A New Hybrid Neural Network Method for State-of-Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Structure and Estimation Algorithm
2.1. Dilated CNN
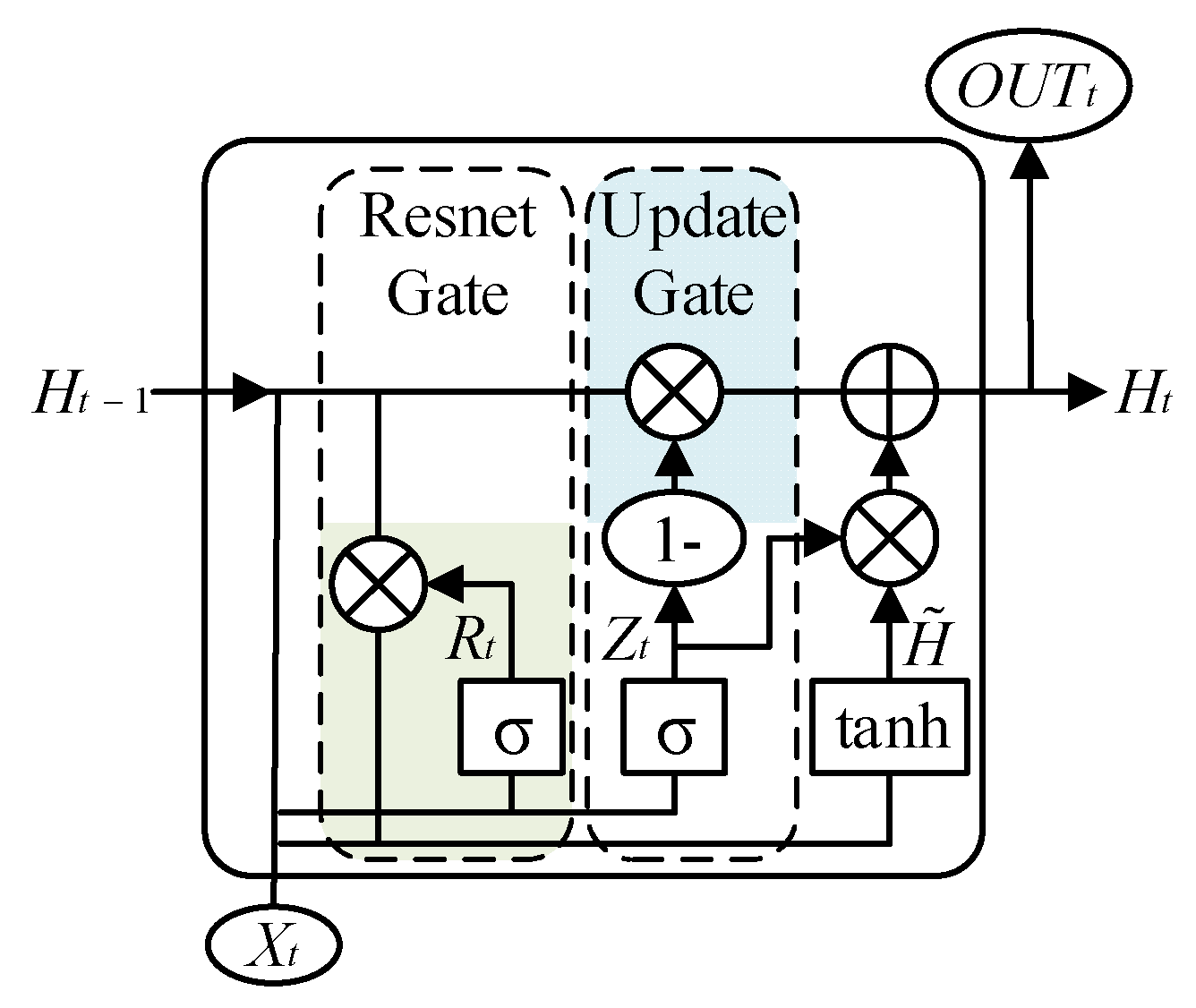
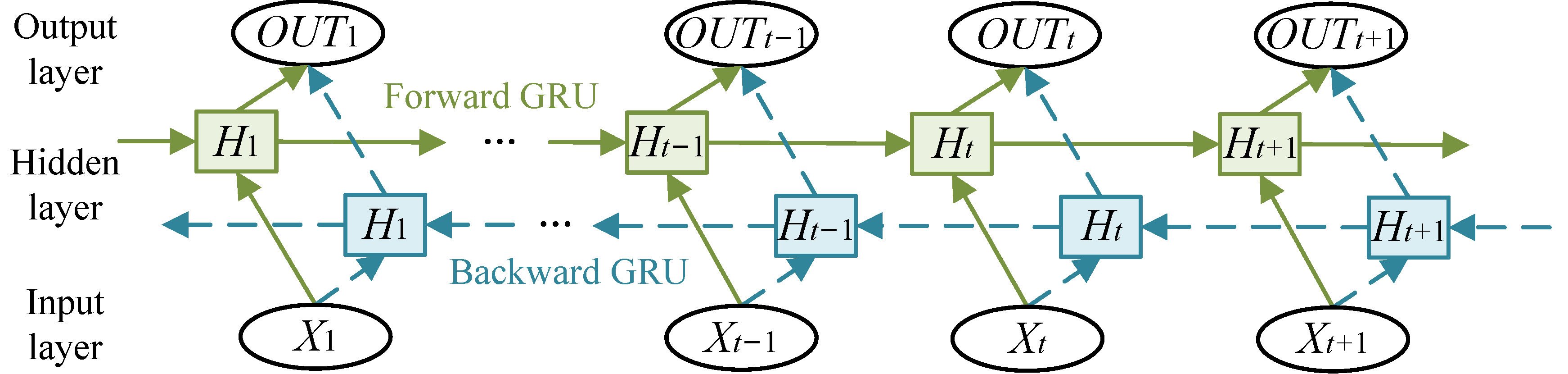
