Research on Rock Physics Modeling Methods for Fractured Shale Reservoirs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Rock Physics Modeling Theory
2.1. Rock Physical Boundary Theory
2.2. Inclusion Theory
2.3. Fluid Replacement Theory
2.4. Fracture Equivalent Theory
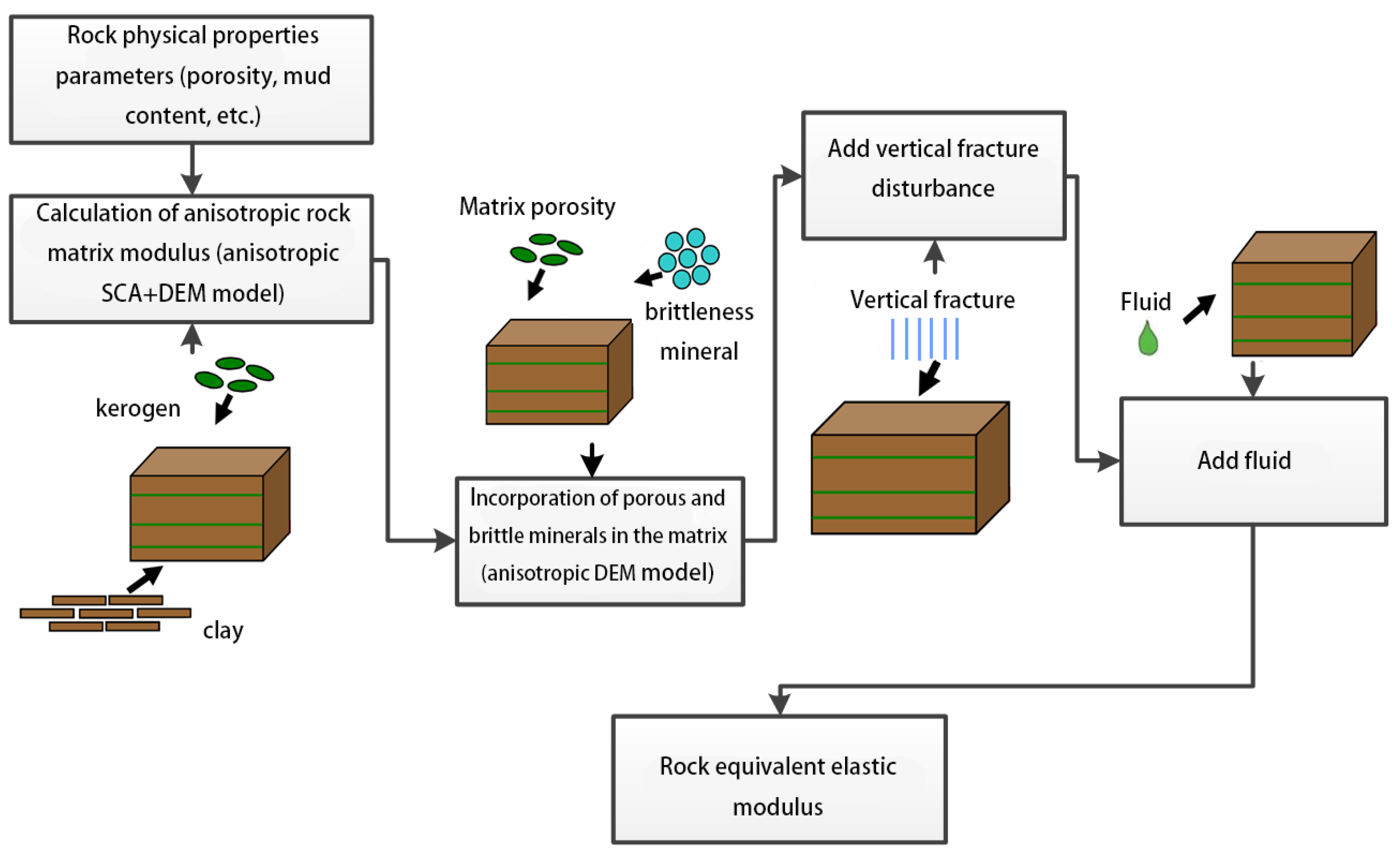
3. Fractured Shale Rock Physics Modeling Method
4. Shale Rock Physics Modeling, Validation, and Analysis
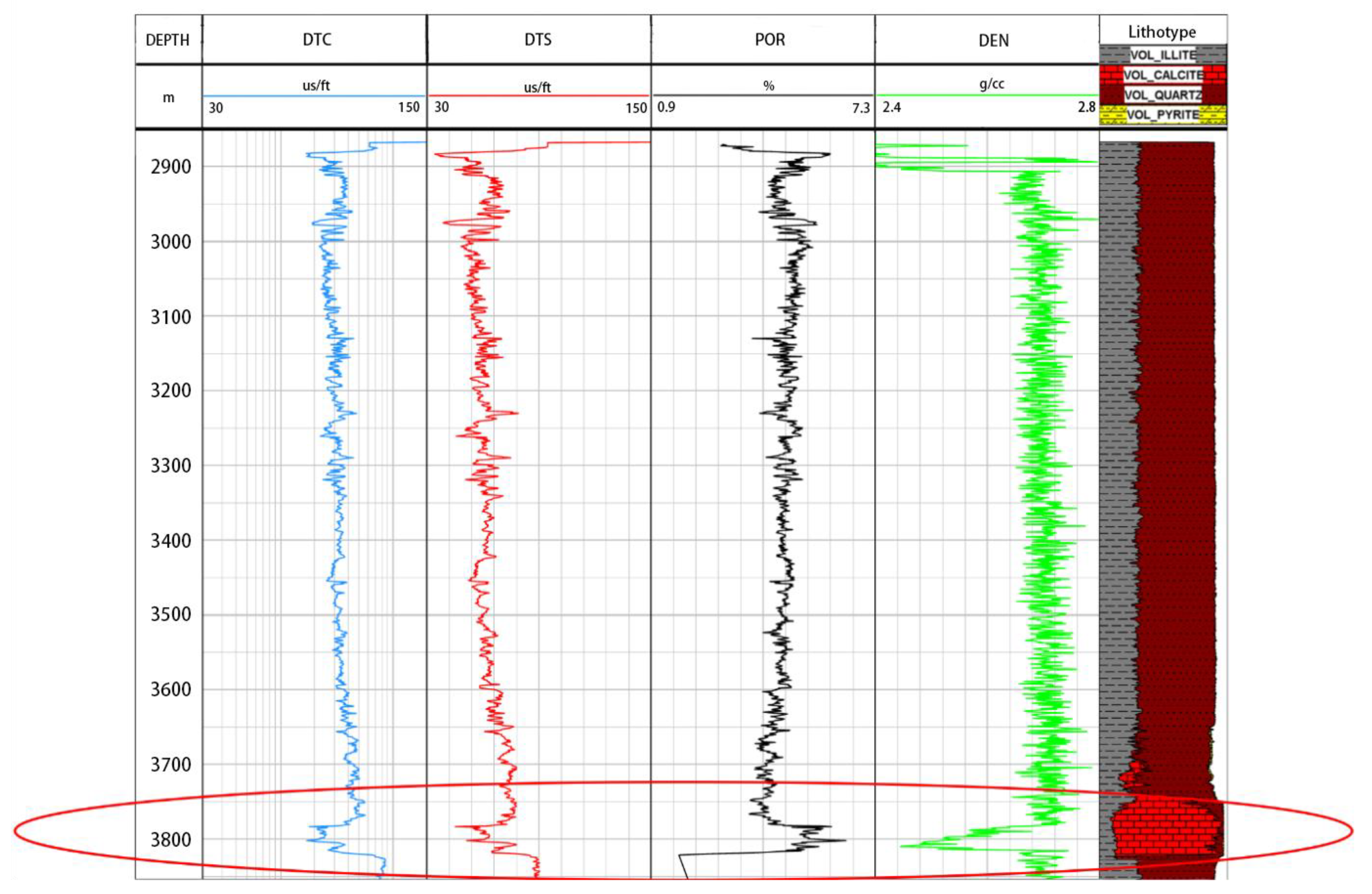
4.1. Practical Applications
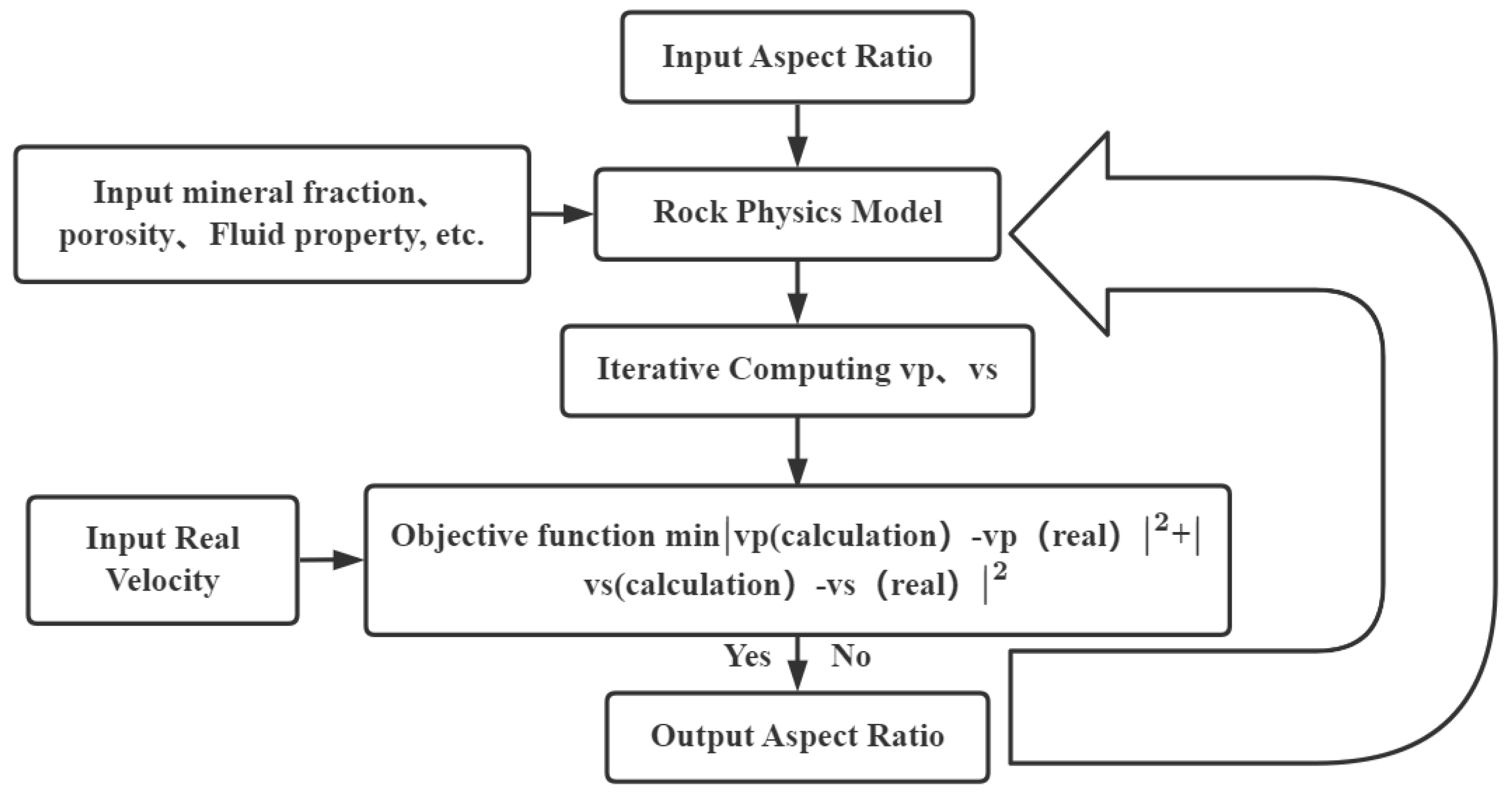
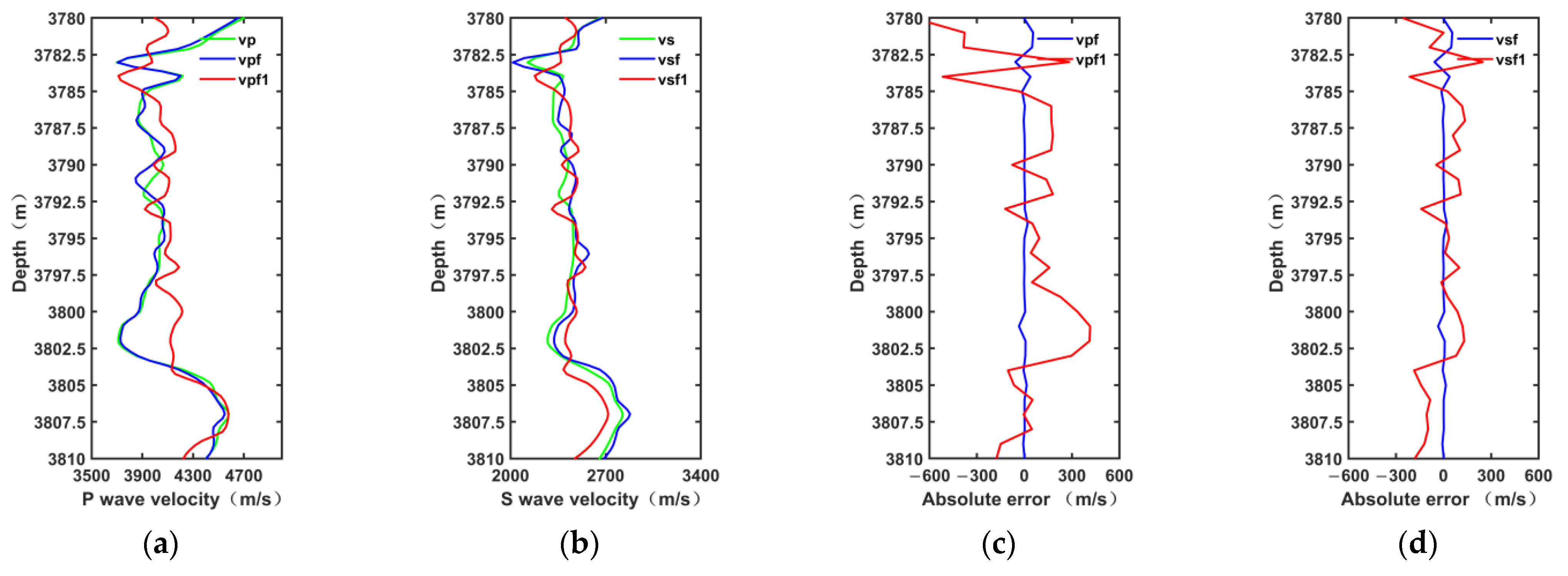
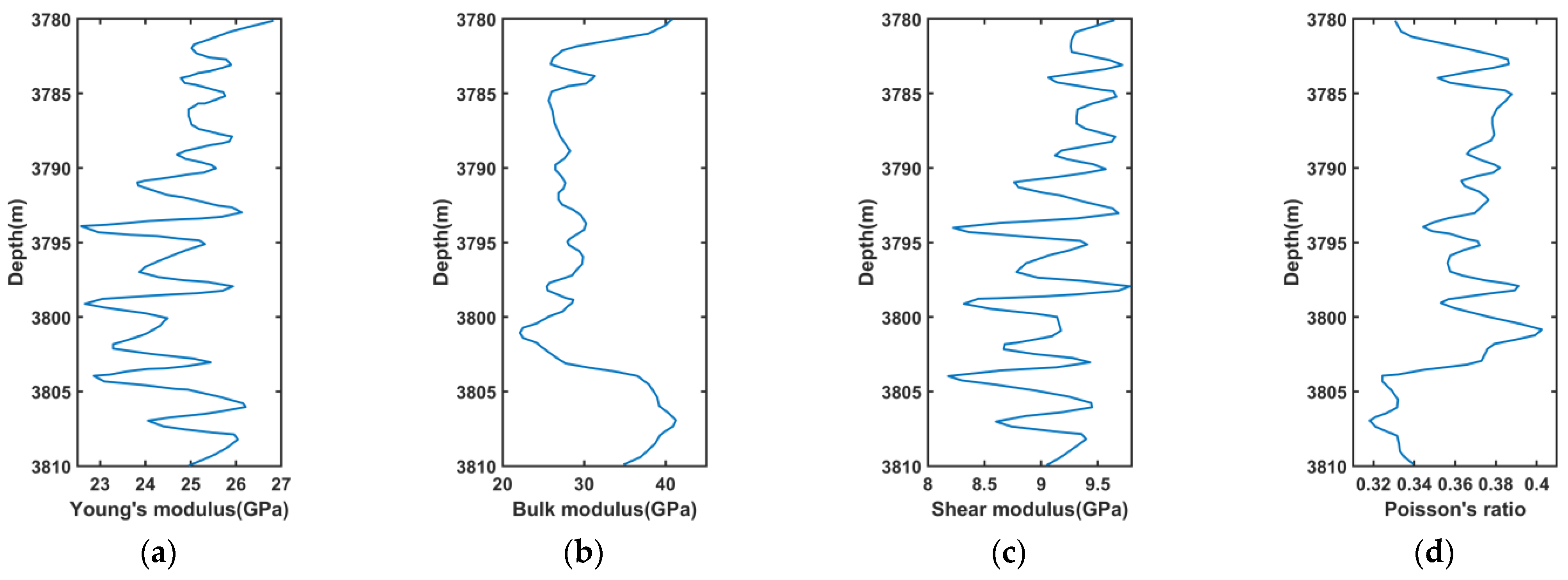
4.2. Shale Rock Physics Model Validation
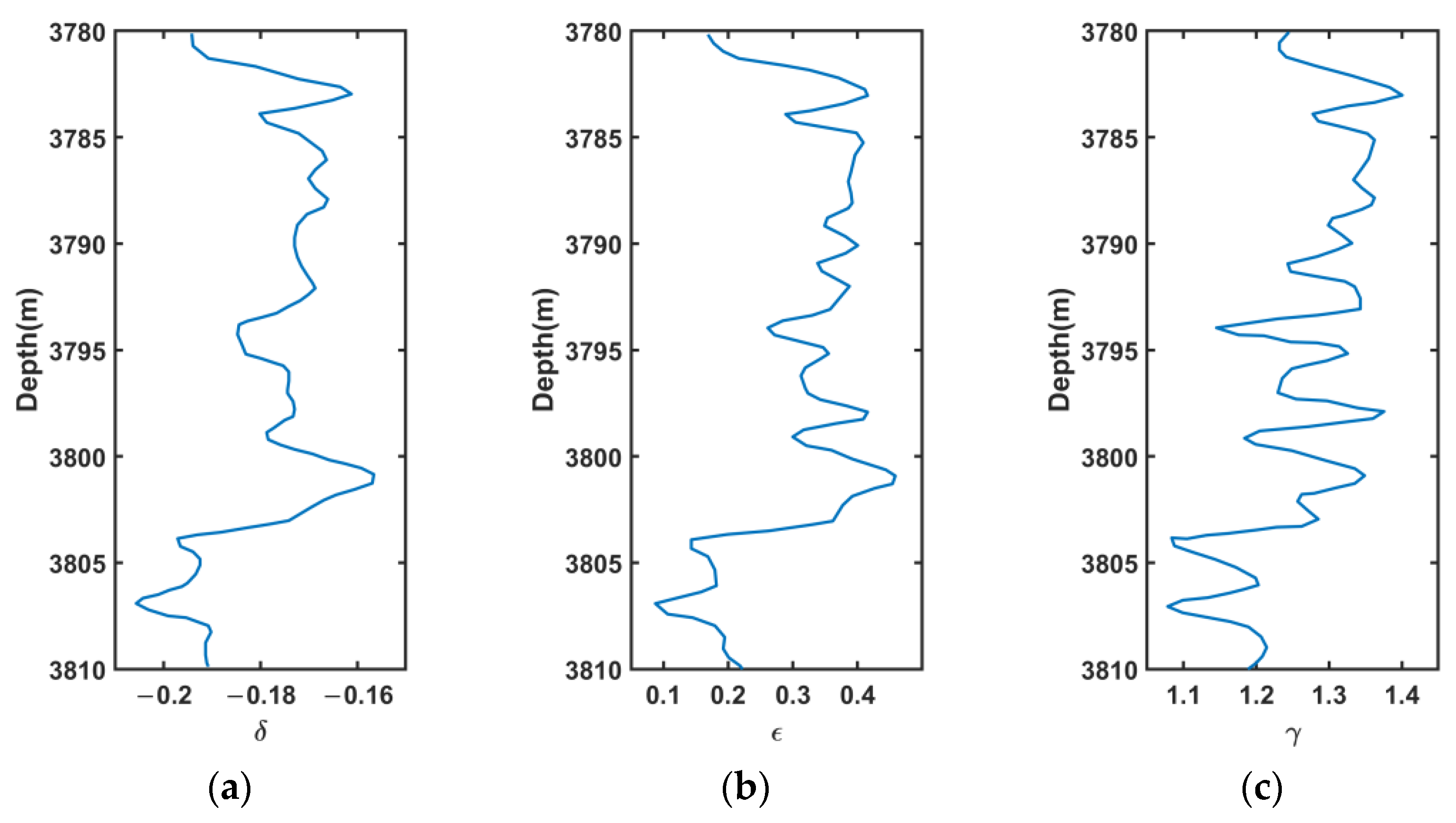
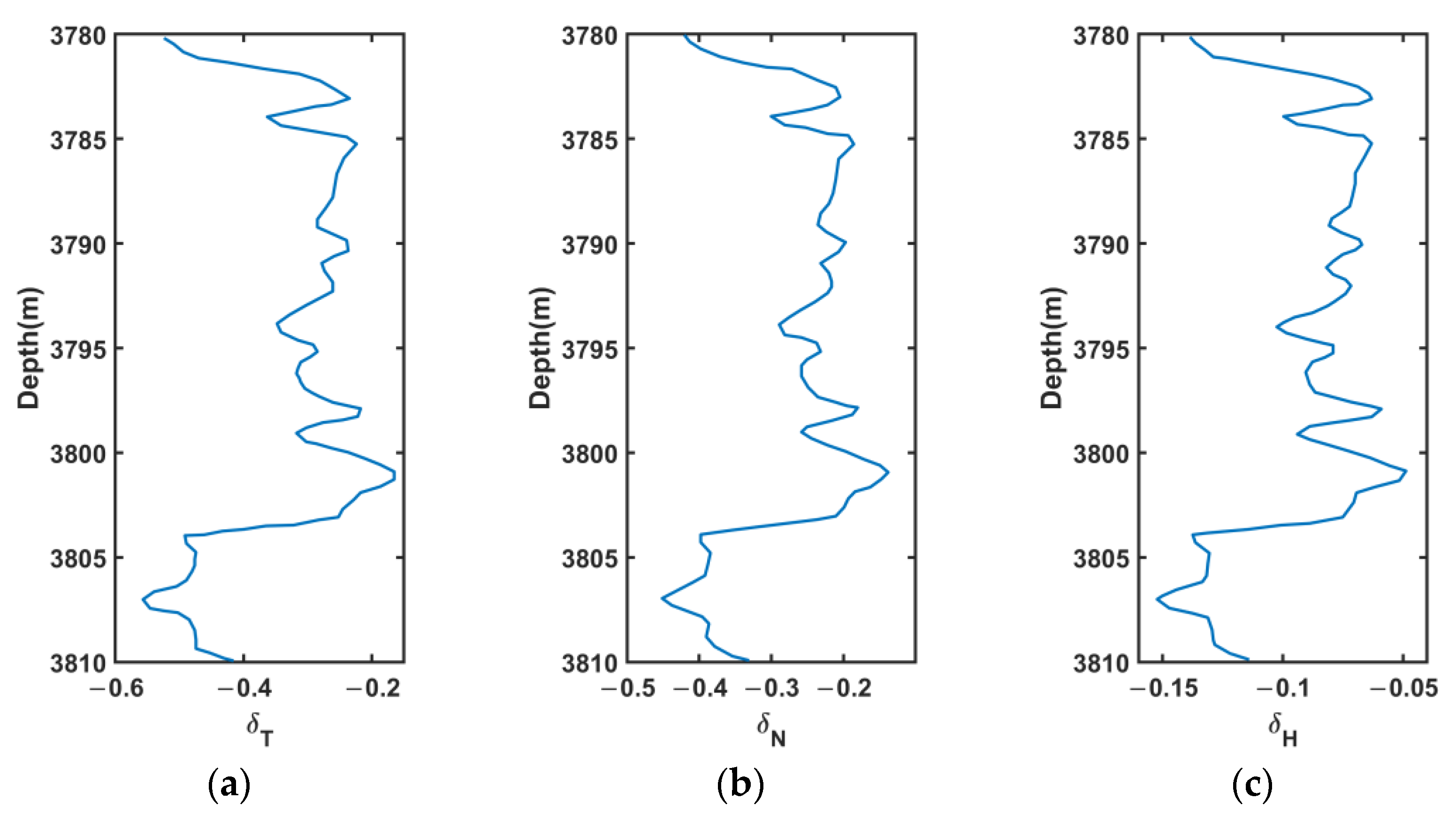
4.3. Analysis of Anisotropy Parameters of the Shale Rock Physics Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Curtis, J.B. Fractured shale-gas systems. AAPG Bull. 2002, 86, 