Abstract
To quantify the uncertainties propagating from the fuel depletion calculation to the criticality calculation in the burnup credit system, this paper evaluates the effects of the nuclide concentration uncertainty on the criticality calculation based on Monte Carlo uncertainty sampling methods, and analyzes the assumption that the measured-to-calculated nuclide concentration ratio obeys a normal distribution with uncorrelation among isotopes in the Monte Carlo uncertainty sampling method by using the sensitivity and uncertainty analysis method and the Latin hypercube sampling method. The results indicated that the Monte Carlo uncertainty sampling method could effectively quantify the uncertainties with a calculation accuracy within 3%, and the criticality uncertainty calculation for the assumption that the measured-to-calculated concentration ratios obey normal distributions was more conservative than that of the samples according to their actual distributions. Thus, the assumption of a normal distribution is reasonable in the sampling process. Moreover, the uncertainty results of the criticality calculation considering the correlations among important isotopes presented a decrease of approximately 5% over those without the isotopic correlations. Therefore, introducing the correlations of significant isotopes could reduce the uncertainty of the criticality calculation for spent-nuclear-fuel storage systems.
1. Introduction
Energy is a key driving force for sustainable socio-economic development [1]. The rapid advancement of industry and technology has led to a sustained increase in the societal energy demand, resulting in a significant rise in carbon emissions and an escalation in the frequency of extreme weather events worldwide [2]. Due to localized conflicts in Russia and Ukraine, coupled with OPEC’s reduction in oil production, there has been a sustained volatility in energy market prices. This has prompted a growing inclination towards the utilization of cleaner and more stable energy sources [3]. To achieve the PARIS Agreement’s goal of limiting the temperature rise to within 1.5 °C above preindustrial levels, the development of green energy and utilization of alternative energy sources to fossil fuels are needed [4,5]. As an almost carbon-free source of heat and electricity, nuclear power plays an important role in tackling weather, climate, and energy crises.
As of 2022, the countries with more than 30 operational reactors in the world are the United States, China, France, Russia, and Japan [6]. The United States has 93 operable nuclear reactors with a combined net capacity of 95.8 gigawatts (GWe), and the nuclear power generation accounted for 19.6% of the country’s electricity production in 2022. China has 55 operable nuclear reactors with a combined net capacity of 53.3 GWe, and the nuclear power generation represented 5.0% of the country’s electricity production in 2022. France operates 56 nuclear reactors with a combined net capacity of 61.4 GWe, and the nuclear power generation contributed to 69.0% of the country’s electricity production in 2022. Russia has 37 operable nuclear reactors with a combined net capacity of 27.7 GWe, and the nuclear power generation accounted for 20.0% of the country’s electricity production in 2022. Japan has 33 operable nuclear reactors with a combined net capacity of 31.7 GWe, and the nuclear power generation represented 7.2% of the country’s electricity production in 2022. Light-water reactors (LWRs) are dominant around the world [7,8], including Generation II and Generation III pressurized-water reactors (PWRs) and boiling-water reactors (BWRs) [9]. Some of the Generation IV plants include high-temperature gas-cooled reactors and molten-salt reactors [10,11]. Nuclear power plants produce accumulated minor actinides (MAs) and long-lived fission products (LLFPs) during operation. Through a closed fuel cycle based on partition–transmutation technology, nuclear power plants can recycle uranium/plutonium isotopes and transform long-lived and high-level waste into short-lived and low-level waste [12]. Nevertheless, as the initial enrichment of spent nuclear fuel (SNF) increases (e.g., the enrichment from 3.2% to 4.95%) and the processing SNF numbers of reprocessing facilities rise (e.g., the uranium isotope-processing capacity in reprocessing dissolvers rising from 300 kg to 500 kg), there are significant challenges to the disposal of SNF in reprocessing plants [13]. With the prerequisite of ensuring criticality safety in reprocessing plants, the enhancement of the processing capacity of SNF in reprocessing plants holds significant importance for improving the energy utilization efficiency and the economics of power plants.
Because the policy of nuclear power plant reprocessing has always relied on overestimating the reactivity to achieve a sufficiently conservative safety margin for reactor safety, the criticality equipment in the conventional reprocessing plants (such as SNF storage pools and reprocessing dissolvers) are typically calculated assuming the SNF to be fresh fuel for the calculation [14]. While this approach ensures that the criticality equipment in the reprocessing plant meets the criticality safety limit requirement, it also overestimates the reactivity of the SNF and consequently restricts the processing capacities of reprocessing plants for SNF. This results in a significant reduction in the safe-storage capacities of containers for SNF, incurring substantial economic costs. In the absence of large-scale commercial reprocessing plants, the utilization of burnup credit (BUC) technology, which considers the reactivity decrease due to fuel depletion, can significantly reduce the effective multiplication factor (keff) of the criticality equipment in reprocessing plants. Because the calculated results are closer to the reactivity in real SNF assemblies, it becomes possible to undertake improved design studies on the criticality equipment in spent-fuel reprocessing through the application of BUC technology. This improvement aims to enhance the reprocessing capacity of criticality equipment via the sacrifice of a certain safety margin, while ensuring the overall safety of the operation.
From the perspective of the application process of BUC technology, its computational procedure can be divided into the depletion calculation and criticality calculation. Compared with the conventional assumption of fresh fuel in the calculations, the depletion calculation involved in BUC technology encompasses a wide range of isotopes, and the numerical burnup calculation is notably complicated. Taking the depletion calculation of fuel assemblies in a reactor as an example, the actual fuel depletion process is closely related to factors such as the enrichment, burnable poisons, control rods, power history, and others in the fuel assembly. Even with the adoption of a coupled diffusion–depletion calculation process and the comprehensive tracking of the fuel assembly position throughout the cycles, it remains challenging to fully account for the actual depletion process of the fuel assembly in the reactor. Moreover, because the depletion calculation requires the decomposition of the burnup chain and the selection of an effective numerical calculation method to obtain the spent-fuel composition at a specific burnup [15], the approximation introduced by the burnup chain decomposition and the inherent error of the numerical calculation method make it difficult to obtain an accurate nuclear fuel composition for the depletion calculation [16,17]. Hence, when the BUC technique is applied, it is essential to analyze the spent-fuel composition used in the depletion calculation in a reasonable and conservative manner and quantify the nuclide concentration uncertainties in the criticality calculation. This analytical process contributes to the evaluation of the criticality safety margins in the spent-fuel storage system.
Quantifying the nuclide concentration uncertainties in the depletion calculation requires the experimentally measured values from radiochemical analyses of SNF samples. Since the 1980s, many countries have initiated research on BUC technology. The Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) in the United States, responding to the request of the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), conducted experiments to analyze isotopes in SNF samples and validated depletion codes for various reactor fuel assemblies, such as the German Obrigheim reactor and Calvert Cliffs Unit 1 reactor [18]. The OECD/NEA expert group invited 17 nuclear research institutions worldwide to compare the calculation results from the Phase I-A to Phase VII benchmarks using different depletion codes [19]. This work yielded a series of data results related to BUC technology, including depletion calculation methods, SNF nuclide concentrations, power distribution, and related aspects. Furthermore, a visualization database with operational history and design data, SFCOMP, has been developed for the measurement of spent-nuclear-fuel isotopic concentrations [20]. The database can provide assay data with a referenced, standardized, cross-checked source of published experimental data for the use of data evaluators [21]. There are many computational works carried out according to these benchmarks in the international field, which mainly focus on the uncertainty about the nuclear cross-section data library, the critical computational uncertainty, etc. For example, Chen Hao carried out a mechanism analysis of the contributions of nuclear data to the criticality calculation uncertainty for high-temperature gas-cooled reactors by using nuclear data covariance matrices [22]. Marco Pecchia computes the uncertainty for the criticality calculation of the spent-fuel storage pool based on perturbation theory by perturbing conditions related to the geometry of the spent-fuel assembly, fuel enrichment, etc. [23]. Nevertheless, there are fewer relevant studies on the effects of the uncertainty of the nuclide concentration on the criticality calculation. I.C. Gauld analyzes the uncertainty of the nuclide concentration for spent fuel in boiling-water reactors via the ratio values between the experimental nuclide concentrations and the calculated nuclide concentrations from the depletion code [24]. Hyungju Yun used Monte Carlo (MC) uncertainty sampling to calculate the keff bias and bias uncertainty of the GBC-32 dry-storage system [25]. Although the methods in the I.C. Gauld and Hyungju Yun papers can be used to quantify the uncertainty that fuel burnup calculations transmit to the criticality calculations, it is required to assume that the ratio of the measured-to-calculated (M/C) concentrations follows a normal distribution and ignores the correlation among isotopes in the MC uncertainty sampling method. Meanwhile, there is a lack of relevant direct proof against the assumption of normal distribution and the assumption of nuclide uncorrelation in MC uncertainty sampling. Therefore, a quantitative analysis study on the two assumptions in the MC uncertainty sampling method is needed to evaluate their impacts on the criticality calculations.
To accurately evaluate the impacts of the two assumptions on the criticality safety, a total of 151 benchmark cases of PWR spent-fuel assemblies were selected from the SFCOMP database in this study. The isotopic bias and bias uncertainty in the SNF samples were obtained via the ratio values between the depletion calculation results of the Monte Carlo code RMC and the measurement values of the SNF samples in the destructive radiochemical analyses, and an evaluation was conducted to analyze the assumption of a normal distribution for the M/C concentration ratio by using the sensitivity and uncertainty (S/U) analytical method. Subsequently, the impact of the nuclide concentration uncertainty on the criticality calculation in BUC technology was quantified by using the MC uncertainty sampling method and isotopic correction factor method. The complexity of the depletion calculation makes it challenging to compute the correlations among isotopes according to the burnup chains. Consequently, this study proposes the Latin hypercube sampling (LHS) method, which takes into account the isotopic correlations for assessing their effects on the uncertainty in the criticality calculation.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows. Section 2 describes the sampling calculation method for quantifying the uncertainty. Section 3 presents the quantitative results of the isotope bias and bias uncertainty and the quantitative analysis of the bias and bias uncertainty in the criticality calculation. Section 4 assesses the impact of the assumptions used in the MC uncertainty sampling method on the criticality safety. Section 5 concludes the paper.
