1. Introduction
Power systems in many countries are undergoing significant structural and technological transformations in response to the complex challenges of the modern world, driven by both environmental protection requirements and energy security concerns. This transition encompasses the modernization of existing generation assets and the development of new technologies for electricity generation, transmission, storage, and management. In many cases, these changes span the entire value chain of the energy sector—from generation, through distribution, to end use. A key driver of this process is the growing pressure of climate policy, aimed at mitigating the adverse effects of climate change and reducing the environmental impact of energy-related activities. In recent years, increasing emphasis has been placed on sustainable development, integrating economic, social, and environmental objectives. Within this framework, the urgent need to radically reduce greenhouse gas emissions—particularly carbon dioxide (CO
2), identified by scientific research as the main anthropogenic contributor to global warming—has become especially critical [
1,
2].
CO2 emissions from the power sector—particularly from conventional coal- and gas-fired power plants—constitute a significant share of total global greenhouse gas emissions. Reducing these emissions is therefore essential to meeting the objectives of the Paris Agreement and other international climate commitments. In response, many countries, along with international and regional organizations, are implementing comprehensive strategies to decarbonize the energy sector. These strategies encompass a broad spectrum of measures, ranging from support mechanisms for renewable energy sources (RES) and the development of energy storage technologies and demand-side management systems to the electrification of the transport and industrial sectors.
The technological transformation of the energy sector entails a gradual transition away from fossil fuels toward cleaner, more sustainable energy sources. Priority is given to renewables such as solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass energy, which have substantially lower life-cycle emissions. Many countries are pursuing intensive legislative and investment initiatives to increase the share of renewable energy sources (RES) in their national energy mixes. Combined with the development of modern smart grids, the digitization of energy management systems, and advances in energy efficiency, these measures are establishing the foundation for a future-oriented, low-carbon energy economy. Within this transition, particular emphasis is placed on enhancing the efficiency of energy conversion in conventional thermal power plants, reducing overall energy consumption, and increasing the share of renewable sources in the energy balance [
3].
In response to the growing demand for higher energy efficiency and reduced greenhouse gas emissions, energy generation technologies based on modern technical and material solutions are undergoing intensive development. Of particular importance here are steam power plants equipped with turbines operating at supercritical and ultra-supercritical parameters [
4,
5], which enable a significant increase in the efficiency of the Rankine cycle compared to conventional installations. Operating under supercritical (i.e., above 22.1 MPa and 374.1 °C) and supercritical conditions requires the use of advanced corrosion- and creep-resistant materials, as well as modern methods of designing and operating thermal systems [
5,
6,
7].
At the same time, gas–steam systems, also known as combined cycle systems, are developing rapidly. These combine the Brayton (gas) cycle with the Rankine (steam) cycle [
8]. In such configurations, the exhaust gases from a gas turbine are used to generate steam, which then drives a steam turbine. This allows for the recovery of a substantial portion of heat that would otherwise be lost in a single-cycle system, resulting in overall efficiencies as high as 60–63% [
5].
The advantage of these modern solutions is not only their high efficiency, but also their operational flexibility and the possibility of integration with emission-reducing technologies such as carbon capture and storage (CCS), oxy-fuel combustion, or biomass co-firing. Furthermore, these systems can be adapted to work with new alternative fuels, such as hydrogen or ammonia, making them an important link in the future low-emission energy economy [
7].
Both steam and gas–steam cycles are the subject of intensive research aimed at optimizing systems through the use of innovative configurations, such as heat regeneration, intermediate superheating, turbine inlet air cooling (intercooling), and advanced methods of gas cooling in the topping cycle [
8]. These examples demonstrate that there is significant potential for further increasing energy production efficiency through the integration and improvement of existing technologies.
In addition, emerging trends in the design of power generation systems increasingly take into account aspects such as source diversification, energy storage, and integration with renewable energy sources, which further increases the attractiveness of supercritical and combined-cycle technologies in the context of the energy transition [
4].
Parallel to the development of advanced energy technologies based on fossil fuels, solutions utilizing alternative fuels such as biomass and biogas are gaining increasing importance. Their potential arises not only from their renewable nature but also from the possibility of local sourcing, which aligns with the principles of sustainable development and carbon footprint reduction [
9]. These fuels can be effectively applied in both large-scale industrial installations and small distributed energy systems, making them a versatile component of the energy transition. Of particular interest are technologies that convert forest and agricultural biomass, as well as organic waste, into electricity and heat.
In the context of alternative fuels, increasing attention is being given to so-called “fuels of the future,” notably hydrogen, which is regarded as one of the key solutions for decarbonizing the energy and industrial sectors [
10]. As an energy carrier, hydrogen can be produced from renewable sources (so-called green hydrogen) and utilized in fuel cells, gas turbines, or as an additive to natural gas. Due to its zero-emission combustion—where the only product is water vapor—hydrogen can play a significant role in reducing CO
2 emissions in the power sector. Alongside hydrogen, high-purity methane is also attracting interest, both of natural origin and obtained through biomass fermentation or organic waste gasification. These fuels can be efficiently combusted in gas turbine systems, including those with external combustion chambers, which enhance the design and operational flexibility of power plants [
11].
Distributed energy systems are also being deployed, based on low-power installations adapted to local and decentralized operating conditions. These systems are characterized by their compact design, high operational flexibility, and the capability to operate either in island mode or as auxiliary units supporting larger grid systems. A particular advantage of microturbines is their ability to operate on a wide range of fuels, including wood gas, biomethane, and biomass-derived synthetic gas (syngas) [
12]. Consequently, they are applied not only in agricultural holdings and small industrial facilities but also in modern cogeneration systems and hybrid renewable energy installations.
Powering these systems with renewable fuels—particularly those derived from biomass—makes it possible to reduce emissions while utilizing locally available resources. The use of high-efficiency microturbines, often equipped with partial-flow stages and optimized for low fuel consumption and minimal exhaust emissions, enables competitive operating performance. An additional advantage is the ability to integrate them with high-efficiency permanent-magnet electric generators, which provide stable voltage output and high efficiency in mechanical-to-electrical energy conversion [
12].
Distributed energy systems—owing to their modularity, short start-up times, and strong capability to operate alongside variable renewable energy sources such as photovoltaics and wind turbines—have become an essential component of modern energy infrastructure. Their development is supported by numerous research initiatives and climate policies aimed at promoting local energy independence and reducing transmission losses.
Technological advances in thermal energy over recent decades have significantly improved the efficiency of energy conversion processes in modern power plants. Innovations in materials, the development of advanced computational methods, the automation of control processes, and enhancements in thermodynamic system design have enabled the creation of installations with markedly higher efficiency and lower environmental impact compared to earlier generations of power plants. Particularly notable progress has been achieved in steam power plants operating at supercritical and ultra-supercritical parameters, which enable operation at extremely high temperatures and pressures [
13].
Modern high-capacity steam power plants—often exceeding 1000 MW—achieve record efficiency levels. The isentropic efficiency of high-pressure turbines reaches 93–95%, while in medium-pressure turbines it can be even higher due to a more favorable distribution of thermal loads and the mechanical properties of materials in this pressure range. The efficiency of modern steam boilers can reach 95%, ensuring highly effective conversion of the chemical energy of fuel into the thermal energy of steam. Electric generators driven by turbines achieve efficiencies exceeding 98% through the use of advanced conductive alloys, the optimization of magnetic flux distribution, and the minimization of thermal and mechanical losses. Even seemingly minor components, such as feedwater pumps, achieve efficiencies of around 85%, which has a measurable impact on the performance of the entire system [
13].
