Ion-Exchange Strategy Enabling Direct Reformation of Unreliable Perfluorinated Cationic Polymer for Robust Proton Exchange Membrane towards Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Re-PfCPs
2.3. Synthesis of PfSO3K, PfSO3H and Re-PfSO3H
2.4. Membrane Preparation
2.5. Characterization and Measurements
2.6. Fabrication of Membrane Electrode Assemblies (MEA)
3. Results and Discussion
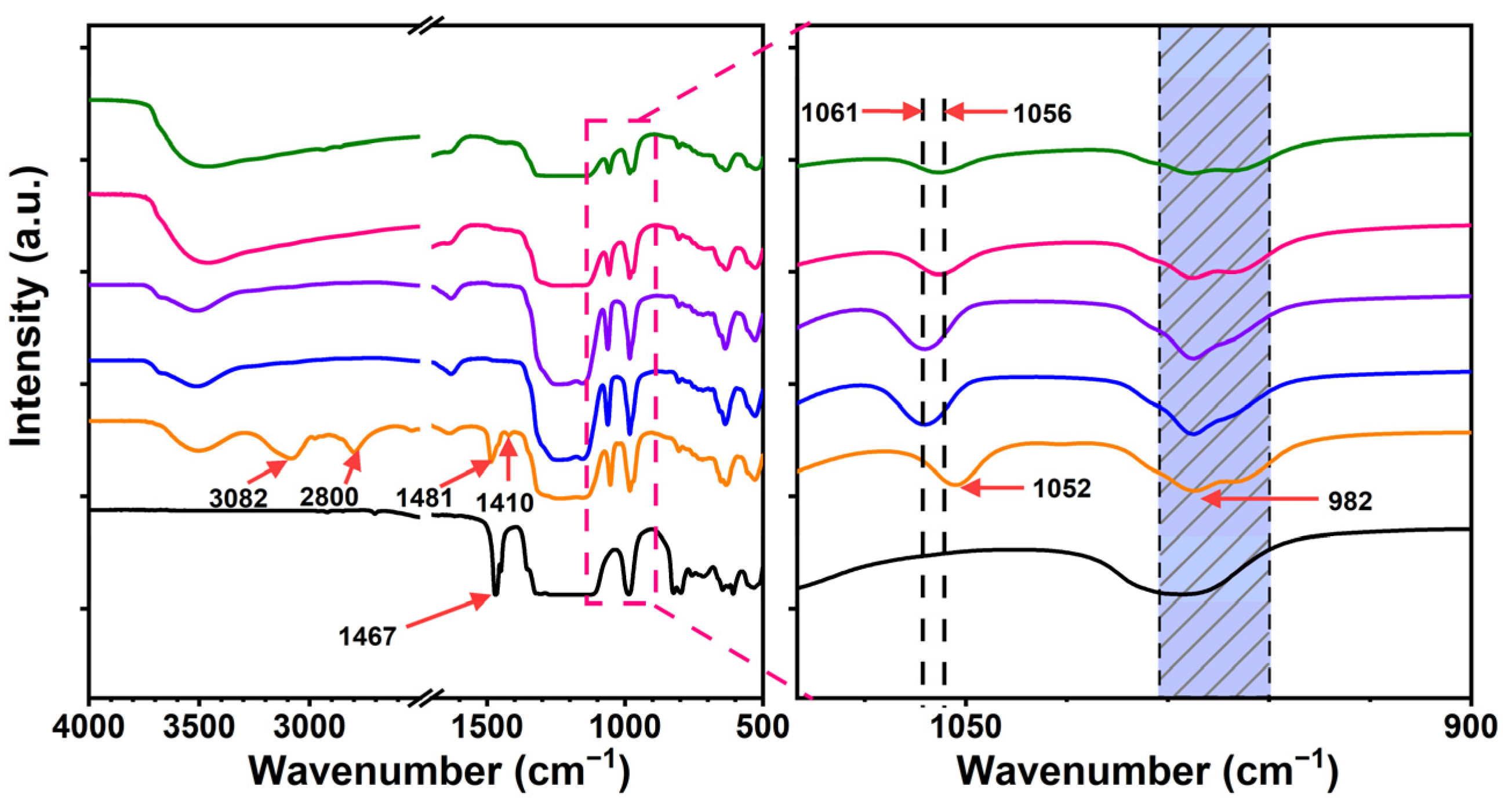
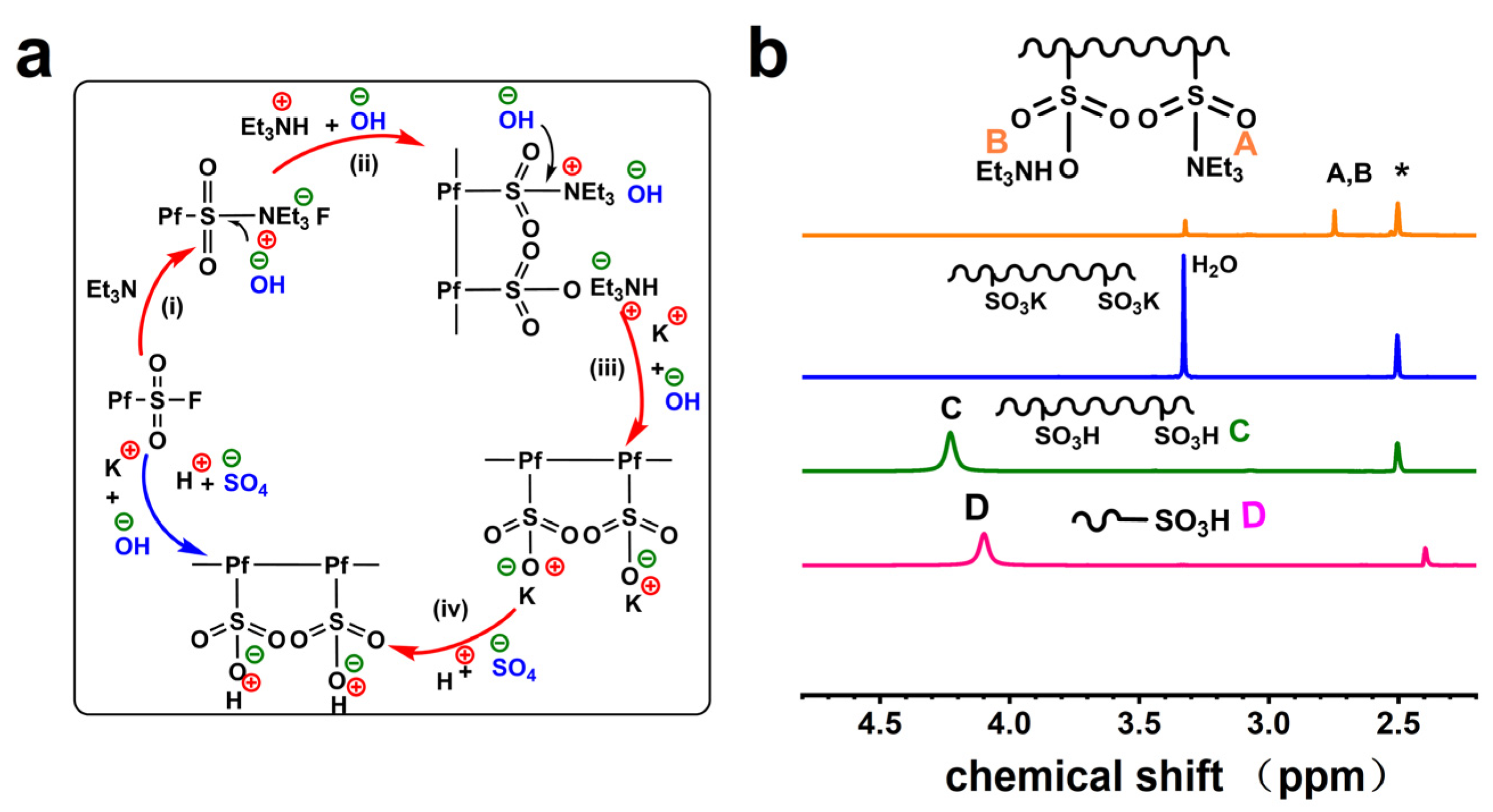
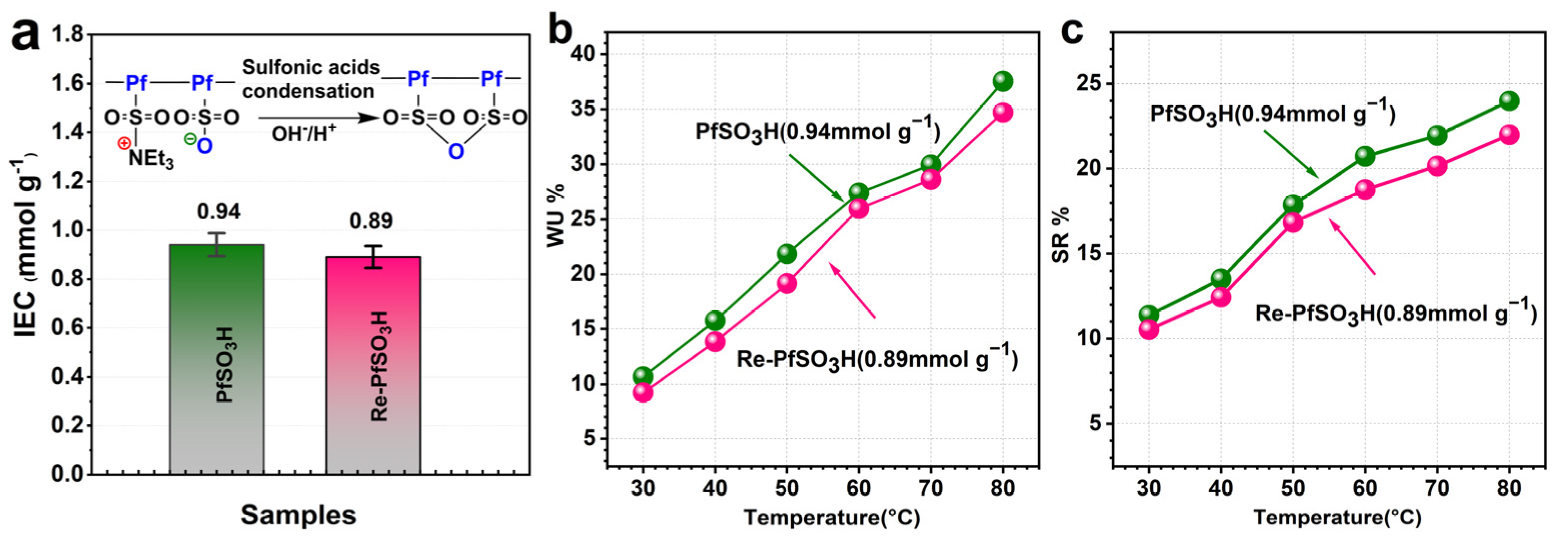
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Polymers
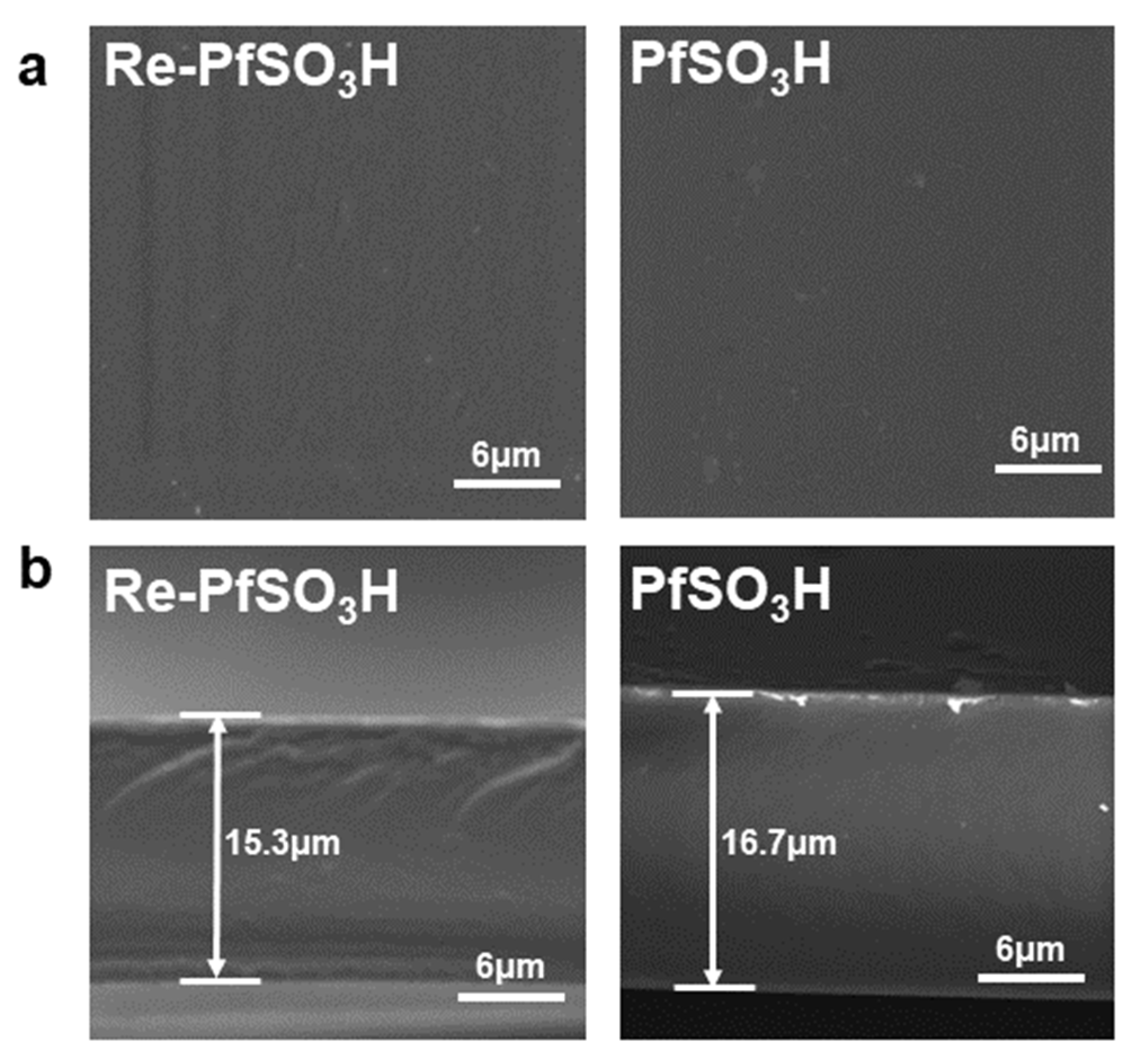
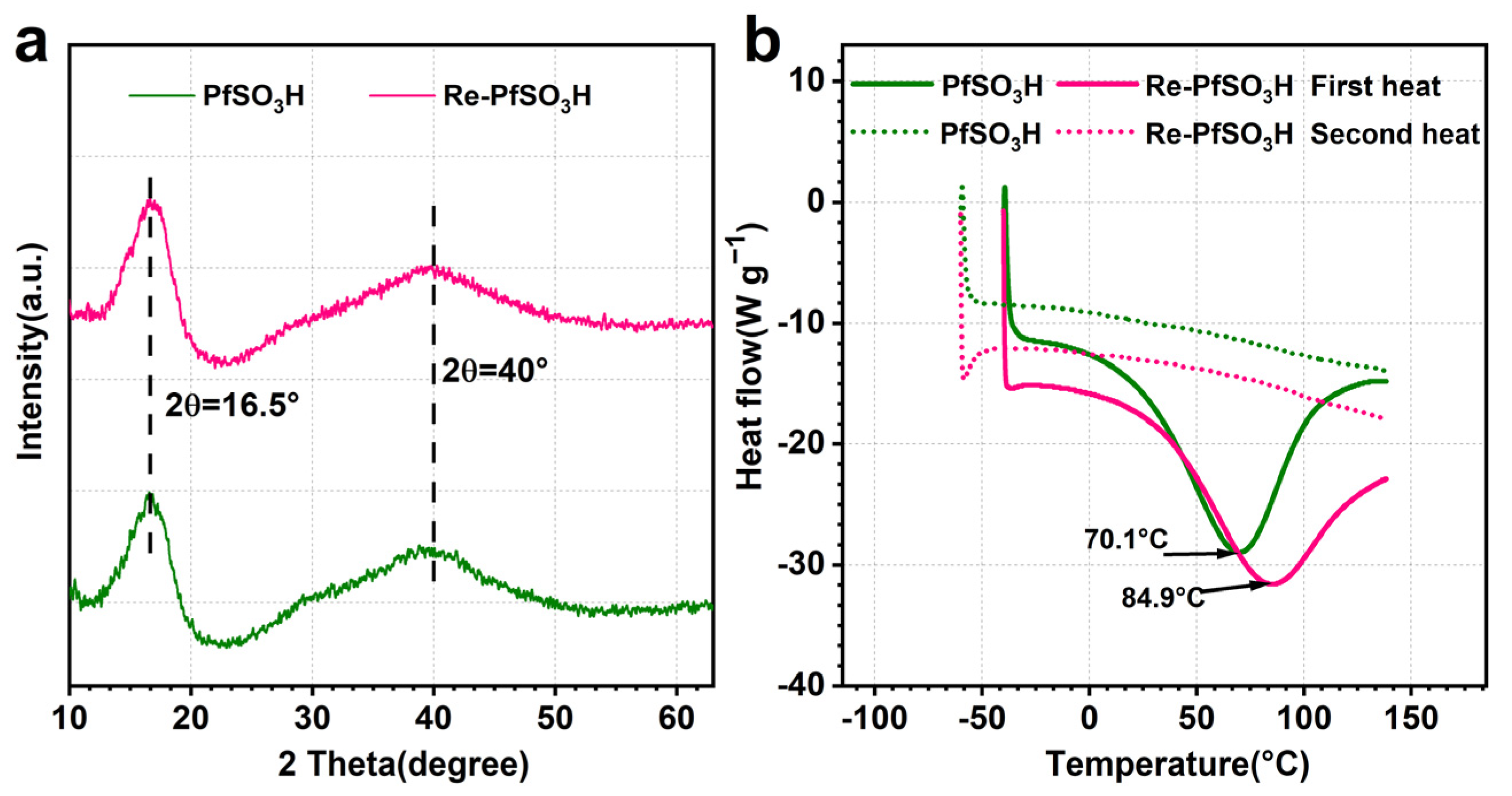
3.2. Membrane Morphology and Crystalline Structure
3.3. Physical and Ion Transport Properties
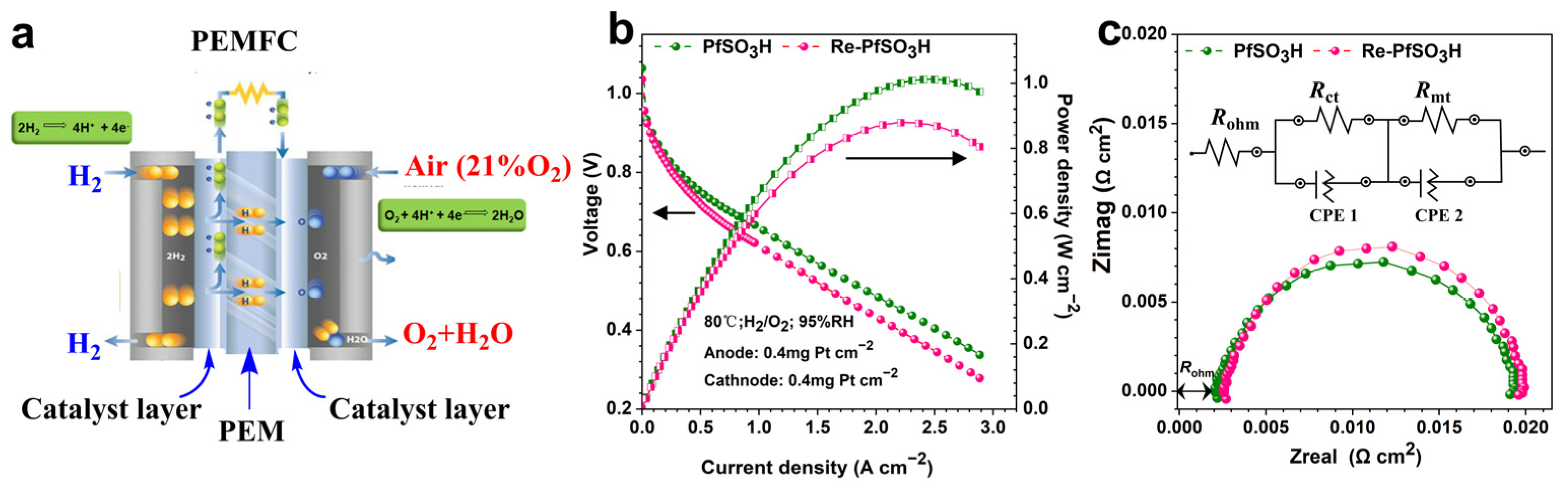
3.4. Single Cell Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Chen, N.; Wang, H.H.; Kim, S.P.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, W.H.; Hu, C.; Bae, J.Y.; Sim, E.S.; Chung, Y.-C.; Jang, J.-H. Poly (fluorenyl aryl piperidinium) membranes and ionomers for anion exchange membrane fuel cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, W.W.; Gao, W.T.; Gao, X.L.; Zhang, Q.G.; Zhu, A.M.; Liu, Q.L. Highly conductive fluorinated poly (biphenyl piperidinium) anion exchange membranes with robust durability. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 645, 120200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Pan, J.; Zou, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Fang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Yan, F. High-performance poly (biphenyl piperidinium) type anion exchange membranes with interconnected ion transfer channels: Cooperativity of dual cations and fluorinated side chains. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, N.; Hu, C.; Klok, H.A.; Lee, Y.M.; Hu, X. Fluorinated poly (aryl piperidinium) membranes for anion exchange membrane fuel cells. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2210432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min-suk, J.J.; Arges, C.G.; Ramani, V. A perfluorinated anion exchange membrane with a 1, 4-dimethylpiperazinium cation. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 6158–6160. [Google Scholar]
