A Binary Archimedes Optimization Algorithm and Weighted Sum Method for UFLS in Islanded Distribution Systems Considering the Stability Index and Load Priority
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The proposed binary technique in the AOA selects the best load shed based on the minimum stability index and power mismatch.
- The proposed UFLS scheme employs a WSM to rank the load shed based on load priority, load category, stability index, and load size.
- The proposed UFLS scheme improves the frequency response, increases the voltage stability, and reduces the load shed by considering the power reserve of the mini hydro DG.
2. Load Priority Using Binary AOA
2.1. Binary AOA
- Step 1: Initialization
- Step 2: Updating density and volume
- Step 3: Updating acceleration
- Step 4: Updating position
2.2. Proposed Fitness Function
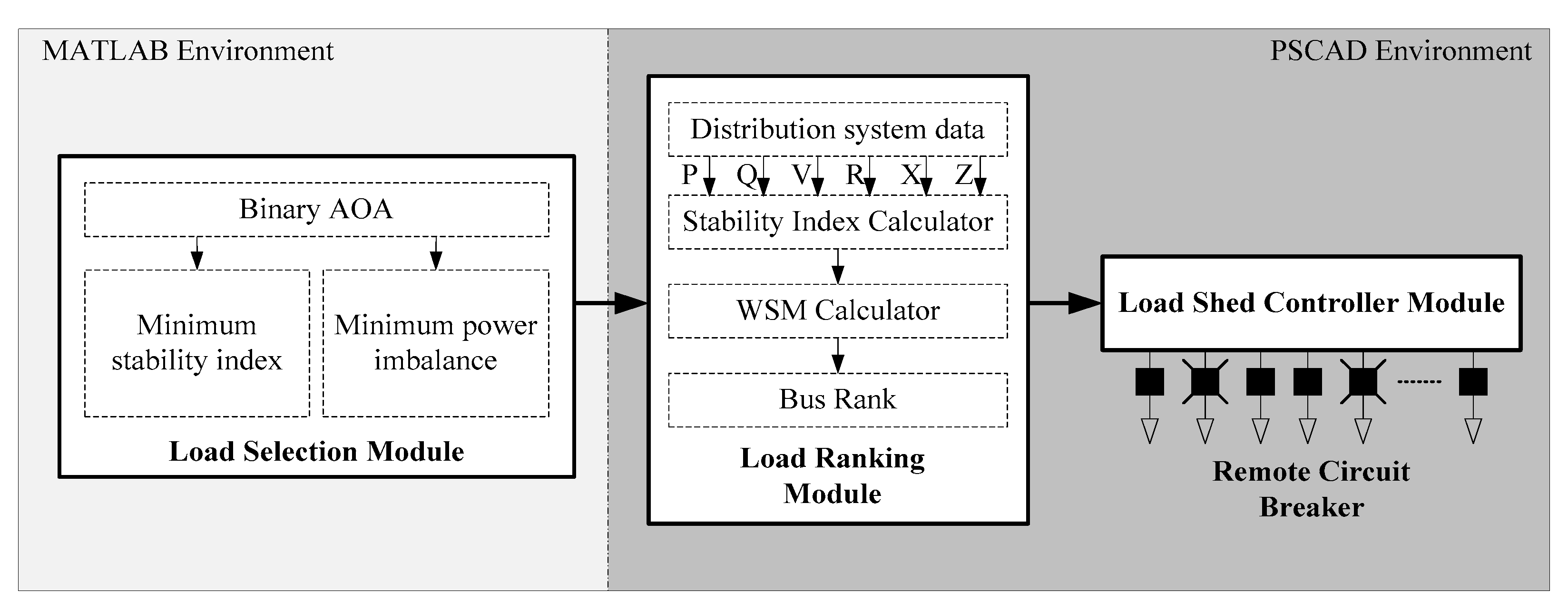
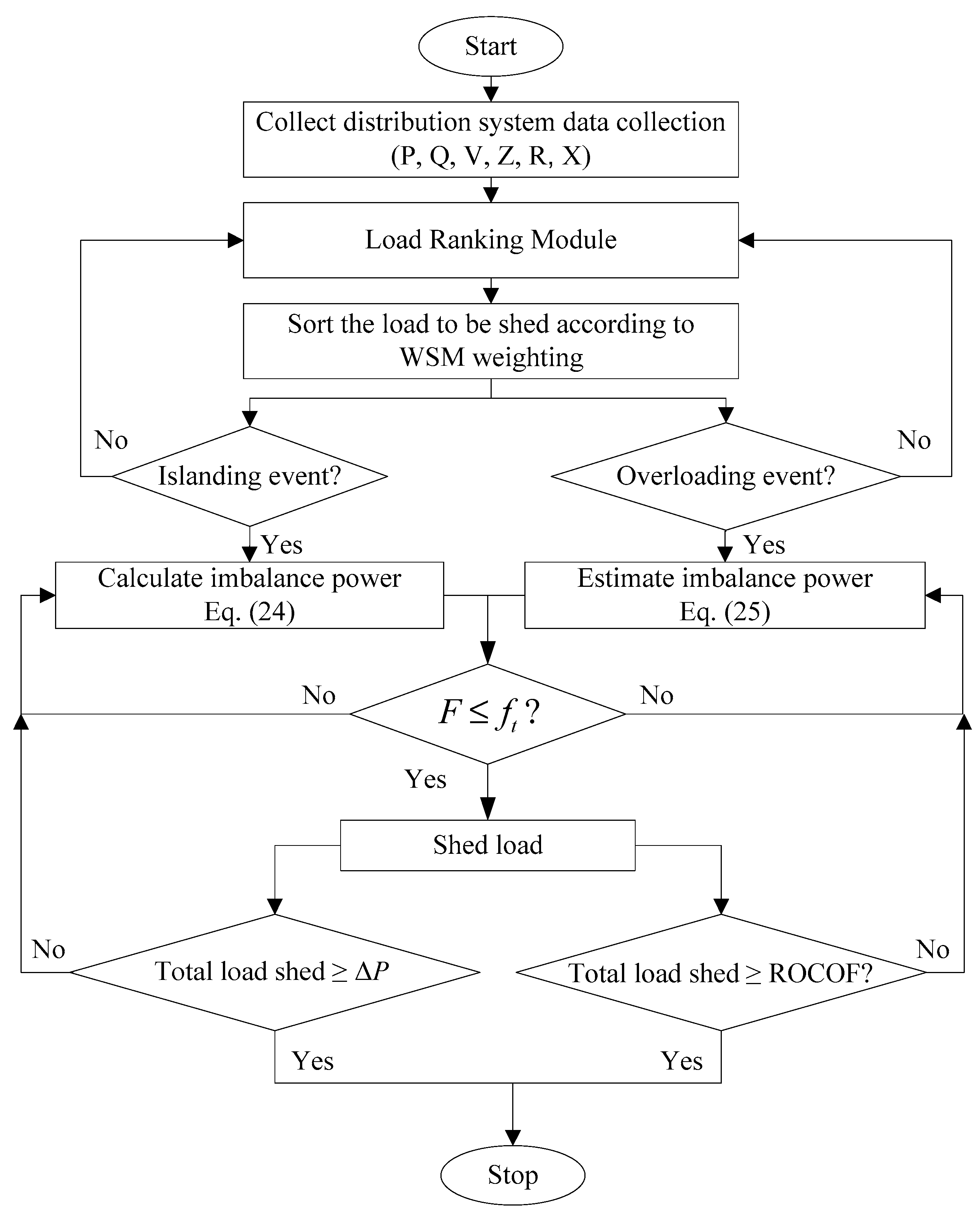
3. The Proposed UFLS Using BAOA and WSM
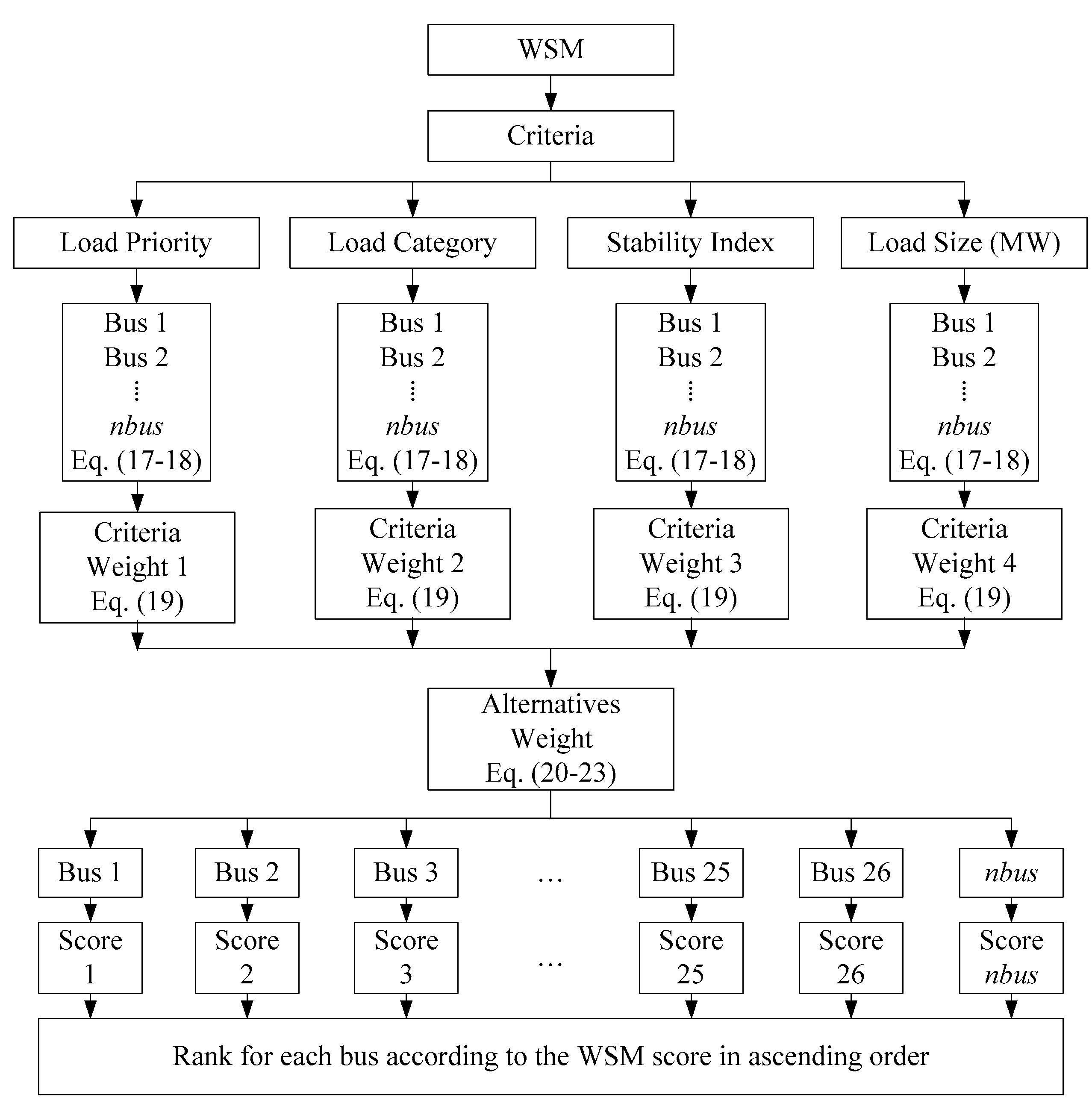
3.1. The Weighted Sum Menthod (WSM) in the Load Ranking Module (LRM)
3.1.1. Criteria Weights Using the Entropy Method
- The arrays of the decision matrix (criteria for each load) are normalized to obtain the common scale values for the elements of the different criteria, as shown in (17).
- 2.
- The entropy of the normalized elements in the decision matrix is computed as in (18).
- 3.
- The weighting of each criterion is defined based on the entropy method as in (19).
3.1.2. Alternative Weights Using the WSM
- Identify the criteria as either beneficial or nonbeneficial to determine whether maximum or minimum values are required. The decision matrix is normalized according to the beneficial and nonbeneficial criteria, as shown in (20) and (21), respectively.
- 2.
- Convert to the weighted normalized decision matrix by multiplying both beneficial and nonbeneficial elements of the decision matrix by each criterion’s weight and summing the elements of all criteria for each alternative. The rank of each load to be shed is obtained from the score for each alternative, Aij, as shown in (22) and (23).
