1. Introduction
Gas production from shale/tight gas reservoirs has advanced significantly in recent decades. Hydraulic fracturing is one of the primary techniques to unlocking resources from the low-permeability reservoirs. After hydraulic fracturing, wells undergo a flowback process for fracture cleanup, facilitating gas production [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8]. Flowback operations commonly involve frequent choke-size adjustments, and flowback rates and pressure are highly sensitive to choke-size adjustments [
4,
5,
9]. Recent studies have demonstrated that flowback choke-size managements are critical for preventing proppant return [
10,
11,
12] and securing long-term production from unconventional gas wells [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. However, effective choke-size managements thus requires a reliable performance model to capture the relationships between rates, pressure, and choke size.
Theoretically modeling the choke flow is challenging for multiphase flowback due to the rapid and significant changes in rates and pressure, which can change dramatically within hours to days. Also, the flow regime transits quickly from water-dominated flow in the early stages to gas-dominated flow later [
4,
5,
9,
11]. Multiphase flow through choke is theoretically linked to the Reynolds number, which depends on fluid density, viscosity, and flow velocity [
19,
20,
21,
22]. However, the critical Reynolds number for multiphase flowback through chokes remains unclear. Also, studies have reported large variations in flowback water salinity and temperature [
23,
24], which cause large fluctuations in fluid density and Reynolds number, adding complexity to choke-performance modeling.
Empirical correlations have traditionally been developed to describe the multiphase flow through choke, particularly for gas and oil production [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40]. Flowback studies have employed these empirical correlations to describe water and gas flow through choke [
41,
42,
43]. However, these empirical correlations were originally developed for steady-state oil and gas flow. The accuracy of empirical correlation and coefficients in capturing the multiphase flow of water and gas through choke for flowback remains uncertain.
Empirical correlations of multiphase flow through choke apply within certain ranges of gas/liquid ratio and flow conditions [
21,
26,
28]. For example, the Gilbert-type correlation assumes critical flow, where flow velocity at the choke exceeds the speed of sound [
44]. The multiphase flow rates are independent of downstream pressure, and only upstream pressure is thus required for the Gilbert-type correlation. However, it remains uncertain whether the sonic velocity conditions are met during flowback, and how downstream pressure affects the accuracy of choke-performance predictions.
A recent flowback study [
42] employed Perkins correlation [
34], which incorporates the upstream and downstream pressure to describe multiphase flowback through chokes. However, the robustness of Perkins correlation for multiphase flowback is limited by the small datasets for calibration. Also, the measurements of downstream pressure are often unavailable during flowback, restricting the broader applications of the Perkins model in flowback choke-size managements. Beyond pressure, factors such as variations in water salinity and wellhead temperature further complicate accurate choke–performance correlation.
Machine learning (ML) provides an alternative to tackling engineering problems where physical models are incomplete and relationships between variables are highly nonlinear. Numerous studies have applied ML algorithms to model the multiphase flow through chokes [
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52], primarily targeting for oil and gas flow. ML techniques have been applied to predict gas and condensate flow behavior through chokes [
48]. However, limited work has explored the usage of ML to model the multiphase flowback of water and gas through chokes, leaving a gap in understanding flowback dynamics.
In this study, we present an ML investigation to establish the choke–performance correlation for multiphase flowback. We compiled a dataset containing 18,660 flowback records of 37 shale gas wells from the Horn River Basin. We trained and tested ML algorithms on the flowback dataset to capture the relationship between choke size, pressure, and flow rates. We also evaluated the contribution of variables to choke performance. Based on our findings, we developed a simplified empirical correlation to describe gas/water multiphase flow during flowback.
2. Methodology
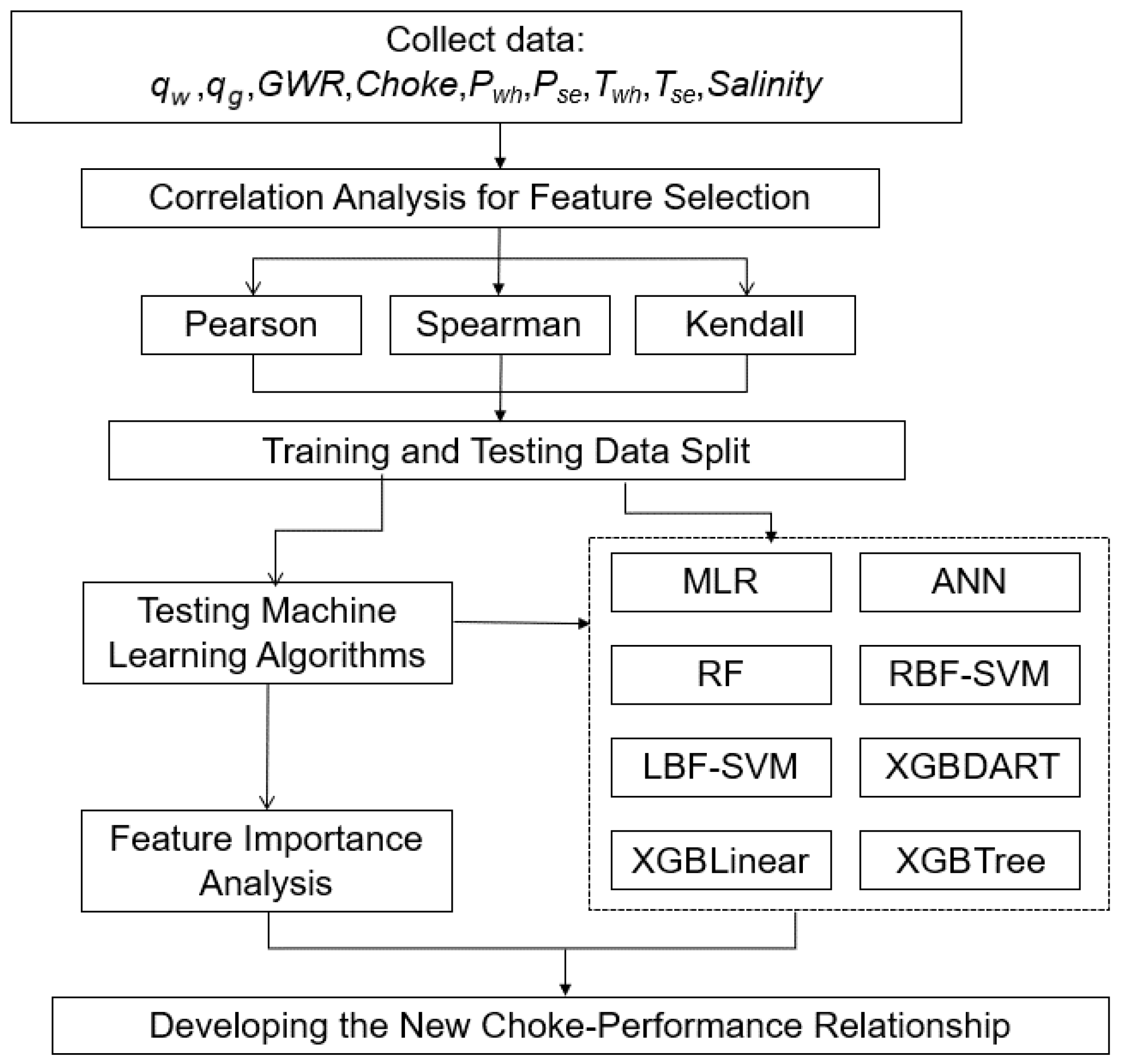
We conducted this work mainly through the following 5 key steps: (a) We collected and preprocessed multiphase flowback data from shale gas wells. (b) We assessed the traditional empirical correlations by fitting to collected flowback data. (c) We conducted correlation analysis of flowback features to identify potential patterns. (d) We implemented machine learning (ML) algorithms on flowback data to link flowback measurements with choke size, and identified the most important features for choke–performance relationship. (e) We developed four new choke–performance relationships for multiphase flowback data through multivariate correlation of key features.
2.1. Data Collection and Preprocessing
In this study, we compiled a flowback dataset from 37 shale gas wells in the Horn River Basin. The flowback dataset includes 18,660 surface measurements of water rate (), gas rate (), choke size (), wellhead pressure (), separator pressure (), wellhead temperature (), separator temperature (), and salinity. We preprocessed the data to ensure quality and consistency. A percentile-based method was used to identify and remove outliers (the threshold of and percentiles is employed for outlier removal). Records with missing values were excluded to prevent bias in the analysis of choke performance.
2.2. Empirical Choke–Performance Correlations
In this study, we examined the accuracy of traditional empirical choke–performance correlations for multiphase flowback data by linear regression fitting.
Table 1 lists the traditional empirical correlations, together with coefficients for each correlation. We tested empirical choke–performance correlations on flowback data via the following steps: first, we converted the flowback measurements to field units; second, we input the converted wellhead pressure, gas/water ratio, and choke size into empirical formulas, and calculated the water rate using the coefficients listed in
Table 1; and third, we conducted linear fitting on the calculated and measured water rate.
2.3. Data-Driven Investigation of Multiphase Flowback Through Choke
As illustrated in
Figure 1, we investigate the multiphase flowback through choke via the following key procedures:
(1)
Correlation Analysis for Feature Selection: We began by analyzing the relationships among flowback variables to select the most relevant features for machine learning. Pearson, Spearman, and Kendall correlation coefficients [
56,
57,
58] were used to evaluate the strength and consistency of these relationships.
(2) Training and Testing Data Split: Next, we split the dataset into training and testing sets. To determine the optimal ratio, we evaluated five scenarios with training-to-testing splits ranging from 50% to 90%.
(3)
Testing Machine Learning Algorithms: We implemented 8 ML algorithms using Python 3.10.7 in the flowback dataset, and assessed the performance of ML algorithms in describing the choke performance. The ML algorithms include Multiple Linear Regression (MLR), Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machines with both linear and radial basis functions (SVM-Linear and SVM-Radial), and 3 versions of Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBDART, XGBLinear, and XGBTree) [
59,
60]. We employed these ML algorithms mainly considering their wide applications in data-driven studies of oil and gas industry. Each ML algorithm was run 100 times to eliminate the effects of randomness in training/testing splits.
In this study, we employed the performance metrics of Mean Absolute Error (
), Root Mean Squared Error (
), and the Coefficient of Determination (
) [
61] to evaluate the predictive performance of 8 ML algorithms.
,
, and
are defined by
where
N represents the number of recorded data;
is the actual measured value of the wellhead data recorded during flowback; and
is the predicted value.
where
is the mean of the data recorded.
(4) Feature Importance Analysis: We determined the feature importance of flowback measurements using the outputs from ML algorithms. Also, we designed 5 scenarios with different combinations of flowback features to determine the optimum set of flowback features for describing the choke–performance relationship.
(5) Developing the New Choke–Performance Relationship: We established the new choke–performance relationship by considering the key features determined by the feature importance analysis. We also obtained the coefficients for the choke–performance relationship by fitting the relationship to real flowback measurement data. We further conducted a comparative analysis to obtain the recommended choke-size ranges for the new choke–performance relationship.