2.2. GRU and BiGRU
2.3. The Proposed Overall Network Structure
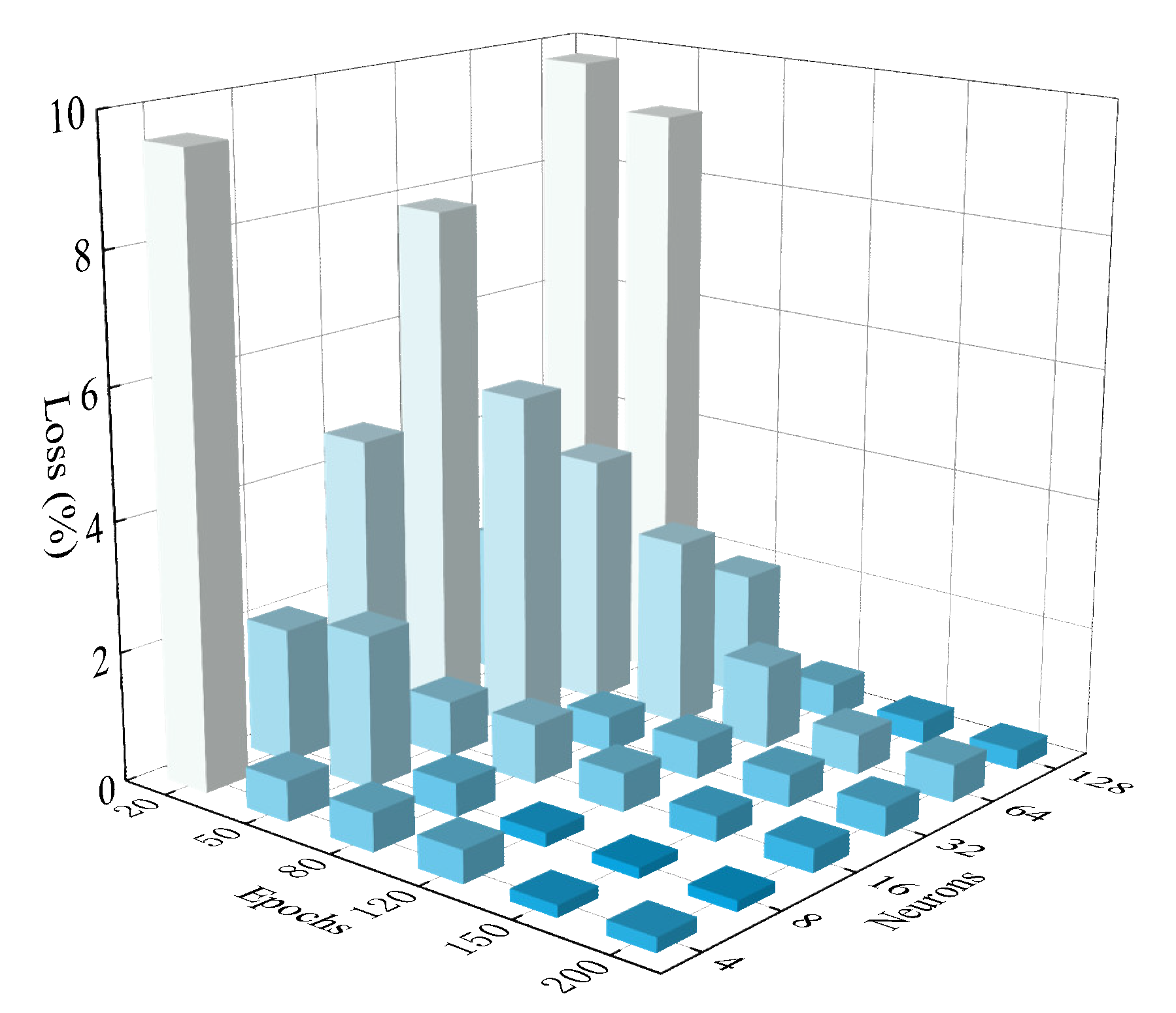
