Abstract
The energy blockchain is a platform based on blockchain technology, creating a secure, transparent, and decentralized system for peer-to-peer transactions and automated smart contracts. This platform has the ability to facilitate the exchange and management of energy resources, such as electricity or renewable energy certificates. Our research aims to clarify the growth trends of energy systems with blockchain technology throughout the world. The novelty of this study is to understand the main factor in energy blockchain patent granting using a patent decomposition analysis and log mean Divisia index analysis and discover the relative importance in the R&D shift from electricity to other technology. Additionally, the IPC for energy blockchain technology primarily focuses on configuring and managing energy systems, including electricity, gas, and water supply. We also present a comprehensive overview of how countries and companies engage with energy blockchain technology and find China leads with 59% of patents, followed by the U.S. with 20%, but their specific tech shares differ. Participants span beyond traditional energy sectors, including electric and electronic machinery, IT firms, transport manufacturers, startups, and universities dedicated to blockchain technology.
1. Introduction
The idea of blockchain initially emerged as the underlying technology supporting Bitcoin (Nakamoto, 2008) [1] and blockchain technology attracted attention predominantly because of its application in financial transactions, particularly with Bitcoin. In particular, the rise and temporary peak in Bitcoin’s price in 2017 drew substantial attention to blockchain technology. However, its potential soon transcended the field of digital currencies. Blockchain technology, characterized by security, transparency, and decentralization is widely used in energy trading, supply chain management, and healthcare and has formed an innovative technology (e.g., digital grid platform), which attracted researchers and investors from various fields beyond finance (ACS blockchain report, 2018) [2]. Investors and researchers began recognizing its significance in revolutionizing traditional industries, prompting exploration into its extensive applications. For example, we find that even the Chinese government, which banned cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, has many supportive policies toward blockchain technology (Xiao and Xu, 2024) [3].
PwC and the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment (2018) [4] jointly published a report that highlighted over 65 existing and emerging blockchain use cases for environmental applications during the World Economic Forum. These use cases encompass a range of innovative applications, such as novel business models for energy markets, real-time data management solutions, and the integration of carbon credits or renewable energy certificates onto blockchain platforms. For example, blockchain technology could address information asymmetry, enhancing the allocation of water resources as it could provide a common data source for households, industries, water managers, and policymakers, facilitating informed decisions on water quality and quantity. This transparency could guide consumers on water usage and enable data-driven allocation decisions. Moreover, it could counter corrupt behavior by preventing data manipulation by local authorities. According to the report on Blockchain in Energy by Wood Mackenzie [5], 59% of blockchain energy projects are focused on creating peer-to-peer energy markets. These markets involve individuals trading and purchasing surplus energy from fellow participants within a shared network. Such markets bring advantages by diminishing central authority control, such as that of wholesale entities, thereby benefiting a wider audience. Thus, blockchain’s application in the energy sector offers numerous advantages: cost reduction, environmental sustainability, and increased transparency for stakeholders while not compromising privacy (Blockchain in Energy and Sustainability) [6]. The traditional electric power trading model relies on third parties, and the trading process has the disadvantage of complication, low efficiency, large losses, and high costs. However, blockchain technologies combined with IoT devices enable consumers to trade and purchase energy directly from the grid rather than from institutions (Huang, 2020) [7]. CoinDesk Japan (2019) [8] summarized prominent instances within Japanese energy companies where blockchain technology was actively integrated. They observed that electric power and gas companies were prominently engaged in conducting demonstration experiments and establishing P2P power trading platforms and these platforms enable individuals to buy and sell generated power with high environmental value such as solar power generation.
Energy companies, varying from electricity suppliers to oil and gas enterprises, are acknowledging the transformative influence of blockchain technology. Furthermore, our findings reveal that both energy companies and governments on a global scale are directing their attention towards the potential applications of energy blockchain technology across various public services. Xu and Duan (2022) [9] discovered that the adoption of blockchain technology by manufacturers benefits both retailers and consumers. Moreover, even in cases where the operational cost of blockchain technology is relatively high, manufacturers find it profitable to adopt blockchain due to government subsidies provided to either the manufacturer or the consumer. Popkova et al., (2023) [10] identified numerous successful instances worldwide where blockchain has been effectively applied to address climate change and facilitate the transition to clean energy. For example, the blockchain ecosystem DAO IPCI in Russia garnered approval and support from multiple organizations dedicated to mitigating climate change. Their research also strengthens the idea that blockchain is poised to play a crucial role in effectively addressing climate challenges and enabling a smooth transition to clean energy solutions. The applicability of blockchain technology and distributed ledger technologies can help to present a promising pathway to address governance and efficiency challenges in urban water management and sanitation services in Spain (Furones and Monzón, 2023) [11].
In conclusion, the applicability of blockchain technology in energy systems significantly elevates transaction efficiency and reduces wastage during energy transmission processes. Consequently, the advancement of energy blockchain technology is supposed to contribute to the realization of a carbon-neutral society and policymakers play a pivotal role by formulating supportive policies and offering substantial incentives for the research and development of energy blockchain technology, thereby fostering its advancement.
A patent is a granted right that recognizes the contributions of individuals engaged in research and design (R&D), serving as a pathway for advancing science and technology. The establishment of patents aims to empower inventors to prevent others from producing, utilizing, or vending their inventions for a designated duration, consequently protecting the inventors’ rights (WIPO) [12]. The energy system patent with blockchain technology represents the scientific and technological knowledge accumulated in that blockchain technology. In recent years, an increase in the number of energy blockchain patents in the world (shown in Figure 1) effectively reflects the development of energy blockchain technology.