Despite such high technological efficiency, the energy production process remains subject to unavoidable losses. Even in a turbine with an internal efficiency of 95%, the remaining 5% of energy is dissipated due to various physical and technological phenomena. These losses are multifaceted and include, among others, leakage in external glands—accounting for approximately 0.5% of total energy loss—and mechanical losses in bearings and rotating assemblies, which may amount to only 0.01% but become significant during long-term system operation. Additional sources of inefficiency include steam flow friction in turbine flow channels, losses caused by secondary flows, imperfections in the expansion process, and hydraulic as well as thermal resistance in auxiliary systems [
14].
As the design of individual components advances, the precise selection of operating parameters and the implementation of advanced diagnostic and control systems become increasingly important. The application of numerical modeling (CFD—Computational Fluid Dynamics) and multi-criteria optimization tools not only minimizes losses but also extends the service life of critical components operating under extreme temperatures and mechanical loads [
15].
It should also be noted that further improvements in technological efficiency in conventional thermal units are increasingly constrained by physical and material limitations, primarily associated with resistance to corrosion, creep, and thermal fatigue under extreme operating conditions. Consequently, the development of the energy sector focuses not only on enhancing the efficiency of individual components but also on implementing more complex hybrid heat cycles, integrating renewable energy sources, and optimizing entire power systems.
Similarly—and in some cases with even more impressive efficiency—modern gas turbines demonstrate exceptional performance, forming the backbone of many contemporary power generation systems in both the commercial and distributed energy sectors [
16]. Owing to the intensive development of turbomachinery design, advanced cooling technologies, and the use of modern heat-resistant and heat-proof materials, gas turbines achieve very high efficiency levels. The efficiency of axial compressors—the primary component of the air supply system—can exceed 90%, attributable to their multi-stage design, blades with optimized angles of attack, and highly developed flow aerodynamics [
17].
The efficiency of modern gas turbines, which expand compressed and heated exhaust gases, can reach 92–94%. This is made possible by advanced blade cooling techniques—such as film cooling and perforation cooling—the application of thermal barrier coatings (TBC), and optimized arrangements of expansion stages. Combustion chambers also exhibit very high performance, with efficiencies exceeding 99% in converting the chemical energy of fuel into heat. This ensures that almost the entire calorific value of the fuel is utilized, with air–fuel mixing occurring under precisely controlled conditions [
17].
However, it should be noted that further improvements in the efficiency of individual components—such as turbines, compressors, and combustion chambers—are increasingly constrained by physical and material limits. Achieving marginal efficiency gains often requires disproportionately high research and development expenditures and may involve operational challenges such as higher operating temperatures, increased thermal stresses, reduced component durability, and higher maintenance costs [
17]. In practice, this means that enhancing the overall efficiency of energy systems solely through the optimization of individual components is becoming less cost-effective and technologically more difficult to implement.
For this reason, research aimed at modifying and optimizing entire thermodynamic cycles is gaining increasing importance. Rather than focusing exclusively on improving the efficiency of individual components, engineers and scientists are analyzing alternative thermal cycle configurations, integration with heat recovery systems (e.g., recuperators, regenerators), the application of interstage cooling and superheating, as well as the hybridization of systems with renewable energy sources. Examples of such approaches include Brayton cycles with regeneration and compressor cooling, cycles in which the work is divided between several parallel modules, and the integration of a gas turbine with a steam power plant in combined cycle gas turbine (CCGT) systems, where overall efficiencies can exceed 60% [
18].
In addition, innovative systems such as supercritical carbon dioxide (sCO2) cycles are gaining increasing attention, offering high energy density and compactness while maintaining competitive efficiency. Many of these solutions employ dynamic cycle modeling, CFD simulations, and multi-criteria optimization, enabling the precise selection of design and operating parameters for specific conditions and fuel types. Although modern gas turbines have achieved extremely high unit efficiencies, the future of thermal power generation depends not solely on further minimizing component losses but primarily on a systemic approach that integrates technologies, maximizes heat recovery, and enables flexible cooperation within distributed, smart energy systems.
Steam power plants traditionally operate on a modified Rankine cycle, in which thermal energy produced in a steam boiler is converted into mechanical energy in a steam turbine and subsequently into electrical energy in a generator. Gas power plants, in contrast, operate on the Brayton cycle, where compressed air is heated in a combustion chamber and the resulting exhaust gases drive a gas turbine. In both cases, the optimization of thermodynamic parameters and the application of innovative design solutions play a key role in maximizing energy conversion efficiency.
In modern steam power plants, particularly those operating at ultra-supercritical parameters, a range of advanced technological solutions is being implemented. One example is the use of complex regeneration systems designed to recover heat from the condensate and utilize it for feedwater heating, which significantly reduces fuel consumption and increases cycle efficiency. Interstage steam superheating is also applied to counteract the drop in steam temperature in subsequent turbine stages, thereby improving isentropic efficiency and reducing the risk of steam condensation and turbine blade erosion [
19].
In this type of installation, the working fluid—most often steam—operates under extreme conditions, with pressures reaching 30–35 MPa and temperatures exceeding 700 °C [
19]. Such high operating parameters enable performance close to the thermodynamic limit defined by the Carnot cycle but, at the same time, present serious technological challenges. In particular, components operating under these conditions must be manufactured from advanced engineering materials resistant to corrosion, oxidation, creep, and thermal fatigue. Commonly used solutions include nickel alloys (e.g., Inconel), heat-resistant steels (e.g., P92, T23), and thermal barrier coatings (TBC), which protect key components from degradation [
19].
In addition, advanced welding technologies, precise thermal and mechanical treatments, and equipment condition monitoring systems are required to enable the continuous assessment of residual durability. The implementation of such advanced solutions entails high investment and operating costs, necessitating careful technical and economic evaluation. Analyses indicate that only the optimal integration of systems within more complex configurations—such as gas–steam cycles—provides a favorable efficiency-to-investment-cost ratio. Current pressure and temperature values achieved in ultra-supercritical power plants appear to be close to the limits of modern material and structural technology. Further advancements in this field will require not only new materials with superior mechanical and thermal properties but also innovative design concepts, such as closed turbine systems using supercritical carbon dioxide (sCO
2), which offer compact construction and high efficiency at relatively lower operating temperatures [
20].
For this reason, the future of steam power plants will likely not rely solely on further increases in steam temperatures and pressures, but rather on their integration with other energy systems, enhanced operational flexibility (e.g., frequent starts and stops), the implementation of digital technologies, and the utilization of waste heat and renewable energy sources in hybrid systems. In the most advanced thermodynamic steam systems, efficiency slightly exceeds 50%, with projections indicating potential increases to around 55% in the future. However, the integration of CO
2 sequestration systems reduces this efficiency by several percentage points. In the case of gas turbines, efficiency typically exceeds 38%, in some cases reaching 42%, and, according to certain sources, even 44–46%. Examples include high-efficiency turbines manufactured by General Electric (models 9HA and LMS100), Siemens (H and F series), and Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems (J series), which operate at turbine inlet temperatures exceeding 1500–1600 °C. The highest efficiencies are currently achieved in combined cycle power plants, exceeding 61%. Record values include 62.22% net efficiency at the Bouchain power plant in France and 63.08% gross efficiency at the Nagoya power plant in Japan. Forecasts suggest that 65% efficiency may be achievable in the near future. In smaller-scale systems, such as distributed energy units, efficiencies are significantly lower. Micro gas turbines reach efficiencies of up to 30%, while thermal systems based on Organic Rankine Cycles achieve only a dozen or so percent, rarely exceeding 20% [
16,
18,
19].
