MPC optimization process and provides the foundation for state prediction and constrained control input computation. Based on the established dynamics, the system’s state-space representation is formulated as follows:
The state variables are selected as: , and the control variables are defined as:
To enable model-based prediction, the above dynamic model is expanded using a Taylor series as follows:
where , and , .
Since the constructed dynamic model is inherently nonlinear, control methods designed based on this model usually result in lower computational efficiency compared to linear models. Therefore, to enhance the computational speed of the solution process, linearization is performed. Specifically, a Taylor series expansion is applied to the function , retaining only the first-order terms while omitting higher-order terms:
By defining: , , , the above expression can be rewritten in an incremental form:
To facilitate numerical computation, the newly derived state-space equation, which is continuous and locally linearized, must be discretized. Among common discretization techniques—such as forward Euler, backward Euler, and central difference methods—the forward Euler method is adopted in this study due to its simplicity and computational efficiency.
By applying forward Euler discretization to the above equation, the following formulation is obtained:
which can be rearranged as:
Thus, the discrete state-space model is obtained.
Building upon this discrete formulation, the prediction equation is constructed to describe the evolution of vehicle states over the prediction horizon. This equation forms the basis of the state-control prediction model used in the recursive optimization process of MPC. By iteratively updating the system’s future responses, it enables accurate forecasting and serves as a core constraint within the control optimization framework. Based on the above derivation, the discretized linearized model can be expressed as:
Define:
Then, the system state-space representation can be formulated as:
where , , . Here, is the output matrix, and represents the system output.
Based on the above prediction model, the next step is to formulate an optimization objective that enables effective vehicle motion control. The primary goal is to regulate the motion state of the platform by adjusting the longitudinal acceleration, and additional yaw moment, thereby ensuring precise trajectory tracking. Specifically, the control strategy aims to minimize lateral deviation and heading error during path following, allowing the unmanned ground platform to stably and accurately follow the desired trajectory. To this end, a composite lateral motion control cost function is constructed to quantitatively evaluate and optimize the tracking performance, as formulated by:
In this formulation, represents the tracking accuracy of the state variables, reflecting the system’s capability to follow the target trajectory. denotes the control increment, which reflects the smoothness and stability of the control actions. The term refers to the slack variable, which is introduced to relax the constraints when the optimization solver fails to find a feasible solution within the specified iteration step. The slack variable thus plays a crucial role in ensuring real-time feasibility and robustness by preventing infeasibility caused by overly stringent constraints. To simplify the optimization process, the control objective function is reformulated as a Quadratic Programming (QP) problem, which can be expressed as follows:
Here, denotes the terminal weight matrix of the system, is the state weighting matrix, and represents the control input weighting matrix. All weighting matrices , , and are defined as diagonal matrices. By adjusting the parameters of , , and , the penalty level for lateral and yaw errors in the control process can be flexibly modified to meet the desired control performance.
By solving the optimization problem defined by the objective function, the desired longitudinal acceleration, and additional yaw moment can be obtained. These control outputs are then sent to the underlying controller to achieve dynamic redistribution of the torques and steering angles of the four in-wheel motors and wheels, ensuring precise and stable path following performance.
4. Adaptive Energy-Saving Torque Distribution Strategy
The torque optimization and allocation controller aim to optimize the distribution of driving torques among the four wheels, thereby fulfilling the requirements for additional yaw moment generation and longitudinal force necessary for speed tracking. This approach not only ensures precise trajectory tracking but also maintains vehicle stability during dynamic maneuvers. This study transforms the adaptive control problem into a multi-objective optimization problem, whose key objectives include ensuring vehicle speed stability, maximizing the comprehensive utilization of tire forces, and minimizing energy consumption.
The weighting coefficients , , and in Equation (24) are dynamically adjusted based on real-time vehicle states to balance competing objectives:
where
- : Yaw angle error (deg), reflecting trajectory deviation;
- : Road friction coefficient, estimated via tire slip observer;
- : Longitudinal velocity (m/s);
- : Baseline weights calibrated as (0.40, 0.35, 0.25);
- : Safety threshold for low-friction surfaces;
- m/s: Vehicle’s maximum operational speed.
(1) Ensuring Vehicle Stability: It is essential that the four-wheel torque distribution satisfies the desired additional yaw moment as specified by the upper-level controller. This requirement can be formulated as the following cost function:
(2) Minimizing Tire Utilization Ratio: To describe the tire stability margin, the following tire utilization ratio is employed, which represents the ratio between the actual road adhesion and the maximum possible adhesion:
where represents the road adhesion coefficient, and denote the front-left, front-right, rear-left, and rear-right wheels, respectively. refers to the longitudinal force, denotes the lateral force, and indicates the vertical load.
(3) Energy Consumption: During the compound steering process, slip steering inevitably occurs, resulting in significant slip rates at the wheels. This leads to noticeable sliding between the wheels and the ground, where slip friction consumes substantial energy, thereby reducing the endurance capability of the unmanned platform.
Therefore, in the torque distribution strategy for the unmanned platform, it is essential not only to ensure steering stability but also to optimize wheel energy consumption.
By analyzing the friction surface within the tire-ground contact patch, it can be established that the slip energy consumption power is related to the relative slip velocity of the wheel and the longitudinal force. This relationship can be expressed as follows:
where represents the relative slip velocity of the wheel, which can be expressed as:
The objective function for steering energy efficiency is formulated by minimizing the sum of the squared slip power of each wheel, which can be expressed as:
where matrices and are defined as follows:
While meeting the requirements of additional yaw moment, differential driving force, and longitudinal force, the constraints of the maximum output torque of the in-wheel motors and road adhesion conditions should also be considered:
(1) Actuator Capability Constraints: The distribution of driving forces must comply with the physical limitations of the in-wheel motors. Specifically, the driving force of each wheel must be confined within its permissible output range to prevent actuator saturation or overload. This constraint can be mathematically expressed as:
(2) Dynamic Equilibrium Constraints: In addition to actuator limitations, the torque distribution scheme must also satisfy the vehicle’s dynamic equilibrium requirements. These include the constraints imposed by the tire-road contact forces, ensuring that the resultant longitudinal and lateral forces as well as the generated yaw moment align with the desired vehicle motion dynamics under various driving conditions.
