A LiDAR-Based Active Yaw Control Strategy for Optimal Wake Steering in Paired Wind Turbines
Abstract
1. Introduction
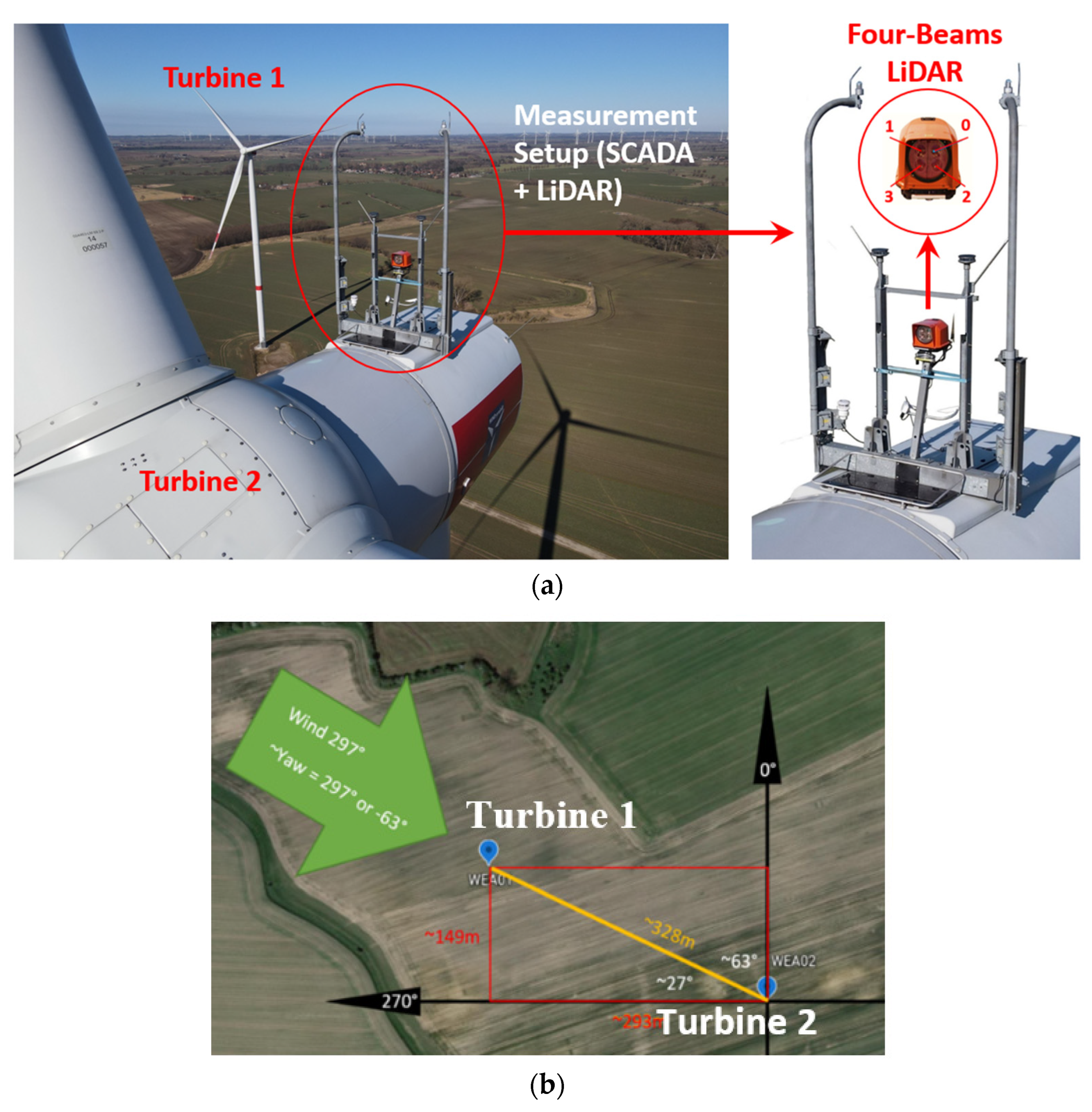
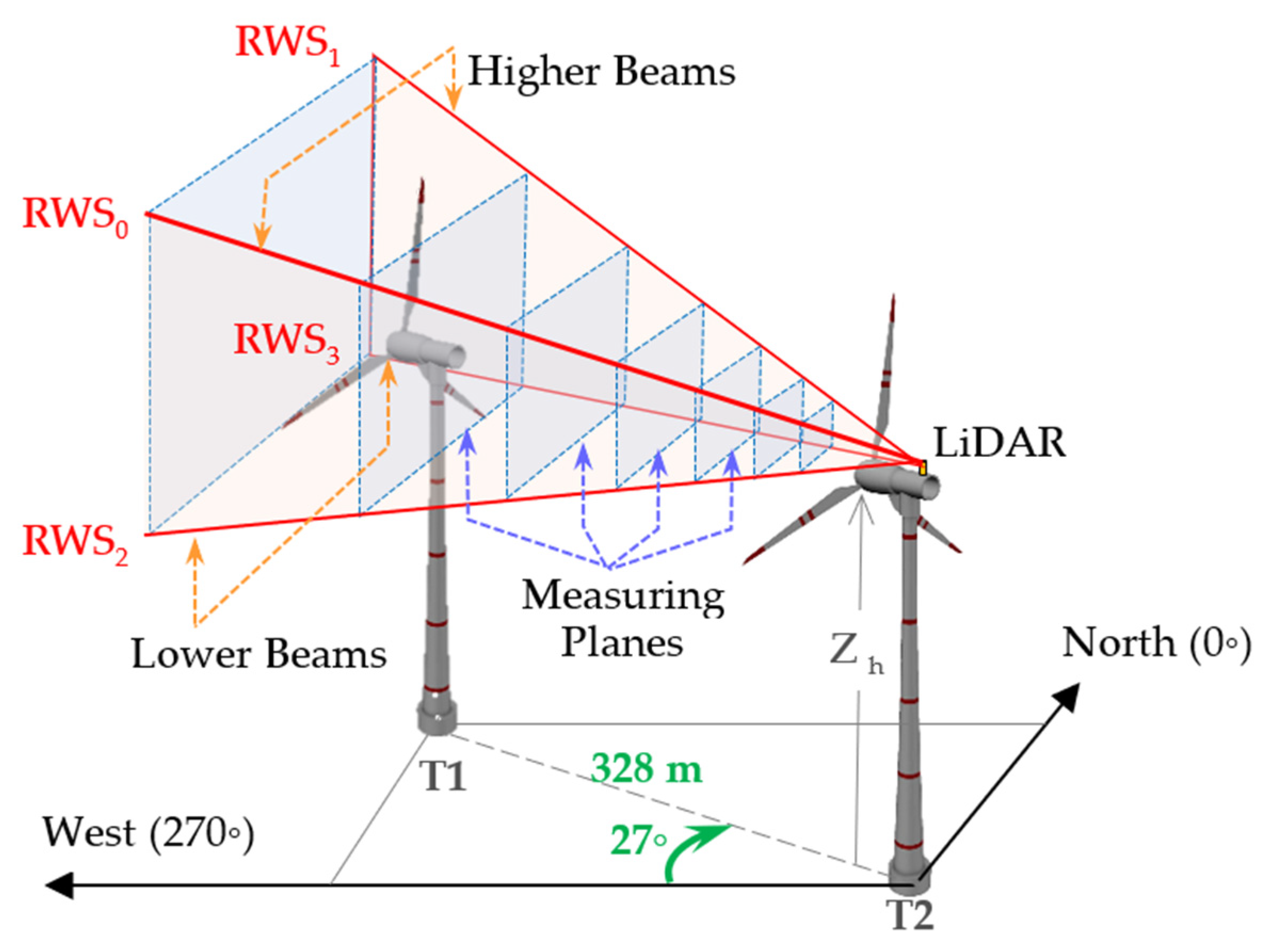
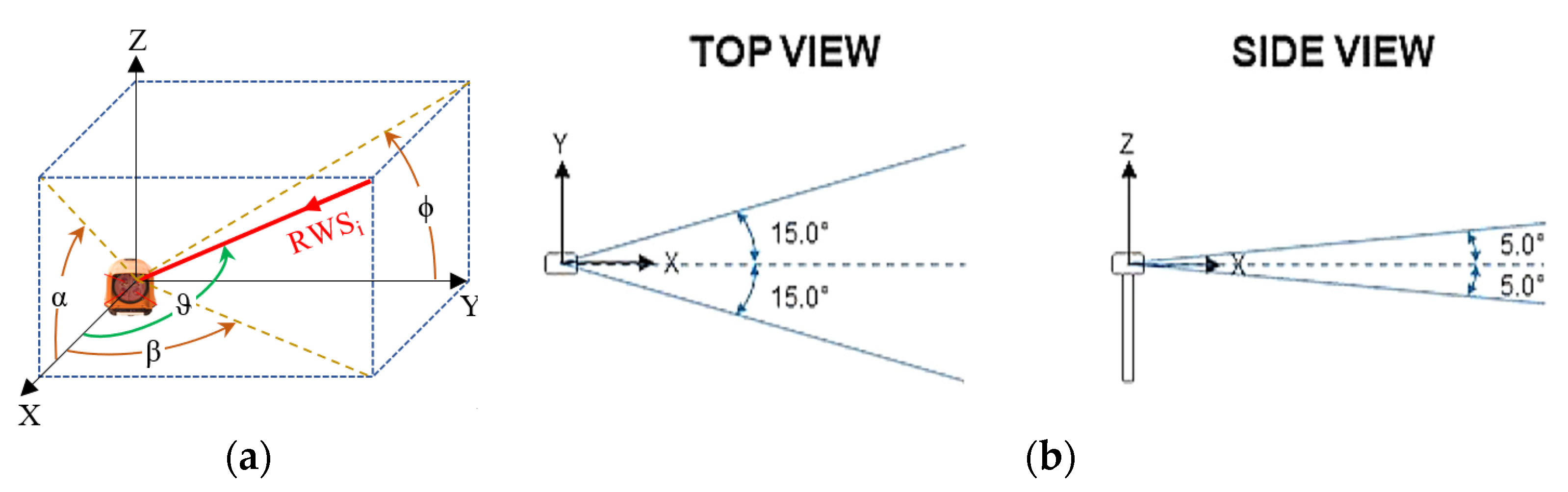
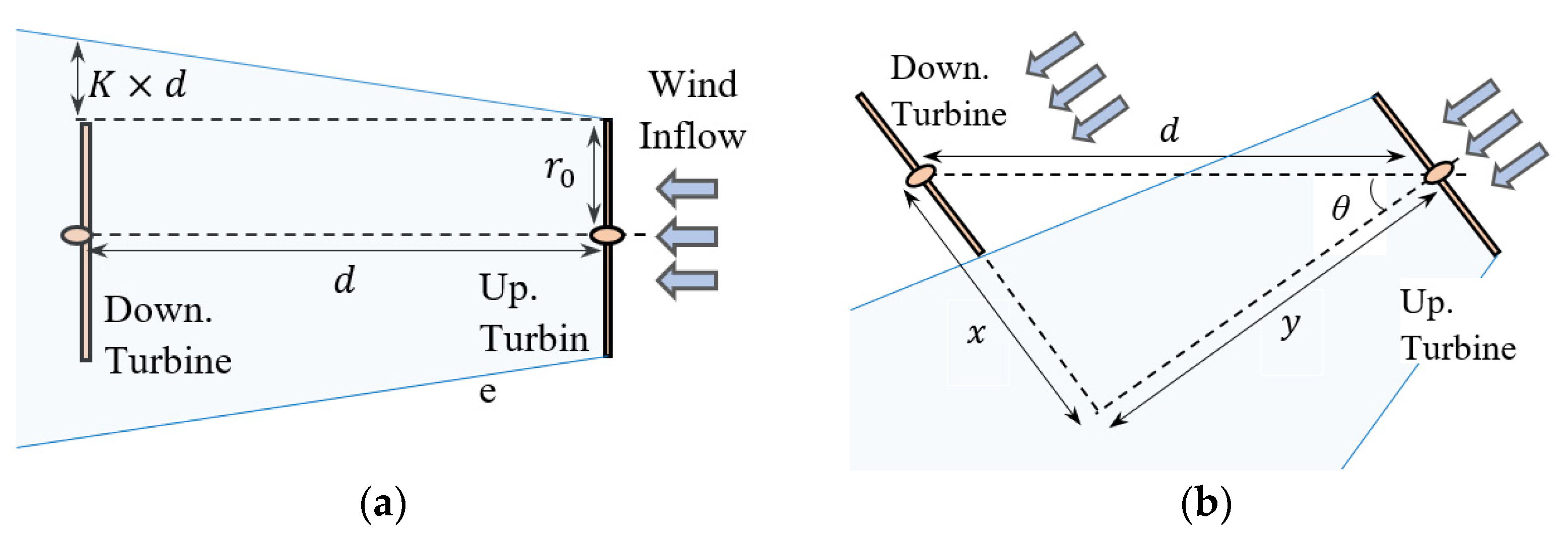
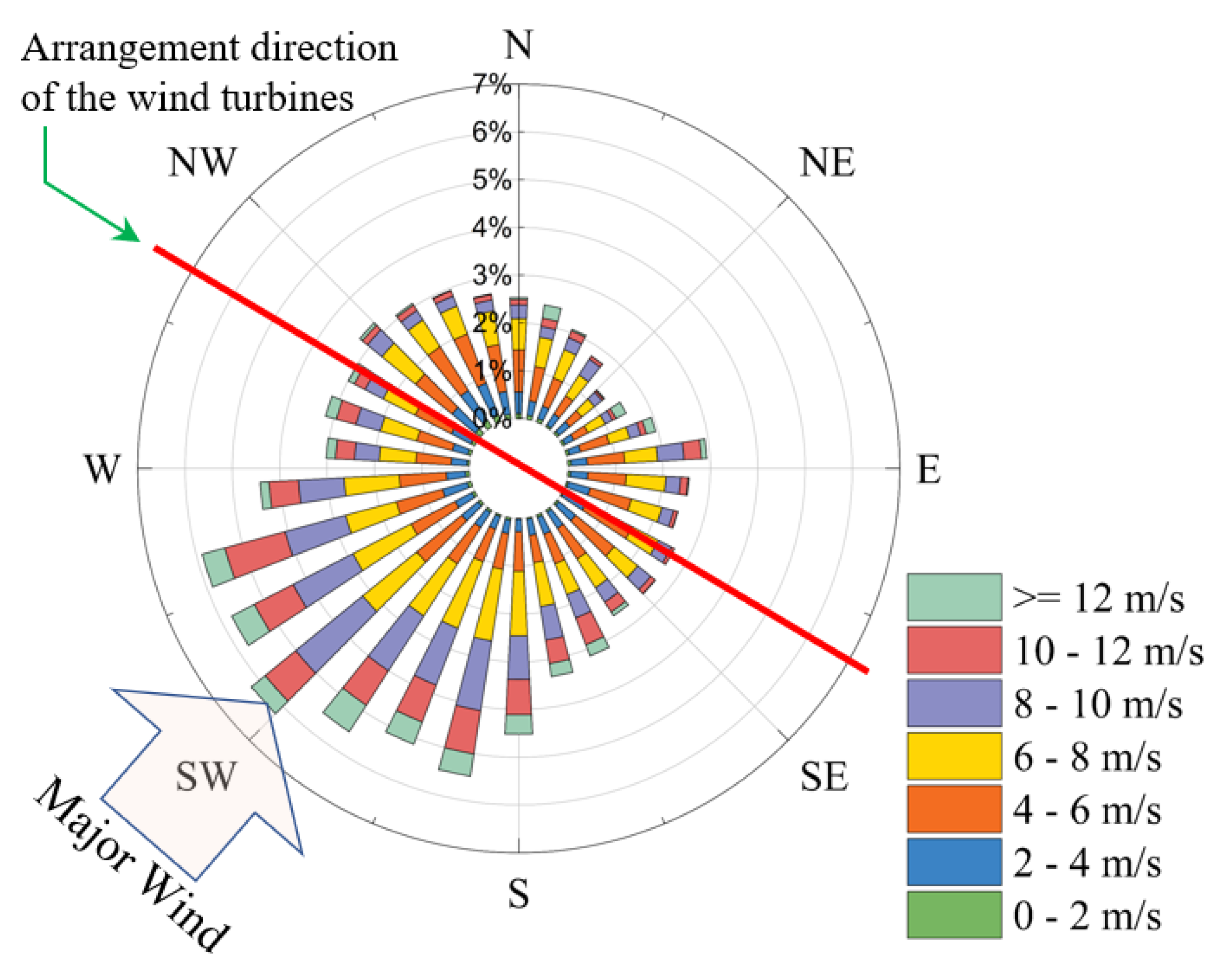
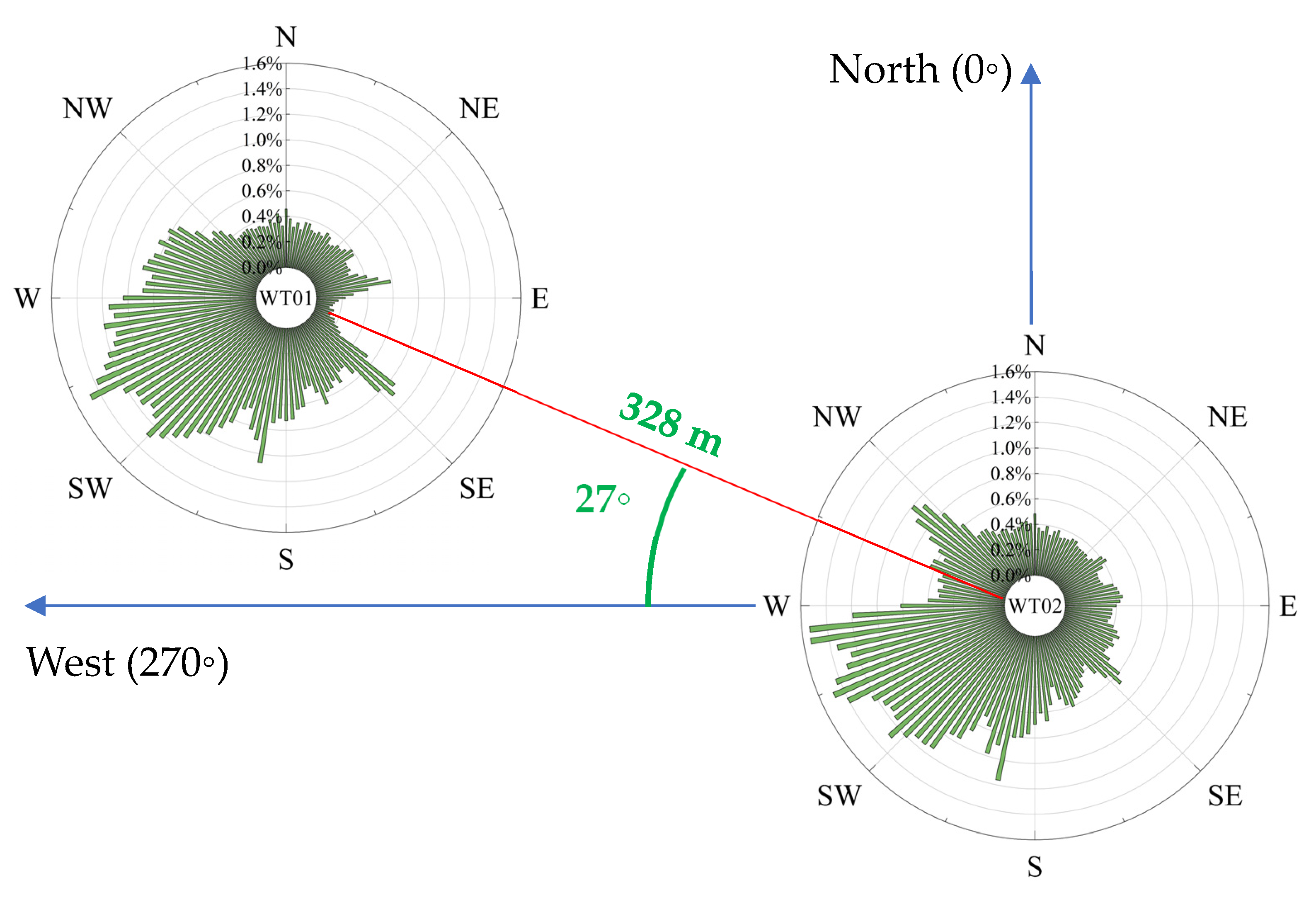
2. Materials and Methods
