Energy Recovery from Natural Gas Pressure Reduction Stations with the Use of Turboexpanders: Static and Dynamic Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Development of Calculation Model
- —pressure, bar;
- —specific volume, m3/kg;
- R—individual gas constant, J/kgK;
- T—temperature, °C;
- —characteristic constants of the equations of state, -.
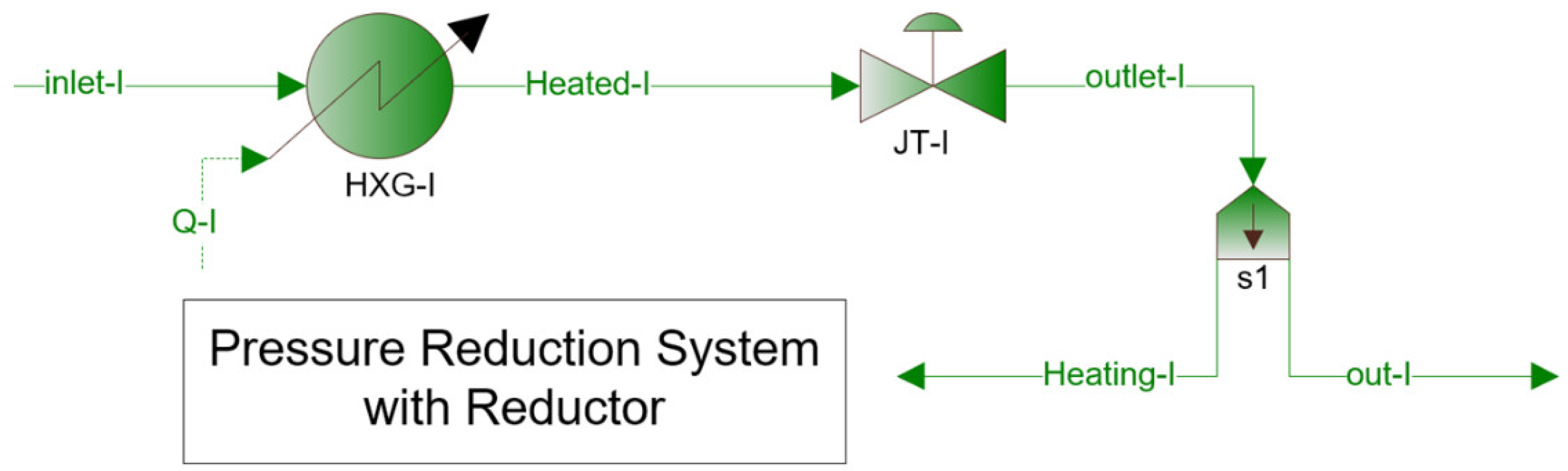
2.1.1. PRS with Pressure Reducer
- —gas volume flow, m3/s;
- Pd—thermal power, kWheat;
- Hi—calorific value of the natural gas, kJ/m3;
- —chimney loss, -;
- —combustion loss, -;
- —heat loss, -;
- —standstill loss, -;
- —efficiency of the heating system, -.
- nominal gas flow rate through the reducer —22,000 m3/h;
- gas temperature at inlet/outlet of PRS —4/5 °C;
- gas pressure at inlet/outlet of PRS —25/8 bar;
- gas density (normal conditions) —0.829 kg/m3.
- —demand for thermal power, kWheat;
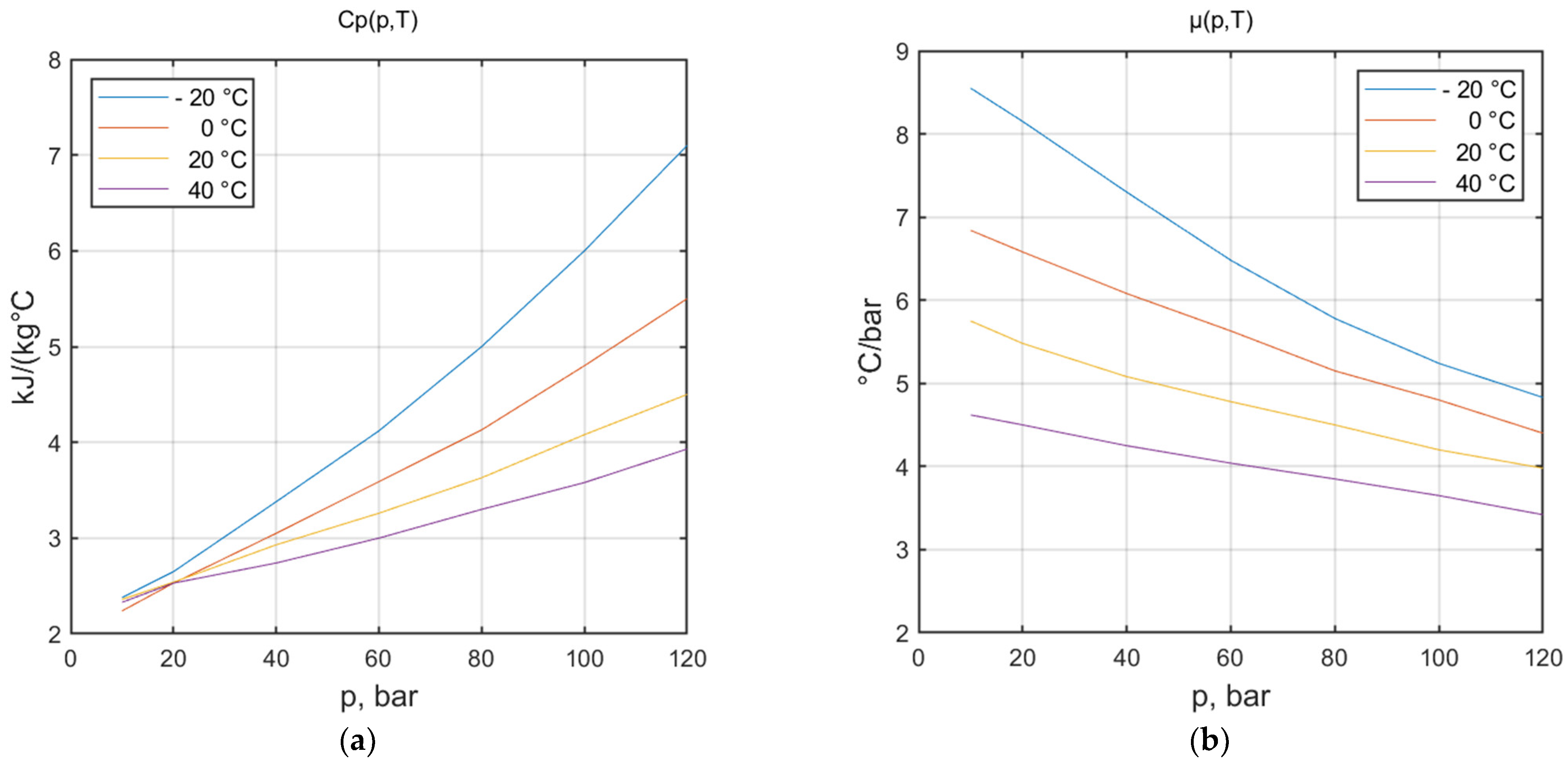
- —average value of specific heat at constant pressure, J/kg °C;
- —average value of the Joule Thomson coefficient, -;
- —average value of absolute gas pressure, bar;
- —natural gas pressure in normal conditions, bar (adopted 1 bar).