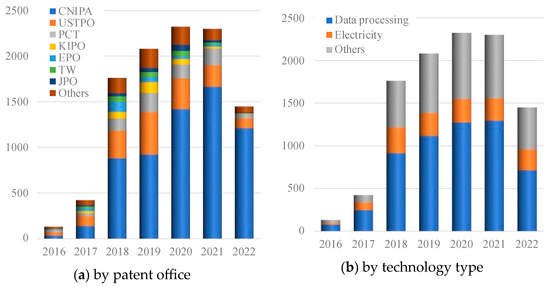
Figure 1.
Trend of energy blockchain patent granted: 2016 to 2022 (number of items). Note: CNIPA: China National Intellectual Property Administration; USPTO: United States Patent and Trademark Office; PCT: Patent Cooperation Treaty; KIPO: Korea Intellectual Patent Office; TW: Taiwan Intellectual Patent Office; EPO: European Patent Office; JPO: Japan Patent Office.
Figure 1a shows the number of energy system patents with blockchain technology categorized by application countries and technology groups and indicates that the number of energy blockchain patent publications has grown greatly from 131 in 2016 to 2299 in 2021. Particularly, energy blockchain technology granted by China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA) increased by 1630 from 2016 to 2021, which occupies almost 75% of the energy blockchain patent rise globally. On the other hand, patents granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) have the second share in the world and change smoothly compared with that of CNIPA. The reason for the decrease in patents granted in 2022 is considered to be that patents have a time lag of 18 months between application and publication; thus, there are some patents that have not been published yet. Also, the decline in patent publications observed in 2022 can be influenced by various factors beyond the 18-month lag in patent publication such as the outbreak of COVID-19. During the COVID-19 period, many countries worldwide underwent lockdowns, restricting people’s movement and consumption behaviors. This led to reduced profits for numerous businesses and decreased funding allocated for R&D activities. Simultaneously, the uncertainty surrounding future expectations due to the pandemic also diminished corporate investments in R&D efforts, thereby resulting in a decline in the number of patents.
Figure 1b shows the change in patent share of each energy blockchain technology group from 2016 to 2022. Data processing patents granted obtain the highest share among the three technology groups and increase rapidly. The quantity of patents approved in the others also grows greatly from 2017 to 2018 and increases stably from 2018 to 2022. On the contrary, the share of patents granted in electricity is small and increasing slowly in this period. These two figures indicate the short-term trends of energy blockchain patenting categorized by country and technology group. However, the information conveyed in Figure 1 might not be comprehensive enough to elucidate the reasons behind the fluctuations in the number of patents granted across various energy blockchain technology groups.
To examine the reason why the trend in energy blockchain technology changed, we analyze the R&D strategies of the innovators. These approaches or tactics represent the driving forces of advancements in technology (Fujii, 2016) [13]. It is worth mentioning that energy blockchain technologies contribute to making progress in economic performance unequally. Some energy blockchain technologies directly benefit from making profits by inventing new products and services, while others benefit indirectly or have limits. Thus, it is essential to clarify the characteristics of each technology group of energy blockchain patents by a determinant analysis of inventions to make policies that effectively promote and stimulate research and development endeavors within such technologies (Fujii and Managi, 2018) [14]. This is the first study to use a decomposition framework to identify the main factors of energy blockchain technology invention. Fujii and Managi (2019) [15] were pioneers in applying the decomposition method to technological innovations. This methodology can clarify the key drivers that promote innovation.
The goal of this research is to pinpoint the factors influencing the publication of patents in energy blockchain technology across different technology groups. Additionally, we aim to explore how the industry sectors of creators and national R&D policies impact the development of energy blockchain technology in different countries using company-level data. This research introduces a novel approach by utilizing patent decomposition analysis and log mean Divisia index analysis to discern the primary factor behind the granting of patents in energy blockchain technology. While prior studies primarily focused on the total number of patent publications, our approach seeks to separate the impact of R&D strategy and R&D scale factors. By taking control of the scale effect, this research tries to derive a pure measure of the priority given to publications from patent data.
Table 1 presents the key technology attributes of the leading five IPC patent publications within the domain of energy blockchain technology. Among the 10,493 patent applications associated with this field, a significant subset of 498 primary patents is categorized under G06Q 50/06, which pertains to technical aspects related to electricity, gas, or water supply. It commands the largest share of 4.7%, signifying its substantial presence in the energy blockchain technology. Additionally, two other prominent technology categories emerge in G06Q 10/06 and G06Q 40/04. These categories encompass 373 and 258 patent applications, respectively, which are related to resources, workflows, human project management, and exchange (e.g., stocks, commodities, derivatives, or currency exchange). In addition, G06Q50/00, H04L9/32, and H04L29/06 are also notable categories that ranked fourth and fifth in terms of the number of patent applications.

Table 1.
Top 5 patent classifications in energy blockchain technology.
These findings highlight that the advancement of energy blockchain technology is primarily concentrated across various areas, with a significant emphasis on crucial sectors such as energy supply, resource management, and exchange. The prevalence of patent applications in these areas stresses the transformative potential of energy blockchain technology in reshaping how energy resources are generated, allocated, and utilized.
