A Review on the Internalization of Externalities in Electricity Generation Expansion Planning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Externalities and Electricity Generation
2.1. The Concept of Externalities
2.2. Externalities of Electricity Production
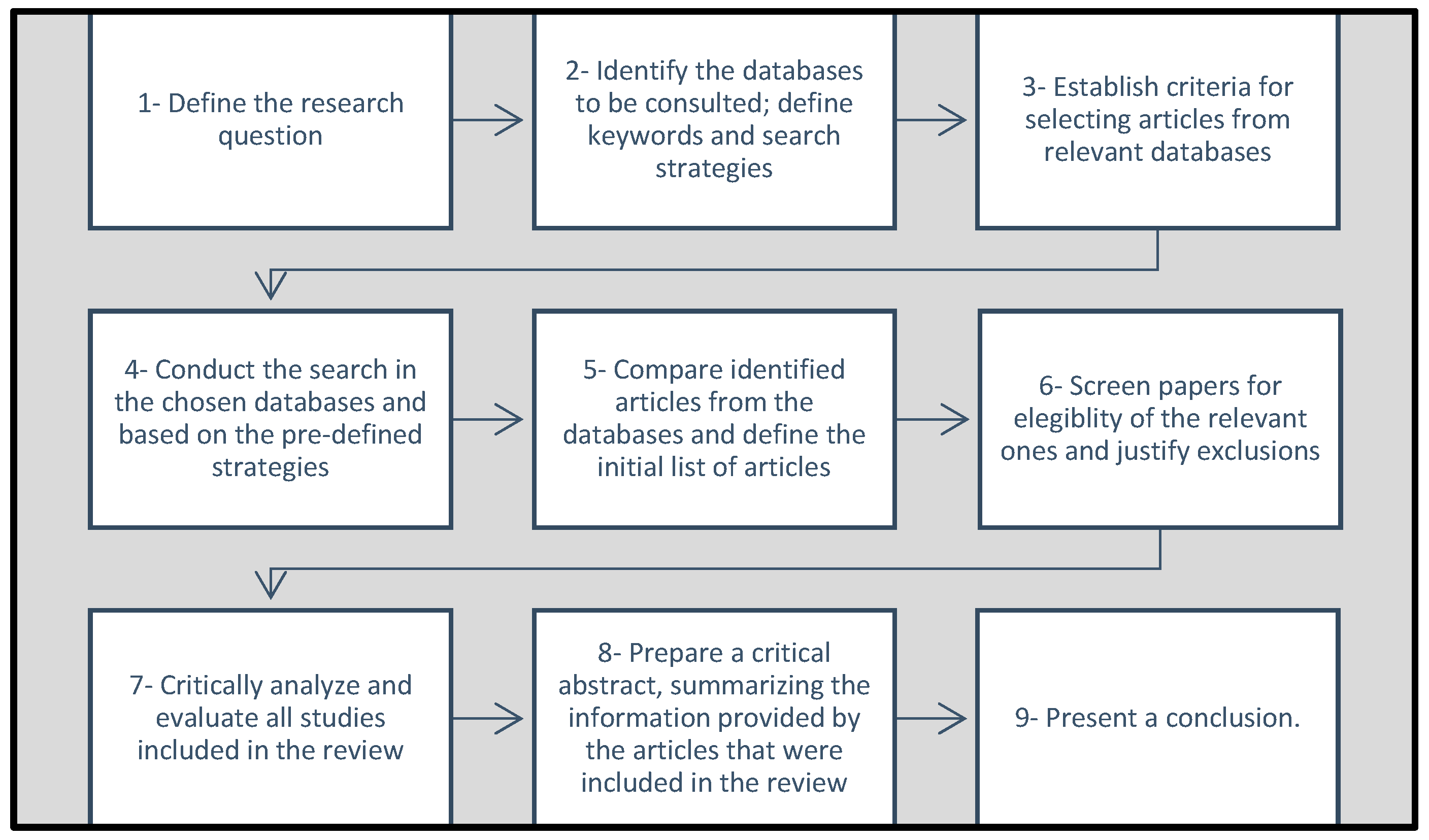
3. Methodology
- Published in the defined timeframe for the analysis;
- Related to the generation of electricity;
- Clear definition of the geographical scope of the work;
- Clear definition of which externalities were included in the study; and
- Research papers published in journals (conferences and review papers excluded).
