A Cogging Torque Minimization Procedure for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on a Progressive Modification of the Rotor Lamination Geometry †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Section 2 proposes an overview of the main design techniques for cogging torque minimization described in the most recent literature.
- Section 3 provides a brief analytical description of the cogging torque phenomenon.
- Section 4 describes the basic IPMSM model and reports the related FEM analysis and the cogging torque computation carried out from this model.
- Section 5 deals with the procedure of the rotor lamination modification of the basic IPMSM model, obtaining 13 other IPMSM structures. For each of the proposed models, FEM analysis and cogging torque computation are performed.
- Section 6 is focused on comparing the cogging torque between the IPMSM models and the results are analyzed and discussed.
- Section 7 reports the second example of IPMSM structure, obtaining similar promising results obtained for the first IPMSM model.
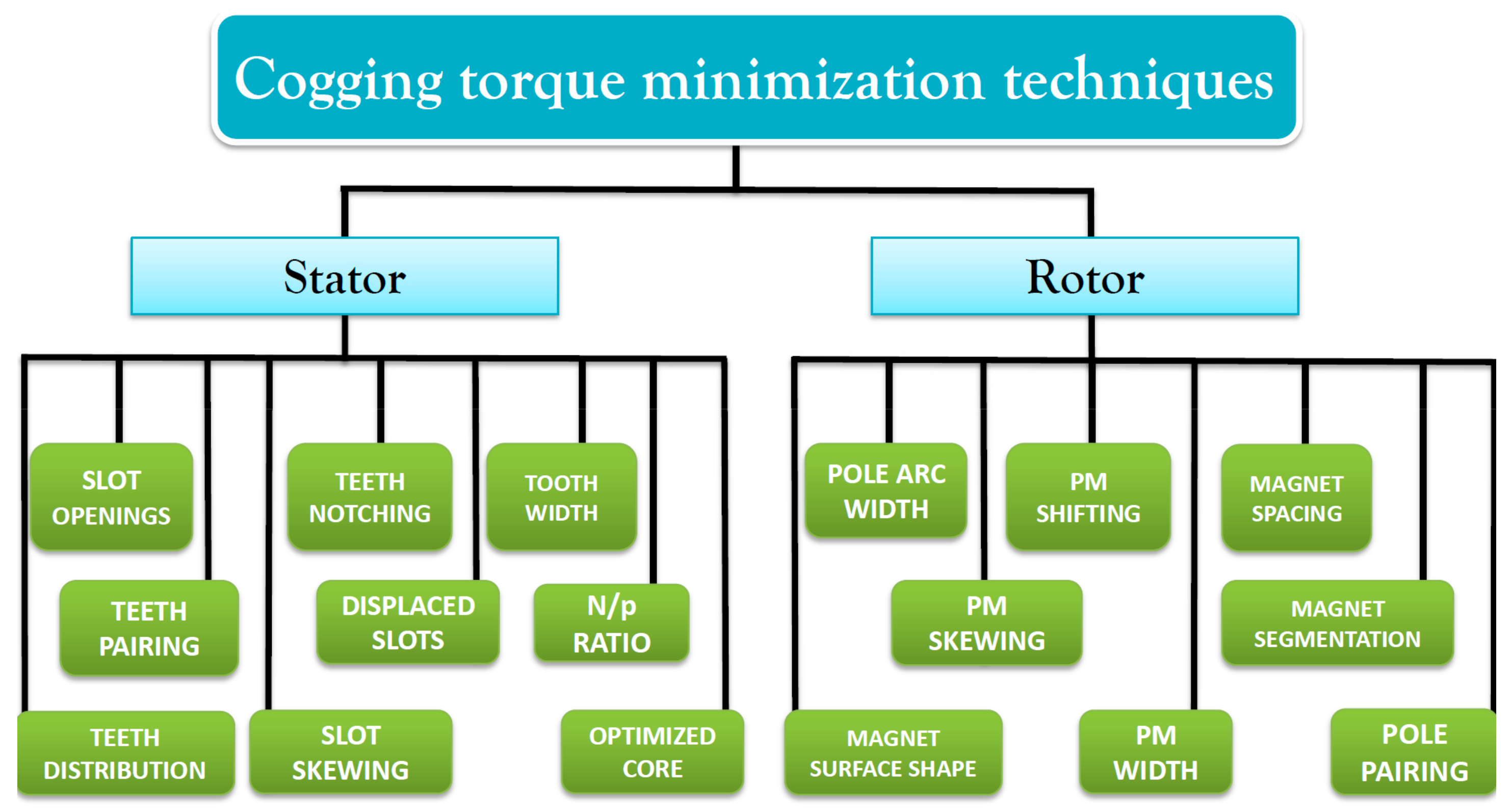
2. An Overview of the Cogging Torque Minimization Techniques
3. The Cogging Torque Phenomenon
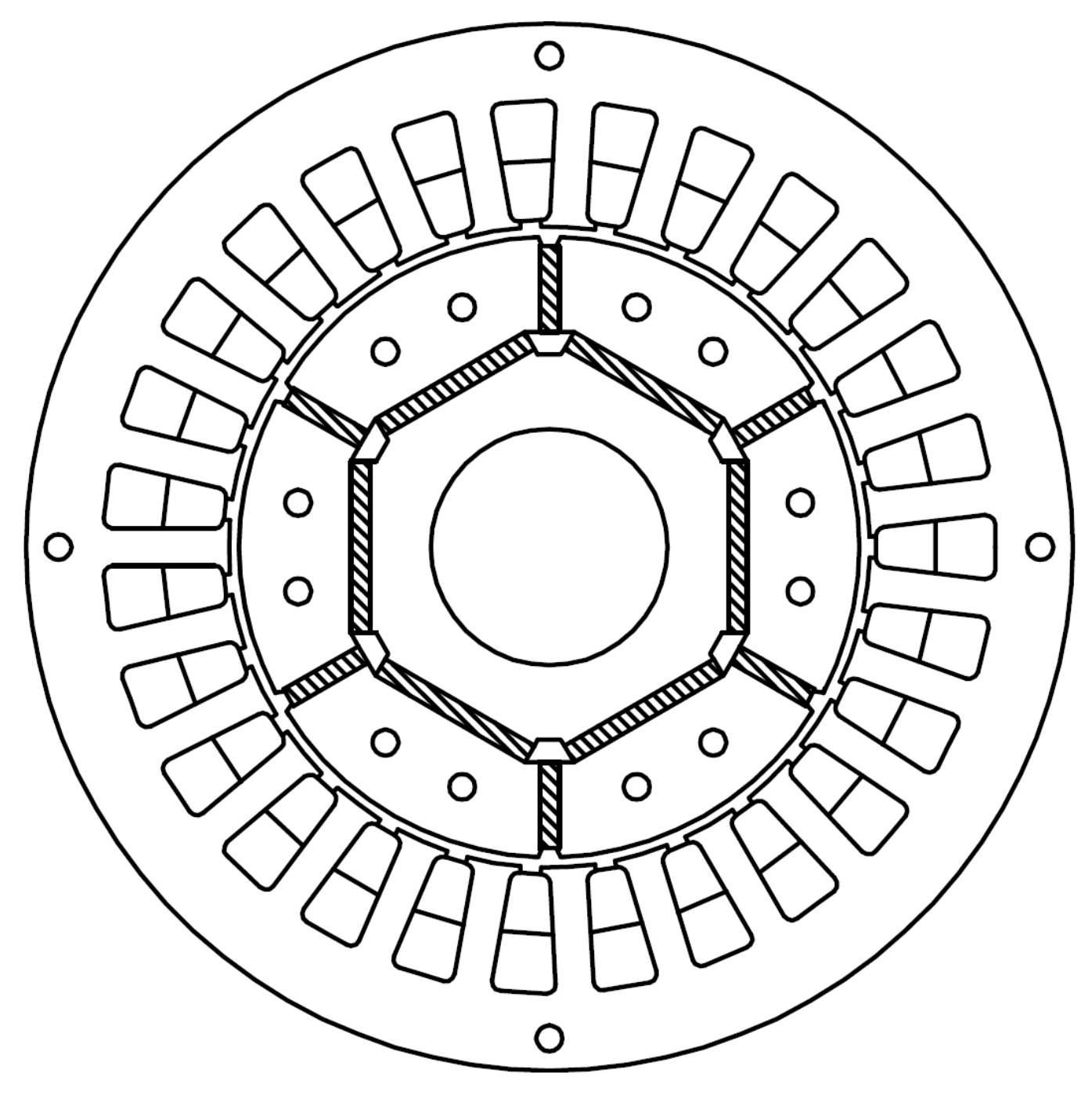
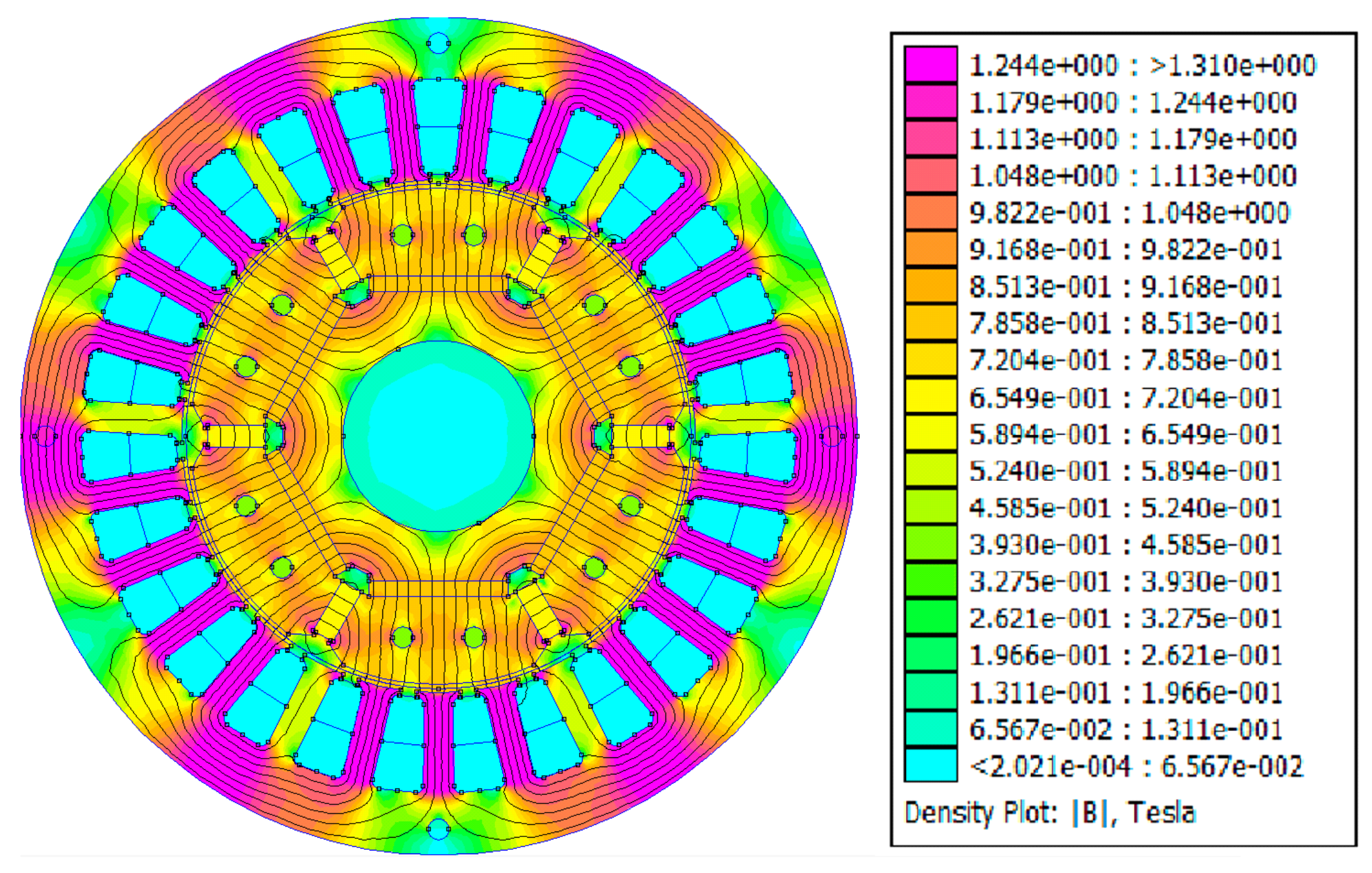
4. Basic IPMSM Structure and FEM Analysis
- pre-processing, which consists in designing the geometry of the machine, selecting the type of materials and assigning the boundary conditions.
- solution, consisting of the determination of the FEM solution of the problem.
- post-processing, which processes the solutions in terms of scalar or vector quantities.
