A Systematic Approach of Global Sensitivity Analysis and Its Application to a Model for the Quantification of Resilience of Interconnected Critical Infrastructures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling for Resilience Analysis
2.1. Modeling Approach
2.2. System Parameters
2.3. System Resilience Metric
2.4. Resilience Indicators for ICIs
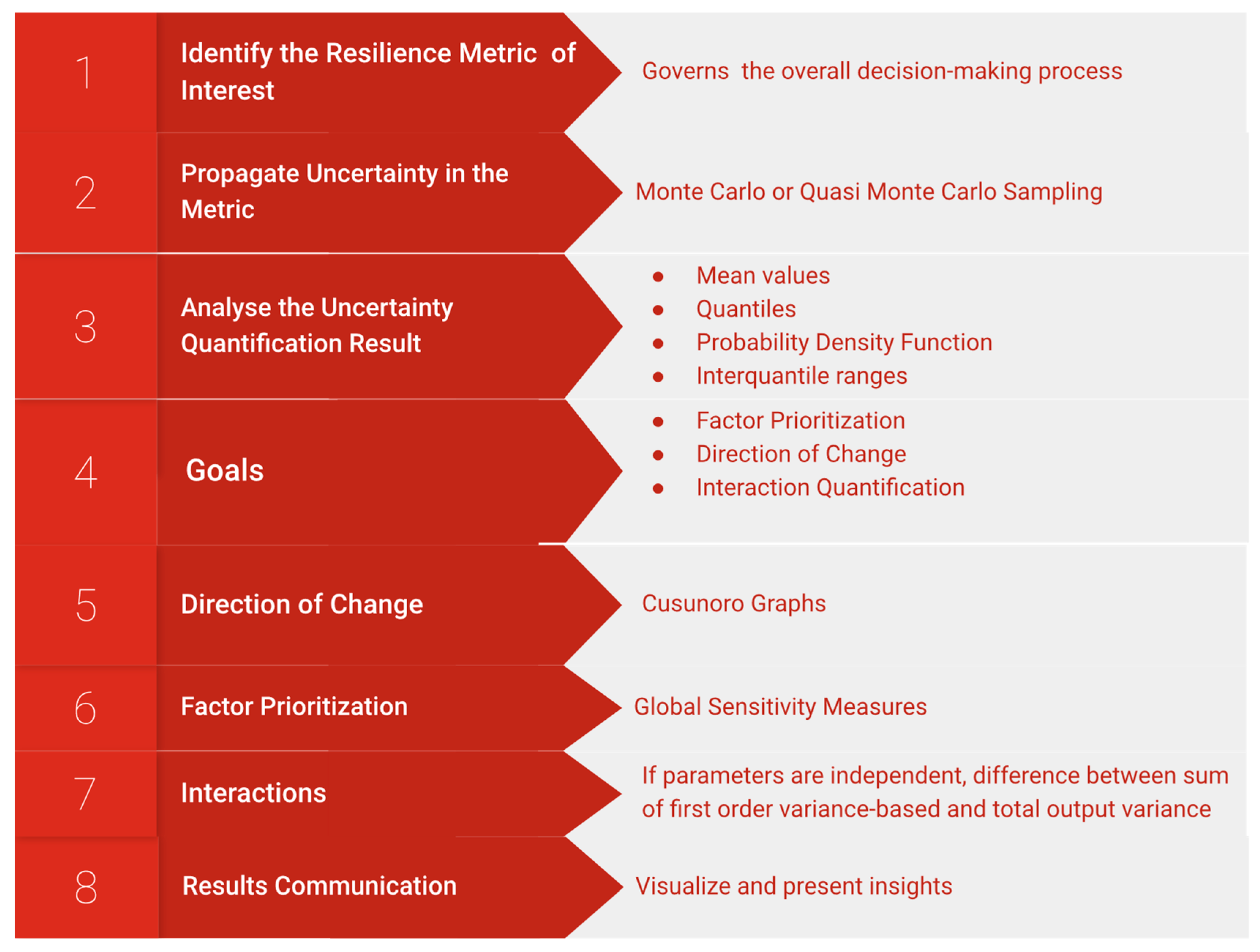
3. Global Sensitivity Approach
3.1. A General Framework for Global Sensitivity Methods
3.2. Computational Issues of Global Sensitivity Methods
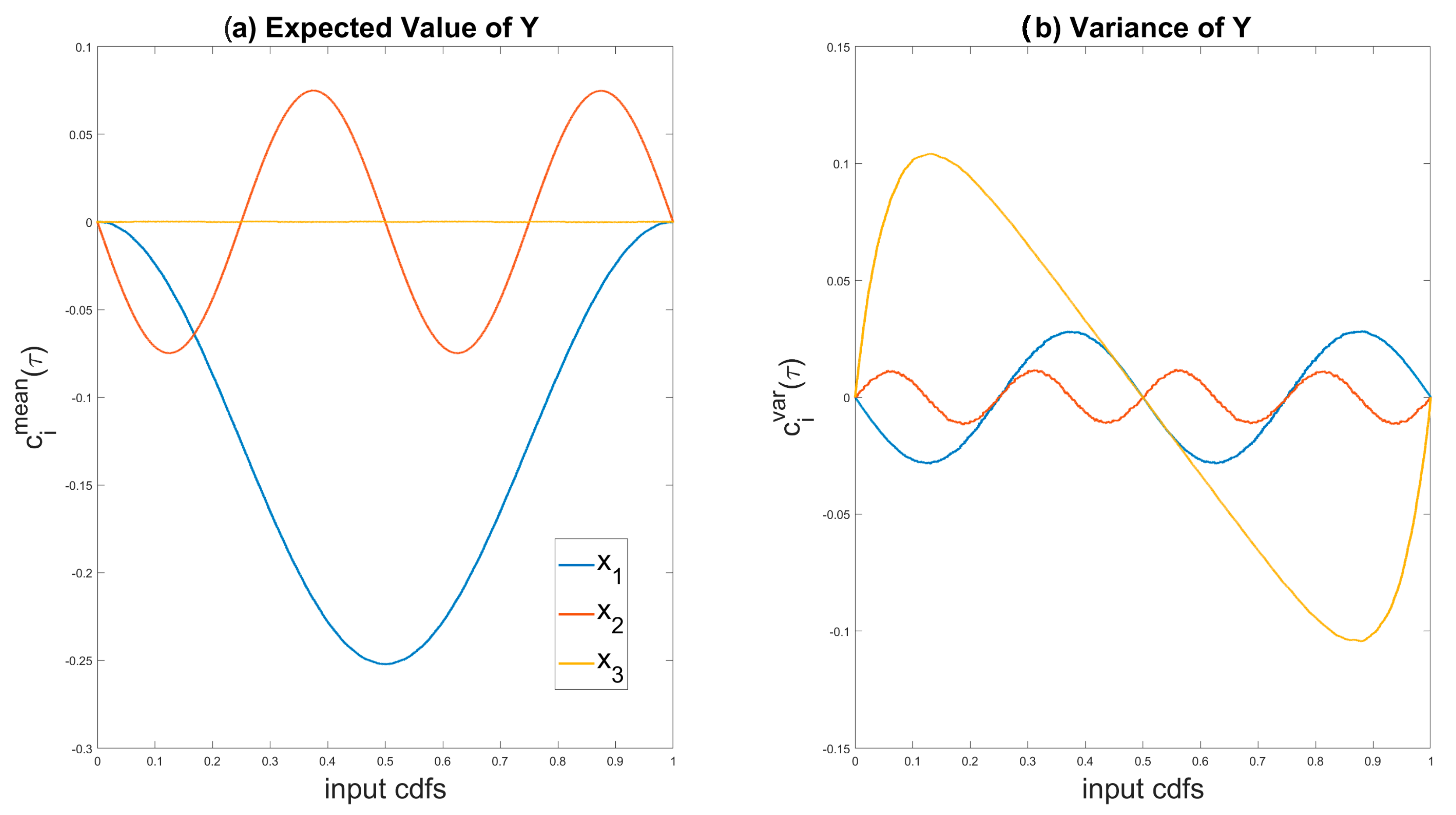
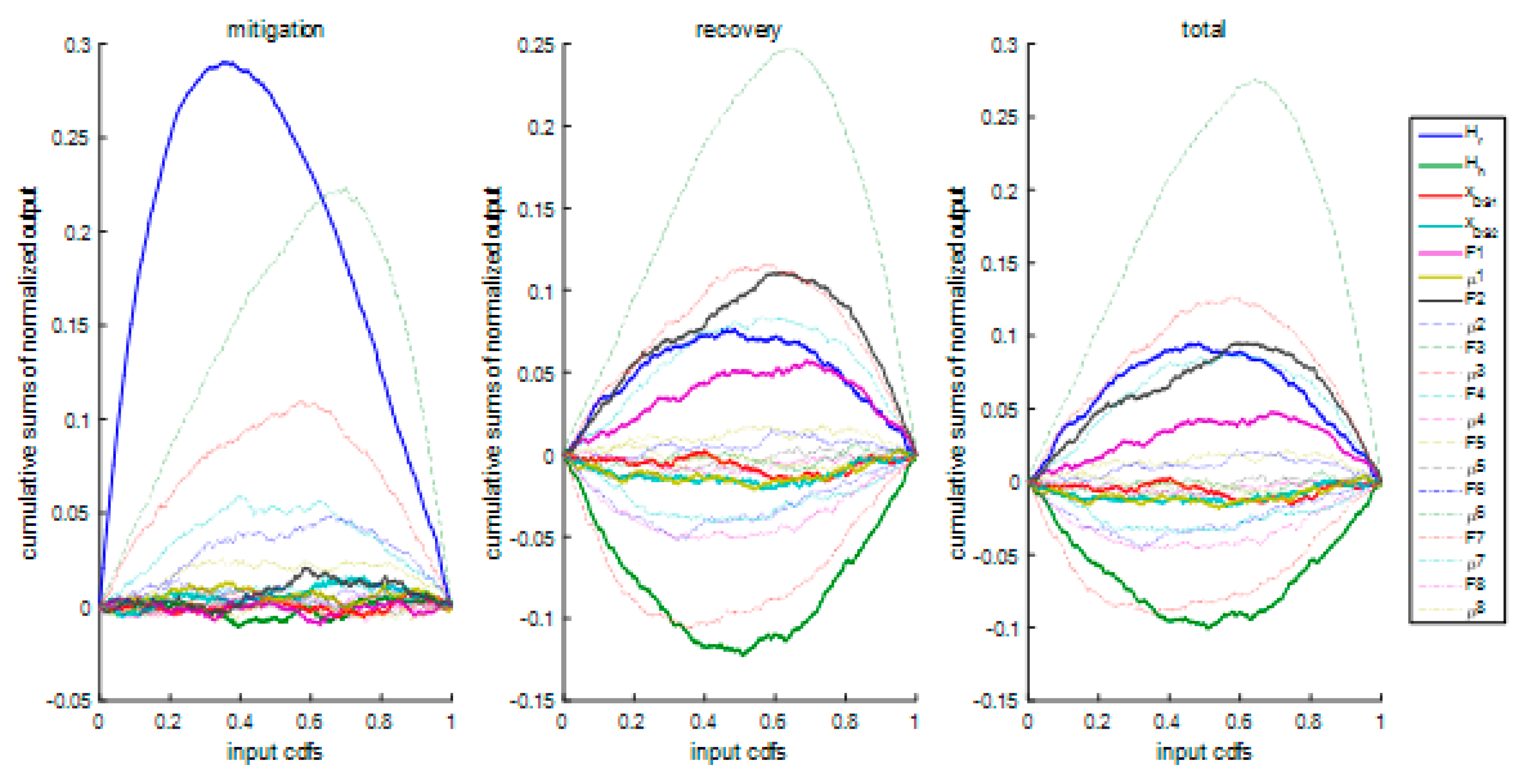
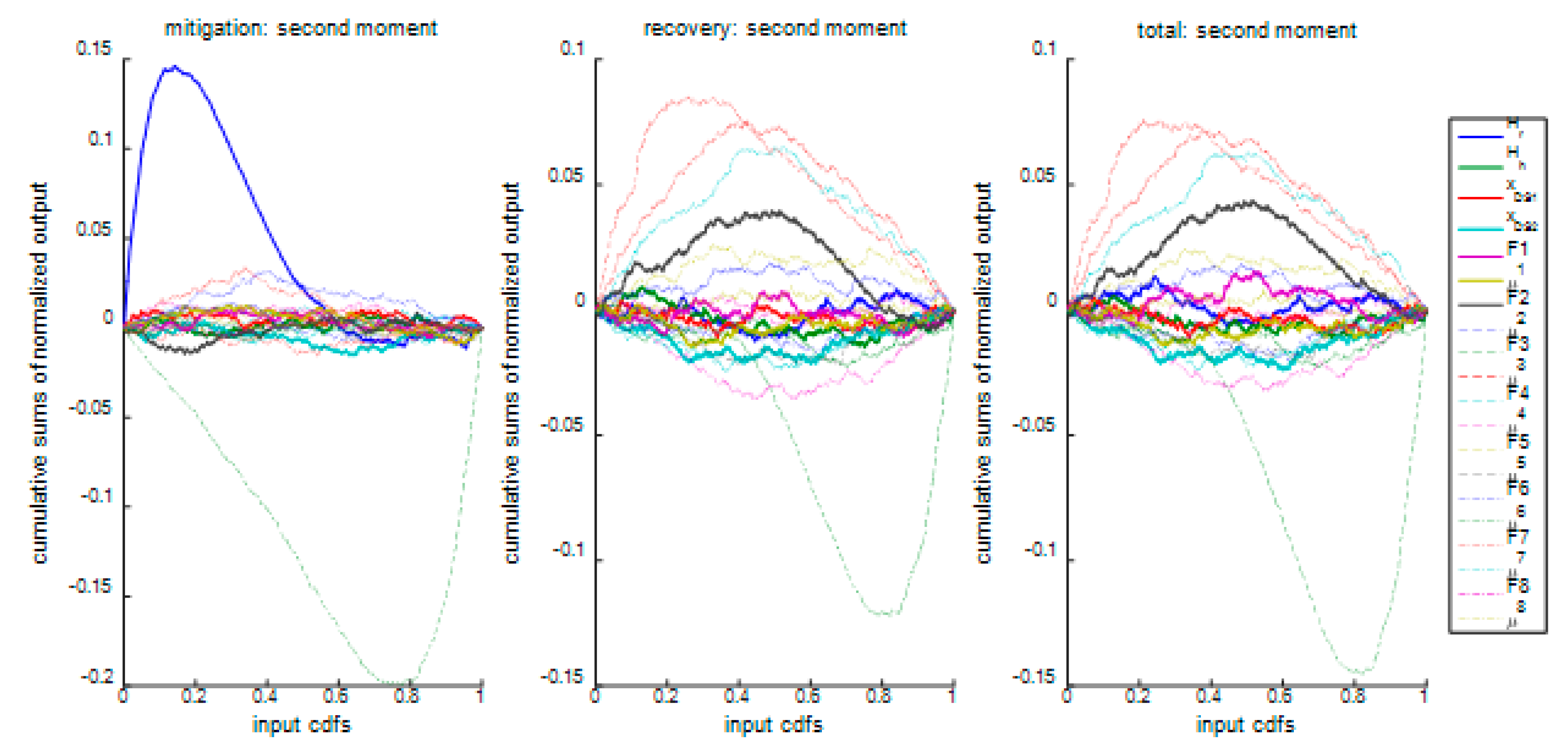
3.3. Visual Tools for Sensitivity Analysis
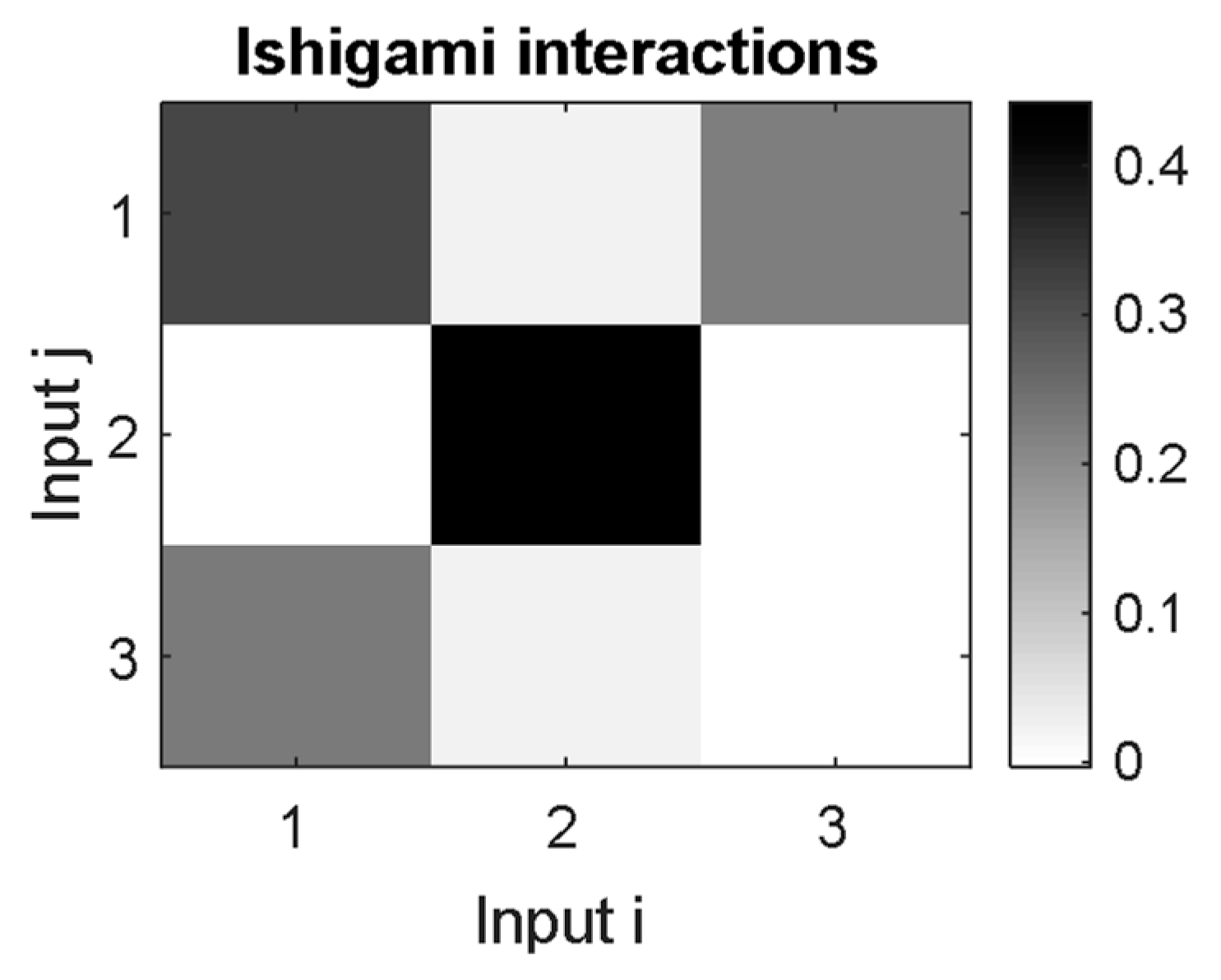
3.4. A Tool for Interaction Analysis
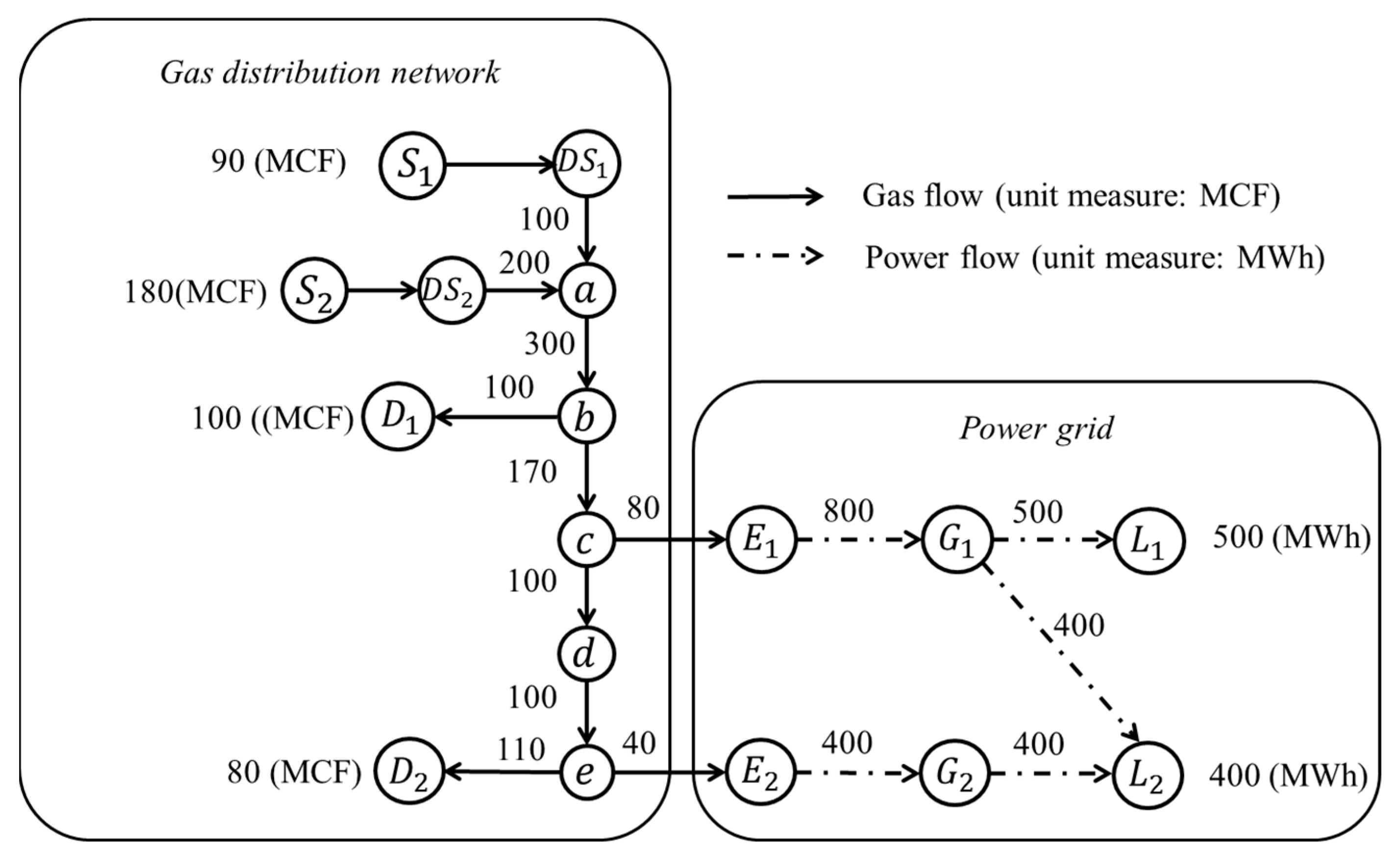
4. Case Study
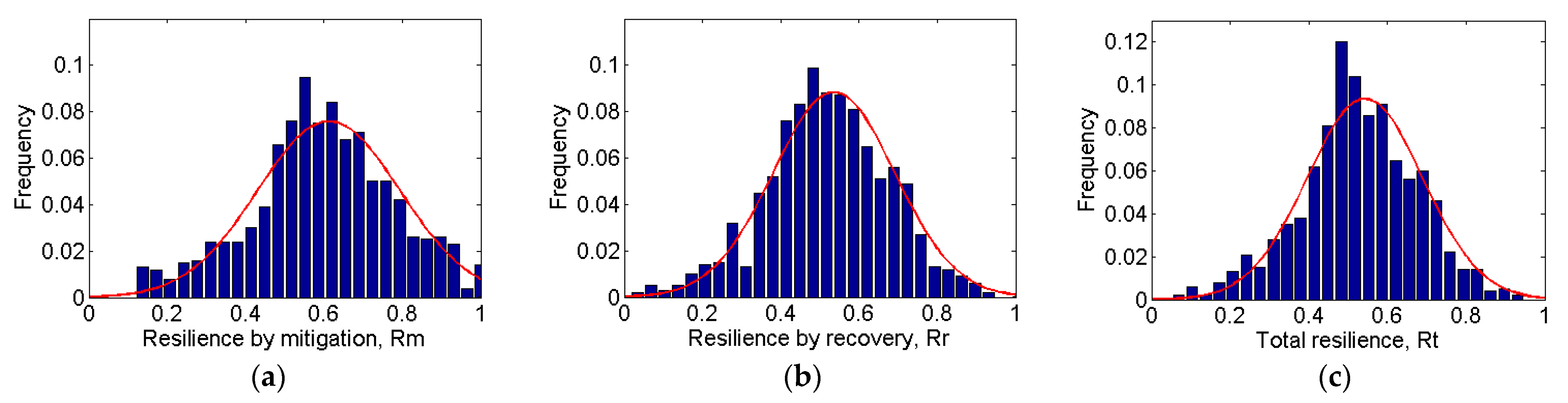
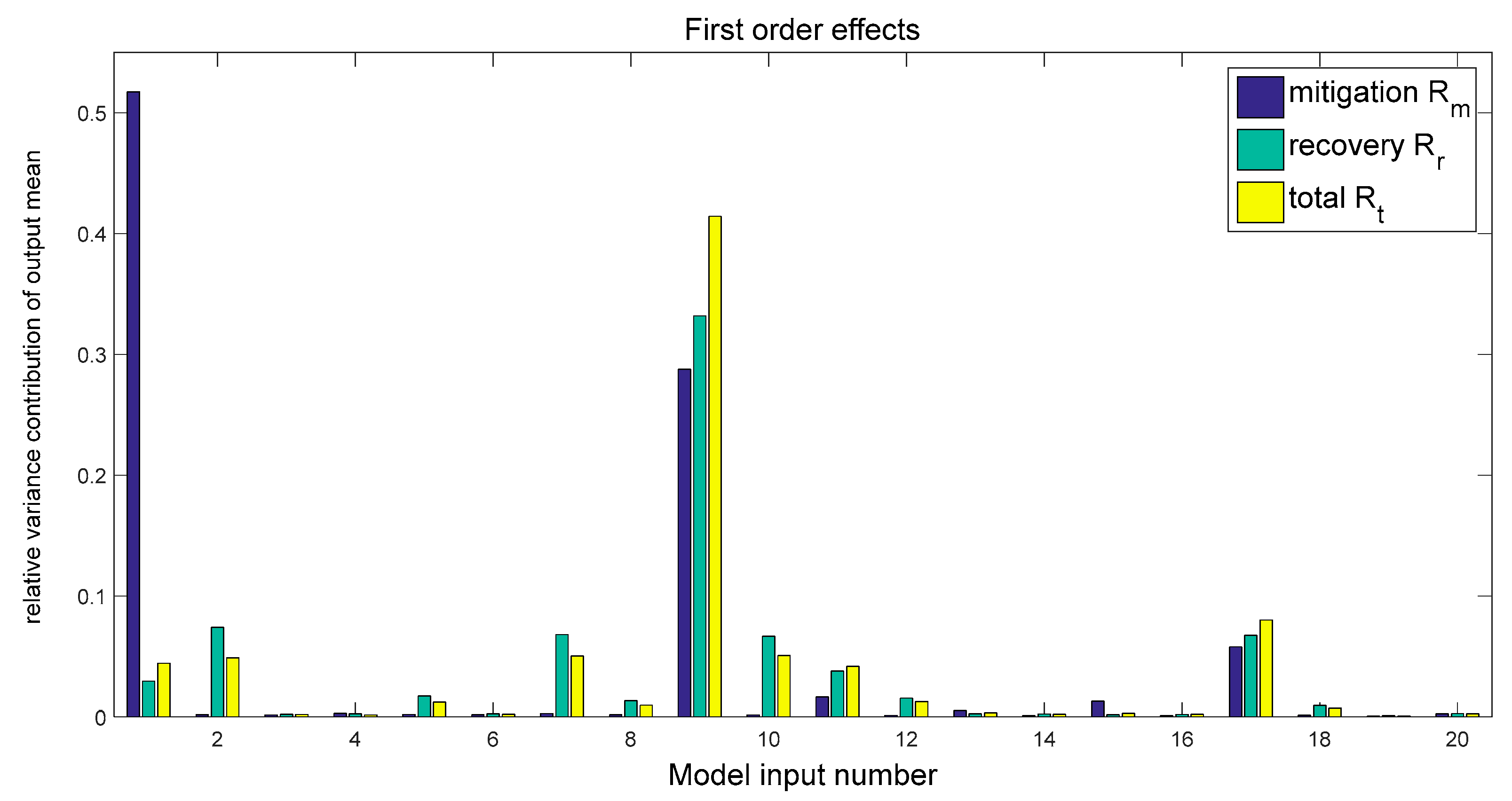
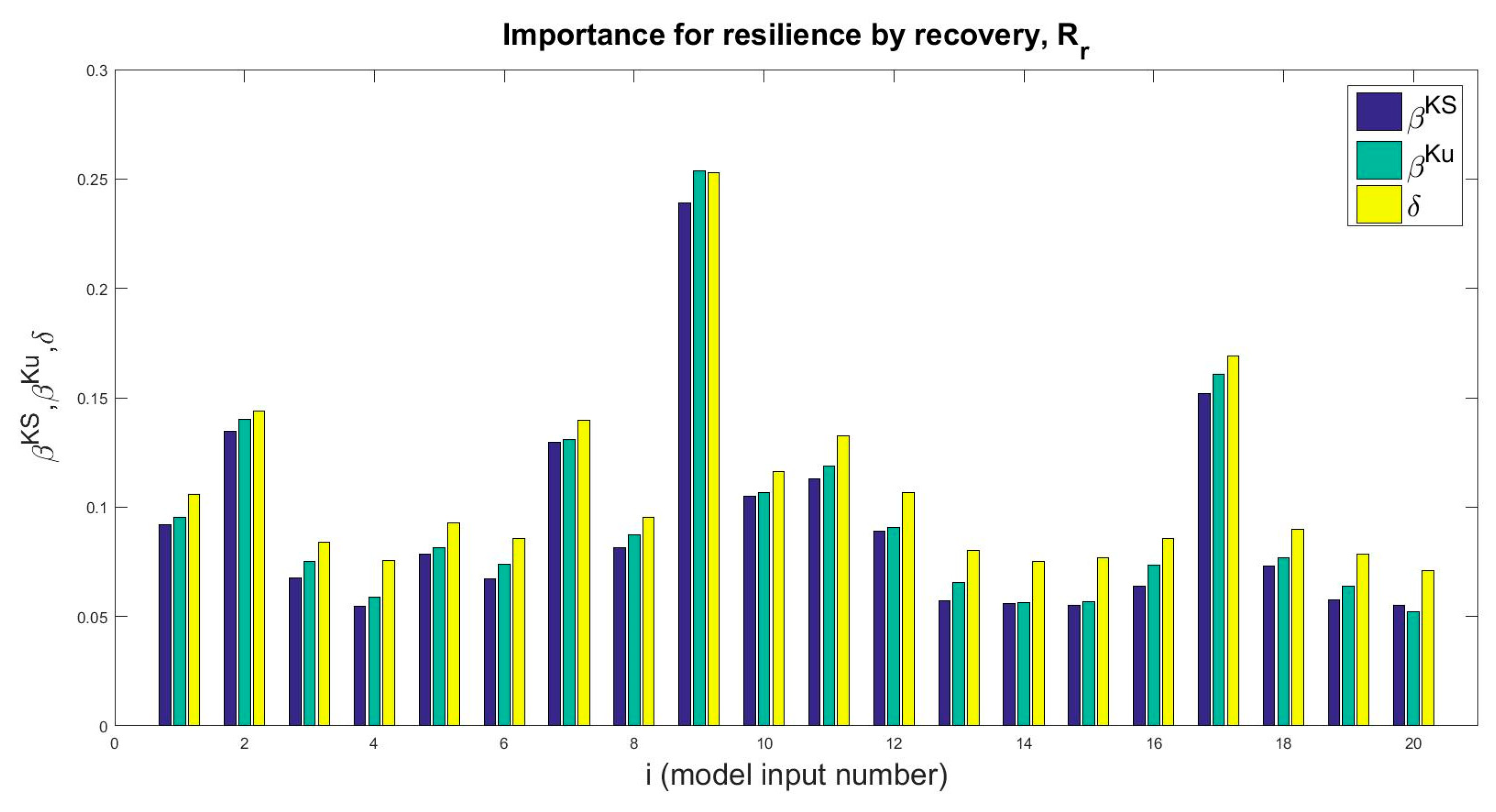
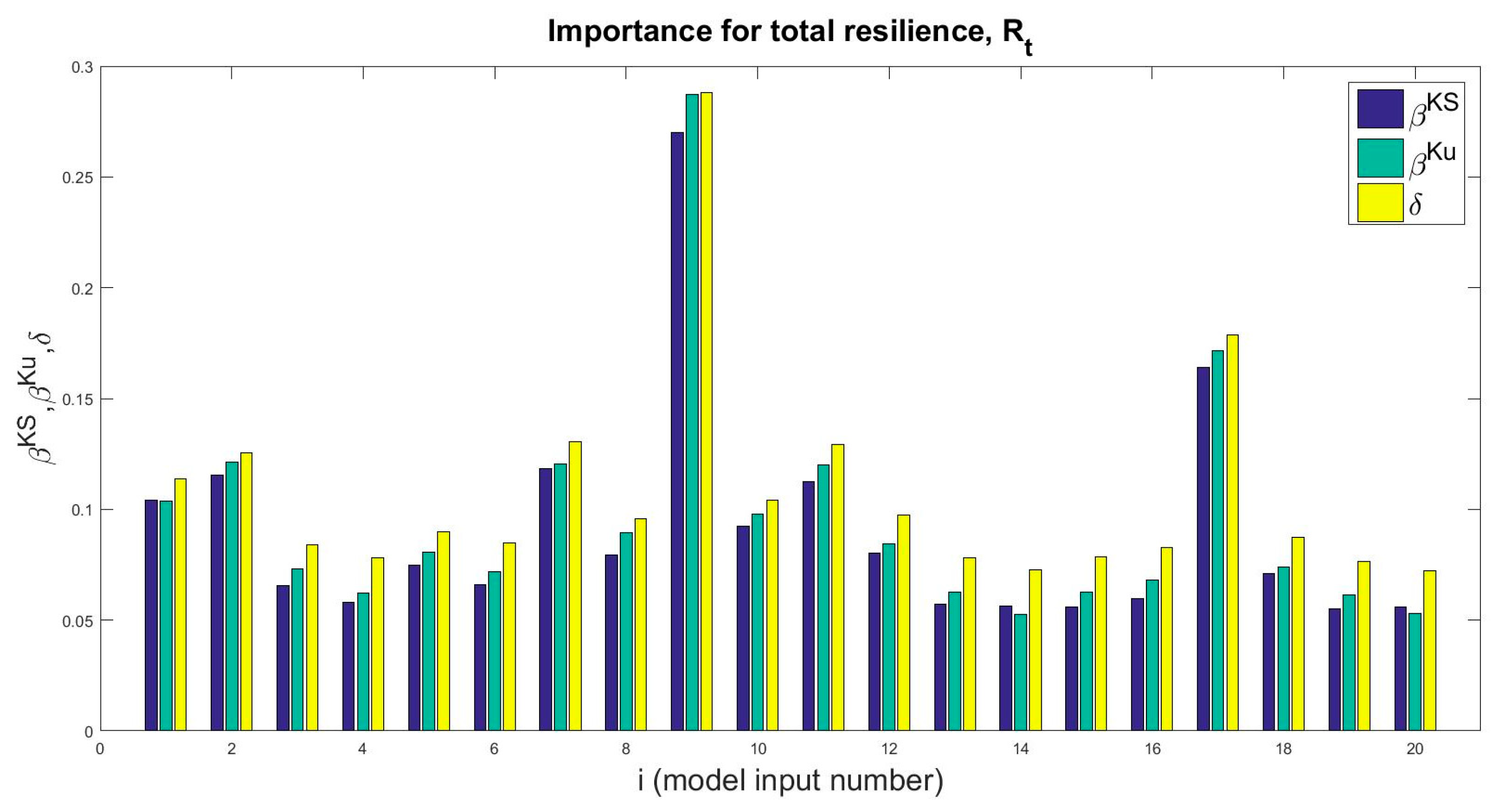
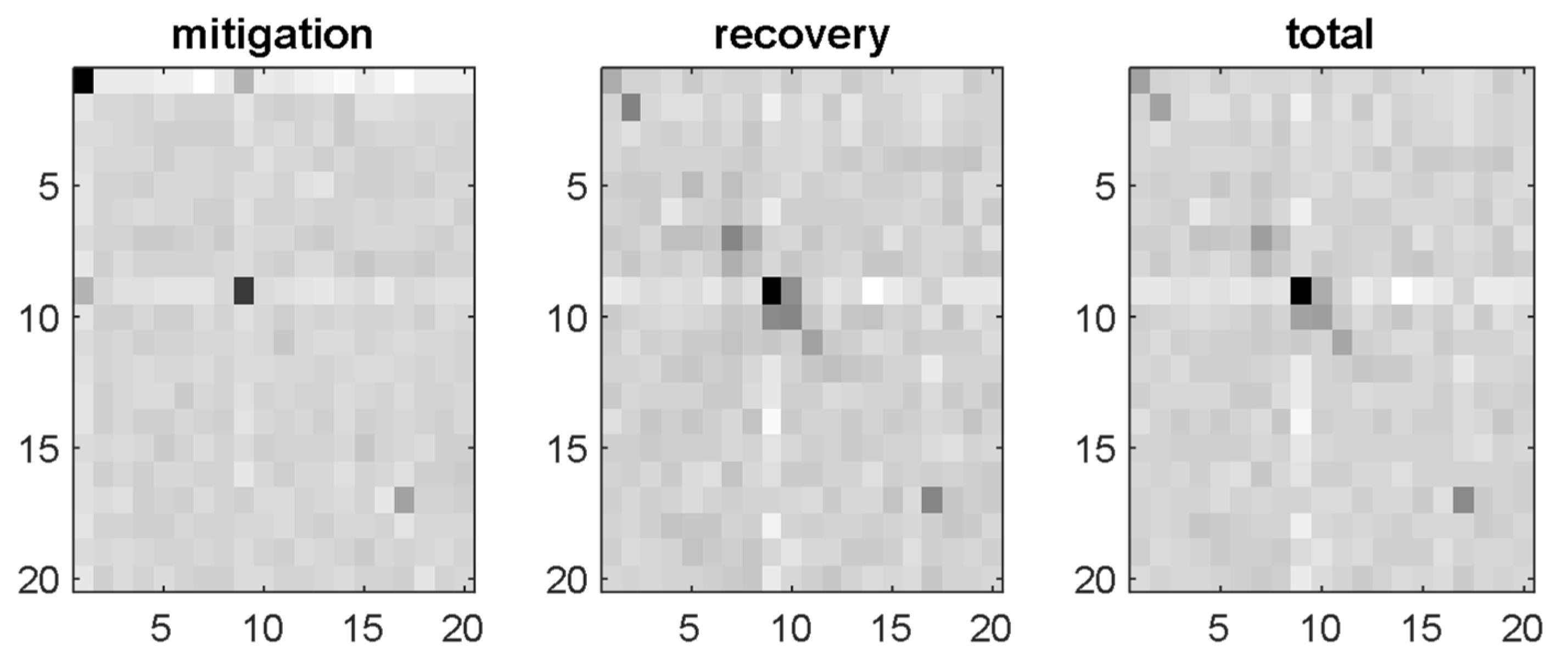
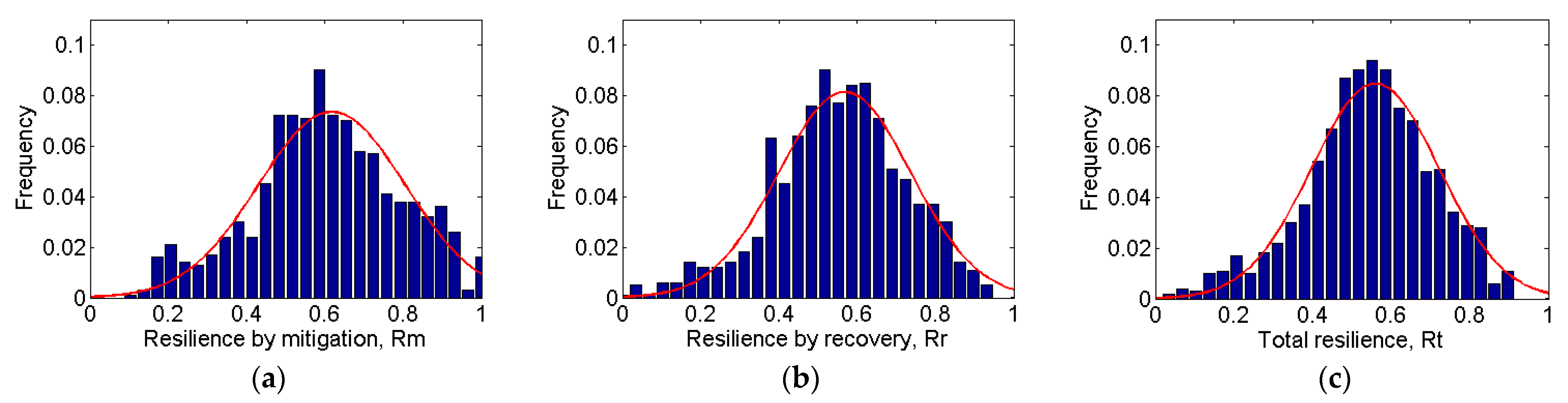
5. Sensitivity Analysis Results
6. Discussion and Interpretation
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Protecting America’s Infrastructures: The Report of the President’s Commission on Critical Infrastructure Protection; The President’s Commission on Critical Infrastructure Protection: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Mottahedi, A.; Sereshki, F.; Ataei, M.; Qarahasanlou, A.N.; Barabadi, A. The Resilience of Critical Infrastructure Systems: A Systematic Literature Review. Energies 2021, 14, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU Commission. Communication from the Commission on a European Programme for Critical Infrastructure Protection; Commission of the European Communities: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, D.L.; Tang, A.; Pierre, J.-R. Performance of lifelines during the 1994 Northridge earthquake. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1995, 22, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao-Hua, Y.; Li-Li, X.; En-Jie, H. A comprehensive study method for lifeline system interaction under seismic conditions. Acta Seismol. Sin. 2004, 17, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, W.; Zio, E. Vulnerable Systems; Springer: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, A. A framework for studying mortality arising from critical infrastructure loss. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. Prot. 2014, 7, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zio, E. Challenges in the vulnerability and risk analysis of critical infrastructures. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2016, 152, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.A.; Kapur, K.C.; Christie, R.D. Methodology for assessing the resilience of networked infrastructure. IEEE Syst. J. 2009, 3, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vugrin, E.D.; Camphouse, R.C. Infrastructure resilience assessment through control design. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. 2011, 7, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkov, I.; Eisenberg, D.A.; Plourde, K.; Seager, T.P.; Allen, J.; Kott, A. Resilience metrics for cyber systems. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2013, 33, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimellaro, G.P.; Reinhorn, A.M.; Bruneau, M. Framework for analytical quantification of disaster resilience. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 3639–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Dueñas-Osorio, L.; Min, X. A three-stage resilience analysis framework for urban infrastructure systems. Struct. Saf. 2012, 36–37, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, P.; Dudenhoeffer, D.; Hartley, S.; Permann, M. Critical Infrastructure Interdependency Modeling: A Survey of U.S. and International Research. Ida. Natl. Lab. 2006, 25, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rinaldi, S.; Peerenboom, J.; Kelly, T. Identifying, understanding, and analyzing critical infrastructure interdependencies. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2001, 21, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, S.M. Modeling and simulating critical infrastructures and their interdependencies. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2004; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ferrario, E.; Zio, E. Resilience analysis framework for interconnected critical infrastructures. ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part B Mech. Eng. 2017, 3, 021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iman, R.L.; Helton, J.C.; Campbell, J.E. Risk Methodology for Geologic Disposal of Radioactive Waste: Sensitivity Analysis Techniques; Nuclear Regulatory Commission: Rockville, MD, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Iman, R.L.; Hora, S.C. A Robust Measure of Uncertainty Importance for Use in Fault Tree System Analysis. Risk Anal. 1990, 10, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helton, J.C.; Davis, F.J. Illustration of Sampling-Based Methods for Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analysis. Risk Anal. 2002, 22, 591–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltelli, A. Sensitivity Analysis for Importance Assessment. Risk Anal. 2002, 22, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.R.; Frey, H. Comparison of Sensitivity Analysis Methods Based on Applications to a Food Safety Risk Assessment Model. Risk Anal. 2004, 24, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamboni, M.; Sanaa, M.; Tenenhaus-Aziza, F. Sensitivity analysis for critical control points determination and uncertainty analysis to link FSO and process criteria: Application to listeria monocytogenes in soft cheese made from pasteurized milk. Risk Anal. 2014, 34, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iman, R.L.; Johnson, M.E.; Watson, C.C.J. Sensitivity Analysis for Computer Model Projections of Hurricane Losses. Risk Anal. 2005, 25, 