Abstract
MIL-53(Fe) was prepared and modified with benzoic acid to prepare MIL-53(Fe)-BA additive, which was used to improve the catalytic oxidation rate of sulfite, prevent the scaling of the desulfurization tower, and improve the desulfurization efficiency during the wet flue gas desulfurization (WFGD) process of power plants. MIL-53(Fe)-BA exhibits abundant Lewis acid sites because of the appearance of coordination unsaturated Fe atoms. Due to the excellent sorption capacity, Ca(OH)2 was used as the main SO2 desulfurizer. The composite desulfurizers were prepared by mixing MIL-53(Fe)-based additives and Ca(OH)2, and were characterized by SEM, XRD, and FT-IR. A desulfurization unit was set up at laboratory scale to study the effect of catalytic oxidation additives on sulfite oxidation and desulfurization efficiency. The results showed that the addition of MIL-53(Fe)-BA can increase the oxidation capacity of sulfite by 159%, and greatly improve the desulfurization efficiency. These composite desulfurizers broaden the adaptability of the desulfurizing system to high-sulfur coals, and provide support for improving the desulfurizing efficiency of power plants.
1. Introduction
Fossil fuels have been widely used since the industrial revolution in the 1860s. The harmful gases such as SOx and NOx have been continuously discharged into the atmosphere, resulting in the generation of acid rain, which seriously endangers human health. Effectively removing SO2 from flue gas has been a research goal of many scientists [1]. At present, the desulfurization process is mainly divided into wet desulfurization, semi-dry desulfurization, and dry desulfurization [2]. The limestone–gypsum wet flue gas desulfurization (WFGD) technology has the characteristics of high desulfurization efficiency and low cost, and is most widely used in coal desulfurization [2].
However, with the world’s increasing attention to CO2 emissions and the proposal of China’s goals of “carbon peaking” in 2030 and “carbon neutralization” in 2060, the world has higher and higher requirements for CO2 emission reduction. In the existing limestone–gypsum WFGD process, CaCO3 reacts with SO2 to generate calcium sulfate dihydrate (gypsum) and release CO2 (Equation (1)). Taking the power plant with a planned total installed capacity of 600 MW as an example, using the current limestone–gypsum WFGD process, the annual CO2 emission can reach 25,900 tons, seriously affecting the realization of the world’s CO2 emission reduction target. Therefore, new, environmentally friendly, low-carbon desulfurizer has become one of the materials urgently needed for power plant desulfurization.
Ca (OH)2, as a potential substitute for CaCO3 desulfurization, has attracted more and more attention because of the potential to achieve low CO2 emission and highly efficient desulfurization [3,4]. The chemical reaction of Ca(OH)2 with SO2 is shown in Equation (2). Therefore, if Ca(OH)2 is used to replace CaCO3 in the WFGD process, there will be no CO2 emission in the whole process. Ca(OH)2 was researched for partial or full replacement of CaCO3 in the WFGD process, and the results showed that SO2 at the outlet of the plant meets the standard, and the consumption of desulfurizer was reduced [4].
Compared with traditional CaCO3 slurry (pH = 8.2~8.7), Ca(OH)2 exhibits higher pH (13.2), stronger alkalinity, and higher desulfurization rate [4]. However, in the reaction process of Ca(OH) 2 and SO2, CaSO3·1/2H2O was formed in the first step, and then was completely oxidized to form CaSO4·2H2O (gypsum). Ideally, CaSO3·1/2H2O in the slurry pool can be completely oxidized to CaSO4 by the air introduced into the desulfurization tower. According to the crystal growth theory [5], gypsum preferentially precipitates on the seed crystals. Because most of the seed crystals are concentrated in the slurry of the desulfurization tower, therefore, under the condition of complete oxidation, the desulfurization system is not subject to scaling [5].
However, due to the complexity and variability of the coal market, the coal quality is unstable, the sulfur content of the coal fluctuates greatly, and high sulfur or uneven coal blending often exists. Therefore, when high-sulfur coals are used, SO32− cannot be completely oxidized, and CaSO3 in the slurry tends to be saturated relative to CaSO4. Because the gypsum content in the desulfurization tower is very low, the crystallization process of CaSO4 is prevented because of insufficient seed crystals. Thus, incomplete oxidation occurs and leads to crystallization and precipitation of CaSO3 and CaSO4 on the surfaces of the equipment, resulting in scaling and blockage, which will eventually reduce the desulfurization efficiency and affect the stable operation of the system. As a result of using high-sulfur coals, the lack of oxidation capacity will lead to scaling and blockage of the desulfurization tower. Therefore, adding catalytic oxidation additives is a necessary step to ensure the normal operation of desulfurization system.
To promote the catalytic oxidative desulfurization, many catalysts have been researched, including metal oxides such as Fe2O3 [6,7], which has also been proven to play an important catalytic role in converting sulfite into sulfate, titanium containing porous materials [8,9], reduced graphene oxide [10,11,12], and metal organic frameworks (MOFs) [13,14,15,16,17,18]. Among them, MOFs have attracted much attention because of variable metal centers, high specific surface areas, and large pore volumes. MOFs are crystalline porous materials composed of organic ligand linked secondary building units (SBU), which exhibit both the rigidity of inorganic compounds and the flexibility of organic ligands. In addition, the abundant metal centers in MOFs can also provide a large number of catalytic active centers for chemical reactions. Because Fe3+ has been proven to have high catalytic oxidation activity [6,7], catalytic oxidation additives based on Fe3+ containing MOFs are very promising [19,20,21].