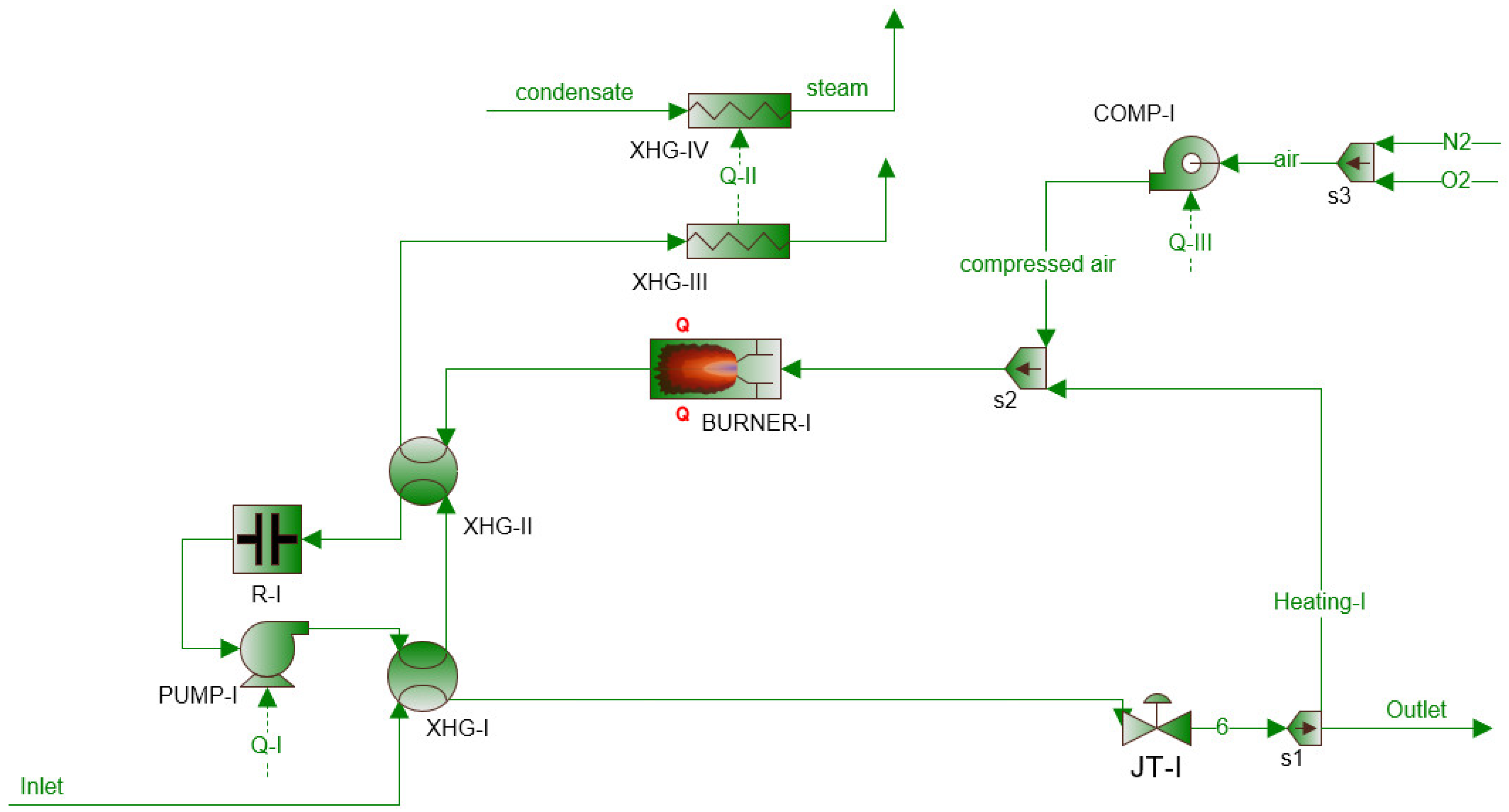
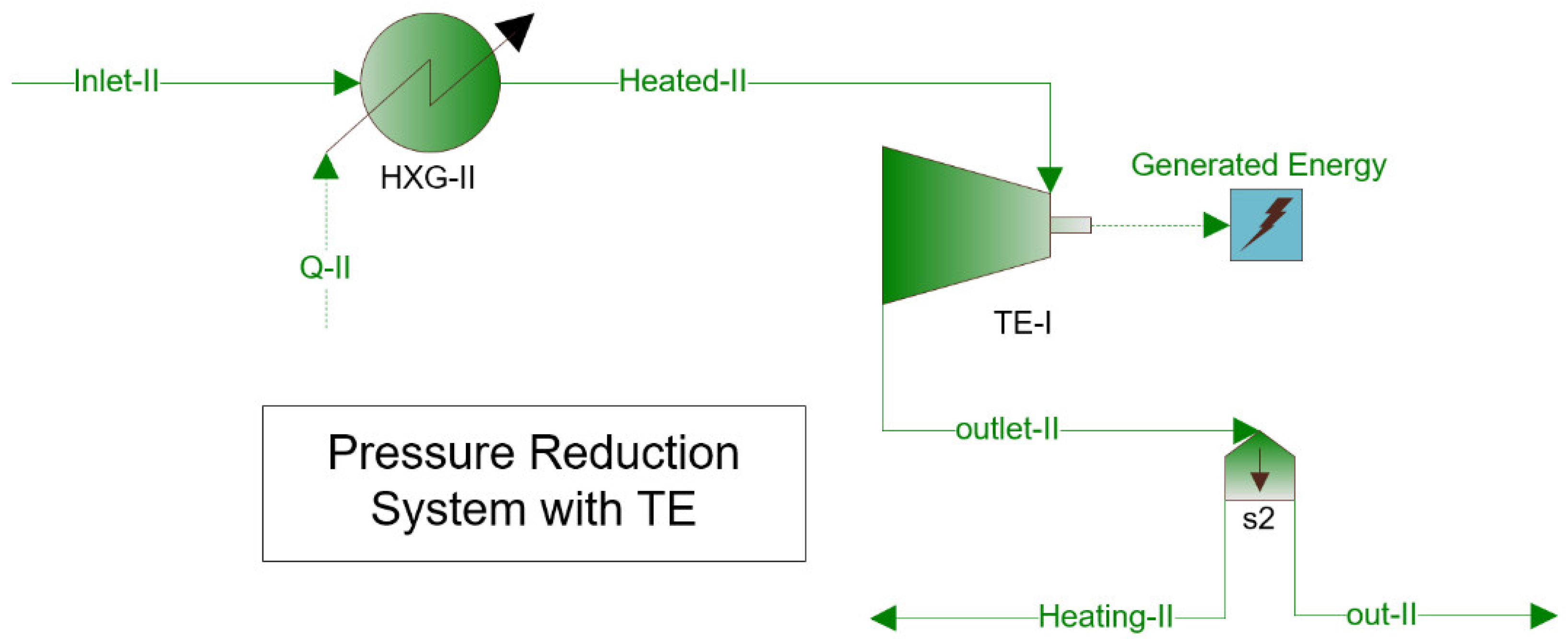
2.1.2. PRS with Turboexpander
- —power generated at the generator terminals, We;
- —adiabatic efficiency coefficient of turbine, -;
- —mechanical efficiency coefficient of turbine, -;
- —power generator efficiency, -;
- —gas mass flow, kg/s;
- —gas enthalpy change in the turbine, J/kg.