1277–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; Borgonovo, E.; Galeotti, M.; Roson, R. Uncertainty in Climate Change Modelling: Can Global Sensitivity Analysis be of Help? Risk Anal. 2014, 34, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koks, E.E.; Bockarjova, M.; de Moel, H.; Aerts, J.C.J.H. Integrated direct and indirect flood risk modeling: Development and sensitivity analysis. Risk Anal. 2015, 35, 882–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucurachi, S.; Borgonovo, E.; Heijungs, R. A Potocol for the Global Sensitivity Analysis of Impact Assessment Models in Life Cycle Assessment. Risk Anal. 2016, 36, 357–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.E.; Mitchell, J.E.; Wallace, W.A. Restoration of services in interdependent infrastructure systems: A network flows approach. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C Appl. Rev. 2007, 37, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozick, L.K.; Turnquist, M.A.; Jones, D.A.; Davis, R.D.; Lawton, C.R. Assessing the performance of interdependent infrastructures and optimising investments. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. 2005, 1, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, N.K.; Wolthusen, S.D. Connectivity models of interdependency in mixed-type critical infrastructure networks. Inf. Secur. Tech. Rep. 2007, 12, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodan, I.; Zio, E. A model predictive control framework for reliable microgrid energy management. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2014, 61, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltelli, A.; Ratto, M.; Andres, T.; Campolongo, F.; Cariboni, J.; Gatelli, D.; Saisana, M.; Tarantola, S. Global Sensitivity Analysis. The Primer; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Saltelli, A.; Tarantola, S.; Campolongo, F. Sensitivity Analysis as an Ingredient of Modelling. Stat. Sci. 2000, 19, 377–395. [Google Scholar]
