Hydrodynamics of Energy-Efficient Axial-Flow Cyclones for Environmentally Safe Cleaning of Gas and Dust Emissions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis and Methods
2.1. Gas Flow
2.2. Two-Phase Flow
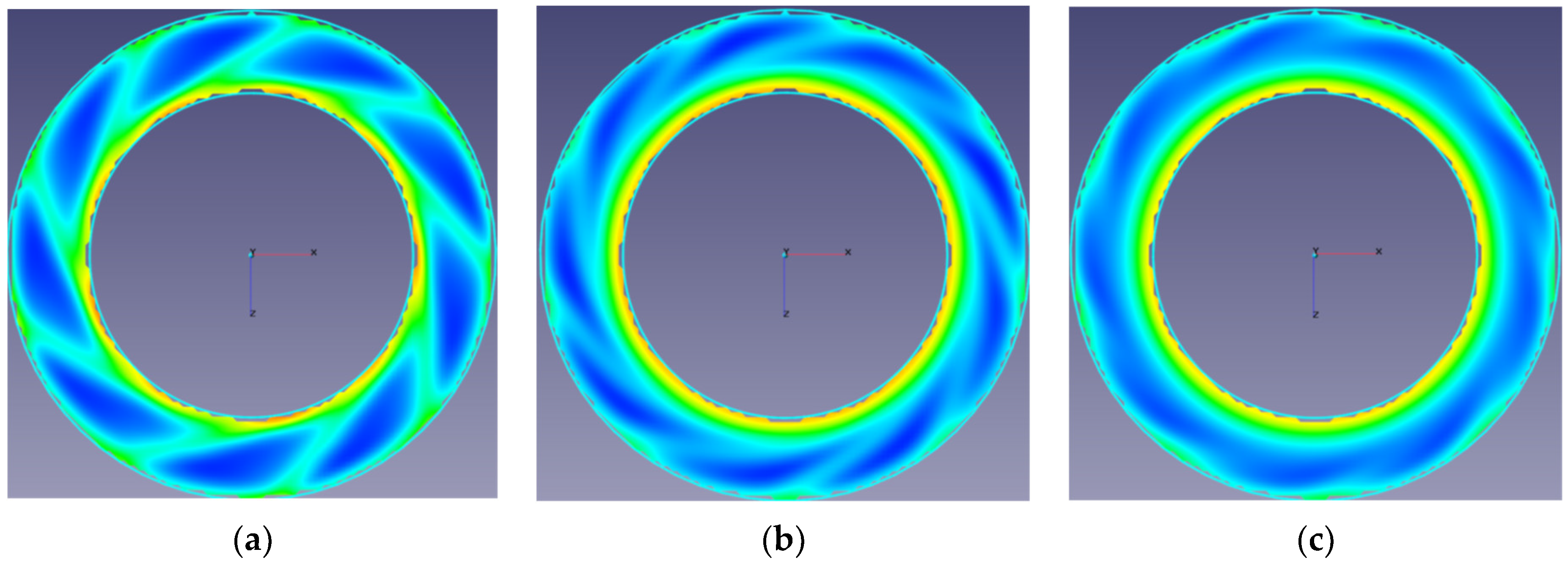
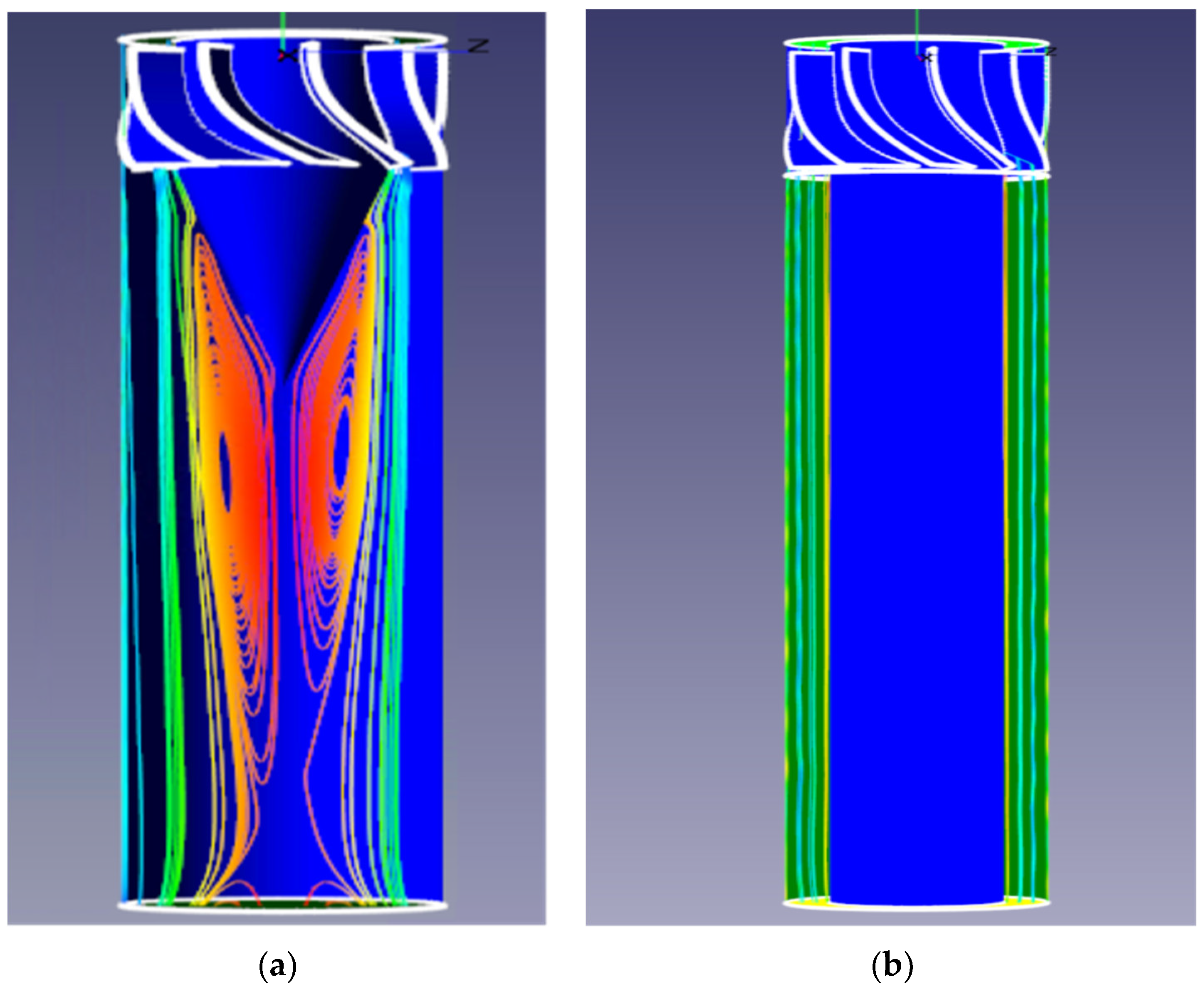
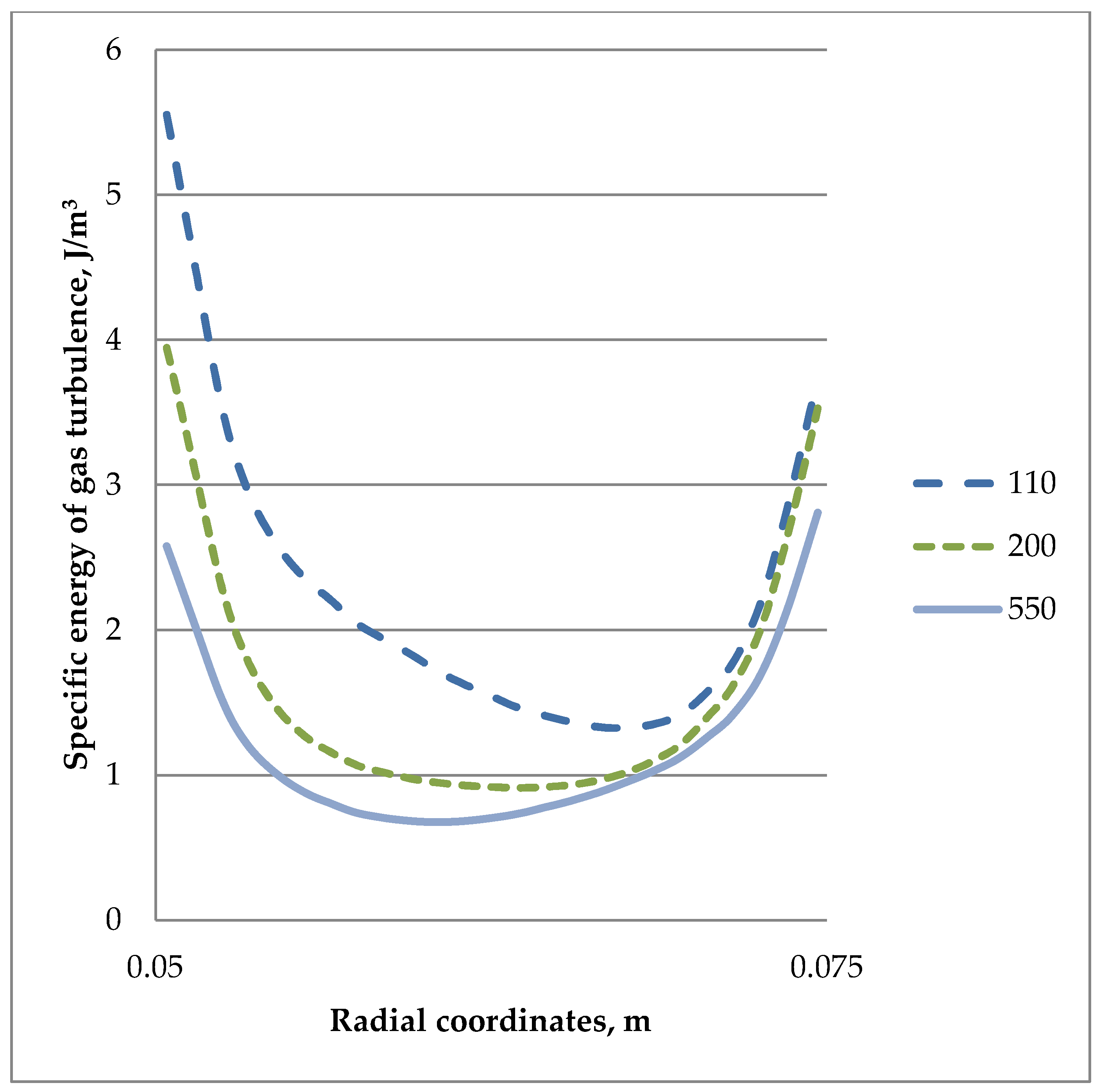
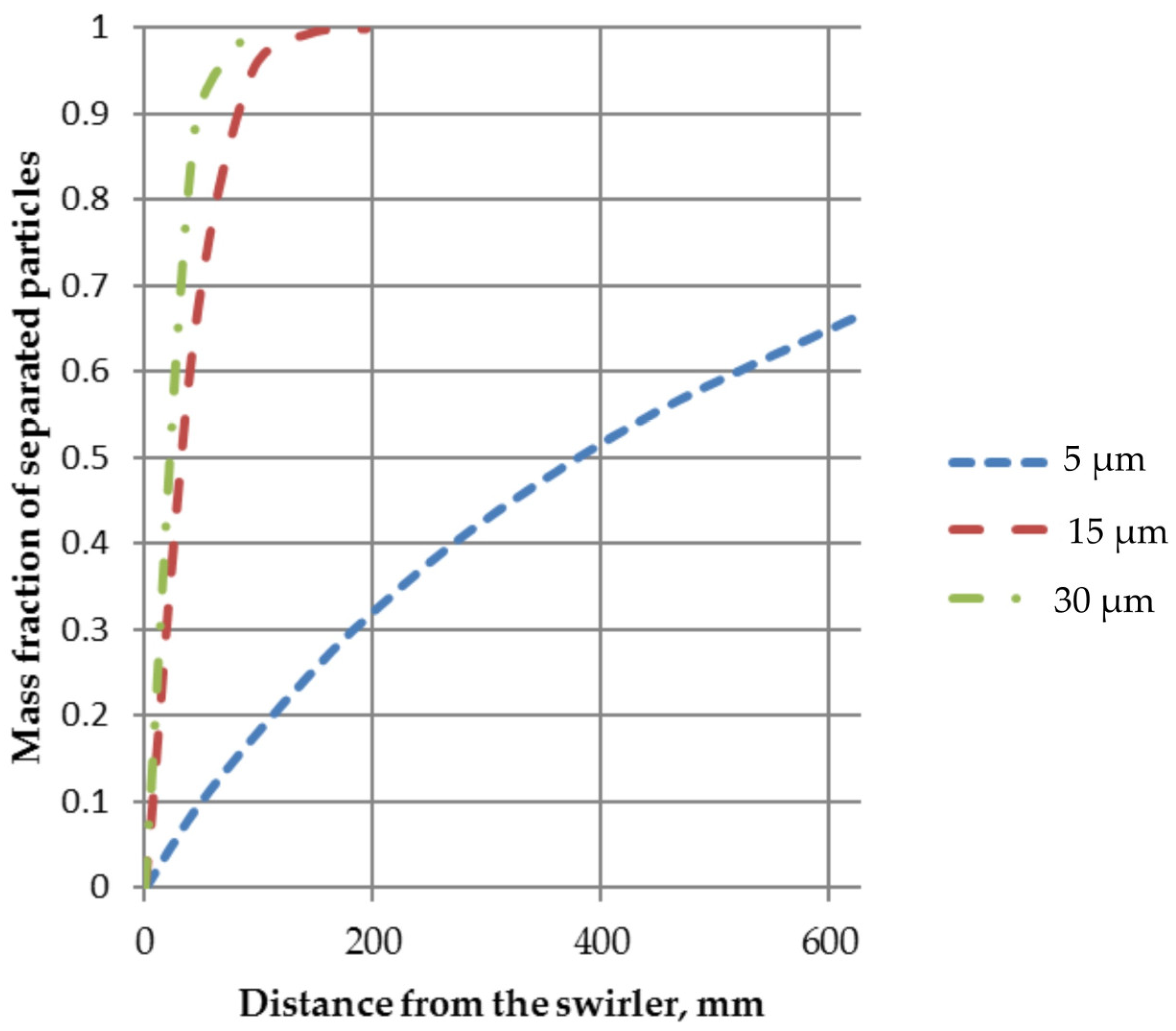
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cortés, C.; Gil, A. Modeling the gas and particle flow inside cyclone separators. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2007, 33, 409–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y. Performance evaluation of a new cyclone separator—Part I experimental results. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 141, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y. Performance evaluation of a new cyclone separator—Part II simulation results. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 160, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehteram, M.A.; Tabrizi, H.B.; Mesbah, M.; Ahmadi, G.; Mirsalim, M.A. Experimental study on the effect of connecting ducts on demisting cyclone efficiency. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2012, 39, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hreiz, R.; Gentric, C.; Midoux, N.; Lainé, R.; Fünfschilling, D. Hydrodynamics and velocity measurements in gas–liquid swirling flows in cylindrical cyclones. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2014, 92, 2231–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, K.; Lacor, C. The effect of cyclone inlet dimensions on the flow pattern and performance. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 1952–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, W.B.; Shaw, B.W. Efficiency and pressure drop of cyclones across a range of inlet velocities. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2006, 22, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misyulya, D.I.; Kuzmin, V.V.; Markov, V.A. Comparative analysis of the technical characteristics for cyclone dust collectors. Sci. Work. DSTU Chem. Technol. Inorg. Subst. 2012, 3, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- Toptalov, V.S.; Martsulevich, N.A.; Flisyuk, O.M. Purification of smoke and process gases in direct-flow cyclones. Her. SPSTU 2021, 56, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toptalov, V.S.; Martsulevich, N.A.; Flisyuk, O.M. Dusty gas movement in separating chamber of direct-flow cyclone. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference “Actual Scientific & Technical Issues of Chemical Safety” ASTICS-2020, Kazan, Russia, 6–8 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Deng, S.; Chen, Z.; Guan, J.; Chen, M. Numerical analysis of a novel gas-liquid pre-separation cyclone. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 194, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boysan, F.; Ayers, W.; Swithenbank, J. A fundamental mathematical modelling approach to cyclone design. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1982, 60, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, A.J.; Derksen, J.J.; Van den Akker, H.E.A. An experimental and numerical study of turbulent swirling flow in gas cyclones. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 2055–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, J.J.; Van den Akker, H.E.A. Simulation of vortex core precession in a reverse-flow cyclone. AIChE J. 2000, 46, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, J.J. Separation performance predictions of a Stairmand high-efficiency cyclone. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, K.; Lacor, C. The effect of the dust outlet geometry on the performance and hydrodynamics of gas cyclones. Comput. Fluids 2012, 68, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Wang, B.; Xu, D.; Chen, Y.; Yu, A. CFD–DEM simulation of the gas–solid flow in a cyclone separator. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 834–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winfield, D.; Cross, M.; Croft, N.; Paddison, D.; Craig, I. Performance comparison of a single and triple tangential inlet gas separation cyclone: A CFD Study. Powder Technol. 2013, 235, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassaj, O.R.; Toghraie, D.; Afrand, M. Effects of multi inlet guide channels on the performance of a cyclone separator. Powder Technol. 2019, 356, 353–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, J.; Mao, Y. Effects of different inlet structures on the flow field of cyclone separators. Powder Technol. 2020, 372, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Mao, Y.; Wei, Y. Analysis of the effect of vortex on the flow field of a cylindrical cyclone separator. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestrin, E.; Decker, R.; Noriler, D.; Bastos, J.; Meier, H. An alternative for the collection of small particles in cyclones: Experimental analysis and CFD modeling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 184, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaei, M.; Lu, B.; Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Wu, H. CFD Modeling of Gas–Solid Cyclone Separators at Ambient and Elevated Temperatures. Processes 2019, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Huang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, H.; Lyu, J. Effects of the inlet duct length on the flow field and performance of a cyclone separator with a contracted inlet duct. Powder Technol. 2021, 393, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.-W.; Liu, Z.-X.; Wei, Y.