1921–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Vernik, L.; Nur, A. Ultrasonic velocity and anisotropy of hydrocarbon source rocks. Geophysics 1992, 57, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcione, J.M.; Helle, H.B.; Avseth, P. Source-rock seismic-velocity models: Gassmann versus Backus. Geophysics 2011, 76, N37–N45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Q.; Chapman, M.; Li, X. A shale rock physics model and its application in the prediction of brittleness index, mineralogy, and porosity of the Barnett Shale. Soc. Explor. Geophys. 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, N.; Huo, Z.Z.; Sun, Z.D.; Liu, Z.S.; Sun, Y.Y. An investigation of a new rock physics model for shale. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 1990–1998. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.X.; Wang, H.; Zou, H.; Liu, Z.H.; Song, L.T.; Wang, X.B. Microtexture, seismic rock physical properties and modeling of Longmaxi Formation shale. Chin. J. Geophys. 2015, 58, 2123–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.; Zou, C.C.; Meng, X.H.; Jia, S.; Wan, Y. 3D digital core modeling of shale gas reservoir rocks: A case study of conductivity model. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2016, 27, 706–715. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, S.B.; Pan, S.L.; Zuo, H.L.; Gou, Q.Y.; Wang, C. Study on Physical Modeling Method of Shale Rock in Deep Fractured Reservoirs in South Sichuan. Proc. China Pet. Geophys. Explor. Annu. Conf. 2022, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Sevostianov, I.; Yilmaz, N.; Kushch, V. Effective elastic properties of matrixcomposites with transversely-isotropic phases. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2005, 42, 455–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M. Modeling the effect of multiple sets of mesoscale