3. Field Application with Well/Flowback Information
In this section, we describe the field and well information for application. We report the flowback behaviors of typical shale gas wells, and the statistic results of flowback features of target wells.
3.1. Field and Well Information
In this study, we collected flowback data from 37 shale gas wells completed in the Horn River Basin (more details about the field and target wells can be found in our previous studies [
13,
62]). The shale gas wells are multi-fractured horizontal wells. After hydraulic fracturing, the shale gas wells remain shut for several months before flowback. Tubing string were placed at the end of flowback, and thus water and gas mainly flowed through the casing during flowback. In this study, we treat the casing pressure data as the wellhead pressure for flowback.
3.2. Flowback Operations and Surface Measurements of Typical Well
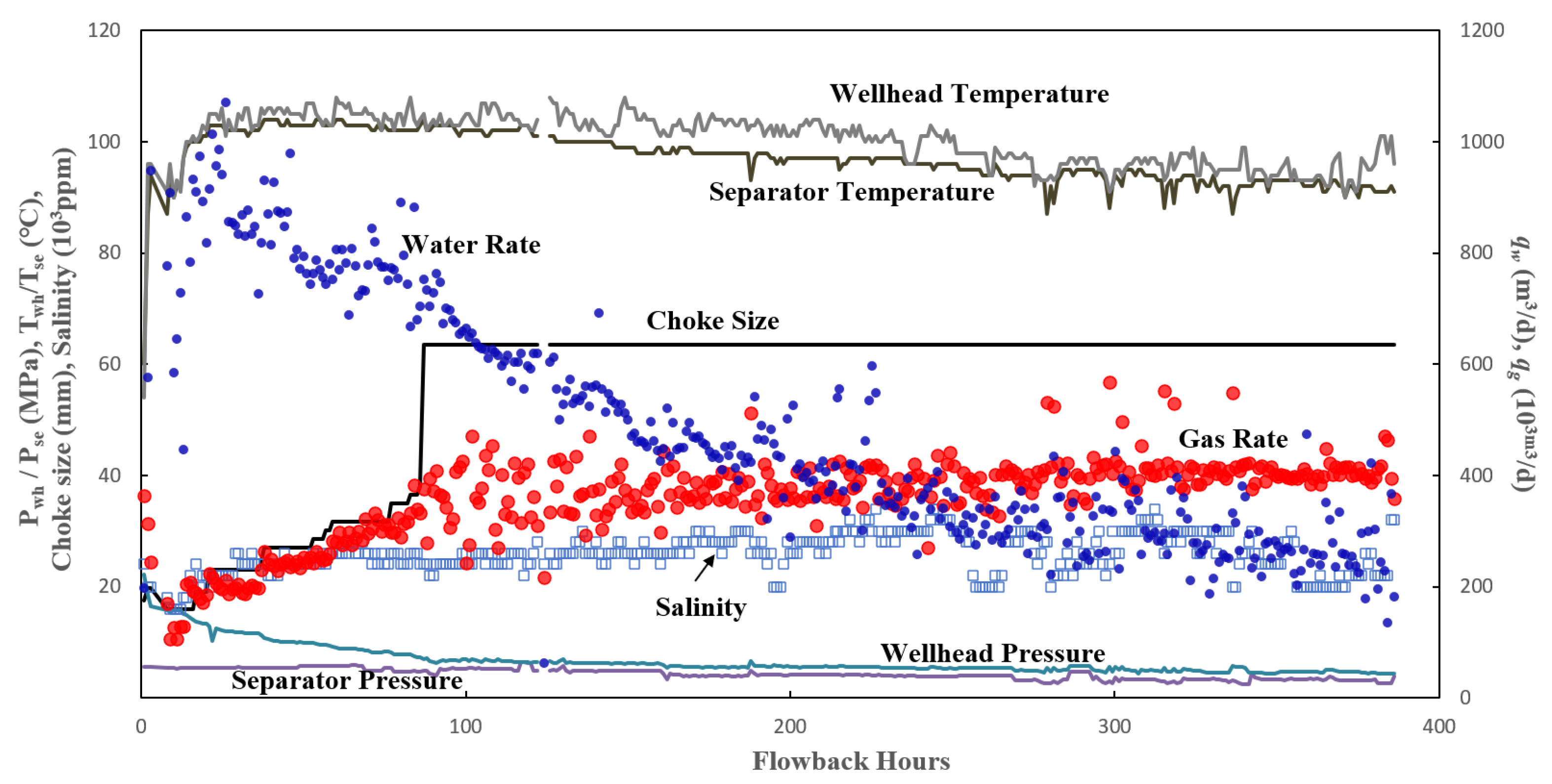
Figure 2 shows the typical flowback profiles of rates, pressure, choke size, and salinity data for a multi-fractured horizontal well completed in the Horn River Shale. The flowback data were reported hourly for target wells over a period of 7–30 days (more details on the flowback measurements can be found in previous studies [
9,
13,
63,
64,
65]). Flowback generally begins with a relatively small size of choke, and the choke is gradually opened up to accelerate fracture cleanup. Each choke setting typically lasts for several hours to a few days. Most changes in choke size occur early in the flowback period, with the choke eventually stabilizing at a larger size during later stages.
Overall, the flowback profiles show declining trends in wellhead and separator pressure. Water rate initially increases with enlarging choke size, and then gradually decreases over flowback hours. The decreasing water rate is attributed to pressure depletion and multiphase flow effects within fractures [
13,
66]. Gas rate follows a similar pattern with water rate. Fluctuations in rates and pressure are primarily linked to the choke-size adjustments during flowback. Previous studies [
5,
67] have reported a “V-shape” behavior in flowback gas/water ratio.
The flowback profiles show pronounced responses of pressure and rates to the change in choke size during early flowback. As shown in
Figure 2, a slight increase in choke size leads to a dramatic drop in pressure and increase in rates at early flowback. Comparatively, the flowback rates and pressure become less sensitive to choke-size changes when flowback profiles are stabilized.
Wellhead temperature initially increases, and then declines slightly during flowback. The increase in wellhead temperature is mainly caused by thermal recovery, which is described by the fracturing water being warmed by the formation rock during the extended shut-in periods after hydraulic fracturing [
24]. The subsequent decline in wellhead temperature is mainly related to decreasing pressure.
The results of flowback salinity show a steady increase over time, and generally stabilizes after several hundred hours. The trend of flowback salinity reflects an increase in fluid density, and is thought to result from the mixing of injected fracturing fluid with in situ formation water. This trend has also been used as an indicator of fracture complexity in previous studies [
23,
68].
3.3. Statistical Analysis of Flowback Surface Measurements
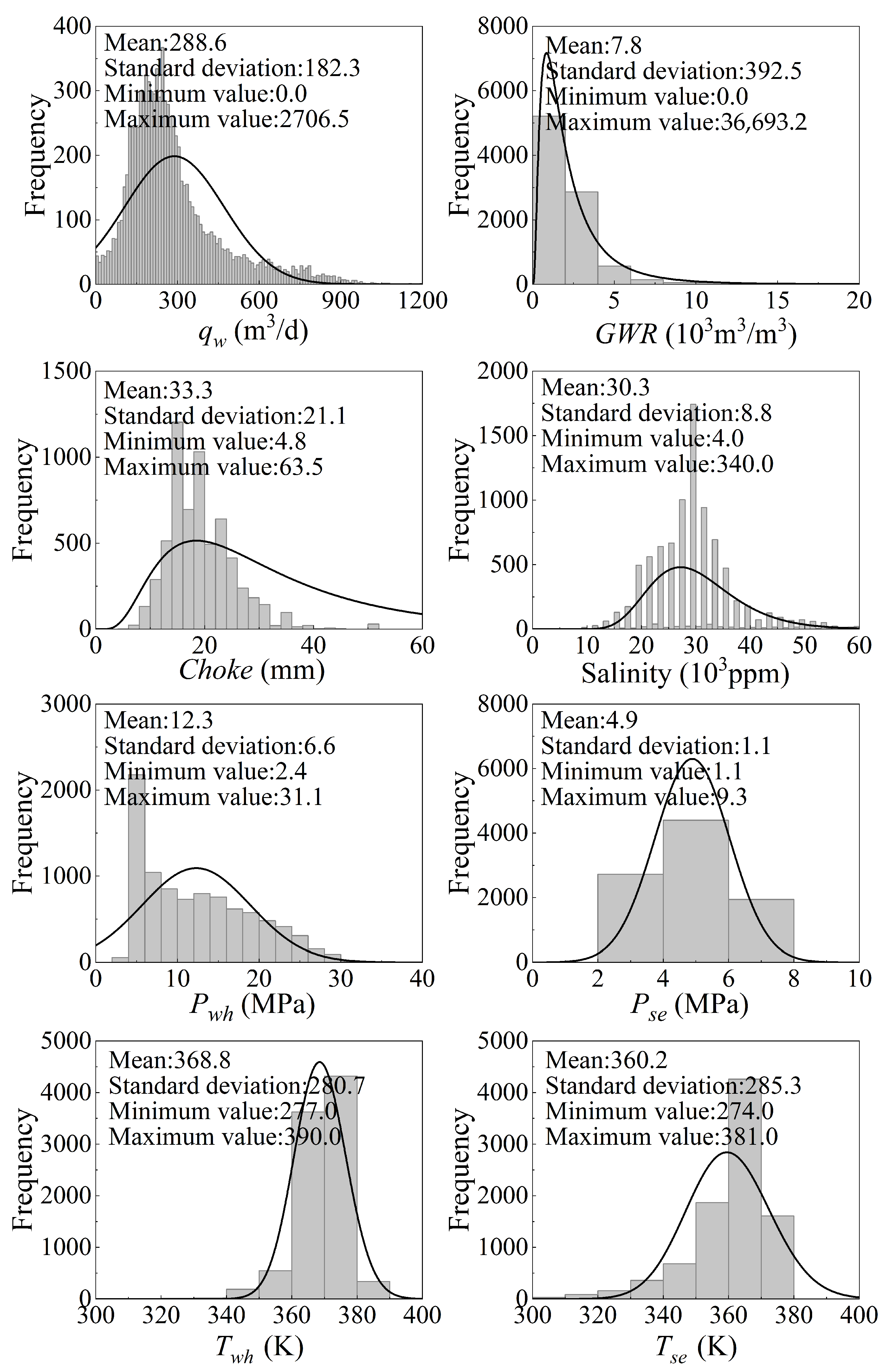
Figure 3 shows the histograms of 18,660 flowback measurements, including
,
,
,
,
,
,
, and salinity data (see
Table 2 for the statistic results of each flowback measurement).