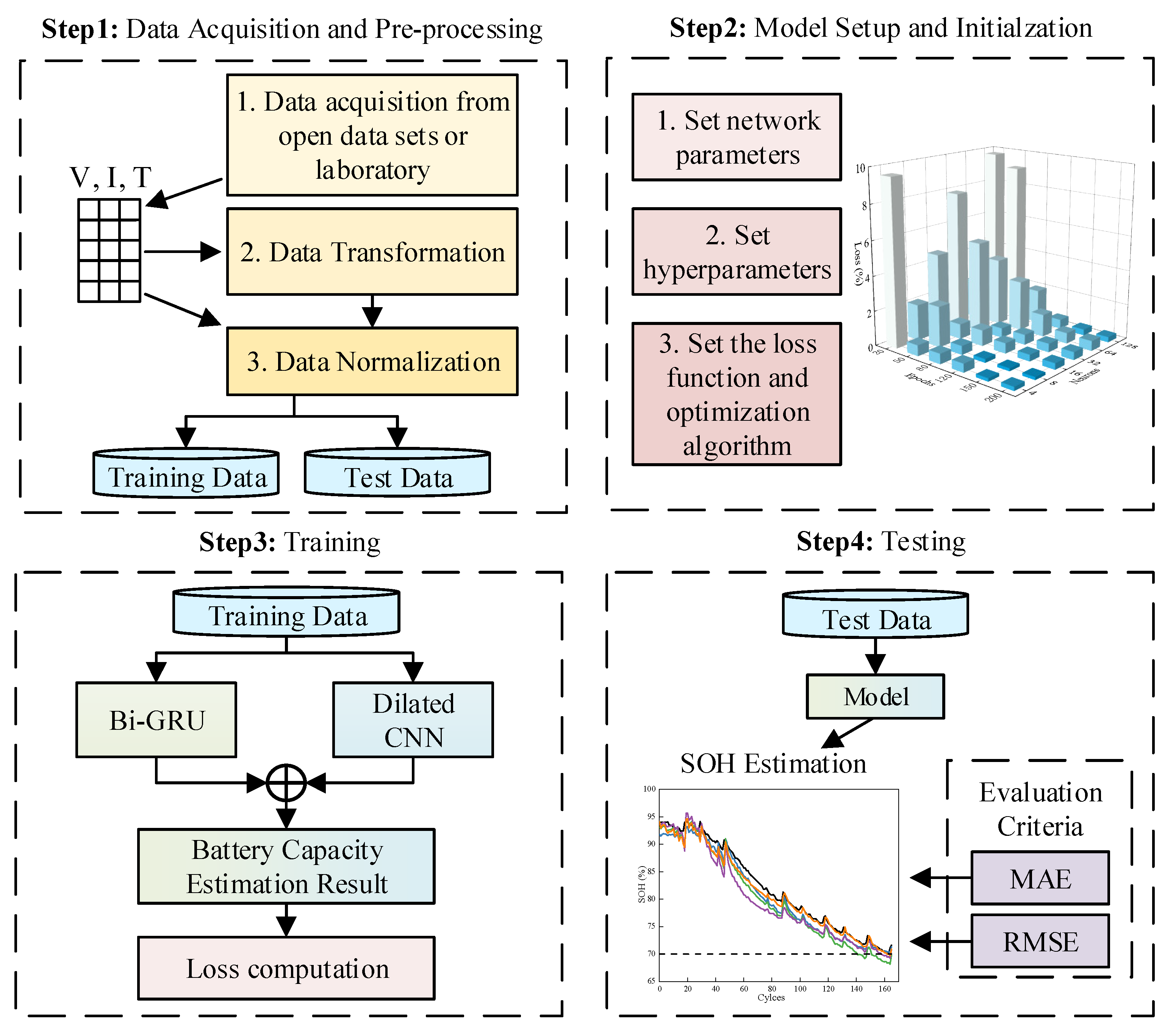
2.4. SOH Estimation Algorithm Based on Proposed Network
3. Experiment and Analysis