5. The Proposed Minimization Procedure of the Cogging Torque
6. Results and Discussions
7. Investigation on Other IPMSM Structures
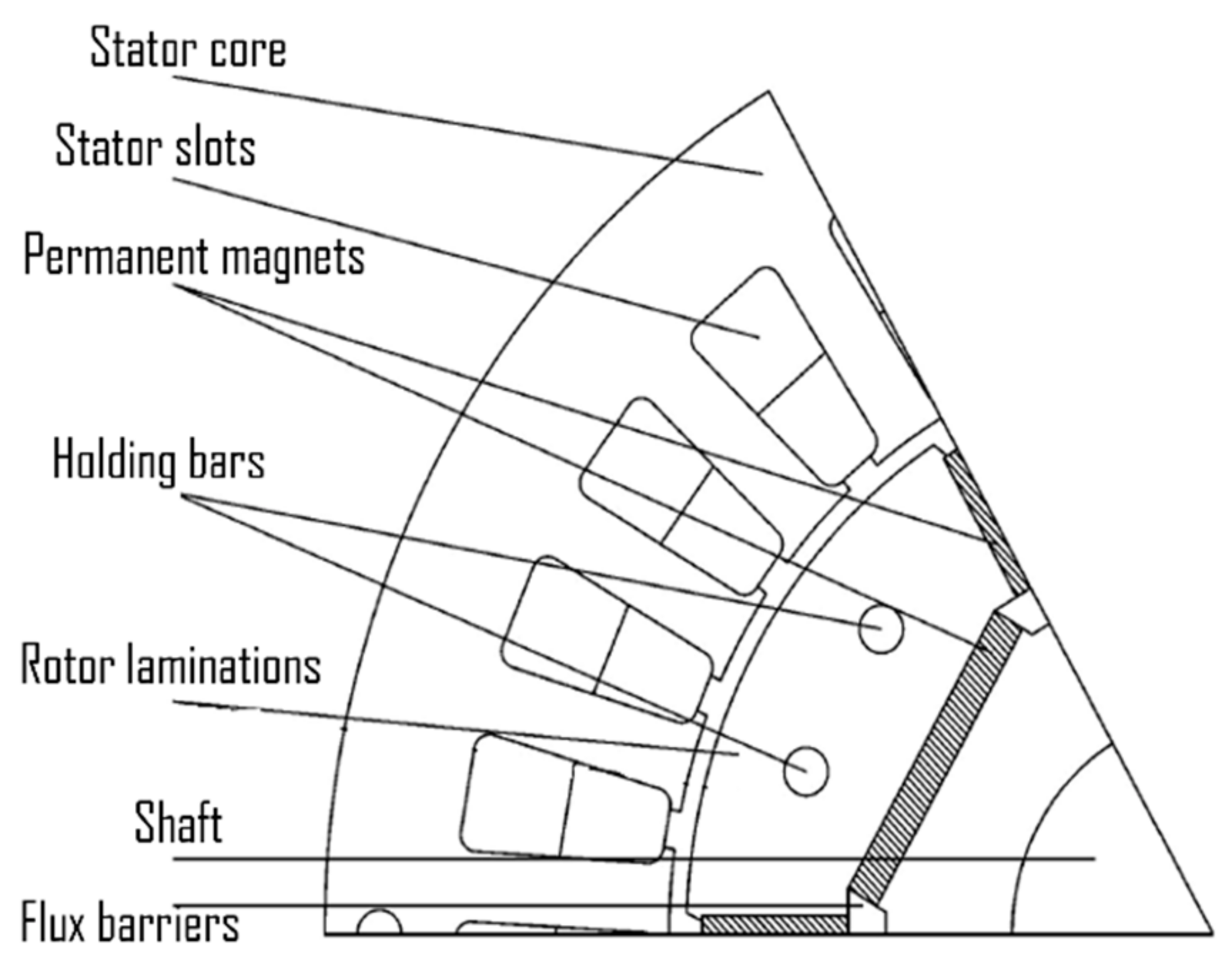
7.1. Rotor Geometry Modification
7.2. Modification of Stator Slots and Winding Arrangement
7.3. Modification of the PM Width
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| N | Number of slots |
| p | Number of pole pairs |
| Wms | Magnetic energy stored in the air-gap |
| φ | Angular position of the rotor |
| μ0 | Magnetic permeability of air |
| Bm | Magnetic flux density |
| Pm | Magnetic permeance |
| ΘPM | Magnetomotive force produced by the PMs |
| δ0 | Air-gap length |
| La | Axial length of the machine |
| R1 | Outer stator radius |
| R2 | Inner stator radius |
| t | Least common multiple between p and N |
| ask | Skew angle |
| ksk | Skew factor |
| βopt | Optimal ratio between rotor pole arc and width |
References
- Jahns, T.; Soong, W. Pulsating torque minimization techniques for permanent magnet ac motor drives-a review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 43, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogidi, P.; Barendse, S.; Khan, M.A. Influence of rotor topologies and cogging torque minimization techniques in the detection of static eccentricities in axial-flux permanent-magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Panda, S.; Xu, J.-X. Torque ripple minimization in pm synchronous motors using iterative learning control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Namuduri, C.; Mir, S. Controller induced parasitic torque ripples in a pm synchronous motor. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2000 IEEE Industry Applications Conference, Thirty-Fifth IAS Annual Meeting and World Conference on Industrial Applications of Electrical Energy (Cat. No.00CH37129), Rome, Italy, 8–12 October 2000; Volume 1, pp. 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Goryca, Z.; Różowicz, S.; Różowicz, A.; Pakosz, A.; Leśko, M.; Wachta, H. Impact of Selected Methods of Cogging Torque Reduction in Multipolar Permanent-Magnet Machines. Energies 2020, 13, 6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pristup, A.G.; Toporkov, D.M. Comparing of cogging torque reduction methods in permanent magnet machines with fractional slot windings. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 87, 032032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Slemon, G. Reduction of cogging torque in permanent magnet motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1988, 24, 2901–2903. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Xing, Z.; Yu, A.; Li, C. Reduction of cogging torque and electromagnetic vibration based on different combination of pole arc coefficient for interior permanent magnet synchronous machine. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2021, 5, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Slemon, G.R. A method of reducing ripple torque in permanent magnet motors without skewing. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 2028–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.A.; Ikram, J.; Iftikhar, A.; Bukhari, S.S.H.; Khan, N.; Ro, J.-S. Minimization of Cogging Torque in Axial Field Flux Switching Machine Using Arc Shaped Triangular Magnets. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 227193–227201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsari, S.A.; Heydari, H.; Dianati, B. Cogging torque mitigation in axial flux magnetic gear system based on skew effects using an improved quasi 3-d analytical method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjiku, J.; Khan, M.A.; Barendse, P.S.; Pillay, P. Influence of slot openings and tooth profile on cogging torque in axial-flux pm machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 7578–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorrell, D.G.; Popescu, M. Odd stator slot numbers in brushless dc machines-an aid to cogging torque reduction. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 3012–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Jiang, S.Z.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Chan, C.C. Analytical methods for minimizing cogging torque in permanent-magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 2023–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.S.; Lipo, T.A. Reducing Torque Ripple Using Axial Pole Shaping in Interior Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ming, G.; Zhang, L.; Fang, Y. Improved Stator/Rotor-Pole Number Combinations for Torque Ripple Reduction in Doubly Salient PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, W.; Luk, P.C.K. A new technique of cogging torque suppression in direct-drive permanent-magnet brushless machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 46, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.S.; Izui, K.; Nishiwaki, S.; Kawamoto, A.; Nomura, T. Topology optimization of the stator for minimizing cogging torque of ipm motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 3024–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Quan, X.; Tong, X.; Lin, M. Cogging Torque Reduction in Double-Rotor Hybrid Excited Axial Switched-Flux Permanent Magnet Machine. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2020, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.S.; Seol, J.-S. New cogging-torque reduction method for brushless permanent-magnet motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2003, 39, 3503–3506. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Influence of design parameters on cogging torque in permanent magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2000, 15, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Lei, G.; Guo, Y. Cogging torque minimization of smc pm transverse flux machines using shifted and unequal-width stator teeth. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Qiao, D.; Pei, Y.; Jung, S.Y. Reducing cogging torque in surface-mounted permanent-magnet motors by nonuniformly distributed teeth method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Lipo, T.A.; Howe, D. Minimization of cogging torque in axial-flux permanent-magnet machines: Design concepts. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 3614–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, W.; Zhu, Z. Comparison of cogging torque reduction in permanent magnet brushless machines by conventional and herringbone skewing techniques. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2013, 28, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaniszyn, M.; JagieLa, M.; Wrobel, R. Optimization of permanent magnet shape for minimum cogging torque using a genetic algorithm. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 1228–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.W.; Bilgin, B.; Yang, Y.; Sathyan, A.; Dadkhah, H.; Emadi, A. Rotor skew pattern design and optimisation for cogging torque reduction. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2016, 6, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Hua, W.; Zhang, G. Analysis and Reduction of Cogging Torque for Flux-Switching Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 5854–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Cha, H.-R. Analysis of Torque Ripple and Cogging Torque Reduction in Electric Vehicle Traction Platform Applying Rotor Notched Design. Energies 2018, 11, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Jung, S.Y. Cogging torque minimization and torque ripple suppression in surface-mounted permanent magnet synchronous machines using different magnet widths. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 2295–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simón-Sempere, V.; Simón-Gómez, A.; Burgos-Payán, M.; Cerquides-Bueno, J.-R. Optimisation of Magnet Shape for Cogging Torque Reduction in Axial-Flux Permanent-Magnet Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2825–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Ho, S.L.; Fu, W.N. Optimization of permanent magnet surface shapes of electric motors for minimization of cogging torque using fem. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2478–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulec, M.; Aydin, M. Magnet asymmetry in reduction of cogging torque for integer slot axial flux permanent magnet motors. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2014, 8, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, M.; Gulec, M. Reduction of cogging torque in doublerotor axial-flux permanent-magnet disk motors: A review of costeffective magnet-skewing techniques with experimental verification. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5025–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Lipo, T.A.; Kwon, B.I. Torque pulsation minimization in spoke-type interior permanent magnet motors with skewing and sinusoidal permanent magnet configurations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.C. A novel method for minimization of cogging torque and torque ripple for interior permanent magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Islam, R.; Sebastian, T.; Chandy, A.; Ozsoylu, S.A. Cogging torque minimization in pm motors using robust design approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Bolognani, S. Design techniques for reducing the cogging torque in surface-mounted pm motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2000, 1, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Barcaro, M.; Bianchi, N. Torque ripple reduction in fractionalslot interior pm machines optimizing the flux-barrier geometries. In Proceedings of the 2012 XXth International Conference on Electrical Machines, Marseille, France, 2–5 September 2012; pp. 1496–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, M.; di Tommaso, A.O.; Emma, S.; Miceli, R. Analysis, characterization and minimization of ipmsms cogging torque with different rotor structures. In Proceedings of the 2015 Tenth International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies (EVER), Monte Carlo, Monaco, 31 March–2 April 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Caruso, M.; Di Tommaso, A.O.; Miceli, R.; Schettino, G.; Viola, F. A cogging torque minimization procedure for IPMSMs based on different laminate geometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2016 Eleventh International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies (EVER), Monte Carlo, Monaco, 6–8 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakkoli, M.; Madani, S. A new approach to analysis and mitigation of pm motor cogging torque. In Proceedings of the 2008 34th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics, Orlando, FL, USA, 10–13 November 2008; pp. 2003–2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Lipo, T.; il Kwon, B. Dual-stator two-phase permanent magnet machines with phase-group concentrated-coil windings for torque enhancement. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, W.; Zhang, G.; Xia, C. Torque ripple minimization of pmsm using pi type iterative learning control. In Proceedings of the IECON 2014—40th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Dallas, TX, USA, 9 October –1 November 2014; pp. 925–931. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Xiao, X.; Li, Y. Torque ripple reduction of the torque predictive control scheme for permanent-magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumega, M.; Rafajdus, P.; Scelba, G.; Stulrajter, M. Control Strategies for the Identification and Reduction of Cogging Torque in PM Motors. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electrical Drives and Power Electronics (EDPE), The High Tatras, Slovakia, 24–26 September 2019; pp. 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Jiang, X.; Tu, Y.; Li, N.; Li, Q. Investigation of cogging torque reduction for a 6/10 hybrid axial field flux-switching permanent magnet machine by harmonic field current injection. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2020, 14, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgin, M.T.; Guven, M.K.; Aydin, M. A New Harmonic Current Injection Technique to Reduce Cogging Torque in Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Motors. IEEE Trans. 2022, 58, 8201304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, P.; Saponara, S. Cogging Torque Reduction in Brushless Motors by a Nonlinear Control Technique. Energies 2019, 12, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Xiang, Z.; Dai, L.; Huang, S.; Ni, D.; Yao, C. Cogging Torque Dynamic Reduction Based on Harmonic Torque Counteract. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8103405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, C.; Immovilli, F.; Lorenzani, E.; Bellini, A.; Davoli, M. Review of Design Solutions for Internal Permanent-Magnet Machines Cogging Torque Reduction. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2685–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparin, L.; Cernigoj, A.; Markic, S.; Fiser, R. Additional Cogging Torque Components in Permanent-Magnet Motors Due to Manufacturing Imperfections. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, M.; Di Tommaso, A.O.; Genduso, F.; Miceli, R.; Galluzzo, G.R. A General Mathematical Formulation for the Determination of Differential Leakage Factors in Electrical Machines with Symmetrical and Asymmetrical Full or Dead-Coil Multiphase Windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 8413120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caruso, M.; Di Tommaso, A.O.; Miceli, R.; Rizzo, R. Computer-aided analysis and design procedure for rotating induction machine magnetic circuits and windings. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, M.; Di Tommaso, A.O.; Marignetti, F.; Miceli, R.; Galluzzo, G.R. A general mathematical formulation for winding layout arrangement of electrical machines. Energies 2018, 11, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

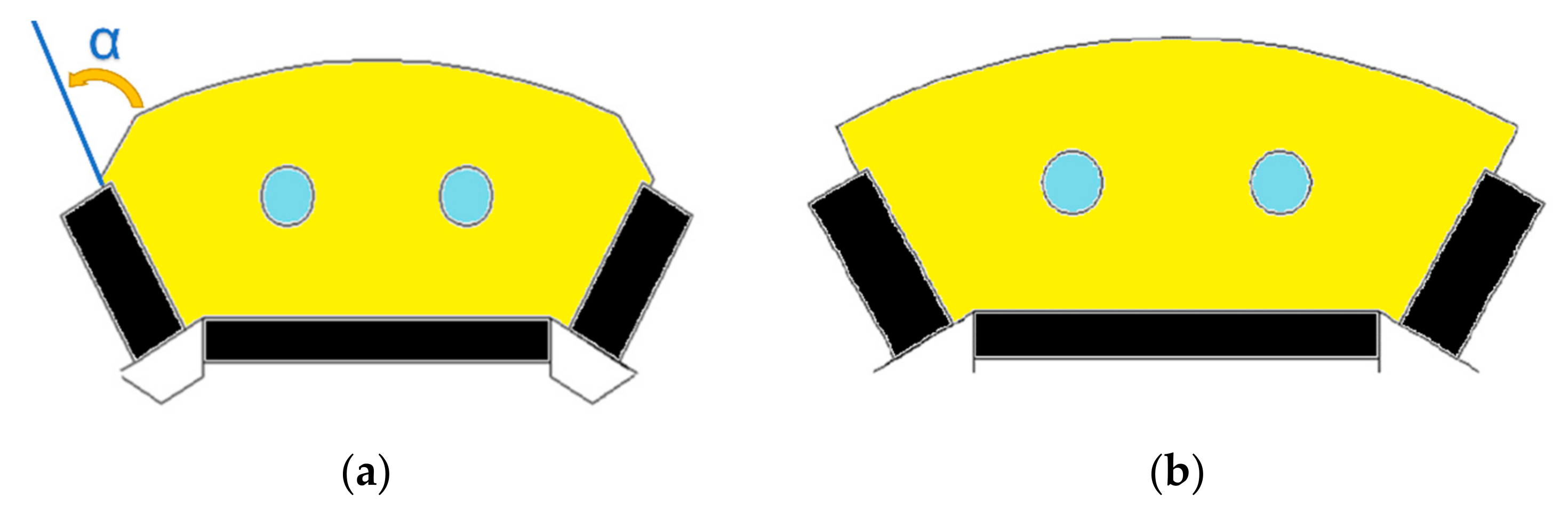
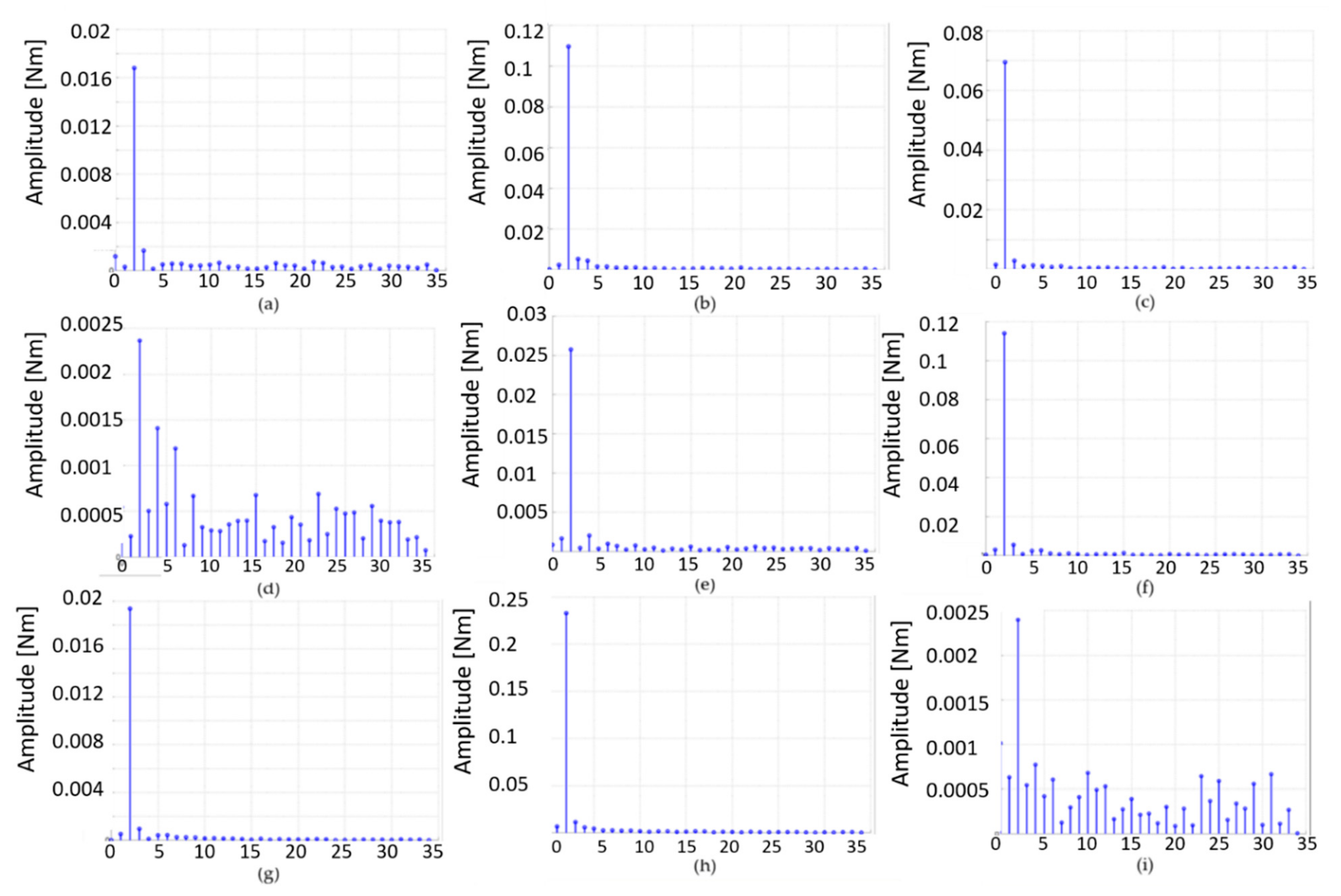

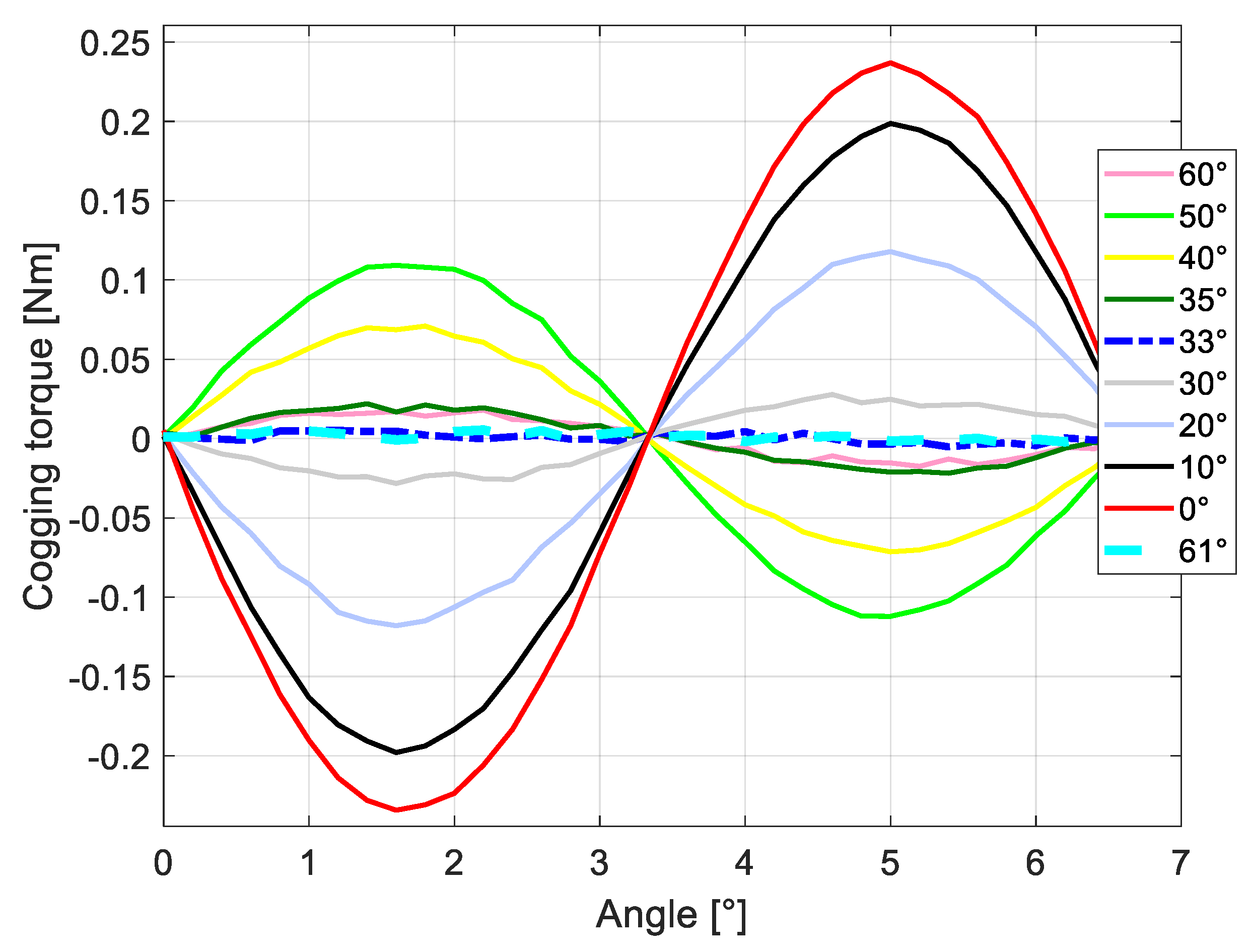
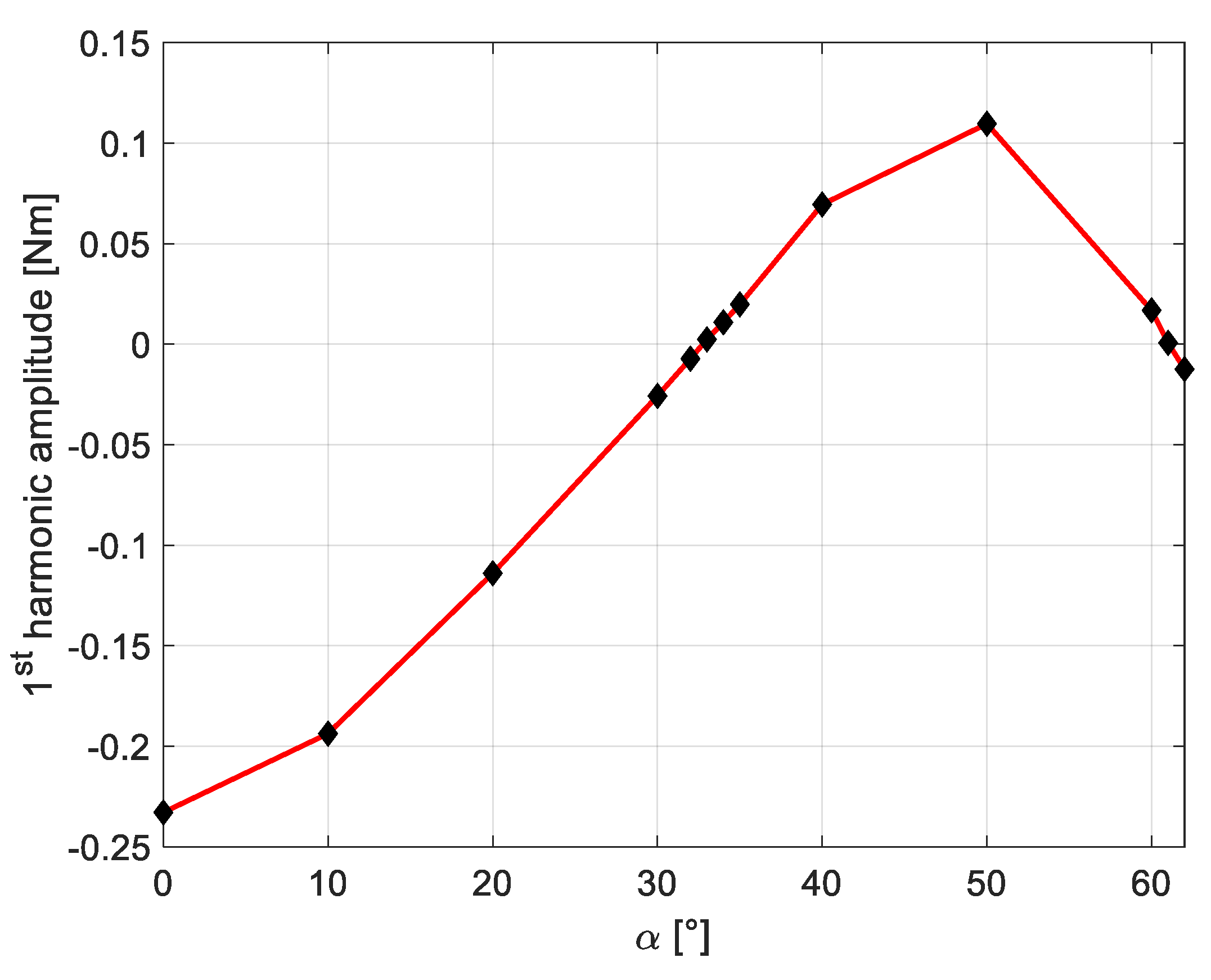