- Borgonovo, E.; Hazen, G.; Plischke, E. A Common Rationale for Global Sensitivity Measures and their Estimation. Risk Anal. 2016, 36, 1871–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgonovo, E. A New Uncertainty Importance Measure. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2007, 92, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baucells, M.; Borgonovo, E. Invariant Probabilistic Sensitivity Analysis. Manag. Sci. 2013, 59, 2536–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgonovo, E.; Tarantola, S.; Plischke, E.; Morris, M.D. Transformation and Invariance in the Sensitivity Analysis of Computer Experiments. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 2014, 76, 925–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa, F.; Klein, T.; Lagnoux, A. Sensitivity Analysis Based on Cramer von Mises Distance. SIAM/ASA J. Uncertain. Quantif. 2018, 6, 522–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Veiga, S. Global Sensitivity Analysis with Dependence Measures. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2015, 85, 1283–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lozzo, M.; Marrel, A. New improvements in the use of dependence measures for sensitivity analysis and screening. J. Stat. Comput. Simul. 2016, 86, 3038–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lozzo, M.; Marrel, A. Sensitivity analysis with dependence and variance-based measures for spatio-temporal numerical simulators. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2017, 31, 1437–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plischke, E.; Borgonovo, E. Fighting the Curse of Sparsity: Probabilistic Sensitivity Measures from Cumulative Distribution Functions. Risk Anal. 2020, 40, 2639–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soboĺ, I.M. Sensitivity Estimates for Nonlinear Mathematical Models. Math. Model. Comput. Exp. 1993, 1, 407–414. [Google Scholar]
- Gamboa, F.; Janon, A.; Klein, T.; Lagnoux, A.; Prieur, C. Statistical inference for Sobol pick-freeze Monte Carlo method. Statistics 2016, 50, 881–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. On the General Theory of Skew Correlation and Non-linear Regression; Dulau and Company: London, UK, 1905; Volume XIV. [Google Scholar]