4. Results
5. Discussion and Future Research Directions
5.1. A Regional Perspective Can Bring Additional Benefits to the GEP Problem
5.2. Expanding the Models beyond GHG Is Fundamental for a Whole Sustainable Perspective
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cerqueira, P.A.; Soukiazis, E.; Proença, S. Assessing the Linkages between Recycling, Renewable Energy and Sustainable Development: Evidence from the OECD Countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 9766–9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, D.L.; Echeverri, L.G.; Busch, S.; Pachauri, S.; Parkinson, S.; Rogelj, J.; Krey, V.; Minx, J.C.; Nilsson, M.; Stevance, A.S.; et al. Connecting the Sustainable Development Goals by Their Energy Inter-Linkages. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 033006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuso Nerini, F.; Tomei, J.; To, L.S.; Bisaga, I.; Parikh, P.; Black, M.; Borrion, A.; Spataru, C.; Castán Broto, V.; Anandarajah, G.; et al. Mapping Synergies and Trade-Offs between Energy and the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, H.; Rashidinejad, M.; Abdollahi, A. A Comprehensive Sequential Review Study through the Generation Expansion Planning. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 1369–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Bao, G.; Wang, X. Multi-Period Generation Expansion Planning for Sustainable Power Systems to Maximize the Utilization of Renewable Energy Sources. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.L.; Legey, L.F.L. A Model for Long-Term Electricity Expansion Planning with Endogenous Environmental Costs. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2013, 51, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istrate, I.R.; García-Gusano, D.; Iribarren, D.; Dufour, J. Long-Term Opportunities for Electricity Production through Municipal Solid Waste Incineration When Internalising External Costs. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehlmann, M.; Glenk, K.; Lloyd-Smith, P.; Meyerhoff, J. Quantifying Landscape Externalities of Renewable Energy Development: Implications of Attribute Cut-Offs in Choice Experiments. Resour. Energy Econ. 2021, 65, 101240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamala, C.; Moreno, R.; Sauma, E.; Calabrese, J.; Osses, P. Why Reducing Socio-Environmental Externalities of Electricity System Expansions Can Boost the Development of Solar Power Generation: The Case of Chile. Sol. Energy 2021, 217, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrapertosa, F.; Cosmi, C.; Di Leo, S.; Loperte, S.; Macchiato, M.; Salvia, M.; Cuomo, V. Assessment of Externalities Related to Global and Local Air Pollutants with the NEEDS-TIMES Italy Model. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gies, E. The Real Cost of Energy: All Energy Production Has Environmental and Societal Effects. but Calculating Them- A Nd Pricing Energy Accordingly-Is No Easy Task. Nature 2017, 551, S145–S147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dranka, G.G.; Ferreira, P. Planning for a Renewable Future in the Brazilian Power System. Energy 2018, 164, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gils, H.C.; Simon, S.; Soria, R. 100% Renewable Energy Supply for Brazil-The Role of Sector Coupling and Regional Development. Energies 2017, 10, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, J.M.L.; Cesaretti, M.A.; Carajilescov, P.; Maiorino, J.R. Sustainability Deterioration of Electricity Generation in Brazil. Energy Policy 2015, 87, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.J.; Ferreira, P.; Araújo, M.; Portugal-Pereira, J.; Lucena, A.F.P.; Schaeffer, R. Scenarios for the Future Brazilian Power Sector Based on a Multi-Criteria Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Panigrahi, C.K.; Samanta, S. Externalities of Clean Energy Technologies: A Study. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1253, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornes, R.; Sandler, T. The Theory of Externalities, Public Goods, and Club Goods; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Derani, C.D.; Neto, A.d.A. Valoração Econômica Dos Bens Ambientais. Hiléia Revista de Direito Ambiental da Amazônia 2007, 9, 49–69. [Google Scholar]