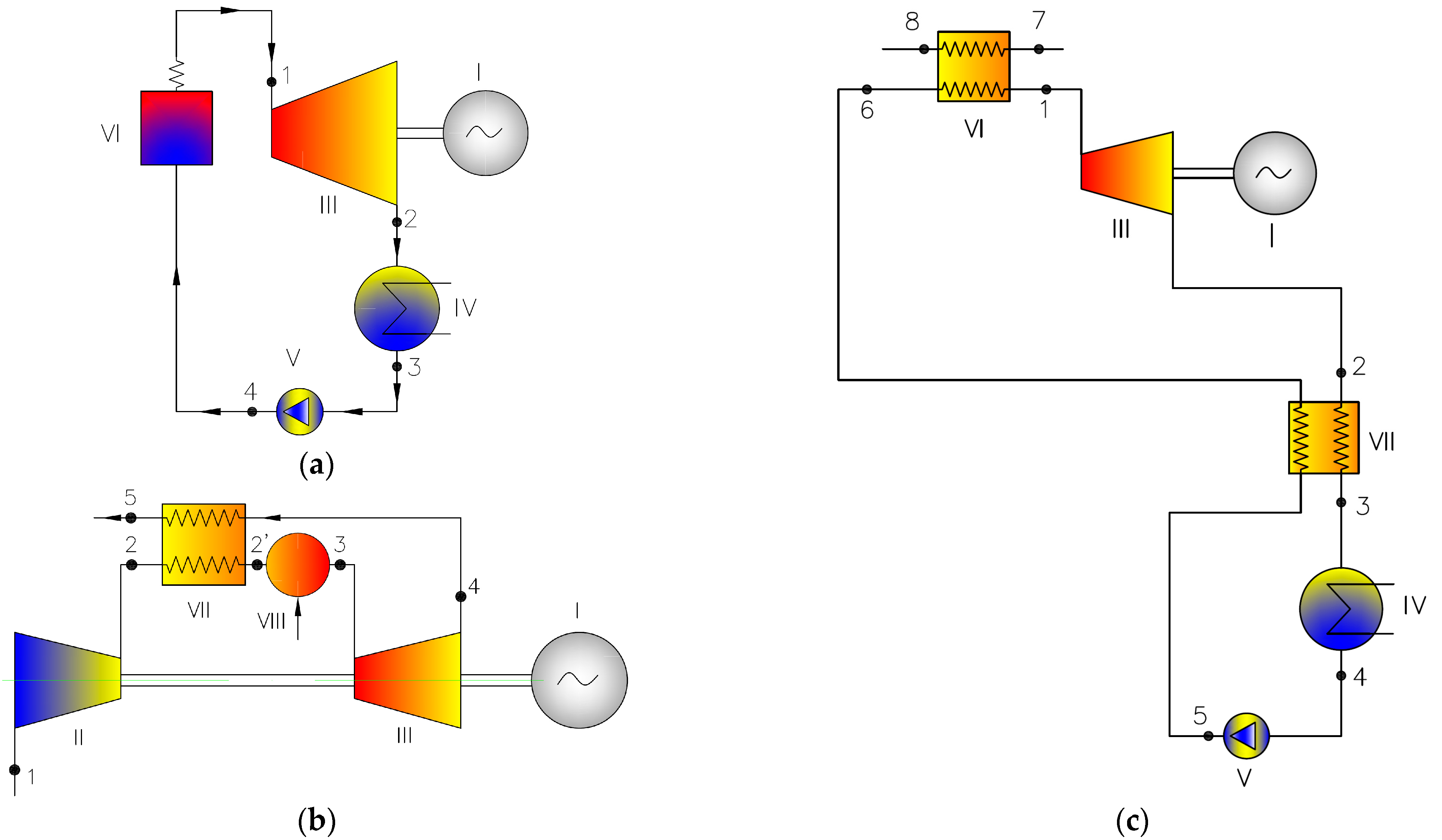
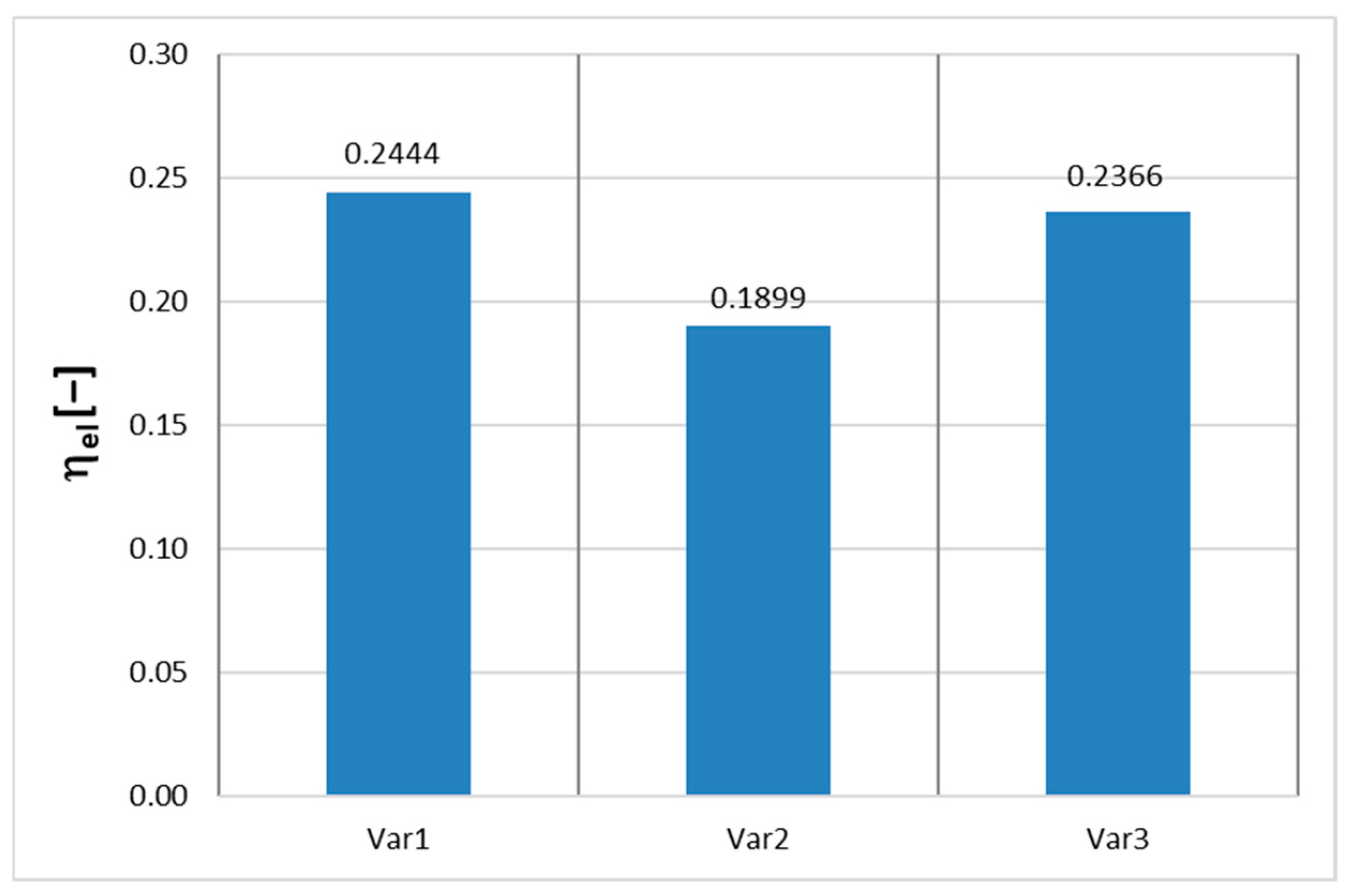
A review of the literature indicates that at low upper temperature levels, currently used energy cycles achieve relatively low efficiencies. To illustrate this issue, calculations were carried out for three configurations: a steam turbine cycle (
Figure 1a—Var1), a gas turbine system with a regenerator (
Figure 1b—Var2), and an Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) (
Figure 1c—Var3).