Among them, represents the left and right wheel indexes defined as:
(3) Stability Envelope Constraints: To ensure the overall stability of the vehicle, the torque allocation must also satisfy the stability envelope constraints. These constraints restrict the resultant longitudinal and lateral tire forces within safe operational boundaries, preventing excessive tire utilization or loss of traction. This is particularly critical during high dynamic maneuvers or when multiple wheel failures occur, where maintaining stable yaw and lateral dynamics becomes challenging.
To clarify the physical meaning of Equation (35), the key variables are defined as follows: represents the vehicle’s side-slip angle, describing the angle between the center-of-mass velocity direction and the vehicle’s longitudinal axis (unit: degree, °), with larger values indicating higher sideslip and control-loss risks; is the dimensionless road adhesion coefficient, reflecting road-tire adhesion capacity (e.g., ~0.8–1.0 on dry asphalt, ~0.1 on icy/snowy roads) and determining the tire’s maximum adhesion boundary; is the gravitational acceleration, representing Earth’s gravitational influence; denotes the vehicle’s longitudinal speed along its longitudinal axis (unit: meter per second, m/s), a basic motion-state parameter; and is the turning radius (unit: meter, m), the distance from the instantaneous rotation center to the vehicle’s center of mass during a turn, determining the turn’s curvature.
5. Experimental Evaluation of Adaptive Energy-Saving Control Strategies
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed control strategy, experiments were conducted under various road conditions. These experiments aim to evaluate the control performance of the strategy in different driving scenarios.
5.1. Evaluation S-Shaped Road Conditions
This experiment investigates vehicle path tracking control based on a simplified vehicle model. A target trajectory composed of complex curves was predefined and represented in a two-dimensional plane using horizontal (X, in meters) and vertical (Y, in meters) coordinates. The trajectory features multiple turns and elevation changes, intended to replicate the complexity of real-world road conditions. A centerline was established as the benchmark reference path for tracking performance evaluation.
During the experiment, the test vehicle was commanded to travel along the target trajectory starting from the initial point at a desired speed of 12 m/s. The vehicle followed the trajectory based on control commands, with control inputs adjusted in real time according to position deviations. The final path tracking results are visualized in Figure 4.
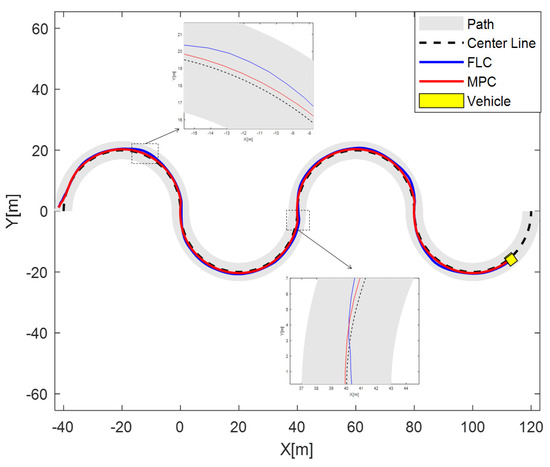
Figure 4.
Trajectory on S-shaped road.
Figure 4 illustrates the trajectory tracking performance of the Model Predictive Control (MPC) strategy and the Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) strategy on a complex S-shaped path. In the figure, the black dashed line represents the reference centerline, the red solid line shows the actual trajectory produced by the MPC controller, and the blue solid line depicts that of the FLC controller. The gray shaded area indicates the actual drivable path, and the yellow square marks the vehicle’s final position during the experiment.
The results demonstrate that the MPC-based controller effectively enables the vehicle to follow the reference path under complex curvature conditions. As observed in the zoomed-in views of Figure 4, the trajectory generated by the MPC controller remains smooth and closely aligned with the centerline in regions of constant curvature. In contrast, the FLC-generated trajectory shows larger deviations in these areas. Although slight deviations occur for MPC when curvature changes abruptly, the overall tracking accuracy remains within acceptable limits, while FLC has more significant deviations at such points, indicating that MPC is more capable of handling real-time path tracking tasks with reasonable robustness compared to FLC.
Notably, the MPC approach achieves a favorable balance between computational efficiency and control precision. Its model-based optimization framework allows for anticipatory behavior and constraint handling, which are essential for managing dynamic transitions along the S-shaped path. FLC, relying on fuzzy rules, lacks such anticipatory capabilities. These findings affirm the effectiveness of MPC in maintaining stability and trajectory fidelity, even under moderately complex road geometries, and highlight the advantages of MPC over FLC in this scenario.
Figure 5 presents the distribution of lateral and longitudinal tracking errors for both the Model Predictive Control (MPC) and Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) strategies during the trajectory tracking task. The orange-colored boxplots and scatter points represent the error distribution of MPC, while the blue ones correspond to FLC.
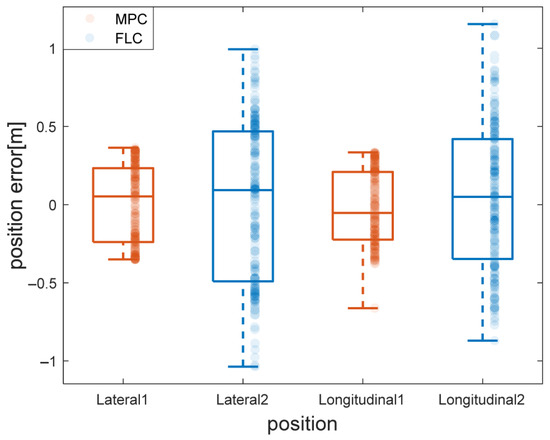
Figure 5.
Comparison of position error distributions between MPC and FLC during trajectory tracking on S-shaped road.
For MPC, the error distributions reveal that the majority of its lateral and longitudinal errors remain within a tolerable range, with most values concentrated within ±0.2 m. While a limited number of outliers extends up to ±0.4 m, these deviations are infrequent and occur primarily in regions with abrupt curvature changes or transient dynamics. In contrast, FLC shows a wider spread of errors. Its error values not only have a larger range (extending close to ±1 m in some cases) but also a more dispersed distribution, indicating less consistency in tracking accuracy compared to MPC.
The scatter plot illustrates that MPC maintains a relatively consistent control performance, with a dense cluster of error points near the zero-error line and moderate dispersion across the entire dataset. For FLC, the error points are more scattered, reflecting greater variability in its tracking performance. This indicates that the MPC controller achieves more satisfactory tracking accuracy and stability under complex path conditions than FLC.