Researchers have explored the catalytic oxidation performance and mechanism of several Fe-based MOFs [22,23,24]. For example, iron-based MOFs exhibited high catalytic activity because of large amount of LASs and abundant pores, which are favorable for fast mass transfer [22]. Iron-based MIL-88A(Fe) showed an excellent catalytic ozonation activity due to the existence of large amount of LASs, where O3 was catalytically decomposed to reactive oxygen species at the surface LASs of MIL-88A(Fe) [23]. Additionally, MIL-100(Fe) exhibited better catalytic activity than that of commercial Fe2O3 in the selective catalysis of H2S to sulfur. DFT calculation indicated that the difference is due to the discrepancy in the amount of LASs [24]. Thus, the Lewis acid sites (LASs), which originated from the coordinated unsaturated metal sites in MOFs, are the active centers to promote the oxidation of the catalytic substrate. Therefore, the regulation of LASs has been proven to be an effective method to regulate the catalytic oxidation activity of Fe-based MOFs [21]. Although previous work such as ligand modification [25] and metal doping [21,26] have been proven feasible, convenient and efficient regulation of MOFs is still a challenge.
In this study, we selected MIL-53(Fe) (Fe(OH)BDC·xH2BDC, H2BDC is terephthalic acid) as the catalytic oxidation additives of Ca(OH)2. We hope that the composite desulfurizer prepared by combining MIL-53(Fe) and Ca (OH)2 can improve the catalytic oxidation rate of sulfite, prevent the scaling of desulfurization tower caused by high sulfur–coal environment, and improve the desulfurization efficiency at the same time. To increase the LASs of MIL-53(Fe), we replaced some terephthalic acid ligands with benzoic acid during the preparation process to generate more LASs through coordination defects of Fe atoms and improve the catalytic activity. Although benzoic acid vapor is irritating, it will form a stable coordination bond with iron atom, and the prepared complex will not decompose during the wet desulfurization process and pollute the environment [27]. While the use of MIL-53(Fe)-BA increase some costs, the high stability in the slurry assures its recycling in the desulfurization tower and environmental friendliness. Therefore, this technology exhibits the potential application prospect in the wet desulfurization industry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Calcium hydroxide slurry (30 wt.%) was supplied by Guangdong Energy Group Science and Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China), with particle size of less than 10 μm, and an SSA of 28.79 m2/g. The 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (AR), benzoic acid (AR), FeCl3·6H2O (AR), Na₂S₂O₃ (AR), hydrochloric acid (AR), iodine (AR), methanol (AR) and DMF (AR) were purchased from Aladdin Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) and used without further treatment.
2.2. Preparation of MIL-53(Fe)
FeCl3·6H2O (0.675 g) and 1,4-terephthalic acid (0.206 g) were mixed in 15 mL DMF. Then, the resulting mixture was poured into a 50 mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined stainless steel autoclave. After that, the autoclave was placed into an oven at 150 °C for 15 h. After cooling to room temperature, the obtained samples were washed with deionized water and soaked in ethanol for 24 h. Finally, an orange sample was obtained after the vacuum drying for 24 h (vacuum: 50 mbar, temperature: 60 °C).
2.3. Preparation of MIL-53(Fe)-BA
MIL-53(Fe)-BA was obtained with a slight modification of the preparation method of MIL-53(Fe). Typically, 0.038 g benzoic acid was added dropwise into the mixture of FeCl3·6H2O and 1,4-terephthalic acid. After the vacuum drying, the orange-colored MIL-53(Fe)-BA was obtained.
2.4. Preparation of MIL-53(Fe)/Ca (OH)2 Desulfurizers
The mass ratio of MIL-53(Fe) and Ca(OH)2 was controlled to be 1%, 2% and 3% respectively, and then appropriate amount of MIL-53(Fe) was added to 6.25 wt.% Ca (OH)2 slurry. MIL-53(Fe)/Ca(OH)2 desulfurizers were obtained after 1 h sonication. The mass percentage of MIL-53(Fe) refers to 3% unless otherwise specified in this paper.
2.5. Preparation of MIL-53(Fe)-BA/Ca (OH)2 Desulfurizers
The mass percent of MIL-53(Fe)-BA in the composite of MIL-53(Fe)-BA/Ca(OH)2 was controlled to be 1 wt.%, 2 wt.%, and 3 wt.%, and then the appropriate amount of MIL-53(Fe)-BA was added to 6.25 wt.% Ca(OH)2 slurry. MIL-53(Fe)-BA/Ca(OH)2 desulfurizers were obtained after 1 h sonication. The mass percentage of MIL-53(Fe)-BA refers to 3 wt.% unless otherwise specified.
2.6. Characterization
The morphologies of MOFs and desulfurizers were observed on a scanning electron microscope (SEM, JSM-7500F) using an accelerating voltage of 200 kV. The crystal structure was verified by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD, D/MAX2200 Rigaku) using Cu Ka (1.541 Å) as the radiation source. The intensity data were collected over a 2-theta range of 5°~60° with a step size of 0.02° using a counting time of 0.2 s per point. The tested data were analyzed by JADE 6.0 software. XRD samples were prepared according to the following steps. First, grind the desulfurizer with a mortar, and then add the powder to the middle of the groove of the sample rack to make the loose sample powder slightly higher than the plane of the sample rack. Then press the surface of the sample gently using a glass slide, so that the surface of the powder is scraped flat and is consistent with the plane of the frame, and scrape off the excess powder that is not in the groove. FT-IR was recorded in KBr pellet technique with a PerkinElmer Spectrum 100 Fourier transform spectrometer.