2. Methods
2.1. Method for Determination of Isotope Biases and Bias Uncertainties
In the BUC application, the determination of isotopic biases and bias uncertainties in spent-fuel samples is based on the ratio values between the measured nuclide concentrations and those calculated using the depletion code. This approach has gained international acceptance as a reliable method [25].
The ratio values () between the measured isotopic concentrations and the calculated values are computed using Equation (1):
where and represent the measured and calculated concentrations, respectively, of the nuclides (n) in the evaluated fuel sample (j).
Assume that are samples drawn from the normal-distribution population (N(μ,σ2)). When the sample size is sufficiently large, follows a normal distribution with the sample mean () and variance () [25]. The sample mean () and standard deviation () can be written as follows:
where represents the M/C concentration ratio defined in Equation (1). is the number of evaluated fuel samples.
However, the number of samples obtained is usually limited. Tolerance intervals can be introduced to account for the uncertainty due to the sample size. Tolerance intervals use sample data to estimate the uncertainty of the population’s upper and lower bounds for representing a specified proportion. For example, discrete data points following the normal distribution with the limited sample size of , a proportion (1 − γ) of the sampled population and a confidence level of 1 − β, are assigned a two-sided tolerance-limit factor () via the sample size, and the corresponding tolerance interval is [,].
The standard deviation corrected by the tolerance factor can be written as follows:
In the tolerance interval, the isotopic sample mean () can be considered as the isotopic bias. can be referred to as the isotopic bias uncertainty.
2.2. Method for Calculation of Bias and Bias Uncertainty in Criticality Calculations
The main methods for quantifying the uncertainty in criticality calculations are the isotropic correction factor method and the MC-based uncertainty sampling method [25]. In this paper, the LHS approach with an isotopic covariance matrix is proposed to estimate the influence of the isotopic correlations on the criticality safety. The following sections provide introductions to the three methods.
2.2.1. Method for Calculation of Bias and Bias Uncertainty in Criticality Calculations
The isotropic correction factor (ICF) method makes use of the most limiting nuclide concentration uncertainty values to envelope the uncertainty of the nuclide concentration. This method can calculate the upper bound of the criticality computational uncertainty, as shown in Equation (5):
where is the calculated value for the nuclide (n). represents the corrected value obtained by adjusting the calculated value () via isotope bias and bias uncertainty. The maximum value of the concentrations for all fissile isotopes is , and the minimum value of the concentrations for all neutron-absorbing isotopes is . While this method has a sufficiently conservative value for the keff in criticality calculations, the overestimation of the reactivity restricts the feasibility of achieving high-density storage in the designed spent-fuel pool. As a result, the capacity of the reprocessing facility to dispose of spent fuel is constrained.
2.2.2. MC Uncertainty Sampling Method
The MC uncertainty sampling method is a widely used quantitative analysis technique for assessing parameter uncertainties. During the sampling process, this method assumes that all sample distributions of the values follow the normal distribution, and that different isotopes are independent and uncorrelated. The MC uncertainty sampling method is illustrated as follows:
where represents the calculated value of the nuclide (n) having a burnup (b). is the corrected value obtained by adjusting the isotopic bias and bias uncertainty of the nuclide (n) having a burnup (b) in the kth criticality calculation. and represent the isotopic bias and the isotopic bias uncertainty, respectively, for the nuclide (n) having a burnup (b). is the random number sampled from the standard normal distribution for the nuclide (n) in the kth criticality calculation.
Assuming that the calculated value of the nuclide is , the measured value () of this nuclide should approximate . The true value of the nuclide could potentially be any value in the samples calculated using the MC uncertainty sampling method (). Hence, a larger number of sampling calculations are required to ensure the reliability of quantifying the uncertainty results.
Subsequently, the sampled nuclide concentrations are applied in the criticality safety analysis model. After the important isotopic concentrations are corrected, the corrected isotopes form new spent-fuel samples in a criticality safety analysis model. A series of criticality calculations are then performed on these samples to determine the keff uncertainty. The results of the ith criticality calculation and their standard deviation are determined using Equations (7) and (8):
where represents the mean of the ith criticality calculation; is the standard deviation of the criticality calculation; represents the result of the ith criticality calculation in the total NC criticality calculations.
A series of criticality calculations for the samples in Equation (7) will converge to . The difference between the reference value (keff–REF) (i.e., the calculation value without isotopic concentration adjustment in the criticality code) and the represents the keff bias resulting from the isotopic bias, as follows in Equation (9):
The one-sided tolerance-limit factor () with a 95% probability and 95% confidence level is chosen to determine the keff bias uncertainty in Equation (10):
The bias and bias uncertainty in the keff resulting from isotopic bias and bias uncertainty can then be expressed as follows:
2.2.3. LHS Method with Isotopic Covariance Matrix
Aiming to account for the correlations among the nuclides in the sampling process, this paper employs the LHS method with the isotopic covariance matrix. The relationship among the covariance matrix (Σ), the correlation coefficient matrix (R), and the standard deviation matrix (V1/2) is as follows:
The eigenvalue decomposition of the covariance matrix in Equation (12) is represented as follows:
where λi is the eigenvalue of the covariance matrix. Equation (13) is transformed into Equation (14):
According to multivariate statistical analysis, if the number of nuclides is m, is the random vector given by the Monte Carlo sampling. follows the standard normal distribution (N(0, 1)) and is mutually independent. Thus, also follows the normal distribution () with the mean () and variance (). The LHS method with the isotopic covariance matrix is then given in Equation (15):
where and represent the isotopic correction value and random vector using the LHS method for the nuclide (n) having a burnup (b), respectively.
3. Computations and Results
3.1. Introduction to Calculation Codes
RMC is a new Monte Carlo transport code developed by the Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China [26]. It can handle complex geometries with different materials and temperatures using continuous energy point-wise cross sections. RMC can be utilized for various purposes, including criticality calculations, depletion calculations, perturbation and sensitivity analysis, and more. In this study, the depletion and criticality calculation of RMC 3.5 was employed to perform the calculations based on the SFCOPM database and the ENDF/B-V nuclear data library.
3.2. Selection of the SNF Benchmark
Because the uncertainty of the calculated isotopic concentrations needs to be quantified by applying the measured isotope data, a potential problem in selecting the type of spent-fuel benchmark is whether the experimental database is representative for the SNF properties. A significant amount of the currently available measurement data was obtained from fuel assemblies irradiated in the 1970s. Internationally, there are still no standardized criteria to assess the applicability of the isotope database.
In light of the diverse range of SNF samples, this study selected 151 experiment benchmarks from the SFCOMPO2.0 database [21]. These benchmarks included chemical assay nuclide concentration data on SNF assemblies from 14 PWR nuclear power plants. The benchmarks for the calculations of the PWR SNF assemblies are shown in Table 1. The fuel enrichment spanned from 2.453 wt% to 4.66 wt% and the burnup depth ranged from 6.9 GWd/MTU to 75 GWd/MTU in these assemblies. Meanwhile, the experimental benchmarks with control rods and gadolinium-containing fuel rods were also included to ensure an adequately broad representation of the SNF types.

Table 1.
Calculation benchmarks for PWR SNF assembly.
3.3. Determination of the Isotopic Bias and Bias Uncertainty in SNF Assembly
This study selected 28 isotopes that have significant impacts on the criticality safety calculation in BUC technology, including 12 actinides (234U, 235U, 236U, 238U, 237Np, 238Pu, 239Pu, 240Pu, 241Pu, 242Pu, 241Am, and 243Am) and 16 fission products (95Mo, 99Tc, 101Ru, 103Rh, 109Ag, 133Cs, 143Nd, 145Nd, 147Sm, 149Sm, 150Sm, 151Sm, 152Sm, 151Eu, 153Eu, and 155Gd) [18]. These 28 isotopes are commonly considered in burnup credit criticality safety analysis.
The 151 SNF benchmarks were computed via the RMC code. The calculated values were then compared with the experimental values. Following the analysis method described in Section 2.1, the isotopic biases () can be calculated. Because the isotopic bias varies with burnup, a linear regression analysis of the value was performed to divide the burnup intervals.
Analyzing the dependency relationship between the isotopic bias and burnup interval was achieved with a linear regression model. Within a defined burnup interval, the application of a piecewise function to determine the isotopic bias and bias uncertainty helps minimize the significant dependency of the isotopic bias on the burnup [27]. For example, the burnup interval 5–78 GWd/MTU was divided into two or three subintervals, and the isotopic bias and isotopic bias uncertainty were kept constant within each burnup subinterval. The calculated results are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Isotopic bias and bias uncertainty for SNF composition.
As shown in Table 2, the major actinide nuclides, 235U, 238U, 239Pu, 240Pu, 241Pu, and 242Pu, are divided into three burnup subintervals: low burnup (5–15 GWd/MTU), medium burnup (15–40 GWd/MTU), and high burnup (40–75 GWd/MTU). For the actinide nuclides, 234U, 236U, 238Pu, 241Am, 243Am, and 237Np, two different sets of isotopic bias and bias uncertainty values are determined for the burnup subintervals: 5–40 GWd/MTU and 40–75 GWd/MTU. A single set of isotopic bias and bias uncertainties are used to envelope fission products with limited sample data (e.g., 15 samples for 101Ru and 17 samples for 133Cs).