Overall, these results confirm that conventional MPC offers a robust and predictable control solution for trajectory tracking, balancing real-time optimization and constraint satisfaction, and outperforms FLC in terms of tracking error consistency. Detailed quantitative metrics are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparison of tracking position errors under different control algorithms during trajectory tracking on S-shaped road.
Table 2 presents the statistical characteristics of trajectory tracking errors for both the Model Predictive Control (MPC) and Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) strategies, with detailed analyses in lateral and longitudinal directions. Results reveal distinct performance differences, highlighting MPC’s superiority in complex trajectory scenarios.
For MPC, in terms of lateral errors, the average error is 0.2248 m, RMSE (Var) is 0.0610 m, and max/min errors are 0.3635 m/−0.3509 m, showing controlled, non-divergent lateral tracking and reflecting its ability to handle curvature transitions while preserving path fidelity. In the longitudinal direction, the average error is 0.1999 m, RMSE (Var) is 0.0500 m, confirming stable longitudinal control robust to disturbances and modeling imperfections.
For FLC, lateral errors have a significantly larger average (0.4411 m) and RMSE (0.2511 m), with max/min errors (0.9930 m/−1.1037 m) indicating wider divergence and weaker lateral stability under variable curvatures. Longitudinal errors show notably higher average (0.3848 m) and RMSE (0.2072 m), with larger deviations (max/min errors 1.1543 m/−0.8703 m) reflecting limited robustness to external factors.
Overall, statistical metrics confirm MPC provides a stable, accurate control framework—offering a better trade-off between prediction accuracy and real-time feasibility than FLC. This makes MPC a more practical solution for autonomous vehicle control in structured, moderately complex environments.
Figure 6 illustrates the variation of the four-wheel steering angles during the S-shaped path tracking process when using the MPC control strategy. In the figure, represents the steering angles of the front left, front right, rear left, and rear right wheels, respectively.
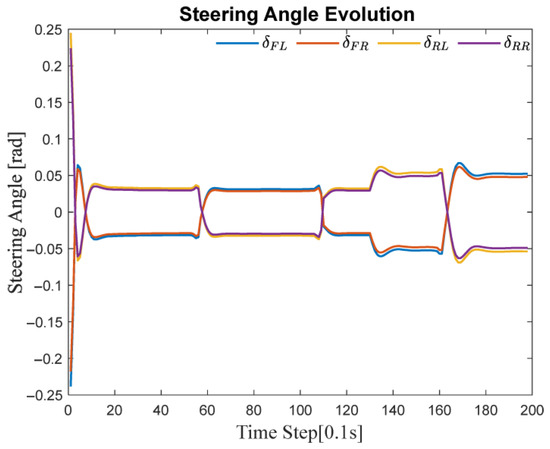
Figure 6.
Steering angle evolution during trajectory tracking on S-shaped road.
It can be observed that all four wheels exhibit coordinated variation characteristics when following a path with continuously changing curvature. Notably, during sections where the path curvature changes significantly, there are clear differences in both phase and amplitude between the front and rear wheels. This reflects the rapid response capability of the four-wheel independent steering control strategy in adapting to trajectory changes.
These results confirm that the MPC control strategy can dynamically and rapidly adjust the steering angles of all four wheels in response to real-time changes in the path. This enhances the vehicle’s maneuverability and stability during navigation on complex paths.
Figure 7 presents the dynamic variation curves of the four in-wheel motor driving forces during the same path tracking process. In road sections characterized by continuous curvature changes, multiple dynamic reallocations of driving force distribution occurred to ensure both vehicle stability and path tracking accuracy.
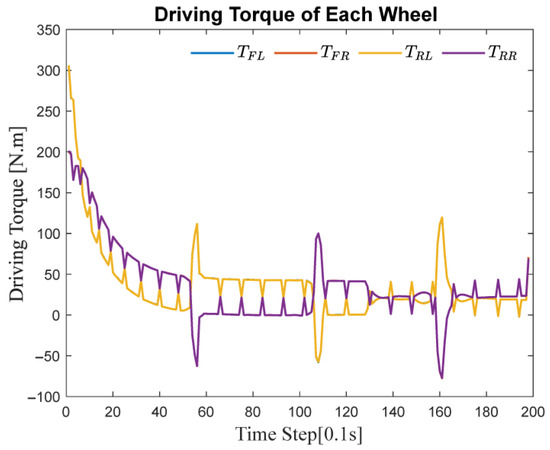
Figure 7.
Driving torque of each wheel during trajectory tracking on S-shaped road.
Specifically, frequent adjustments in the magnitude of driving forces for each wheel were observed, and the rear wheels even exhibited brief instances of force reversal. This phenomenon arises because, in high-curvature sections, the vehicle requires greater lateral force to maintain cornering motion. The control strategy addresses this need by adaptively adjusting the driving forces of each wheel, thereby altering the vehicle’s longitudinal and lateral dynamics to meet the demands of turning.
Importantly, these dynamic changes in driving force distribution are not random but are adaptively regulated based on the vehicle’s real-time state and path information. Such adaptive adjustment ensures that the vehicle maintains excellent driving performance under varying curvature and operating conditions, thereby preventing issues such as slipping or loss of control and ensuring safe and accurate trajectory tracking.
Figure 8 presents the torque-speed efficiency map of the in-wheel motors under an S-curve trajectory, with overlaid working points of the four independently driven wheels. The efficiency contour ranges from 0.55 to 0.95, with the high-efficiency zone (η ≥ 0.85) concentrated in the region of 300–600 rpm and 100–250 N·m. This area remains consistent with that observed in prior scenarios, providing a benchmark for evaluating energy performance.
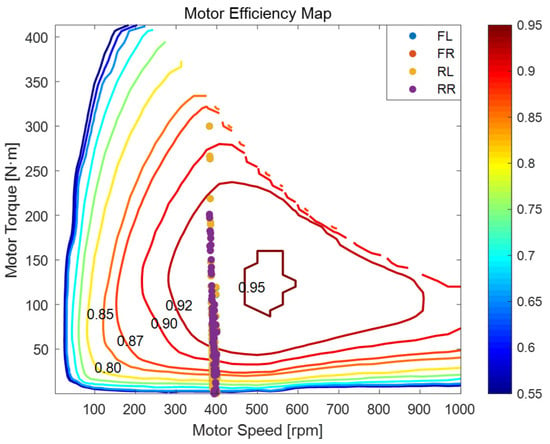
Figure 8.