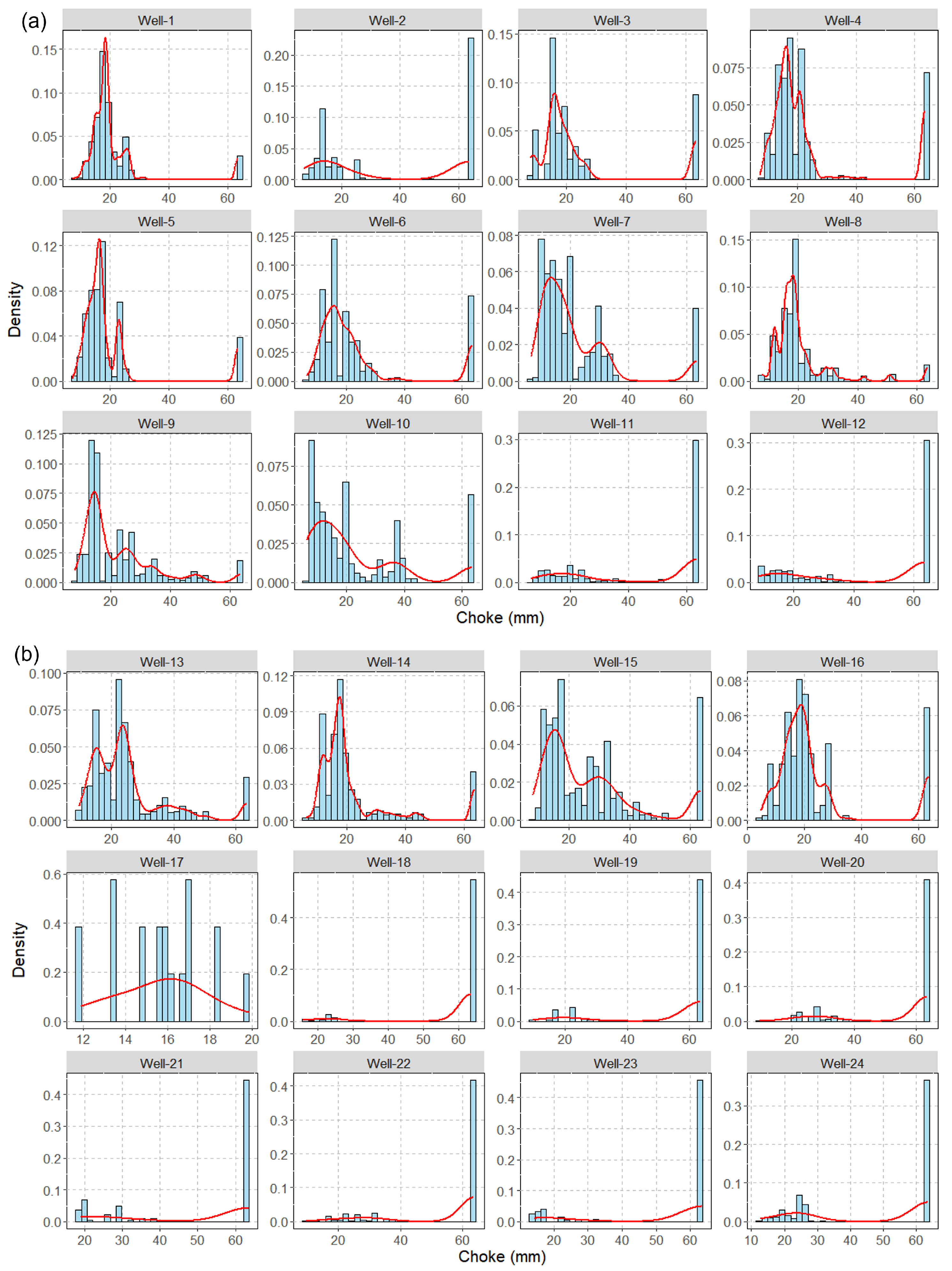
Most wells undergo hundreds of choke-size adjustments over flowback. The wells started flowback with a small-sized choke at 4.762 to 7.938 mm, and ended at the choke of 63.5 mm within 20 days of flowback (see
Table A1 and
Figure A1 in
Appendix A).
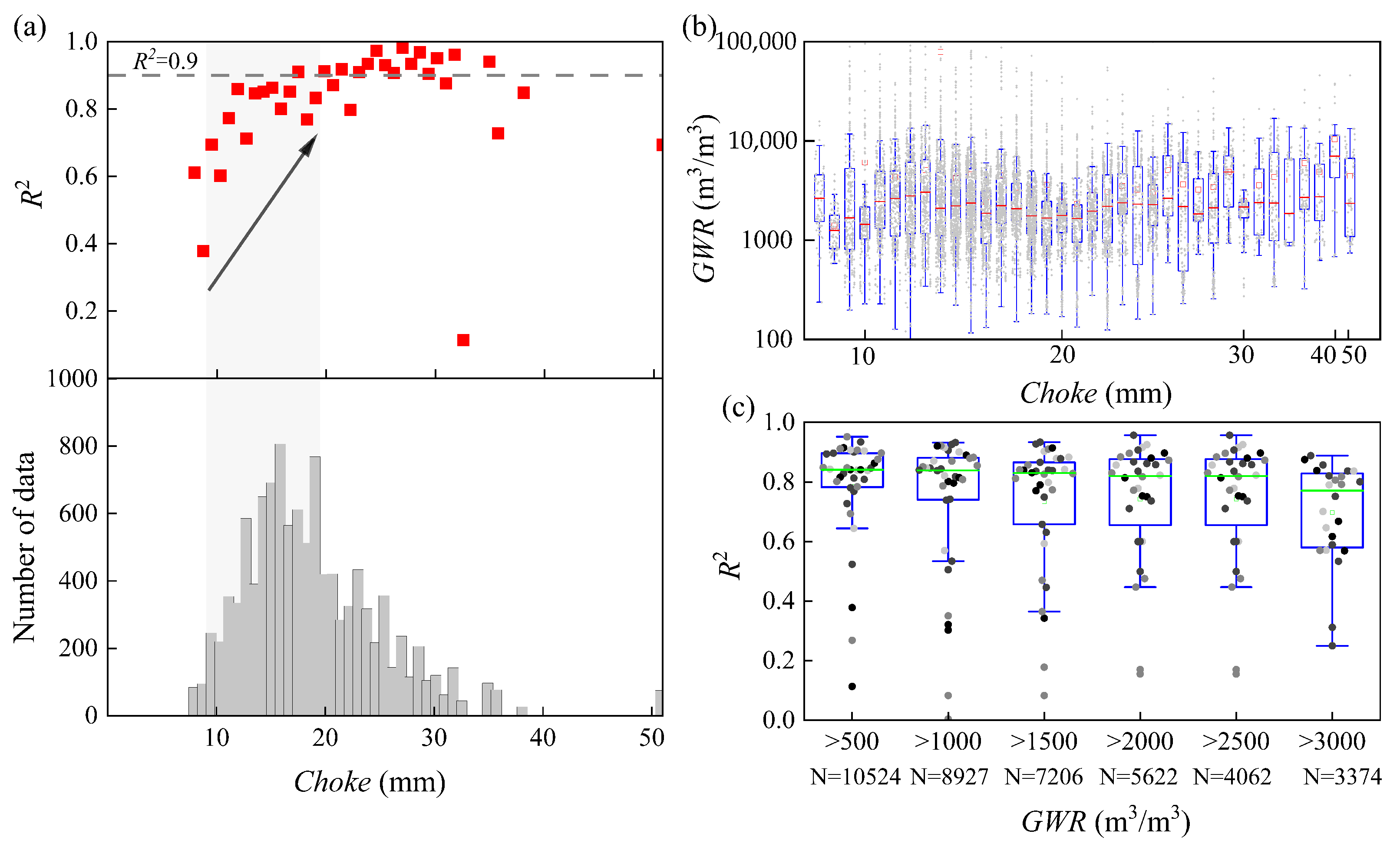
Figure 3 plots the distribution of choke size for flowback. The choke size generally varies from 4.762 mm to 50.8 mm (choke sizes greater than 50.8 mm were excluded from analysis due to the limited number of corresponding measurements). The choke-size data generally follow a normal distribution with a mean value of 19.3 mm (standard deviation: 6.2 mm).
Figure 3 shows asymmetric histograms for water rate, gas rate, and wellhead pressure. Water rate data follow a lognormal distribution with a long tail, suggesting a wide range across the dataset. Most wells were opened for flowback with a water rate of hundreds of cubic meters per day, which declined to just a few cubic meters per day within one to two weeks. A harmonic trend has been reported on water rate decline for shale gas wells [
13,
66]. The large variation in water rate is largely attributed to differences in fracturing treatment size and choke settings during early flowback.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Empirical Formula Fitting
Table 3 summarizes the fitting performance (
) of five empirical formulas [
26,
27,
28,
54,
55] applied to the flowback dataset. The five empirical formulas were originally developed to model gas and oil flow through chokes. Each formula was fitted to the flowback measurements, and the corresponding coefficients (
a,
b,
c, and
d) are also reported in
Table 3.
Overall, the results show an below 0.333, indicating that the empirical formulas are not suitable for capturing the complex relationship between flow rates, pressure, and choke size during multiphase flowback of water and gas.
4.2. Engineering Characteristics
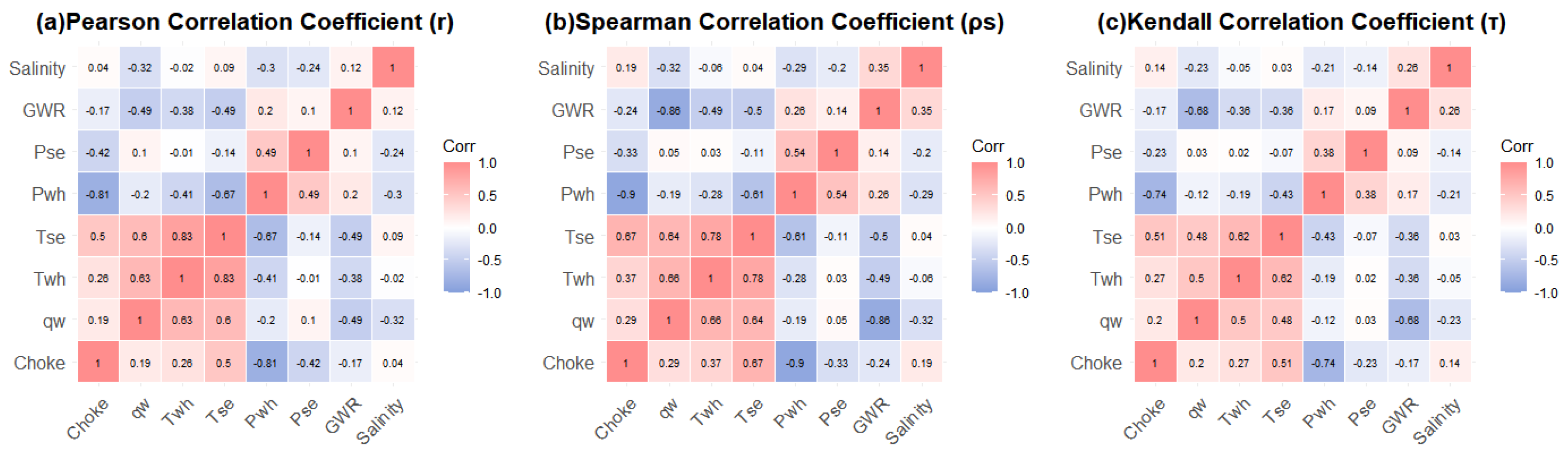
In
Figure 4, we plot the correlation matrix between flowback parameters (
18,660), including
,
,
,
,
,
,
, and
. We employed the Pearson, Spearman, and Kendall coefficient (
r,
, and
) correlations to measure the correlation between flowback parameters.