- Kleijnen, J.P.C.; Helton, J.C. Statistical analyses of scatterplots to identify important factors in large-scale simulations, 1: Review and comparison of techniques. Reliab. Eng. Saf. 1999, 65, 147–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, M.; Oakley, J.E.; Chilcott, J. Managing Structural Uncertainty in Health Economic Decision Models: A Discrepancy Approach. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C 2012, 61, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, M.; Oakley, J.E. An Efficient Method for Computing Partial Expected Value of Perfect Information for Correlated Inputs. Med. Decis. 2013, 33, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, M.; Oakley, J.E.; Brennan, A.; Breeze, P. Estimating the Expected Value of Sample Information Using the Probabilistic Sensitivity Analysis Sample. Med. Decis. Mak. 2015, 35, 570–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soboĺ, I.M. On the distribution of points in a cube and the approximate evaluation of integrals. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1969, 7, 86–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ökten, G.; Liu, Y. Randomized quasi-Monte Carlo methods in global sensitivity analysis. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 210, 107520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.B. Halton sequences avoid the origin. SIAM Rev. 2006, 48, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.B. Latin supercube sampling for very high-dimensional simulations. ACM Trans. Model. Comput. Simul. 1998, 8, 71–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damblin, G.; Ghione, A. Adaptive use of replicated Latin Hypercube Designs for computing Soboĺ sensitivity indices. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 212, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plischke, E. An Adaptive Correlation Ratio Method Using the Cumulative Sum of the Reordered Output. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2012, 107, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigami, T.; Homma, T. An Importance Quantification Technique in Uncertainty Analysis for Computer Models. In Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Uncertainty Modeling and Analysis, College Park, MD, USA, 3–5 December 1990; pp. 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantola, S.; Kopustinskas, V.; Bolado-Lavin, R.; Kaliatka, A.; Ušpuras, E.; Vaišnoras, M. Sensitivity analysis using contribution to sample variance plot: Application to a water hammer model. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2012, 99, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fort, J.-C.; Klein, T.; Rachdi, N. New Sensitivity Analysis Subordinated to a Contrast. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 2016, 45, 4349–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudret, B. Global sensitivity analysis using polynomial chaos expansion. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2008, 93, 964–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plischke, E. An effective algorithm for computing global sensitivity indices (EASI). Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2010, 95, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Rudi, A.; Borgonovo, E.; Rosasco, L. Faster kriging: Facing high-dimensional simulators. Oper. Res. 2020, 68, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Description | Symbol | Bounds | Unit Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Response time | Hr | [0, 30] | hours |
| Time horizon | Hh | [50, 100] | hours |
| The initial storage of the buffer DS1 | [1000, 4000] | MCF | |
| The initial storage of the buffer DS2 | [2000, 8000] | MCF |
| Vulnerable Element | Failure Magnitude Fi | Units of Fi | Recovery Rate μi | Units of μi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Supplier | [0, 90] | MCF | [0, 1.8] | MCF/h |
| 2 | Supplier | [0, 180] | MCF | [0, 3.6] | MCF/h |