Motor Efficiency Map of MPC during trajectory tracking on S-shaped road.
Figure 9 shows the Motor Efficiency Map of FLC under the same S-curve trajectory for comparison. When contrasting Figure 8 (MPC) and Figure 9 (FLC), the MPC-related working points in Figure 8 exhibit a more favorable distribution.
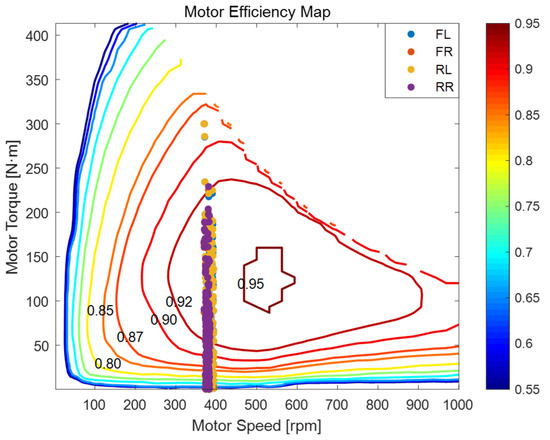
Figure 9.
Motor Efficiency Map of FLC during trajectory tracking on S-shaped road.
The operating points of the four motors—front-left (FL), front-right (FR), rear-left (RL), and rear-right (RR)—in Figure 8 are distinguished by different color markers and exhibit notable distribution characteristics. All four sets of points are generally clustered around 400 rpm and 100–180 N·m, but subtle differences reveal the influence of wheel position and motion dynamics. In Figure 9, the working points of FLC are more scattered, especially in the torque distribution, indicating less optimal torque allocation.
The FL and FR motors in Figure 8 show a broader spread in torque compared to the rear motors, reflecting their active role in path correction during lateral oscillations of the S-curve. In particular, the FR motor demonstrates a slight upward shift in torque values during sharp transitions, suggesting compensatory action for tighter inner curvature. Meanwhile, the RL and RR motors maintain a tighter distribution around the high-efficiency centroid, indicating a more consistent propulsion role with less variation in driving load. In Figure 9, the FLC’s motor torque distribution is less organized, with the front motors not showing such a clear and effective role in path correction, and the rear motors having more scattered operating points, implying less stable propulsion.
Despite the inherent demands of S-shaped navigation, most working points in Figure 8 remain within or near the high-efficiency envelope. This reflects the MPC controller’s ability to dynamically allocate torque in real time while minimizing energy losses across all four motors. In Figure 9, more of FLC’s working points are outside the high-efficiency envelope, indicating higher energy losses. The close concentration of the rear wheel data in Figure 8 further implies their critical role in ensuring stability and maintaining longitudinal momentum during alternating turns, which is less evident in Figure 9.
In summary, the motor behavior under the S-curve trajectory in Figure 8 showcases differentiated wheel roles governed by their position and load, while consistently upholding efficiency-aware control. This reinforces the adaptability and energy effectiveness of the MPC control strategy under complex dynamic conditions, outperforming FLC as seen in Figure 9. Detailed quantitative metrics are summarized in Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 3.
Statistical indicators of the efficiency of each hub motor of MPC during trajectory tracking on S-shaped road.

Table 4.
Statistical indicators of the efficiency of each hub motor of FLC during trajectory tracking on S-shaped road.
Table 3 reports the statistical indicators of motor efficiency for each of the four independently driven hub motors—namely, the front-left (FL), rear-left (RL), left-rear (LR), and right-rear (RR) motors—during the circular trajectory tracking scenario under the Model Predictive Control (MPC) strategy. Table 4 presents the corresponding data for the Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) strategy. The efficiency metrics include the maximum, minimum, mean, and variance (Var) values, offering a comprehensive overview of each motor’s operational performance under continuous cornering conditions for both control methods.
All motors under MPC achieve a peak efficiency close to 94% (FL and LR: 0.9401; RL and RR: 0.9387), indicating that the MPC-based control strategy consistently operates the motors within their high-efficiency region. Among them, the rear-left (RL) and rear-right (RR) motors exhibit the highest mean efficiencies, reaching 0.8816 and 0.8815, respectively, with variances of 0.0048, suggesting stable and energy-optimal torque control in rear-wheel modules.
The front-left (FL) and left-rear (LR) motors show slightly lower mean efficiencies (0.8630 and 0.8628), though still within a high-efficiency range. Their variances (0.0046 and 0.0047) are also relatively low, indicating limited fluctuation in their operating states. Overall, all motors maintain minimum efficiencies above 47% (FL: 0.5068; RL: 0.4724; LR: 0.4933; RR: 0.4686), confirming the robustness of the MPC-based allocation strategy in sustaining efficient energy usage across all wheels throughout the circular path.
Table 4 shows FLC motor efficiency stats. Peak efficiencies are slightly lower than MPC. Mean efficiencies are close, but variances (e.g., RL, RR) are higher, meaning more operating state fluctuations. Minimum efficiencies are acceptable but differ from MPC, reflecting FLC’s distinct efficiency management.
In comparison, the MPC strategy demonstrates superior performance in terms of maintaining higher peak efficiencies, more stable operating states (lower variances in most cases), and consistent high-efficiency operation across all motors, which is crucial for energy-efficient trajectory tracking.
While the statistical efficiency metrics offer insight into localized energy performance at the actuator level, a more comprehensive evaluation of the system-wide energy consumption is necessary to assess the overall energy-saving potential of the vehicle under various driving conditions.
To evaluate the energy efficiency of the proposed control strategy, the state of charge (SOC) of the power battery is monitored under different driving conditions. In this study, SOC is estimated using an energy-based method, where the consumed electrical energy of the motors is accumulated and normalized by the total battery capacity. The SOC at time is calculated as:
where is the initial state of charge, denotes the total energy consumed by the motors up to time , and is the nominal battery capacity.
Formula (38) calculates the total power of the multi-motor system. It sums up each motor’s power , which is derived from motor torque , speed , and drive efficiency considering speed-torque-loss relationships.
This approach offers a straightforward and effective way to track energy consumption in simulation environments. Based on this method, the SOC trajectory under the S-shaped route is recorded as shown in Figure 4. The battery’s nominal capacity is 50 and its initial capacity is 80%.