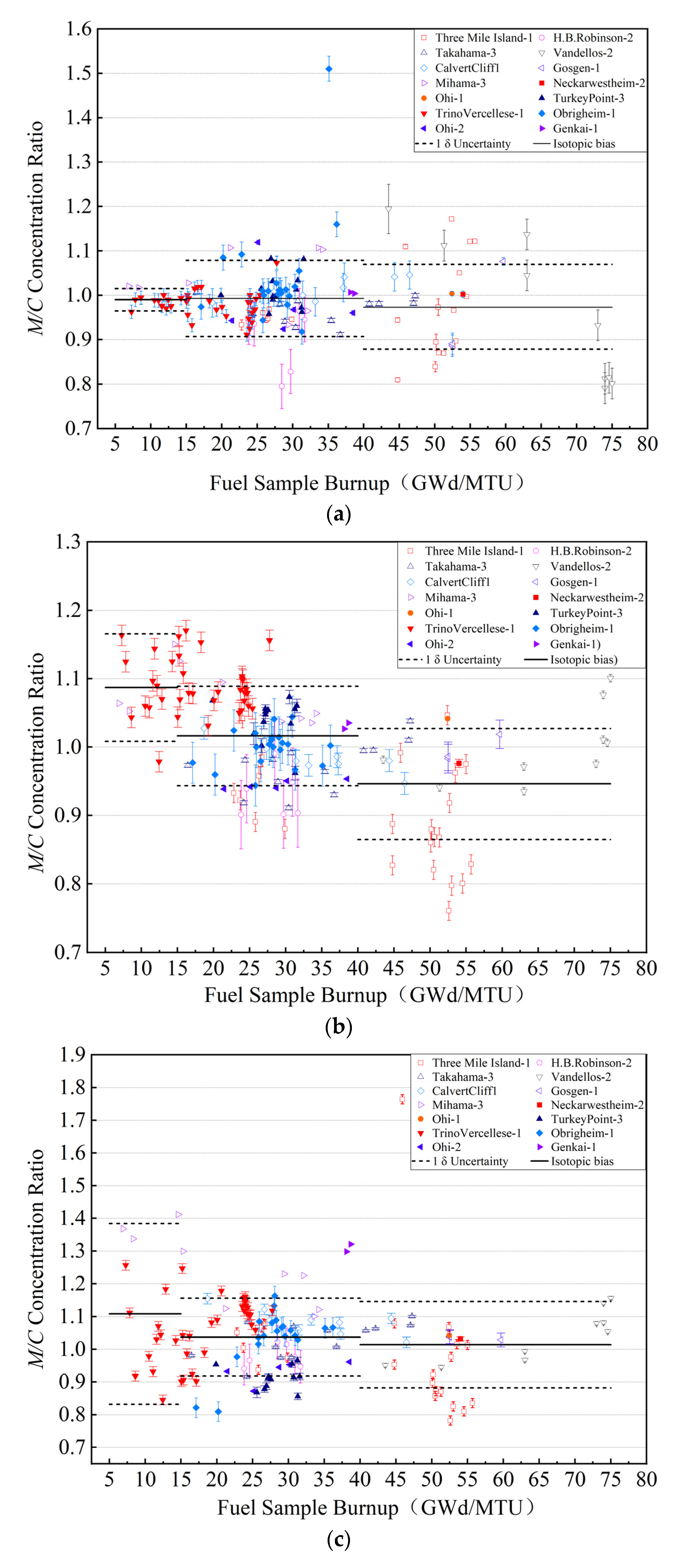
The isotopic biases versus the fuel sample burnup are plotted in Figure 1 for 235U, 239Pu, and 241Pu. The SNF isotopic biases in the burnup subinterval are distributed within an approximate 1 δ uncertainty around the sample mean value, and the SNF isotopic biases are constant in the burnup subintervals.
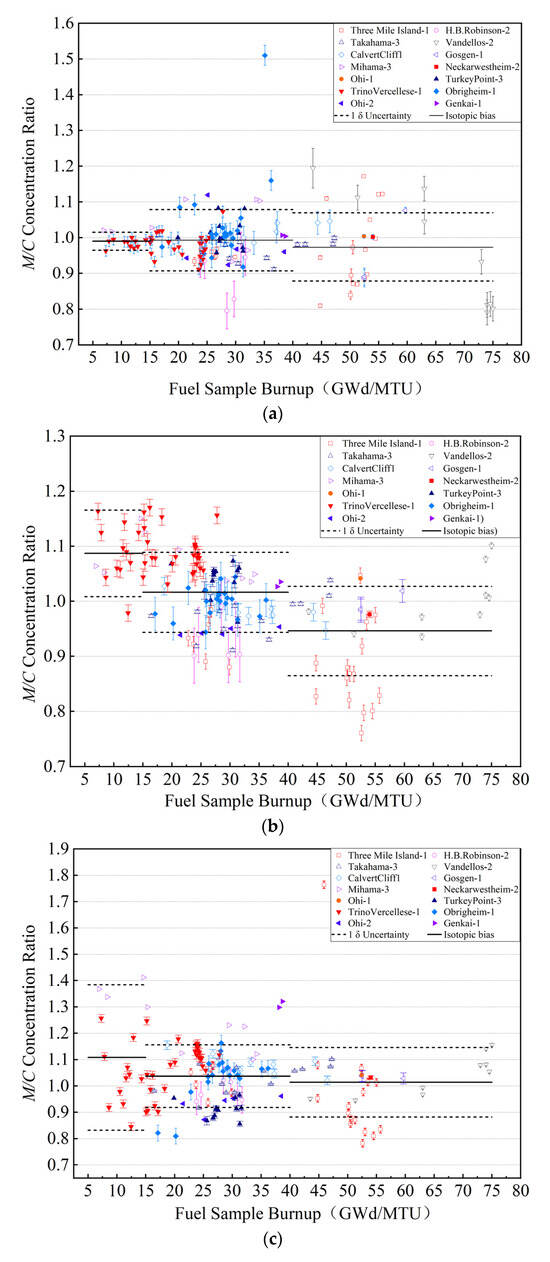
Figure 1.
Isotopic bias and bias uncertainty for (a) 235U, (b) 239Pu, and (c) 241Pu.
The calculated results indicated that the isotopic bias varies as a function of the sample burnup. Compared to analyzing the isotopic bias and bias uncertainty in terms of the average burnup over the history of the spent-fuel irradiation, the isotopic bias as a piecewise function of burnup could more accurately reflect the uncertainty in the prediction of the isotopic concentrations at different burnups via the burnup code.
3.4. Determination of Isotopic Bias and Bias Uncertainty in SNF Assembly
Taking the 17 × 17 fuel assembly of the AFA-3G fuel type with an initial enrichment of 4.95% as an example, the criticality calculation is performed for a single assembly stored in the SNF-pool storage cell for burnup at 10 GWd/MTU, 30 GWd/MU, and 45 GWd/MTU using the RMC code. The geometric parameters of the SNF-pool storage cell are detailed in Table 3 (with fully reflective boundary conditions). The MC uncertainty sampling method in Section 2.2 is utilized to calculate the bias and bias uncertainty for the criticality calculation after obtaining the calculated nuclide concentration.

Table 3.
The geometric parameters of the SNF-pool storage cell.
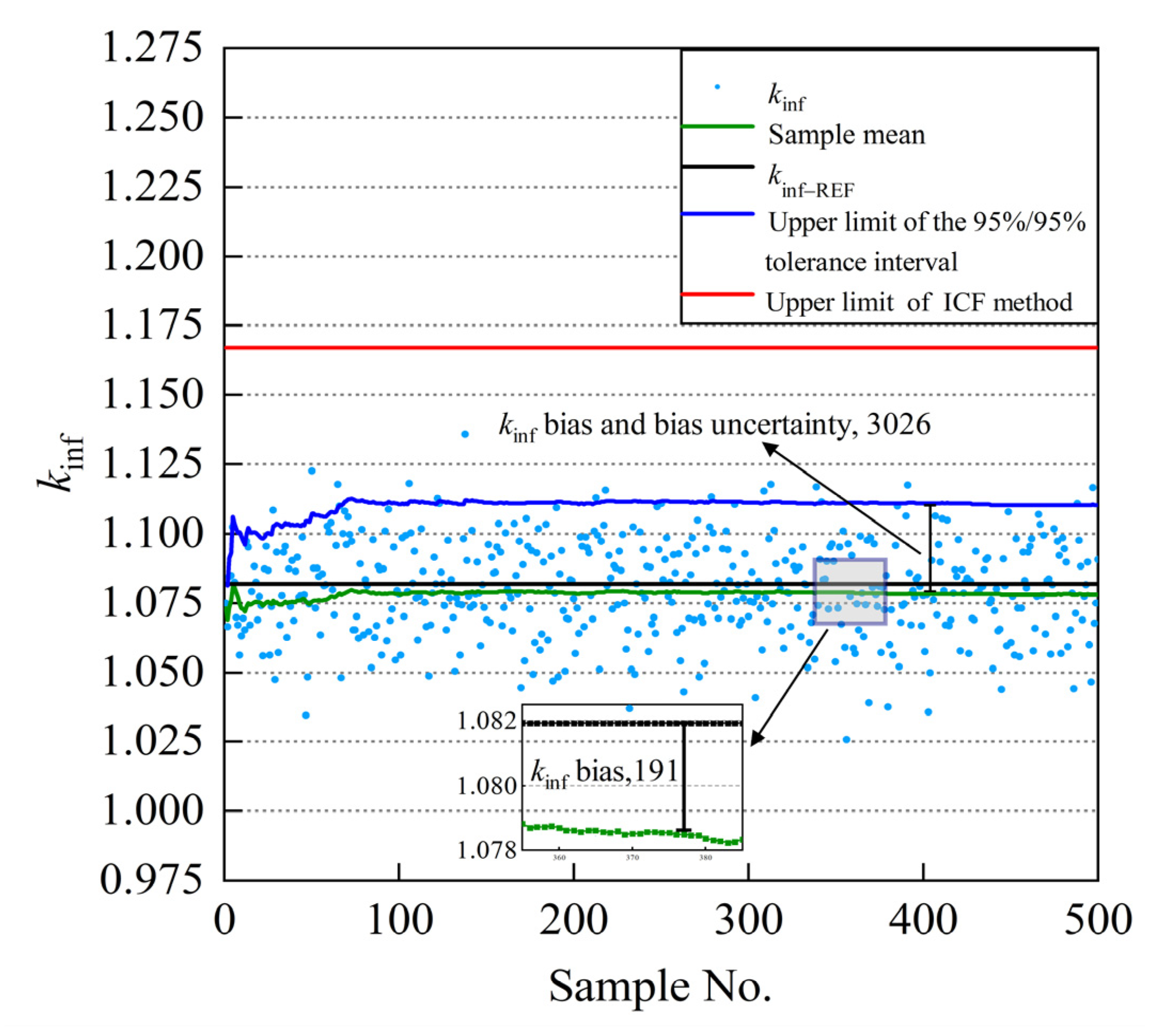
Figure 2 illustrates the infinite medium multiplication factor (kinf) calculation results based on the MC uncertainty sampling method for SNF assembly burnup at 30 GWd/MTU. As depicted in Figure 2, and gradually converge with the increase in the number of samples. When the number of criticality calculations is 500 times, the variation range of the is within the range of , and the calculation results are then converged and credible based on the MC uncertainty method. Furthermore, it can be shown from the sampling results that the criticality calculations of the ICF method significantly overestimated the actual reactivity in the spent-fuel assemblies compared with the MC uncertainty sampling method. As a result, the SNF storage racks designed according to the ICF method exhibited wider storage rack cell pitch or arranged neutron absorbers with larger absorption cross sections than those designed using the MC uncertainty sampling method. Although the excessively conservative calculation method ensured the SNF storage safety, it also sacrificed the economy of the nuclear power plant.
