Abstract
This paper proposes a novel hybrid equalizer circuit (HEC) for a battery management system (BMS) to implement the passive HEC (P-HEC), active HEC (A-HEC), or active/passive (AP-HEC) with the same equalizer circuit architecture. The advantages of an HEC are that it is simple, cost-effective, highly energy efficient, and fail safe. The P-HEC can further use a cooling fan or heater instead of a conventional resistor as a power dissipation element to convert the energy of the waste heat generated by the resistor to adjust the battery temperature. Even if the P-HEC uses the resistor to consume energy as in conventional methods, the P-HEC still dramatically improves the component lifetime and reliability of the BMS because the waste heat generated by the equalizer resistor is outside of the BMS board. Three significant advantages of an A-HEC are its (1) low cost, (2) small volume, and (3) higher energy efficiency than the conventional active equalizer circuits (AECs). In the HEC design, the MOSFETs of the switch array do not need high-speed switching to transfer energy as conventional AECs with DC/DC converter architecture because the A-HEC uses an isolated battery charger to charge the string cell. Therefore, the switch array is equal to a cell selector with a simple ON/OFF function. In summary, the HEC provides a small volume, cost-effective, high efficiency, and fail-safe equalizer circuit design to satisfy cell balancing demands for all kinds of electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems (ESSs).
1. Introduction
Due to growing concerns about the environmental impact of fossil fuels, policymakers are increasingly turning their attention to clean energy and electric vehicles [1,2,3,4,5]. Therefore, the energy storage system (ESS) plays a critical role, and the lithium-ion battery (LIB) shares more than 90% of the ESS market. For these ESSs, they need to consist of many LIBs grouped in series and in parallel to assemble a battery pack to provide sufficient power and the desired energy. In practice, the difference in each cell’s characteristics (e.g., internal capacity, impedance, self-discharge rate, etc.) will influence the voltage difference of all the series-connected cells of the battery pack. Therefore, a battery management system (BMS) [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21] was designed to protect, monitor, and control the state of all cells of the battery pack. A good BMS can ensure safe operation, maximize the available capacity, and provide a real-time estimate of the remaining discharge capacity of the battery pack [19].
However, much effort and resources are required to test a BMS with a real ESS. Furthermore, by pushing the ESS operation under extreme operating conditions, it is almost impossible to verify that the BMS functions are safe and reliable. Therefore, some research uses a hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) simulation tool to test BMS. The HIL can be used to simulate string cells of a battery pack [20] to test BMS functions for cells, e.g., test passive equalizer function [21]. Briefly, HIL is a good auxiliary tool in the development stage of a BMS, which can significantly reduce the development time and testing risk of the BMS. In many practical experiences, most battery pack failures are caused by the cell voltage imbalance issue, which means the voltage difference is enormous, drastically reducing the battery pack’s available power, capacity, lifespan, and safety. Therefore, most BMS designs have an equalization unit to solve the imbalance issue [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35].
In general, the BMS is composed of measurement, communication, calculation, memory, equalization units, etc. The equalization unit is also called the cell balancing unit. The equalization unit is composed of two parts: an equalization control strategy [23,24,25,26,27,28,29] and an equalization circuit (EC) [28,29,31,32,33,34]. Its purpose is to reduce the maximum and minimum cell voltage differences of the battery pack to avoid battery overcharge and overdischarge, which can improve the safety and lifespan. Besides, the low cell voltage difference also increases the available capacity of the battery pack. Therefore, the equalization unit is the most crucial part of all BMS units. Retired vehicle lithium battery packs with good cell balance can be reused in energy storage systems for secondary use to produce huge economic and environmental benefits. Various ECs have been proposed in the past, which can be divided into two types: (1) the passive equalizer circuit (PEC) [28], also called dissipative balance, discharges the energy with a power resistor to the series-connected cell with the highest voltage, and (2) the active equalizer circuit (AEC) [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,36,37,38], also called non-dissipative balance, charges the energy to the cell with the lowest voltage. Many review articles have provided a detailed summary or comparison for the equalization design [17,26,28,30,32,33,36]. Therefore, the following summary is more focused on commercialization.
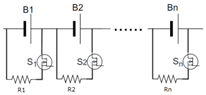
The commonly used PEC architecture [28] is shown in Figure 1. The advantages of PEC are that it is very simple, easy to apply and low cost, and all switches () and discharge resistors () are placed on the BMS circuit board (where i = 1, 2, …, n). Therefore, the temperature of BMS board will increase a great deal when performing the cell balancing. In most commercial products, the typically balancing resistor is 33 Ω [39], and the current of each channel is around 100~127 mA which maps to 3.3~4.2 V and the waste heat of the PEC is around 0.3~0.5 W per channel in the BMS board. To avoid overheating the BMS board, the BMS also limits the number of balanced channels.
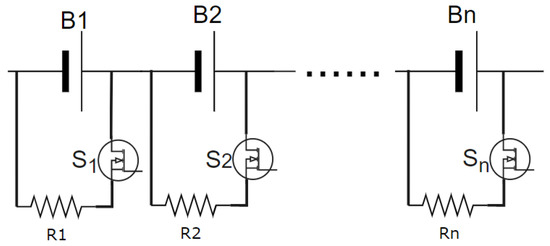
Figure 1.
The circuit of PEC [28].
Briefly, the AEC uses the switch array, capacitors, inductors, or transformers to absorb the energy from the cell with the highest voltage and release the energy to the cell with the lowest voltage. Many kinds of AECs are shown in Figure 2, but most are based on the DC/DC converter principle.
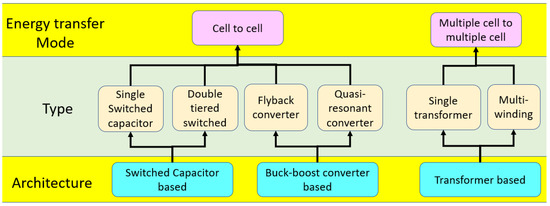
Figure 2.