- —average value of specific heat at constant pressure, J/kg °C;
- —temperature at the inlet to the turbine, °C;
- —temperature at the outlet from the turbine, °C.
- —22,000 m3/h;
- —36 °C;
- —5 °C;
- —15,388 kg/h.
2.1.3. PRS with TE and PEM Fuel Cell
2.2. PRS Input Parameters
2.2.1. Static Simulation Data—PRS with Pressure Reducer/TE
- Inlet gas temperature ranges from 4 °C to 12 °C with a step 2;
- Inlet gas pressure ranges from 25 to 55 bar with a step 10;
- Gas flow rates range from 4000 m3/h to 22,000 m3/h with a step 4000;
- Constant temperature at the outlet, 5 °C;
- Constant pressure at the outlet, 8 bar.
2.2.2. Dynamic Simulation Data—PRS with Pressure Reducer/TE
2.2.3. Static Simulation Data—PRS with TE and PEM Fuel Cell
3. Results
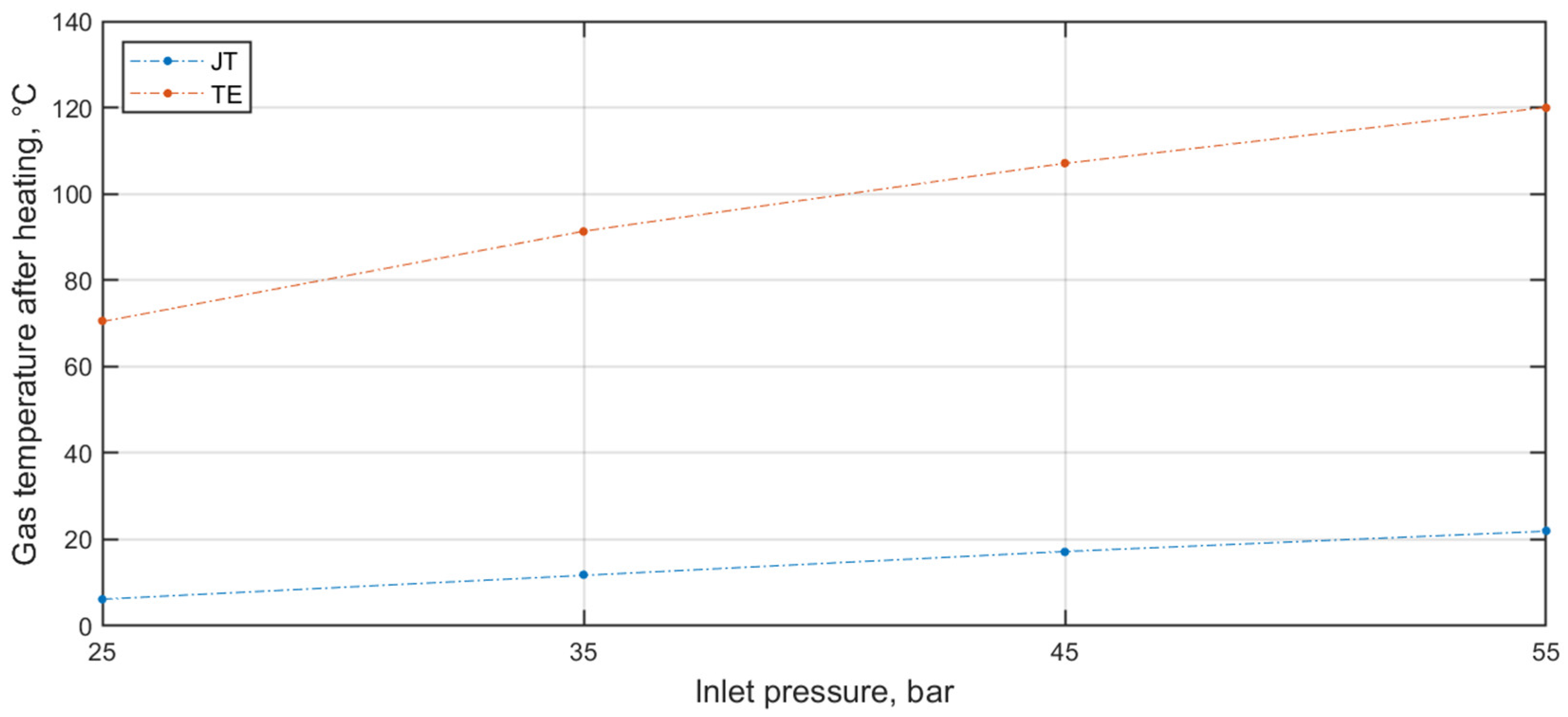
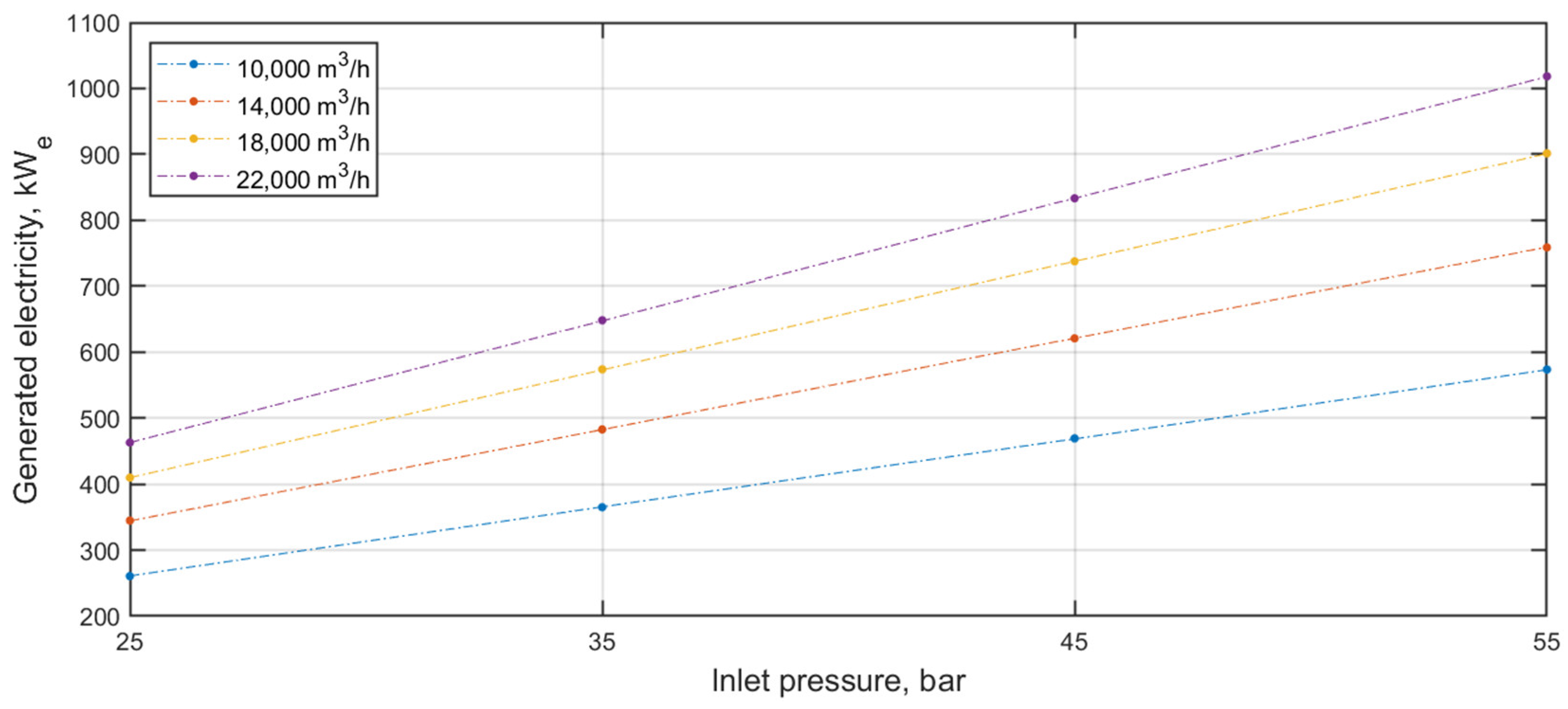
3.1. Static Simulation Results—PRS with Pressure Reducer/TE
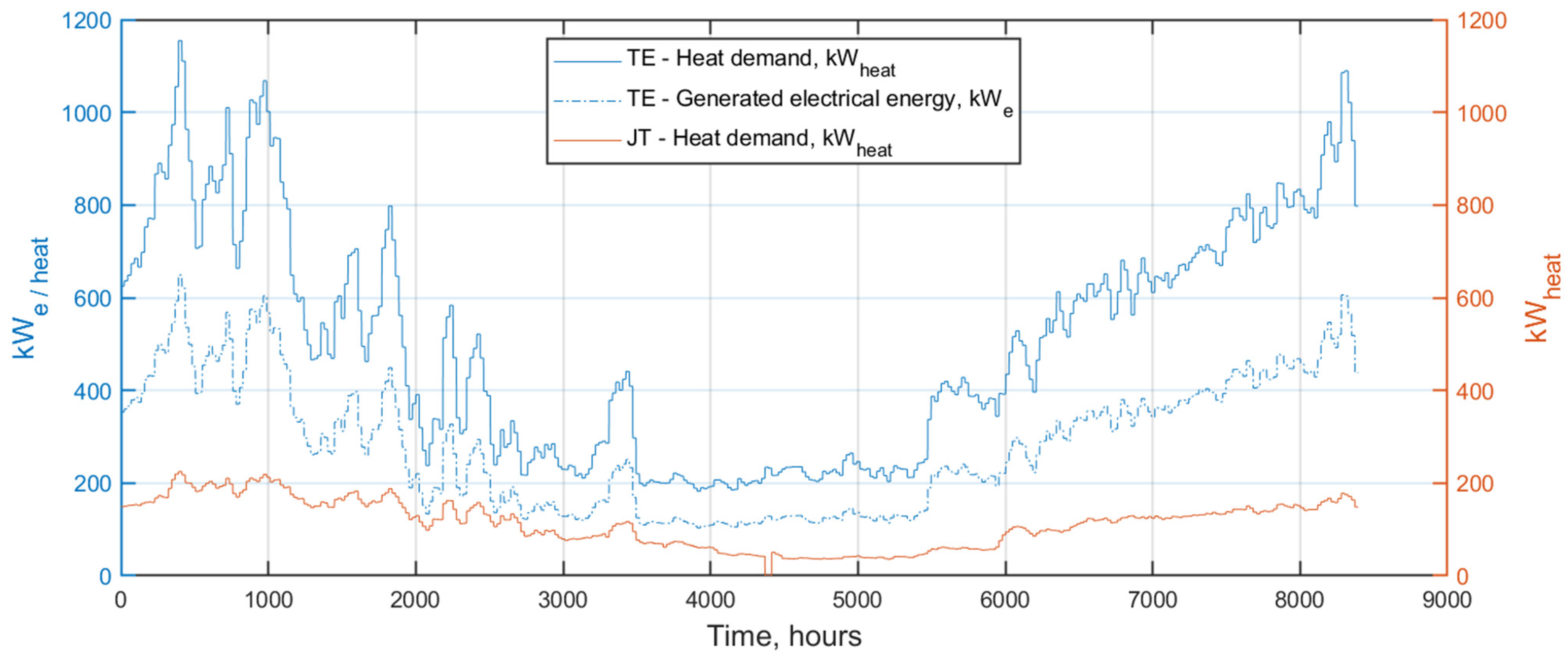
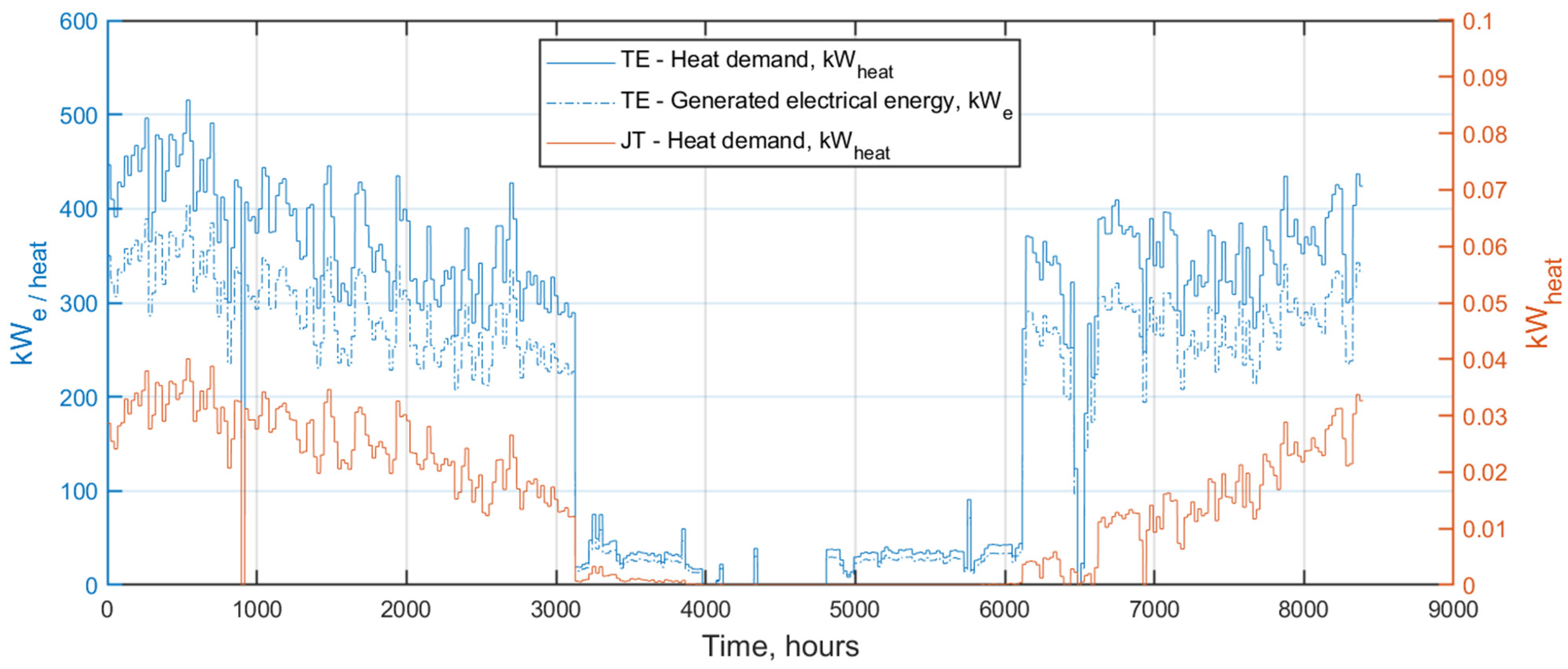
3.2. Dynamic Simulation Results—PRS with Pressure Reducer/TE
3.3. Static Simulation Results—PRS with TE and PEM Fuel Cell
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbols | |
| average value of specific heat at constant pressure, J/kg °C | |
| gas enthalpy change, J/kg | |
| pressure drop in the exchanger, bar | |
| Hi | calorific value of the gas, kJ/m3 |
| N | demand for thermal power, kWe |
| power generated, We | |
| average value of absolute gas pressure, bar | |
| natural gas pressure in normal conditions, bar | |
| Pd | thermal power, kWheat |
| gas pressure at inlet/outlet of PRS, bar | |
| standstill loss, - | |
| gas mass flow, kg/s | |
| Qn | nominal gas flow rate through the reducer/turboexpander, m3/h |
| heat loss, - | |
| combustion loss, - | |
| chimney loss, - | |
| temperature at the inlet/outlet of turbine, °C | |
| gas temperature at inlet/outlet of PRS, °C | |
| average gas temperature, °C | |
| amount of gas used for preheating, m3/h | |
| gas volume flow, m3/h | |
| Greek Letters | |
| adiabatic efficiency coefficient, - | |
| efficiency of the heating system, - | |
| isentropic efficiency of TE, - | |
| mechanical efficiency coefficient, - | |
| heating system efficiency, - | |
| gas density (normal conditions), kg/m3 | |