The prominent presence of patent applications in fields related to energy supply signifies a concerted effort to revolutionize the way traditional energy and renewable energy are sourced, distributed, and managed. Furthermore, this endeavor is in alignment with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) established by the United Nations which aims to build universal access to affordable, dependable, sustainable, and modern energy.
To understand the features of energy blockchain technology, we followed the study of the ACS Blockchain Report and divided the patent publication data into the following three energy blockchain technology categories: (1) data processing, (2) electricity, and (3) other energy blockchain technology. Figure 2 represents the research framework of this study.
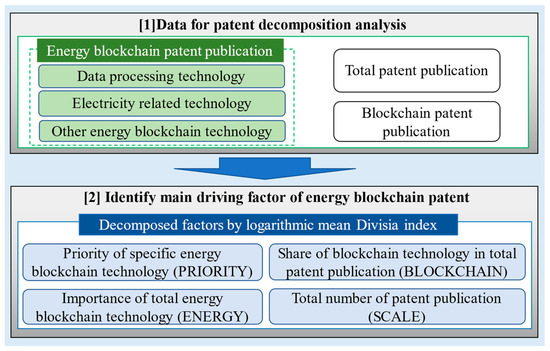
Figure 2.
Research framework of this study.
2. Methods and Data
2.1. Method
This research utilizes a decomposition analysis framework to clarify the main factors involved in granting energy system patents with blockchain technology. We used IPC code to identify energy blockchain patents with reference to previous studies (Table 1).
The research framework of this study is shown in Figure 2. We use the following four factors to decompose the energy blockchain patent granted: the priority given to a specific energy blockchain technology (PRIORITY), the importance of the energy blockchain technology among all blockchain patents granted (ENERGY), the share of the blockchain technology patents out of all granted patents (BLOCKCHAIN), and the scale of R&D activity (SCALE).
We have defined the “PRIORITY” indicator as the ratio of patents granted for a particular energy blockchain technology to the amount of energy blockchain patents granted. An increase in this indicator signifies that the number of patents granted for a specific energy blockchain technology is growing at a faster rate than the number of energy blockchain patents, indicating that inventors are directing more of their research resources toward specific types of energy blockchain technology innovations. An uptrend in “PRIORITY” suggests a focused research effort on specific energy blockchain types over others.
Next, we introduced the “ENERGY” indicator, which is calculated as the number of patents granted for all energy blockchain technologies divided by the number of blockchain patents granted. An increase in this indicator signals that the number of energy blockchain patents granted is growing at a faster rate than the number of blockchain patents. This demonstrates that inventors are channeling their research resources into energy blockchain technology, highlighting a prioritization of energy blockchain technology inventions over other types of blockchain technology when “ENERGY” is on the rise.
Also, we defined the “BLOCKCHAIN” indicator, calculated as the number of patents granted for blockchain technology divided by the total number of patents granted across all fields. If the number of patents granted for blockchain technology increases more quickly than the sum of all patents granted, this indicator will present an increase. This indicates that inventors are dedicating a significant portion of their research resources to blockchain technology, showing a prioritization of blockchain technology inventions over other technology types when “BLOCKCHAIN” is on the rise.
Finally, the “SCALE” indicator is the total number of patents granted, representing the scale of research and development (R&D) activities. To explain this indicator, we posit that more intensive R&D endeavors result in more patent inventions. Thus, the amount of patents granted serves as a reflection of the level of R&D activity. If the “SCALE” indicator increases, it indicates a rise in overall R&D activities, which, in turn, is expected to lead to an increase in the number of blockchain patents granted.
Here, we present the decomposition methodology applying the patent group related to “Electricity” technology as a particular category of energy system patents with blockchain technology granted, as indicated in the following equation.
We consider the change in “Electricity” patents granted from year (Electricityt−1) to year t (Electricityt). Using Equation (1), the growth ratio of electricity patents can be represented as follows:
We convert Equation (2) into a natural logarithmic function, resulting in Equation (3). Importantly, the presence of zero values in the dataset poses problems in the formulation of the decomposition due to the properties of logarithmic functions. To address this issue, the literature on the logarithmic mean Divisia index (LMDI) suggests replacing zero values with a small positive number (Ang and Liu, 2007) [16].
Multiplying both sides of Equation (3) by weight factor yields Equation (4) as follows.
Therefore, changes in the number of patents granted for electricity technologies (∆Electricity) are decomposed by changes in PRORITY (first term), ENERGY (second term), BLOCKCHAIN (third term), and SCALE (fourth term). The term operates as an additive weight for the estimated number of patents granted for data processing technologies. This decomposition methodology was devised by Ang et al., (1998) [17] and is termed the LMDI.
The unique feature of this research lies in its evaluation of companies’ R&D strategies through LMDI analysis. Previous research has primarily concentrated solely on the number of patents approved, influenced by applicants emphasizing specific groups of inventions and the whole magnitude of research activity. Our research aims to extract the intrinsic significance of patent publications based on granted patents while managing the influence of the scale effect. Similar to Fujii (2016) [13], who utilized a decomposition framework in patent data analysis focusing on priority and scale factors, introduced an approach aimed at distinguishing between the shifts in priority for a particular energy blockchain technology and the broader changes in blockchain technology overall.