Classification of AEC [33].
Figure 3 shows the fundamental topology of an AEC with the DC/DC converter working principle, and all switches are the bidirectional switch (BS) which consists of a back-to-back MOSFET string, called BS-MOSFET. Obviously, all switches in Figure 3 need high-speed switching to transfer energy between the string cell and the transformer.
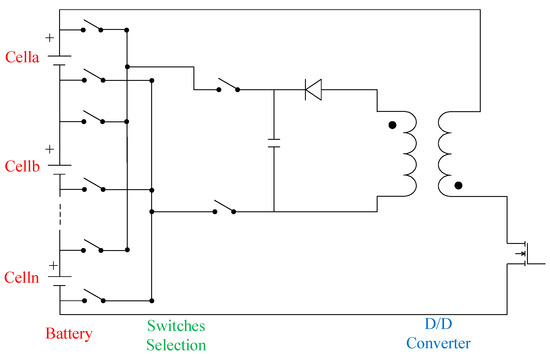
Figure 3.
Unidirectional flyback-based balancing topology for AEC [36].
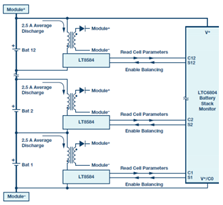
Based on the topology of Figure 3, the chipmaker analog device had commercialized the active balancing control IC LT8584 [40]. The AFE IC (LTC680x family) can drive the active balancing IC LT8584 and the transformer NA5743-AL to generate 2.5 A balancing current from the cell to the module. Moreover, the standalone balancing IC (LT3300 family) enables a bidirectional balancing current between cell and module up to 10 A.
Figure 4 shows another implementation of the AEC with a single switched capacitor (SSC) with DC/DC converter principle, and the switches in Figure 4 also need high-speed switching to transfer energy between the auxiliary battery, capacitor, and string cells.
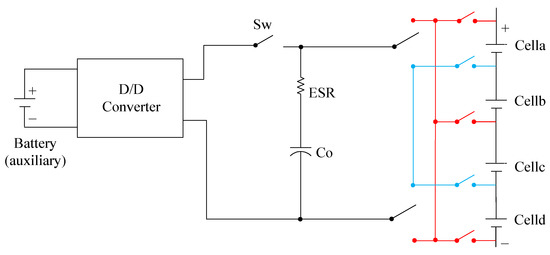
Figure 4.
Implementation of modularized SSC and BC balancing system [34,35].
In fact, the working principle of most AECs is based on a DC/DC converter architecture to transfer energy between string cells or the module, and the energy storage components (e.g., capacitor or inductor) can be regarded as an energy transfer buffer. Therefore, the switches of the switch array of the AECs are not only used to select the string cell for sinking/draining energy but also needed high-speed switching for transferring energy through the energy buffer (e.g., inductor or capacitor). Due to high-speed switching requirements, most of the switching arrays composed of BS-MOSFETs in AEC circuits are mostly driven by gate drivers. Based on the above descriptions, it is easy to find the cost of AECs is related to the component’s specification and the number of power resistors, inductors, capacitors, transformers, and BSs.
Thus, the low-cost or the low-series cell string pack prefers the PEC. The AEC is more applicable to high-end or high-series cell string packs. Therefore, this paper proposes the HEC architecture, which can be both PEC and AEC or either PEC or AEC. The advantages of the proposed HEC are its (1) cost-effective, (2) high efficiency, and (3) fail-safe features.
2. Operation Principle of Hybrid Equalizer
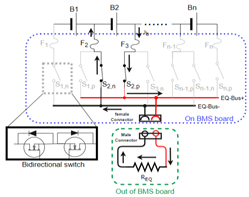
In Figure 5, the HEC corresponds to a PEC by replacing the discharge unit with a power resistor, which is called a P-HEC. All the switches in Figure 5 are replaced with BS-MOSFET, as shown in Figure 6.
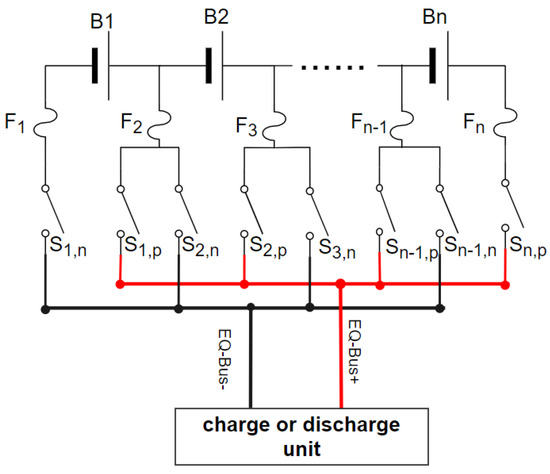
Figure 5.
Hardware architecture of the HEC.
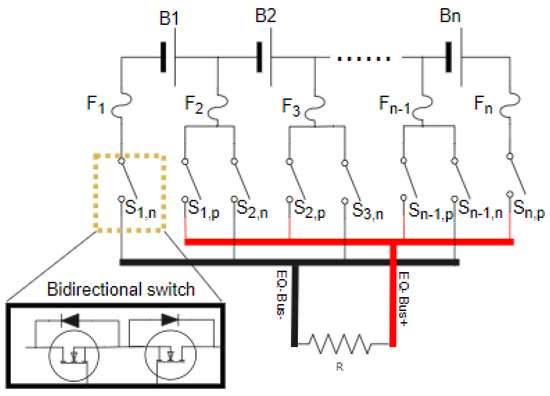
Figure 6.
Implementation of the PEC with HEC architecture.