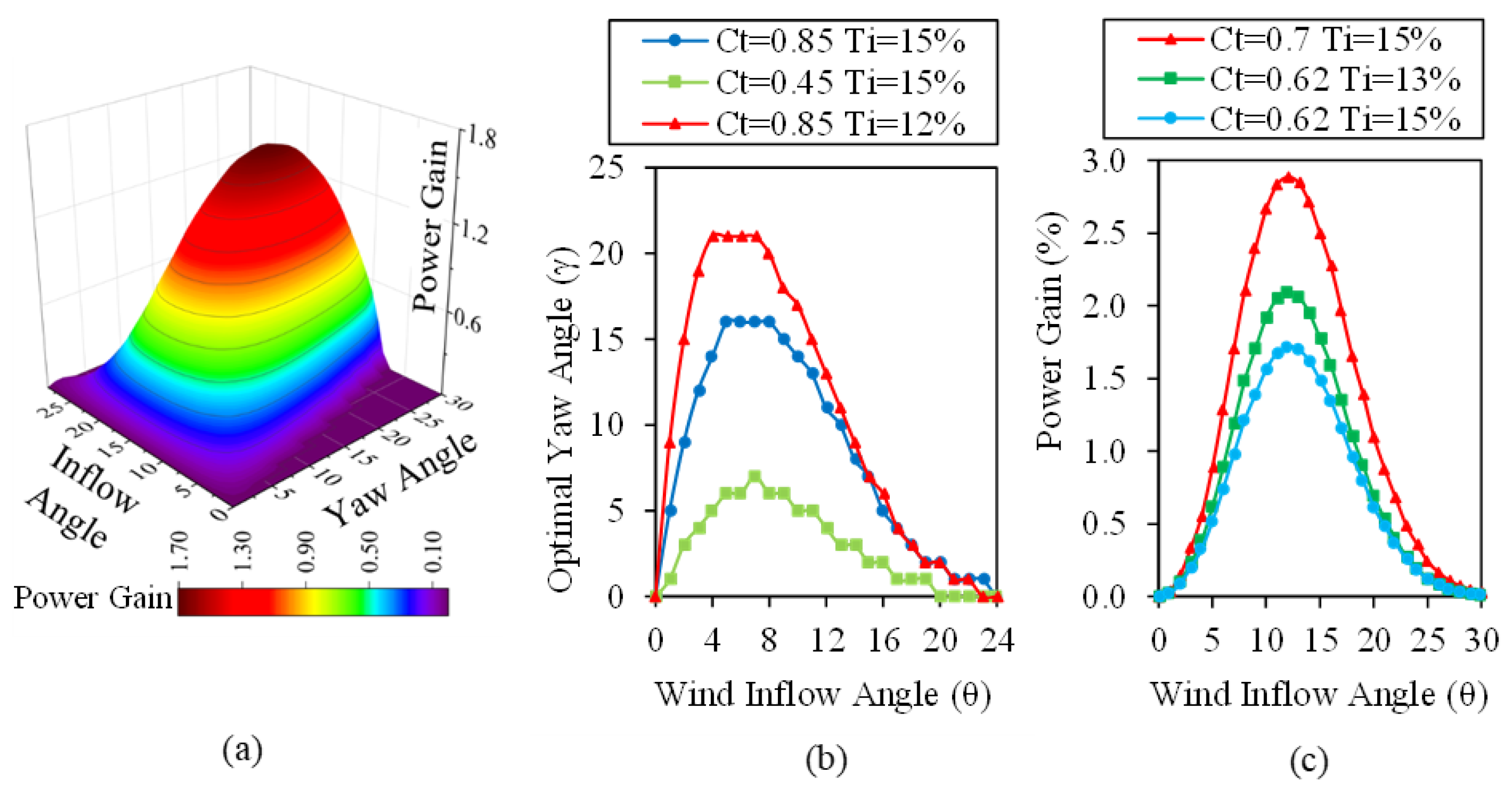
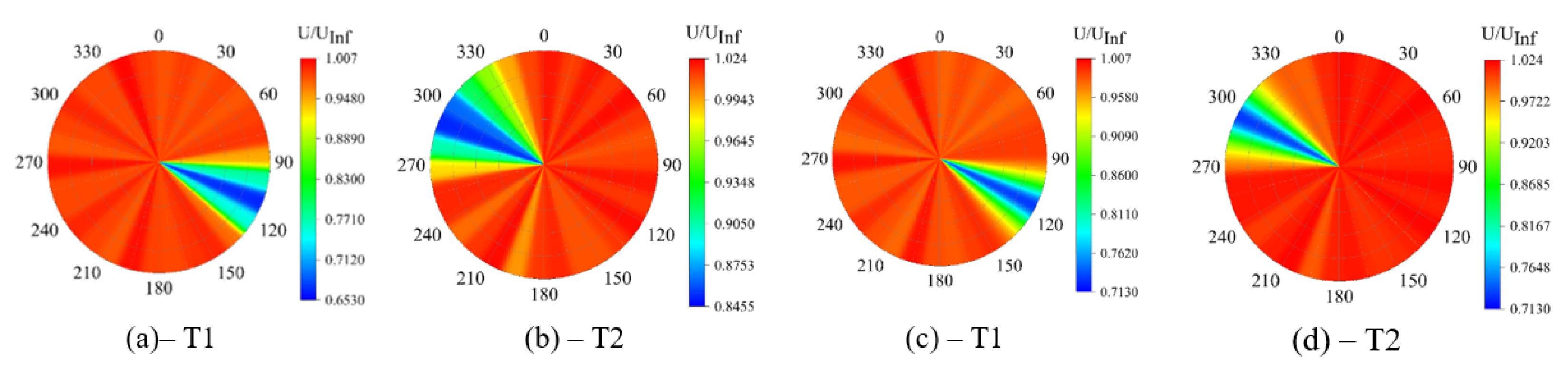
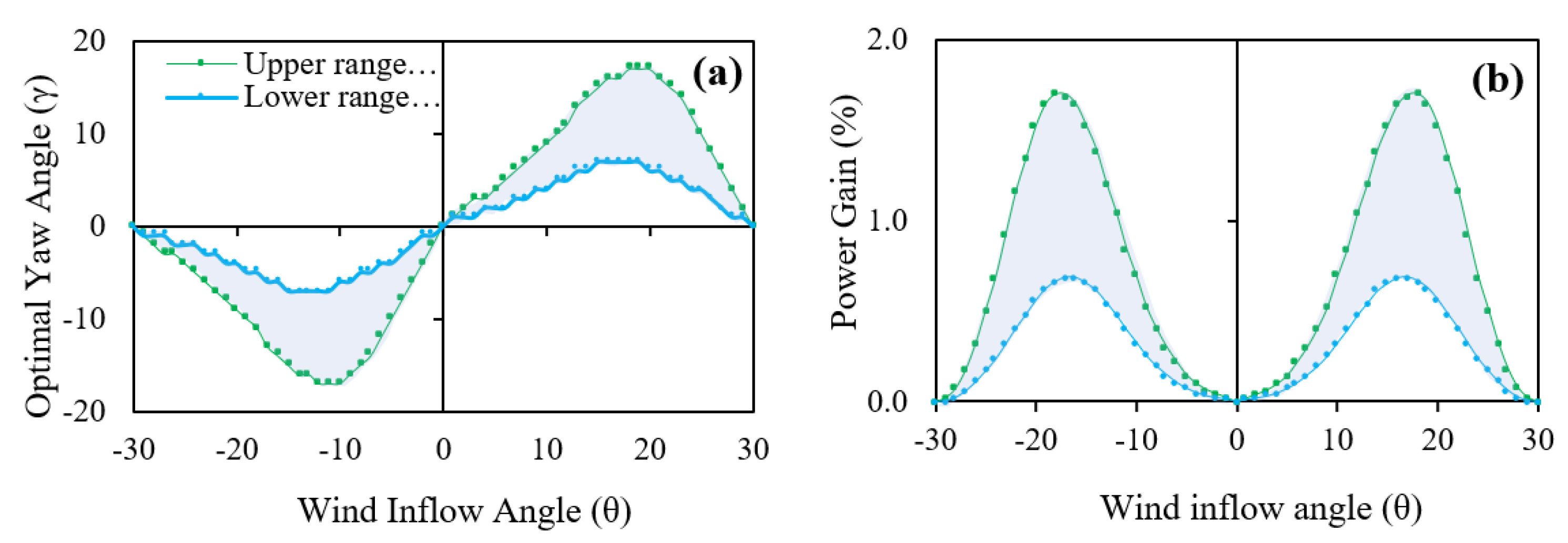
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irena. Future of Wind: Deployment, Investment, Technology, Grid Integration and Socio-Economic Aspects. Available online: https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2019/Oct/IRENA_Future_of_wind_2019.