3.2. Load-Shed Controller Module (LSCM)
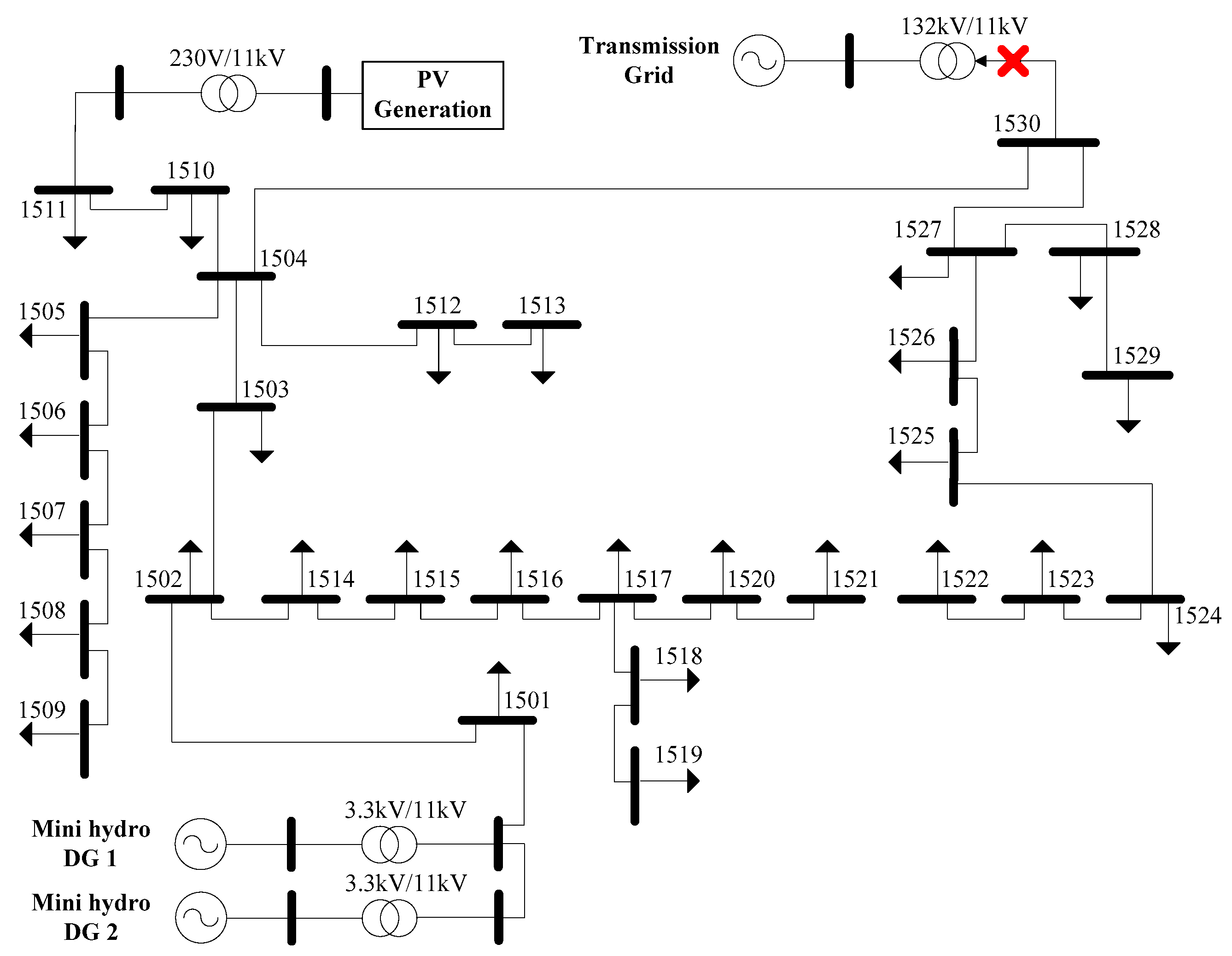
4. Test-System Modeling
5. Results and Discussion
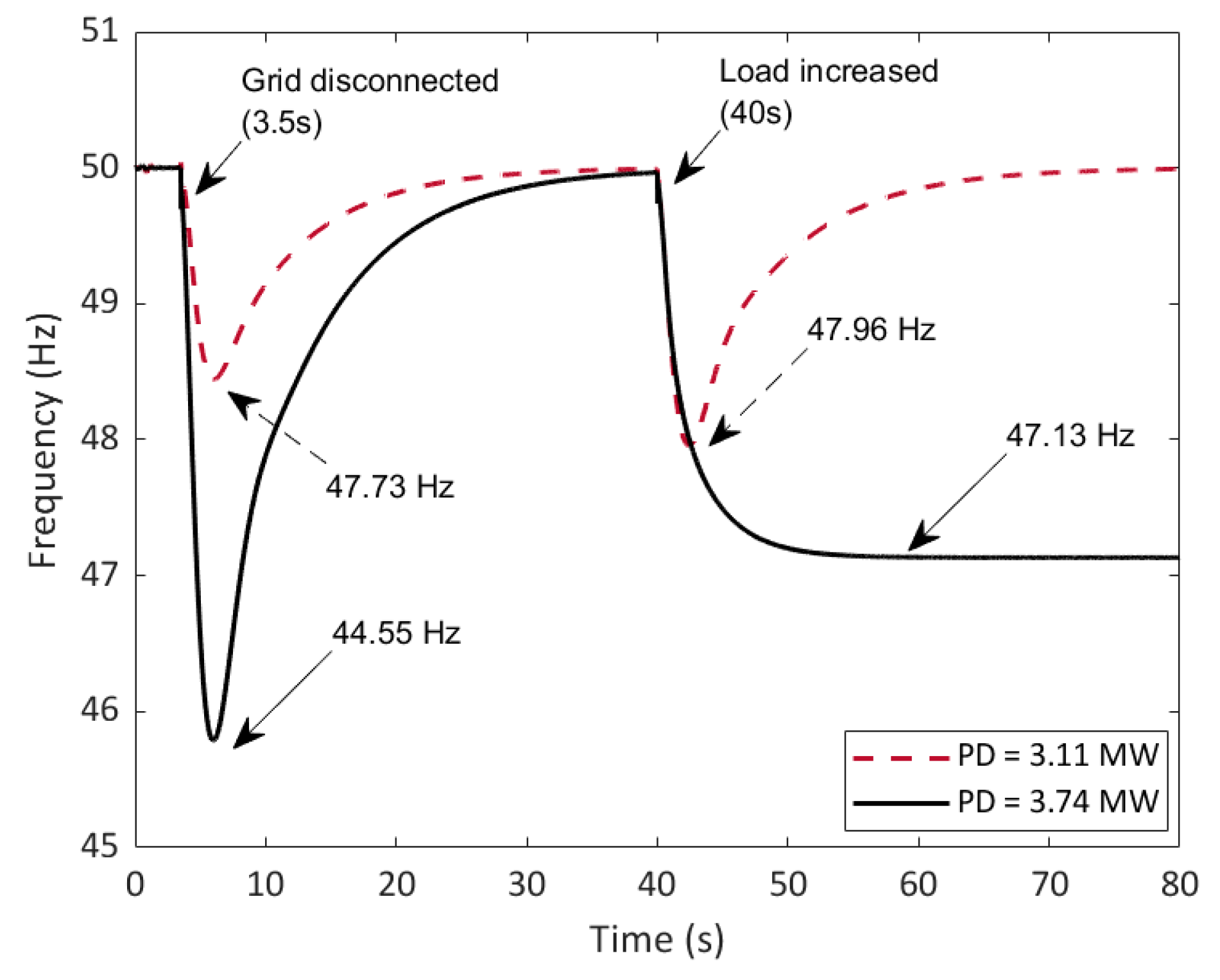
5.1. Frequency Response without UFLS
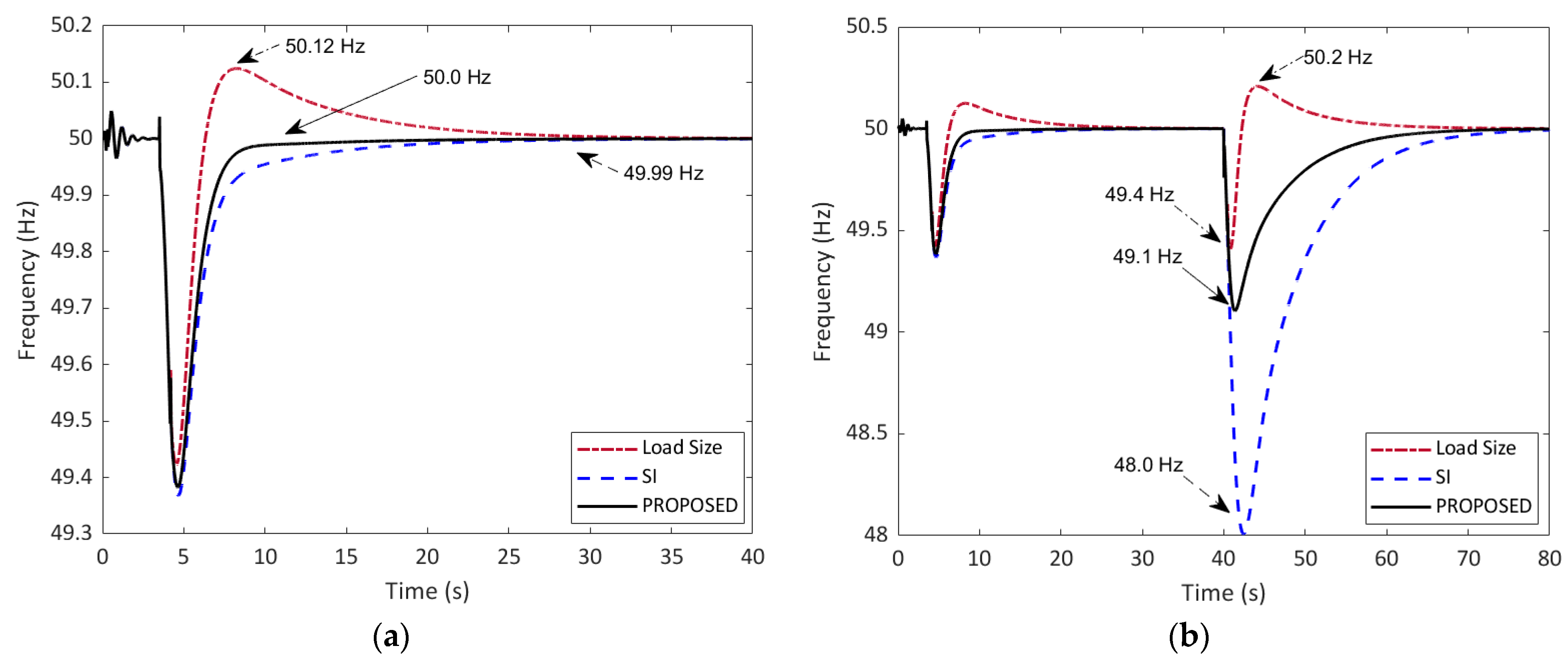
5.2. Frequency Response with UFLS Using Individual Stability Index and Load Size
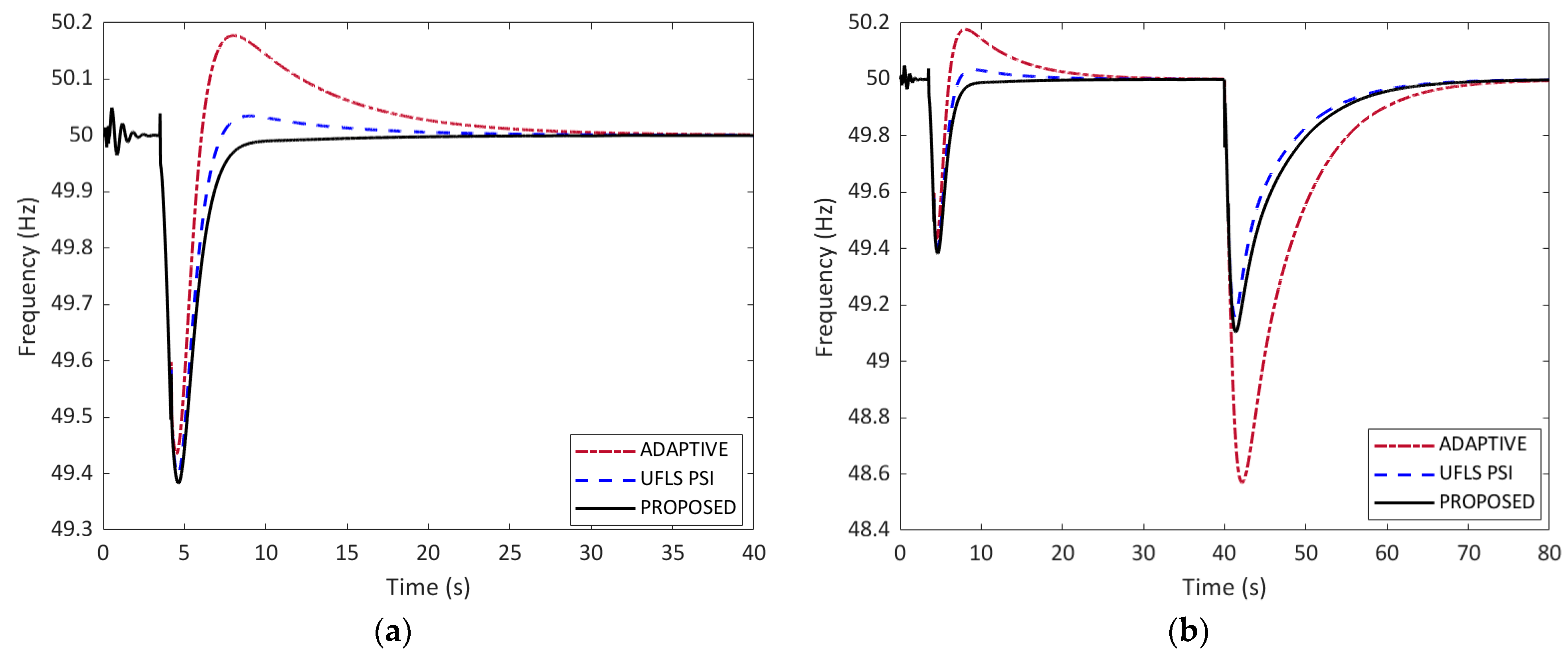
5.3. Comparison of the Frequency Responses and Load Shedding for Case 1
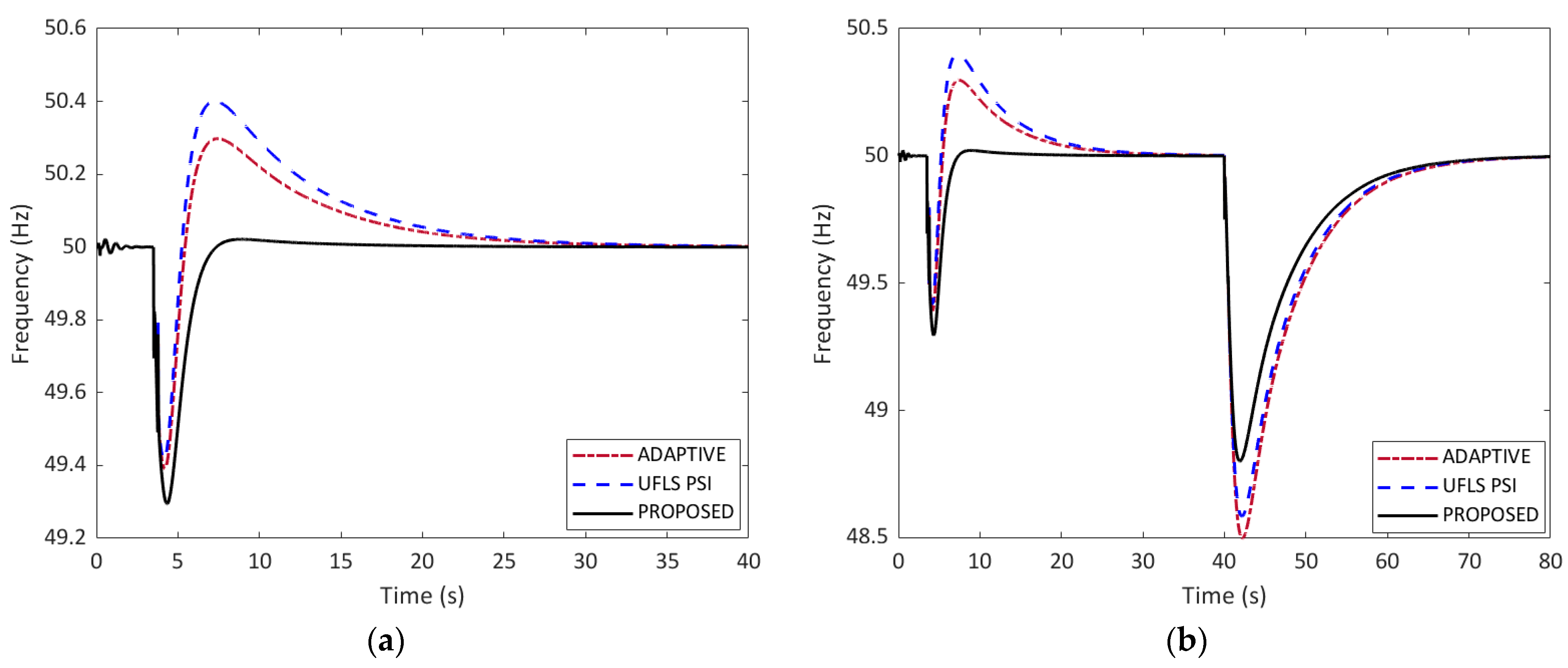
5.4. Comparison of the Frequency Responses and Load Shedding for Case 2
5.5. Comparison of the Frequency Responses and Load Shedding for Case 3
5.6. Voltage Profile and Stability Index of The Proposed UFLS
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UFLS | Under-Frequency Load Shedding |
| AOA | Archimedes Optimization Algorithm |
| BAOA | Binary Archimedes Optimization Algorithm |
| WSM | Weighted Sum Method |
| DG | Distributed Generation |
| ROCOF | Rate of Change of Frequency |
| LSM | Load-Selection Module |
| LRM | Load-Ranking Module |
| LSCM | Load-Shed Controller Module |
| RCB | Remote Circuit Breaker |
| SI | Stability Index |