Figure 7 is an example to illustrate the principle of P-HEC. To discharge the B2 cell through the EQ-Bus, the BMS controls the and switches to be conducting. A discharge unit can be a fan or a heater to regulate the battery temperature or be a power resistor to dissipate the cell energy as conventional ones. The is installed out of the BMS board with proper cooling to prevent the BMS board temperature rising quickly when executing the balance operation. The cell balancing current () is related to the resistance of , conducting resistance of and , and the resistance of all connected parts from B2+ to B2−. For example, the is 1 Ω and the resistance of the BSs and wires is 0.5 Ω so that the total resistance is 1.5 Ω. The balancing current is 2.27 A ( = 3.4 V) to 2.8 A ( = 4.2 V) within cell operation voltage range. The fuse and switch specification will be calculated after given . When the HEC is only used as PEC, it allows the opposite electrode of EQ-Bus. Therefore, the switches and can be replaced with a single switch to save costs.
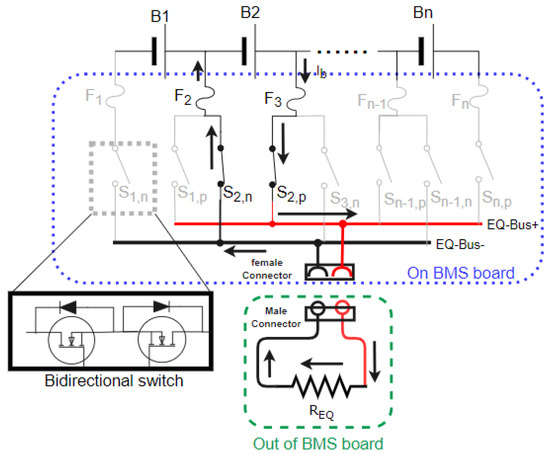
Figure 7.
Discharge the energy of B2 cell with the power resistor out of BMS board.
Figure 8 shows how the proposed HEC design can satisfy the fail-safe function when any switch of the switch array fails in short-circuit. Figure 8 assumes the incurs a short-circuit failure, and a short current () blows the fuse F2 or F3 when discharging the B2 cell by conducting and . The current path of the short current () goes through . Therefore, the HEC can avoid the cell being continuously discharged when the failed switch keeps conducting. In addition, it is easy to identify the failure switch path by detecting the balancing current or voltage change.
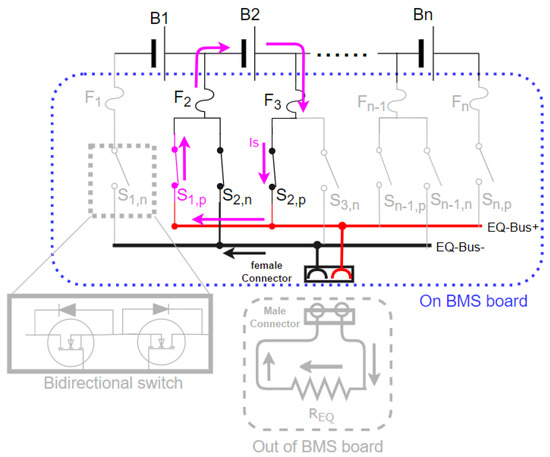
Figure 8.
Switch fail-safe demonstration to blow fuse when fails and keeps conducting.
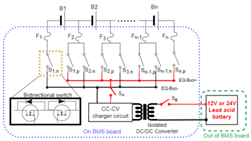
Figure 9 shows an HEC implement AEC architecture by replacing the charge unit of Figure 5 to an isolated CC-CV battery charger, which is called an A-HEC. The isolated CC-CV battery charger is composed of an isolated DC/DC converter and a CC-CV battery charger circuit. The switch controls the input power, and the controls the charger output power to the EQ-Bus.
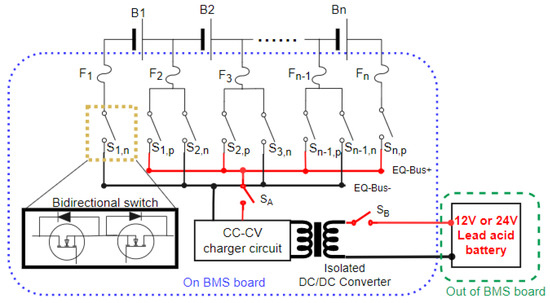
Figure 9.
Implementing the AEC with HEC architecture.
Figure 10 shows the HEC architecture can be either PEC or AEC, but only one mode can be used at one time. It can be P-HEC by conducting the switch and be A-HEC by conducting the switch and . The switches must be isolated switches because of the different ground levels.
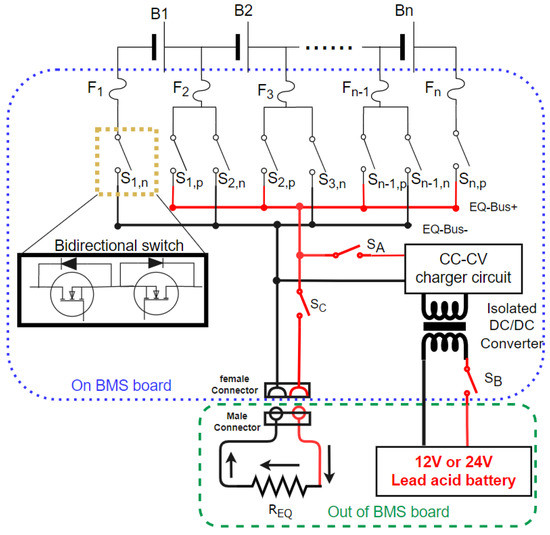
Figure 10.
Implementing AEC and PEC with HEC architecture.