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Kragh, K.; Fleming, P. Rotor Speed Dependent Yaw Control of Wind Turbines Based on Empirical Data. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition; Aerospace Sciences Meetings; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nashville, TN, USA, 9–12 January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Barthelmie, R.J.; Rathmann, O.; Frandsen, S.T.; Hansen, K.S.; Politis, E.; Prospathopoulos, J.; Rados, K.; Cabezón, D.; Schlez, W.; Phillips, J. Modelling and Measurements of Wakes in Large Wind Farms. Proc. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 75, 12049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakir, M.N.; Abasin, A.R.; Irshad, A.S.; Elias, S.; Yona, A.; Senjyu, T. Practical Wind Turbine Selection: A Multicriterion Decision Analysis for Sustainable Energy Infrastructure. Pract. Period. Struct. Des. Constr. 2024, 29, 04024028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Porté-Agel, F. Power Production and Blade Fatigue of a Wind Turbine Array Subjected to Active Yaw Control. Energies 2023, 16, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, P.A.; Ning, A.; Gebraad, P.M.O.; Dykes, K. Wind Plant System Engineering Through Optimization of Layout and Yaw Control. Wind. Energy 2016, 19, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholbrock, A.; Fleming, P.; Wright, A.; Slinger, C.; Medley, J.; Harris, M. Field Test Results from Lidar Measured Yaw Control for Improved Yaw Alignment with the NREL Controls Advanced Research Turbine; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2014.