| SIC | Stability Index Calculator |
| PSI | Power Stability Index |
Appendix A
| Nonvital (Bus) | |||||||||||||||
| Rank | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | ||||
| Case 1 | 1525 | 1522 | 1526 | 1510 | 1511 | 1515 | 1518 | 1503 | 1502 | 1519 | 1506 | ||||
| (Score) | (0.677) | (0.676) | (0.638) | (0.549) | (0.540) | (0.283) | (0.282) | (0.268) | (0.261) | (0.224) | (0.221) | ||||
| Case 2 | 1525 | 1522 | 1526 | 1510 | 1511 | 1515 | 1518 | 1503 | 1502 | 1519 | 1506 | ||||
| (Score) | (0.546) | (0.545) | (0.521) | (0.486) | (0.480) | (0.320) | (0.319) | (0.310) | (0.306) | (0.282) | (0.280) | ||||
| Case 3 | 1510 | 1511 | 1525 | 1522 | 1526 | 1515 | 1518 | 1503 | 1502 | 1519 | 1506 | ||||
| (Score) | (0.644) | (0.631) | (0.557) | (0.556) | (0.503) | (0.277) | (0.276) | (0.256) | (0.245) | (0.196) | (0.193) | ||||
| Semi-Vital (Bus) | |||||||||||||||
| Rank | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 17 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | ||||
| Case 1 | 1509 | 1514 | 1524 | 1527 | 1513 | 1520 | 1517 | 1507 | 1523 | 1508 | 1505 | ||||