In summary, the proposed HEC combines three essential parts: (1) a switch array, (2) fuses, (3) the charging unit, or the discharging unit. The proposed HEC uses the switch array architecture of conventional AECs to implement the PEC and AEC. The P-HEC can solve the thermal issue of conventional PECs by placing the discharge unit out of the BMS board. The discharge unit might not only be a power resistor for dissipating the energy but also could be a fan or heater to reuse the energy to regulate the battery temperature. Furthermore, the balancing current (>2 A) of the P-HEC is more than 20 times that of the conventional PEC (10–127 mA) with a power resistor on the BMS board. The proposed HEC also adopts the auxiliary lead–acid battery of the EV to provide energy to the isolated DC/DC charger to charge the cell with the lowest voltage in the battery pack. The isolated charger is composed of an isolated DC/DC converter and a CC-CV charger circuit. The significant advantages are shown below: (1) simple and easy to implement with low-cost components, (2) its volume is much smaller. Whether the proposed HEC is a P-HEC or an A-HEC, the proposed HEC also satisfies the fail-safe requirement of functional safety because the balancing current will be cut off by blowing a fuse when any switch of the switch array fails in short-circuit state. The BMS also can detect the cell voltage or balancing current to identify the failed switch.
3. Cost-Effective Bidirectional Switch Circuit Design for HEC
The switch array of the HEC is very similar to the traditional AEC, but the basic control concept is entirely different even though the BSs of the switch array use the same BS-MOSFET structure. In conventional AECs based on the DC/DC converter principle, the BS-MOSFET in many AEC articles needs a gate driver [29] or an isolation optocoupler (TLP250) [34] to high-speed switch the BS-MOSFET to transfer the energy between the cell and the energy storage components. The disadvantage is the number of gate drivers dramatically increases the cost of the switch array. However, the BS-MOSFETs of the HEC only use an ON/OFF switch, which is equal to a string cell selector for performing cell balancing. Therefore, Section 3 proposes a low-cost control circuit to replace the gate driver to control the BS-MOSFETs.
3.1. Low-Cost BS-MOSFET Drive Circuit
Based on the working principle of Figure 7, we further explain how to design the low-cost BS-MOSFET switch circuit. Therefore, the BS-MOSFET control circuit and the working principle are shown in Figure 11.
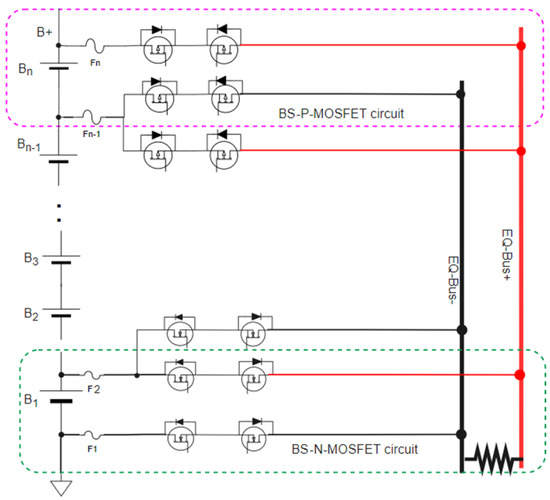
Figure 11.
The BS-MOSFET switch and control circuit design.
In Figure 11, we use two back-to-back P-MOSFETs to be the BS-P-MOSFET drive circuit if the minimum voltage of the node is 8 V. Otherwise, we use two back-to-back N-MOSFETs to be the BS-N-MOSFET drive circuit for the maximum voltage of the node is <8 V and the battery pack voltage B+ is 8 V.
3.2. BS-P-MOSFET Drive Circuit
Figure 11 can be simplified as Figure 12, where only two cells are series connected. The B1 in Figure 12 corresponds to the battery consisting of B1 to Bn−1 of Figure 11. The B2 in Figure 12 corresponds to the Bn of Figure 11. We use Figure 12 to demonstrate the principle of a BS-P-MOSFET driving circuit with a B2+ path to the EQ-Bus+ because the circuit of the B2− path to the EQ-Bus- is the same structure. Therefore, we only use B2+ to demonstrate the operation principle.
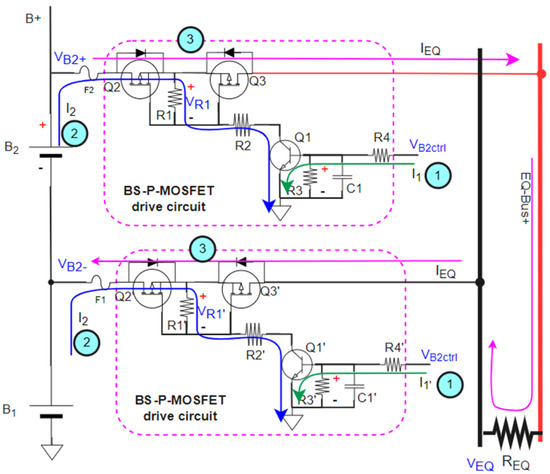
Figure 12.
Simplified Figure 11 as a battery pack with 2S configuration for demonstrating BS-P-MOSFET drive circuit.
3.2.1. Schematic and Calculation for BS-P-MOSFET Circuit
In Figure 12, the principle of step 1 to step 3 to switch on the BS-P-MOSFET path is shown below.
Step 1: Switch on the transistor Q1 by giving control voltage .
where is recommended before switch on Q1 and the current of R3 can be ignored after conducting Q1; is recommended and C1 is parallel with R3 to avoid malfunction.
Step 2: Switch on the P-MOSFETs Q2 and Q3 after Q1 is switched on and the current I1 drives and.
where , is recommended for switch on, and for switch off.
Step 3: Finish to conduct BS-P-MOSFET path to EQ-BUS.
3.2.2. Implementation and Test Results for BS-P-MOSFET Circuit
The transistor Q1 uses the BC846, and the Q2 and Q3 use a dual P-MOSFET (MTB60B06Q8) in SOP8 package for size reduction, whose basic specification is shown in Figure 13 and Figure 14 shows the implementation of the BS-P-MOSFET drive circuit.
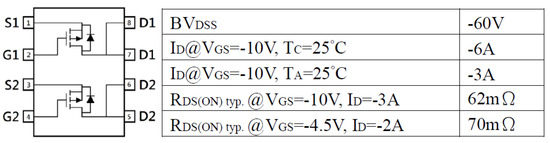
Figure 13.