Detailed calculations were carried out for three variants of thermodynamic cycles (
Figure 1), corresponding to systems currently applied in small- and medium-power installations. The analyzed configurations include: a classic steam turbine cycle (variant 1—Var1), a gas turbine system with a regenerator (variant 2—Var2), and an Organic Rankine Cycle (variant 3—Var3). To ensure consistent boundary conditions, the upper cycle temperature in each variant was set to 700 K, corresponding to low-temperature heat sources such as waste heat or cogeneration systems. The calculations accounted for all major energy losses observed in real systems, including turbine and compressor losses, pressure drops in heat exchangers, heat exchanger effectiveness (including regenerators), and mechanical losses. The numerical values of the assumed parameters are presented in
Table 1.
All calculations were carried out using proprietary computational scripts integrated with the REFPROP library (version 9.0, NIST) for determining the thermophysical properties of the working fluids [
21]. A real gas model was applied for the air cycles, while models compliant with IAPWS-IF97 or the appropriate equations of state for organic fluids were used for the steam and ORC cycles. Standard thermodynamic relations were employed, with iterative methods applied in cases requiring variable specific heat capacity calculations. By adopting identical input assumptions and using the same computational platform, the comparability of results across the different cycle configurations was ensured. The results for each analyzed configuration are presented in
Figure 2. Efficiency is defined as the ratio of net power at the generator terminals to the heat flow supplied to the cycle. The reported values refer to net efficiency, accounting for mechanical losses, turbine and compressor losses, system pressure drops (including those in heat exchangers), and generator efficiency.
As shown in
Figure 2, the steam turbine cycle (Var1) achieved an efficiency of less than 25%, which—when considered in the context of developing high-efficiency power systems—represents a moderate and relatively unpromising result. This limitation is primarily due to the low temperature gradient between the heat source and the cooler, as well as substantial losses associated with the condensation of water vapor. Moreover, steam cycles are highly sensitive to pressure losses and require large heat exchangers, which reduces their suitability for low-power applications.
Even lower efficiency was recorded for the second variant—the gas turbine system with regeneration (Var2)—where overall efficiency did not exceed 19%. Despite the use of a regenerator, which theoretically enables partial heat recovery from exhaust gases, efficiency is constrained by the low maximum cycle temperature. Additional limitations include the reduced effectiveness of compression and expansion processes in small-scale turbomachinery, as well as heat recovery losses resulting from imperfect regeneration.
The ORC cycle (Var3), although operating with a low-temperature heat source, demonstrated comparatively favorable performance. However, its efficiency—while slightly higher than that of the gas turbine cycle—remains limited due to the thermophysical properties of organic fluids and significant losses associated with operation at low pressures.
2. Isothermal Turbines
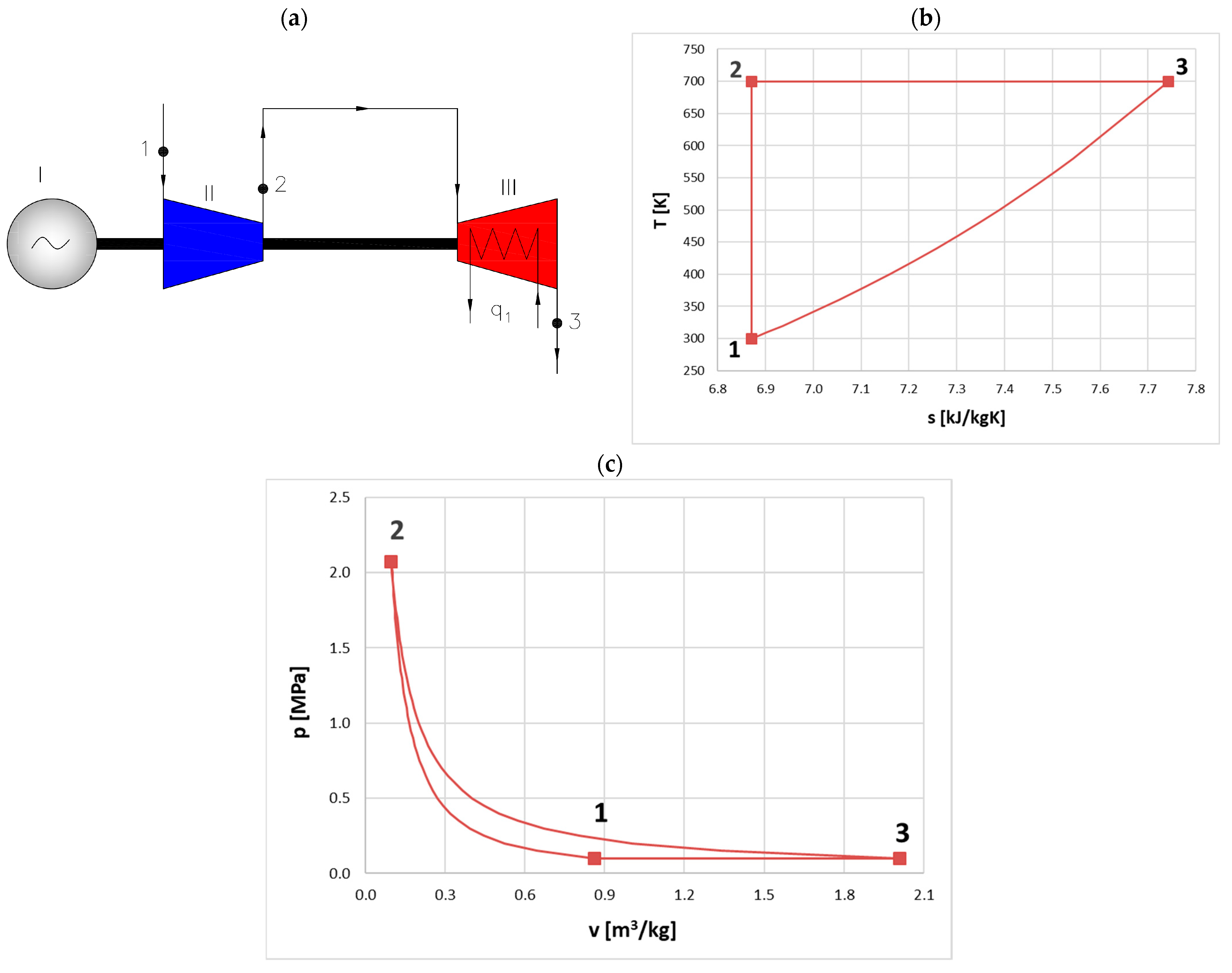
These limitations have led to increasing interest in alternative thermodynamic cycles capable of achieving higher efficiencies under fixed temperature conditions. Theoretically, the Carnot cycle provides the highest possible efficiency, and its generalized versions—such as the Ericsson and Stirling cycles—represent promising alternatives. However, despite their high theoretical potential (
Figure 3), modern steam and gas turbine systems remain several dozen percentage points below these idealized cycles. For instance, even the most efficient gas turbine sets achieve efficiencies only slightly above 40%, whereas a Carnot cycle operating at the same temperature levels could, in theory, achieve nearly twice that value.