- Vandiver, M.A.; Horan, J.L.; Yang, Y.; Tansey, E.T.; Seifert, S.; Liberatore, M.W.; Herring, A.M. Synthesis and characterization of perfluoro quaternary ammonium anion exchange membranes. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2013, 51, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Zignani, S.C.; Gatto, I.; Pedicini, R.; Oldani, C.; Cattaneo, A.; Aricò, A.S. Aquivion-based anion exchange membranes: Synthesis optimization via dispersant agents and reaction time. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhao, S.; Tan, H.; Wang, R.; Zhai, M.; Zhang, H.; Qin, H.; Tang, H. Construction of reliable ion-conducting channels based on the perfluorinated anion-exchange membrane for high-performance pure-water-fed electrolysis. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilli, P.; Bonizzoni, S.; Lohmann-Richters, F.; Beverina, L.; Papagni, A.; Mustarelli, P. Aquivion®-based anionic membranes for water electrolysis. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 405, 139834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonizzoni, S.; Stilli, P.; Lohmann-Richters, F.; Oldani, C.; Ferrara, C.; Papagni, A.; Beverina, L.; Mustarelli, P. Facile chemical modification of Aquivion® membranes for anionic fuel cells. ChemElectroChem 2021, 8, 2231–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, D.M.; Stephens, S.H.; Poynton, S.D.; Murphy, S.; Ong, A.L.; Varcoe, J.R. The reaction between Nafion sulfonyl fluoride precursor membrane and 1, 4-dimethylpiperazine does not yield reliable anion-exchange membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosnjakovic, A.; Danilczuk, M.; Schlick, S.; Xiong, P.N.; Haugen, G.M.; Hamrock, S.J. An attempt to generate anion exchange membranes by amination of the perfluorinated 3M precursor leads to the hydrolysis of the precursor. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 467, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.B.; Mohammadi, F.; Hooshyari, K. Effect of deep eutectic solvents hydrogen bond acceptor on the anhydrous proton conductivity of Nafion membrane for fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 605, 118116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Ye, P.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Lei, J.; Wang, L.; Xue, R. Ultra-Stable, Highly Proton Conductive, and Self-Healing Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Molecule Intercalation Technique and Noncovalent Assembly Nanostructure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2210453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W.; Sun, G.; Xin, Q. FT-IR study of the microstructure of Nafion® membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 233, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, H.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Pei, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of perfluorinated ionomers and their anion exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 515, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Gobrogge, E.; Beyer, F.L. States of water in recast Nafion® films. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 637, 119645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandavalli, S.; Park, J.H.; Winter, H.H.; Myers, D.J.; Ulsh, M.; Mauger, S.A. Viscoelasticity Enhancement and Shear Thickening of Perfluorinated Sulfonic Acid Ionomer Dispersions in Water–Alcohol Solvent Mixtures. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 6988–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domhoff, A.; Martin, T.B.; Silva, M.S.; Saberi, M.; Creager, S.; Davis, E.M. Enhanced Proton Selectivity in Ionomer Nanocomposites Containing Hydrophobically Functionalized Silica Nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Zhang, G.; Jang, S.; Lee, S.; Suo, Z.; Kim, S.M. Fatigue-Resistant Polymer Electrolyte Membranes for Fuel Cells. Adv. Mater. 