| 3 | Link | [0, 300] | MCF | [0, 6] | MCF/h |
| 4 | Link | [0, 170] | MCF | [0, 3.4] | MCF/h |
| 5 | Link | [0, 100] | MCF | [0, 2] | MCF/h |
| 6 | Link | [0, 100] | MCF | [0, 2] | MCF/h |
| 7 | Link | [0, 800] | MWh | [0, 16] | MWh/h |
| 8 | Link | [0, 400] | MWh | [0, 8] | MWh/h |
| Distribution of Resilience Indicators | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Resilience by mitigation | 0.6121 | 0.1815 |
| Resilience by recovery | 0.5356 | 0.1557 |
| Total resilience | 0.5425 | 0.1471 |
| Distribution of Resilience Metrics | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| Resilience by mitigation | 0.6177 | 0.1874 |
| Resilience by recovery | 0.5678 | 0.1692 |
| Total resilience | 0.5597 | 0.1625 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zio, E.; Borgonovo, E.; Plischke, E. A Systematic Approach of Global Sensitivity Analysis and Its Application to a Model for the Quantification of Resilience of Interconnected Critical Infrastructures. Energies 2024, 17, 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081823
Liu X, Zio E, Borgonovo E, Plischke E. A Systematic Approach of Global Sensitivity Analysis and Its Application to a Model for the Quantification of Resilience of Interconnected Critical Infrastructures. Energies. 2024; 17(8):1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081823
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xing, Enrico Zio, Emanuele Borgonovo, and Elmar Plischke. 2024. "A Systematic Approach of Global Sensitivity Analysis and Its Application to a Model for the Quantification of Resilience of Interconnected Critical Infrastructures" Energies 17, no. 8: 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081823
APA StyleLiu, X., Zio, E., Borgonovo, E., & Plischke, E. (2024). A Systematic Approach of Global Sensitivity Analysis and Its Application to a Model for the Quantification of Resilience of Interconnected Critical Infrastructures. Energies, 17(8), 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17081823