The Ericsson cycle, as an example of a generalized Carnot cycle, consists of the following sequence of processes: isothermal compression, isobaric heating of the working medium in a recuperator with 100% effectiveness, isothermal expansion in an expander, and isobaric heat transfer—also in a recuperator. The Stirling cycle has a similar structure but replaces the isobaric processes with two isochoric processes. Other configurations are also possible, including, for example, two polytropic processes combined with isothermal expansion and compression, along with 100% efficient regeneration. All such configurations fall within the class of generalized Carnot cycles, which provide the maximum possible efficiency for given temperature conditions.
The growing demand for efficient energy recovery and conversion from low-temperature sources—such as industrial waste heat, geothermal energy, ocean thermal energy, and solar radiation—is driving the development of high-efficiency thermodynamic cycles. Systems employing isothermal or quasi-isothermal expansion in turbines are attracting particular attention, as they minimize fluctuations in the working fluid temperature, reduce thermal losses, and improve efficiency compared to conventional adiabatic processes.
Research has shown that the implementation of isothermal distribution in steam cycles [
22], Organic Rankine Cycles (ORCs) [
23,
24], or compressed air energy storage (Isothermal CAES) [
25] can bring their performance closer to that of the Carnot cycle. This can be achieved, among others, by injecting steam or water into the expander, employing liquid pistons that provide cooling of the expanding medium, or integrating heat exchangers within the expansion stages. In steam cycles with direct generators, it is possible to apply solutions operating under isothermal conditions, enabling relative efficiencies exceeding 80% of the Carnot cycle limit [
22].
In CAES systems, isothermal compression and expansion are achieved through intensive heat transfer techniques—such as spray cooling, the use of water foam, or porous media in a liquid piston—which can yield compression efficiencies of up to 95%. In both conventional CAES and its variants (including ICAES and LPCAES), isothermal compression is realized via direct heat transfer, for example through water droplet injection or the use of a liquid piston. Experimental and simulation studies have demonstrated that an appropriately selected liquid-to-gas mass ratio and optimized chamber geometry can increase expansion efficiency by several percentage points and maintain stable temperature and pressure conditions throughout the operating cycle [
26,
27].
Integrating CAES systems with combustion engines and the Kalina cycle enables additional utilization of compression and exhaust heat, thereby improving efficiency in both charge and discharge modes and enhancing operational flexibility [
25]. Similar quasi-isothermal expansion concepts are applied in Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) systems for low-temperature waste heat recovery (80–100 °C), where staged heating of the working fluid within the expander improves both energy performance and economic viability. Other approaches—such as two-phase expansion in screw expanders or the use of ionic working fluids in compressors and liquid pistons—offer potential for further reducing thermal losses and increasing power density [
28,
29].
Hybrid solutions combining features of ORC, Stirling, Brayton, and Rankine cycles, as well as two-phase systems, have also been reported. Examples include a quasi-isothermal ORC with staged turbine heating, two-phase air–water expansion in screw expanders, and the application of ionic fluids in compression systems with liquid pistons. In all cases, the key objectives are to increase power density and minimize exergy losses [
30].
Solutions employing liquid pistons in flow mode are of particular importance, as they provide high thermal efficiency with results closely matching experimental measurements [
31,
32].
Two-phase air–water expansion in screw expanders can further increase mechanical power output by up to 10.8% due to enhanced heat transfer within the working chambers [
33].
Innovative electrochemical quasi-Carnot cycles (EQCC), inspired by the Carnot principle, are also under development. These systems convert thermal energy directly into electrical energy through reversible electrochemical reactions, with no rotating components, and can operate with very small temperature differences, making them competitive for low-temperature heat source applications [
34,
35].
Particularly noteworthy is the pioneering concept of an isothermal expansion gas microturbine presented in [
36], in which the authors proposed a turbine operating at a constant expansion temperature through controlled heat supply to the working fluid stream. A schematic of such a system is shown in
Figure 4. Although this design remains at the experimental stage, its underlying principles are consistent with the global trend toward developing systems with the highest possible energy efficiency.
In the context of advancing energy-efficient technologies, it can be anticipated that the first commercial implementations of turbo units with isothermal expansion will emerge in the near future. These cycles—similar in nature to generalized Carnot cycles such as the Ericsson or Stirling cycles—offer the theoretical potential to achieve efficiencies close to the maximum limit dictated by the temperature difference between the heat source and the cooler. Their deployment could represent a breakthrough in distributed energy systems, micro power plants, and low- to medium-scale cogeneration installations.
Thermodynamic analyses indicate that isothermal or quasi-isothermal turbine cycles offer a promising pathway for low-temperature applications—both in energy storage and waste heat recovery—by providing a favorable balance between efficiency, energy density, and design simplicity, making them competitive with conventional adiabatic solutions. In summary, current research on isothermal turbine cycles covers:
Steam and ORC concepts—application of direct steam generators, post-expansion heat regeneration, two-phase cycles, and multi-stage reheating;
CAES energy storage—liquid piston technologies, spray cooling, integration with combustion engines, the Kalina cycle, and polygeneration configurations;
Electrochemical cycles—implementation of quasi-adiabatic processes to achieve near-Carnot efficiencies at low temperature differentials;
Hybrid systems—combining the advantages of different cycles to enhance efficiency and operational flexibility with low-temperature heat sources.
In this paper, the authors present the results of calculations for an innovative cycle incorporating an air turbine with isothermal expansion, operating at a relatively low upper temperature of 700 K.
4. High-Efficiency Combined Cycle Concepts Based on Isothermal Expansion
In the proposed solution, the high temperature of the air exiting the isothermal turbine—identical to the maximum temperature of the cycle—is of key importance. In this configuration, the exhaust air serves as a high-grade heat source that can be utilized in an additional bottoming cycle, thereby creating a combined system. Four variants of thermodynamic configurations were analyzed:
- a.
Single-pressure combined gas–steam system with water/steam as the working medium—
Figure 7a (Var6);
- b.
Single-pressure combined gas–steam system with a so-called “dry” organic medium —
Figure 7b (Var7);
- c.
Two-pressure combined gas–steam system with water/steam as the working medium—
Figure 8a (Var8);
- d.