| (Score) | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.089 | ||||
| Case 2 | 1509 | 1514 | 1524 | 1513 | 1520 | 1517 | 1507 | 1523 | 1527 | 1508 | 1505 | ||||
| (Score) | (0.130) | (0.130) | (0.130) | (0.130) | (0.130) | (0.130) | (0.130) | (0.130) | (0.130) | (0.130) | (0.130) | ||||
| Case 3 | 1509 | 1514 | 1524 | 1527 | 1513 | 1520 | 1517 | 1507 | 1523 | 1508 | 1505 | ||||
| (Score) | (0.069) | (0.069) | (0.069) | (0.069) | (0.069) | (0.069) | (0.069) | (0.069) | (0.069) | (0.069) | (0.069) | ||||
| Vital (Bus) | |||||||||||||||
| Rank | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | ||||||||||
| Case 1 | 1516 | 1529 | 1528 | 1521 | 1501 | ||||||||||
| (Score) | (0.059) | (0.059) | (0.059) | (0.059) | (0.059) | ||||||||||
| Case 2 | 1516 | 1529 | 1528 | 1521 | 1501 | ||||||||||
| (Score) | (0.087) | (0.087) | (0.087) | (0.087) | (0.087) | ||||||||||
| Case 3 | 1516 | 1529 | 1528 | 1521 | 1501 | ||||||||||
| (Score) | (0.046) | (0.046) | (0.046) | (0.046) | (0.046) | ||||||||||
References
- Tenaga, S. A Malaysia Energy Statistics Handbook 2020; Energy Commission: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2020.