Table 4 lists the correlation coefficients between
and the remaining seven flowback features.
The positive and negative values of
r,
, and
for rates, pressure, and choke generally align with the trends described by empirical formulas (as listed in
Table 4). Water rate shows a positive correlation with choke size and a negative correlation with gas/water ratio. As shown in
Table 3, the results indicate a strong dependence of water rate on
,
,
, and
.
Overall, the results highlight strong correlations between choke size and several flowback variables, including , , , and . High inter-correlation among flowback measurements suggests strong interdependence between these parameters. Based on this analysis, we selected , , , , , , and as input features for machine learning.
4.3. Comparing the Machine Learning Algorithms
Figure 5 compares the ML-predicted and measured water rates during flowback. We evaluated eight ML algorithms: MLR, ANN, RF, RBF-SVM, LBF-SVM, XGBDART, XGBLinear, and XGBTree (refer to
Appendix C for the settings of hyperparameters of each ML algorithm). We split the flowback data into training and testing data at a 70:30 ratio. We ran each algorithm 100 times to reduce the impact of random variation in data splitting.
Overall, RF, XGBTree, XGBDART, and ANN achieve higher prediction accuracy than the other four algorithms. Among them, RF consistently outperforms all the others on both training and testing datasets. Comparatively, RBF-SVM, MLR, LBF-SVM, and XGBLinear produce lower accuracy. MLR and LBF-SVM may be limited in capturing the nonlinear relationships between water rate, pressure, and choke size.
In
Figure 6, we compare the performance metrics (
,
, and
) of eight ML algorithms on the testing data. Among the eight algorithms, RF achieves the highest
and lowest
and
. Also, the boxplots show a relatively small variation in
,
, and
across 100 runs. We thus recommend RF as a reliable ML algorithm for characterizing multiphase flowback behaviors through chokes.
4.4. Feature Selection for Choke Performance
4.4.1. Feature Importance Analysis from Machine Learning
Figure 7 compares the feature importance for predicting
using RF, XGBTree, XGBDART, and ANN algorithms. Consistently, GWR is the most influential input across the four algorithms. Also, RF, XGBTree, and XGBDART assign high importance to wellhead/separator temperature, followed by wellhead/separator pressure. The results of ANN suggest that choke size shows a notable contribution to water rate prediction. XGBTree and XGBDART further suggest that salinity may slightly affect water rate prediction, although its influence is minor compared with other variables. These findings indicate that GWR, wellhead temperature, wellhead pressure, and choke size are key parameters influencing multiphase flowback of water and gas.
In
Figure 7d, the results of ANN exhibit greater variability in feature importance across runs compared with RF, XGBTree, and XGBDART algorithms. One may expect that feature importance estimates may be more sensitive to random data splits in ANN models than in ensemble-based approaches.
4.4.2. Optimal Feature Combinations
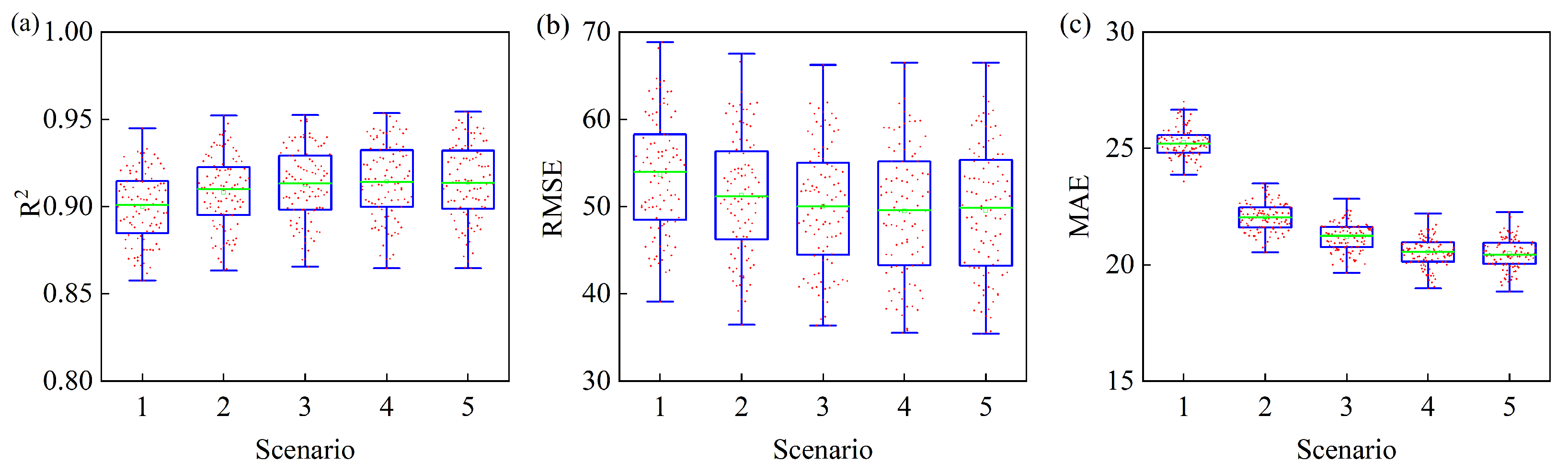
Figure 8 compares the performance metrics for five scenarios using the RF algorithm with different combinations of input features (refer to
Table 5 for the combination of features for each scenario). Each scenario was run 100 times to reduce the impact of randomness in training and testing splits (see
Figure 9 for the corresponding results of the RF algorithm for five scenarios with average
values for testing data).
As shown in
Figure 8, the average
generally increases from Scenario 1 to Scenario 5, while
and
generally decrease. The addition of separator pressure in Scenario 2 led to a notable reduction in prediction errors, highlighting its importance in characterizing choke performance. These findings support the use of wellhead and separator pressures as practical substitutes for upstream and downstream pressures in flowback analysis.
Comparing Scenarios 2, 3, and 4 highlights that including wellhead and separator temperatures further enhanced model accuracy. However, Scenario 4 achieved the highest average and lowest and among the five scenarios, suggesting that the effects of salinity are insignificant for describing choke–performance relationship during flowback. Therefore, we selected , , , , , , and for establishing choke–performance relationship.
4.5. The Effects of Training/Testing Split Ratio
Figure 10 compares the boxplots of
,
, and
for 10 runs using training/testing split ratios ranging from 50% to 90%. RF algorithm and features from Scenario 4 were used for the comparative analysis.
Table 6 lists the statistical results of 100 runs for each split ratio.
We observe a general improvement in predictive performance with a higher training/split ratio. As the split ratio increases, the average rises slightly, while and decline. The highest accuracy was achieved at a 90% split, suggesting that a larger training set enhances model performance. However, the benefits became marginal as the ratio increases further.
Figure 10 shows that the variability of prediction results increases with the split ratio. As shown by the widening boxplots in
Figure 10, the range of
,
, and
grows from a 50% to 90% split.
Table 6 confirms this trend through the corresponding maximum and minimum values. The greater spread implies a reduced model stability at a higher split ratio, which may result from increased noise in the training data or limited sample size in the test set. To balance accuracy and stability, we select a 70/30 training/testing split for the subsequent machine learning investigations.
5. Establishing the New Choke–Performance Relationship
In this section, we introduce four new choke–performance relationships and compare their fitting accuracy against the traditional Gilbert-type formula.
5.1. Choke–Performance Relationships
Equation (
4) describes the Gilbert-type choke–performance relationship, which requires four coefficients (
a,
b,
c, and
d). As described by Equations (
5)–(
7), we propose three new types of choke–performance relationships by incorporating the effects of separator pressure and temperatures at both the wellhead and separator (see the results of feature analysis in
Section 4.4). The new choke–performance relationships require six coefficients (
a,
b,
c,
d,
e, and
f), and the coefficients are determined by multivariate least squares fitting.
Here, represents the water production volume, m3/d; Choke denotes the size of the choke valve, mm; indicates the wellhead pressure, MPa; represents the pressure in the separator, MPa; signifies the wellhead temperature, K; is the temperature in the separator, K; is the gas/water ratio, m3/m3; and a, b, c, d, e, and f are empirical coefficients obtained by multivariate least squares fitting to flowback measurements.
In
Table 7, we compare
and the coefficients for four types of choke–performance relationships with and without the conditions of
, respectively (we excluded the choke size which has less than 100 measurements for the fitting). Overall, we observe an improved fitting accuracy by including
, suggesting the positive influence of
on the model.
Incorporating temperature and separator pressure slightly increases
by comparing the fitting results of Equations (
4)–(
7). Comparatively, the inclusion of separator pressure alone shows limited benefit by comparing the fitting results of Equations (
6) and (
7). Also, a high fitting accuracy is reached by Equation (
6). Consequently, we employ Equation (
6) for subsequent analyses, considering the fitting accuracy under the two pressure ratio conditions.
Interestingly, we reach a relatively higher fitting accuracy after screening the flowback data by . The results generally align with earlier studies which suggest that the Gilbert-type model performs best under critical flow conditions (i.e., when downstream-to-upstream pressure ratio is below 0.5). However, we recognize the mismatch between actual downstream pressure and the separator pressure used in our model. Future studies should examine the critical ratio of for the choke-performance relationships.
5.2. The Effects of Choke-Size Range
In
Figure 11a, we plot the fitting results of
for each choke size (7.938 to 50.800 mm) based on the proposed choke-performance model (Equation (
6)). We excluded the choke size with fewer than 20 data points, and also excluded the choke size of 63.5 mm due to high variation in
for the comparative analysis.
As shown in
Figure 11a,
generally increases with choke size increasing from 7.938 to 19.844 mm, aligning with the increasing number of measurements (see
Figure 11a below). The results indicate that larger datasets improve the reliability of the fitted coefficients.
In general, the proposed model performs best for choke sizes between 17.462 and 34.925 mm. In this range,
values typically exceed 0.9 (
Figure 12). However, exceptions exist in choke sizes of 30 mm and 32.544 mm, which show a lower accuracy (see
Figure A2 in
Appendix B) primarily due to smaller datasets (
and
, respectively). We therefore recommend applying the proposed model and coefficients specifically within the 17.462–34.925 mm range.
In
Figure 11a, the results show a decreasing trend in
for a choke size greater than 30.162 mm. The reduced accuracy at large choke sizes is partially attributed to fewer available measurements. Also,
Figure 11b shows a relatively larger variation in
for a choke size bigger than 30.162 mm, which may further reduce model accuracy.
By applying a natural logarithm to Equation (
6), the proposed model becomes conceptually similar to a multiple linear regression. However, the results of the multiple linear regression indicate limited predictive performance at extremely high water rates (refer to
Figure 5). The proposed model is thus expected to perform more reliably under stabilized water rate conditions during flowback.