2023, 36, 2308288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Huang, G.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.-L.; Li, J.-C.; Yan, J.-M.; Zhang, X.-B. Soluble and Perfluorinated Polyelectrolyte for Safe and High-Performance Li−O2 Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, P.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, W.; Xu, J.; Lei, J.; Ding, H.; Feng, W.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y. High-temperature low-humidity proton exchange membrane with “stream-reservoir” ionic channels for high-power-density fuel cells. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Qian, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Fang, P.; He, C. High-performance fuel cells using Nafion composite membranes with alignment of sulfonated graphene oxides induced by a strong magnetic field. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 653, 120516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.; Nederstedt, H.; Jannasch, P.; Lindström, R.W. Poly(arylene alkylene)s functionalized with perfluorosulfonic acid groups as proton exchange membranes for vanadium redox flow batteries. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 671, 121390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotnaya, U.M.; Privalov, A.F.; Kresse, B.; Vogel, M.; Ponomarev, I.I.; Volkova, Y.A.; Sinitsyn, V.V. Diffusion in Sulfonated Co-Polynaphthoyleneimide Proton Exchange Membranes with Different Ratios of Hydrophylic to Hydrophobic Groups Studied Using SFG NMR. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 8823–8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; Foglia, F.; Clancy, A.J.; Brett, D.J.L.; Miller, T.S. Nafion Matrix and Ionic Domain Tuning for High-Performance Composite Proton Exchange Membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2304061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma Andersen, S. The importance of ion selectivity of perfluorinated sulfonic acid membrane for the performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Fuel Cell Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 061010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, L.; Meng, H.; Wang, H.; Guan, P.; Li, M.; Zou, Y.; Feng, W.; Zhang, M.; et al. Rational Materials and Structure Design for Improving the Performance and Durability of High Temperature Proton Exchange Membranes (HT-PEMs). Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2303969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Kim, I.S.; Miyatake, K. Proton-conductive aromatic membranes reinforced with poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers for high-performance durable fuel cells. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Lu, S.; Xiang, Y. Porous Proton Exchange Membrane with High Stability and Low Hydrogen Permeability Realized by Dense Double Skin Layers Constructed with Amino tris (methylene phosphonic acid). Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2210036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusoglu, A.; Vezzù, K.; Hegde, G.A.; Nawn, G.; Motz, A.R.; Sarode, H.N.; Haugen, G.M.; Yang, Y.; Seifert, S.; Yandrasits, M.A.; et al. Transport and Morphology of a Proton Exchange Membrane Based on a Doubly Functionalized Perfluorosulfonic Imide Side Chain Perflourinated Polymer. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 38–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collette, F.M.; Thominette, F.; Escribano, S.; Ravachol, A.; Morin, A.; Gebel, G. Fuel cell rejuvenation of hygrothermally aged Nafion®. J. Power Sources 2012, 202, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuc, V.D.; Tinh, V.D.C.; Kim, D. Simultaneous improvement of proton conductivity and chemical stability of Nafion membranes via embedment of surface-modified ceria nanoparticles in membrane surface. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 642, 119990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayadevi, T.S.; Goo, B.-H.; Paek, S.Y.; Choi, O.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, O.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, T.