Dual p-channel power MOSFET (MTB60B06Q8).
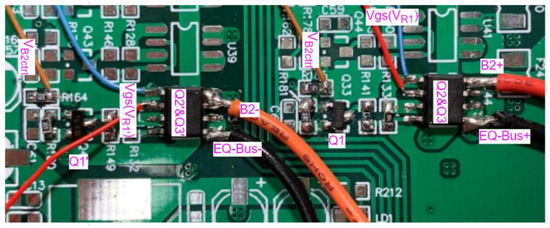
Figure 14.
The implementation of BS-P-MOSFET drive circuit.
Based on the operation principle of Figure 12, the settings are defined as B1 = 42 V (corresponding to the B1~Bn-1 string of the battery pack) and B2 = 4 V (corresponding to the Bn). Other settings are R1 = 20 kΩ, C1 = 10 nF, R2 = 75 kΩ, R3 = 50 kΩ, and R4 = 50 kΩ. We use the constant resistor mode of electrical load to simulate for obtaining . Therefore, the calculated result is , , and the voltage range of and is 9.2 V (B+ = 46 V) and 8.4 V (B+ = 42 V), respectively. Figure 15 and Figure 16 show the signal of , , and to exhibit the transient state of the switch on and off.
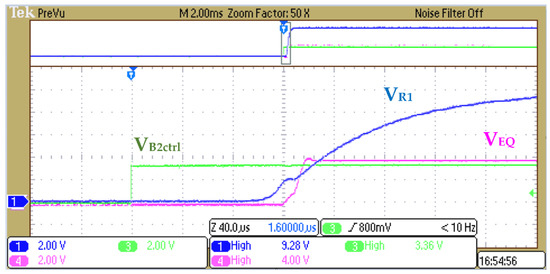
Figure 15.
Transient state of turn on Q2 and Q3 with .
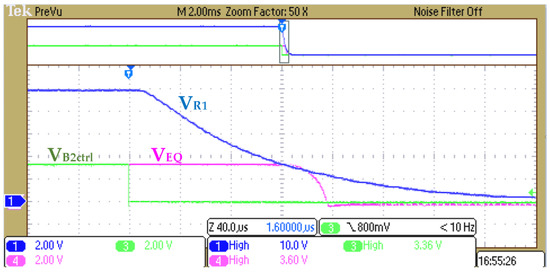
Figure 16.
Transient state of turn off Q2 and Q3 with .
3.3. BS-N-MOSFET Drive Circuit
Figure 11 can be simplified as Figure 17, where only two cells are series connected. The B1 in Figure 12 corresponds to the B1 cell of Figure 11. The B2 in Figure 17 corresponds of B2 to Bn of Figure 11. We use Figure 17 to demonstrate the principle of BS-N-MOSFET driving circuit with B1+ path to EQ-Bus+ because the circuit of B1− path to EQ-Bus- is the same structure. Therefore, we only use B1+ to demonstrate the operation principle.
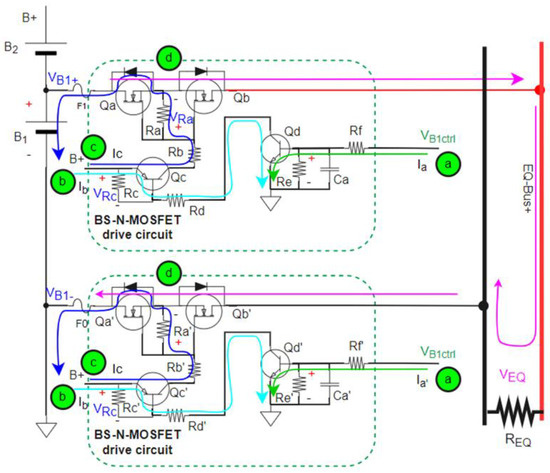
Figure 17.
Simplified Figure 11 as a battery pack with 2S configuration for demonstrating BS-N-MOSFET drive circuit.
3.3.1. Schematic and Calculation for BS-N-MOSFET Circuit
In Figure 17, the principle of step 1 to step 4 for conducting the BS-N-MOSFET path is shown below:
Step 1: Conduct the transistor Qd by giving control voltage .
where is recommended before conducting Qd and the current of Re can be ignored after conducting Qd; is recommended and Ca is parallel with Re to avoid malfunction.
Step 2: Conduct the transistor Qc after Qd is conducted and the current Ia drives;
where is recommended before conducting Qc and the current of Rc can be ignored after conducting Qc; is recommended to avoid malfunction.
Step 3: Conduct the N-MOSFETs Qa and Qb after Qc is conducted and the current Ib drives;
where , and is recommended.
Step 4: Finish to conduct BS-N-MOSFET path to EQ-BUS.
3.3.2. Implementation and Test Results for BS-N-MOSFET Circuit
The transistor Qd uses the BC846 and Qc uses the MMBT5401, and the Qa and Qb use a dual N-MOSFET (MTB20A06KQ8) in SOP8 package for size reduction, whose basic specification is shown in Figure 18 and Figure 19 shows the implementation of the BS-N-MOSFET drive circuit.
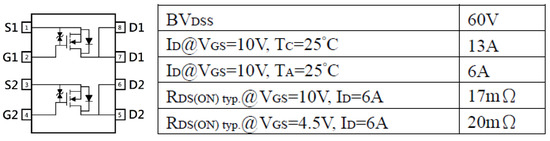
Figure 18.
Dual n-channel power MOSFET(MTB20A06KQ8).
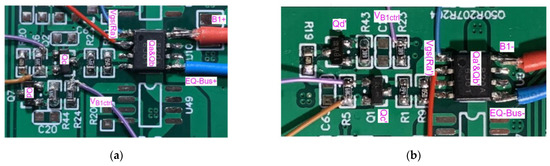
Figure 19.