- Mahmoodi, E.; Khezri, M.; Ebrahimi, A.; Ritschel, U.; Chamorro, L.P.; Khanjari, A. A Simple Model for Wake-Induced Aerodynamic Interaction of Wind Turbines. Energies 2023, 16, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Yue, H. Design and Assessment of a LIDAR-Based Model Predictive Wind Turbine Control. Energies 2022, 15, 6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fang, L.; Song, D.; Su, M.; Yang, X.; Huang, L.; Joo, Y.H. Review of Control Strategy of Large Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines Yaw System. Wind. Energy 2021, 24, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Schlipf, D.; Cheng, P.W. Evaluation of Lidar-Assisted Wind Turbine Control Under Various Turbulence Characteristics. Wind. Energy Sci. 2023, 8, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simley, E.; Fürst, H.; Haizmann, F.; Schlipf, D. Optimizing Lidars for Wind Turbine Control Applications—Results from the IEA Wind Task 32 Workshop. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, D.P. Inflow Measurements by Nacelle Mounted Lidars for Wind Turbine and Farm Control. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Kongens Lyngby, Denmark, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Boorsma, K.; Wagenaar, J.W.; Savenije, F.J.; Boquet, M.; Bierbooms, W.; Giyanani, A.; Rutteman, R. LiDAR Application for WInd Energy Efficiency; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bottasso, C.; Pizzinelli, P.; Riboldi, C.; Tasca, L. LiDAR-Enabled Model Predictive Control of Wind Turbines with Real-Time Capabilities. Renew. Energy 2014, 71, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, H.; Kogaki, T. Lidar-Assisted Yaw Control for Wind Turbines Using a 9-Beam Nacelle Lidar Demonstrator. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1452, 012056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Yang, H.; Lu, L. Optimal Yaw Strategy and Fatigue Analysis of Wind Turbines Under the Combined Effects of Wake and Yaw Control. Appl. Energy 2023, 337, 120878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Su, M.; He, J. Wind Power Prediction Through Acoustic Data-Driven Online Modeling and Active Wake Control. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 319, 118920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, M.F.; Bossuyt, J.; Martínez-Tossas, L.A.; Meyers, J.; Meneveau, C. Wake Structure in Actuator Disk Models of Wind Turbines in Yaw under Uniform Inflow Conditions. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 43301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastankhah, M.; Porté-Agel, F. Experimental and Theoretical Study of Wind Turbine Wakes in Yawed Conditions. J. Fluid. Mech. 2016, 806, 506–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Xie, X. Numerical Investigation of the Yawed Wake and Its Effects on the Downstream Wind Turbine. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 33303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartl, J.; Mühle, F.; Stran, L. Wind Tunnel Study on Power and Loads Optimization of Two Yaw-Controlled Model Wind Turbines. Wind. Energy Sci. Discuss. 2018, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, P.; King, J.; Dykes, K.; Simley, E.; Roadman, J.; Scholbrock, A.; Murphy, P.; Lundquist, J.K.; Moriarty, P.; Fleming, K.; et al. Initial Results from a Field Campaign of Wake Steering Applied at a Commercial Wind Farm—Part. Wind. Energy Sci. 2019, 4, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FLORIS, FLOw Redirection and Induction in Steady State. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/wind/floris.html (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- Jensen, N.O. A Note on Wind Generator Interaction; Risø National Laboratory: Roskilde Fjord, Denmark, 1983; ISBN 8755009719.