-H. Nafion Composite Membranes Impregnated with Polydopamine and Poly(Sulfonated Dopamine) for High-Performance Proton Exchange Membranes. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 12956–12970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutter, M.; Greve, C.; Maier, M.; Schilling, M.; Mauel, A.; Hilgert, A.; Hoffmann, H.; Hagemeier, W.; Rosin, A.; Muggli, M.; et al. Recycling of perfluorosulfonic acid-based membranes and their Re-application in PEM fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 693, 122370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.F.; Sun, P.Z.; Wahab, O.J.; Tan, Y.T.; Barry, D.; Periyanagounder, D.; Pillai, P.B.; Dai, Q.; Xiong, W.Q.; Vega, L.F.; et al. Proton and molecular permeation through the basal plane of monolayer graphene oxide. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Lv, Z.; Cai, W.; Sun, S.; et al. PAF-6 Doped with Phosphoric Acid through Alkaline Nitrogen Atoms Boosting High-Temperature Proton-Exchange Membranes for High Performance of Fuel Cells. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2303535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paren, B.A.; Thurston, B.A.; Kanthawar, A.; Neary, W.J.; Kendrick, A.; Maréchal, M.; Kennemur, J.G.; Stevens, M.J.; Frischknecht, A.L.; Winey, K.I. Fluorine-Free Precise Polymer Electrolyte for Efficient Proton Transport: Experiments and Simulations. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 6041–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Liao, J.; Xu, Y.; Shen, J. Porphyrin Helical Nanochannel-Assembled Polybenzimidazole Membranes Doped with Phosphoric Acid for Fuel Cells Operating in a Temperature Range of 25–200 °C. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2310762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Ohto, T.; Nishiuchi, T.; Nagata, Y.; Fujita, J.-i.; Ito, Y. Suppression of Methanol and Formate Crossover through Sulfanilic-Functionalized Holey Graphene as Proton Exchange Membranes. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2304082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Kang, M.; Yun, H.; Park, H.; Hong, C.S. Emerging Porous Solid Electrolytes for Hydroxide Ion Transport. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Lim, J.; Lee, S.; Han, S.; Seong, J.; Bin Baek, S.; Soo Lah, M. Superprotonic Conductivity of MOFs Confining Zwitterionic Sulfamic Acid as Proton Source and Conducting Medium. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202302376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, A.; Tan, R.; Liu, Y.; Liang, X.; Sheng, F.; Tang, G.; Ge, L.; Wu, L. Sulfonated microporous polymer membranes with fast and selective ion transport for electrochemical energy conversion and storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9564–9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Hu, B.; Du, J.; Cheng, D.; Zang, H.Y.; Ge, X.; Tan, H.; Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Jin, Z. Precise Molecular-Level Modification of Nafion with Bismuth Oxide Clusters for High-performance Proton-Exchange Membranes. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 6141–6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wu, H.; Cao, Y.; Fan, C.; Zhao, R.; He, X.; Yang, P.; Shi, B.; You, X.; Jiang, Z. Weakly humidity-dependent proton-conducting COF membranes. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2005565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Guiver, M.D. A paradigm shift for a new class of proton exchange membranes with ferrocyanide proton-conducting groups providing enhanced oxidative stability. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 616, 118536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Lan, T.; Xu, J.; Zhao, P.; Lei, J. Adjusting structure-activity relationship to obtain hybrid proton exchange membrane with enhanced transport efficiency by introducing functionalized nano-coated MOFs. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 694, 122409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuc, V.D.; Kim, D. Ultra-thin, mechanically durable reinforced sulfonated poly (fluorenyl biphenyl) indole proton exchange membrane for fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 694, 122393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, L.; Guan, J.; Sang, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, G.; Li, S.; Zhang, S. Side chain sulfonic acid polymers with intrinsic pores in the main chain as proton exchange membranes for fuel cells and redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 687, 122036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Hu, Z.; Chen, S. PTFE-reinforced pore-filling proton exchange membranes with sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) s and poly (aryl ether sulfone) s. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 694, 122431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, X.; Jia, W.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, A.; Liu, X. Ion-Exchange Strategy Enabling Direct Reformation of Unreliable Perfluorinated Cationic Polymer for Robust Proton Exchange Membrane towards Hydrogen Fuel Cells. Energies 2024, 17, 2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122954
Xie X, Jia W, Liu C, Li Y, Xu A, Liu X. Ion-Exchange Strategy Enabling Direct Reformation of Unreliable Perfluorinated Cationic Polymer for Robust Proton Exchange Membrane towards Hydrogen Fuel Cells. Energies. 2024; 17(12):2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122954
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Xuqiu, Wenjing Jia, Changyuan Liu, Yongzhe Li, Anhou Xu, and Xundao Liu. 2024. "Ion-Exchange Strategy Enabling Direct Reformation of Unreliable Perfluorinated Cationic Polymer for Robust Proton Exchange Membrane towards Hydrogen Fuel Cells" Energies 17, no. 12: 2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122954
APA StyleXie, X., Jia, W., Liu, C., Li, Y., Xu, A., & Liu, X. (2024). Ion-Exchange Strategy Enabling Direct Reformation of Unreliable Perfluorinated Cationic Polymer for Robust Proton Exchange Membrane towards Hydrogen Fuel Cells. Energies, 17(12), 2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17122954