Figure 10 shows MPC’s SOC curve for the S-shaped path. It declines smoothly, with minor inflection points at steps 60, 120, 160 (linked to curvature changes). These small fluctuations reflect MPC’s responsiveness to dynamic driving, yet overall SOC drop stays minimal—proving MPC’s effective torque allocation for energy efficiency.
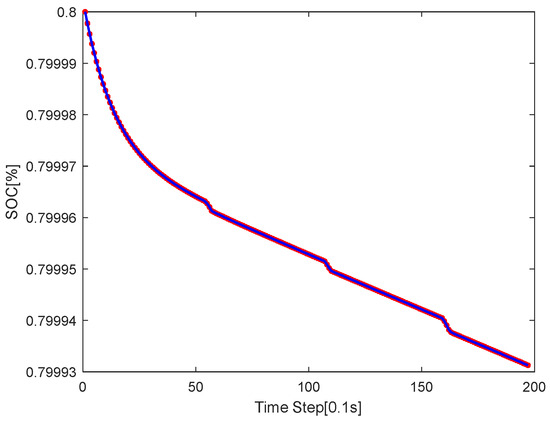
Figure 10.
The SOC curve graph of the S-shaped road of MPC.
Figure 11 presents FLC’s SOC curve on the same path. Unlike MPC’s stability, FLC’s curve fluctuates far more–with larger, frequent drops and rises. This shows FLC struggles to optimize torque in real-time for path changes, causing inconsistent energy use.
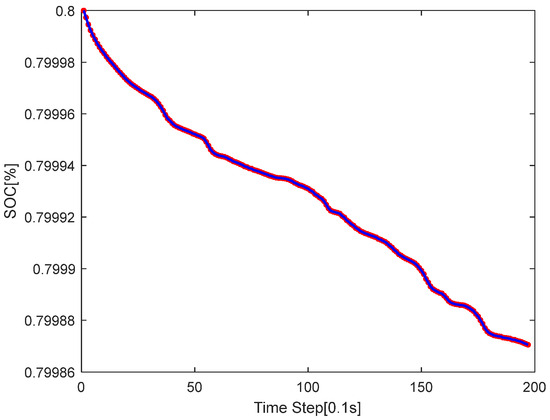
Figure 11.
The SOC curve graph of the S-shaped road of FLC.
In short, MPC outperforms FLC in energy management for S-shaped trajectories. MPC keeps SOC stable via smart torque allocation, while FLC’s erratic SOC shows weaker adaptability to dynamic paths. This highlights MPC’s edge in balancing performance and energy efficiency for complex driving scenarios.
5.2. Evaluation Circular Path Conditions
To further validate the control strategy’s adaptability across different road environments, a circular path with multiple curvatures was selected for additional testing. During the experiment, the test vehicle was again commanded to follow the trajectory from the starting point at a desired speed of 12 m/s, adjusting control inputs in real time according to position deviations. The path tracking results are visualized in Figure 10.
Figure 12 illustrates the trajectory tracking performance of both the Model Predictive Control (MPC) and Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) strategies on a complex closed-loop path. In the figure, the black dashed line represents the reference centerline, the red solid line indicates the actual trajectory generated by the MPC controller, and the blue solid line shows that of the FLC controller. The gray shaded area denotes the drivable road region, and the yellow square marks the vehicle’s final position in the experiment.
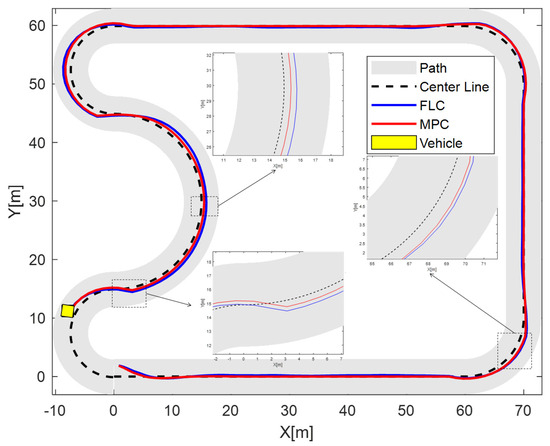
Figure 12.
Trajectory tracking on circular road.
This path features multiple curvature changes and continuous steering demands, providing a challenging scenario for path tracking. Throughout the test, the MPC controller enabled the vehicle to follow the reference trajectory with high consistency. In contrast, the FLC-generated trajectory shows larger deviations in some curved segments. Lateral tracking errors of MPC remained within a more acceptable and narrower range compared to FLC, demonstrating MPC’s stronger robustness and practical effectiveness.
As shown in the zoomed-in views, the MPC-generated trajectory maintains minimal deviation from the centerline during straight-line segments and remains smooth and well-aligned with the reference path even in regions with abrupt or continuous curvature variations. However, the FLC trajectory has more obvious deviations in these curved areas. These results highlight the MPC controller’s ability to handle varying path geometries through predictive optimization, while balancing real-time feasibility and control accuracy, outperforming FLC in complex path tracking.
In summary, MPC achieves more reliable vehicle guidance along complex routes compared to FLC, making it a more suitable and practical solution for real-time autonomous path tracking tasks in structured driving environments.
Figure 13 presents the distribution of lateral and longitudinal tracking errors for both the Model Predictive Control (MPC) and Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) strategies during the trajectory tracking task. The box plots, with MPC in orange and FLC in blue, illustrate their statistical performance differences.
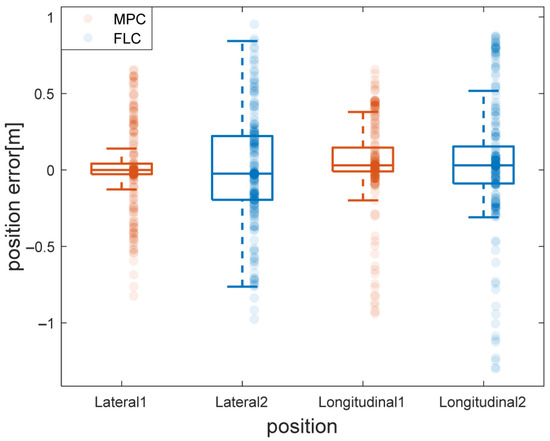
Figure 13.
Comparison of position error distributions between MPC and FLC during trajectory tracking on circular road.
