Process Performance and Biogas Output: Impact of Fluctuating Acetate Concentrations on Methanogenesis in Horizontal Anaerobic Reactors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate and Inoculum
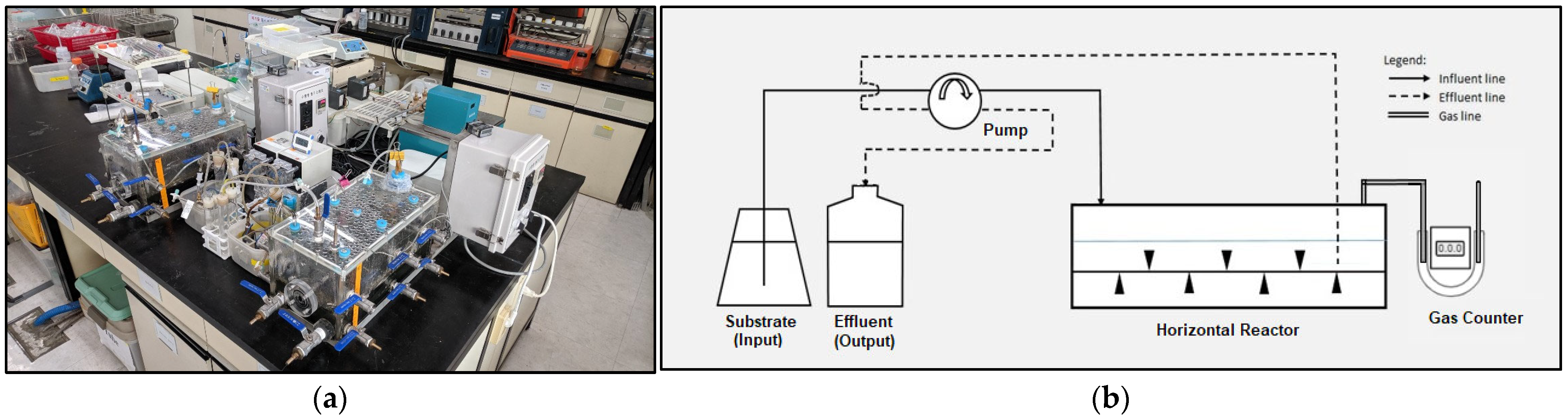
2.2. Horizontal Anaerobic Reactor (HAR)
2.3. Experimental Conditions and Setup
2.4. Physicochemical Analyses
2.5. Microbial Community Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
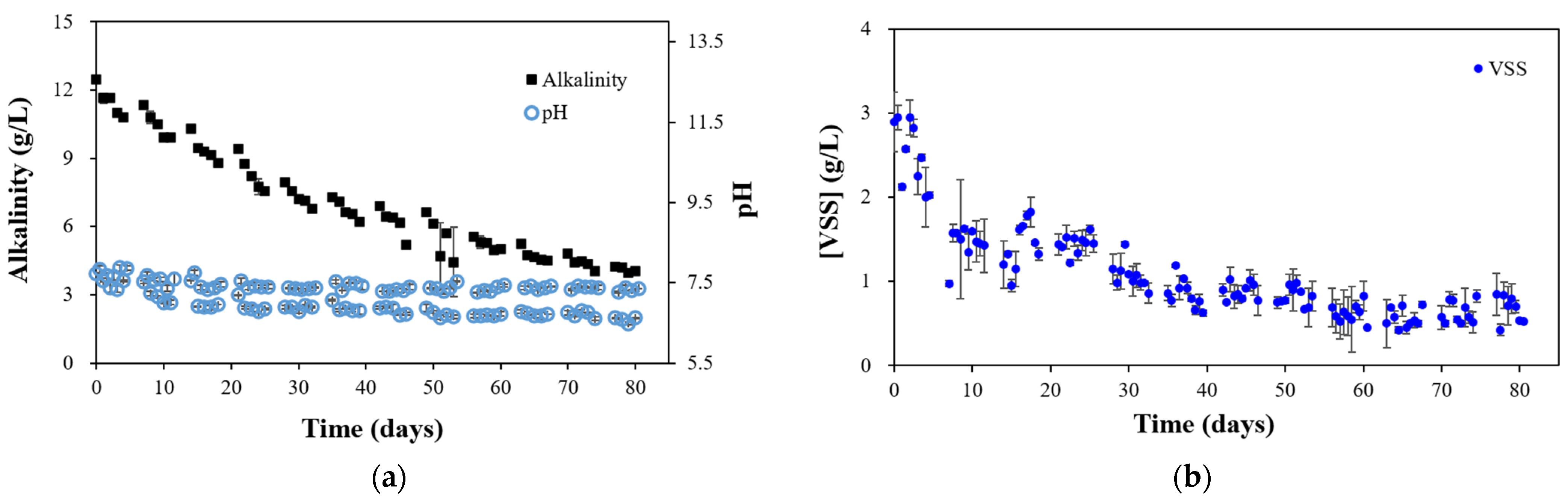
3.1. Horizontal Anaerobic Reactor (HAR) Performance
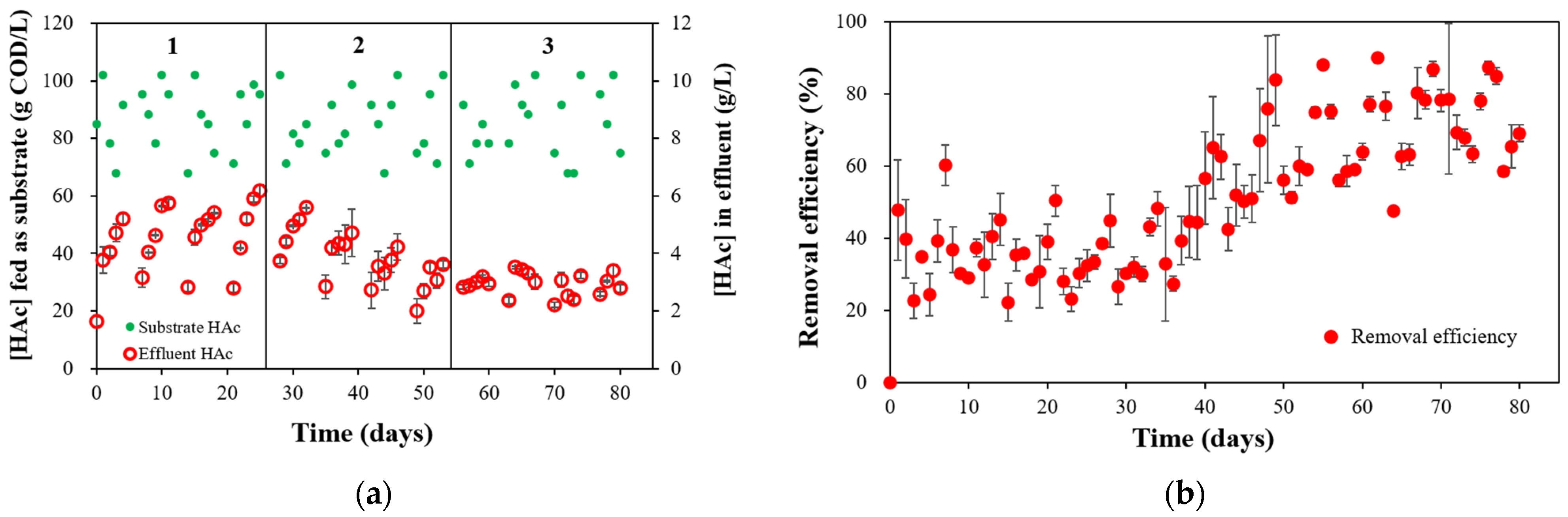
3.2. Substrate Degradation
3.3. Biogas Production and Composition
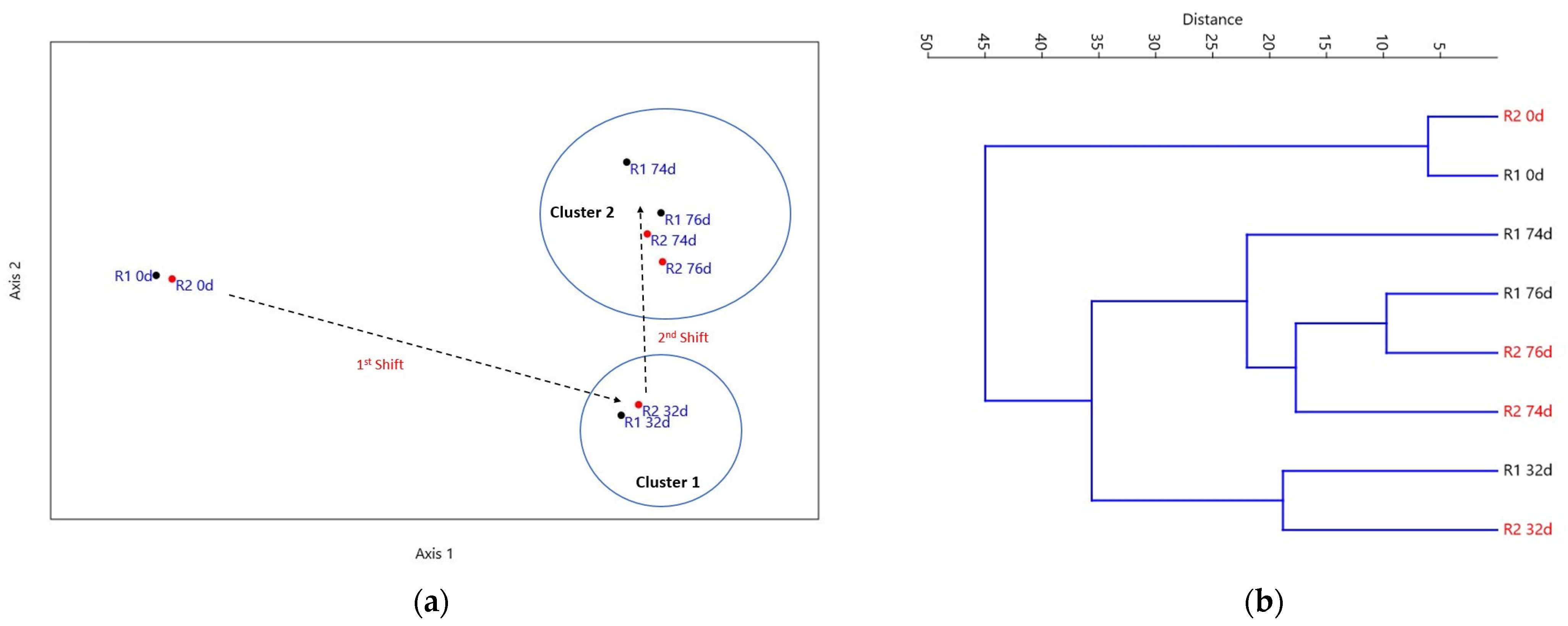
3.4. Microbial Community Analysis
3.5. Statistical Analysis
3.6. Implications, Applications, and Recommendations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Jo, Y.; Rhee, C.; Choi, H.; Shin, J.; Shin, S.G.; Lee, C. Long-term effectiveness of bioaugmentation with rumen culture in continuous anaerobic digestion of food and vegetable wastes under feed composition fluctuations. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 338, 125500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, K.; Wei, L. Effects of organic loading rates on high-solids anaerobic digestion of food waste in horizontal flow reactor: Methane production, stability and mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Switching from wet to dry anaerobic digestion of food waste with different dilution times under no mechanical mixing condition. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurgaliyev, N.; Akimzhanov, A.; Klivenko, A.; Sabitova, A.; Astemessova, K.; Turlybekova, G.; Nyssanbayeva, S.; Kurmangaliyev, R. Mathematical Model of Biomethane Yield at Anaerobic Methane Fermentation of Organic Wastes: Influence of Various Parameters and Factors. Eng. Sci. Publ. 2024, 26, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, C.P.C.; Lim, L.Y.; Lee, C.T.; Klemeš, J.J.; Ho, C.S.; Ho, W.S. The characterisation and treatment of food waste for improvement of biogas production during anaerobic digestion—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1545–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; El-Mashad, H.M.; Hartman, K.; Wang, F.; Liu, G.; Choate, C.; Gamble, P. Characterization of food waste as feedstock for anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeghems, G.; Buysse, J. Changing old habits: The case of feeding patterns in anaerobic digesters. Renew. Energy 2016, 92, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurade, M.B.; Saha, S.; Salama, E.S.; Patil, S.M.; Govindwar, S.P.; Jeon, B.-H. Acetoclastic methanogenesis led by Methanosarcina in anaerobic co-digestion of fats, oil and grease for enhanced production of methane. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, K.; Paruch, L.; Gaby, J.C.; Linjordet, R. Feeding frequency influences process performance and microbial community composition in anaerobic digesters treating steam exploded food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziels, R.M.; Beck, D.A.C.; Stensel, H.D. Long-chain fatty acid feeding frequency in anaerobic codigestion impacts syntrophic community structure and biokinetics. Water Res. 2017, 117, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleyböcker, A.; Liebrich, M.; Verstraete, W.; Kraume, M.; Würdemann, H. Early warning indicators for process failure due to organic overloading by rapeseed oil in one-stage continuously stirred tank reactor, sewage sludge and waste digesters. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 123, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulat, D.G.; Fabian Jacobi, H.; Feilberg, A.; Adamsen, A.P.S.; Richnow, H.-H.; Nikolausz, M.; Kelly, R.M. Changing feeding regimes to demonstrate flexible biogas production: Effects on process performance, microbial community structure, and methanogenesis pathways. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonk, F.; Popp, D.; Weinrich, S.; Sträuber, H.; Kleinsteuber, S.; Harms, H.; Centler, F. Intermittent fasting for microbes: How discontinuous feeding increases functional stability in anaerobic digestion. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.C.; de Toledo, R.A.; Shim, H. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and domestic wastewater—Effect of intermittent feeding on short and long chain fatty acids accumulation. Renew. Energy 2018, 124, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cheng, H.; Liu, J.; Hazen, T.C.; Huang, V.; He, Q. Unexpected competitiveness of Methanosaeta populations at elevated acetate concentrations in methanogenic treatment of animal wastewater. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño-Cerezo, S.; Pastor, J.M.; Renilla, S.; Bernal, V.; Iborra, J.L.; Cánovas, M. An insight into the role of phosphotransacetylase (pta) and the acetate/acetyl-CoA node in Escherichia coli. Microb. Cell Fact. 2009, 8, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, G.P.; Gogarten, J.P. Evolution of acetoclastic methanogenesis in Methanosarcina via horizontal gene transfer from cellulolytic Clostridia. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 1124–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, H.; Claus, P.; Casper, P.; Conrad, R. Carbon isotope fractionation during acetoclastic methanogenesis by Methanosaeta concilii in culture and a lake sediment. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Lin, R.; Li, L.; Wu, B.; Deng, C.; O’SHea, R.; Sun, Y.; Murphy, J.D. Assessment of pretreatment and digestion temperature on anaerobic digestion of whiskey byproducts and microbial taxonomy. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 243, 114331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillet, F.; Crestey, E.; Gaval, G.; Haddad, M.; Lebars, F.; Nicolitch, O.; Camacho, P. Utilization of dissolved CO2 to control methane and acetate production in methanation reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 416, 131722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, M.S.M.; Stams, A.J.M.