- Authority Malaysia, S.E.D. Malaysia Renewable Energy Roadmap; SEDA: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, F.; Arumugam, R.; Vaziri, M.Y. Unintentional islanding and comparison of prevention techniques. In Proceedings of the 37th Annual North American Power Symposium, Ames, IA, USA, 25 October 2005; pp. 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Laghari, J.; Mokhlis, H.; Karimi, M.; Bakar, A.; Mohamad, H. Computational Intelligence based techniques for islanding detection of distributed generation in distribution network: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 88, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, L.; Rouco, L.; Echavarren, F.M. A review of the state of the art of UFLS schemes for isolated power systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2018, 99, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Mohamad, H.; Mokhlis, H.; Bakar, A. Under-frequency load shedding scheme for islanded distribution network connected with mini hydro. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2012, 42, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedi, H.; Sanaye-Pasand, M. New centralised adaptive load-shedding algorithms to mitigate power system blackouts. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2009, 3, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzija, V. Adaptive Underfrequency load shedding based on the magnitude of the disturbance estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2006, 21, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhelou, H.H.; Golshan, M.E.H.; Njenda, T.C.; Hatziargyriou, N.D. An overview of UFLS in conventional, modern, and future smart power systems: Challenges and opportunities. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2020, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapari, N.M.; Mokhlis, H.; Abu Bakar, A.H.; Mohamad, H.; Laghari, J.A.; Dahalan, M.R.M. Load shedding scheme based on rate of change of frequency and ranked stability index for islanded distribution system connected to mini hydro. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2017, 12, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Liu, G.; Popov, M.; Terzija, V.; Azizi, S. Underfrequency load shedding using locally estimated RoCof of the center of inertia. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2021, 36, 4212–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallad, J.; Mekhilef, S.; Mokhlis, H.; Laghari, J.; Badran, O. Application of hybrid meta-heuristic techniques for optimal load shedding planning and operation in an islanded distribution network integrated with distributed generation. Energies 2018, 11, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarwar, S.; Mokhlis, H.; Othman, M.; Shareef, H.; Wang, L.; Mansor, N.N.; Khairuddin, A.S.M.; Mohamad, H. Application of polynomial regression and MILP for under-frequency load shedding scheme in islanded distribution system. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 659–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.A.; Rosli, H.M.; Mokhlis, H.; Karimi, M.; Selvaraj, J.; Sapari, N.M. A new under-voltage load shedding scheme for islanded distribution system based on voltage stability indices. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2017, 12, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larik, R.M.; Mustafa, M.W.; Aman, M.N.; Jumani, T.A.; Sajid, S.; Panjwani, M.K. An improved algorithm for optimal load shedding in power systems. Energies 2018, 11, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Małkowski, R.; Nieznański, J. Underfrequency load shedding: An innovative algorithm based on fuzzy logic. Energies 2020, 13, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talaat, M.; Hatata, A.; Alsayyari, A.S.; Alblawi, A. A smart load management system based on the grasshopper optimization algorithm using the under-frequency load shedding approach. Energy 2020, 190, 116423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, H.M.; Mokhlis, H.; Mansor, N.N.; Sapari, N.; Halim, S.A. A Modified DEP and AHP for Load Shedding Scheme of Islanded Distribution System Incorporating Stability Index. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2022, 17, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, F.A.; Hussain, K.; Houssein, E.H.; Mabrouk, M.S.; Al-Atabany, W. Archimedes optimization algorithm: A new metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems. Appl. Intell. 