For MPC, most tracking errors concentrate within ±0.2 m, with outliers toward ±0.6 m—showing consistent control, though rare deviations happen in dynamic/curved segments. Its scatter plot has a moderately concentrated point cloud around the zero-error line, with bounded dispersion, confirming MPC’s ability to manage accuracy under varying conditions.
For FLC, error distributions are wider: lateral/longitudinal errors spread further (e.g., Lateral2 outliers near ±1 m). Its scatter points are more dispersed, reflecting less stable tracking.
These findings affirm MPC’s superiority in maintaining trajectory stability over FLC, especially in structured environments needing real-time feasibility and predictable error behavior. Detailed quantitative results are in Table 5.

Table 5.
Comparison of tracking position errors under different control algorithms during trajectory tracking on circular road.
Table 5 presents the statistical results of lateral and longitudinal tracking errors for both Model Predictive Control (MPC) and Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) strategies during the trajectory tracking task, enabling a direct performance comparison.
For MPC’s lateral tracking, an average error of 0.1666 m and an RMS error of 0.0697 m indicate stable control across path segments. Max/min lateral errors of 0.6559 m/−0.8239 m show path adherence despite complex curvatures, though occasional deviations occur. In the longitudinal direction, an average error of 0.1835 m (RMS: 0.0847 m) confirms consistent performance, with the 0.6560 m max error in high-curvature/acceleration regions highlighting potential for model refinement within tolerable bounds.
For FLC, lateral tracking has a higher average error (0.2683 m) and RMS (0.1254 m), with max/min errors of 0.9532 m/−0.9758 m, indicating larger, more frequent deviations. Longitudinally, an average error of 0.2657 m and RMS of 0.1680 m, plus a max error of 0.8781 m (min: −1.3013 m), reflect less stable control.
These results validate MPC’s superiority, as it delivers smaller errors, tighter variance, and more consistent tracking than FLC. MPC balances accuracy, efficiency, and real-time applicability, making it reliable for autonomous control in structured/dynamic environments, while FLC’s larger errors and fluctuations expose limitations in handling complex path dynamics.
Figure 14 shows the dynamic variations of the steering angles for each wheel during circular path tracking using the MPC control strategy. In the figure, denotes the steering angle responses of the front left, front right, rear left, and rear right wheels, respectively.
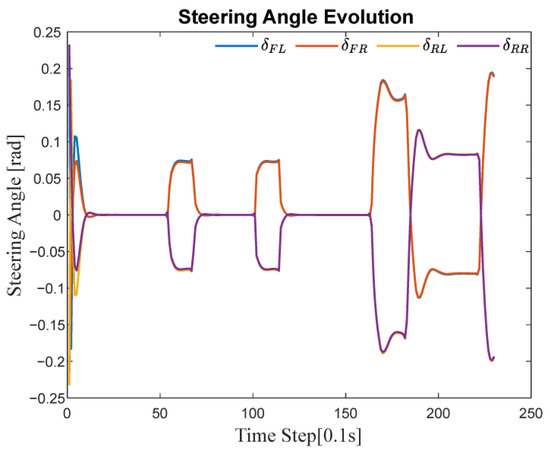
Figure 14.
Steering angle evolution during trajectory tracking on circular road.
As observed from the time-domain curves, all four wheels exhibit clear coordination in their steering angle variations. During the path tracking process, the steering actions of the wheels are not independent but instead work in concert. This coordinated behavior ensures vehicle stability during continuous turning maneuvers and prevents trajectory deviations or handling difficulties caused by inconsistent wheel steering angles.
In sections where the path curvature changes significantly, there are notable differences in phase and amplitude between the front and rear wheel steering angles. This highlights the rapid response capability of the four-wheel independent steering control strategy in adapting to trajectory changes.
These results confirm that the MPC control strategy enables real-time and rapid adjustments of the steering angles for all four wheels according to changes in the path. This enhances both maneuverability and stability of the vehicle when driving on complex trajectories.
Figure 15 illustrates the time-domain variations of the driving torques for all four wheels during the closed-loop path tracking process. In the figure, denotes the driving torques of the four in-wheel motors, respectively.
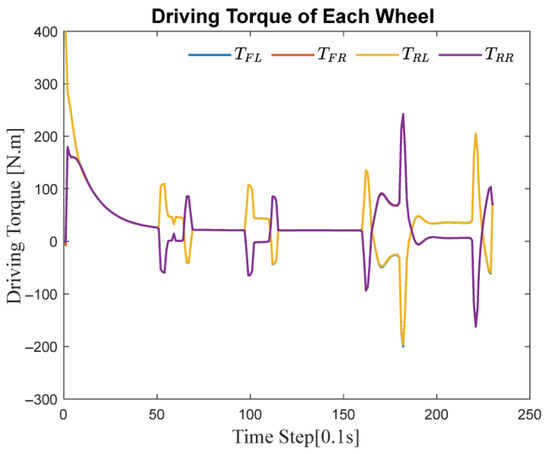
Figure 15.
Driving torque of each wheel during trajectory tracking on circular road.
As shown by the curves, the driving forces of each wheel are rapidly adjusted at locations where sudden changes in path curvature occur. In certain time intervals, some wheels even exhibit reverse torque input, which demonstrates the system’s excellent dynamic torque reconstruction capability to meet the varying traction demands under different operating conditions.
In particular, during segments with continuous curves, the distribution of driving forces among the four wheels becomes distinctly asymmetric. This fully reflects the control strategy’s flexibility in force distribution.
It is important to note that the dynamic changes in driving torque are not random, but rather adaptively adjusted based on the vehicle’s real-time state and path information. Such adaptive regulation allows the vehicle to maintain optimal driving performance under various curvatures and operating conditions, effectively preventing issues such as skidding or loss of control and ensuring safe and accurate trajectory tracking.
Figure 16 shows MPC’s in-wheel motor torque-speed efficiency distribution during circular tracking. Its background contours mark efficiency (warmer = higher), with the high-efficiency zone (η ≥ 0.85) in 100–250 N·m torque and 300–600 rpm speed. Color-coded markers (FL, FR, RL, RR wheels) cluster densely at 400–450 rpm and 100–180 N·m, staying in the high-efficiency zone, reflecting circular driving steady-state.