| average value of the Joule Thomson coefficient, - | |
| ε | required calculation accuracy, - |
| Acronyms | |
| AC | air conditioner |
| CaMAaA | control and Measurement Apparatus and Automation |
| CCTV | closed-Circuit TeleVision |
| EOS | equation of state |
| GC | gas chromatography |
| PEMFC | proton-exchange membrane fuell cell |
| PRS | natural gas regulation stations/natural gas reducing and metering station |
| SSWiN | burglary and panic signaling system |
| TSO | transmission system operator |
References
- Chaczykowski, M.; Osiadacz, A.J.; Uilhoorn, F.E. Exergy-Based Analysis of Gas Transmission System with Application to Yamal-Europe Pipeline. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osiadacz, A.; Chaczykowski, M. Stacje Gazowe: Teoria, Projektowanie, Eksploatacja; Fluid Systems: Warsaw, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Szargut, J.; Ziębik, A. Podstawy Energetyki Cieplnej; Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN SA: Warsaw, Poland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cascio, E.L.; Ma, Z.; Schenone, C. Performance Assessment of a Novel Natural Gas Pressure Reduction Station Equipped with Parabolic Trough Solar Collectors. Renew. Energy 2018, 128, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheuban, J. Turboexpanders: Harnessing the Hidden Potential of Our Natural Gas Distribution System. Available online: https://jacobrheuban.com/2009/03/09/turboexpanders-harnessing-the-hidden-potential-of-our-natural-gas-distribution-system/#more-442 (accessed on 16 September 2022).
- Ardali, E.K.; Heybatian, E. Energy Regeneration in Natural Gas Pressure Reduction Stations by Use of Gas Turbo Expander; Evaluation of Available Potential in Iran. In Proceedings of the 24th World Gas Conference, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 5–9 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Galyas, A.B.; Tihanyi, L.; Szunyog, I.; Kis, L. Investigation of Pressure Regulator Replacement by TurboExpander in Hungarian Gas Transfer Stations. Acta Technol. 2018, 4, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Unar, I.N.; Aftab, A.; Abro, M. Estimation of Power Production Potential from Natural Gas Pressure Reduction Stations in Pakistan Using ASPEN HYSYS. Mehran Univ. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2015, 34, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, C.R. Hybrid Turbo Expander and Fuel Cell System for Power Recovery at Natural Gas Pressure Reduction Stations. Master’s Thesis, Mechanical and Materials Engineering Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada, 12 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- WGospodarce.pl. PAP/KG Polski System Przesyłowy Gazu–Ponad 11 Tys. Km Gazociągów. Available online: https://wgospodarce.pl/informacje/111107-polski-system-przesylowy-gazu-ponad-11-tys-km-gazociagow (accessed on 11 September 2022).
- pgnig.pl. PGNiG Broszura Informacyjna Wierzchowice. Available online: https://pgnig.pl/documents/29748/961630/PMG+wierzchowice_folder.pdf/c601d1f3-7bfa-46e0-8eed-201926094ff3 (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- igg.pl. Izba Gospodarcza Gazownictwa. Available online: https://www.igg.pl/node/264 (accessed on 13 September 2022).
- BRE Promax, version 5.0; Bryan Research & Engineering, LLC: Bryan, TX, USA, 2022.
- Kowalski, C. Kotły Gazowe Centralnego Ogrzewania Wodne Niskotemperaturowe; Wydawictwo Naukowo-Techniczne WNT: Warsaw, Poland, 1994; pp. 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Kuczyński, S.; Łaciak, M.; Olijnyk, A.; Szurlej, A.; Włodek, T. Techno-Economic Assessment of Turboexpander Application at Natural Gas Regulation Stations. Energies 2019, 12, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, H.P.; Soares, C. Turboexpanders and Process Applications; Gulf Professional Publishing: Woburn, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Osiadacz, A.; Chaczykowski, M.; Kwestarz, M. An Evaluation of the Possibilities of Using Turboexpanders at Pressure Regulator Stations. J. Power Technol. 2017, 97, 289. [Google Scholar]
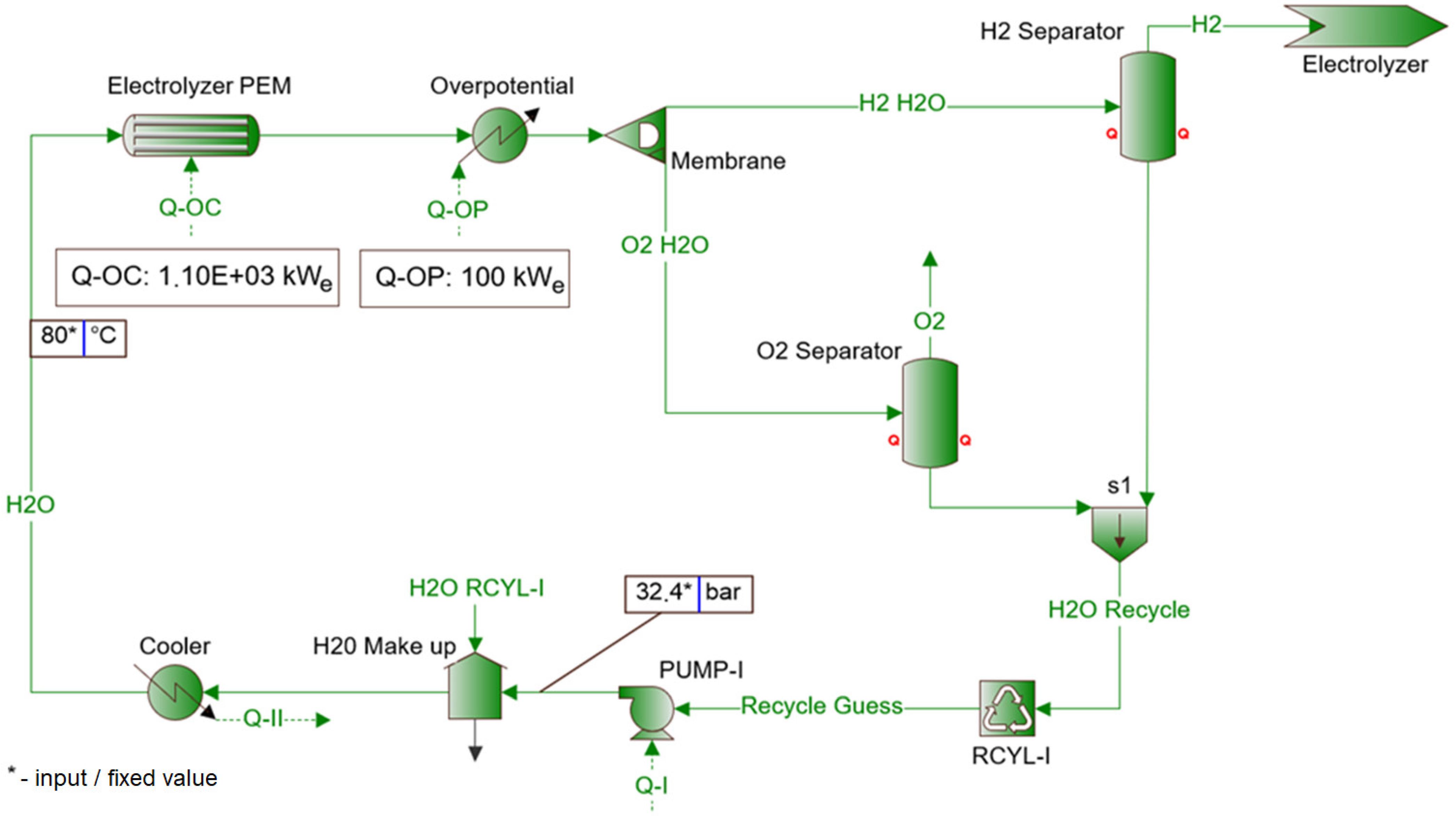
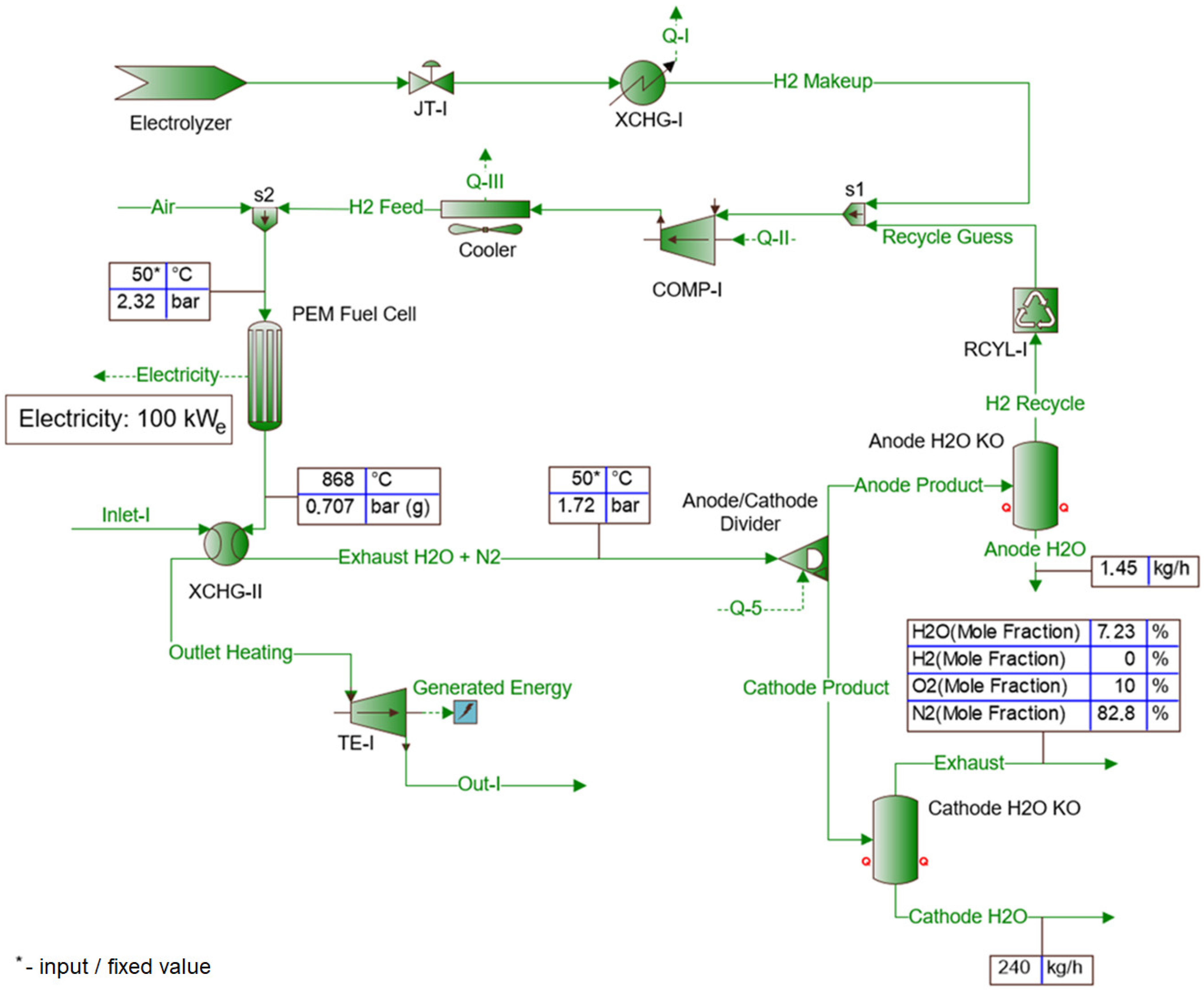
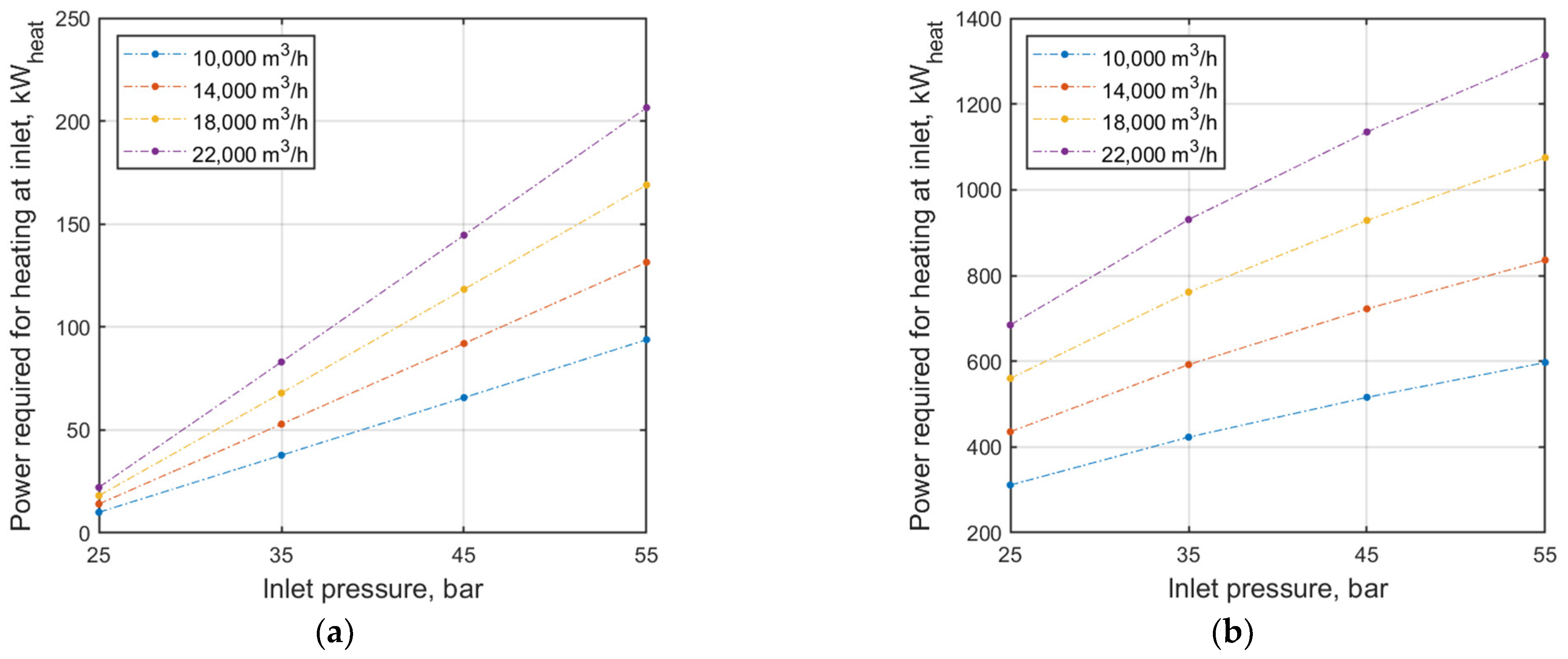
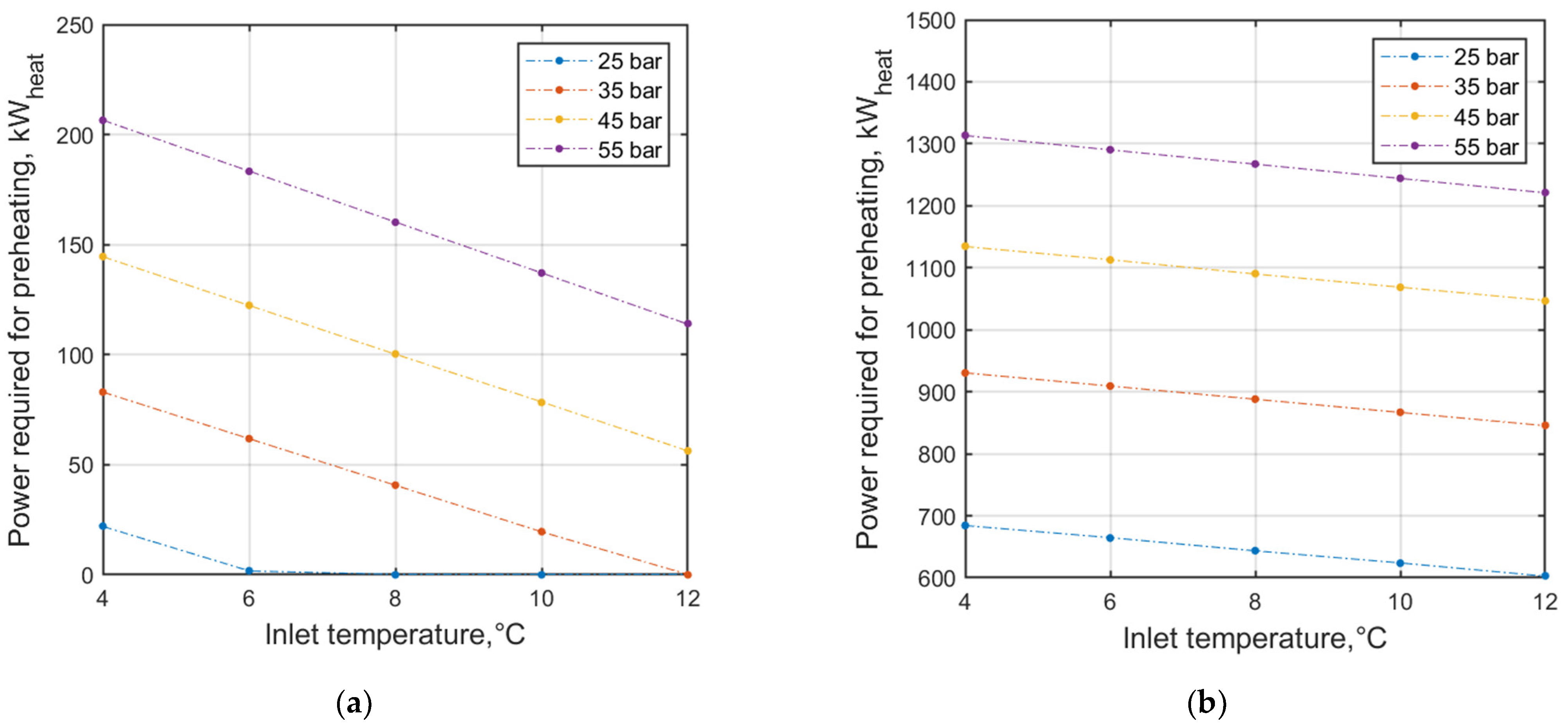
| Parameter | Symbol | Unit | Iteration Step | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||
| JT coefficient | °C/bar | 0.5 | 0.59 | |
| Average value of absolute gas pressure | bar | 17.5 | 17.5 | |
| Average gas temperature | °C | 9.25 | 14.75 | |
| Calculated JT coefficient | - | 0.59 | 0.585 | |