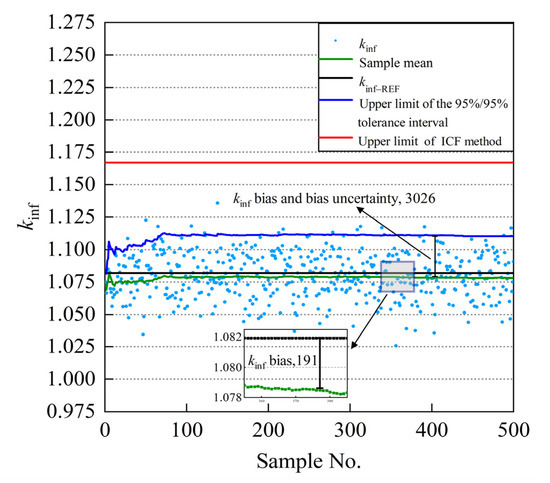
Figure 2.
The kinf bias and bias uncertainty for burnup at 30 GWd/MTU.
Table 4 presents the detailed results of the kinf bias and bias uncertainty at different burnups in the SNF assembly. The results indicated that the uncertainty of the criticality calculations increases with an increase in burnup. This tendency primarily results from the fact that the uncertainty in the depletion calculation of a part of the actinides and fission products tends to increase at high burnup.

Table 4.
The kinf bias and bias uncertainty at different burnups in SNF assembly.
4. Assessment of Assumptions Used in the MC Uncertainty Sampling Method
There are two assumptions in the MC uncertainty sampling method, which are the assumption that the values follow a normal distribution and the uncorrelation assumption among isotopes. This chapter will provide a detailed analysis of the two assumptions.
4.1. Assessment of the Normal-Distribution Assumption of M/C Concentration Ratio
In this section, the S/U analysis method is employed to calculate the sensitivity for all the isotopes and quantify the impact of the individual nuclide bias and uncertainty on the criticality calculation. This helps to identify the relatively important isotopes for the criticality calculation, and to evaluate the normal-distribution assumption of the values in the MC uncertainty sampling method.
4.1.1. MC Uncertainty Sampling Method
The sensitivity coefficient is a physical quantity that defines the relationship between the input variables and the variation in the model output results. The sensitivity coefficients (Sn) for the isotopes can be derived as shown in Equation (16):
Equation (16) represents the perturbation in the cross section () of the nuclide (n) on the kinf. The impact of the nuclide concentration uncertainty on the criticality safety calculation can be quantified by using the obtained isotopic uncertainty combined with sensitivity coefficients. The specific calculation process is presented as follows:
where represents the kinf bias propagated to the criticality calculation through the nuclide concentration for the nuclide (n) from the measurement data of fuel sample j in Equation (17). is the kinf bias resulting from all the calculated nuclide concentration biases in Equation (18). represents the 1σ kinf bias uncertainty caused by the uncertainty () in the calculated nuclide concentrations. Equations (18) and (19) can be used not only to quantify the bias and uncertainty for all the nuclide concentrations propagating to the kinf bias and bias uncertainty, but it can also be applied to calculate the contribution of individual nuclide concentration bias and uncertainty to the kinf bias and bias uncertainty. Moreover, the uncertainty results obtained from the S/U method for the criticality calculation can serve as reference values for the validation of the results calculated from the MC uncertainty sampling method.
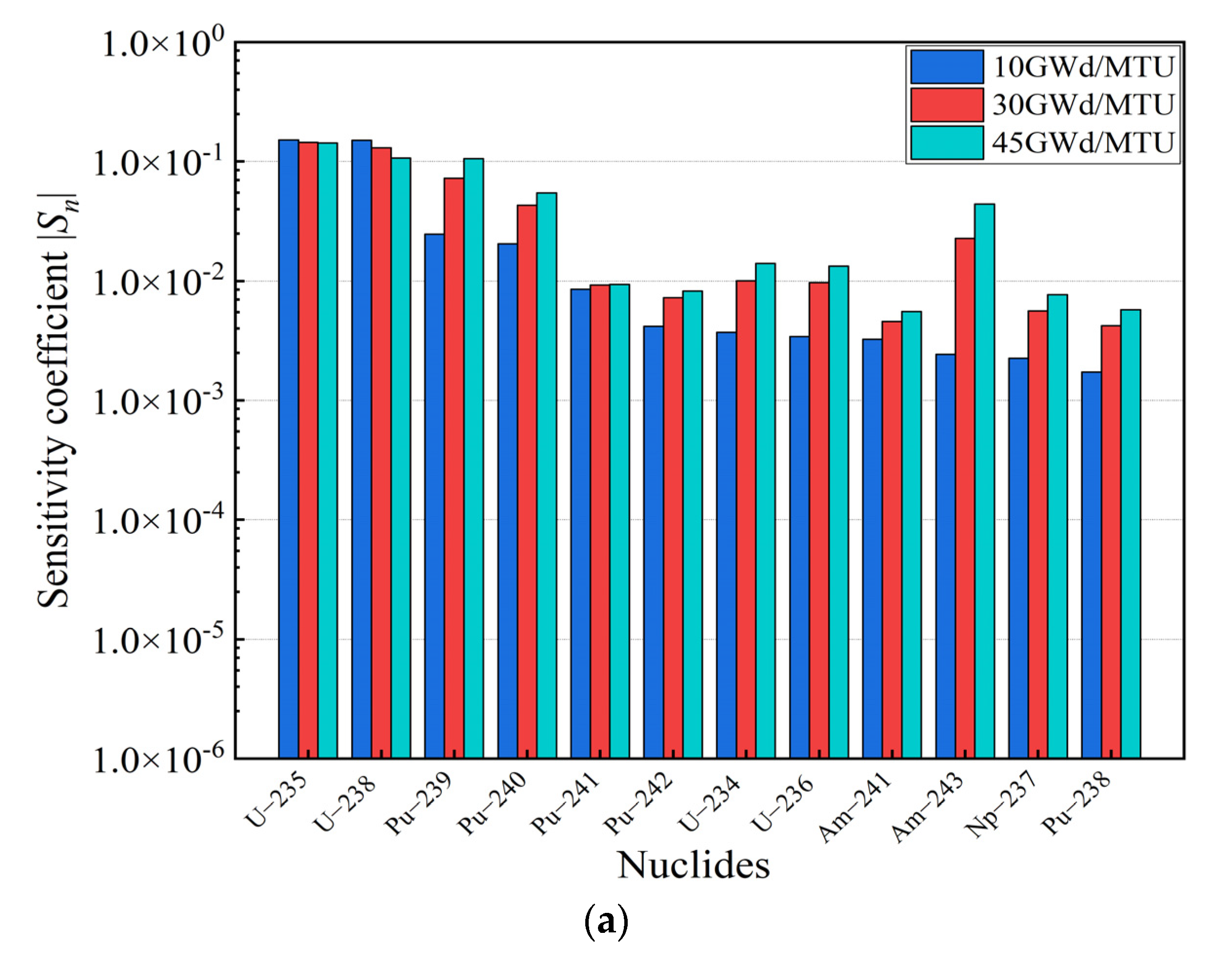
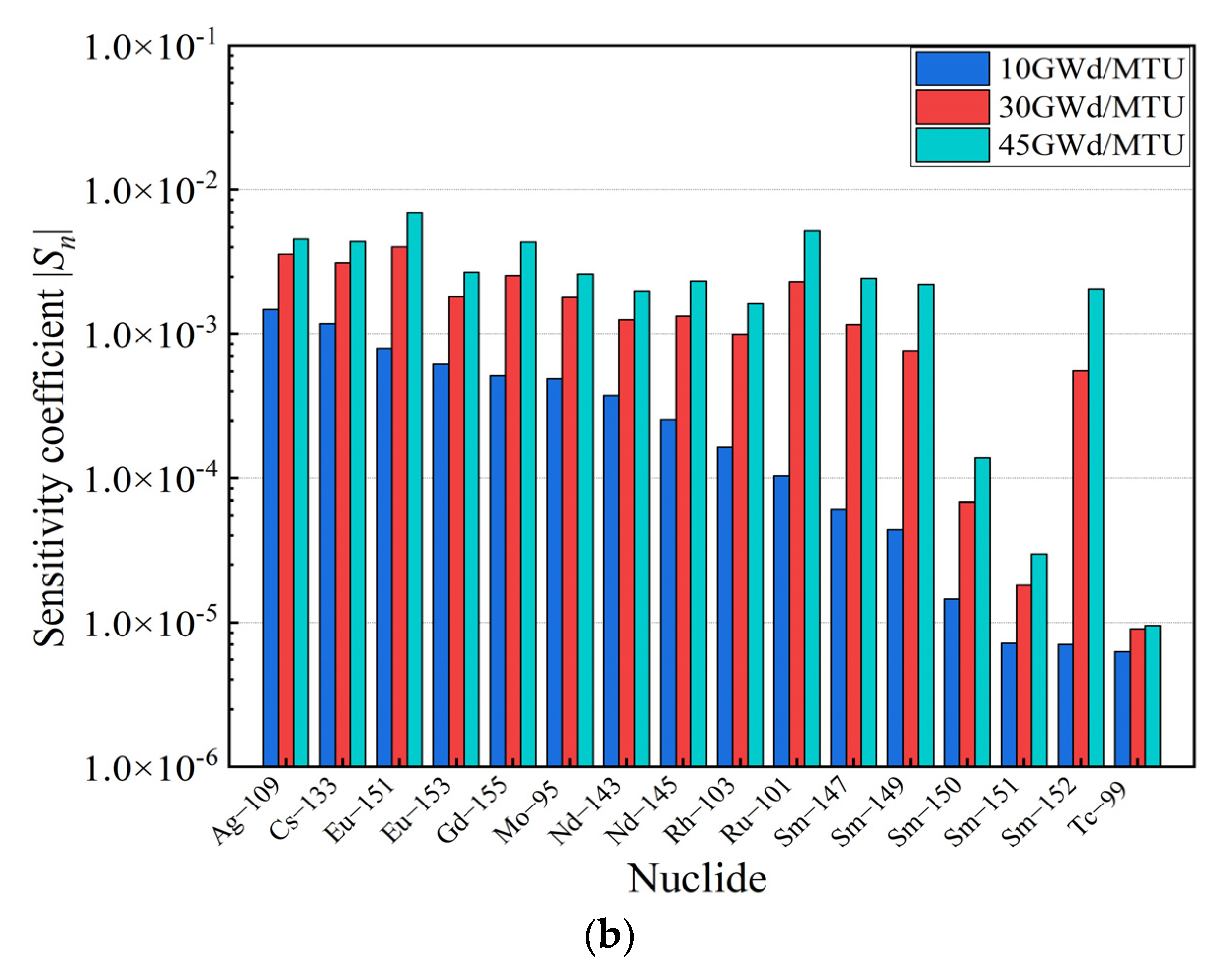
The sensitivity analysis of the SNF storage model described in Section 4 was performed by utilizing the RMC code for burnup at 10 GWd/MTU, 30 GWd/MTU, and 45 GWd/MTU. The sensitivity coefficients at different burnups are presented in Figure 3.
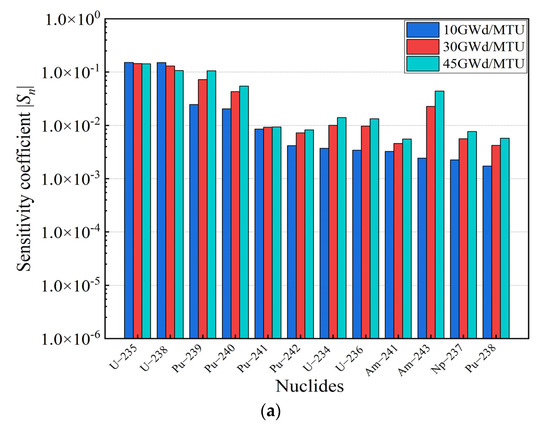
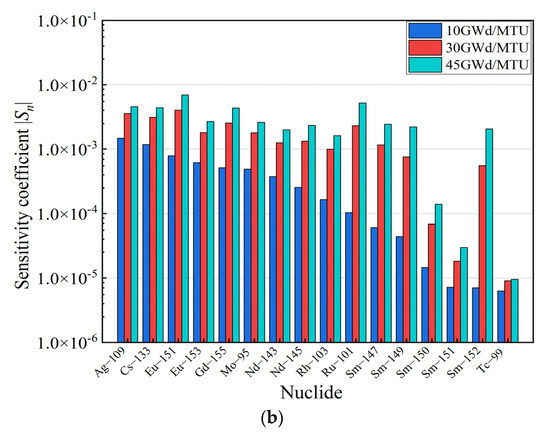
Figure 3.
Sensitivity coefficients for burnup at 10 GWd/MTU, 30 GWd/MTU, and 45 GWd/MTU. (a) Actinides. (b) Fission products.
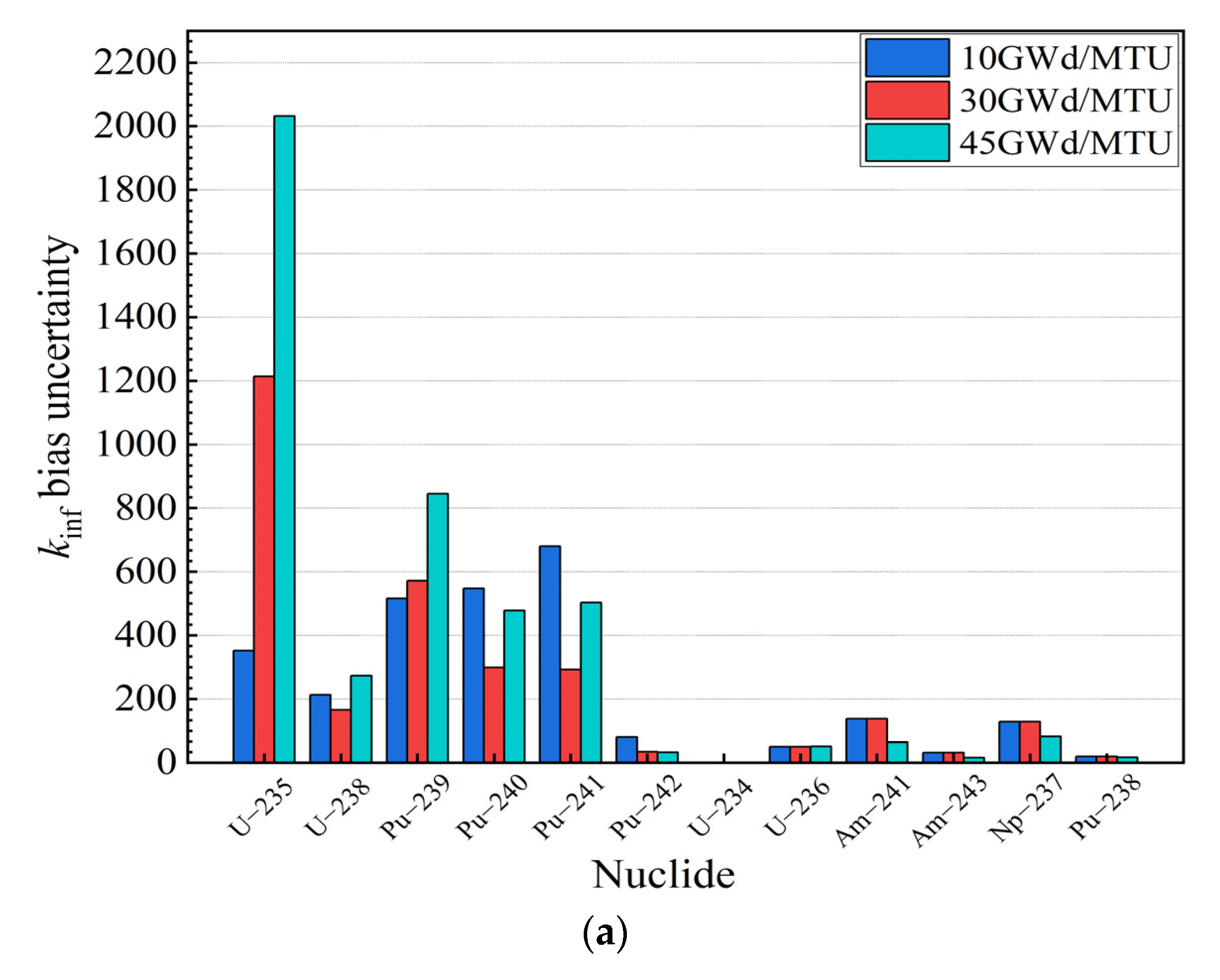
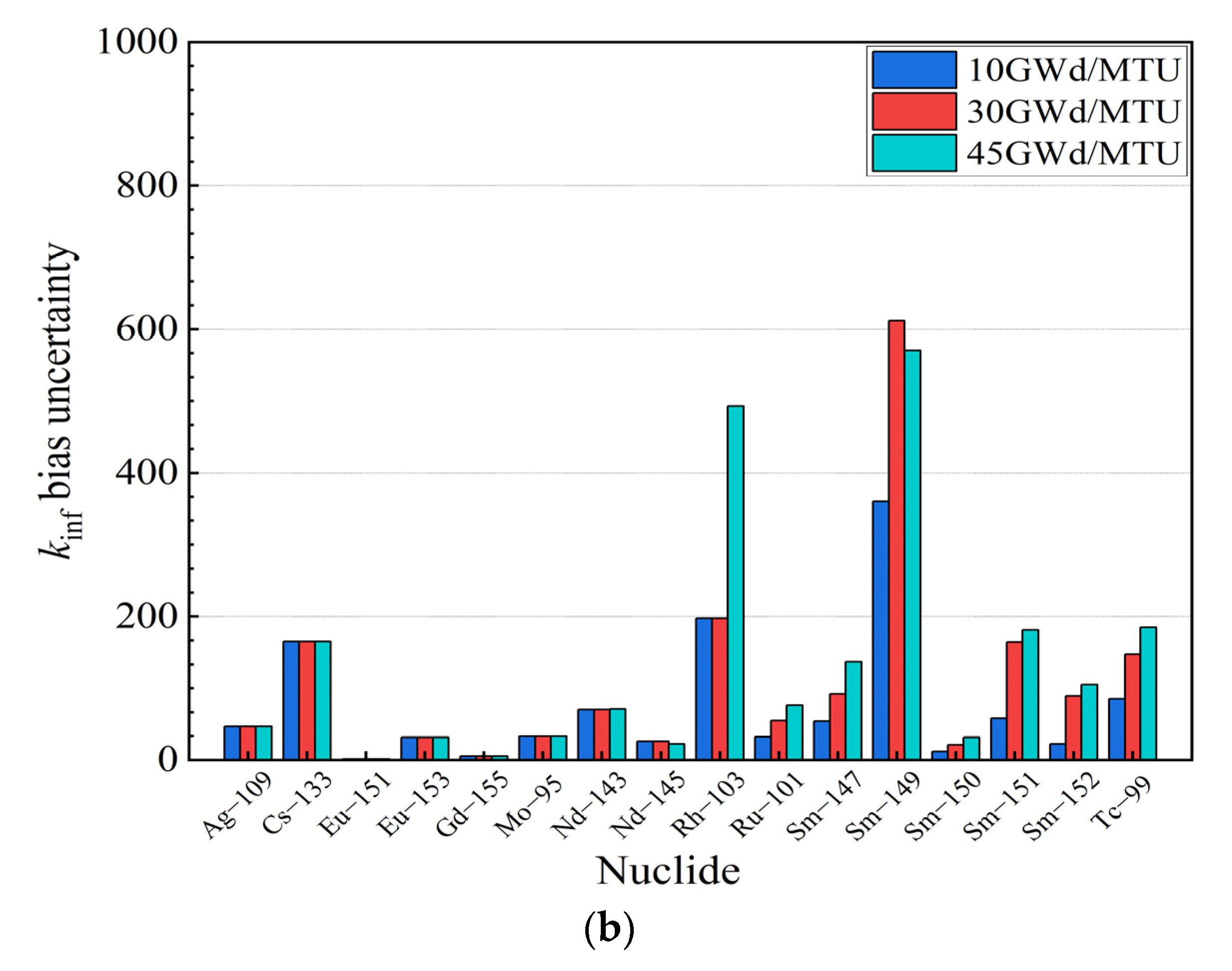