2.7. Catalytic Oxidation of Calcium Sulfite
The catalytic oxidation of calcium sulfite experiment was carried out on the experimental setup shown in Figure 1. A beaker was used as the reactor, and 6.25 wt.% Ca(OH)2 slurry was used as the main desulfurizer. The temperature of the water bath was set to 50 °C, and the pH value of the slurry was continuously monitored by ZD-2 pH titrator. First, Ca(OH)2 slurry was poured into the beaker, then the reactor was sealed with plastic wrap. N2 was injected into the reactor to remove the air to prevent the oxidation of CaSO3 in the slurry. After that, SO2 was injected into the beaker until the pH value of the slurry lowered to 5.5. When pH was stable, the gas was changed from SO2 to compressed air (0.1 m3/h), and the SO32− concentration at this time was set as the initial concentration. Subsequently, samples were taken out at every 10 min interval to analyze the SO32− concentration in the slurry. The whole oxidation process lasts for 1 h.
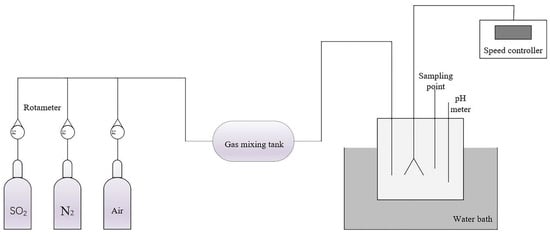
Figure 1.
Scheme of calcium sulfite catalytic oxidation experiment.
The concentration of SO32− is determined by iodometric method. First, 20 mL of iodine solution with a concentration of 0.05 mol/L was added to 10 mL slurry from the reactor. To the resulting mixture, 5 mL of hydrochloric acid (1 + 4) solution was added to provide the acidic environment required for the reaction. Then, the mixture was kept in the dark for 5 min. Second, 0.05 mol/L Na2S2O3 solution was used to titrate the solution until the pale yellow color disappeared. The Na2S2O3 volume consumed during each titration V1 was recorded. Third, the blank test of distilled water was carried out in the same way. Thus, the concentration of CaSO3 (c) was calculated according to Equation (3).
where V1 is Na2S2O3 volume consumed for the titration of sample containing SO32− (mL), and V2 is Na2S2O3 volume consumed for the titration of distilled water (mL). M is concentration of Na2S2O3 (mol/L), and V is the sample volume (mL).
The oxidation percentage (Xt) of sulfite after t mins was calculated according to Equation (4).
where Δ is the difference of calcium sulfite concentration between a certain time and the initial time, and is the initial concentration of sulfite.
2.8. Desulfurization Process
The desulfurization efficiency was assessed on the desulfurization tower shown in Figure 2, which simulates the typical limestone–gypsum WFGD process. The diameter of the desulfurization tower and the reaction tank at the bottom are 160 mm and 420 mm, respectively. The distance between four spray layers is 180 mm. The flue gas flow was set to 15 m3/h, the SO2 concentration at the inlet was 2000~5000 mg/m3, the liquid–gas ratio was 6~16 L/Nm3, and the desulfurization liquid was 6.25 wt.% Ca(OH)2 slurry containing MIL-53(Fe)-based additives. The air pumped by the fan and the SO2 (purity > 99.999%) from the steel cylinder were mixed by the gas mixer and entered the desulfurization tower through the bottom, which was in reverse contact with the Ca(OH)2 slurry uniformly sprayed from the top of the desulfurization tower, and the purified flue gas was discharged from the top of the tower. Two mechanical agitators were installed on the reaction pool at the bottom of the tower to mix the slurry evenly. SO2 concentration was monitored in real time by BH-4/BH-90 flue gas analyzer, and the pH value of slurry was measured in real time by Mettler Toledo FE28 pH meter. SO2 gas flow, air flow, and circulating slurry flow were measured by D08-3F mass flowmeter, GL10-15F rotameter, and LZB-6 rotameter, respectively.
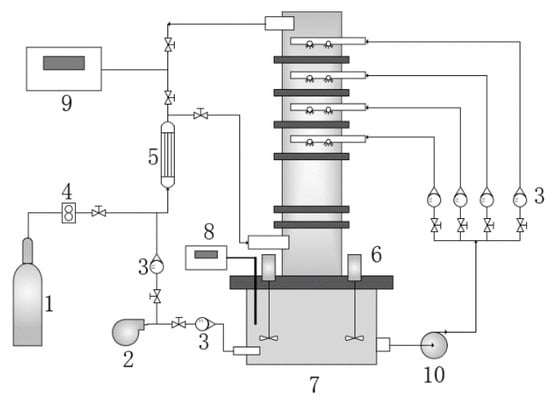
Figure 2.
Scheme of desulfurization tower. 1—SO2 cylinder, 2—blower, 3—rotor flowmeter, 4—mass flowmeter, 5—gas mixer, 6—mechanical agitator, 7—spray tower, 8—pH meter, 9—flue gas analyzer, 10—slurry circulating pump.
The desulfurization performance of Ca(OH)2 and composite desulfurizers containing Ca(OH)2 and MIL-53(Fe)-based catalytic oxidation additives were studied under the con-ditions of different additive dosage, different liquid–gas ratio, and different SO2 inlet con-centration. The desulfurization efficiency is calculated according to Equation (5).
where ηSO2 is desulfurization efficiency (%), is the inlet SO2 concentration (mg/m3), and is the outlet SO2 concentration (mg/m3).