- Jiménez, Á.; Crespo, A.; Migoya, E. Application of a LES Technique to Characterize the Wake Deflection of a Wind Turbine in Yaw. Wind. Energy 2010, 13, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebraad, P.M.O.; Teeuwisse, F.W.; van Wingerden, J.W.; Fleming, P.A.; Ruben, S.D.; Marden, J.R.; Pao, L.Y. Wind Plant Power Optimization Through Yaw Control Using a Parametric Model for Wake Effects-a CFD Simulation Study. Wind. Energy 2016, 19, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinner, M.; Simley, E.; King, J.; Fleming, P.; Pao, L.Y. Power Increases Using Wind Direction Spatial Filtering for Wind Farm Control: Evaluation Using FLORIS, Modified for Dynamic Settings. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2021, 13, 023310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letizia, S.; Robey, R.; Bodini, N.; Gomez, M.S.; Lundquist, J.K.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Moriarty, P.J. Tilted Lidar Profiling: Development and Testing of a Novel Scanning Strategy for Inhomogeneous Flows. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2024, 16, 043310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, P.; Bitsuamlak, G.; Cao, S. Analytical Solutions for Yawed Wind-Turbine Wakes with Application to Wind-farm Power Optimization by Active Yaw Control. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 304, 117691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastankhah, M.; Porté-Agel, F. Wind Farm Power Optimization Via Yaw Angle Control: A Wind Tunnel Study. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2019, 11, 023301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, M.F.; González, C.M.; Martínez, J.J.P.; Quesada, J.B.; Larrañaga, F.P.; Yadav, N.K.; Chawla, J.S.; Dabiri, J.O. Influence of Atmospheric Conditions on the Power Production of Utility-Scale Wind Turbines in Yaw Misalignment. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2020, 12, 063307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugger, P.; Fuertes, F.C.; Vahidzadeh, M.; Markfort, C.D.; Porté-Agel, F. Characterization of Wind Turbine Wakes with Nacelle-Mounted Doppler LiDARs and Model Validation in the Presence of Wind Veer. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, T.; Jenkins, N.; Sharpe, D.; Bossanyi, E. Wind Energy Handbook; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 111999392X. [Google Scholar]
- Bastankhah, M.; Porté-Agel, F. A New Analytical Model for Wind-Turbine Wakes. Renew. Energy 2014, 70, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, J.; Urbán, A.M.; Andersen, S.J. Analytical Model for the Power–Yaw Sensitivity of Wind Turbines Operating in Full Wake. Wind. Energy Sci. 2020, 5, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Fan, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, A.; Chen, S.; Joo, Y.H. Power Extraction Efficiency Optimization of Horizontal-Axis Wind Turbines Through Optimizing Control Parameters of Yaw Control Systems Using an Intelligent Method. Appl. Energy 2018, 224, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, C.L.; Vasel-Be-Hagh, A. Wake Steering Via Yaw Control in Multi-Turbine Wind Farms: Recommendations Based on Large-Eddy Simulation. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 33, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rak, B.P.; Pereira, R.S. Impact of the Wake Deficit Model on Wind Farm Yield: A Study of Yaw-Based Control Optimization. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2021, 220, 104827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; He, J.; Ge, M.; Ma, H.; Du, B.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. Study of Three Wake Control Strategies for Power Maximization of Offshore Wind Farms with Different Layouts. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 268, 116059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puech, A.; Read, J. An Improved Yaw Control Algorithm for Wind Turbines via Reinforcement Learning BT—Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases; Amini, M.-R., Canu, S., Fischer, A., Guns, T., Kralj Novak, P., Tsoumakas, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 614–630. [Google Scholar]
- Howland, M.F.; Quesada, J.B.; Martínez, J.J.P.; Larrañaga, F.P.; Yadav, N.; Chawla, J.S.; Sivaram, V.; Dabiri, J.O. Collective Wind Farm Operation Based on a Predictive Model Increases Utility-Scale Energy Production. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, H.; Porté-Agel, F. Experimental Investigation and Analytical Modelling of Active Yaw Control for Wind Farm Power Optimization. Renew. Energy 2021, 170, 1228–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, M.F.; Dabiri, J.O. Influence of Wake Model Superposition and Secondary Steering on Model-Based Wake Steering Control with SCADA Data Assimilation. Energies 2021, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beek, M.T.; Viré, A.; Andersen, S.J. Sensitivity and Uncertainty of the FLORIS Model Applied on the Lillgrund Wind Farm. Energies 2021, 14, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, D.; Castellani, F.; Becchetti, M.; Lombardi, A.; Terzi, L. Wind Turbine Systematic Yaw Error: Operation Data Analysis Techniques for Detecting It and Assessing Its Performance Impact. Energies 2020, 13, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Power Gain (Percent) | ||
| Overlap | Full Year | |
| E = 1.3 (Upper range) | 0.58 | 0.21 |
| E = 2.5 (Lower range) | 0.23 | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmoodi, E.; Khezri, M.; Ebrahimi, A.; Ritschel, U.; Kamandi, M. A LiDAR-Based Active Yaw Control Strategy for Optimal Wake Steering in Paired Wind Turbines. Energies 2024, 17, 5635. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225635
Mahmoodi E, Khezri M, Ebrahimi A, Ritschel U, Kamandi M. A LiDAR-Based Active Yaw Control Strategy for Optimal Wake Steering in Paired Wind Turbines. Energies. 2024; 17(22):5635. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225635
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmoodi, Esmail, Mohammad Khezri, Arash Ebrahimi, Uwe Ritschel, and Majid Kamandi. 2024. "A LiDAR-Based Active Yaw Control Strategy for Optimal Wake Steering in Paired Wind Turbines" Energies 17, no. 22: 5635. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225635
APA StyleMahmoodi, E., Khezri, M., Ebrahimi, A., Ritschel, U., & Kamandi, M. (2024). A LiDAR-Based Active Yaw Control Strategy for Optimal Wake Steering in Paired Wind Turbines. Energies, 17(22), 5635. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225635