- Pigou, A.C. The Economics of Welfare, 3rd ed.; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 1928; ISBN 1137375639. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, D.W.; Turner, R.K. Economics of Natural Resources and the Environment; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1990; ISBN 9780801839870. [Google Scholar]
- Mankiw, N.G. Macroeconomics, 7th ed.; Worth Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 91, ISBN 9781429218870. [Google Scholar]
- Trapp, G.S.; Rodrigues, L.H. Evaluation of the Total Systemic Cost of Wind Power Generation in Face of the Replacement of Hydroelectric and Thermoelectric Sources Considering Socioeconomic and Environmental Externalities. Gest. Prod. 2016, 23, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, B.C.; Olewiler, N.D. Environmental Economics, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Ryerson Higher Education, 2015; ISBN 9780070893108. Available online: https://www.amazon.com/Environmental-Economics-Nancy-Olewiler-Barry/dp/0070893101 (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- Becker, U.; Becker, T.; Gerlach, J. The True Costs of Automobility: External Costs of Cars Overview on Existing Estimates in EU-27 Chair of Transport Ecology; Technische Universität Dresden: Dresden, Germany, 2016; Volume 49. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.L.; Laratte, B.; Guillaume, B.; Hua, A. Quantifying Environmental Externalities with a View to Internalizing Them in the Price of Products, Using Different Monetization Models. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 109, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafaj, P.; Kypreos, S. Internalisation of External Cost in the Power Generation Sector: Analysis with Global Multi-Regional MARKAL Model. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 828–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.; Foster, I.; Kortum, S.; Munson, T.; Cervantes, F.P.; Weisbach, D. Trade and Carbon Taxes. Am. Econ. Rev. 2010, 100, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moch, F. Principios de Economía, 3rd ed.; Mc Graw Hill: Madrid, Spain, 2006; ISBN 8448146565. [Google Scholar]
- Söderholm, P.; Sundqvist, T. Pricing Environmental Externalities in the Power Sector: Ethical Limits and Implications for Social Choice. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 46, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochedo, P.R.R.; Soares-Filho, B.; Schaeffer, R.; Viola, E.; Szklo, A.; Lucena, A.F.P.; Koberle, A.; Davis, J.L.; Rajão, R.; Rathmann, R. The Threat of Political Bargaining to Climate Mitigation in Brazil. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streimikiene, D.; Roos, I.; Rekis, J. External Cost of Electricity Generation in Baltic States. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streimikiene, D.; Alisauskaite-Seskiene, I. External Costs of Electricity Generation Options in Lithuania. Renew. Energy 2014, 64, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovacool, B.K.; Monyei, C.G. Positive Externalities of Decarbonization: Quantifying the Full Potential of Avoided Deaths and Displaced Carbon Emissions from Renewable Energy and Nuclear Power. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 5258–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecki, A.; Ernst, S.; Skrodzka, W.; Wojnicki, I. The Externalities of Energy Production in the Context of Development of Clean Energy Generation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11506–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovacool, B.K.; Kim, J.; Yang, M. The Hidden Costs of Energy and Mobility: A Global Meta-Analysis and Research Synthesis of Electricity and Transport Externalities. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2021, 72, 101885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, H.; Donato, M. Etapas Na Condução de Uma Revisão Sistemática. Acta Med. Port. 2019, 32, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, S.; Kwon, J.; Madan, J. A Practical Guide to Conducting a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Health State Utility Values. Pharmacoeconomics 2018, 36, 1043–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unsihuay-Vila, C.; Marangon-Lima, J.W.; Zambroni De Souza, A.C.; Perez-Arriaga, I.J. Multistage Expansion Planning of Generation and Interconnections with Sustainable Energy Development Criteria: A Multiobjective Model. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2011, 33, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Soloveitchik, D.; Olshansky, M. Incorporating Environmental Externalities into the Capacity Expansion Planning: An Israeli Case Study. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 2489–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Koo, J.; Lee, C.J.; Yoon, E.S. Optimization of Korean Energy Planning for Sustainability Considering Uncertainties in Learning Rates and External Factors. Energy 2012, 44, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitizadeh, M.; Kaji, M.; Aghaei, J. Risk Based Multiobjective Generation Expansion Planning Considering Renewable Energy Sources. Energy 2013, 50, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Ferreira, P.; Araújo, M. Evaluating Future Scenarios for the Power Generation Sector Using a Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) Tool: The Portuguese Case. Energy 2013, 52, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, B.; Missaoui, R. Multi-Criteria Analysis of Electricity Generation Mix Scenarios in Tunisia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 39, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xiong, W.; Tang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X. Determining the Appropriate Amount of Subsidies for Wind Power: The Integrated Renewable Power Planning (IRPP) Model and Its Application in China. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2014, 6, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Ferreira, P.; Vaz, A.I.F. Short-Term Electricity Planning with Increase Wind Capacity. Energy 2014, 69, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Xu, Y.; Kang, J.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Z. Nonlinear Integrated Resource Strategic Planning Model and Case Study in China’s Power Sector Planning. Energy 2014, 67, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhani, R.; Doluweera, G.; Bergerson, J. Internalizing Land Use Impacts for Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Energy Systems: A Case of California’s Photovoltaic Implementation. Appl. Energy 2014, 116, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.A.; Chungpaibulpatana, S. Electricity Generation Expansion Planning with Environmental Impact Abatement: Case Study of Bangladesh. Energy Procedia 2014, 52, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barteczko-Hibbert, C.; Bonis, I.; Binns, M.; Theodoropoulos, C.; Azapagic, A. A Multi-Period Mixed-Integer Linear Optimisation of Future Electricity Supply Considering Life Cycle Costs and Environmental Impacts. Appl. Energy 2014, 133, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryanpur, V.; Shafiei, E. Optimal Deployment of Renewable Electricity Technologies in Iran and Implications for Emissions Reductions. Energy 2015, 91, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štreimikiene, D.; Šliogeriene, J.; Turskis, Z. Multi-Criteria Analysis of Electricity Generation Technologies in Lithuania. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.J.; Ferreira, P.; Araújo, M. A Methodology to Incorporate Risk and Uncertainty in Electricity Power Planning. Energy 2016, 115, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, K.; Bhuvanesh, A.; Kannan, S.; Thangaraj, C. Least Cost Generation Expansion Planning with Solar Power Plant Using Differential Evolution Algorithm. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, B.-J.; Liao, H.; Wei, Y.-M. A Multi-Period Power Generation Planning Model Incorporating the Non-Carbon External Costs: A Case Study of China. Appl. Energy 2016, 183, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juroszek, Z.; Kudelko, M. A Model of Optimization for Local Energy Infrastructure Development. Energy 2016, 96, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakouri, G.H.; Aliakbarisani, S. At What Valuation of Sustainability Can We Abandon Fossil Fuels? A Comprehensive Multistage Decision Support Model for Electricity Planning. Energy 2016, 107, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, P.N. A Bottom-up Optimization Model for the Long-Term Energy Planning of the Greek Power Supply Sector Integrating Mainland and Insular Electric Systems. Comput. Oper. Res. 2016, 66, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Wu, J.-H.; Hsu, Y.