3. Results and Discussion
Lewis acid sites (LASs) of MIL-53(Fe) were modulated using benzoic acid as modulator (Figure 3). During the crystal formation process, benzoic acid can partly replace H2BDC. As a result, defects were formed in the crystal structure around some Fe atoms, which caused coordinationally unsaturated metal sites, while the crystal frame was retained. This modulation also improved the pore sizes since the adjoining pores can be merged together, which is favorable for the exposure of catalytic LASs and fast mass transport [28,29].
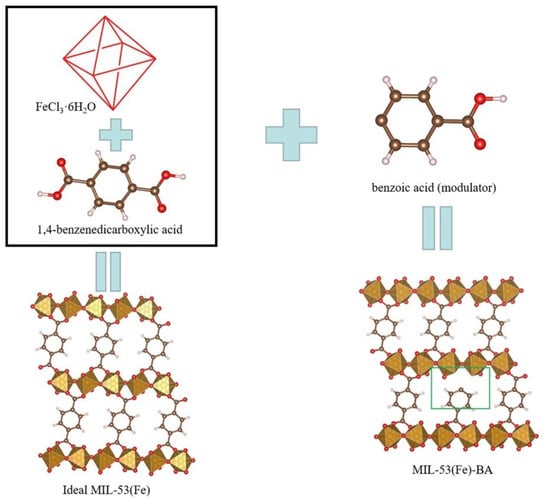
Figure 3.
Scheme for the synthesis of defective MIL-53(Fe)-BA using benzoic acid as modulator.
The SEM image of MIL-53(Fe) is shown in Figure 4a, which exhibits irregular bulky morphology in the size range of 2~10 µm. After the addition of benzoic acid, the shape and size of MIL-53(Fe)-BA remains basically the same as MIL-53(Fe), indicating there is no obvious change in the morphology (Figure 4b). Pure Ca(OH)2 desulfurizer with average particle size in the range of 100~200 nm (Figure 4c) is much smaller than that of traditional industrial limestone (typically 44 µm) [2], signifying the fast reaction with SO2. After the mixture of MIL-53(Fe)-BA with Ca(OH)2, we can see that MIL-53(Fe)-BA crystals were surrounded by nanoparticles of Ca(OH)2 (Figure 4d), which is favorable for the catalytic reaction of Fe3+, and generated sulfite from Ca(OH)2 and SO2 [25].
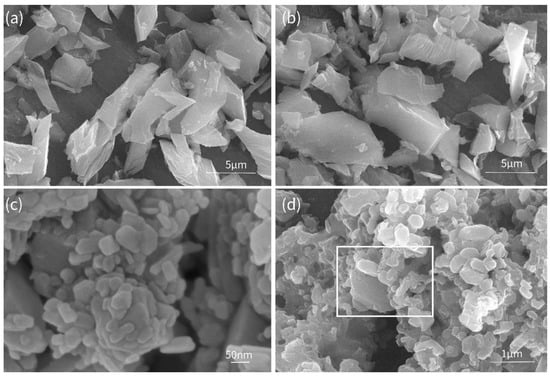
Figure 4.
SEM images of modified MIL-53- and new Ca (OH)2-based desulfurizers. (a) MIL-53(Fe), (b) MIL-53(Fe)-BA, (c) Ca(OH)2, and (d) MIL-53(Fe)-BA/Ca (OH)2.
It can be seen from Figure 5 that the characteristic diffraction peaks of MIL-53(Fe) appear at 5.89°, 9.21°, 11.46°, 12.65°, 17.61°, 18.56°, 25.41° and 28.01° respectively, which are consistent with the peak positions of the standard MIL-53(Fe) spectrum [30]. There is no obvious impurity peak in the XRD, indicating that pure phase of MIL-53(Fe) was formed. The sharp diffraction peaks assure that the prepared MOFs have high crystallinity. The XRD diffraction pattern of MIL-53(Fe)-BA synthesized by adding benzoic acid is basically consistent with that of MIL-53(Fe), indicating that the addition of benzoic acid has not changed the crystal shape of MIL-53(Fe), which further supports the SEM observation. Only a tiny peak at 10.5° hints a little change of crystal growth direction, which was reported before for the Fe-based MOFs [31]. The pure Ca(OH)2 desulfurizer exhibits characteristic diffraction peaks at 17.96°, 28.62°, 34.04°, 47.00°, 50.74°, and 54.34° [3]. After the mixture of MIL-53(Fe)-based catalytic oxidation additives and Ca(OH)2 desulfurizer, the characteristic peaks of MIL-53(Fe)-BA/Ca (OH)2 desulfurizers are very similar to those of Ca(OH)2, except a tiny peak at 12.65° proving the existence of a small percent of MIL-53(Fe)-BA additive.
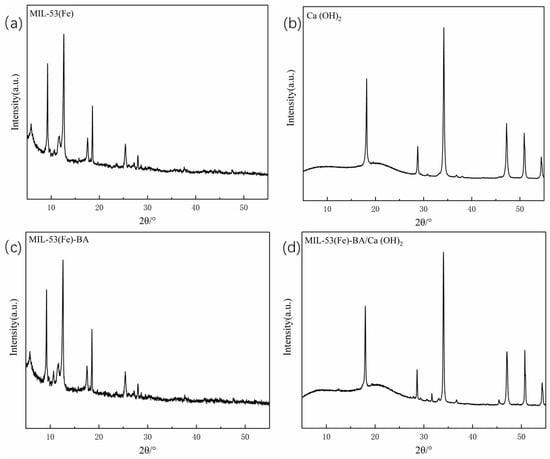
Figure 5.