2021, 51, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R.C. A discrete binary version of the particle swarm algorithm. In Proceedings of the Computational Cybernetics and Simulation 1997 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–15 October 1997; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Eminoglu, U.; Hocaoglu, M.H. A voltage stability index for radial distribution networks. In Proceedings of the 42nd International Universities Power Engineering Conference, Brighton, UK, 4–6 September 2007; pp. 408–413. [Google Scholar]
- Berhad, T.N. Electricity Supply Application Handbook, 2nd ed.; Tenaga Nasional Berhad: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Terzija, V.; Koglin, H.J. Adaptive underfrequency load shedding integrated with a frequency estimation numerical algorithm. IEE Proc. Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2002, 149, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bus | Load Priority | Load Category | Stability Index | Load Size (MW) | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SI1 | Load1 | W1 | ||
| SIith | Loadith | With | |||
| 11 | SI11 | Load11 | W11 | ||
| 12 | SI12 | Load12 | W12 | ||
| SIith | Loadith | With | |||
| 23 | SI23 | Load23 | W23 | ||
| SIith | Loadith | With | |||
| nbus | SInbus | Loadnbus | Wnbus |
| Category | Loads Connected (Buses) |
|---|---|
| Nonvital | 1502, 1503, 1506, 1510, 1511, 1515, 1518, 1519, 1522, 1525, 1526 |
| Semi-vital | 1505, 1507, 1508, 1509, 1513, 1514, 1517, 1520, 1523, 1524, 1527 |
| Vital | 1501,1516, 1521, 1528, 1529 |
| Case Study | Generation | Total Demand |
|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 2 mini hydros | 3.11 MW |
| Case 2 | 2 mini hydros | 3.74 MW |
| Case 3 | 2 mini hydros and PV generation | 3.74 MW |
| Islanding Event | Main utility grid is disconnected at 3.5 s after normal operation is stabilized |
| Overloading Event | Sudden overloading occurs subsequently, after 40 s |
| Results | Adaptive UFLS | UFLS Using PSI | Proposed UFLS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loads shed (buses) | Nonvital: 1502, 1503, 1511, 1510, 1515, 1518, 1522, 1525 (8 buses) | Nonvital: 1502, 1511, 1510, 1518, 1519, 1525 (6 buses) | Nonvital: 1510, 1522, 1525, 1526 (4 buses) |
| Load shed size | 0.517 MW | 0.399 MW | 0.329 MW |
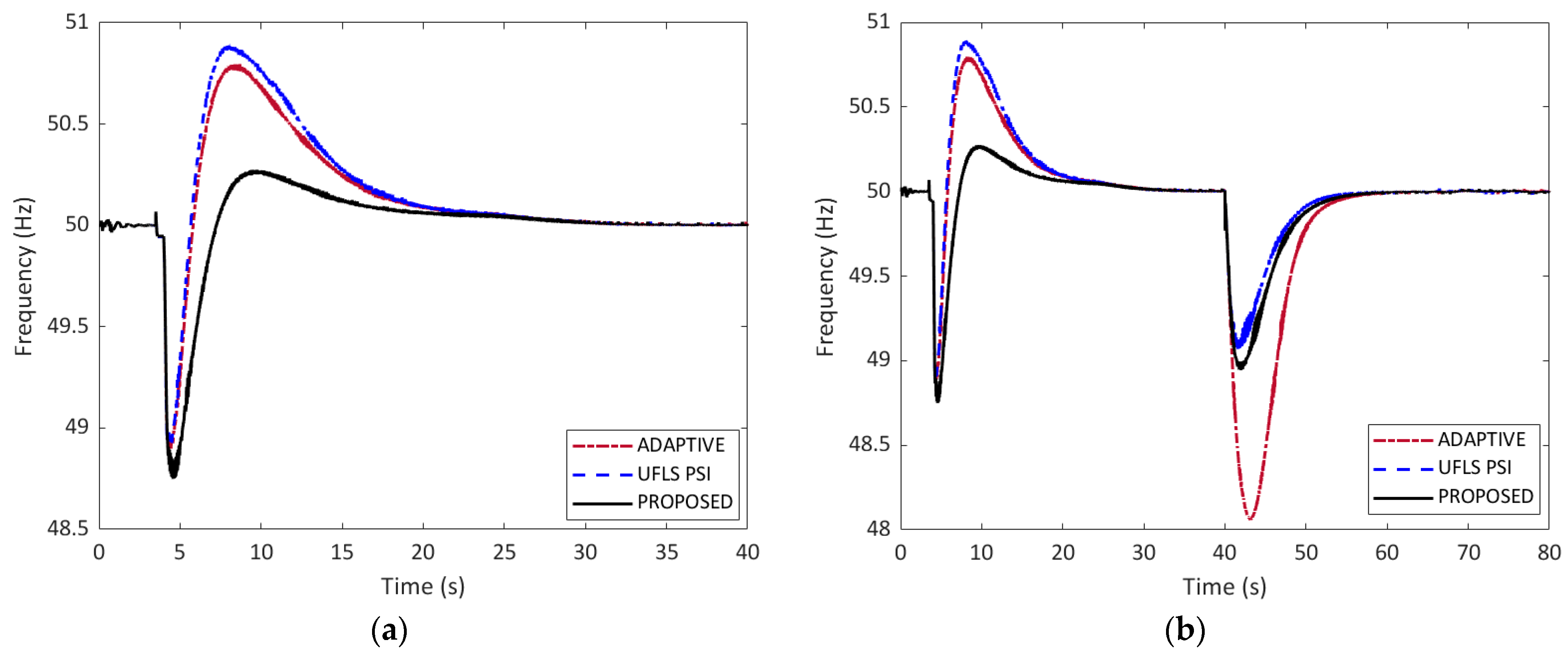
| Frequency undershoot | 49.43 Hz | 49.39 Hz | 49.38 Hz |
| Frequency overshoot | 50.18 Hz | 50.03 Hz | 50.00 Hz |
| Time to reach 50.0 Hz | 30.50 s | 25.23 s | 16.47 s |
| Results | Adaptive UFLS | UFLS Using PSI | Proposed UFLS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loads shed (buses) | Nonvital:1502, 1503, 1511, 1510, 1515, 1518, 1519, 1522, 1525 (9 buses) | Nonvital:1502, 1506, 1511, 1510, 1518, 1519, 1525, 1526 (8 buses) | Nonvital: 1506, 1511, 1510, 1519, 1522, 1525, 1526 (7 buses) |
| Load shed size | 0.467 MW | 0.453 MW | 0.437 MW |
| Frequency undershoot | 48.57 Hz | 49.16 Hz | 49.13 Hz |
| Frequency overshoot | 50.00 Hz | 50.00 Hz | 50.00 Hz |
| Time to reach 50.0 Hz | 73.57 s | 67.58 s | 68.03 s |
| Results | Adaptive UFLS | UFLS Using PSI | Proposed UFLS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loads shed (buses) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1509, 1514, 1524 (3 buses) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1505 (1 bus) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1509, 1514 (2 buses) |
| Load shed size | 1.079 MW | 1.126 MW | 0.969 MW |
| Frequency undershoot | 49.39 Hz | 49.42 Hz | 49.29 Hz |
| Frequency overshoot | 50.29 Hz | 50.40 Hz | 50.02 Hz |
| Time to reach 50.0 Hz | 29.41 s | 29.93 s | 16.48 s |
| Results | Adaptive UFLS | UFLS Using PSI | Proposed UFLS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loads shed (buses) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1509, 1513, 1514, 1524 (4 buses) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1505, 1507 (2 buses) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1509, 1514, 1520, 1524 (4 buses) |
| Load shed size | 0.588 MW | 0.471 MW | 0.532 MW |
| Frequency undershoot | 48.49 Hz | 48.58 Hz | 48.80 Hz |
| Frequency overshoot | 50.00 Hz | 50.00 Hz | 50.00 Hz |