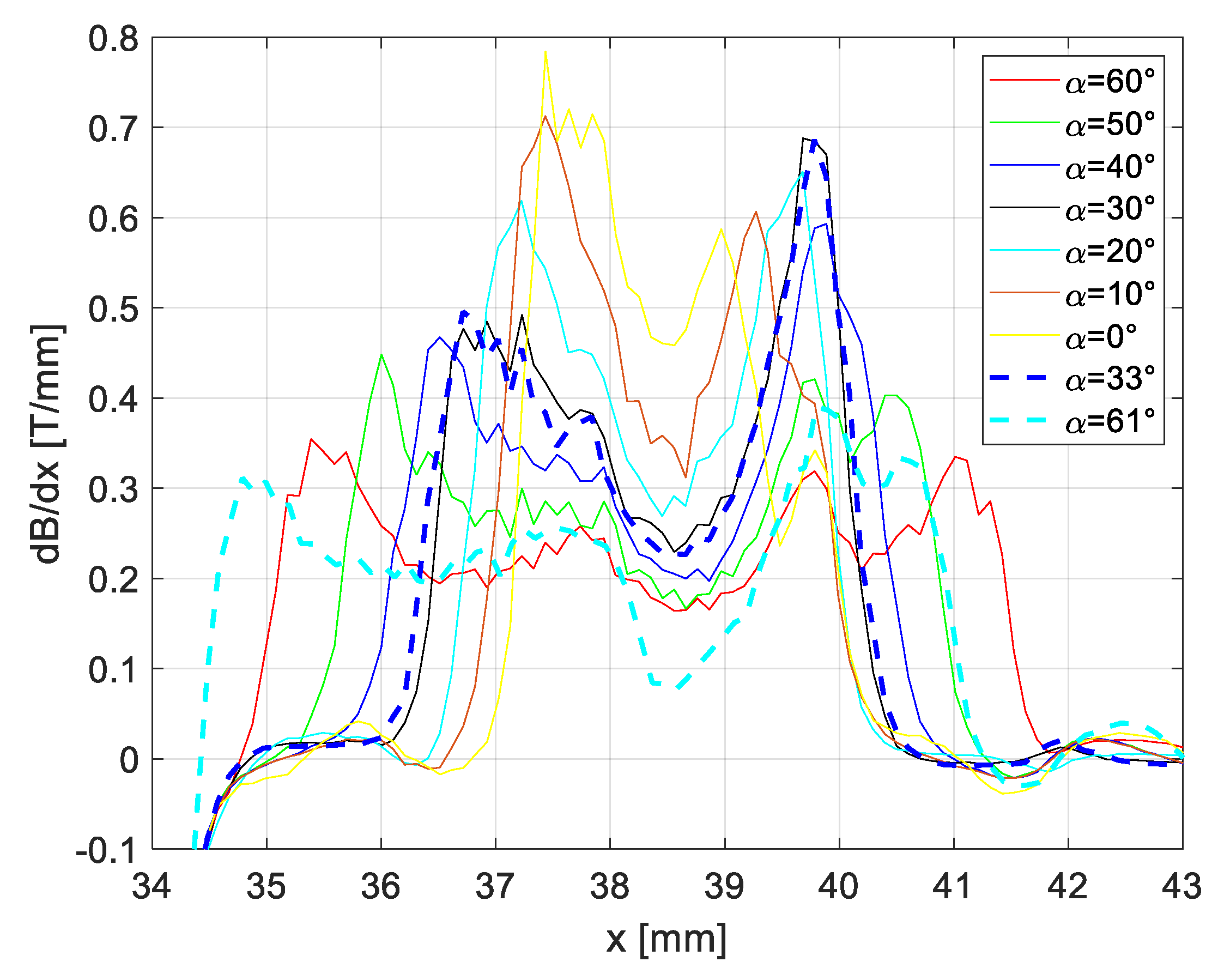
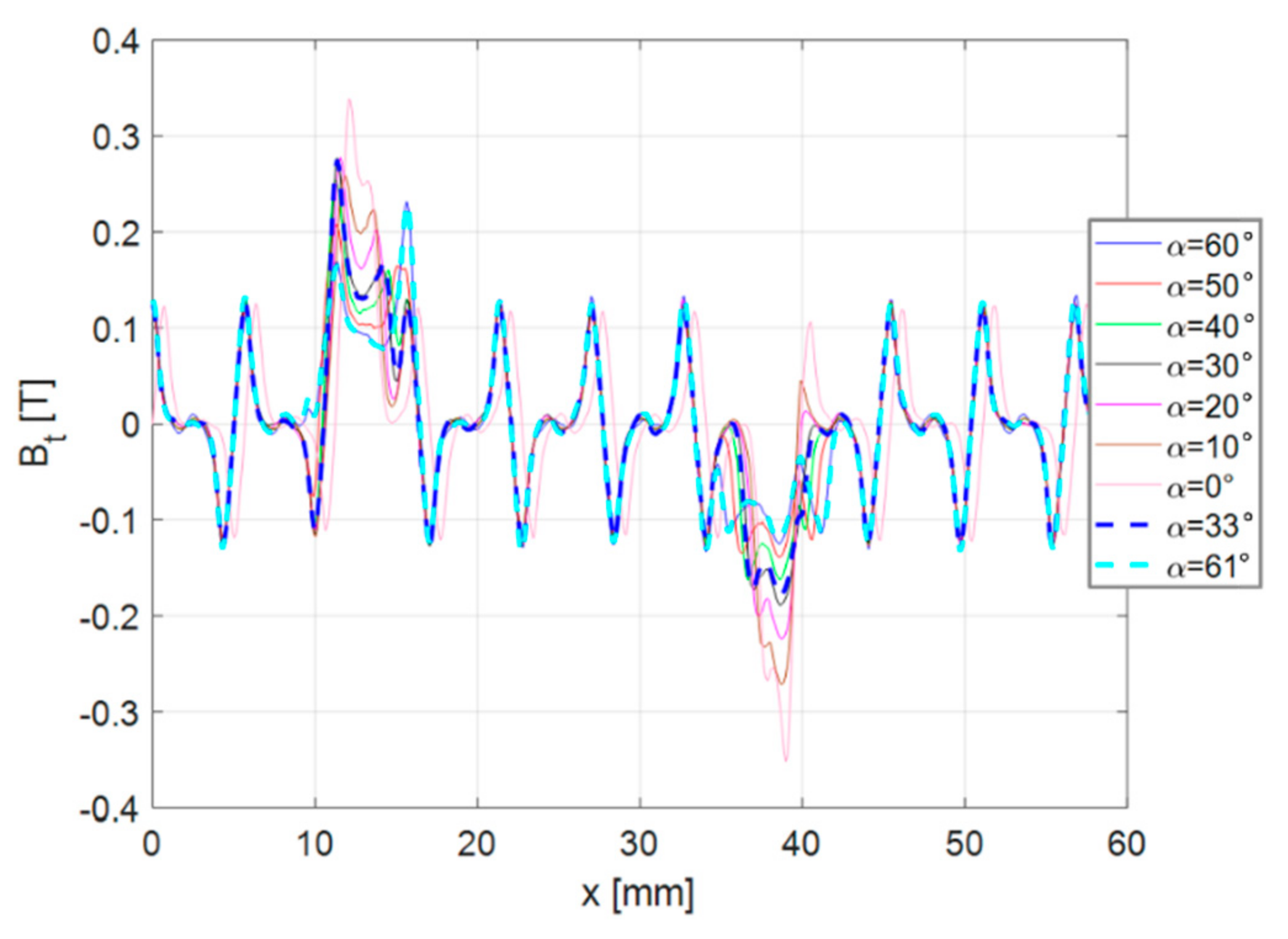
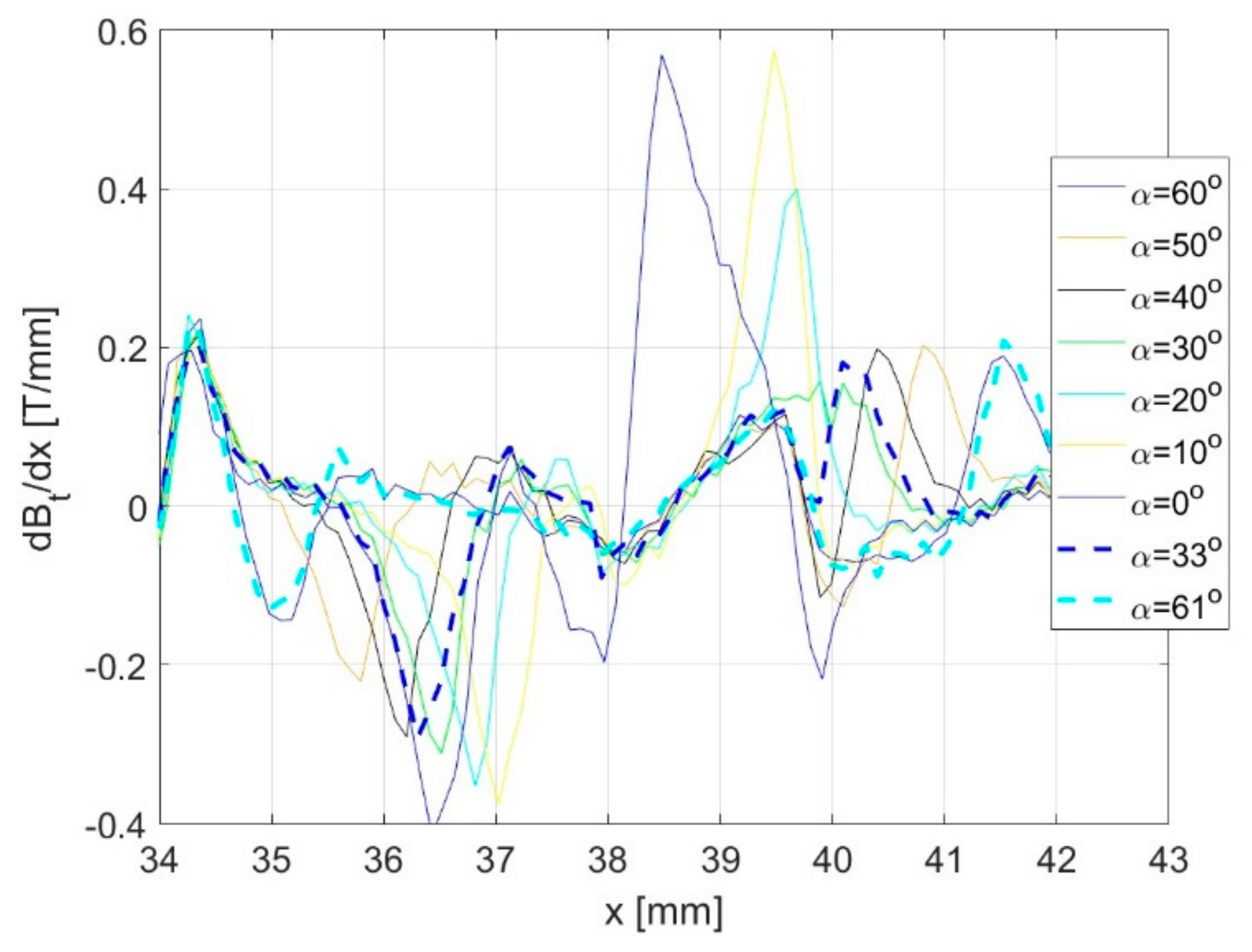
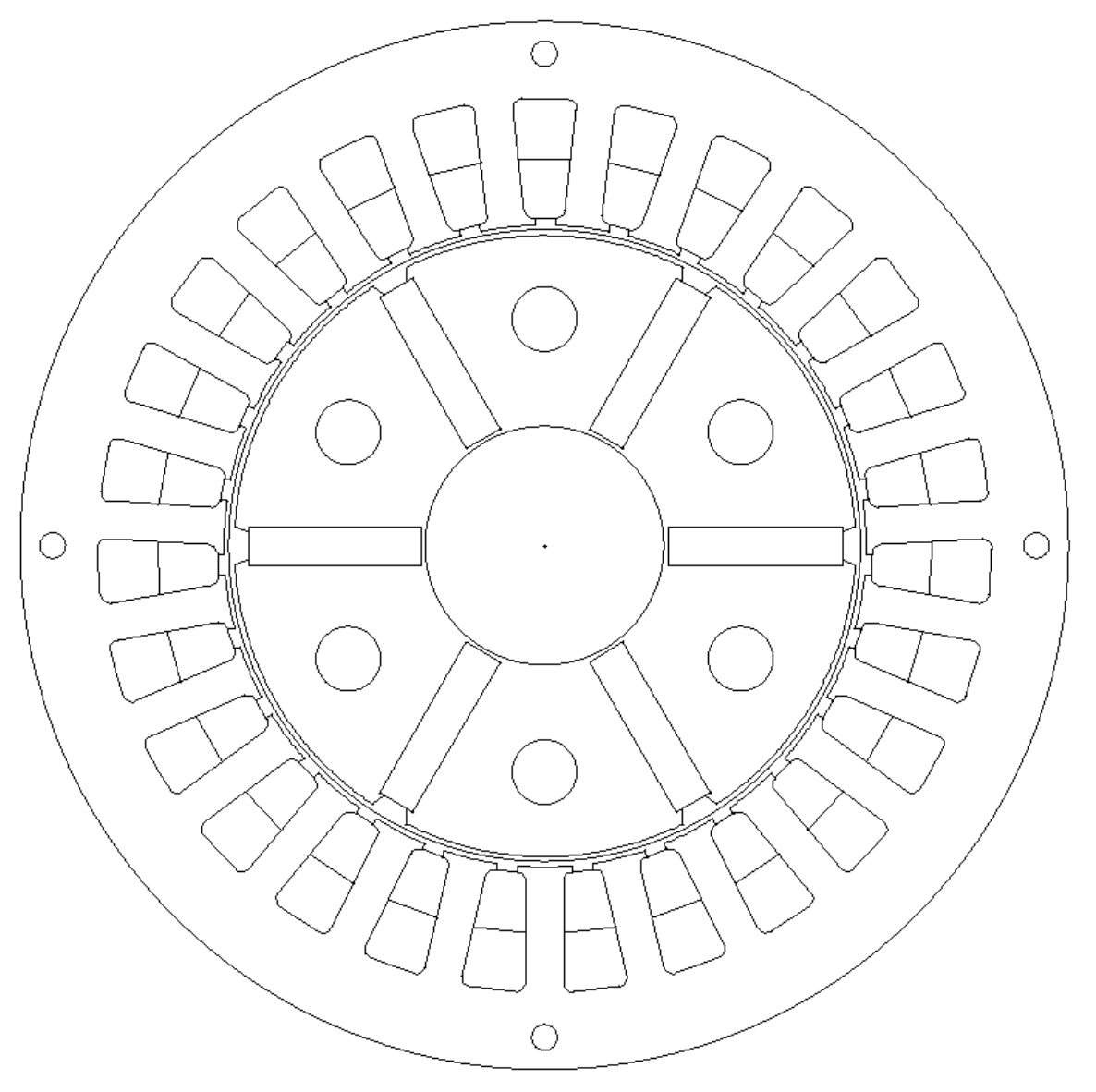




| Quantity | Value |
|---|---|
| Voltage [V] | 132 |
| Current [A] | 3.6 |
| Speed [rpm] | 4000 |
| Torque [Nm] | 1.8 |
| Number of pole pairs | 3 |
| Stator resistance [Ω] | 2.21 |
| Magnetic permeability of stator core [H/m] | 6.3 × |
| Magnetic permeability of laminations [H/m] | 2.5 × |
| Magnetic flux density of PMs [MGOe] | 40 |
| Geometrical Data | Value [mm] |
|---|---|
| Outer stator diameter | 81 |
| Inner stator diameter | 49.6 |
| Outer rotor diameter | 48 |
| Inner rotor diameter | 18.46 |
| Axial rotor length | 59 |
| PM width | 13.45 |
| PM thickness | 3 |
| Air-gap | 0.8 |
| PM type | NdFeB |
| α [°] | Tx | Tx% |
|---|---|---|
| 60 | 0.017 | 7.3 |
| 50 | 0.100 | 43.4 |
| 40 | 0.069 | 30.0 |
| 33 | 0.003 | 1.3 |
| 30 | 0.025 | 10.8 |
| 20 | 0.110 | 47.8 |
| 10 | 0.190 | 82.6 |
| 0 | 0.230 | 100 |
| 61 | 0.003 | 1.3 |
| Quantity | α = 60° | α = 33° |
|---|---|---|
| Air-gap magnetic field energy [J] | 0.893 | 0.91 |
| Stress tensor force [N] | 0.04 | 0.042 |
| Average magnetic field [A/m] | 2.95 A/m | 3.02 A/m |
| Generated torque [Nm] | 2.25 | 2.28 |
| Iron core losses | 6.12 | 6.55 |
| α [°] | Tx [Nm] | Tx% |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | 0.0220 | 68% |
| 20 | 0.0086 | 27% |
| 15 | 0.0016 | 5% |
| 10 | 0.0130 | 40% |
| 5 | 0.0185 | 58% |
| 0 | 0.0320 | 100% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caruso, M.; Di Tommaso, A.O.; Miceli, R.; Viola, F. A Cogging Torque Minimization Procedure for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on a Progressive Modification of the Rotor Lamination Geometry. Energies 2022, 15, 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15144956
Caruso M, Di Tommaso AO, Miceli R, Viola F. A Cogging Torque Minimization Procedure for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on a Progressive Modification of the Rotor Lamination Geometry. Energies. 2022; 15(14):4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15144956
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaruso, Massimo, Antonino Oscar Di Tommaso, Rosario Miceli, and Fabio Viola. 2022. "A Cogging Torque Minimization Procedure for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on a Progressive Modification of the Rotor Lamination Geometry" Energies 15, no. 14: 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15144956
APA StyleCaruso, M., Di Tommaso, A. O., Miceli, R., & Viola, F. (2022). A Cogging Torque Minimization Procedure for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on a Progressive Modification of the Rotor Lamination Geometry. Energies, 15(14), 4956. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15144956