The XRD patterns of the synthesized MIL-53(Fe)-based additives and new desulfurizers. (a) MIL-53(Fe), (b) Ca(OH)2, (c) MIL-53(Fe)-BA, and (d) MIL-53(Fe)-BA/Ca(OH)2.
FT-IR spectra of MIL-53(Fe)-based additives and desulfurizers are shown in Figure 6. The peaks at 748 cm−1 and 1017 cm−1 are attributed to the C–H bending vibration and out of plane bending vibration of the aromatic rings. The peak at 1380 cm−1 is attributed to the C–H bending vibration, while 1582 cm−1 is caused by the C=C skeleton vibration of aromatic rings [31]. After the modulation, a new peak at 1682 cm−1 appeared, which is attributed to the successful introduce of carboxyl group of benzoic acid [27,30,31]. As for Ca(OH)2 and MIL-53(Fe)-BA/Ca(OH)2 desulfurizers, the typical characteristic peaks at 860 cm−1, 1640 cm−1, and 1400–1500 cm−1 justified the presence of Ca(OH)2 [3,4].
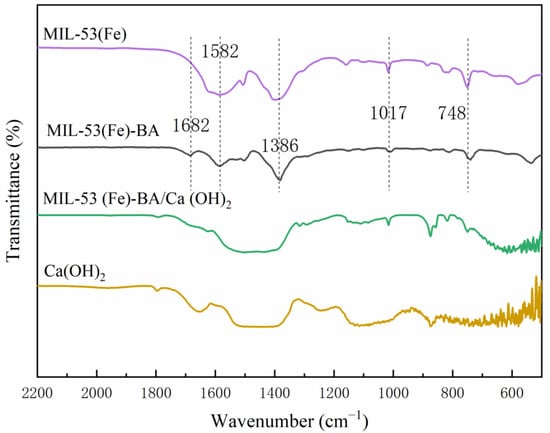
Figure 6.
The FT-IR spectra of the synthesized MIL-53(Fe)-based additives and new desulfurizers.
Assessment of catalytic oxidation is based on the setup shown in Figure 1. The ventilation capacity, water bath temperature, pH, and agitation strength are adjustable parameters, which can simulate the environment of catalytic oxidation of sulfite. As shown in Figure 7, when there is no additive, the oxidation percentage of sulfite after 60 min was as low as 27%. After adding MIL-53(Fe)-based additives, the oxidation percentage increased to 55% and 70% for MIL-53(Fe) and MIL-53(Fe)-BA, respectively. For MIL-53(Fe)-BA, the oxidation capacity increased by 159%. The total oxidation rate of calcium sulfite involves the oxygen diffusion rate Rc, the dissolution rate Rb, and the intrinsic oxidation rate Ra. Without catalyst, the total oxidation rate is controlled by Rb and Rc. According to the free radical reaction mechanism of Bäckstrom catalytic oxidation [32], under the catalytic condition of MIL-53(Fe), SO32− reacts with oxygen molecules under acidic conditions to form , thereby triggering the free radical chain reaction, accelerating the mass transfer process of oxygen, greatly improving the intrinsic oxidation Ra, and finally improving the total oxidation reaction rate R. This is also consistent with the result of sulfite oxidation promoted by Cobalt-based metal–organic frameworks [32]. In addition, the catalytic oxidation activity of MIL-53(Fe)-BA is better than that of MIL-53(Fe). The main reason is that through the coordination of benzoic acid, more LASs are formed around the iron atom. LASs can act as electron acceptors to adsorb the sulfur atoms with electron-rich properties in sulfite, thus improving the catalytic oxidation efficiency [20,29]. The significant improvement of oxidation ability guarantees sufficient conversion of sulfite in the slurry tank to sulfate, thus greatly reducing the scaling risk [27,33].
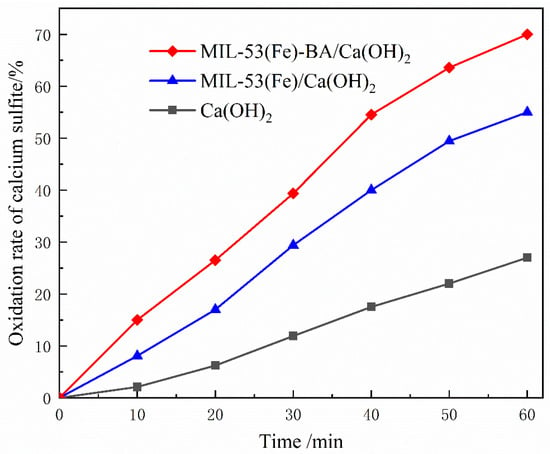
Figure 7.
Catalytic oxidation of sulfite by MIL-53(Fe)-based additives.
To verify the beneficial effects of as-prepared additives under the actual WFGD conditions, a series of desulfurization experiments were carried out on the simulated laboratory-scale desulfurization tower (Figure 2), including the effects of additive content, liquid–gas ratio, and inlet SO2 concentration.