2.2. Data
We obtained data concerning granted patents from Orbis Intellectual Property and the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO). The research period is from 2016 to 2021, and this study covers patent application data in 65 countries and regions. The search results are up to 30 October 2022 and the number of patents found related to energy blockchain technology is 10,493. It is worth mentioning that the search results have certain limitations due to the 18-month lag period of patents.
From the energy blockchain patent dataset, we found that the China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA), the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), the European Patent Office (EPO) and Japan Patent Office (JPO) are the major applicant countries and organization. Therefore, in this study, we conduct a comparative analysis of the ratio of patent applications in the five major countries and compare the relative significance and R&D priorities of each country and organization.
As indicated in Table 2, this research emphasizes three energy blockchain technology types: (1) data processing technology (DATA PROCESSING), (2) electricity technology (ELECTRICITY), and (3) other energy blockchain technology (OTHER). Following Fujii et al., (2016) [13] and Fujii and Managi (2018) [14], we use only the primary IPC code and the main applicant’s name to construct the patent database to avoid double-counting patent data.

Table 2.
Description of energy blockchain patent groups.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparative Analysis of Energy Blockchain Patents Granted
3.1.1. When Was a Specific Energy Blockchain Patent Invented and Where?
Table 3 indicates the variation in energy blockchain technology patents granted across different technology groups at each patent office. The findings reveal a discrepancy in the distribution of patent shares for distinct types of energy blockchain technology among various countries. Despite the fact that the largest total of energy blockchain patents granted worldwide are received by China, CNIPA has the least share of electricity at 10%, unlike most other patent offices that have a share of electricity at around 15%. Another finding is that USPTO owns the largest share of electricity at 19%, and the share of data processing is only 42% in the USPTO, which is notably lower when compared to the figures observed in other patent offices. The PCT, the JPO, and the patent offices of other countries show similar trends with respect to the technology share pattern of blockchain patent publications.

Table 3.
Data description of energy blockchain patents granted (item).
Next, we discuss the numerical variation in energy blockchain patents granted. As displayed in Table 3, all the patent offices except the EPO published the largest number of energy blockchain patents from 2021 to 2022. Notably, the total number of energy blockchain patents of all patent offices granted more than tripled during these periods. In particular, JPO published many energy blockchain patent publications in these years, which have no patents granted from 2016 to 2018.
3.1.2. Who Invented Each Energy Blockchain Patent?
Table 4 indicates the top 20 applicants for energy blockchain patents granted in the world. The participants are not only from traditional fields but include electric and electronic machinery, computer software companies, banking and insurance companies, transport manufacturing companies, and even many universities devoted to blockchain technology and the bottom lines show the total number of energy blockchain patents granted to universities in China and the U.S. As shown in Table 4, strong force intellectual capital, which owns the greatest number of inventors of 208, is the global top receiver of energy blockchain patents granted. Furthermore, we can see that of the top 20 applicants, China has the highest number of applicants with 13, 5 applicants are U.S. companies, and the remaining 2 applicants are from Germany and Japan. In particular, the companies and universities of other countries are not included in the top 20 countries evaluated for the 2016–2022 period, which connotes that energy blockchain patents in other countries are obtained by several applicants.

Table 4.
Energy blockchain patents granted and technology portfolios from 2016 to 2022.
Following that, we explore the distribution of energy blockchain patents among various applicants. Table 4 indicates that the patent portfolio of energy blockchain varies among applicants. BAIDU and Nanjing University gained the highest share of the data processing technology. On the other hand, an impressive 93% of Northstar Battery Company’s patent applications are related to electricity technology, signifying its dominant position in this field compared to other applicant companies. With the largest share of electricity technology patents among all applicants, Northstar Battery Company has solidified its commitment to developing reliable and sustainable power solutions. Additionally, Honda Motor and Toyota Motor North America commanded a significant share of 80% and 76% of electricity technology, respectively. Notably, the patents granted to both Honda and Toyota mainly focused on the IPC code B60L53/66 (data transfer between charging stations and vehicles). The prevalence of patents related to data transfer between charging stations and vehicles indicates that both Honda and Toyota are actively involved in research and development efforts to enhance electric vehicle technology through energy blockchain solutions. In conclusion, the companies listed above-obtained patents across a diverse range of energy blockchain technology fields.
According to Table 4, a large proportion of the energy blockchain patents granted to Chinese universities were for technology based on data processing which is the same trend as companies. In recent years, China has achieved splendid development in the number of granted patents, especially those granted to public universities because the Chinese government set up a goal to promote growth in patent activities in the Medium and Long-Term Science and Technology Development Plan (2006–2020). In contrast, although the U.S. has many patents obtained by U.S. companies, there are seldom patents obtained by U.S. universities compared with Chinese universities, which shows a different result.
3.1.3. Who Invented a Patent Energy Blockchain Technology and Where?
In this part, we discuss the distribution of energy blockchain patent applications by applicant. As shown in Table 5, Chinese companies have a large share of energy blockchain patent inventions. On the other hand, the shares of patented publications of Chinese companies from the other patent offices are particularly small. In comparison with Chinese companies, U.S. companies have a higher share in energy blockchain patents granted by the other patent offices. Specifically, Northstar Battery Company only has 29% of all energy blockchain patents issued by the USPTO, and the remaining share of 71% was issued by CNIPA, PCT, EPO, and the other patent offices.

Table 5.
Distribution by country or organization of energy blockchain patents.