-J. Two-Stage Stochastic Programming Model for the Regional-Scale Electricity Planning under Demand Uncertainty. Energy 2016, 116, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbowski, M.; Lyzwa, W.; Musial, I. MILP Model for Long-Term Energy Mix Planning with Consideration of Power System Reserves. Appl. Energy 2016, 169, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosugi, T. Endogenizing the Probability of Nuclear Exit in an Optimal Power-Generation Mix Model. Energy 2016, 100, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrizio, P.; Leduc, S.; Chinese, D.; Kraxner, F. Internalizing the External Costs of Biogas Supply Chains in the Italian Energy Sector. Energy 2017, 125, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Ferreira, P.; Vaz, A.I.F. Generation Expansion Planning with High Share of Renewables of Variable Output. Appl. Energy 2017, 190, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awopone, A.K.; Zobaa, A.F.; Banuenumah, W. Techno-Economic and Environmental Analysis of Power Generation Expansion Plan of Ghana. Energy Policy 2017, 104, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afful-Dadzie, A.; Afful-Dadzie, E.; Awudu, I.; Banuro, J.K. Power Generation Capacity Planning under Budget Constraint in Developing Countries. Appl. Energy 2017, 188, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.-J.; Li, R.; Li, X.-Y.; Chen, H. An Optimal Production Planning Model of Coal-Fired Power Industry in China: Considering the Process of Closing down Inefficient Units and Developing CCS Technologies. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, M.D.; Coit, D.W.; Felder, F.A.; Carlton, A. Generation Expansion Planning Considering Health and Societal Damages—A Simulation-Based Optimization Approach. Energy 2018, 164, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, N.; Thopil, G.A. Life Cycle Analysis of External Costs of a Parabolic Trough Concentrated Solar Power Plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gusano, D.; Istrate, I.R.; Iribarren, D. Life-Cycle Consequences of Internalising Socio-Environmental Externalities of Power Generation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Guo, Z.; Liu, P.; Li, Z. Advances in Clean and Low-Carbon Power Generation Planning. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2018, 116, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yu, B.; Wang, L. Costs and Benefits of Renewable Energy Development in China’s Power Industry. Renew. Energy 2019, 131, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, M.; Coit, D.; Felder, F.; Carlton, A. Assessing the Effects of Power Grid Expansion on Human Health Externalities. Socioecon. Plann. Sci. 2019, 66, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, D.; Sauma, E.; Pozo, D. Power System Expansion Planning under Global and Local Emission Mitigation Policies. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 1250–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I. Power Generation Expansion Plan and Sustainability in a Developing Country: A Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, P.; Li, Z. Multi-Regional Power Generation Expansion Planning with Air Pollutants Emission Constraints. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 112, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.-C.; Hsu, H.-W.; Wu, M.-C.; Lee, M.-Y. Future Thinking on Power Planning: A Balanced Model of Regions, Seasons and Environment with a Case of Taiwan. Futures 2020, 122, 102599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Ullah, K.; Imran, K.; Mahmood, I.; Mahmood, A. Electricity Supply Pathways Based on Renewable Resources: A Sustainable Energy Future for Pakistan. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranka, G.G.; Ferreira, P.; Vaz, A.I.F. Cost-Effectiveness of Energy Efficiency Investments for High Renewable Electricity Systems. Energy 2020, 198, 117198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, T.; Yang, Q.; Deng, X.; Xu, J.; Gao, J. Generation Expansion Planning Considering the Output and Flexibility Requirement of Renewable Energy: The Case of Jiangsu Province. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Sauma, E. Power Systems Expansion Planning with Time-Varying CO2 Tax. Energy Policy 2020, 144, 111630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahdadi Mehrabadi, R.; Parsa Moghaddam, M.; Sheikh-El-Eslami, M.K. Generation Expansion Planning in Multi Electricity Markets Considering Environmental Impacts. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadamosi, S.L.; Nwulu, N.I. A Multi-Period Composite Generation and Transmission Expansion Planning Model Incorporating Renewable Energy Sources and Demand Response. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 39, 100726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitiwi, D.Z.; Lynch, M.; Bertsch, V. Enhanced Network Effects and Stochastic Modelling in Generation Expansion Planning: Insights from an Insular Power System. Socioecon. Plann. Sci. 2020, 71, 100859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Ullah, K.; Imran, K.; Mahmood, A.; Arentsen, M. LEAP Simulated Economic Evaluation of Sustainable Scenarios to Fulfill the Regional Electricity Demand in Pakistan. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 46, 101292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verástegui, F.; Lorca, Á.; Olivares, D.; Negrete-Pincetic, M. Optimization-Based Analysis of Decarbonization Pathways and Flexibility Requirements in Highly Renewable Power Systems. Energy 2021, 234, 121242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, L.; Khatiwada, D.; Harahap, F.; Silveira, S. Decarbonization Pathways for the Power Sector in Sumatra, Indonesia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 150, 111507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musonye, X.S.; Davíðsdóttir, B.; Kristjánsson, R.; Ásgeirsson, E.I.; Stefánsson, H. Environmental and Techno-Economic Assessment of Power System Expansion for Projected Demand Levels in Kenya Using TIMES Modeling Framework. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2021, 63, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Perwez, U.; Ullah, K.; Kim, C.-H.; Asghar, N. Long-Term Scenario Pathways to Assess the Potential of Best Available Technologies and Cost Reduction of Avoided Carbon Emissions in an Existing 100% Renewable Regional Power System: A Case Study of Gilgit-Baltistan (GB), Pakistan. Energy 2021, 221, 119855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, R. The Incorporation of Environmental Costs into Power System Planning in Brazil; University of London: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Lund, H.; Arler, F.; Østergaard, P.A.; Hvelplund, F.; Connolly, D.; Mathiesen, B.V.; Karnøe, P. Simulation versus Optimisation: Theoretical Positions in Energy System Modelling. Energies 2017, 10, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Rosa, A. Fundamentals of Renewable Energy Processes, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; ISBN 9780123746399. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, P.; Lima, F.; Ribeiro, F.; Vieira, F. A Mixed-Method Approach for the Assessment of Local Community Perception towards Wind Farms. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 33, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oree, V.; Sayed Hassen, S.Z.; Fleming, P.J. Generation Expansion Planning Optimisation with Renewable Energy Integration: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. How Persistent Are Regional Disparities in Employment? OECD: Paris, France, 2005; ISBN 9264010459. [Google Scholar]
- Zemo, K.H.; Panduro, T.E.; Termansen, M. Impact of Biogas Plants on Rural Residential Property Values and Implications for Local Acceptance. Energy Policy 2019, 129, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrell, J.; Lee, K. The Cost of Wind: Negative Economic Effects of Global Wind Energy Development. Energies 2020, 13, 3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, K.B.; Mourshed, M. Challenges and Gaps for Energy Planning Models in the Developing-World Context. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, F.; Benders, R.M.J.; Moll, H.C. Modelling Energy Systems for Developing Countries. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 3473–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremeskel, D.; Bekele, G.; Ahlgren, E.O. Energy System Modeling Tools: Review and Comparison in the Context of Developing Countries. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE PES/IAS PowerAfrica, PowerAfrica 2020, Nairobi, Kenya, 25–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santika, W.G.; Anisuzzaman, M.; Bahri, P.A.; Shafiullah, G.M.; Rupf, G.V.; Urmee, T. From Goals to Joules: A Quantitative Approach of Interlinkages between Energy and the Sustainable Development Goals. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2019, 50, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravena, C.; Hutchinson, W.G.; Longo, A. Environmental Pricing of Externalities from Different Sources of Electricity Generation in Chile. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Jing, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.F.; Zhao, J.H. Review on Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Aid in Sustainable Energy Decision-Making. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 2263–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, D.; Catalano, G.; Genco, M.; Pancott, C.; Sirtori, E.; Vignetti, S.; Bo, C. Del Economic Appraisal Tool Fo Cohesion Policy 2014–2020: Guide to Cost-Benefit Analysis of Investment Projects; Directorate-General for Regional and Urban Policy: Brussel, Belgium, 2015; ISBN 978-92-79-34796-2.