The desulfurization efficiency and cost should be comprehensively considered for the use of additives. Increasing the dosage of additives will not only increase the desulfurization efficiency, but also bring high costs. Therefore, there should be an optimal dosage of additives. For both MIL-53(Fe) and MIL-53(Fe)-BA, when the additive dosage was less than 3 wt.%, the desulfurization efficiency increased almost linearly with the increase of additive (Figure 8). For MIL-53(Fe), the desulfurization efficiency increased from 89.2% to 95.0%. The rapid improvement of desulfurization efficiency is due to the high specific surface area of MIL-53(Fe), which provides many Fe3+ active sites. In contrast, for MIL-53(Fe)-BA, the desulfurization efficiency increased significantly from 89.2% to 99.1%. The high desulfurization efficiency is comparable to the state-of-the-art technology of coupling WFGD with condensation desulfurization using a condensing heat exchanger [34]. This further improvement of desulfurization efficiency was due to the presence of more LASs in MIL-53(Fe)-BA after benzoic acid modification, which greatly improved the desulfurization efficiency [31,35]. When the catalyst concentration continued to increase over 3%, we found that the increase in desulfurization efficiency slowed down. In the typical WFGD process, the mechanism of the sulfite oxidation is coordination catalytic oxidation of free radicals [36]. Fe3+ reacts with the substrate to form dihydroxy iron and dimeric dihydroxy iron complexes, which react with SO32− under the environment of O2 to form , thus initiating the free radical reaction [36]. According to Barron’s experiments, the total reaction rate is controlled by the chain transfer [37]. When the content of additives reaches 3%, enough free radicals have been formed in the system. Therefore, increasing the content of additives has little effect on the further improvement of desulfurization efficiency.
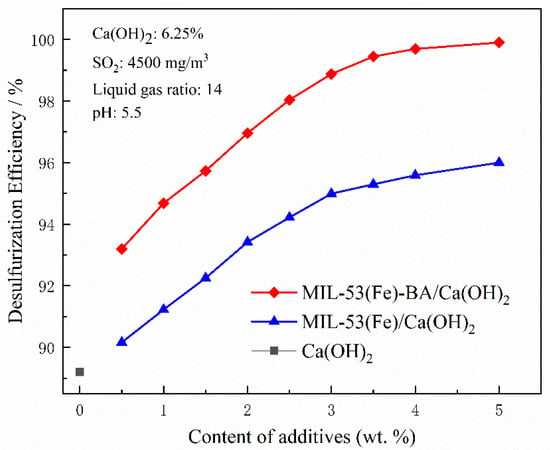
Figure 8.
Effect of additive amount on desulfurization efficiency.
Liquid–gas ratio is another important operating parameter of WFGD, and its value is directly related to the performance and economy of WFGD. SO2 in the flue gas contacts with more desulfurizers when the liquid–gas ratio increases, thus increasing the reaction probability between SO2 and Ca(OH)2, and improving the desulfurization efficiency. At the same time, the load of the circulating slurry pump increases, the corresponding power consumption increases, and the operation cost increases. Here, the liquid–gas ratio is changed by changing the number of spray layers. The desulfurization efficiency of the system under different liquid–gas ratios is shown in Figure 9: when the liquid–gas ratio increases from 10 to 20, the desulfurization efficiency is greatly improved whether additives are added or not. Under the same liquid–gas ratio, the addition of additives significantly improves the desulfurization efficiency. The lower the liquid–gas ratio, the more obvious the effect of additives. Compared with MIL-53(Fe), MIL-53(Fe)-BA exhibited higher desulfurization efficiency because of more Lewis acid sites [31]. We also noticed that when Ca(OH)2 is used as desulfurizer, the liquid–gas ratio needed is lower than that of traditional CaCO3, which decreased by ~23% [38]. The main reason is that Ca(OH)2 has stronger alkalinity and faster reaction speed than limestone. After adding MIL-53(Fe) additive, the required liquid–gas ratio is further reduced, which greatly reduces the energy consumption of the power plant.
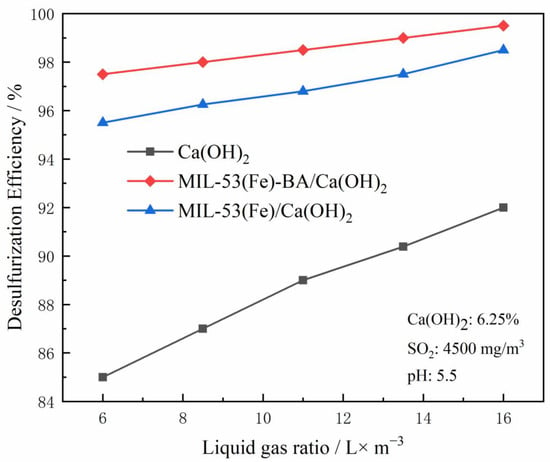
Figure 9.
Effect of liquid–gas ratio on desulfurization efficiency.
For desulfurization, whether it can adapt to various SO2 concentrations is an important evaluation parameter. The change of desulfurization efficiency under different SO2 concentrations is shown in Figure 10. With the increase of SO2 concentration at the inlet, the desulfurization efficiency decreases, especially for the desulfurizers without additives. When the inlet SO2 concentration was increased from 2000 mg/m3 to 4500 mg/m3, the desulfurization efficiency of pure Ca(OH)2 was reduced from 94.0% to 90.2%, decreased by 3.8%. This is because when the concentration of SO2 at the inlet increases, the concentration of calcium bisulfite in the slurry droplets increases, which hinders the absorption of sulfur dioxide. After adding MIL-53(Fe), the desulfurization efficiency was reduced from 99.1% to 97.5%, decreased by 1.6%, while the desulfurization efficiency of MIL-53(Fe)-BA decreased from 99.9% to 99.1%, only decreased by 0.8%. Increasing the inlet SO2 concentration will reduce the pH value of the gas–liquid interface and reduce the oxidation rate of sulfite. Thus, after the introduction of MIL-53-based additives, the desulfurization efficiency was increased because of the increased oxidation rate. Therefore, MIL-53(Fe)-BA with higher activity can more effectively offset the reduction of desulfurization efficiency.