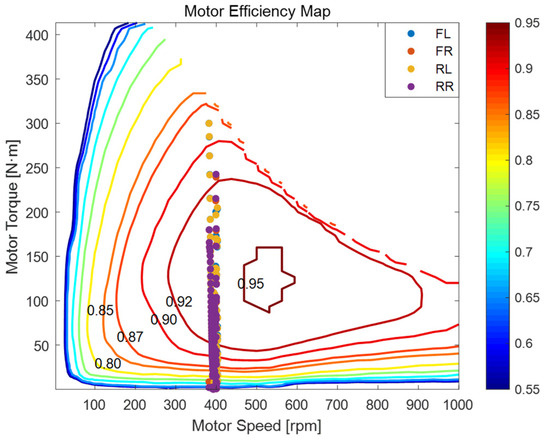
Figure 16.
Motor Efficiency Map of MPC during trajectory tracking on circular road.
These points’ positions tie to wheel roles: outer front FL needs more torque for yaw moment; inner front FR needs less due to small turning radius. Rear RL/RR show symmetric, slightly different behavior for torque balance and efficiency.
Figure 17 (FLC) has a similar high-efficiency zone, but its wheel operating points are more scattered, some in lower-efficiency areas—FLC struggles to coordinate torque for optimal motor operation.
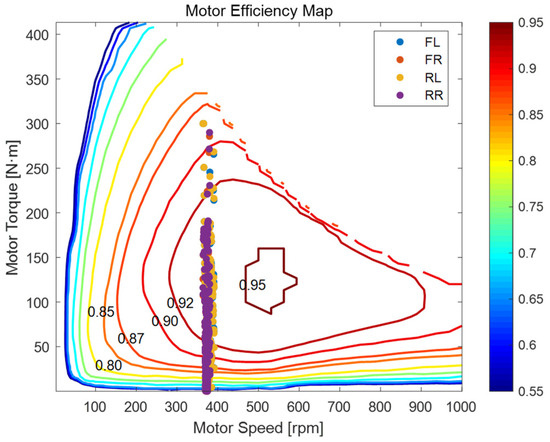
Figure 17.
Motor Efficiency Map of FLC during trajectory tracking on circular road.
Overall, MPC better coordinates torque, keeping motors in optimal zones for energy efficiency and stability in curved paths, outperforming FLC. Stats are in Table 6 and Table 7.

Table 6.
Statistical indicators of the efficiency of each hub motor of MPC during trajectory tracking on circular road.

Table 7.
Statistical indicators of the efficiency of each hub motor of FLC during trajectory tracking on circular road.
Table 6 reports the statistical indicators of motor efficiency for each of the four independently driven hub motors—front-left (FL), rear-left (RL), left-rear (LR), and right-rear (RR)—during the circular trajectory tracking scenario, covering both MPC and FLC strategies. The metrics (max, min, mean, variance) detail each motor’s performance.
For MPC: All motors hit ~94.1% peak efficiency, showing the strategy keeps them in the high-efficiency region. FL and LR have the highest average efficiencies (0.8847, 0.8845) and minimal variance (0.0016), meaning stable, efficient operation. RL and RR have lower mean efficiencies (0.8525, 0.8515) and larger variances (0.0077, 0.0082), hinting at more state fluctuations—possibly from asymmetric loads or lateral forces in cornering. Still, all motors stay above 70% efficiency at minimum, proving energy robustness.
For FLC: Peak efficiencies (FL: 0.9383; RL: 0.9367; LR: 0.9383; RR: 0.9367) are lower than MPC’s ~94.1%. Mean efficiencies (FL: 0.8617; RL: 0.8470; LR: 0.8625; RR: 0.8466) are also lower, and variances (FL: 0.0024; RL: 0.0110; LR: 0.0023; RR: 0.0111) are larger in some cases (RL, RR), showing less stable operation. Minimum efficiencies (FL: 0.5720; RL: 0.4860; LR: 0.5874; RR: 0.4686) are notably lower than MPC’s, reflecting weaker energy robustness.
In comparison, MPC outperforms FLC in maintaining higher, more stable motor efficiencies during circular tracking—showing better energy management and robustness.
While the statistical efficiency metrics offer insight into localized energy performance at the actuator level, a more comprehensive evaluation of the system-wide energy consumption is necessary to assess the overall energy-saving potential of the vehicle under various driving conditions. The SOC trajectory under the circular route obtained based on the calculation method of formula (35) is shown in Figure 18.
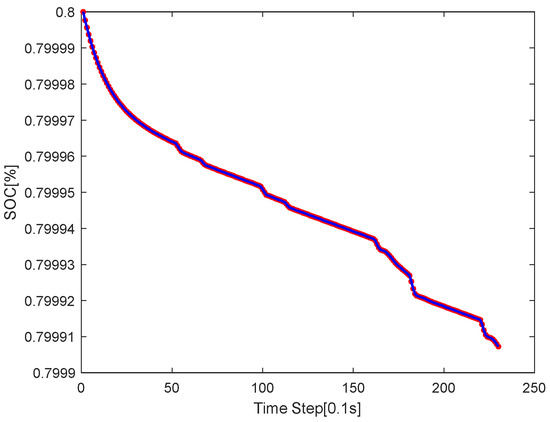
Figure 18.
The SOC curve graph of the circular road of MPC.
Figure 18 illustrates the evolution of the battery’s state of charge (SOC) as the vehicle follows the circular trajectory. The curve shows a smooth and gradual downward trend, indicating continuous energy consumption throughout the maneuver. The consistency of the SOC gradient reflects a stable power demand pattern, which is characteristic of the uniform curvature and constant-speed nature of circular driving.
Several minor fluctuations are observed at specific time steps (e.g., around 80, 160, and 210), likely corresponding to dynamic adjustments in motor torque due to lateral load redistribution or minor control oscillations. These variations are less pronounced than those observed in the S-shaped path, suggesting that energy consumption under the circular trajectory is more stable and predictable.
Figure 19 presents FLC’s SOC curve on the same path. Unlike MPC’s stability, FLC’s curve has larger, more frequent fluctuations—showing weaker real-time torque optimization. This leads to inconsistent energy use, highlighting FLC’s struggle to match MPC’s efficiency in circular trajectories.