Figure 11c compares
with
across all the choke sizes. Excluding low
values from the dataset generally reduces
, suggesting the proposed model is more effective under low-
conditions. However, the limited data for large choke sizes also contributes to reduced accuracy. Therefore, the proposed choke-performance model shows satisfying performance in characterizing multiphase flowback. Future work is encouraged to validate the model with more flowback data, particularly for larger choke sizes and a wider range of
conditions.
6. Significance, Limitations, and Future Works
Our data-driven study demonstrated that ML models were a valuable tool for characterizing multiphase flowback through chokes at wellhead. Also, a simplified version of an empirical choke-performance model we proposed provides reliable predictions under multiphase conditions for flowback. The ML and empirical models offer tools that help monitor the choke conditions [
69] during flowback. The models also offer a practical way to estimate flared gas volumes [
70,
71,
72,
73] during early flowback, using common field data such as water rate, choke size, and wellhead pressure. While the results are promising, this study is subject to several limitations that suggest opportunities for future research, as outlined below.
We selected the flowback data from 37 Horn River wells mainly because of the abundance of hourly flowback measurements. We also clarify that the findings of this study should not be constrained by a specific field or basin, and further validation is needed wherever flowback data from other fields are available.
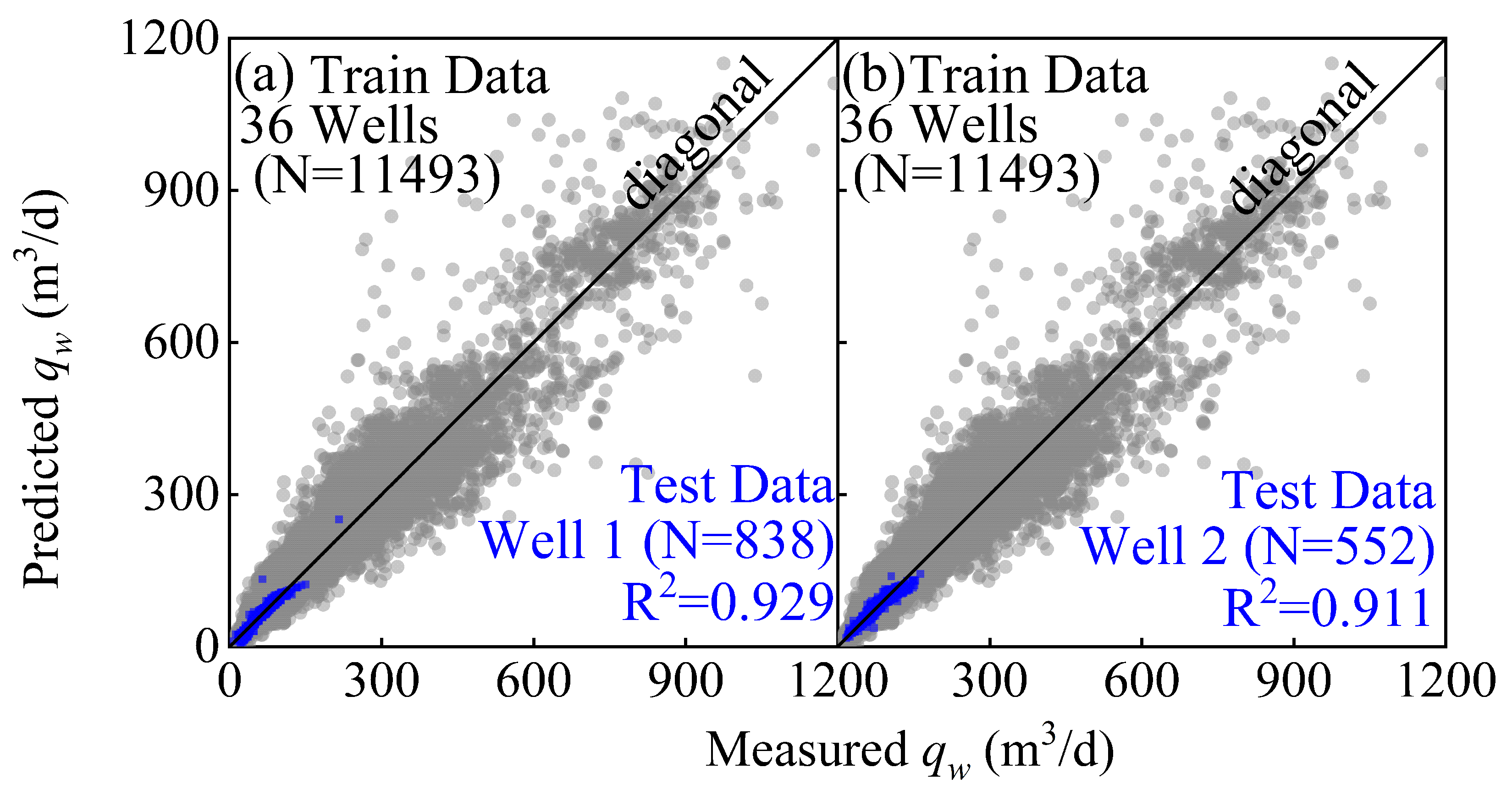
We acknowledge the potential for data leakage due to the random sampling approach used to split the training and testing datasets across 37 wells. The random sampling method may allow neighboring data points from the same well and day to appear in both training and testing sets, which may artificially boost model performance. To address this concern, we conducted an additional test using a well-by-well data split. Specifically, we used flowback data from 36 wells for training and reserved one well for testing, and the results suggested that the model maintained a high predictive accuracy (see two case studies in
Appendix D). The results suggest that the data-leakage effects are likely minimal. Future studies are recommended to employ time-series ML methods for multiphase choke flowback data, which may better capture temporal patterns and reduce the risk of data leakage related to sampling across time.
This study used a standard set of ML algorithms for data-driven investigation on the problem of multiphase flowback through chokes. We chose these algorithms based on their proven effectiveness in petroleum-engineering applications. Using multiple algorithms also allowed us to identify the most suitable one for our flowback data and ensure strong predictive performance. Future studies are recommended to explore more advanced ML techniques to further enhance model accuracy and generalization.
7. Summary and Conclusions
In this study, we collected a total of 18,660 measurements of a multiphase flowback dataset from 37 shale gas wells from the Horn River Basin. We performed eight machine learning algorithms on the flowback dataset to predict the choke performance, and identified the key features for describing choke–performance relationship. We further established a new choke–performance relationship for multiphase flowback based on the results of machine learning. A set of coefficients for the new choke–performance relationship is recommended for certain ranges of choke size during flowback. The key conclusions are summarized as follows:
(1) In this study, the empirical choke–performance correlations and coefficients traditionally developed for oil and gas flow are inadequate for modeling gas and water flowback data.
(2) Applying the machine learning algorithms of Random Forest, XGBTree, XGBDART, and ANN on the flowback data leads to a high prediction accuracy in choke performance. The prediction accuracy of Random Forest is improved by including the separator pressure and temperature into the inputs of choke size, gas/water ratio, and wellhead pressure and temperature.
(3) This study developed a new choke–performance relationship which links the flowback rate with choke size, gas/water ratio, wellhead pressure/temperature, and separator temperature. The accuracy of new choke–performance relationships and coefficients has been validated for choke sizes ranging from 17.462 to 34.925 mm. The new choke–performance relationship presented in this study needs further validation in other fields wherever more flowback data are available.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.F.; Software, K.H. and Y.G.; Validation, Y.F.; Formal analysis, Y.F.; Investigation, K.H. and Y.G.; Data curation, K.H. and Y.G.; Writing—original draft, K.H. and Y.G.; Writing—review & editing, Y.F.; Visualization, K.H.; Project administration, Y.F.; Funding acquisition, Y.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U22B2073 and No. 52104044).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52104044, and U22B2073). We also thank the British Columbia Energy Regulator (BCER) for making their wells’ data available to the University of Alberta.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| The fitting parameters of the formula. |
| N | The number of recorded data. |
| The water rate, in /d. |
| The gas rate, in /d. |
| The water rate, in STB/day. |
| The size of choke, in mm. |
| The size of choke, in inch/64. |
| The gas-to-water ratio, in /. |
| The gas-to-water ratio, in Scf/STB. |
| The wellhead pressure, in MPa. |
| The wellhead pressure, in psig. |
| The separator pressure, in MPa. |
| The wellhead temperature, in K. |
| The separator temperature, in K. |
| The salinity of flowback water, in ppm. |
| r | Pearson correlation coefficient. |
| Spearman correlation coefficient. |
| Kendall correlation coefficient. |
| The coefficient of determination. |
| The root mean squared error. |
| The mean absolute error. |
| Machine learning. |
| Multiple linear regression model. |
| Artificial neural network model. |
| Random forest model. |
| Support vector machine. |
| Linear basis function–support vector machine model. |
| Radial basis function–support vector machine model. |
| Extreme gradient boosting. |
| Extreme gradient boosting tree model. |
| Dropout additive regression trees model. |
| Extreme gradient boosting linear model. |
Appendix A
Table A1.
Statistical analysis of choke size for each well (17,646 records of measurements after being preprocessed).
Table A1.
Statistical analysis of choke size for each well (17,646 records of measurements after being preprocessed).