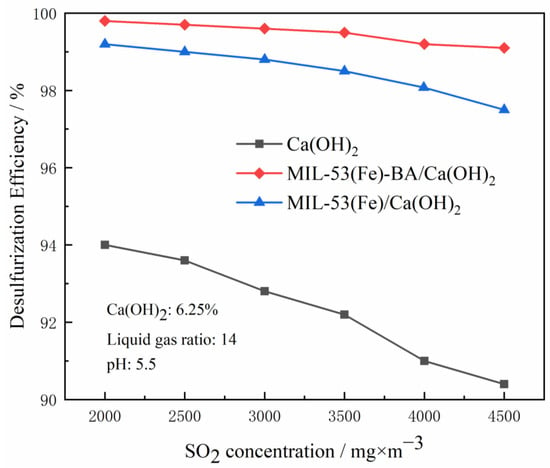
Figure 10.
Effect of SO2 concentrations on desulfurization efficiency.
4. Conclusions
In general, an efficient catalytic oxidation additive was prepared by modifying MIL-53(Fe) with benzoic acid. Compared to pure Ca(OH)2 slurry, the addition of MIL-53(Fe)-BA improved the oxidation capacity of SO32− by 159%, which can effectively reduce the risk of scaling in a desulfurization tower caused by high sulfur–coal environment. When the dosage was 3 wt.%, the desulfurization efficiency increased from 89.2% to 99.1%. MIL-53(Fe)-BA also exhibited superior desulfurization efficiency even in high concentration of SO2. Under the same liquid–gas ratio, additive dosage, and SO2 concentration, the desulfurization behavior of MIL-53(Fe)-BA was better than that of MIL-53(Fe) because of the introduction of Lewis acid sites, which greatly improved the catalytic performance and desulfurization efficiency. Thus, the use of Fe-based MOFs in the preparation of Ca(OH)2-based desulfurizers is an easy and good method to improve their desulfurization capacity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.C.; Data curation, S.L., C.Y. and S.P.; Formal analysis, Z.W.; Investigation, D.Z.; Resources, F.-Q.L.; Writing—original draft, Y.Y.; Writing—review & editing, F.-Q.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (52073311) and Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2020A1515011274 and 2021A1515012281).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, Z.T.; Dong, K.; Tian, L.; Zhan, S.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Tu, J.Y. Numerical analyses of sulfur dioxide transport by an atmospheric circulating drop. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Zhou, X.C.; Yang, L.J.; Sun, Z.Q.; Wu, H. Emission Characteristics of Soluble Ions in Fine Particulates in Limestone-Gypsum Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization System. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 3836–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, G.; Reissner, H.K.; Staudinger, G. Cyclic activation of calcium hydroxide for enhanced desulfurization. Chem. Eng. Process. 2002, 41, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renedo, M.J.; Fernandez-Ferreras, J. Characterization and Behavior of Modified Calcium-Hydroxide-Based Sorbents in a Dry Desulfurization Process. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 6350–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendel, P.M.; Gavrieli, I.; Wolff-Boenisch, D.; Ganor, J. Towards establishing a combined rate law of nucleation and crystal growth—The case study of gypsum precipitation. J. Cryst. Growth 2018, 485, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.J.; Wang, T.; Cheng, L.; Li, C.Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.C. Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO by CO reduction over prevulcanized Fe2O3/AC catalysts. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 2015–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Huang, T.; Jiang, X.; Li, J.J.; Jiang, W.J. The effects of metal oxide blended activated coke on flue gas desulphurization. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 55135–55143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, Z.P.; Ren, J.T.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Z.Y. Efficient oxidative desulfurization over highly dispersed molybdenum oxides supported on mesoporous titanium phosphonates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 315, 110921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilian, Z.; Chermahini, A.N.; Momeni, M.M.; Sarpiri, J.N.; Motalebian, M. A new catalytic system for oxidative desulfurization of model diesel by hierarchical TiO2 nanotube arrays on titanium foil. J. Porous Mater. 2021, 28, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.C.; Ng, S.F.; Ong, W.J. Life cycle assessment of environmental impacts associated with oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuels catalyzed by metal-free reduced graphene oxide. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, A.; Saeed, M.; Munir, M.; Intisar, A.; Haider, S.; Tariq, S.; Hussain, N.; Kousar, R.; Bilal, M. Development of reduced graphene oxide-supported novel hybrid nanomaterials (Bi2WO6@rGO and Cu-WO4@rGO) for green and efficient oxidative desulfurization of model fuel oil for environmental depollution. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimu, A.; Tanimu, G.; Ganiyu, S.A.; Gambo, Y.; Alasiri, H.; Alhooshani, K. Metal-Free Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization of Fuels-A Review. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 3394–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.F.; Liu, S.T.; Shi, H.F.; Wang, W.D. Phosphomolybdic acid-based sulfur-containing metal-organic framework as an efficient catalyst for dibenzothiophene oxidative desulfurization. J. Sulfur Chem. 2022, 43, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, M.Y.; Dai, B. An amino functionalized zirconium metal organic framework as a catalyst for oxidative desulfurization. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 9785–9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.X.; Que, W.B.; Shen, X.H.; Yin, R.L.; Xu, X.L.; Zheng, D.; Feng, J.X.; Dai, X.J.; Niu, X.X.; Wu, F.F.; et al. Unlocking active metal site of Ti-MOF for boosted heterogeneous catalysis via a facile coordinative reconstruction. Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 025401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.T.; Yang, P.; Li, N.; Fan, Y. Defective MIL-125 Nanocrystals with Enhanced Catalytic Performance for Oxidative Denitrogenation. J. Cluster Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, F.M.; Shahhosseini, S.; Rezaee, M. Cobalt-based sandwich-type polyoxometalate supported on amino-silane decorated magnetic graphene oxide: A recoverable catalyst for extractive-catalytic oxidative desulfurization of model oil. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, A.R.; Ma, Y.L.; Qing, S.L. Preparation of formate-free PMA@MOF-808 catalysts for deep oxidative desulfurization of model fuels. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 39427–39440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allers, T.; Luckas, M.; Schmidt, K.G. Modeling and Measurement of the Dissolution Rate of Solid Particles in Aqueous Suspensions—Part II: Experimental Results and Validation. Chem. Eng. Technol 2003, 26, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Huo, W.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, Z.Y.; Cen, K.F.; Ni, M.J.; Chen, L.M. Effects of Magnesium and Ferric Ions on Crystallization of Calcium Sulfate Dihydrate Under the Simulated Conditions of Wet Flue-gas Desulfurization. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2008, 24, 688–693. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.Y.; Wang, L.P.; Yang, T.Y.; Yang, G.P.; Wang, D.; Ni, H.G.; Wu, M.H. Tuning Lewis acidity of iron-based metal-organic frameworks for enhanced catalytic ozonation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 127075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.Y.; Wu, M.H.; Hu, Q.; Wang, L.L.; Lv, C.C.; Zhang, L. Iron-based metal-organic frameworks as novel platforms for catalytic ozonation of organic pollutant: Efficiency and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 367, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.Y.; Li, L.B.; Wu, M.; Crittenden, J.C. Enhanced photocatalytic ozonation of organic pollutants using an iron-based metal-organic framework. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 251, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-X.; Fang, Z.-P.; Dai, Z.-J.; Cai, J.-M.; Shen, L.-J.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Au, C.-T.; Jiang, L.-L. Iron-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks as Platform for H2S Selective Conversion: Structure-Dependent Desulfurization Activity. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 4483–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.F.; Drake, T.; Murakarni, A.; Oliveres, P.; Skone, J.H.; Lin, W.B. Tuning Lewis Acidity of Metal-Organic Frameworks via Perfluorination of Bridging Ligands: Spectroscopic, Theoretical, and Catalytic Studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10553–10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.B.; Lu, C.M.; Guo, D.X.; Zhang, X.L.; Han, K.H. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over iron-cerium mixed oxide catalyst: Catalytic performance and characterization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.Y.; Shen, L.J.; Xu, C.B.; Zhao, W.T.; Cao, Y.N.; Jiang, L.L. MOF-derived porous Fe2O3 with controllable shapes and improved catalytic activities in H2S selective oxidation. CrystEngcomm 2018, 20, 3449–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.P.; Stenger, H.G.; Wachs, I.E. Molecular structure-reactivity relationships for the oxidation of sulfur dioxide over supported metal oxide catalysts. Catal. Today 1999, 53, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Gu, Y.; Liu, D.; Sun, Y. Advances in Oxidative Desulfurization of Fuel Oils over MOFs-Based Heterogeneous Catalysts. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Sert, E.; Atalay, F.S. Synthesis, characterization of a metal organic framework: MIL-53 (Fe) and adsorption mechanisms of methyl red onto MIL-53 (Fe). J. Taiwan. Inst. Chem. E. 2016, 65, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Qi, S.; Cao, Y.; Shen, L.; Au, C.; Jiang, L. Morphology evolution of acetic acid-modulated MIL-53(Fe) for efficient selective oxidation of H2S. Chin. J. Catal. 2021, 42, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, Q.; Xing, L.; Yang, L.J.; Qi, T.Y.; Xu, P.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, L.D. Cobalt-based metal-organic frameworks promoting magnesium sulfite oxidation with ultrahigh catalytic activity and stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 559, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.Y.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhu, B.Z. The promoting mechanism of doping Mn, Co, and Ce on gas adsorption property and anti-SO2 oxidation over gamma-Fe2O3 (001) surface: A density functional theory study. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 628, 127218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Lu, J.W.; Song, X.D.; Tang, L.S.; Li, Y.Z.; Dong, Y. Energy conservation and efficiency improvement by coupling wet flue gas desulfurization with condensation desulfurization. Fuel 2021, 285, 119209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.P.; Dou, C.Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, Z.H.; Lv, H.K. Experimental Study on SO2-to-SO3 Conversion Over Fe-Modified Mn/ZSM-5 Catalysts During the Catalytic Reduction of NOx. Catal. Surv. Asia 2019, 23, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.; Fabian, I.; van Eldik, R. Kinetics and Mechanism of the Iron(III)-catalyzed Autoxidation of Sulfur(IV) Oxides in Aqueous Solution. Evidence for the Redox Cycling of Iron in the Presence of Oxygen and Modeling of the Overall Reaction Mechanism. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, C.H.; O’Hern, H.A. Reaction kinetics of sodium sulfite oxidation by the rapid-mixing method. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1966, 21, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, K.; Luo, G.S. Effects of nanoparticles with different wetting abilities on the gas-liquid mass transfer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 114, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).