| Calculated specific heat | J/kg °C | 2.4 | 2.7 | |
| - | 0.9 | 0.05 < 0.1 | ||
| Parameter | Symbol | Unit | Calculations | Simulation Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JT coefficient | °C/bar | 0.585 | 0.592 | |
| Thermal power demand | kWheat | 20.73 | 22.135 |
| Parametr | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural gas composition | CH4 | 96.5 | %mol |
| C2H6 | 0.9 | ||
| C3H8 | 1.8 | ||
| N2 | 0.2 | ||
| O2 | 0.6 | ||
| Gas density (normal conditions) | ρn | 0.829 | kg/m3 |
| Heating system efficiency | ηn | 0.85 | - |
| Pressure drop in the exchanger | ΔpXHG | 0.02 | bar |
| Isentropic efficiency of TE | ηize | 0.8 | - |
| Month | Station | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | |||||||||||
| Tin | pin | pout | Tin | pin | pout | Tin | pin | pout | Tin | pin | pout | Tin | pin | pout | |
| °C | bar | °C | bar | °C | bar | °C | bar | °C | bar | ||||||
| I | 5.91 | 29.87 | 7.83 | 5.19 | 31.51 | 2.96 | 4.83 | 34.55 | 5.59 | 5.0 | 15.99 | 2.50 | 6.99 | 43.69 | 25.47 |
| II | 4.40 | 31.81 | 7.71 | 4.02 | 31.01 | 2.97 | 3.63 | 39.83 | 5.61 | 5.0 | 15.34 | 2.50 | 6.55 | 42.18 | 25.54 |
| III | 4.14 | 30.98 | 7.82 | 4.62 | 30.68 | 2.96 | 4.55 | 37.42 | 5.58 | 5.0 | 14.84 | 2.50 | 6.67 | 40.98 | 25.56 |
| IV | 6.03 | 31.17 | 7.92 | 6.67 | 28.49 | 2.94 | 6.34 | 35.27 | 5.58 | 5.0 | 14.45 | 2.50 | 8.19 | 41.79 | 25.62 |
| V | 8.27 | 29.69 | 7.93 | 10.37 | 30.09 | 2.93 | 9.94 | 33.18 | 5.57 | 5.0 | 11.79 | 2.50 | 10.66 | 44.01 | 26.03 |
| VI | 10.82 | 27.31 | 7.85 | 14.78 | 27.85 | 2.93 | 14.02 | 36.38 | 5.58 | 5.0 | 11.79 | 2.50 | 13.87 | 44.87 | 26.36 |
| VII | 16.31 | 28.09 | 7.88 | 17.41 | 33.08 | 2.92 | 17.11 | 35.01 | 5.57 | 5.0 | 11.73 | 2.51 | 15.74 | 44.04 | 26.09 |
| VIII | 18.00 | 34.22 | 7.85 | 18.22 | 32.17 | 2.92 | 16.99 | 37.75 | 5.56 | 5.0 | 11.71 | 2.52 | 16.55 | 44.00 | 26.03 |
| IX | 15.90 | 29.76 | 7.83 | 15.61 | 30.16 | 2.93 | 15.41 | 37.65 | 5.55 | 5.0 | 11.79 | 2.51 | 16.33 | 45.83 | 25.97 |
| X | 14.11 | 31.19 | 7.81 | 12.87 | 29.96 | 2.94 | 12.59 | 37.95 | 5.56 | 5.0 | 12.10 | 2.50 | 14.59 | 46.14 | 25.48 |
| XI | 10.79 | 28.57 | 7.78 | 9.94 | 30.48 | 2.94 | 9.87 | 38.00 | 5.56 | 5.0 | 12.60 | 2.52 | 11.54 | 44.65 | 26.34 |