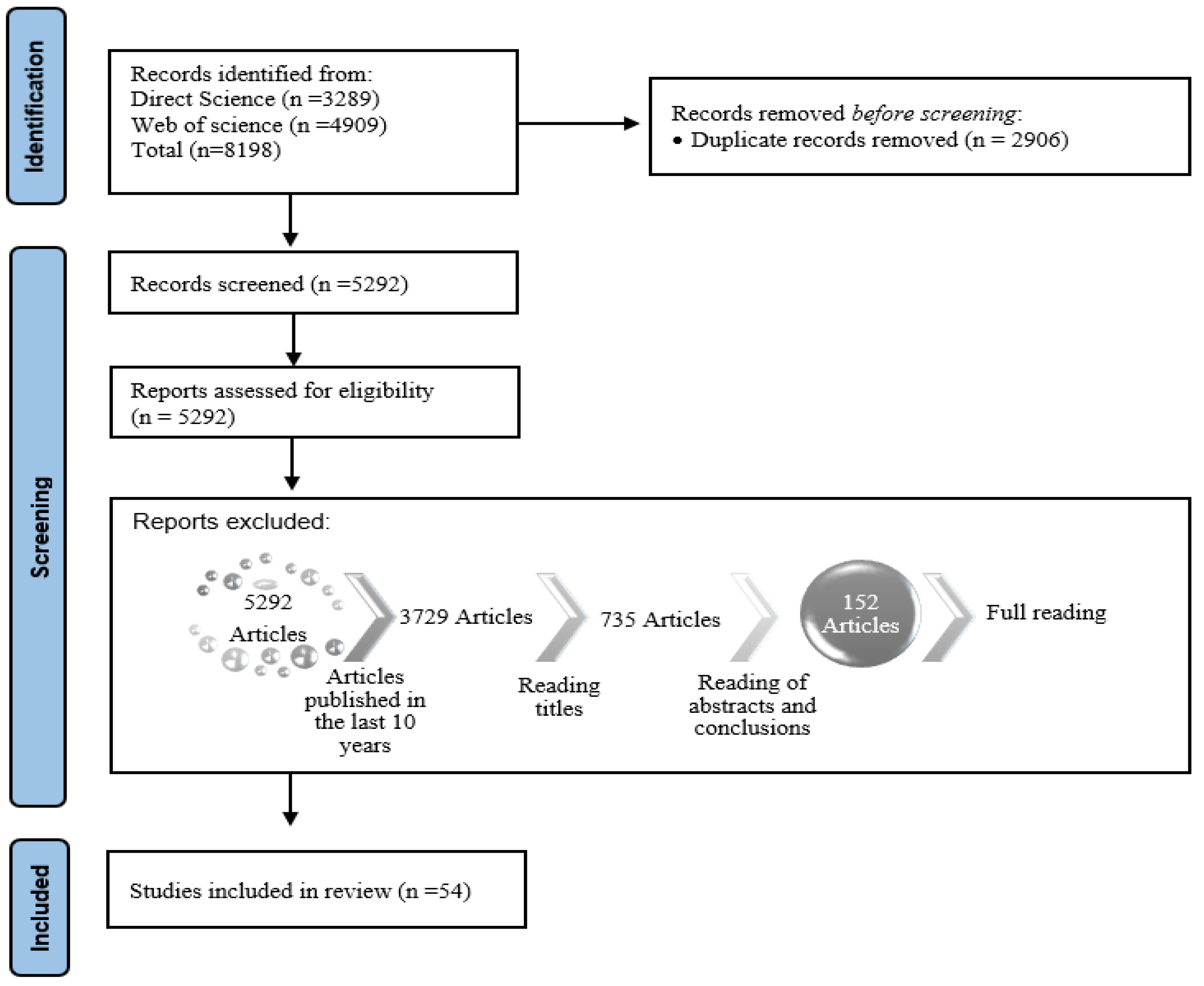
| Keywords | Number of Articles Science Direct | Number of Articles Web of Science |
|---|---|---|
| “Generation expansion planning” OR GEP | 10,734 | 3701 |
| “Generation expansion planning” OR GEP OR “electricity planning” | 11,460 | 9806 |
| (“Generation expansion planning” OR GEP OR “electricity planning” OR “power planning” OR “electrical plan” or “electricity energy plan”) | 14,451 | 10,974 |
| (“Generation expansion planning” OR GEP OR “electricity planning” OR “power planning” OR “electrical plan” or “electricity energy plan) AND (externality OR “externalities OR “external cost” OR “external tax”) | 3289 | 4909 |
| Authors | Year | Method for GEP | Socio-Environmental Effects Addressed | Inclusion of Externalities | Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [39] | 2011 | Optimization | CO2 emissions (life cycle) | Objective function (emissions) | Unspecified case study |
| [40] | 2011 | Optimization (Wien Automatic System Planning-WASP-IV) | CO2 emissions, particulate matter (PM), NOx, and SO2, | Objective function (cost) | Israel |
| [41] | 2012 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Korea |
| [42] | 2013 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (emissions) | Hypothetical case |
| [6] | 2013 | Optimization | Unspecified estimated total environmental cost | Objective function (cost) | Brazil |
| [43] | 2013 | MCDA | Employment, visual impact, noise pollution, local income, CO2 emissions, land use, public health, water consumption | Independent criteria. Participation of decision makers | Portugal |
| [44] | 2014 | MCDA | CO2 emissions, PM, NOx, SO2, nuclear waste | Independent criteria. Participation of decision makers | Tunisia |
| [45] | 2014 | Scenario analysis | NOx, PM, greenhouse gas (GHG) | Levelized cost of energy scenarios | Fujian, China |
| [46] | 2014 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Portugal |
| [47] | 2014 | Optimization | CO2, NOx and SO2 emissions, other unspecified estimated total environmental cost | Objective function (cost) and restrictions | China |
| [48] | 2014 | Scenario analysis (System advisor Model-SAM) | Land use | Life cycle cost, scenarios | California, USA |
| [49] | 2014 | Scenario analysis (Long-range Energy Alternatives Planning-LEAP) | CO2 emissions | Scenarios | Bangladesh |
| [50] | 2014 | Optimization | GHG (life cycle), ozone layer, acidification and photochemical pollution | Objective function (CHG emissions) | UK |
| [51] | 2015 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Iran |
| [52] | 2016 | MCDA | Several (20), e.g., job creation, economic security, contribution to education, science and culture, social acceptance and perception, climate change and pollution, waste creation, or adaptation to local natural conditions | Independent criteria. Participation of decision makers | Lithuania |
| [53] | 2016 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Portugal |
| [54] | 2016 | Optimization | Unspecified estimated environmental cost of emissions | Objective function (cost) and restrictions | India |
| [55] | 2016 | Optimization | CO2 emissions and others (unspecified) | Objective function (cost) | China |
| [56] | 2016 | Optimization | CO2 emissions, PM, NOx, and SO2, | Objective function (cost) | Kietrz, Poland |
| [57] | 2016 | Optimization | CO2 emissions and nuclear waste, land and water use, job creation, social acceptance, and security | Objective function (cost) | Iran |
| [58] | 2016 | Optimization | CO2, NOx, and SO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) and restrictions | Greece |
| [59] | 2016 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Restrictions | Taiwan |
| [60] | 2016 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Poland |