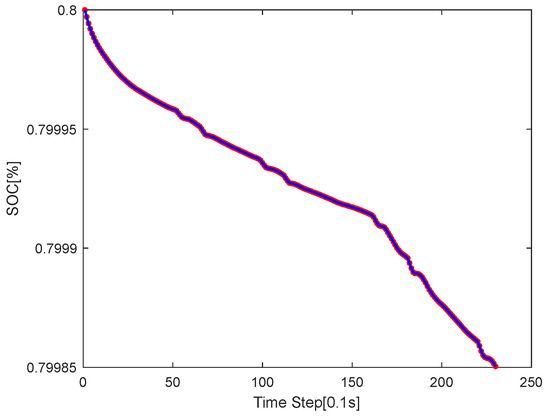
Figure 19.
The SOC curve graph of the circular road of FLC.
Overall, the SOC drops from 0.8 to approximately 0.79981 over the simulation period, demonstrating the energy efficiency of the proposed control strategy under continuous cornering conditions. The relatively small decrease in SOC further confirms the effectiveness of the torque allocation mechanism in minimizing energy consumption during steady-state maneuvers.
In summary, the MPC control strategy enables real-time optimization of driving torque allocation in response to complex driving conditions. This fully leverages the advantages of the four in-wheel motor drive system, enhances overall vehicle performance, and provides a reliable power guarantee for traversing complex paths.
6. Conclusions
This study proposed a hierarchical model predictive control framework for four-wheel independently driven unmanned ground vehicles (4WID-UGVs), aiming to achieve cooperative optimization between energy efficiency and dynamic stability. The upper-level controller ensures accurate trajectory tracking by solving for the optimal longitudinal acceleration and additional yaw moment, while the lower-level controller implements a multi-objective torque allocation strategy that balances energy consumption, wheel utilization, and vehicle stability. Simulation results under S-shaped and circular path scenarios demonstrate that the proposed strategy effectively maintains tracking errors within approximately 0.2 m and achieves an average motor efficiency exceeding 85%, verifying both the precision and energy-saving capability of the method.
Future research will focus on enhancing the proposed framework’s adaptability to real-world uncertainties and fault scenarios, such as varying terrain conditions and partial actuator failures. In addition, efforts will be made to integrate data-driven learning modules—such as Bayesian predictors or reinforcement learning agents—into the control loop, thereby enabling more robust decision-making and adaptive fault tolerance. Experimental validation on a physical prototype platform will also be pursued to further verify the practical applicability and scalability of the proposed control strategy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, validation, and methodology, Y.Z.; methodology and writing—original draft preparation, J.M.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.M., C.G., H.W. and L.W.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52402522) and the Fundamental Research Program of Shanxi Province (Grant No. 202403011211003). This research was also funded by the Technology Innovation Leading Talent Team for Special Unmanned Systems and Intelligent Equipment 202204051002001.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this analysis are publicly available and access is provided in the text.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Hao, C.; Weichao, Z.; Guodong, Y.; Haoxuan, D. Eco-driving control strategy of connected electric vehicle at signalized intersection. J. Southeast Univ./Dongnan Daxue Xuebao 2021, 51, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhini, F.; Talj, R.; Doumiati, M. Driving towards energy efficiency: A novel torque allocation strategy for in-wheel electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 26th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Bilbao, Spain, 24–28 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Baras, N.; Dasygenis, M. UGV Coverage Path Planning: An Energy-Efficient Approach through Turn Reduction. Electronics 2023, 12, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Liang, S.; Chen, J.; Gao, X. A multi-objective optimal torque distribution strategy for four in-wheel-motor drive electric vehicles. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 64627–64640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Tao, G.; Zang, Z.; Dong, H.; Wang, B.; Gong, J. Isolating trajectory tracking from motion control: A model predictive control and robust control framework for unmanned ground vehicles. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, N.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, K.; Xu, H. Coordinated optimal control of AFS and DYC for four-wheel independent drive electric vehicles based on MAS model. Sensors 2023, 23, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, M.; Chen, G.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Y. A hierarchical energy efficiency optimization control strategy for distributed drive electric vehicles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part D J. Automob. Eng. 2019, 223, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhuang, W.; Zhong, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Tan, C. Integrated energy-oriented lateral stability control of a four-wheel-independent-drive electric vehicle. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2019, 62, 2170–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R.; Sarhadi, P.; Paykani, A.; Refaat, S.S.; Asef, P. Optimal Torque Allocation for All-Wheel-Drive Electric Vehicles Using a Reinforcement Learning Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2024 13th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 11–14 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, H.; Jia, F.; Liu, Z. Multi-objective optimal control allocation for an over-actuated electric vehicle. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 4824–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, F.; Bernardino, J.; Durães, J.; Cunha, J. A Survey on Sensor Failures in Autonomous Vehicles: Challenges and Solutions. Sensors 2024, 24, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Jie, H.; Hong, W. Nonlinear model predictive path tracking control for autonomous vehicles based on orthogonal collocation method. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weißmann, A.; Görges, D.; Lin, X. Energy-optimal adaptive cruise control combining model predictive control and dynamic programming. Control. Eng. Pract. 2018, 72, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, P.; Borrelli, F.; Asgari, J.; Tseng, H.E.; Hrovat, D. Predictive active steering control for autonomous vehicle systems. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2007, 15, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Yim, S. Model predictive control-based integrated path tracking and velocity control for autonomous vehicle with four-wheel independent steering and driving. Electronics 2021, 10, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Kim, J.; Jung, J.-W. Improved model predictive control by robust prediction and stability-constrained finite states for three-phase inverters with an output $ LC $ filter. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 12673–12685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Yang, M. Hierarchical control of differential steering for four-in-wheel-motor electric vehicle. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Park, G.; Sankar, G.S.; Nam, K.; Choi, S.B. Model predictive control framework for improving vehicle cornering performance using handling characteristics. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 3014–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Feng, J.; Fang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yin, G.; Mao, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, F. An energy-oriented torque-vector control framework for distributed drive electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 9, 4014–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grymin, D.J.; Neas, C.B.; Farhood, M. A hierarchical approach for primitive-based motion planning and control of autonomous vehicles. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2014, 62, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, G.; Ren, Y.; Wang, F.; Fang, R.; Li, A. Hierarchical Control for Distributed Drive Electric Vehicles Considering Handling Stability and Energy Efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Automated Vehicle Validation Conference (IAVVC), Austin, TX, USA, 16–18 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, C.; Cheng, S.; Luan, Z. Hierarchical deep reinforcement learning based multi-agent game control for energy consumption and traffic efficiency improving of autonomous vehicles. Energy 2025, 323, 135669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).