Two-pressure combined gas–steam system with organic medium—
Figure 8b (Var9).
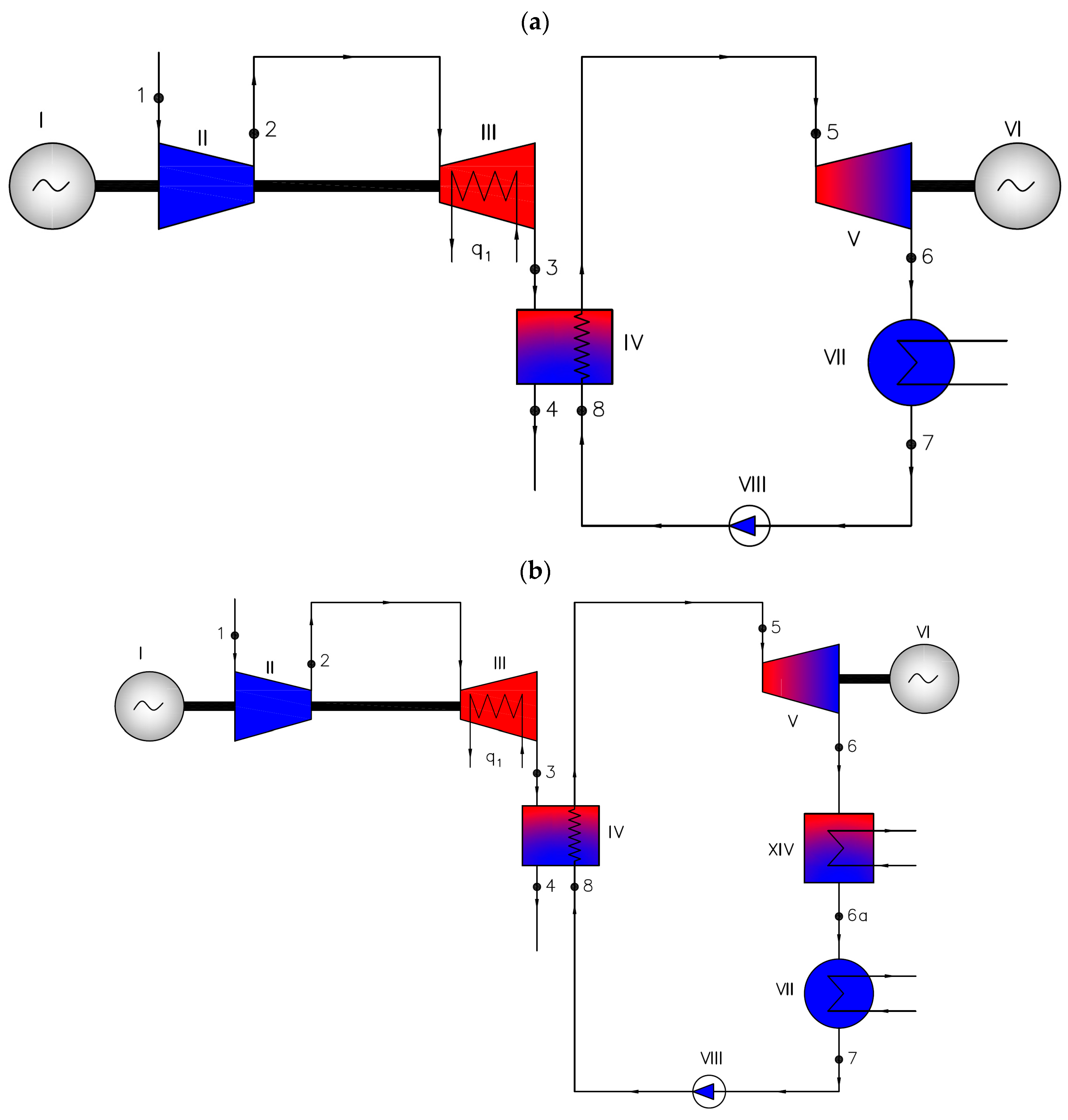
Figure 7.
Single-pressure combined gas–steam cycle for water/steam as the working medium—Var6 (a) and so-called “dry” organic media—Var7 (b), where I—gas cycle generator, II—compressor, III—isothermal air turbine, IV—heat exchanger (waste heat boiler), V—steam turbine, VI—steam cycle generator, VII—condenser, VIII—main steam cycle pump, XIV—heat exchanger, q1—heat supplied to the system, and 1, 2, … 8 are successive characteristic points of the cycle.
Figure 7.
Single-pressure combined gas–steam cycle for water/steam as the working medium—Var6 (a) and so-called “dry” organic media—Var7 (b), where I—gas cycle generator, II—compressor, III—isothermal air turbine, IV—heat exchanger (waste heat boiler), V—steam turbine, VI—steam cycle generator, VII—condenser, VIII—main steam cycle pump, XIV—heat exchanger, q1—heat supplied to the system, and 1, 2, … 8 are successive characteristic points of the cycle.
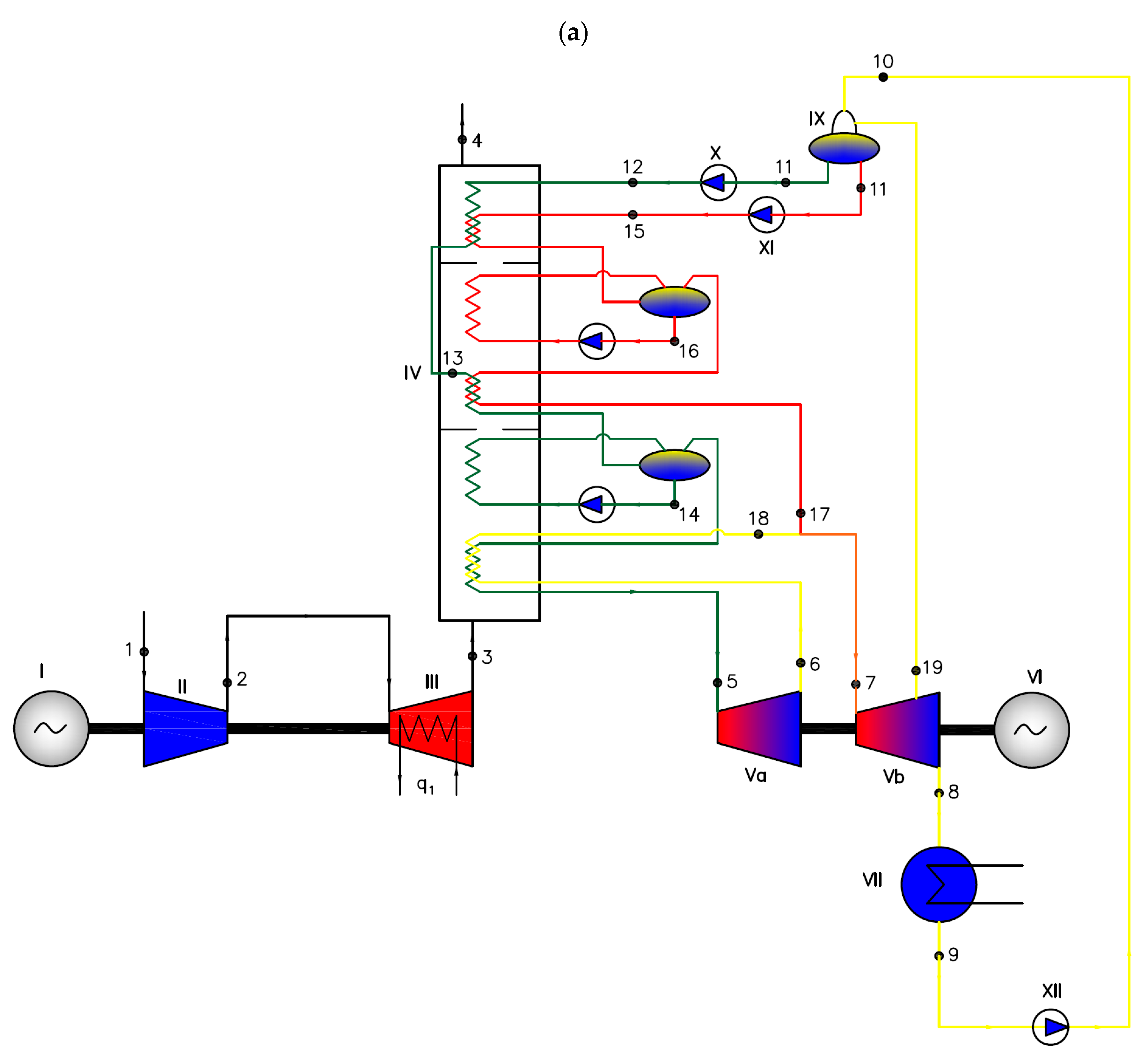
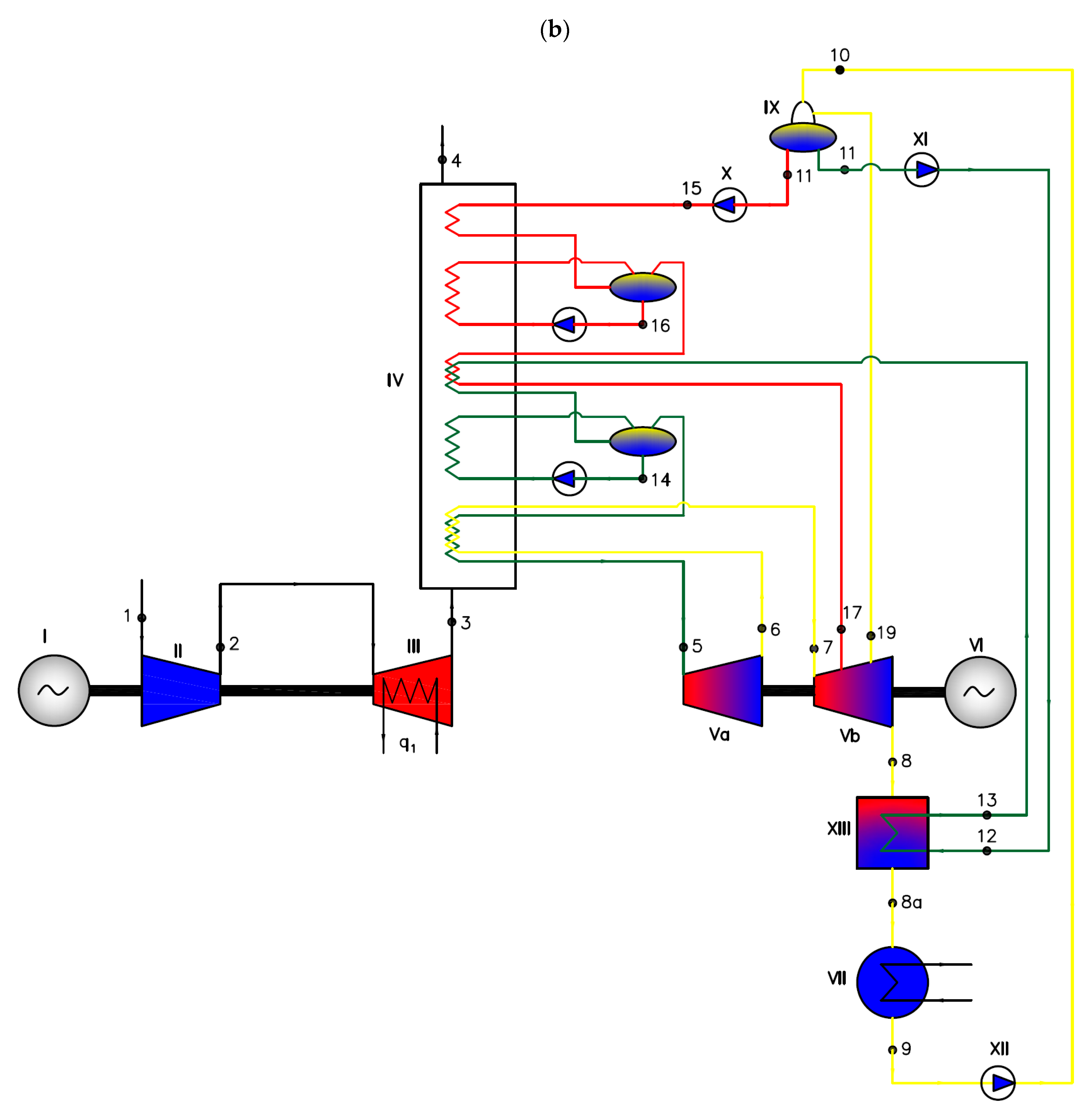
Figure 8.
Two-pressure combined gas–steam cycle with water/steam as the working medium—Var8 (a) and with an organic medium—Var9 (b), where I—gas cycle generator, II—compressor, III—isothermal air turbine, IV—heat exchanger (waste heat boiler), Va/Vb—high-pressure/low-pressure steam turbine, VI—steam cycle generator, VII—condenser, IX—degasser, X—high-pressure pump, XI—low-pressure pump, XII—main steam circulation pump, XIII—regenerator, q1—heat supplied to the system, and 1, 2,... 19 are successive characteristic points of the cycle.