We also find that the share of Northstar Battery Company has no difference between CNIPA, PCT, EPO, and other patent offices, which implies the company applied the same patent publications in different patent offices. HONDA MOTOR from Japan was granted significantly more energy blockchain patents by the CNIPA and USPTO than by the JPO. These results connote that U.S. companies and Japanese companies have significant motivations to obtain energy blockchain patents from CNIPA. Meanwhile, 30% of energy blockchain technology patents granted in Siemens AG from Germany were issued by PCT and became the most in the top 20 ranking.
Table 5 clearly illustrates that universities predominantly apply for energy block-chain patents at domestic patent offices. Specifically, an overwhelming share of 99% of the energy blockchain patents obtained by Chinese universities were granted by CNIPA, with only a small number granted by other patent offices. It is worth mentioning that around 15% of the energy blockchain technology patents granted in China were obtained by Chinese universities, which indicates that universities play a significant role in the development and advancement of energy blockchain technology in China. Indeed, a comparable trend can be observed in other technological domains like nanotechnology (Huang and Wu, 2012) [18].
Furthermore, it appears that U.S. universities tend to apply for energy blockchain patents primarily through the USPTO, mirroring the trend observed with Chinese universities and their preference for CNIPA. Even though the overall number of patents related to energy blockchain technology filed by universities is relatively rare, it does not imply that they do not value energy blockchain technology as much as Chinese universities do. We find that the focus on technology research and development (R&D) shows a notable difference between the U.S. and China. Moreover, there is substantial evidence indicating that the U.S. holds a position of advantage in terms of technological innovation and capabilities. However, it is important to acknowledge that China possesses a distinct advantage in terms of patent volume (Liu et al., 2023) [19].
3.2. Patent Decomposition Analysis
3.2.1. Introduction of the Analysis Outcomes
Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 depict the outcomes of the patent decomposition analysis for three distinct blockchain technology patents granted across various patent offices and the period runs from 2016 to 2021. The line charts track the variations in the number of patents granted for specific energy blockchain technologies, while the bar charts indicate the influence of each segmented factor on the count of patents issued concerning particular blockchain technologies. The cumulative bar values align with the data represented by the plotted lines. This visualization highlights the differences in the driving forces behind patents granted for specific categories of energy blockchain technology.
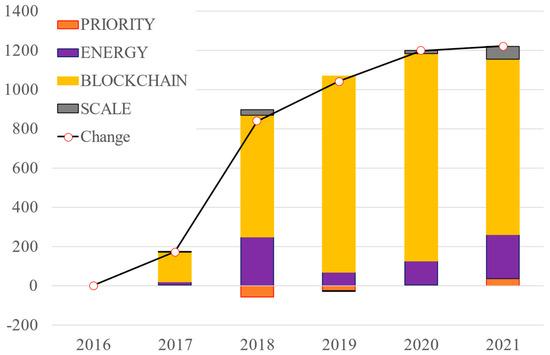
Figure 3.
Decomposition analysis of data processing applications.
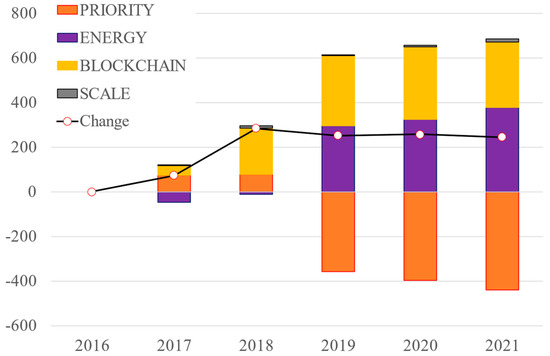
Figure 4.
Decomposition analysis of electricity applications.
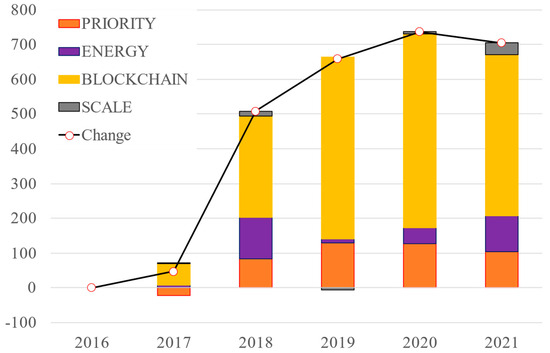
Figure 5.
Decomposition analysis of other energy blockchain applications.
3.2.2. Data Processing Technology
Figure 3 indicates the results of the decomposition analysis of patent applications in data processing technology. As shown in Figure 3, 1219 patents were granted for data processing technology, which increased during this period and the number of patents granted for data processing technology increased significantly during 2017–2020 mainly because of the increase in blockchain technology factor. In December 2017, Bitcoin’s price experienced an unprecedented and temporary peak, reaching an all-time high at that time. Thus, we believe that blockchain technology, which was indeed initially invented and used in the transaction of Bitcoin, attracts significant attention from investors and researchers across various fields.
However, the growth of patent numbers in data processing technology experienced a slowdown from 2019 to 2021, which coincided with the decline in the priority of the blockchain technology factor and this observation suggests a potential correlation between the two trends. First, the price of Bitcoin collapsed after its peak in 2017–2018, which had a notable impact on the perception and interest in blockchain technology, which explains the decrease in patent applications to some extent. As the price of Bitcoin experienced significant volatility and a downward trend, it might have caused investors and researchers to reassess their priorities and shift to other technologies or investment opportunities.