-D.; Li, C.-X.; Wang, S.-H.; Qi, X.-Y.; Huang, W. Numerical analysis on the influence of vortex motion in a reverse Stairmand cyclone separator by using LES model. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celis, G.E.; Loureiro, J.B.; Lage, P.L.; Freire, A.P.S. The effects of swirl vanes and a vortex stabilizer on the dynamic flow field in a cyclonic separator. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 248, 117099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Wang, H.-L. Simulation and experimental study of effect of vortex finder structural parameters on cyclone separator performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnokov, Y.G.; Likhachev, I.G.; Flisyuk, O.M.; Martsulevich, N.A.; Meshalkin, V.P.; Garabadzhiu, A.V. Calculation of flow hydrodynamics in reverse-flow cyclones using the flow vision applied software package. Russ. Chem. J. 2022, 66, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Kondoh, T.; Nagano, Y. A new turbulence model for predicting fluid flow and heat transfer in separating and reattaching flows-II. thermal field calculation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1995, 38, 1467–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglietto, E.; Ninokata, H. Improved Turbulence Modeling for Performance Evaluation of Novel Fuel Designs. Nucl. Technol. 2007, 158, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglietto, E.; Ninokata, H. Anisotropic eddy viscosity modeling for application to industrial engineering internal flows. Int. J. Transp. Phenom. 2006, 8, 85–101. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke, M. Album of Fluid Motion; Parabolic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Rotta, I.K. Turbulent Boundary Layer in Incompressible Fluid; Sudostroenie Publishers: Leningrad, Russia, 1967. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shlikhting, G. Theory of Boundary Layer; Nauka Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 1974. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nigmatulin, R.I. Dynamics of Multiphase Substances; Nauka Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 1987. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Martsulevich, N.A. Chaotic particle movement in a turbulent gas stream. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 1987, 61, 362–367. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Martsulevich, N.A.; Protodyakonov, I.O. Chaotic phase flow in gas-solids stream. J. Appl. Chem. 1984, 57, 947–950. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meshalkin, V.P.; Martsulevich, N.A.; Flisyuk, O.M.; Likhachev, I.G.; Nzioka, A.M. Hydrodynamics of Energy-Efficient Axial-Flow Cyclones for Environmentally Safe Cleaning of Gas and Dust Emissions. Energies 2023, 16, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020816
Meshalkin VP, Martsulevich NA, Flisyuk OM, Likhachev IG, Nzioka AM. Hydrodynamics of Energy-Efficient Axial-Flow Cyclones for Environmentally Safe Cleaning of Gas and Dust Emissions. Energies. 2023; 16(2):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020816
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeshalkin, Valery P., Nicolay A. Martsulevich, Oleg M. Flisyuk, Ilia G. Likhachev, and Antony M. Nzioka. 2023. "Hydrodynamics of Energy-Efficient Axial-Flow Cyclones for Environmentally Safe Cleaning of Gas and Dust Emissions" Energies 16, no. 2: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020816
APA StyleMeshalkin, V. P., Martsulevich, N. A., Flisyuk, O. M., Likhachev, I. G., & Nzioka, A. M. (2023). Hydrodynamics of Energy-Efficient Axial-Flow Cyclones for Environmentally Safe Cleaning of Gas and Dust Emissions. Energies, 16(2), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020816