fractures in porous rock on frequency-dependent anisotropy. Geophysics 2009, 74, D97–D103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Z.; Chen, H.Z.; Yin, X.Y.; Li, N.; Yang, B.J. Method of Fracture Elastic Parameter Inversion Based on Anisotropic. J. Jilin Univ. 2012, 42, 845–851. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.Z.; Yin, X.Y.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, G.Z. Seismic inversion for fracture rock physics parameters using azimuthally anisotropic elastic impedance. Chin. J. Geophys. 2014, 57, 3431–3441. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.Q.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.W.; Dong, N.; Liu, Y.W. Research on anisotropy of shale oil reservoir based on rock physics model. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 13, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Q.; Liu, X.W. Seismic rock physics characterization of anisotropic shale—A Longmaxi Shale case study. J. Geophys. Eng. 2018, 512, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Zhang, G.Z. Detection of natural fractures from observed surface seismic data based on a linear-slip model. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2018, 175, 2769–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.T.; Jing, B.; Tobias, M.; Gang, F.; Zhao, H.B. Rock physics model of tight oil siltstone for seismic prediction of brittleness. Geophys. Prospect. 2020, 68, 1554–1574. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Han, D. Combined effects of permeability and fluid saturation on seismic wave dispersion and attenuation in partially-saturated sandstone. Adv. Geo Energy Res. 2021, 5, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, W.N.; Liu, Y.M.; Liu, K. Acoustic logging response law in shales based on petrophysical model. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 2120–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavko, G.; Mukerji, T.; Dvorkin, J. The Rock Physics Handbook: Tools for Seismic Analysis of Porous Media; Cambridge University press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kuster, G.T.; Toksöz, M.N. Velocity and attenuation of seismic waves in two-phase media: Part one, theoretical formulations. Geophysics 1974, 39, 587–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornby, B.E.; Schwartz, L.M.; Hudson, J.A. Anisotropic effective-medium modeling of the elastic properties of shales. Geophysics 1994, 59, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, A.N. A differential scheme for the effective moduli of composites. Mech. Mater. 1985, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Korringa, J. On the dependence of the elastic properties of a porous rock on the compressibility of the pore fluid. Geophysics 1975, 40, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenberg, M.; Helbig, K. Orthorhombic media: Modeling elastic wave behavior in a vertically fractured earth. Geophysics 1997, 62, 1954–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenberg, M.; Douma, J. Elastic wave propagation in media with parallel fractures and aligned cracks1. Geophys. Prospect. 1988, 36, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.C.; Ma, T.S.; Chen, P. Rock physics modeling of transversely isotropic shale: An example of the Longmaxi formation in the Sichuan basin. Chin. J. Geophys. 2020, 63, 4188–4204. [Google Scholar]
| Components | Bulk Modulus | Shear Modulus | Density |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrite | 147.4 | 132.5 | 4.93 |
| Calcite | 76.8 | 32 | 2.71 |
| Quartz | 37 | 44 | 2.65 |
| Clay | 20.1 | 7 | 2.6 |
| Kerogen | 2.9 | 2.7 | 1.3 |
| Water | 2.25 | 0 | 1 |
| Gas | 0.01 | 0 | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, S.; Pan, S.; Zuo, H.; Wu, Y.; Song, G.; Gou, Q. Research on Rock Physics Modeling Methods for Fractured Shale Reservoirs. Energies 2023, 16, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010226
Yi S, Pan S, Zuo H, Wu Y, Song G, Gou Q. Research on Rock Physics Modeling Methods for Fractured Shale Reservoirs. Energies. 2023; 16(1):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010226
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Shengbo, Shulin Pan, Hengyu Zuo, Yinghe Wu, Guojie Song, and Qiyong Gou. 2023. "Research on Rock Physics Modeling Methods for Fractured Shale Reservoirs" Energies 16, no. 1: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010226
APA StyleYi, S., Pan, S., Zuo, H., Wu, Y., Song, G., & Gou, Q. (2023). Research on Rock Physics Modeling Methods for Fractured Shale Reservoirs. Energies, 16(1), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010226