Furthermore, the decline in patent applications for blockchain technology can also be attributed to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. As WIPO confirmed, there was a general decrease in patent applications granted by major patent offices in 2020, with the exception of CNIPA.
In addition, the decline of patent applications can be explained as the patent applications are not immediately reflected in the latest published data because of the 18-month lag period of patent applications.
3.2.3. Electricity Technology
Figure 4 illustrates the results of the decomposition analysis of patent applications in electricity technology. As depicted in the figure, the number of patent applications related to electricity technology increased quickly from 2017 to 2018, driven by the growth of two factors. Notably, the factor related to blockchain technology played the most significant role in this growth. However, we can see a noticeable decline in the priority of the electricity technology factor from 2019 to 2021. The shift in priority can be attributed to the reduction in patent grants to the main applicants associated with electricity technology. Our research reveals the great contributions of Strong Force Intellectual Capital and Northstar Battery Company in driving the surge in patent numbers within the electricity technology sector from 2017 to 2019, filed a substantial number of blockchain technology patents related to electricity, primarily categorized under the IPC of G05B. These two companies played crucial roles in developing innovation and applying patent applications during this period. However, a notable shift occurred from 2020 to 2021, as patent applications granted to these companies experienced a significant decline. Conversely, there has been a significant increase in the number of electricity blockchain technology patents from Chinese companies between 2020 and 2021. This rise in Chinese patent applications somewhat offset the decrease in the number of patents granted by American companies, resulting in an overall stagnation in the total blockchain technology patent publications related to electricity.
This unique trend indicates that the priority of patent applications specific to electricity technology decreased rapidly during this period. Moreover, this observation highlights that the relative significance of the electricity technology factor, as reflected in patent applications, decreased rapidly compared to other technologies during the same period. This is notable as this trend appears to deviate from the prevailing global focus on renewable electricity energy development, particularly in the aftermath of the Paris Agreement (Fan, 2022) [20]. Most countries and regions worldwide have intensified efforts to alleviate climate change by prioritizing the advancement of renewable electricity sources (Ren et al., 2023) [21]. In this context, the unusual decrease in the priority of patent applications related to electricity technology warrants closer examination. We assume that one plausible explanation could be attributed to economic factors. It is possible that certain governments might not have provided adequate subsidies or incentives to investors in the electricity sector, impacting the enthusiasm for patent applications. An alternative hypothesis is that applicant companies may have redirected their investment focus toward patent applications in other technology areas. Notably, areas such as big data and artificial intelligence (AI) have gathered significant attention due to their perceived profitability (Ren et al., 2022) [22]. This shift in investment priorities might have contributed to the observed decline in patent application priority within the electricity technology sector.
Although the growth rate of energy blockchain patents related to electricity has slowed down, we observed great efforts from automotive companies such as Honda in Japan, Toyota in the U.S., and the FAW group in China, committed to utilizing electricity energy blockchain technology for developing fuel cells, charging systems, and propulsion devices of electric vehicles (EVs). Over the next few decades, EVs are anticipated to experience significant growth, playing a crucial role in obtaining global climate objectives (Shi and Feng, 2022) [23]. Thus, for policymakers, understanding the substantial interest and investment from automotive giants in utilizing energy blockchain technology within the electric vehicle sector can indicate the direction of future policies. Encouraging initiatives that support R&D in energy blockchain applications for sustainable mobility, providing financial incentives, or establishing partnerships between these companies and research institutions might foster innovation in the electric vehicle industry. Additionally, for start-up companies, recognizing the interest of established automotive companies in energy blockchain for electric vehicles could offer opportunities for collaboration or niche development. Identifying areas where these companies might require partnerships, such as improving blockchain-based charging infrastructure or developing more efficient fuel cell technology could be potential entry points for start-ups to contribute to this growing field.
3.2.4. Other Energy Blockchain Technology
Figure 5 shows the results of the decomposition analysis of patent applications in other technologies. It is observed that other technologies experienced a significant increase of 744 patents during 2017–2020 and declined from 2019 to 2021, which has almost the same trend as data processing technology.
There are 2889 patent publications categorized as “other energy blockchain technology” and registered with numerous IPC codes, including A61B5/00 (measuring for diagnostic purposes), G07F15/00 (coin-freed apparatus with meter-controlled dispensing of liquid, gas, or electricity), and various other IPC codes with a relatively small number of patent publications. For instance, the inclusion of A61B5/00 suggests the integration of blockchain in healthcare-related diagnostics, possibly indicating advancements in medical devices or health data management leveraging blockchain’s security and transparency. Additionally, G07F15/00’s presence suggests potential applications in vending machines or metering systems, extending blockchain’s utility to automated transactions in dispensing various resources. The implications of these patents in the energy system are intriguing, hinting at the energy blockchain technology’s adaptability across broader sectors. For example, in healthcare, blockchain-enabled diagnostics could enhance the integrity and accessibility of patient data. Similarly, in vending machines or meter-controlled apparatus, blockchain might streamline transactions and enhance transparency in resource dispensing, potentially impacting aspects of energy distribution or consumption. Thus, this diverse technology group has far-reaching implications, extending its contributions to various fields such as medical machinery, personal identification, self-driving technologies, and more. Tencent Technology, the operator of China’s leading messaging service, WeChat, holds the largest share, at 63%, of patents related to other energy blockchain technology and this trend sets Tencent Technology apart from other applicant companies. Tencent Technology also has played a leading role in the advancement of blockchain technology in China. According to research conducted by The Block [24].