| XII | 8.52 | 31.40 | 7.68 | 7.32 | 31.53 | 2.95 | 6.26 | 34.02 | 5.61 | 5.0 | 12.83 | 2.58 | 8.48 | 43.63 | 26.31 |
| Month | Station | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | ||||||
| Qn | Vp | Qn | Vp | Qn | Vp | Qn | Vp | Qn | Vp | |
| m3/h | m3/h | m3/h | m3/h | m3/h | ||||||
| I | 13,405 | 14.14 | 2847 | 4.85 | 796 | 1.71 | 500 | 0.83 | 22,753 | 0.00308 |
| II | 17,061 | 18.25 | 2992 | 5.10 | 750 | 1.94 | 552 | 0.85 | 57,389 | 0.00279 |
| III | 11,279 | 15.08 | 2504 | 4.24 | 878 | 1.76 | 388 | 0.79 | 21,298 | 0.00244 |
| IV | 5612 | 10.11 | 2072 | 3.27 | 766 | 1.36 | 264 | 0.64 | 19,674 | 0.00189 |
| V | 4706 | 8.05 | 1439 | 2.32 | 740 | 1.03 | 116 | 0.21 | 10,955 | 0.00087 |
| VI | 10,265 | 11.05 | 1291 | 1.83 | 682 | 0.58 | 93 | 0.03 | 1830 | 0.00005 |
| VII | 4325 | 4.28 | 1235 | 1.56 | 688 | 0.44 | 64 | 0.00 | 2459 | 0.00000 |
| VIII | 4268 | 3.46 | 1138 | 1.43 | 672 | 0.52 | 2 | 0.01 | 2459 | 0.00000 |
| IX | 8301 | 5.48 | 1373 | 1.71 | 483 | 0.59 | 14 | 0.08 | 4252 | 0.00004 |
| X | 8137 | 8.10 | 1780 | 2.34 | 561 | 0.98 | 66 | 0.27 | 17,894 | 0.00059 |
| XI | 13,473 | 11.88 | 2129 | 3.05 | 514 | 1.17 | 218 | 0.55 | 20,607 | 0.00123 |
| XII | 15,994 | 13.61 | 2738 | 4.44 | 718 | 1.86 | 500 | 0.92 | 20,874 | 0.00214 |
| Equipment | Quantity [pcs] | Unit Power [kWe] | Installed Power [kWe] | Coefficient of Simultaneity [-] | Peak Power [kWe] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaMAaA cabinet | 1 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 0.80 | 0.96 |
| CCTV and SSWiN cabinet | 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.80 | 0.80 |
| GC | 1 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 1.50 |
| Higrometers | 3 | 0.30 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.90 |
| Boiler | 1 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 0.60 | 1.20 |
| Sockets | 1 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 0.10 | 0.15 |
| Area lighting | 1 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.02 |
| Automatic valves | 2 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Heating cables | 3 | 2.50 | 7.50 | 0.80 | 6.00 |
| Cathodic protection station | 1 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 2.00 |