| Well Name | First Value
(mm) | Maximum
(mm) | Minimum
(mm) | Average
(mm) | Standard Deviation
(mm) | Time Range
(d) | Number of
Choke |
|---|
| Well-1 | 11.906 | 63.500 | 7.144 | 20.869 | 10.814 | 5 | 638 |
| Well-2 | 9.525 | 63.500 | 7.144 | 36.677 | 24.241 | 21 | 544 |
| Well-3 | 7.938 | 63.500 | 7.938 | 24.962 | 17.890 | 20 | 489 |
| Well-4 | 11.112 | 63.500 | 7.144 | 23.792 | 16.616 | 5 | 546 |
| Well-5 | 11.906 | 63.500 | 7.144 | 19.866 | 13.043 | 1 | 571 |
| Well-6 | 12.700 | 63.500 | 6.350 | 24.168 | 16.943 | 19 | 464 |
| Well-7 | 11.906 | 63.500 | 6.350 | 21.512 | 14.120 | 16 | 482 |
| Well-8 | 7.938 | 63.500 | 7.938 | 20.524 | 10.378 | 20 | 488 |
| Well-9 | 7.938 | 63.500 | 7.938 | 22.353 | 12.428 | 39 | 927 |
| Well-10 | 10.319 | 63.500 | 6.350 | 23.056 | 17.249 | 1 | 422 |
| Well-11 | 12.700 | 63.500 | 6.350 | 45.317 | 22.477 | 29 | 1176 |
| Well-12 | 12.700 | 63.500 | 8.731 | 44.418 | 22.729 | 31 | 789 |
| Well-13 | 9.525 | 63.500 | 9.525 | 25.133 | 12.531 | 26 | 622 |
| Well-14 | 12.700 | 63.500 | 6.350 | 22.159 | 14.038 | 18 | 455 |
| Well-15 | 11.906 | 63.500 | 7.938 | 27.021 | 16.310 | 36 | 868 |
| Well-16 | 12.700 | 63.500 | 4.762 | 23.933 | 16.255 | 13 | 335 |
| Well-17 | 11.906 | 19.844 | 11.906 | 15.624 | 2.142 | 1 | 19 |
| Well-18 | 19.050 | 63.500 | 15.875 | 59.231 | 12.638 | 14 | 378 |
| Well-19 | 9.525 | 63.500 | 9.525 | 55.544 | 17.029 | 7 | 176 |
| Well-20 | 20.638 | 63.500 | 9.525 | 54.721 | 15.928 | 10 | 399 |
| Well-21 | 19.050 | 63.500 | 19.050 | 50.989 | 18.615 | 5 | 122 |
| Well-22 | 17.462 | 63.500 | 9.525 | 55.049 | 15.967 | 11 | 385 |
| Well-23 | 14.288 | 63.500 | 14.288 | 53.382 | 18.926 | 6 | 146 |
| Well-24 | 14.288 | 63.500 | 12.700 | 48.814 | 19.773 | 17 | 506 |
| Well-25 | 12.700 | 63.500 | 12.700 | 38.216 | 20.391 | 4 | 89 |
| Well-26 | 19.050 | 63.500 | 19.050 | 56.599 | 14.649 | 12 | 301 |
| Well-27 | 19.050 | 63.500 | 9.525 | 23.918 | 14.932 | 9 | 701 |
| Well-28 | 11.112 | 63.500 | 11.112 | 26.477 | 17.861 | 14 | 376 |
| Well-29 | 11.112 | 63.500 | 9.525 | 27.281 | 17.060 | 18 | 695 |
| Well-30 | 11.112 | 63.500 | 11.112 | 29.753 | 16.742 | 7 | 186 |
| Well-31 | 9.525 | 63.500 | 7.144 | 19.437 | 13.563 | 14 | 779 |
| Well-32 | 12.700 | 63.500 | 9.525 | 21.150 | 10.096 | 23 | 842 |
| Well-33 | 11.112 | 63.500 | 9.525 | 26.286 | 15.694 | 11 | 344 |
| Well-34 | 12.700 | 63.500 | 4.762 | 20.536 | 11.549 | 20 | 781 |
| Well-35 | 11.112 | 63.500 | 7.938 | 26.496 | 17.535 | 4 | 281 |
| Well-36 | 12.700 | 63.500 | 11.112 | 27.953 | 15.952 | 7 | 324 |
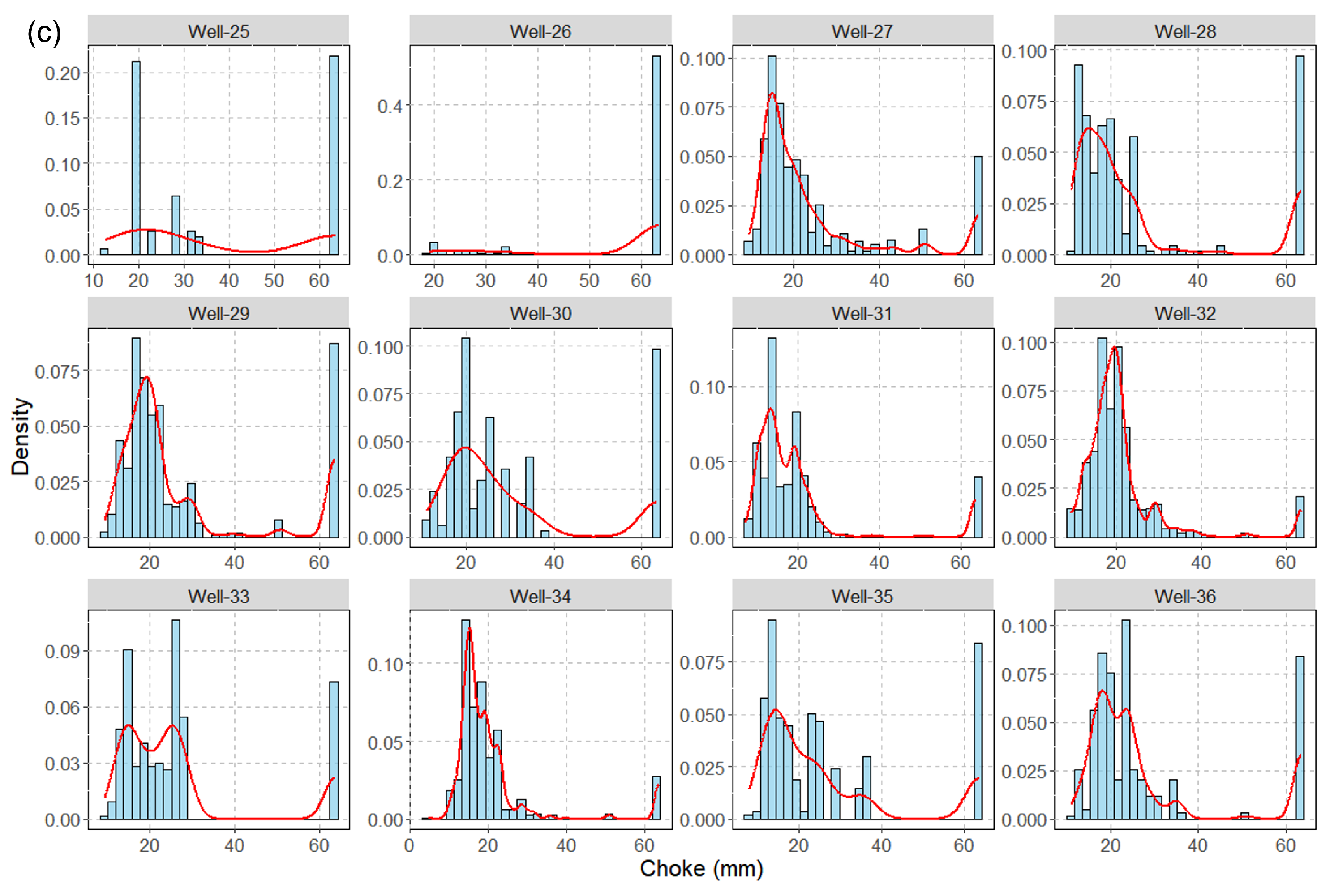
Figure A1.
Statistical analysis of flowback choke size for each well ((a): Well-1 to Well 12, (b): Well-13 to Well-24, and (c): Well-25 to Well 36).
Figure A1.
Statistical analysis of flowback choke size for each well ((a): Well-1 to Well 12, (b): Well-13 to Well-24, and (c): Well-25 to Well 36).
Appendix B
Figure A2.
Scatter plot of the fitting prediction values of the new formula (Formula (6)) and the measured values for the flowback data of different choke sizes and gas/water ratios. The black solid line represents the reference line .
Figure A2.
Scatter plot of the fitting prediction values of the new formula (Formula (6)) and the measured values for the flowback data of different choke sizes and gas/water ratios. The black solid line represents the reference line .
Appendix C
Table A2.
Summary of ML algorithms and corresponding hyperparameters used in this study.
Table A2.
Summary of ML algorithms and corresponding hyperparameters used in this study.
| Model | Hyperparameters |
|---|
| MLR | Repeated k-fold cross-validation.
k is 5.
Number of repetitions is 100. |
| ANN | Repeated k-fold cross-validation.
Maximum iterations are 500.
Neurons per hidden layer are 50–100.
Weight decay is 0.0001. |
| RF | Number of trees in forest is 100.
Number of variables randomly selected is 7.
Random split verification (repeated 3 times). |
| RBF-SVM | C parameter is .
Sigma parameter is automatically calculated (gamma = scale). |
| LBF-SVM | 100 independent random divisions verification.
C parameter is . |
| XGBDART | Maximum depth of a tree is 6.
Iterations are 100.
Step size is 0.1.
Subsample ratio of columns is 0.8.
Subsample ratio of the training instances is 0.6. |
| XGBLinear | Iterations are 100.
Step size is 0.1. |
| XGBTree | Iterations are 100.
Step size is 0.1.
Lambda is 1.0. |
Appendix D
Figure A3.
Two cases illustrating the minimal effects of data leakage sampling on predictive accuracy. Flowback measurements from 36 wells were treated as training dataset, and another well’s flowback data were treated as testing dataset.
Figure A3.
Two cases illustrating the minimal effects of data leakage sampling on predictive accuracy. Flowback measurements from 36 wells were treated as training dataset, and another well’s flowback data were treated as testing dataset.