Figure 8.
Two-pressure combined gas–steam cycle with water/steam as the working medium—Var8 (a) and with an organic medium—Var9 (b), where I—gas cycle generator, II—compressor, III—isothermal air turbine, IV—heat exchanger (waste heat boiler), Va/Vb—high-pressure/low-pressure steam turbine, VI—steam cycle generator, VII—condenser, IX—degasser, X—high-pressure pump, XI—low-pressure pump, XII—main steam circulation pump, XIII—regenerator, q1—heat supplied to the system, and 1, 2,... 19 are successive characteristic points of the cycle.
These results clearly indicate that, with an upper temperature limit of 700 K, achieving high efficiency in small-scale energy systems presents a significant challenge. Overcoming this limitation requires the development of innovative solutions, such as cycles with isothermal expansion, high-efficiency regeneration, or the use of working fluids with tailored thermodynamic properties.
In response to the efficiency constraints outlined above for conventional thermodynamic systems (Var1–Var3)—particularly steam and gas cycles operating with low-temperature heat sources (700 K)—a novel and competitive approach has been proposed, based on an air turbine with isothermal expansion. Expanding the working fluid at a constant temperature theoretically enables efficiencies approaching that of the Carnot cycle, which represents the upper limit for the conversion of thermal energy into mechanical work.