Tencent Technology filed the highest number of blockchain patent applications last year, totaling 718 out of over 5800 patent applications. However, these technologies do not fall within the categories of either data processing technology or electricity technology. Consequently, these patent items are registered under the broader classification of “other energy blockchain technology”.
In conclusion, after comparing patent application trends in the three technology groups, it is evident that the substantial growth in blockchain technology patent applications plays a crucial role in explaining the increase in all three technologies. However, the growth speed of the three technologies varies since the impact of blockchain technology on each technology group is different from each other. The number of patents granted for data processing and others increased substantially due to the development of blockchain technology. But the number of patents granted for electricity did not change significantly, which indicates that electricity was treated as less important than the other two technologies as the relative priority given to electricity was negative, which was supposed to be the novelty of this study.
3.2.5. Decomposition Analysis by Patent Office
Table 6 illustrates the outcomes of the patent decomposition analysis across various patent offices. It reveals distinct primary drivers behind the granted patents across these offices during the specified period. The priority given to energy blockchain technology and blockchain technology became important factors of patent publications for all technology groups in CNIPA. On the other hand, the main driver contributing to the increase in patent publications granted by USPTO is considered as the priority given to energy blockchain technology. Also, the priority given to the Scale factor affected USPTO negatively as the number of patent applications granted by USPTO decreased these years. Additionally, the specific priority given to data processing and electricity decreased a little and the priority given to other blockchain technology increased both at the CNIPA and USPTO.

Table 6.
Results of decomposition analysis by patent office: 2016–2021.
Tseng and Liang (2023) [25] used the Fortune 500 companies in the U.S. and China from 2012 to 2019 as their research sample and found that the scale of corporate assets and investment in R&D activities were crucial driving forces for adopting blockchain technology. Larger-scale enterprises in the U.S., not in China, were adopting blockchain technology. Companies’ investment in innovation and the adoption of blockchain technology contributed to enhancing business performance and the improvement in business performance for U.S. companies using blockchain was greater than that of Chinese companies. Also, while the Chinese government prohibited the mining and trading of Bitcoin, it elevated blockchain technology to a strategic position.
Xiao and Xu (2024) [3] discovered that the supportive policies of the Chinese government could effectively offset the negative impact of the national resistance to cryptocurrencies. Within established blockchain technology alliances or officially recognized companies, the market seemed to exhibit a more noticeable response to government support. Based on these findings, we suggest that future research should further compare and contrast the differences in the adoption of blockchain technology between U.S. and Chinese companies. By deeply understanding the different policies and market environments in these two countries and their impact on corporate behavior, the fundamental reasons for these differences can be clarified. Moreover, research can focus on examining the effectiveness of China’s government-supported blockchain technology policies and conducting more in-depth investigations into the specific policies and measures taken by the Chinese government in supporting the development of blockchain technology. We explored the practical implications of these policies at the corporate level and how these supportive measures foster innovation and development of blockchain technology.
4. Conclusions
By using patent-granted data from 2016 to 2021, this research clarified the tendency and preference variation in energy blockchain technology. We concentrated on the following three technology groups: (1) data processing, (2) electricity, and (3) other energy blockchain technology and applied a patent decomposition analysis framework to explain the tendency and preference variation for patent publications by the previously mentioned three technology groups. Finally, we conclude the main results of this study as follows.
First, patent publications related to data processing and other energy blockchain technology witnessed stable growth from 2016 to 2021, followed by a decline in 2022 and this decline can be attributed to the 18-month delay in patent publications. On the contrary, the number of applications involving electricity technology increased notably from 2016 to 2018 but experienced stagnation thereafter. Furthermore, the International Patent Classification (IPC) of energy blockchain technology predominantly centers around G06Q 50/06, concluding a total of 498 patent applications. This category pertains to the technical field of configuring and managing energy systems, covering electricity, gas, and water supply.
Second, we found that China (CNIPA) has the highest share of energy blockchain technology patent applications, up to 59%, followed by the United States (USTPO) with 20%. The share of different categories of energy system blockchain technology by country shows that despite the fact that China possesses the majority of patents in all categories, it focuses on data processing unlike most other countries, which put emphasis on the electricity sector. Also, the participants are not only from traditional energy supply fields but include electric and electronic machinery, IT companies, transport manufacturing companies, start-up companies, and even many universities devoted to blockchain technology. These participants also exhibit varying specific technology shares within the domain of energy blockchain technology.
Third, the number of patent publications of all three technology groups increased mainly due to the increase in priority of the blockchain technology factor, especially in data processing and other energy blockchain technology. We assume that the priority given to the blockchain technology factor has a strong correlation with the price of Bitcoin as Bitcoin’s price experienced an unprecedented and temporary peak in December 2017. Thus, we believe that blockchain technology, originally conceived and employed for Bitcoin transactions, has garnered substantial interest from investors and researchers spanning various fields. On the contrary, we also observed that the priority given to specific electricity technology dropped quickly after 2018 and the number of patent publications of electrical technology groups stagnated. Given the widespread acknowledgment of climate change’s importance, most countries and regions have recognized that advancing electricity networks and electric vehicle technology can play a crucial role in effectively tackling the issue of climate change. Consequently, we posit that the stagnating number of patent publications associated with specific electrical technology can be attributed to investors’ inclinations to direct their investments towards more lucrative technological fields.