References
- Alkouh, A.; McKetta, S.; Wattenbarger, R.A. Estimation of effective-fracture volume using water-flowback and production data for shale-gas wells. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2014, 53, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezulike, O.D. Complementary Workflows for Analyzing Multiphase Flowback and Post-Flowback Production Data in Unconventional Reservoirs. Doctoral Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezulike, D.O.; Dehghanpour, H. Modelling flowback as a transient two-phase depletion process. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 19, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarkson, C.R.; Williams-Kovacs, J. Modeling Two-Phase Flowback of Multifractured Horizontal Wells Completed in Shale. SPE J. 2013, 18, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dehghanpour, H.; Ezulike, O.; Virues, C. Effectiveness and time variation of induced fracture volume: Lessons from water flowback analysis. Fuel 2017, 210, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Ezulike, O.; Fu, Y.; Dehghanpour, H. Average fracture compressibility from flowback data. SPE Prod. Oper. 2021, 36, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, T.; Fu, Y.; Dehghanpour, H.; Hawkes, R. Coupled Versus Stratified Flow of Water and Hydrocarbon During Flowback and Post-flowback Processes. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, SPE, Denver, CO, USA, 30 March–5 May 2020; p. D031S033R004. [Google Scholar]
- Moussa, T.; Dehghanpour, H.; Fu, Y.; Ezulike, O. The use of flowback data for estimating dynamic fracture volume and its correlation with completion-design parameters: Eagle Ford cases. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 195, 107584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezulike, O.D.; Dehghanpour, H. A complementary approach for uncertainty reduction in post-flowback production data analysis. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 1074–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Feng, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, B.; Lu, M.; Pan, Z. Optimal packing ratio of proppant monolayer for partially-propped horizontal bedding fractures of shale. Gas Sci. Eng. 2025, 135, 205563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Fu, Y.; Xu, L. Evaluating the Effects of Proppant Flowback on Fracture Conductivity in Tight Reservoirs: A Combined Analytical Modeling and Simulation Study. Energies 2024, 17, 4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Liu, Y.T.; Zhang, G.D.; Su, B.; Liu, X.F.; Tang, P.C.; Xia, B.; Hu, Y.F. A new fracturing flowback strategy based on proppant backflow factor (PBF)—A case study from Weirong and Yongchuan shale gas, Sichuan Basin, China. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2025, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Dehghanpour, H.; Motealleh, S.; Lopez, C.; Hawkes, R. Evaluating Fracture Volume Loss During Flowback and Its Relationship to Choke Size: Fastback vs. Slowback. SPE Prod. Oper. 2019, 34, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, T.; Daal, J.; Tucker, J. Maximizing well deliverability in the Eagle Ford shale through flowback operations. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, SPE, Houston, TX, USA, 28–30 September 2015; p. D011S002R005. [Google Scholar]
- Osiptsov, A.; Garagash, I.; Boronin, S.; Tolmacheva, K.; Lezhnev, K.; Paderin, G. Impact of flowback dynamics on fracture conductivity. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 188, 106822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagci, S.; Stolyarov, S. Flowback production optimization for choke size management strategies in unconventional wells. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, SPE, Calgary, AB, Canada, 30 September–2 October 2019; p. D021S023R001. [Google Scholar]
- Potapenko, D.; Theuveny, B.; Williams, R.; Moncada, K.; Campos, M.; Spesivtsev, P.; Willberg, D. State of the art of flow management for frac plug drillout and flowback. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, SPE, Calgary, AB, Canada, 30 September–2 October 2019; p. D021S023R002. [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins, D.; Sieker, R.; Koseluk, D.; Cartaya, H. Managed Pressure Flowback in Unconventional Reservoirs: A Permian Basin Case Study. In Proceedings of the SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference. URTeC, San Antonio, TX, USA, 1–3 August 2016; pp. 2687–2696. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, R.; Molavi, K. Viscosity correction factor for safety relief valves. Process Saf. Prog. 1997, 16, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, R. Correlate pressure drops through fittings. Chem. Eng. 1999, 106, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen, C.M.; Kanstad, S.K. Multiphase Flow Through Chokes-An Evaluation of Frozen, Equilibrium, and Nonequilibrium Flow Models. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 215, 110402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Li, Z.; Bore, T.; Torres, S.A.G.; Scheuermann, A.; Li, L. A lattice Boltzmann exploration of two-phase displacement in 2D porous media under various pressure boundary conditions. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 14, 1782–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, A.; Dehghanpour, H.; Ghanbari, E.; Bearinger, D. Fracture characterization using flowback salt-concentration transient. SPE J. 2016, 21, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lai, F.; Li, Z.; Fu, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y. The effect of temperature on flowback data analysis in shale gas reservoirs: A simulation-based study. Energies 2019, 12, 3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omana, R.; Houssiere, C., Jr.; Brown, K.E.; Brill, J.P.; Thompson, R.E. Multiphase flow through chokes. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, SPE, Denver, CO, USA, 28 September–1 October 1969; p. SPE-2682. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, W. Flowing and gas-lift well performance. In Drilling and Production Practice; SPE: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Baxendell, P. Bean Performance-Lake Wells; Shell Internal Report; Shell: London, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Ros, N. An analysis of critical simultaneous gas/liquid flow through a restriction and its application to flowmetering. Appl. Sci. Res. 1960, 9, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunati, F. Two-phase flow through wellhead chokes. In Proceedings of the SPE Europec Featured at EAGE Conference and Exhibition, SPE, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 16–19 May 1972; p. SPE-3742. [Google Scholar]
- Ashford, F. An evaluation of critical multiphase flow performance through wellhead chokes. J. Pet. Technol. 1974, 26, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashford, F.; Pierce, P.E. The Determination of Multiphase Pressure Drops and Flow Capacities in Downhole Safety Valves (Storm Chokes). Pap. SPE 1974, 5161, 6–9. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Attar, H.; Abdul-Majeed, G. Revised bean performance equation for East Baghdad oil wells. SPE Prod. Eng. 1988, 3, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Attar, H.H. New correlations for critical and subcritical two-phase flow through surface chokes in high-rate oil wells. In Proceedings of the SPE Latin America and Caribbean Petroleum Engineering Conference, SPE, Cartagena, Columbia, 31 May–3 June 2009; p. SPE-120788. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, T.K. Critical and subcritical flow of multiphase mixtures through chokes. SPE Drill. Complet. 1993, 8, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.E.; Dokla, M.E. Gas condensate flow through chokes. In Proceedings of the SPE Europec featured at EAGE Conference and Exhibition, SPE, The Hague, The Netherlands, 17–20 October 1990; p. SPE-20988. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei-Paiaman, A.; Salavati, S. A new empirical correlation for sonic simultaneous flow of oil and gas through wellhead chokes for Persian oil fields. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2013, 35, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalifa, M.A.; Al-Marhoun, M.A. Application of neural network for two-phase flow through chokes. In Proceedings of the SPE Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Annual Technical Symposium and Exhibition, SPE, Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia, 24–27 May 2013; p. SPE-169597. [Google Scholar]
- Kaydani, H.; Najafzadeh, M.; Mohebbi, A. Wellhead choke performance in oil well pipeline systems based on genetic programming. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2014, 5, 06014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surbey, D.; Kelkar, B.; Brill, J. Study of subcritical flow through multiple-orifice valves. SPE Prod. Eng. 1988, 3, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surbey, D.; Kelkar, B.; Brill, J. Study of multiphase critical flow through wellhead chokes. SPE Prod. Eng. 1989, 4, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Hou, T.; Zou, L.; Li, W.; Lin, K. Optimizing Choke Operations in Shale Gas Horizontal Wells: A Comprehensive Study. Improv. Oil Gas Recovery 2025, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, P.N.; Irazuzta, V.L.; Curtti, M.A.; Álvarez, M.G. Flowback and Well Testing Operational Learnings During an Early Production Stage in a Vaca Muerta Field. In Proceedings of the SPE Argentina Exploration and Production of Unconventional Resources Symposium. SPE, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 20–22 March 2023; p. D021S009R001. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J. Piecewise Gilbert-type correlation for two-phase flowback through wellhead chokes in hydraulically fractured shale gas wells. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2024, 42, 428–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasriani, H.R.; Khan, K.; Graham, T.; Ndlovu, S.; Nasriani, M.; Mai, J.; Rafiee, M.R. An investigation into sub-critical choke flow performance in high rate gas condensate wells. Energies 2019, 12, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri, M.S.; Hadavimoghaddam, F.; Ashoorian, S.; Schaffie, M.; Hemmati-Sarapardeh, A. Modeling liquid rate through wellhead chokes using machine learning techniques. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, H.; Wood, D.A.; Choubineh, A.; Tatar, A.; Mohamadian, N. Prediction of oil flow rate through an orifice flow meter: Artificial intelligence alternatives compared. Petroleum 2020, 6, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubineh, A.; Ghorbani, H.; Wood, D.A.; Moosavi, S.R.; Khalafi, E.; Sadatshojaei, E. Improved predictions of wellhead choke liquid critical-flow rates: Modelling based on hybrid neural network training learning based optimization. Fuel 2017, 207, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, H.; Moghadasi, J.; Wood, D.A. Prediction of gas flow rates from gas condensate reservoirs through wellhead chokes using a firefly optimization algorithm. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 45, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Ghamartale, A.; Abbasi, J.; Darvish, H.; Tatar, A. Prediction of Critical Multiphase Flow Through Chokes by Using A Rigorous Artificial Neural Network Method. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2019, 69, 101579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, M.; Elhaj, M.; Abdulraheem, A. Optimization of choke size for two-phase flow using artificial intelligence. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2020, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorjaei, R.G.; Songolzadeh, R.; Torkaman, M.; Safari, M.; Zargar, G. A novel PSO-LSSVM model for predicting liquid rate of two phase flow through wellhead chokes. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAjmi, M.D.; Alarifi, S.A.; Mahsoon, A.H. Improving multiphase choke performance prediction and well production test validation using artificial intelligence: A new milestone. In Proceedings of the SPE Digital Energy Conference and Exhibition. SPE, The Woodlands, TX, USA, 3–5 March 2015; p. D031S022R003. [Google Scholar]
- Barjouei, H.S.; Ghorbani, H.; Mohamadian, N.; Wood, D.A.; Davoodi, S.; Moghadasi, J.; Saberi, H. Prediction performance advantages of deep machine learning algorithms for two-phase flow rates through wellhead chokes. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. 2021, 11, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achong, I. Revised Bean Performance Formula for Lake Maracaibo Wells; Internal Company Report; Shell Oil Co.: Houston, TX, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Pilehvari, A. Experimental Study of Critical Two-Phase Flow Through Wellhead Chokes: University of Tulsa; Technical report, Research report; University of Tulsa Fluid Flow Projects: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, S.; Mohammadi, M.R.; Bahmaninia, H.; Hemmati-Sarapardeh, A.; Schaffie, M.; Norouzi-Apourvari, S.; Ranjbar, M. Experimental measurement and modeling of asphaltene adsorption onto iron oxide and lime nanoparticles in the presence and absence of water. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.A.; Abirami, S. Aspect-based opinion ranking framework for product reviews using a Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient method. Inf. Sci. 2018, 460–461, 23–41. [Google Scholar]
- Lapata, M. Automatic Evaluation of Information Ordering: Kendall’s Tau. Comput. Linguist. 2006, 32, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamian, A.; Heidaryan, E.; Ostadhassan, M. Evaluation of different machine learning frameworks to predict CNL-FDC-PEF logs via hyperparameters optimization and feature selection. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Fu, Y. Production Forecast of Deep-Coalbed-Methane Wells Based on Long Short-Term Memory and Bayesian Optimization. SPE J. 2024, 29, 3651–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Dehghanpour, H. How far can hydraulic fractures go? A comparative analysis of water flowback, tracer, and microseismic data from the Horn River Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 115, 104259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.A. A Comparative Study of Flowback Rate and Pressure Transient Behaviour in Multifractured Horizontal Wells. Master’s Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, M.A.; Ezulike, D.O.; Dehghanpour, H.; Hawkes, R.V. A comparative study of flowback rate and pressure transient behavior in multifractured horizontal wells completed in tight gas and oil reservoirs. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 17, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Adefidipe, O.; Dehghanpour, H. Estimating fracture volume using flowback data from the Horn River Basin: A material balance approach. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 25, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Dehghanpour, H. Advances in flowback analysis: Fracturing water production obeys a simple decline model. In Unconventional Shale Gas Development; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 299–321. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanbari, E.; Dehghanpour, H. The fate of fracturing water: A field and simulation study. Fuel 2016, 163, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharak, A.Z. Analysis of Shale-Water Interactions and Flowback Water Chemistry for Fracture Characterization. Doctoral Thesis, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sæther, J.H. Choke Condition and Performance Monitoring. Master’s Thesis, Norges Teknisk-Naturvitenskapelige Universitet, Trondheim, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Glazer, Y.R.; Davidson, F.T.; Lee, J.J.; Webber, M.E. An inventory and engineering assessment of flared gas and liquid waste streams from hydraulic fracturing in the USA. Curr. Sustain./Renew. Energy Rep. 2017, 4, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.; Alzahabi, A. Pilot Demonstration of a New Tip for Effective Gas Flaring in the Permian Basin: Part 1. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 47440–47451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.T.; Allen, G.; Pitt, J.; Shah, A.; Wilde, S.; Stamford, L.; Fan, Z.; Ricketts, H.; Williams, P.I.; Bateson, P.; et al. Methane flux from flowback operations at a shale gas site. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2020, 70, 1324–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, A.; Bahadur, V. Using excess natural gas for reverse osmosis-based flowback water treatment in US shale fields. Energy 2020, 196, 117145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Flowchart of data-driven investigation on multiphase flowback through chokes.