As illustrated in Figure 3, it can be observed that the sensitivity coefficients of U and Pu isotopes dominated throughout the sensitivity coefficient calculation. Meanwhile, the 235U concentration decreased with an increase in the burnup, and the contribution of the 235U to the reactivity decreased. In contrast, the contribution of 239Pu and 241Pu, fissile isotopes, accumulated with an increase in the burnup, and the contribution of 239Pu and 241Pu to the reactivity increased gradually. These results are consistent with the actual fuel depletion process in PWR fuel assemblies. Moreover, the contribution of nuclides to the kinf bias and bias uncertainty is evaluated in this paper, as shown in Figure 4.
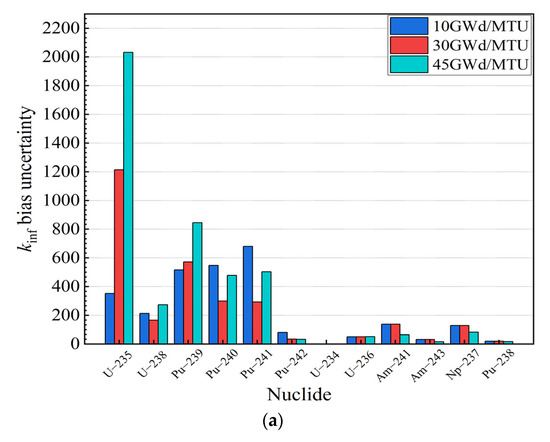
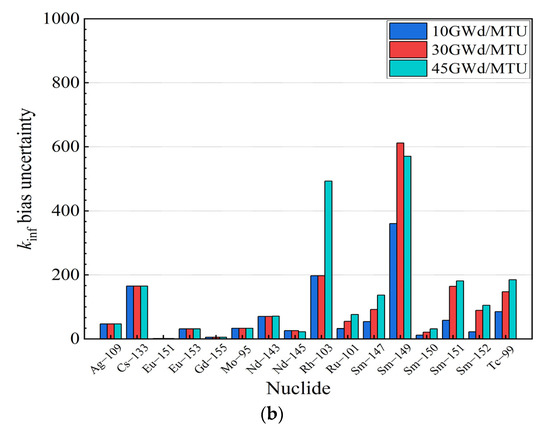
Figure 4.
for burnups at 10 GWd/MTU, 30 GWd/MTU, and 45 GWd/MTU. (a) Actinides. (b) Fission products.
Figure 4 indicates that the uncertainty contributions of the U and Pu isotopes consistently dominated the uncertainty in the criticality calculations at different burnup depths. Among the isotopes, the four fissile nuclides, 235U, 239Pu, 240Pu and 241Pu, had the dominant influence on the criticality calculation results. Furthermore, a few of the fission products also had an impact on the criticality calculation results.
4.1.2. Validation of Assumption for Normal Distribution of Isotopic Bias
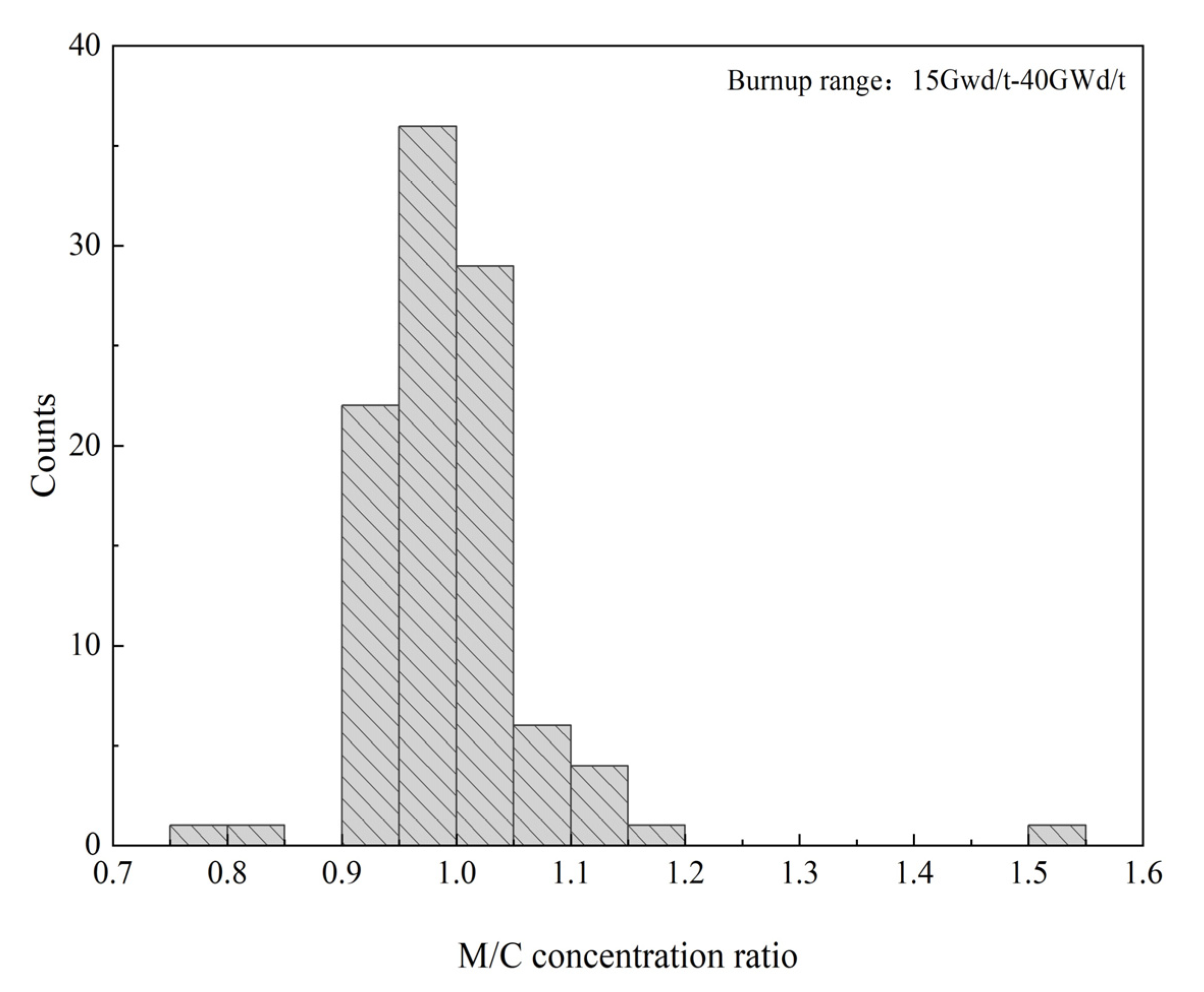
Because the 235U nuclide concentration uncertainty is the largest contributor to the uncertainty in the criticality calculations, this section evaluates the normal-distribution assumption of the values in the MC uncertainty sampling method with 235U as an example. Although the 235U nuclide bias is assumed to follow a normal distribution in the MC uncertainty sampling method, the M/C ratio values for the 235U nuclide cannot conform to a normal distribution in the SNF experimental benchmark in the burnup range of 15 GWd/t–40 GWd/t. The histogram of the M/C concentration ratio values for the 235U distribution is depicted in Figure 5.