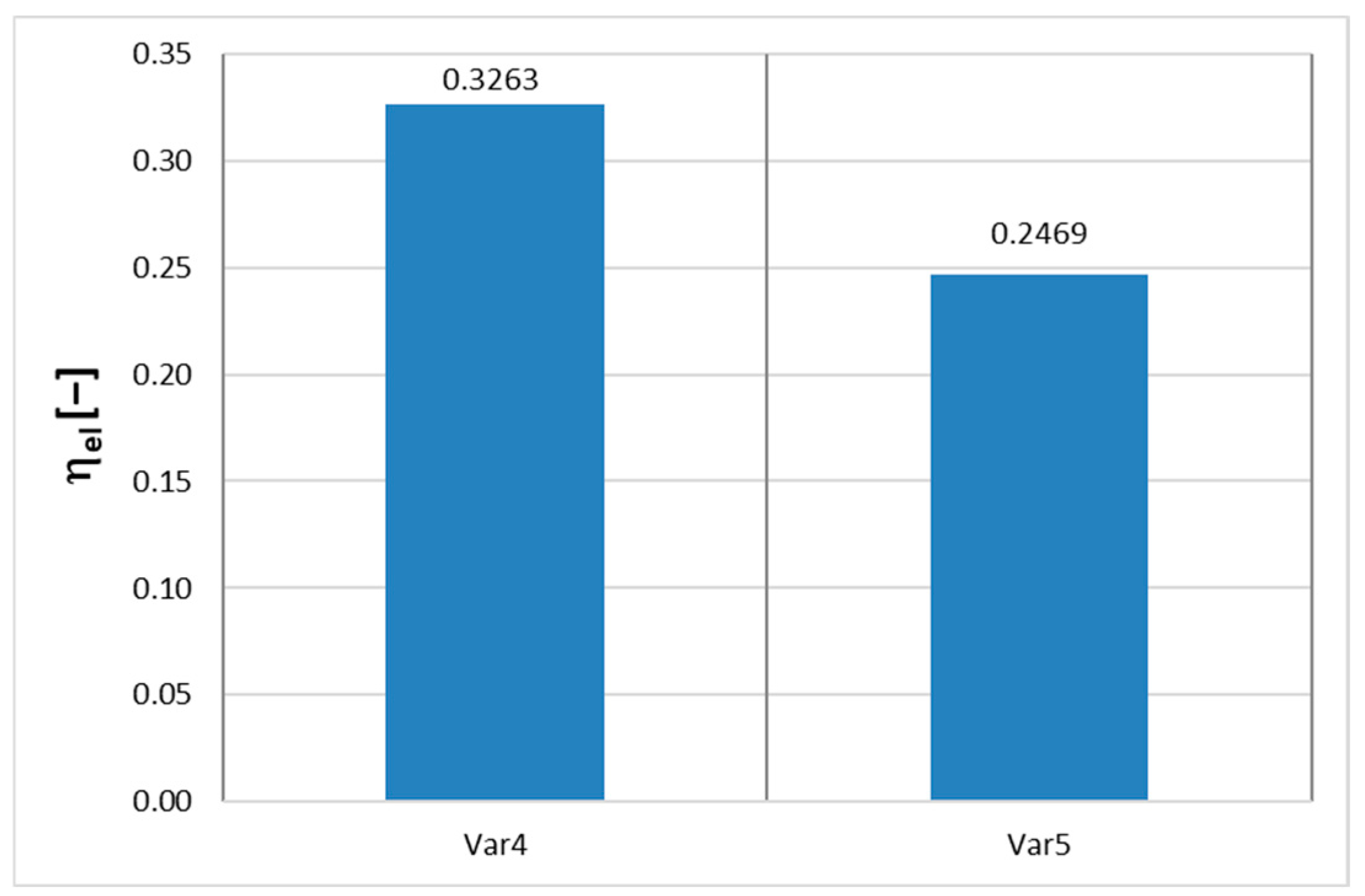
In the analyzed combined variants (Var6 to Var9), for which the results are also presented in
Figure 9, efficiencies exceeding 43% were achieved, which is an unprecedented value for systems operating at a maximum temperature of 700 K. Achieving such high efficiency at a relatively low heat source temperature demonstrates the enormous potential of the isothermal expansion concept as a key element of future distributed, waste and cogeneration energy installations. Furthermore, thanks to clean air and no need to use expensive or toxic agents, this solution can also be beneficial in economic and environmental terms.
The analyses also considered the impact of variations in the individual efficiency values of key cycle components on its performance, determining the system’s sensitivity. A summary of the parameter variations entered and the obtained efficiency results is presented in
Table 2.
The sensitivity analysis (
Table 2) was conducted to determine the impact of changes in the efficiency of key components of the cycle—compressor, turbine and pump—and pressure losses in the air and steam sections on the overall efficiency of the system for variants Var6–Var9. The range of parameter values examined corresponds to realistic deviations resulting from design, operational and manufacturing constraints.
A change in compressor efficiency in the range of 0.85–0.90 has a noticeable impact on the overall efficiency of the systems, particularly in the Var7 variant (an increase of approx. 5.4%) and, to a lesser extent, in Var8 and Var9. The high sensitivity of the Var7 variant results from the greater share of compression work in the energy balance of the cycle with an organic working fluid. In the Var6 variant, this impact is smaller, but still significant from the point of view of optimizing machine operation.
A change in turbine efficiency in the range of 0.85–0.92 has the greatest impact on overall efficiency in the Var8 (increase to 0.4420) and Var9 (to 0.3785) variants. This is due to the fact that in double-pressure systems (Var8, Var9), the turbine plays a dominant role in power generation, and its parameters directly translate into the efficiency of converting thermal energy into mechanical energy. The Var7 variant shows a smaller, but still noticeable sensitivity.
In the analyzed variants, the impact of changes in pump efficiency in the range of 0.80–0.88 on overall efficiency is marginal—the final values remain virtually unchanged (e.g., Var6: 0.4067). This is in line with expectations, as pumps, compared to turbines and compressors, have a relatively small share in the total energy balance of the system.
A change in pressure loss in the air cycle in the range of 3–8% does not significantly affect the efficiency of the system in any of the variants. The results remain within the calculation error range (e.g., Var6: 0.4070–0.4066), which indicates low sensitivity of efficiency to this parameter under the assumed operating conditions.
The impact of pressure losses in the steam cycle is negligible in most cases, but in the Var8 variant, there is a noticeable decrease in efficiency from 0.4373 to 0.4339, with an increase in losses from 8% to 12%. This is due to the fact that in a two-pressure system for steam, greater losses in heat exchangers and steam pipes directly reduce the effective power of the steam turbine.
Sensitivity analysis showed that the efficiency of the compressor and turbine has the greatest impact on the overall efficiency of the systems under consideration, while the efficiency of the pump and pressure losses in the air and steam cycles play a secondary role. These results indicate the need to prioritize the optimization of the design and operation of the rotor components (compressor and turbine) in order to maximize system efficiency. In particular, dual-pressure systems (Var8 and Var9) are more sensitive to changes in turbine efficiency, which should be taken into account in the design process.
In summary, despite slightly higher construction costs and technological requirements related to expansion temperature control, the use of isothermal expansion in air turbines opens up new possibilities for designing high-efficiency, compact, and flexible thermal energy conversion systems, especially where moderate-temperature heat is available.