The implementation for BS-N-MOSFET drive circuit verification: (a) BS-N-MOSFET path for B1+ in front of PCB; (b) BS-N-MOSFET path for B1—at the rear of PCB.
Based on the operation principle of Figure 17, the settings are defined as B1 = 4 V (assumed the first string of the battery pack) and B2 = 42 V (assumed the B2~Bn string of the battery pack). Other settings are Ra = 110 kΩ, Rb = 390 kΩ, Rc = 50 kΩ, Rd = 680 kΩ, Re = 50 kΩ, Rf = 50 kΩ, and Ca = 10 nF. We use the constant resistor mode of electrical load to simulate for obtaining . Therefore, the calculated result is , , and the voltage range of and are 9.38 V and 9.24 V, respectively. Figure 20 and Figure 21 show the signal of , , and to exhibit the transient state of the switch on and off.
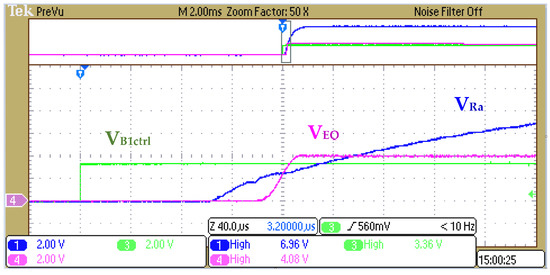
Figure 20.
Transient state of turn on Qa and Qb with .
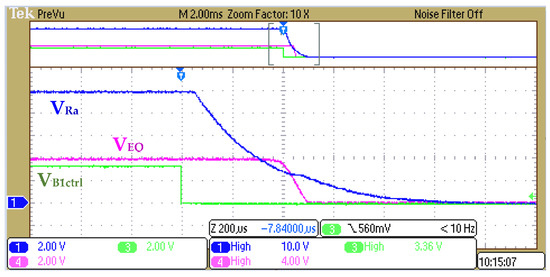
Figure 21.
Transient state of turn off Qa and Qb with .
The above experimental results have verified the transient characteristics of the BS-MOSFET circuit design of the highest string cell and the lowest string cell in the battery pack, respectively. Briefly, the time of the ON/OFF transient state is around 80–100 us. Therefore, the following section will demonstrate the A-HEC design to the BMS board and test the balancing current for the actual battery pack.
Table 1 shows the comparison results between the P-HEC and conventional PECs. P-HEC is suitable for a battery pack with many cells connected in series (>8S configuration), such as electric bicycles, electric scooters, or electric vehicles. The conventional PEC is suitable for the battery pack (2S or 3S configuration) of the notebook, power tool, or tablet computer.

Table 1.
Comparison of the proposed P-HEC with conventional PECs (series cells = N).
Table 2 shows the comparison results between the A-HEC and the commercial active equalizer control IC (LT8584) evolved from Figure 3. The A-HEC is a more cost-effective solution than the LT8584 for the high voltage battery pack (>3S configuration) when the total balancing current of the battery pack/module is less than 3 A. Not only is the channel cost of the HEC low, but also the occupied circuit board area of the equalizer circuit is only 2~3 times of the passive equalizer.

Table 2.
Comparison of the proposed A-HEC with the conventional AEC (series cells = N).
4. Implementation of the A-HEC to the Battery Monitoring Unit of a Battery Pack
Figure 22 shows the implementation of the proposed A-HEC circuit of Figure 9 to the battery monitoring unit (BMU) board, and the maximum balancing charging current can reach 2.2 A. The battery pack has a 22S1P configuration with 25 Ah LTO cells, the cell operating voltage is 1.8~2.7 V and the pack operating voltage is 39.6~59.4 V. The battery packs can be series connected to form a high-voltage battery system in which the system voltage can be up to 600 V.
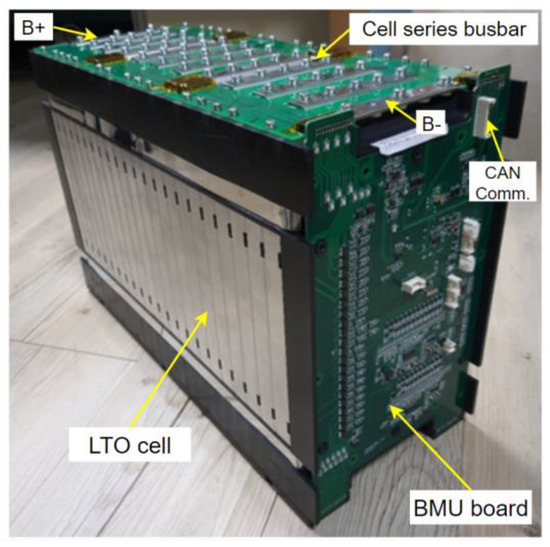
Figure 22.
LTO battery pack with proposed A-HEC circuit on BMU board.
The circuit placement of the A-HEC circuit of the BMU board of Figure 22 is shown in Figure 23. The BS-MOSFET could be BS-N-MOSFET or BS-P-MOSFET, the BS-N-MOSFET and BS-P-MOSFET circuit are used to B1–B3 and B4–B22, respectively. We used a commercial product SCW12B-05 (12 W, η = 83%) as the isolated DC/DC converter of Figure 9 to transfer auxiliary input 18–36 V to isolated output 5 V. In Figure 9, the CC/CV charger circuit is implemented by the LIB charger IC (EUP3271) of which the maximum charge current is 4 A.