Figure 1.
Flowchart of data-driven investigation on multiphase flowback through chokes.
Figure 2.
The flowback profiles of rates, wellhead/separator pressures and temperature, choke size, and salinity for a typical multi-fractured horizontal well completed in the Horn River Shale.
Figure 2.
The flowback profiles of rates, wellhead/separator pressures and temperature, choke size, and salinity for a typical multi-fractured horizontal well completed in the Horn River Shale.
Figure 3.
Statistical distribution of characteristic parameters of 37 wells. The distribution curves were fitted using Gaussian normal distribution and lognormal distribution models.
Figure 3.
Statistical distribution of characteristic parameters of 37 wells. The distribution curves were fitted using Gaussian normal distribution and lognormal distribution models.
Figure 4.
Correlation matrix of (a) Pearson, (b) Spearman and (c) Kendall coefficients between flowback measurements.
Figure 4.
Correlation matrix of (a) Pearson, (b) Spearman and (c) Kendall coefficients between flowback measurements.
Figure 5.
Scatter plots of machine learning-predicted water rate versus measured values for training and testing data using eight algorithms. The training and testing data are represented in black and blue, respectively, with a fixed 7:3 split ratio. The black solid line represents the y = x reference line.
Figure 5.
Scatter plots of machine learning-predicted water rate versus measured values for training and testing data using eight algorithms. The training and testing data are represented in black and blue, respectively, with a fixed 7:3 split ratio. The black solid line represents the y = x reference line.
Figure 6.
Boxplots comparing the prediction performance of (a) , (b) , and (c) of eight machine learning algorithms. Each algorithm was run 100 times for statistic analysis.
Figure 6.
Boxplots comparing the prediction performance of (a) , (b) , and (c) of eight machine learning algorithms. Each algorithm was run 100 times for statistic analysis.
Figure 7.
Boxplots comparing the variable importance interpreted by the (a) RF, (b) XGBTree, (c) XGBDART, and (d) ANN machine learning algorithms based on the statistic results of 100 runs.
Figure 7.
Boxplots comparing the variable importance interpreted by the (a) RF, (b) XGBTree, (c) XGBDART, and (d) ANN machine learning algorithms based on the statistic results of 100 runs.
Figure 8.
Boxplots of (a) , (b) , and (c) for 5 scenarios with different combinations of features feeding into RF algorithm. Each scenario was run 100 times with different random seeds, resulting in a total of 500 observations, as illustrated in the boxplots for each scenario.
Figure 8.
Boxplots of (a) , (b) , and (c) for 5 scenarios with different combinations of features feeding into RF algorithm. Each scenario was run 100 times with different random seeds, resulting in a total of 500 observations, as illustrated in the boxplots for each scenario.
Figure 9.
Fitting results of RF-predicted and measured values of water rate predictions for 5 scenarios for a selected run with fixed training and testing datasets. The training data and test data are represented by black and blue, respectively.
Figure 9.
Fitting results of RF-predicted and measured values of water rate predictions for 5 scenarios for a selected run with fixed training and testing datasets. The training data and test data are represented by black and blue, respectively.
Figure 10.
Boxplots comparing the prediction metrics, including (a) , (b) , and (c) , with training/testing split ratios for Scenario 4 using RF model. At each split ratio, the RF model was run 100 times with a different random seed.
Figure 10.
Boxplots comparing the prediction metrics, including (a) , (b) , and (c) , with training/testing split ratios for Scenario 4 using RF model. At each split ratio, the RF model was run 100 times with a different random seed.
Figure 11.
Fitting results of new choke–performance relationship to the flowback measurements: (a) Comparing for each choke size (upper) with total data sample numbers (lower) for multivariate regression fitting between choke-performance model and measurements; (b) the gas/water ratio changes as a function of choke size; (c) boxplots comparing the fitting results of with varying gas/water ratio (the choke size with limited numbers were excluded for correlation analysis).
Figure 11.
Fitting results of new choke–performance relationship to the flowback measurements: (a) Comparing for each choke size (upper) with total data sample numbers (lower) for multivariate regression fitting between choke-performance model and measurements; (b) the gas/water ratio changes as a function of choke size; (c) boxplots comparing the fitting results of with varying gas/water ratio (the choke size with limited numbers were excluded for correlation analysis).
Figure 12.
Scatter plot of measured water rate with that calculated by the choke–performance relationship (Equation (
6)) with coefficients listed in
Table 7) for the chokes with a fitting
> 0.9. The black solid line represents the reference line y = x. The transparency of colors for data points highlights the values of
.
Figure 12.
Scatter plot of measured water rate with that calculated by the choke–performance relationship (Equation (
6)) with coefficients listed in
Table 7) for the chokes with a fitting
> 0.9. The black solid line represents the reference line y = x. The transparency of colors for data points highlights the values of
.
Table 1.
Empirical correlations and coefficients for multiphase flow through chokes [
53].
Table 1.
Empirical correlations and coefficients for multiphase flow through chokes [
53].
| References | Equation | Empirical Formula | Coefficient |
|---|
| Gilbert [26] | (1) | | , , |
| | | | , |
| Baxendell [27] | (2) | | , , |
| | | | , |
| Ros [28] | (3) | | , , |
| | | | , |
| Achong [54] | (4) | | , , |
| | | | , |
| Pilehvari [55] | (5) | | , , |
| | | | , |
Table 2.
Statistics of 18,660 flowback surface measurements from 37 Horn River Shale gas wells.
Table 2.
Statistics of 18,660 flowback surface measurements from 37 Horn River Shale gas wells.
| Flowback Features | Abbreviations | Maximum Value | Minimum Value | Average Value |
|---|
| Gas Rate () | | 1,087,000 | 71,830 | 429,803 |
| Water Rate () | | 2706 | 0 | 288.6 |
| Gas/Water Ratio () | | 36,693,222 | 33.1 | 7800 |
| Choke Size (mm) | | 63.5 | 4.8 | 33.3 |
| Wellhead Pressure (MPa) | | 31.1 | 2.4 | 12.3 |
| Separator Pressure (MPa) | | 9.3 | 1.1 | 4.9 |
| Wellhead Temperature (K) | | 390.0 | 277.0 | 368.8 |
| Separator Temperature (K) | | 381.0 | 274.0 | 360.2 |
| Salinity (ppm) | | 340,000 | 4000 | 30,266 |
Table 3.
Fitting results for five empirical formulas and coefficients (note that the parameters and coefficients were developed based on field units).
Table 3.
Fitting results for five empirical formulas and coefficients (note that the parameters and coefficients were developed based on field units).
| Empirical Model | Formulas | Coefficients | |
|---|
| Gilbert [26] | | , | 0.287 |
| Baxendell [27] | | , | 0.277 |
| Ros [28] | | , | 0.241 |
| Achong [54] | | , | 0.333 |
| Pilehvari [55] | | , | 0.145 |
Table 4.
Correlation coefficients of water rate with 7 flowback parameters.
Table 4.
Correlation coefficients of water rate with 7 flowback parameters.
| Features | Correlation |
|---|
Pearson
Coefficient ()
|
Spearman
Coefficient ()
|
Kendall
Coefficient ()
|
|---|
| 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.20 |
| −0.49 | −0.86 | −0.68 |
| −0.20 | −0.19 | −0.12 |
| 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.50 |
| 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.48 |
| −0.32 | −0.32 | −0.23 |
Table 5.
Statistics of RF models’ performance metrics for 5 scenarios with different combinations of input features.
Table 5.
Statistics of RF models’ performance metrics for 5 scenarios with different combinations of input features.
| Scenarios | Input Features | Performance Metrics | Maximum Value | Minimum Value | Average Value |
|---|
| | | 0.945 | 0.858 | 0.900 |
| 1 | , , | | 68.871 | 39.108 | 53.641 |
| | | | 27.013 | 23.581 | 25.251 |
| | | 0.952 | 0.863 | 0.908 |
| 2 | , , , | | 67.508 | 36.481 | 51.313 |
| | | | 23.489 | 20.532 | 22.045 |
| , , , | | 0.952 | 0.866 | 0.912 |
| 3 | | 66.235 | 36.399 | 50.055 |
| | | | 22.832 | 19.662 | 21.192 |
| | | 0.953 | 0.865 | 0.914 |
| 4 | , , , | | 66.503 | 35.533 | 49.466 |
| | , | | 22.213 | 18.993 | 20.542 |
| | | 0.954 | 0.865 | 0.914 |
| 5 | , , , | | 66.490 | 35.465 | 49.575 |
| | , , | | 22.271 | 18.851 | 20.474 |
Table 6.
Statistics of performance metrics of 100 runs of RF model for varying training/testing split ratio.
Table 6.
Statistics of performance metrics of 100 runs of RF model for varying training/testing split ratio.
| Training/Testing Split Ratio | Performance Metrics | Maximum Value | Minimum Value | Average Value |
|---|
| | 0.945 | 0.878 | 0.913 |
| 5:5 | | 60.963 | 39.349 | 50.161 |
| | | 22.745 | 20.389 | 21.386 |
| | 0.952 | 0.874 | 0.916 |
| 6:4 | | 61.166 | 36.388 | 49.154 |
| | | 22.049 | 19.394 | 20.873 |
| | 0.953 | 0.865 | 0.914 |
| 7:3 | | 66.512 | 35.542 | 49.470 |
| | | 22.215 | 18.999 | 20.543 |
| | 0.962 | 0.865 | 0.922 |
| 8:2 | | 66.996 | 32.576 | 46.925 |
| | | 21.877 | 18.372 | 20.093 |
| | 0.963 | 0.780 | 0.922 |
| 9:1 | | 82.405 | 30.325 | 46.219 |
| | | 22.850 | 17.769 | 19.855 |
Table 7.
Fitting results of four choke-performance relationships with and without the condition of , respectively (the relationships and coefficients are described in SI units).
Table 7.
Fitting results of four choke-performance relationships with and without the condition of , respectively (the relationships and coefficients are described in SI units).
| Formula | All Flowback Data | Flowback Data with |
|---|
| ( = 10,623)
|
Coefficients
| ( = 9512)
|
Coefficients
|
|---|
| 0.919 | a = 292.1303; b = 0.7344;
c = 1.2602; d = 0.7921 | 0.921 | a = 480.5830; b = 1.0008;
c = 1.3178; d = 0.8091 |
| 0.930 | a = 231.0883; b = 0.8067;
c = 1.0591; d = 0.7723;
e = −0.3309 | 0.933 | a = 375.1778; b = 1.1307;
c = 1.1563; d = 0.7905;
e = −0.4238 |
| 0.932 | a = 633.9690; b = 0.5943;
c = 1.0874; d = 0.7662;
e = −0.8210 | 0.933 | a = 469.2333; b = 0.6581;
c = 1.1816; d = 0.7851;
e = −0.7563 |
| 0.932 | a = 616.4024; b = 0.6647;
c = 1.0757; d = 0.7664;
e = −0.0615; f = −0.6988 | 0.933 | a = 396.6285; b = 1.0439;
c = 1.1577; d = 0.7890;
e = −0.3490; f = −0.1506 |
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).