| [61] | 2016 | Optimization | CO2 emissions. nuclear accidents | Objective function (cost) and restrictions. | Japan |
| [62] | 2017 | Optimization | CO2, CH4, N2O, NH3, non-methane emissions volatile organic compounds (NMVOC), SO2, NOx, and PM10 (life cycle) | Objective function (cost) | Italy |
| [63] | 2017 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Portugal |
| [64] | 2017 | Scenario analysis (LEAP) | CO2 emissions | Scenarios | Ghana |
| [65] | 2017 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) and restrictions | Ghana |
| [66] | 2017 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) and restrictions | China |
| [15] | 2017 | MCDA | employment, visual impact, noise pollution, local income, CO2 emissions, land use, public health, water consumption (life cycle) | Independent criteria, participation of decision makers | Brazil |
| [67] | 2018 | Optimization (COBRA model) | Emissions of NOX, SO2, CO2, CH4) and public health | Objective function (cost) and restrictions | Northeast, USA |
| [68] | 2018 | Scenario analysis (input-output models) | CO2 emissions, public health, loss of biodiversity, local effect on crops and damage to materials (life cycle) | Design/technology analysis | South Africa |
| [69] | 2018 | Optimization (LEAP and OSeMOSYS) | CO2 emissions and human health (life cycle) | Objective function (cost) | Spain |
| [12] | 2018 | Scenario analysis (EnergyPLAN model) | CO2 emissions | Scenarios | Brazil |
| [70] | 2018 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | China |
| [71] | 2019 | Optimization (LEAP and OSeMOSYS) | CO2 emissions | Scenario analysis | China |
| [72] | 2019 | Optimization (COBRA model) | CO2 emissions, PM, NOx, SO2 and ozone | Objective function (cost) and restrictions | Northeast, USA |
| [73] | 2019 | Optimization | CO2 emissions, PM, NOx, and SOx | Objective function (cost) | Chile |
| [74] | 2019 | MCDA | Sevaral (19), e.g., job creation, noise, public health, regional development, relocation of people, water use, CO2 emissions, or land use. | Independent criteria, participation of decision makers | Bangladesh |
| [75] | 2019 | Optimization | NOx, and SO2 emissions | Restrictions | China |
| [76] | 2020 | Optimization | CO2 emissions, PM, NOx, and SOx, | Objective function (emissions) | Taiwan |
| [77] | 2020 | Scenario analysis (LEAP) | Emissions of CH4, NOx, CO, CO2 and SO2, N2O, SOx, volatile organic compounds and PM | Scenarios | Pakistan |
| [78] | 2020 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Brazil |
| [79] | 2020 | Optimization | CO2 emissions, NOx, and SO2, | Restrictions | Jiangsu, China |
| [80] | 2020 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Chile |
| [81] | 2020 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Iran |
| [82] | 2020 | Optimization | CO2 emissions, NOx, and SO2, | Objective function (cost) | Hypothetical case in Nigeria |
| [83] | 2020 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Ireland |
| [84] | 2021 | Scenario analysis (LEAP) | Emissions of CH4, NOx, CO, CO2 and SO2, N2O, SOx, volatile organic compounds and PM | Scenarios | Pakistan |
| [85] | 2021 | Optimization | CO2 emissions | Objective function (cost) | Chile |
| [86] | 2021 | Optimization (LEAP and OSeMOSYS) | CO2 emissions | Scenario analysis | Sumatra, Indonesia |
| [87] | 2021 | Optimization | CO2 emissions (life cycle) | Objective function (cost) and restrictions | Kenya |
| [88] | 2021 | Optimization (LEAP) | CO2 emissions | Scenario analysis | Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, C.R.d.S.; Ferreira, P. A Review on the Internalization of Externalities in Electricity Generation Expansion Planning. Energies 2023, 16, 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041840
Costa CRdS, Ferreira P. A Review on the Internalization of Externalities in Electricity Generation Expansion Planning. Energies. 2023; 16(4):1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041840
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Carlos Roberto de Sousa, and Paula Ferreira. 2023. "A Review on the Internalization of Externalities in Electricity Generation Expansion Planning" Energies 16, no. 4: 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041840
APA StyleCosta, C. R. d. S., & Ferreira, P. (2023). A Review on the Internalization of Externalities in Electricity Generation Expansion Planning. Energies, 16(4), 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041840