Finally, we clarify the value of the decomposition framework in analyzing energy blockchain technology patent applications. The presented results enable a clearer comprehension of the research emphasis of each technological innovation. Such shifts in research priorities play a pivotal role in incentivizing private companies to venture into novel technological domains. While governments worldwide offer an array of policies and subsidies to incentivize private firms in the realm of energy blockchain technology, clarifying how these measures precisely stimulate innovation remains complex. On the other hand, China was the world’s largest Bitcoin producer, but the government initiated a ban on bitcoin mining in 2021 and this kind of policy uncertainty potentially cooled the enthusiasm of investors. The influence of COVID-19 has also affected the investment behavior of private companies, given their varied motivations for engaging in innovative endeavors. Furthermore, the determinants influencing energy blockchain technologies differ based on the specific technology type.
Additionally, it is important to note a limitation of our research, which lies in the challenge of clarifying the impacts of diverse government policies and subsidies on the development of energy blockchain technology initiatives. Hence, there is a pressing need for further investigation to construct a research framework that comprehensively accounts for the causal relation between shifts in corporate priorities and external factors such as subsidies. The identification of determinants behind corporate priority alterations proves instrumental in formulating effective policies aimed at promoting the progression of energy blockchain technology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M. and H.F.; methodology, D.M. and H.F.; writing—original draft preparation, D.M.; writing—review and editing, H.F.; visualization, D.M.; supervision, H.F.; project administration, H.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) [JP20K12283] from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan. The results and conclusions of this article do not necessarily represent the views of the funding agencies.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nakamoto, S. Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. 2008. Available online: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- ACS. Blockchain Innvation: A Patent Analytics Report; 2018; Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/481306094/ACS-Blockchain-Report-pdf (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Xiao, L.; Xu, X.; Xue, W. Blockchain mania without bitcoins: Evidence from the Chinese stock market. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2024, 67 Pt B, 102141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PwC and Stanford Woods Institute. Building Block(Chain)s for a Better Planet; PwC and Stanford Woods Institute: Houston, TX, USA, 2018; Available online: https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/sustainability/assets/blockchain-for-a-better-planet.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Metelitsa, C. Blockchain for Energy 2018: Companies & Applications for Distributed Ledger Technologies on the Grid; GreenTech Media: Boston, MA, USA, 2018; Available online: https://www.woodmac.com/reports/power-markets-blockchain-for-energy-2018-companies-and-applications-for-distributed-ledger-technologies-on-the-grid-58115325/ (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Blockchain in Energy and Sustainability. Available online: https://consensys.net/blockchain-use-cases/energy-and-sustainability/ (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Huang, L.-Y.; Cai, J.-F.; Lee, T.-C.; Weng, M.-H. A Study on the Development Trends of the Energy System with Blockchain Technology Using Patent Analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CoinDesk Japan. Available online: https://www.coindeskjapan.com/9427/ (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Xu, J.; Duan, Y. Pricing and greenness investment for green products with government subsidies: When to apply blockchain technology? Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 2022, 51, 101108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkova, E.G.; Bogoviz, A.V.; Lobova, S.V.; Vovchenko, N.G.; Sergi, B.S. Blockchain, sustainability and clean energy transition. Glob. Transit. 2023, 5, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furones, A.R.; Monzón, J.I.T. Blockchain applicability in the management of urban water supply and sanitation systems in Spain. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patents. World Intellectual Property Organization. Available online: www.wipo.int/patents/en (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Fujii, H. Decomposition analysis of green chemical technology inventions from 1971 to 2010 in Japan. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112 Pt 5, 4835–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Managi, S. Trends and priority shifts in artificial intelligence technology invention: A global patent analysis. Econ. Anal. Policy 2018, 58, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Managi, S. Decomposition analysis of sustainable green technology inventions in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2019, 139, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W.; Liu, N. Handling zero values in the logarithmic mean Divisia index decomposition approach. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W.; Zhang, F.Q.; Choi, K.H. Factorizing changes in energy and environmental indicators through decomposition. Energy 1998, 23, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wu, Y. State-led Technological Development: A Case of China’s Nanotechnology Development. World Dev. 2012, 40, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, J.E.; Bi, D. Comparison of administrative and regulatory green technologies development between China and the U.S. based on patent analysis. Data Sci. Manag. 2023, 6, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Chapman, A. Policy Driven Compact Cities: Toward Clarifying the Effect of Compact Cities on Carbon Emissions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yujie, R.; Tang, X.; Fan, T.; Kang, D. Does the spatial pattern of urban blue–green space at city-level affects its cooling efficiency? Evidence from Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 19, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Tang, X.; Guo, N.; Du, M. The impact mechanism of human activities over climate suitability based on social network data: Evidence from China. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. Manag. 2022, 30, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Feng, D.; Yu, S.; Fang, C.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y. The projection of electric vehicle population growth considering scrappage and technology competition: A case study in Shanghai. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Tech Giant Tencent Launches Blockchain Accelerator Program. Available online: https://finance.yahoo.com/news/chinese-tech-giant-tencent-launches-221738727.html?guccounter=1 (accessed on 26 November 2023).
- Tseng, F.M.; Liang, C.W.; Nguyen, N.B. Blockchain technology adoption and business performance in large enterprises: A comparison of the United States and China. Technol. Soc. 2023, 73, 102230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).