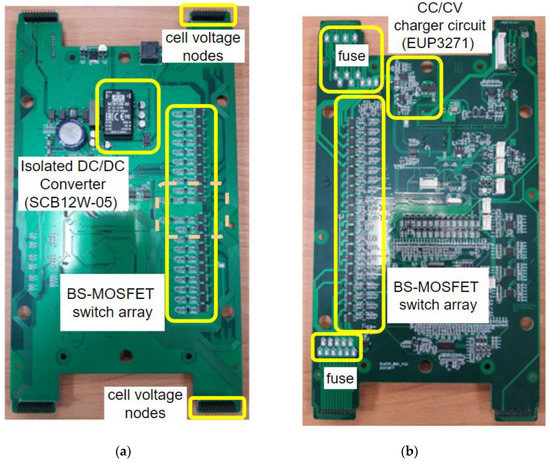
Figure 23.
The BMU board with A-HEC circuit: (a) back; (b) front.
An enlarged view of the BS-MOSFET switch array of Figure 23 is shown in Figure 24, which includes BS-N-MOSFET drive circuit for the B1~B2 cells and BS-P-MOSFET for the B3~B22 cells, respectively.
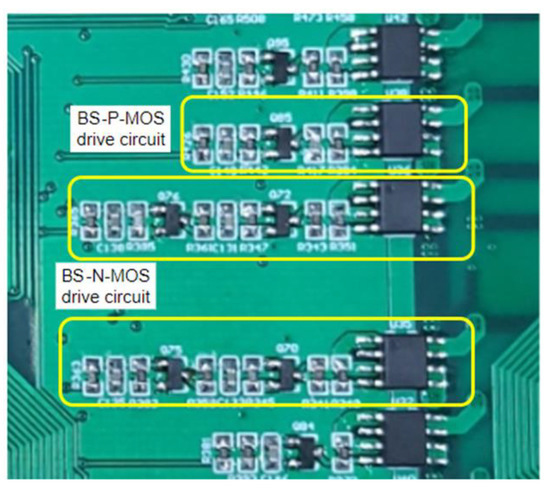
Figure 24.
Enlarged view of the BS-N-MOSFET and BS-P-MOSFET drive circuit.
The balance current experiment results for the proposed A-PEC circuit design of Figure 23 are summarized in Table 3. The balancing current for each node of the battery string is around 1.95–2.25 A.

Table 3.
The balancing current result for each node of the battery string.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposed the cost-effective and simple passive/active HEC design for a BMS. The key idea of the HEC is to let the switch array as a string cell selector for selecting the string cell to charge (A-HEC) or discharge (P-HEC) for cell balancing purposes. Therefore, the BS-MOSFETs of the switch array are equal to an ON/OFF switch and do not need high-speed switching to move energy. Furthermore, we proposed a low-cost and simple control circuit to drive these BS-MOSFET paths of HEC, which had been verified with a 48 V LTO battery pack. The comparison of the proposed HEC with conventional PEC and AEC are shown in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. The power cost per channel, low-temperature rise on the BMS by placing the discharge unit outside the BMS circuit board, and fail-safe function are the competitive advantages of P-HEC. Similarly, the low cost of the BS-MOSFET driving circuit, fail-safe and small size on BMS are the significant features of the A-HEC. The limitation of the HEC is the minimum pack voltage should be higher than 8 V (>3S~4S configuration) for driving the MOSFET and control circuit. Based on the above features, the equalizer circuit design with the HEC topology is a cost-effective solution for various EVs and ESSs with high voltage battery packs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-C.S.; methodology, C.-C.S., C.-H.C. and Y.-L.L.; validation, C.-C.S. and Y.-H.H.; writing—original draft, C.-C.S. and Y.-L.L.; writing—review and editing, C.-C.S. and Y.-L.L.; visualization, C.-C.S. and Y.-L.L.; supervision, C.-C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support was provided by the Department of Industrial Technology in the Ministry of Economic Affairs (111-EC-17-A-27-1583). Research facilities were provided by the Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Abbreviations
| BMS | Battery management system |
| AFE | Analog front end |
| BMU | Battery monitoring unit |
| EV | Electric vehicle |
| ESS | Energy storage system |
| LIB | Lithium-ion battery |
| EC | Equalizer circuit |
| M-AEC | Modularized equalizer circuit |
| PEC | Passive equalizer circuit |
| AEC | Active equalizer circuit |
| HEC | Hybrid equalizer circuit |
| P-HEC | Passive hybrid equalizer circuit |
| A-HEC | Active hybrid equalizer circuit |
| AP-HEC | Active/passive hybrid equalizer circuit |
| BS | bidirectional switch |
| BS-MOSFET | bidirectional switch with back-to-back MOSFET |
| BS-P-MOSFET | bidirectional switch with back-to-back P-MOSFET |
| BS-N-MOSFET | bidirectional switch with back-to-back N-MOSFET |
References
- Viola, F. Electric Vehicles and Psychology. Sustainability 2021, 13, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudet, A.; Larouche, F.; Amouzegar, K.; Bouchard, P.; Zaghib, K. Key Challenges and Opportunities for Recycling Electric Vehicle Battery Materials. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, L.; Richa, K.; Spangenberger, J. Key issues for Li-ion battery recycling. MRS Energy Sustain. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pillot, C. The rechargeable battery market and main trends 2018–2030. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual International Battery Seminar & Exhibit, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 25–28 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Saqli, K.; Bouchareb, H.; Oudghiri, M.; M’Sirdi, N. Critical Review of Ageing Mechanisms and State of Health Estimation Methods for Battery Performance. In Sustainability in Energy and Buildings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 507–518. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, C.-J.; Jiang, S.-B.; Yeh, T.-L.; Sun, C.-C. Fault-Tolerant Battery Power Network Architecture of Networked Swappable Battery Packs in Parallel. Energies 2021, 14, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carkhuff, B.G.; Demirev, P.A.; Srinivasan, R. Impedance-based battery management system for safety monitoring of lithium-ion batteries. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6497–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, R.; Schwartz, R.; Steurich, B. Battery management system. In Lithium-Ion Batteries: Basics and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Lelie, M.; Braun, T.; Knips, M.; Nordmann, H.; Ringbeck, F.; Zappen, H.; Sauer, D.U. Battery management system hardware concepts: An overview. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Cao, D.; Jöst, D.; Ringbeck, F.; Kuipers, M.; Frie, F.; Sauer, D.U. Parameter sensitivity analysis of electrochemical model-based battery management systems for lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Energy 2020, 269, 115104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipu, M.H.; Hannan, M.; Karim, T.F.; Hussain, A.; Saad, M.H.; Ayob, A.; Miah, M.S.; Mahlia, T. Intelligent algorithms and control strategies for battery management system in electric vehicles: Progress, challenges and future outlook. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 126044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, M.; Maghfiroh, H.; Rosadi, R.A.; Kusumaputri, K.D. Battery management system design (BMS) for lithium ion batteries. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2217, 30157. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, T. Design and implementation of a battery management system with active charge balance based on the SOC and SOH online estimation. Energy 2019, 166, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhan, B.; Yetik, O.; Karakoc, T.H. Hybrid Battery Management System Design for Electric Aircraft. Energy 2021, 234, 121227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkmanović, H.; Popović, I. A systematic approach for designing battery management system for embedded applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 Zooming Innovation in Consumer Technologies Conference (ZINC), Novi Sad, Serbia, 26–27 May 2021; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Zhu, J.; Dai, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Q. A review of modeling, acquisition, and application of lithium-ion battery impedance for onboard battery management. ETransportation 2021, 7, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Li, M.; Chen, Z. A comprehensive review of battery modeling and state estimation approaches for advanced battery management systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernaci, C.; Muscato, G.; Scandurra, A. Test of Automotive Battery Management System Control Strategies on Hardware-in-the-Loop Systems: A Low-Voltage Approach. SAE Int. J. Electrified Veh. 2021, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Huang, Y.; Gu, H.; Han, X.; Feng, X.; Dai, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ouyang, M. Remaining discharge energy estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on future load prediction considering temperature and ageing effects. Energy 2022, 238, 121754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.M.; Niri, M.F.; Worwood, D.; Dinh, T.Q.; Marco, J. An Advanced Hardware-in-the-Loop Battery Simulation Platform for the Experimental Testing of Battery Management System. In Proceedings of the 2019 23rd International Conference on Mechatronics Technology (ICMT), Salerno, Italy, 23–26 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, A.; Stevenson, A.; Sarwat, A.I. Performance Analysis of Commercial Passive Balancing Battery Management System Operation Using a Hardware-in-the-Loop Testbed. Energies 2021, 14, 8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.A.; Hasan, M.K.; Mahmud, M.; Motakabber, S.; Ibrahimya, M.I.; Islam, S. A review: Energy storage system and balancing circuits for electric vehicle application. IET Power Electron. 2021, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zou, C.; Wik, T.; Yao, K.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Gao, F. Run-to-run control for active balancing of lithium iron phosphate battery packs. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 1499–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouyang, Q.; Chen, J.; Zheng, J.; Fang, H. Optimal cell-to-cell balancing topology design for serially connected lithium-ion battery packs. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 9, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Chen, J.; Xu, C.; Su, H. Cell balancing control for serially connected lithium-ion batteries. In Proceedings of the 2016 American Control Conference (ACC), Boston, MA, USA, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 3095–3100. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, F.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, X.; Liu, B. A review of equalization strategies for series battery packs: Variables, objectives, and algorithms. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 116, 109464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, W.; Xue, N.; Bhattacharjee, V.; Jiang, J.; Karabasoglu, O.; Pecht, M. Active battery cell equalization based on residual available energy maximization. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Zhou, S.; Cui, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Ling, H.; Yang, S. A comprehensive review on inconsistency and equalization technology of lithium-ion battery for electric vehicles. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 11059–11087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Lee, K.-M.; Choi, Y.-G.; Kang, B. Modularized design of active charge equalizer for Li-ion battery pack. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 8697–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.K.; Shrivastava, P.; Tey, K.S.; Idris, M.Y.I.B.; Mekhilef, S.; Jamei, E.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Stojcevski, A. Advancement of lithium-ion battery cells voltage equalization techniques: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Yu, L.R.; Yang, M.F. A charge equalization scheme for battery string with charging current allocation. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2021, 49, 2935–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Lozano, J.; Romero-Cadaval, E.; Milanes-Montero, M.I.; Guerrero-Martinez, M.A. Battery equalization active methods. J. Power Source 2014, 246, 934–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.; Fan, Z.; Cao, J. Cell equalisation circuits: A review. J. Power Source 2020, 448, 227489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daowd, M.; Antoine, M.; Omar, N.; Lataire, P.; Van Den Bossche, P.; Van Mierlo, J. Battery management system—Balancing modularization based on a single switched capacitor and bi-directional DC/DC converter with the auxiliary battery. Energies 2014, 7, 2897–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daowd, M.; Antoine, M.; Omar, N.; Van den Bossche, P.; Van Mierlo, J. Single switched capacitor battery balancing system enhancements. Energies 2013, 6, 2149–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turksoy, A.; Teke, A.; Alkaya, A. A comprehensive overview of the dc-dc converter-based battery charge balancing methods in electric vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 133, 110274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omariba, Z.B.; Zhang, L.; Sun, D. Review of battery cell balancing methodologies for optimizing battery pack performance in electric vehicles. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 129335–129352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseoglou, M.; Tsioumas, E.; Jabbour, N.; Mademlis, C. Highly effective cell equalization in a lithium-ion battery management system. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 2088–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.; Nork, S. Passive Balancing Allows All Cells to Appear to Have the Same Capacity. Available online: https://www.analog.com/en/technical-articles/passive-battery-cell-balancing.html (accessed on 13 February 2022).
- Scott, K.; Nork, S. Active Battery Cell Balancing. Available online: https://www.analog.com/en/technical-articles/active-battery-cell-balancing.html (accessed on 13 February 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).