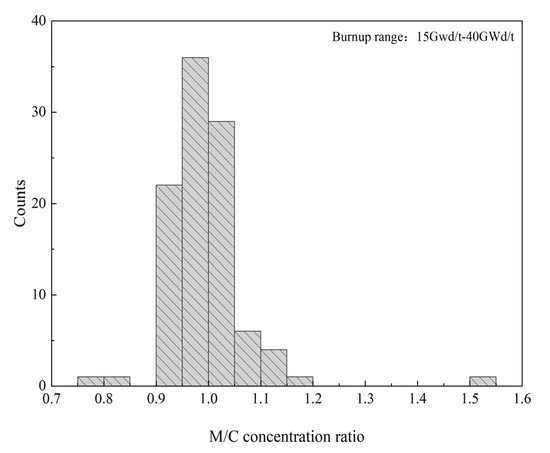
Figure 5.
Histogram of the M/C concentration ratio values for 235U.
As depicted in Figure 5, it is clear that the M/C concentration ratio of the 235U nuclide presents a skewed, unimodal frequency distribution and fails to pass the Shapiro–Wilk normality test. Simultaneously, the kinf bias attributable to the 235U concentration bias was calculated for the burnup ranging from 15 GWd/MTU to 40 GWd/MTU in the experimental benchmarks, as listed in Table 5.

Table 5.
arising from the 235U concentration bias in the different experimental benchmarks.
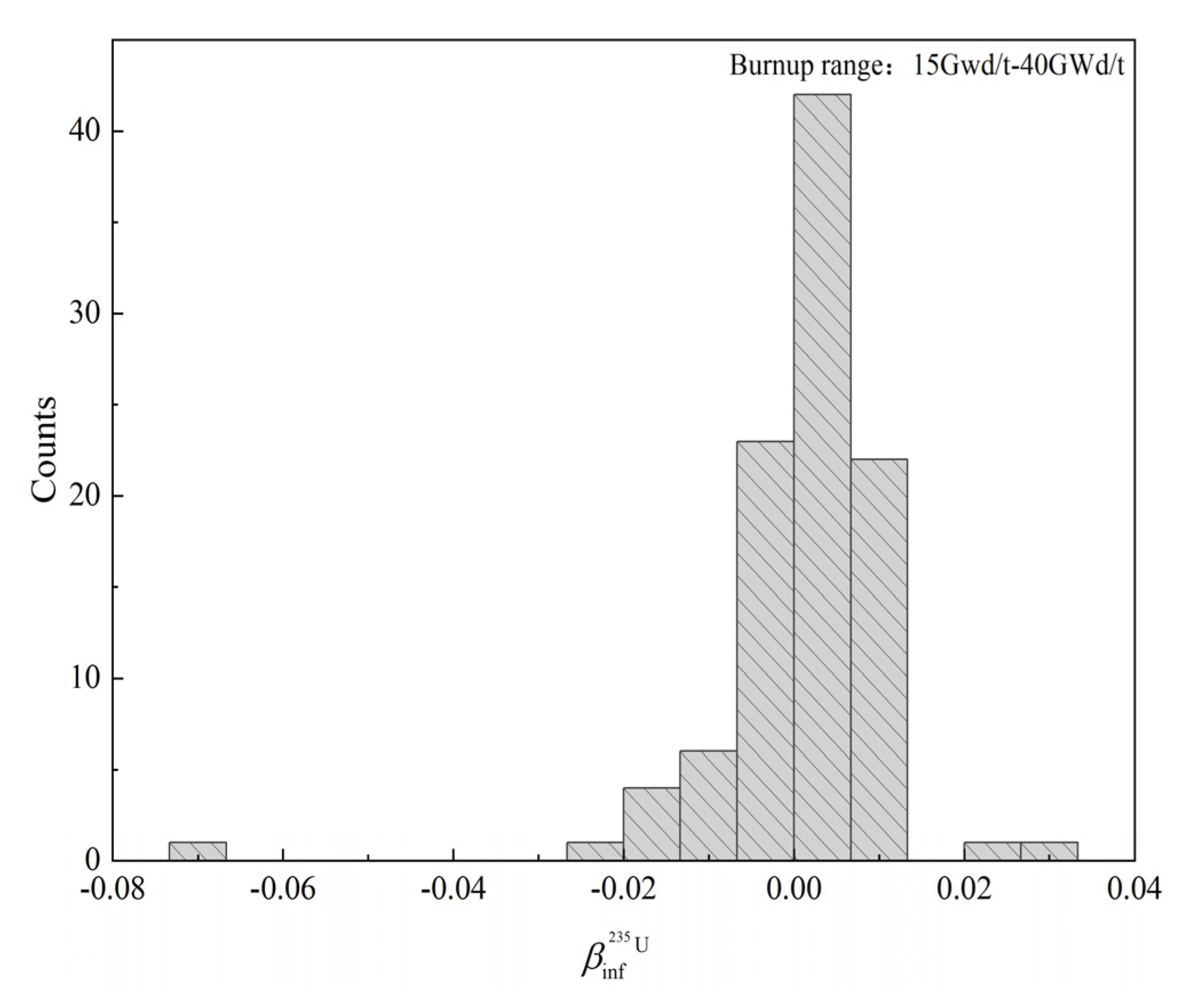
The statistics of the burnup ranging from 15 GWd/MTU to 40 GWd/MTU are shown in Figure 6, which demonstrate that the values also fail to follow the normal-distribution assumption. Hence, the assumption of data normality distribution in the MC uncertainty sampling method needs to be further evaluated.
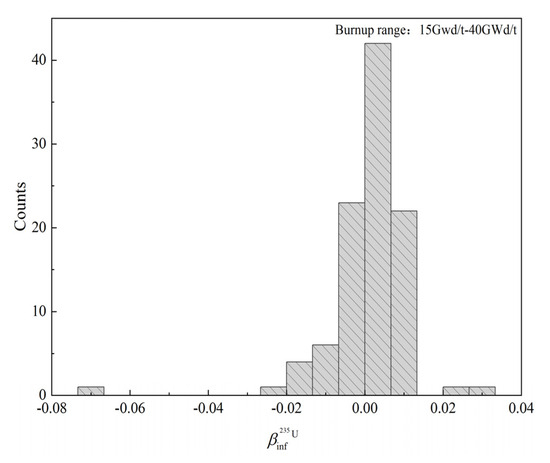
Figure 6.
Histogram plot for values.
For 235U, the kinf bias uncertainty value obtained (2166 pcm) with the MC uncertainty sampling method based on the normality assumption is slightly larger than the kinf bias uncertainty value from the S/U method according to the actual distribution (1214 pcm). In this case, the result indicates that the kinf bias uncertainty values obtained with a normal distribution instead of the actual distribution are more conservative. Table 6 presents the calculation results of the kinf uncertainty based on the S/U method and MC uncertainty sampling method.

Table 6.
The kinf uncertainty values based on the S/U method and MC uncertainty sampling method.
As shown in Table 6, for all the isotopes applied in BUC technology, the uncertainties in the criticality calculation obtained with the actual sample distribution are in agreement with the calculation results based on the normal distribution, which has relative errors within 3%. The above results demonstrated that the MC uncertainty sampling method was reasonable for quantifying the uncertainty of the criticality calculation with the normal-distribution assumption of the M/C concentration ratio, and it exhibited a higher computational efficiency than the S/U method requiring the calculation uncertainty for each nuclide.
4.2. Evaluation of the Uncorrelation Assumption among Isotopes
Although the uncorrelation assumption regarding isotopes is employed in the MC uncertainty sampling method, there will still be dependencies among the isotopes according to the burnup chain in the actual depletion calculation. This section aims to evaluate the impact of the isotopic correlation on the criticality safety by applying the nuclide correlation coefficient matrix in the LHS uncertainty sampling method.
The calculation of the nuclide correlation coefficient matrix primarily focused on isotopes that contribute significantly to the uncertainty of the criticality calculation and exhibited an important dependence on the burnup chain. As shown in Figure 4, it is evident that the uncertainties associated with U and Pu isotopes consistently dominated the contribution to the uncertainty of the criticality calculation. Notably, the three fissile nuclides, 235U, 239Pu, and 241Pu, had a significant impact on the criticality safety calculation. Therefore, the isotopes closely related to them in the burnup chain, 238U, 240Pu, and 242Pu, were selected. Through an analysis of the correlation of the M/C concentration ratio among these six nuclides (235U, 238U, 239Pu, 240Pu, 241Pu, and 242Pu) for the burnup ranging from 15 to 40 GWd/MTU, the correlation coefficient matrix is presented in Table 7. The degree of dependence reflected by the correlation coefficients is presented in Table 8.

Table 7.