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Methanogenesis from acetate: A comparison of the acetate metabolism in Methanothrix soehngenii and Methanosarcina spp. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1992, 88, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Du, B.; He, K.; Yin, Q.; Wu, G. Mechanistic understanding of acclimation and energy metabolism of acetoclastic methanogens under different substrate to microorganism ratios. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Sun, A.; Yang, S.; Ni, R.; Lin, X.; Shu, W.; Price, G.; Song, L. Dominance of acetoclastic methanogenesis in municipal solid waste (MSW) decomposition despite high variability in microbial community composition: Insights form natural stable carbon isotope and metagenomic analyses. Energy Environ. Sustain. 2025, 1, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hanifa Jannat, M.; Hyeok Park, S.; Chairattanawat, C.; Yulisa, A.; Hwang, S. Effect of different microbial seeds on batch anaerobic digestion of fish waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 349, 126834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Quiroga, X.; Aboudi, K.; Álvarez-Gallego, C.J.; Romero-García, L.I. Successful and stable operation of anaerobic thermophilic co-digestion of sun-dried sugar beet pulp and cow manure under short hydraulic retention time. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA-AWWA-WEF. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washinton, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Hwang, S. Group-specific primer and probe sets to detect methanogenic communities using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 89, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, E.; Han, G.; Tongco, J.V.; Shin, S.G.; Hwang, S. Microbial communities underpinning mesophilic anaerobic digesters treating food wastewater or sewage sludge: A full-scale study. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Shin, S.G.; Jannat, M.A.H.; Tongco, J.V.; Hwang, S. Use of food waste-recycling wastewater as an alternative carbon source for denitrification process: A full-scale study. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Koo, T.; Yulisa, A.; Hwang, S. Magnetite as an enhancer in methanogenic degradation of volatile fatty acids under ammonia-stressed condition. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopnarain, A.; Nkuna, R.; Ndaba, B.; Adeleke, R. New insights into the metagenomic link between pre-treatment method, addition of an inoculum and biomethane yield during anaerobic digestion of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 3217–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.A.; Garcia, M.L.; Veskivar, M.; Karim, K.; Al-Dahhan, M.H.; Angenent, L.T. Effect of Shear on Performance and Microbial Ecology of Continuously Stirred Anaerobic Digesters Treating Animal Manure. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2008, 100, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goberna, M.; Gadermaier, M.; García, C.; Wett, B.; Insam, H. Adaptation of Methanogenic Communities to the Cofermentation of Cattle Excreta and Olive Mill Wastes at 37 °C and 55 °C. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Du, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y. Comparison of mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste: Focusing on methanogenic performance and pathogens removal. Renew. Energy 2024, 233, 121184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanov, B.I.; Tzanova, A.I. Influence of Dairy Cattle Diet on Manure’s Methanogenic Potential for Biogas Generation. In Proceedings of the 16th Electrical Engineering Faculty Conference (BulEF 2024), Varna, Bulgaria, 19–22 September 2024; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Varna, Bulgaria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Palacios, P.A.; Sieborg, M.U.; Kuipers, S.B.; Fruergaard, S.; Kofoed, M.V. Temperature tactics: Targeting acetate or methane production in autotrophic H2/CO2 conversion with mixed cultures. Biochem. Eng. J. 2025, 214, 109574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battumur, U.; Yoon, Y.; Bae, G.S.; Kim, C.H. Isolation and characterization of new Methanosarcina mazei strains KOR-3, -4, -5, and -6 from an anaerobic digester using pig slurry. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Duan, H.; Han, W.; Liu, Y.; Shao, L.; Lü, F. Responses of Methanosarcina barkeri to acetate stress. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmissi, M.; Harmand, J.; Alcaraz-Gonzalez, V.; Shayeb, H. Evaluation of alkalinity spatial distribution in an up-flow fixed bed anaerobic digester. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.R.; Hands, C.L.; Coello-Garcia, T.; Sani, B.; Ott, A.; Smith, S.; Davenport, R. A flow cytometry method for bacterial quantification and biomass estimates in activated sludge. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 160, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Hansen, C.L. Evaluating a correlation between volatile suspended solid and adenosine 5’-triphosphate levels in anaerobic treatment of high organic suspended solids wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 63, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongco, J.V.; Kim, S.; Oh, B.; Heo, S.-Y.; Lee, J.; Hwang, S. Enhancement of Hydrolysis and Biogas Production of Primary Sludge by Use of Mixtures of Protease and Lipase. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2020, 25, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.G.; Park, S.H.; Hwang, S. Substrate Characteristics Fluctuations in Full-Scale Anaerobic Digesters Treating Food Waste at Marginal Organic Loading Rates: A Case Study. Energies 2022, 15, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Aghasa, A.; Choi, S.; Hong, S.; Park, T.; Hwang, S. Variations in Lipid Accumulation and Methanogenic Predominance in Full-Scale Anerobic Digestors Treating Food Waste Leachate. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 3223–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Jannat, M.A.H.; Hwang, S. Annual Physicochemical Characteristics and Biogas Potential of Food Waste from a Coastal City in Korea. J. Korea Soc. Waste Manag. 2022, 39, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Gong, C.; Wang, J.; Tian, S.; Zhang, Y. Effects of ultrasound pre-treatment on the amount of dissolved organic matter extracted from food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 155, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shin, S.G.; Han, G.; Koo, T.; Hwang, S. Bacteria and archaea communities in full-scale thermophilic and mesophilic anaerobic digesters treating food wastewater: Key process parameters and microbial indicators of process instability. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Mbadinga, S.M.; Liu, J.F.; Zhou, L.; Yang, S.-Z.; Gu, J.-D.; Mu, B.-Z. Microbiota and their affiliation with physiochemical characteristics of different subsurface petroleum reservoirs. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 120, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, P.S.; Borrel, G.; Gribaldo, S. Evolutionary history of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase/acetyl-CoA synthase, one of the oldest enzymatic complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1166–E1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, D.; Chauhan, S.S.; Ferry, J.G. Life on the thermodynamic edge: Respiratory growth of an acetotrophic methanogen. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, 9059–9080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.G. Methanosarcina acetivorans: A Model for Mechanistic Understanding of Aceticlastic and Reverse Methanogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 545389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botello Suárez, W.A.; da Silva Vantini, J.; Duda, R.M.; Giachetto, P.F.; Cintra, L.C.; Ferro, M.I.T.; de Oliveira, R.A. Predominance of syntrophic bacteria, Methanosaeta and Methanoculleus in a two-stage up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor treating coffee processing wastewater at high organic loading rate. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vrieze, J.; Pinto, A.J.; Sloan, W.T.; Ijaz, U.Z. The active microbial community more accurately reflects the anaerobic digestion process: 16S rRNA (gene) sequencing as a predictive tool. Microbiome 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.S.; Ingram-Smith, C. Methanosaeta, the forgotten methanogen? Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conklin, A.; Stensel, H.D.; Ferguson, J. Growth Kinetics and Competition Between Methanosarcina and Methanosaeta in Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion. Water Environ. Res. 2006, 78, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Welte, C.; Deppenmeier, U. Acetate Activation in Methanosaeta thermophila: Characterization of the Key Enzymes Pyrophosphatase and Acetyl-CoA Synthetase. Archaea 2012, 2012, 315153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tomb, J.F.; Ferry, J.G. Electron transport in acetate-grown Methanosarcina acetivorans. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlin, L.; Gunsalus, R.P. Carbon-dependent control of electron transfer and central carbon pathway genes for methane biosynthesis in the Archaean, Methanosarcina acetivorans strain C2A. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.K.; Im, W.T.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, M.-H.; Shin, H.-S.; Oh, S.-E. Dry anaerobic digestion of food waste under mesophilic conditions: Performance and methanogenic community analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 131, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakat, N.; Schmidt, S.; Scherer, P. Potential impact of process parameters upon the bacterial diversity in the mesophilic anaerobic digestion of beet silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5692–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccune, B. Influence of noisy environmental data on canonical correspondence analysis. Ecology 1997, 78, 2617–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Unit | Value * |
|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 8.14 |
| COD | g CODcr/L | 19.6 ± 0.4 |
| sCOD | g/L | 2.6 ± 0.0 |
| TS | g/L | 28.0 ± 0.4 |
| VS | g/L | 12.6 ± 0.1 |
| VS/TS | % | 45.1 |
| TSS | g/L | 20.3 ± 0.7 |
| VSS | g/L | 12.3 ± 0.4 |
| VFA + Ethanol | g/L | 0.07 ± 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tongco, J.V.; Jannat, M.A.H.; Kim, S.; Park, S.H.; Hwang, S. Process Performance and Biogas Output: Impact of Fluctuating Acetate Concentrations on Methanogenesis in Horizontal Anaerobic Reactors. Energies 2025, 18, 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123120
Tongco JV, Jannat MAH, Kim S, Park SH, Hwang S. Process Performance and Biogas Output: Impact of Fluctuating Acetate Concentrations on Methanogenesis in Horizontal Anaerobic Reactors. Energies. 2025; 18(12):3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123120
Chicago/Turabian StyleTongco, Jovale Vincent, Md Abu Hanifa Jannat, Sangmin Kim, Sang Hyeok Park, and Seokhwan Hwang. 2025. "Process Performance and Biogas Output: Impact of Fluctuating Acetate Concentrations on Methanogenesis in Horizontal Anaerobic Reactors" Energies 18, no. 12: 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123120
APA StyleTongco, J. V., Jannat, M. A. H., Kim, S., Park, S. H., & Hwang, S. (2025). Process Performance and Biogas Output: Impact of Fluctuating Acetate Concentrations on Methanogenesis in Horizontal Anaerobic Reactors. Energies, 18(12), 3120. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18123120