| CaMAaA lighting | 2 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| Area lighting | 10 | 0.12 | 1.20 | 0.30 | 0.36 |
| Measuring cabinets heating | 6 | 0.50 | 3.00 | 0.60 | 1.80 |
| CaMAaA AC | 1 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 0.50 | 0.75 |
| TOTAL | 24.660 | 17.492 | |||
| Electricity Consumption [kWe] | Pressure Reduction Station | Month | ||||||||||||
| XII | XI | X | IX | VIII | VII | VI | V | IV | III | II | I | TOTAL | ||
| PRS I | 1.743 | 1.364 | 1.519 | 1.396 | 1.443 | 1.122 | 1.487 | 1.910 | 0.474 | 2.395 | 1.411 | 1.124 | 17.388 | |
| PRS II | 1.814 | 0.949 | 0.991 | 0.840 | 0.739 | 1.157 | 1.005 | 1.030 | 1.344 | 1.172 | 0.535 | 0.550 | 12.126 | |
| PRS A | PRS E | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JT | TE | JT | TE | |
| Annual natural gas demand for own needs, MWhheat | 992 | 4416.30 | 0.12 | 2089.09 |
| Electricity produced, MWhe | - | 2479.30 | - | 1656.96 |
| PRS | ||
|---|---|---|
| JT | TE + PEM | |
| Annual demand for gas for heating, MWheat | 3504.00 | - |
| Electricity produced (TE), MWhe | - | 6570.00 |
| Produced electricity (PEM), MWhe | - | 876.00 |
| Electricity demand of the electrolyser, MWhe | - | 10,512.00 |
| Total annual costs, PLN | 1,539,167.04 | 1,430,595.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bielka, P.; Kuczyński, S. Energy Recovery from Natural Gas Pressure Reduction Stations with the Use of Turboexpanders: Static and Dynamic Simulations. Energies 2022, 15, 8890. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15238890
Bielka P, Kuczyński S. Energy Recovery from Natural Gas Pressure Reduction Stations with the Use of Turboexpanders: Static and Dynamic Simulations. Energies. 2022; 15(23):8890. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15238890
Chicago/Turabian StyleBielka, Paweł, and Szymon Kuczyński. 2022. "Energy Recovery from Natural Gas Pressure Reduction Stations with the Use of Turboexpanders: Static and Dynamic Simulations" Energies 15, no. 23: 8890. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15238890
APA StyleBielka, P., & Kuczyński, S. (2022). Energy Recovery from Natural Gas Pressure Reduction Stations with the Use of Turboexpanders: Static and Dynamic Simulations. Energies, 15(23), 8890. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15238890