| Time to reach 50.0 Hz | 74.88 s | 74.08 s | 73.04 s |
| Results | Adaptive UFLS | UFLS Using PSI | Proposed UFLS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loads shed (buses) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1509, 1514, 1524 (3 buses) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1505 (1 bus) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1509 (1 bus) |
| Load shed size | 0.971 MW | 1.026 MW | 0.817 MW |
| Frequency undershoot | 48.89 Hz | 48.91 Hz | 48.75 Hz |
| Frequency overshoot | 50.79 Hz | 50.89 Hz | 50.28 Hz |
| Time to reach 50.0 Hz | 30.15 s | 30.17 s | 30.11 s |
| Results | Adaptive UFLS | UFLS using PSI | Proposed UFLS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loads shed (buses) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1509, 1513, 1514, 1524 (4 buses) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1505, 1507, 1508 (3 buses) | Nonvital: (11 buses) Semi-vital: 1509, 1513, 1527 (3 buses) |
| Load shed size | 0.552 MW | 0.612 MW | 0.699 MW |
| Frequency undershoot | 48.06 Hz | 49.06 Hz | 48.94 Hz |
| Frequency overshoot | 50.02 Hz | 50.02 Hz | 50.02 Hz |
| Time to reach 50.0 Hz | 56.58 s | 56.17 s | 54.93 s |
| Results | Islanding | Overloading | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
| Load shed (bus) | √ | X | √ | √ | X | √ |
| Load shed size | √ | √ | √ | √ | X | X |
| Frequency undershoot | X | X | X | X | √ | X |
| Frequency overshoot | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Time to reach 50.0 Hz | √ | √ | √ | X | √ | √ |
| Islanding | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
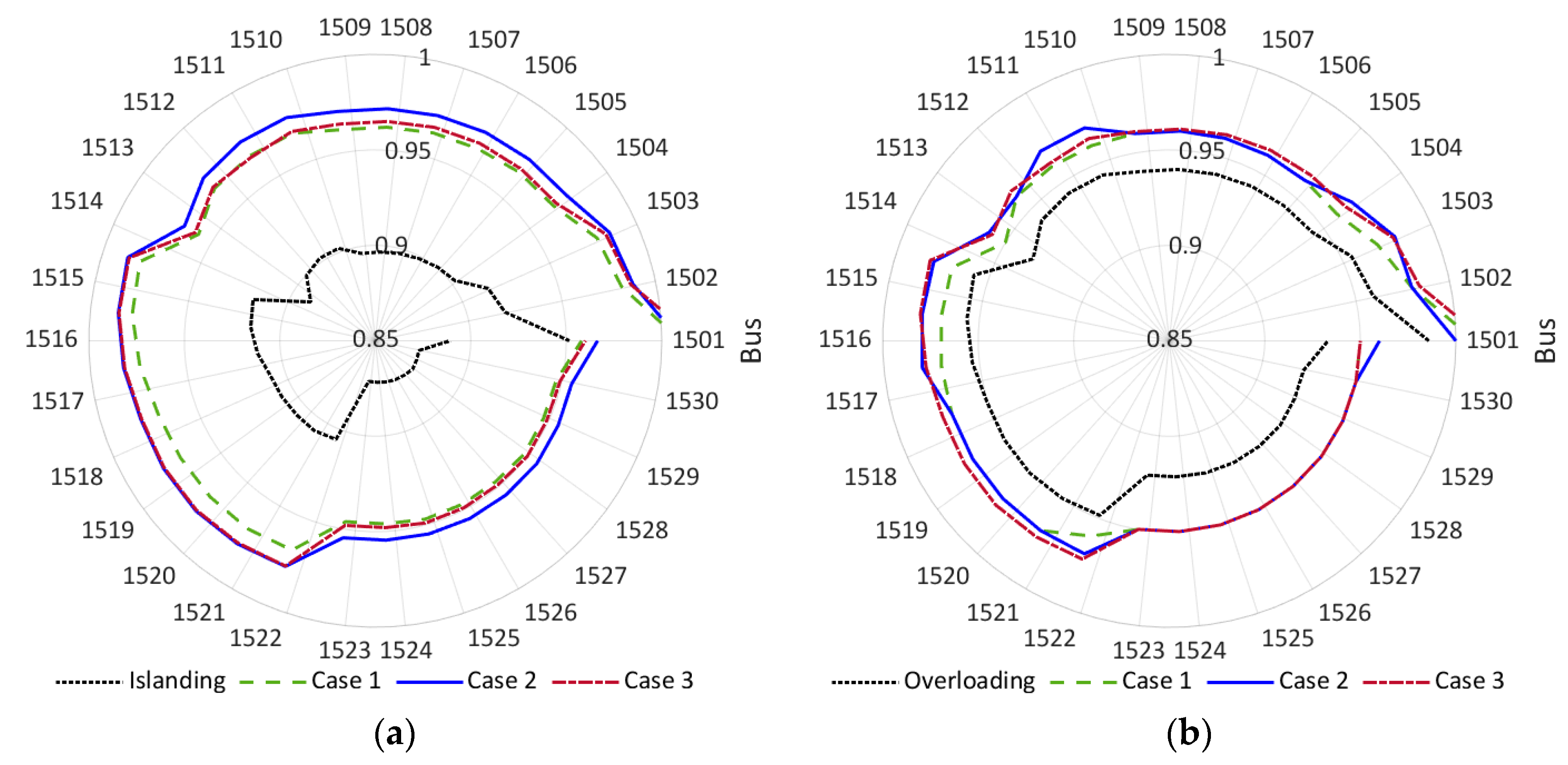
| Minimum Voltage (pu) | 0.87 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| Maximum Voltage (pu) | 0.95 | 1.01 | 1.01 | 1.02 |
| Average Voltage (pu) | 0.89 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| Overloading | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
| Minimum Voltage (pu) | 0.92 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 |
| Maximum Voltage (pu) | 0.98 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.01 |
| Average Voltage (pu) | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| Islanding | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
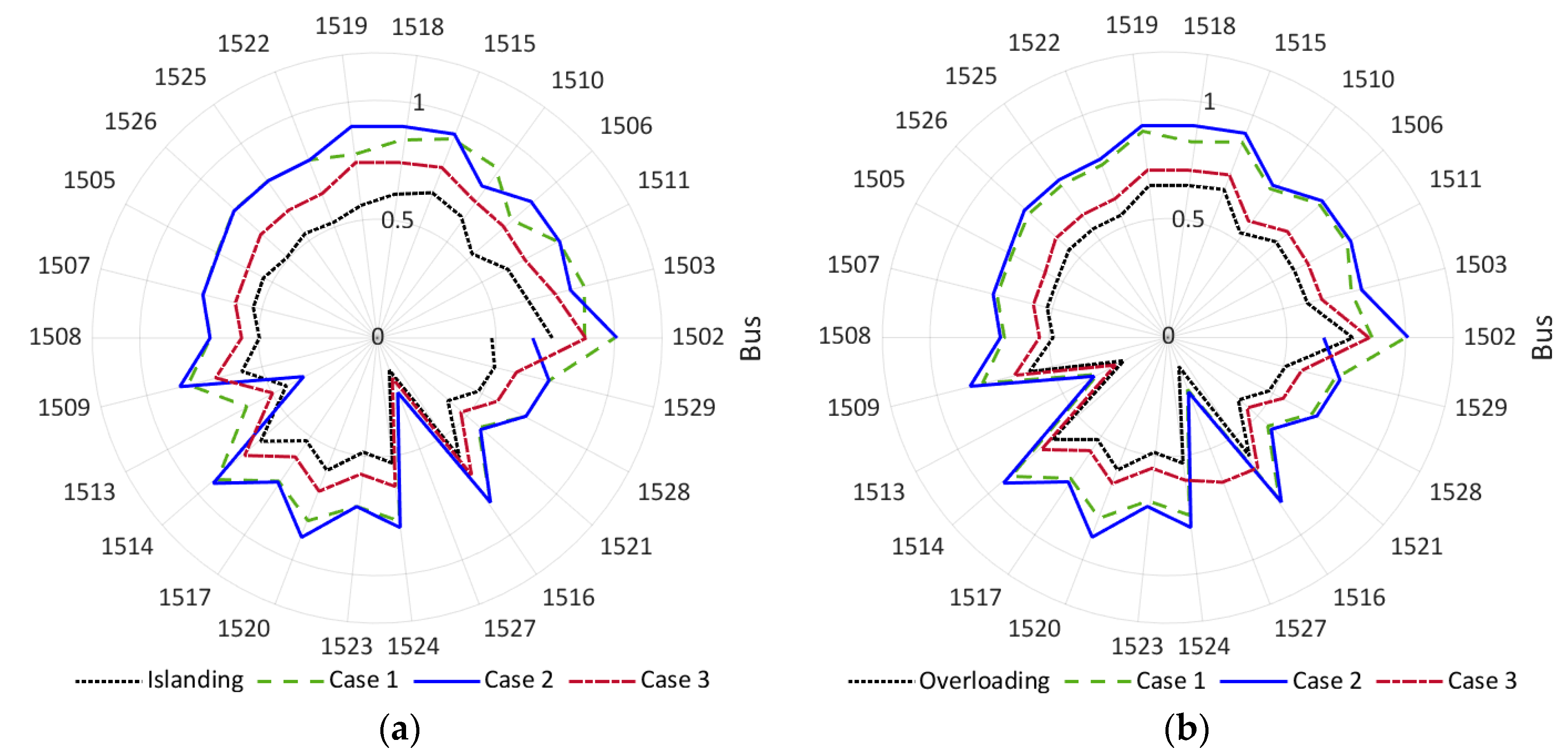
| Minimum Voltage (pu) | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.18 |
| Maximum Voltage (pu) | 0.74 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 0.88 |
| Average Voltage (pu) | 0.54 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.65 |
| Overloading | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | |
| Minimum Voltage (pu) | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.25 |
| Maximum Voltage (pu) | 0.78 | 1.00 | 1.01 | 0.85 |
| Average Voltage (pu) | 0.55 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohd Rosli, H.; Mokhlis, H.; Mansor, N.N.; Md Sapari, N.; Halim, S.A.; Wang, L.; Sulaima, M.F. A Binary Archimedes Optimization Algorithm and Weighted Sum Method for UFLS in Islanded Distribution Systems Considering the Stability Index and Load Priority. Energies 2023, 16, 5144. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135144
Mohd Rosli H, Mokhlis H, Mansor NN, Md Sapari N, Halim SA, Wang L, Sulaima MF. A Binary Archimedes Optimization Algorithm and Weighted Sum Method for UFLS in Islanded Distribution Systems Considering the Stability Index and Load Priority. Energies. 2023; 16(13):5144. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135144
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohd Rosli, Hazwani, Hazlie Mokhlis, Nurulafiqah Nadzirah Mansor, Norazliani Md Sapari, Syahirah Abd Halim, Li Wang, and Mohamad Fani Sulaima. 2023. "A Binary Archimedes Optimization Algorithm and Weighted Sum Method for UFLS in Islanded Distribution Systems Considering the Stability Index and Load Priority" Energies 16, no. 13: 5144. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135144
APA StyleMohd Rosli, H., Mokhlis, H., Mansor, N. N., Md Sapari, N., Halim, S. A., Wang, L., & Sulaima, M. F. (2023). A Binary Archimedes Optimization Algorithm and Weighted Sum Method for UFLS in Islanded Distribution Systems Considering the Stability Index and Load Priority. Energies, 16(13), 5144. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135144