The correlation coefficient matrix of the M/C concentration ratio among six nuclides.

Table 8.
Correlation coefficients and the corresponding correlation levels.
As illustrated in Table 7 and Table 8, it can be observed that only strong correlations exist between certain pairs of isotopes, such as 239Pu and 240Pu, 240Pu and 242Pu, and 241Pu and 242Pu. The following two cases were selected to explore the influence of the isotopic correlation on the sampling results: (1) sampling calculation without considering the negative correlation coefficient and weak correlation coefficient, as shown in the correlation coefficient matrix in Table 9; (2) sampling considering only the strong correlations among the three pairs of isotopes, as depicted in the correlation coefficient matrix in Table 10.

Table 9.
The correlation coefficient matrix excluding negative and weak correlations among isotopes.

Table 10.
The correlation coefficient matrix considering only the strong correlations among isotopes.
The results of the MC sampling method for quantifying the kinf uncertainty values in different cases are shown in Table 11.

Table 11.
The uncertainty calculation results with different correlation coefficient matrices.
As indicated in Table 11, the kinf uncertainty values without considering the correlations among important isotopes represent an increase of approximately 5% over those in the other two cases in the three different cases of covariance coefficient matrices. Consequently, when the uncertainty of the criticality is only considered for important isotopes, introducing the isotopic correlations could reduce the uncertainty of the criticality calculation for SNF storage systems.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, the ratio values between the experimental measurement data and the calculated isotopic concentrations were used to determine the isotopic bias and bias un-certainty. Subsequently, the MC uncertainty sampling method was employed to quantify the influence of the isotopic concentration uncertainties on the bias and bias uncertainty in the criticality calculations. The LHS method and S/U method were used to analyze the assumptions applied in the MC uncertainty sampling method. The following conclusions can be drawn from the study of this paper:
(1) This study selected a total of 151 SNF benchmark cases to obtain the functional relationships between the SNF-sample burnup as a function of the isotopic bias and bias uncertainty based on M/C ratio values in the depletion calculation according to the M/C concentration ratio from the depletion calculation. Simultaneously, through a comparison of the computational results of the MC uncertainty sampling method and the reference results provided by the S/U method, it can be shown that the MC uncertainty sampling method has higher computational efficiency to quantify the uncertainty values in the criticality calculations, and the computational accuracy is within 3%. This demonstrated that the MC uncertainty sampling method can compress a part of the margin to improve the SNF storage capacity in nuclear power plants with the assurance of criticality safety;
(2) As shown from the uncertainty results of the criticality calculations quantified via the S/U method, the uncertainties of the uranium and plutonium isotopes consistently dominated the uncertainties of the criticality calculations. Moreover, the results also indicated that the uncertainty calculations employing a normal distribution were slightly more conservative than those taking the actual distribution for the M/C concentration ratio. Hence, the assumption of a normal distribution for nuclide deviations in the MC uncertainty sampling method is reasonable;
(3) The assessment of the correlations among the U and Pu isotopes (235U, 238U, 239Pu, 240Pu, 241Pu, 242Pu) was conducted via the LHS method. The results indicated that the uncertainty results of the criticality calculation excluding the correlations among important isotopes represented an increase of approximately 5% over those considering the correlations among isotopes. Although introducing important isotopic correlations can reduce the uncertainty in the criticality calculations of SNF storage systems when only the criticality uncertainties of the important isotopes are considered, the choice of a more conservative assumption of nuclide uncorrelation (an increase of only 225 pcm in the criticality uncertainty) safeguards the safety of nuclear power plants without sacrificing the economics.
This research proposes the LHS method with the covariance matrices, which is simpler and more straightforward than tracking the burnup chain. Nevertheless, this paper only considers the correlation among important isotopes. In the future, researchers could possibly choose more benchmarks for the minor actinides and fission products to carry out criticality safety analyses for criticality safety calculations in reprocessing dissolution tanks or other reprocessing facilities.
Author Contributions
Z.N. and X.C. contributed equally to this work and are co-first authors; data curation, M.A.W.; project administration, T.Y.; supervision, J.X.; validation, X.C.; writing—original draft, Z.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no funding.
Data Availability Statement
Essential data are included in the manuscript, and further data are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their great appreciation to the other members of the NEAL (Nuclear Energy and Application Laboratory) Team for their support and contribution to this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Saqib, A.; Chan, T.-H.; Mikhaylov, A.; Lean, H.H. Are the Responses of Sectoral Energy Imports Asymmetric to Exchange Rate Volatilities in Pakistan? Evidence from Recent Foreign Exchange Regime. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 614463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinçer, H.; Yüksel, S.; Mikhaylov, A.; Pinter, G.; Shaikh, Z.A. Analysis of Renewable-Friendly Smart Grid Technologies for the Distributed Energy Investment Projects Using a Hybrid Picture Fuzzy Rough Decision-Making Approach. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11466–11477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Su, M.; Li, R.; Ponce, P. The Effects of Energy Prices, Urbanization and Economic Growth on Energy Consumption per Capita in 186 Countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, R. Per-Capita Carbon Emissions in 147 Countries: The Effect of Economic, Energy, Social, and Trade Structural Changes. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 1149–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinçer, H.; Yüksel, S.; Mikhaylov, A.; Barykin, S.E.; Aksoy, T.; Hacıoğlu, Ü. Analysis of Environmental Priorities for Green Project Investments Using an Integrated Q-Rung Orthopair Fuzzy Modeling. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 50996–51007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Nuclear Power Plants in Operation. Available online: https://www.nei.org/resources/statistics/world-nuclear-power-plants-in-operation (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Silvennoinen, P. Nuclear Fuel Cycle Optimization; Chapter 3—Basic Model of the LWR Fuel Cycle; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1982; pp. 34–48. [Google Scholar]
- Alameri, S.A.; Alkaabi, A.K. Nuclear Reactor Technology Development and Utilization; 1—Fundamentals of Nuclear Reactors; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. 27–60. [Google Scholar]
- Prieto-Guerrero, A.; Espinosa-Paredes, G. Linear and Non-Linear Stability Analysis in Boiling Water Reactors; 2—Description of Boiling Water Reactors; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 25–55. [Google Scholar]
- Alameri, S.A.; Alrwashdeh, M. Preliminary Three-Dimensional Neutronic Analysis of IFBA Coated TRISO Fuel Particles in Prismatic-Core Advanced High Temperature Reactor. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2021, 163, 108551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohuri, B. Molten Salt Reactors and Integrated Molten Salt Reactors; Chapter 2—Integral Molten Salt Reactor; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 59–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kooyman, T. Current State of Partitioning and Transmutation Studies for Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2021, 157, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, P.; Cornet, S.M.; Collins, E.D.; DeAngelis, G.; Del Cul, G.; Fedorov, Y.; Glatz, J.P.; Ignatiev, V.; Inoue, T.; Khaperskaya, A.; et al. A Review of Separation Processes Proposed for Advanced Fuel Cycles Based on Technology Readiness Level Assessments. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2019, 117, 103091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovecký, M.; Závorka, J.; Jiřičková, J.; Ondráček, Z.; Škoda, R. Fixed Neutron Absorbers for Improved Nuclear Safety and Better Economics in Nuclear Fuel Storage, Transport and Disposal. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2023, 55, 2288–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Bi, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H. Investigation and Improvement of the Mini-Max Polynomial Approximation Method for Solving Burnup Equations. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2023, 180, 109482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toit, M.H.D.; Naicker, V.V. Monte Carlo Burnup Oscillations for Thorium-Based EPR Fuel. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2023, 185, 109714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shama, A.; Caruso, S.; Rochman, D. Analyses of the Bias and Uncertainty of SNF Decay Heat Calculations Using Polaris and ORIGEN. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1161076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, J.J.; Vasiliev, A.; Pecchia, M.; Ferroukhi, H.; Caruso, S. Review Calculations for the OECD/NEA Burn-up Credit Criticality Safety Benchmark. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2016, 87, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Ebiwonjumi, B.; Kim, W.; Cherezov, A.; Park, J.; Lee, D. Verification and Validation of Isotope Inventory Prediction for Back-End Cycle Management Using Two-Step Method. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2021, 53, 2104–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bess, J.D.; Blaise, P.; Buss, O.; DeHart, M.; Fleming, M.; Hill, I.; Ilas, G.; Ivanova, T.; Ivanov, E.; Marshall, W.J.; et al. Engagement Opportunities in OECD NEA Benchmark Development. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1085764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilas, G.; Gauld, I.; Ortego, P.; Tsuda, S. Sfcompo Database of Spent Nuclear Fuel Assay Data—The Next Frontier. EPJ Web Conf. 2021, 247, 10019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, C.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Li, F. Mechanism Analysis of the Contribution of Nuclear Data to the Keff Uncertainty in the Pebble Bed HTR. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2018, 120, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecchia, M.; Vasiliev, A.; Ferroukhi, H.; Pautz, A. Criticality Safety Evaluation of a Swiss Wet Storage Pool Using a Global Uncertainty Analysis Methodology. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2015, 83, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauld, I.C.; Mertyurek, U. Validation of BWR Spent Nuclear Fuel Isotopic Predictions with Applications to Burnup Credit. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2019, 345, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Park, K.; Choi, W.; Hong, S.G. An Efficient Evaluation of Depletion Uncertainty for a GBC-32 Dry Storage Cask with PLUS7 Fuel Assemblies Using the Monte Carlo Uncertainty Sampling Method. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2017, 110, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, Z.; She, D.; Xu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, J.; Sun, J.; Fan, X.; Yu, G. RMC—A Monte Carlo Code for Reactor Core Analysis. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2015, 82, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciff, D.; D’agostino, R.B. Practical Engineering Statistics; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).