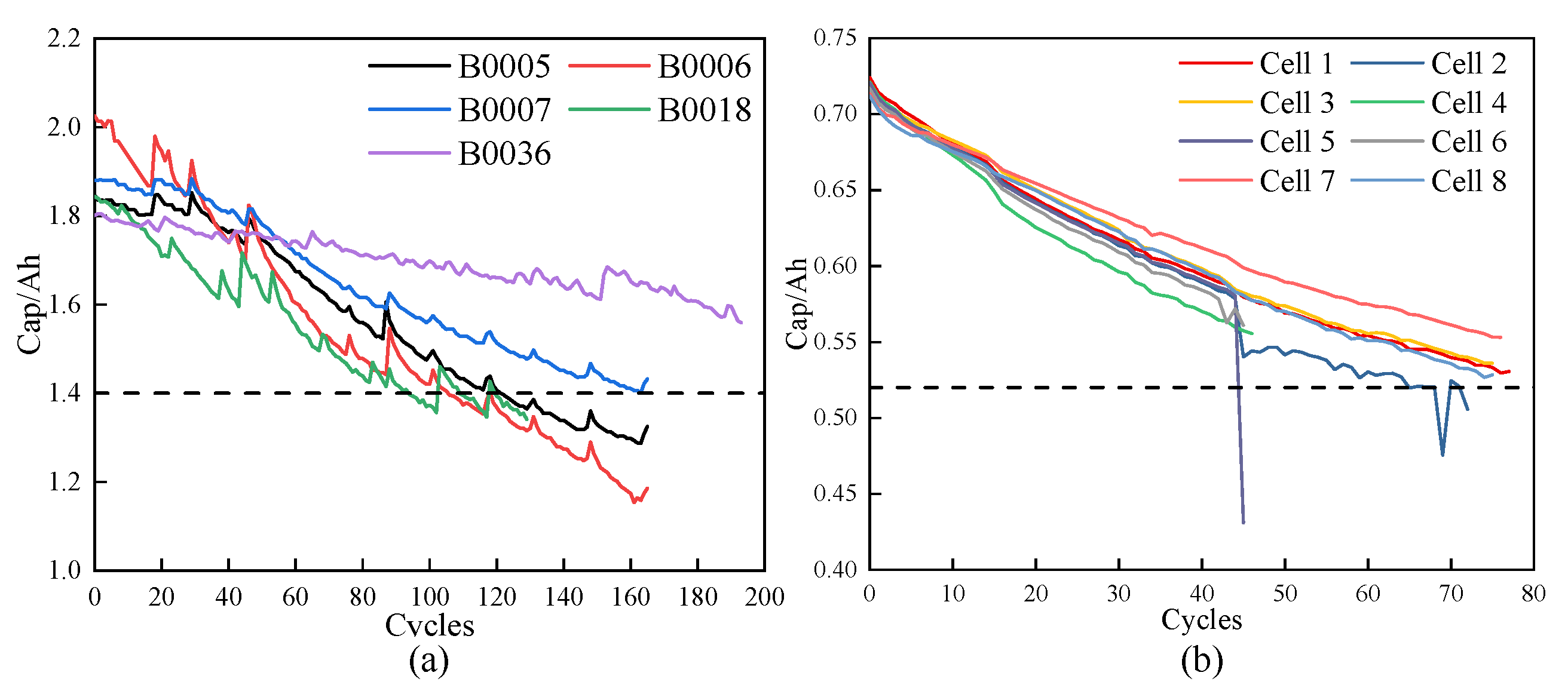
3.1. Experimantal Data
3.2. Experimental Platform
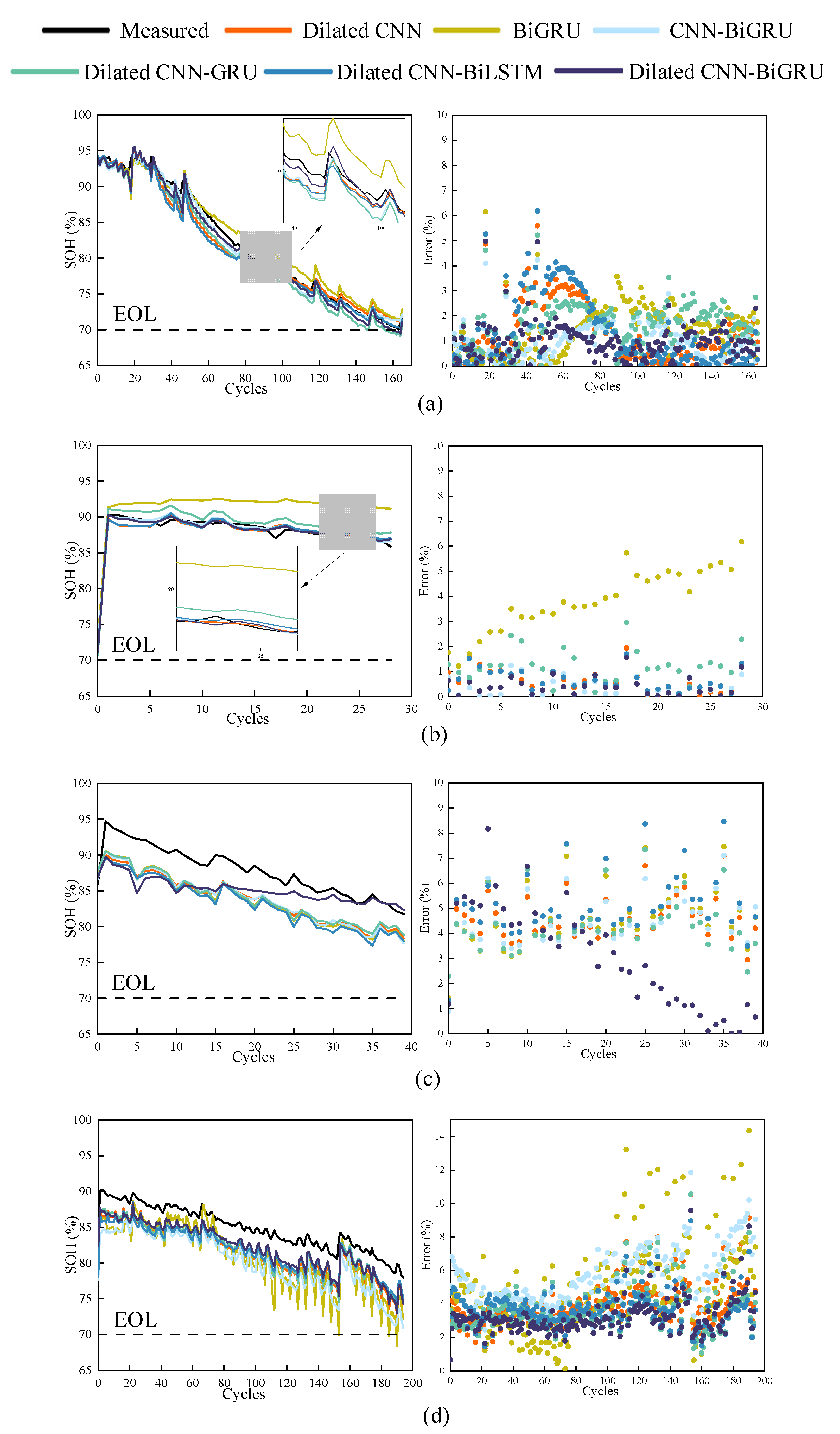
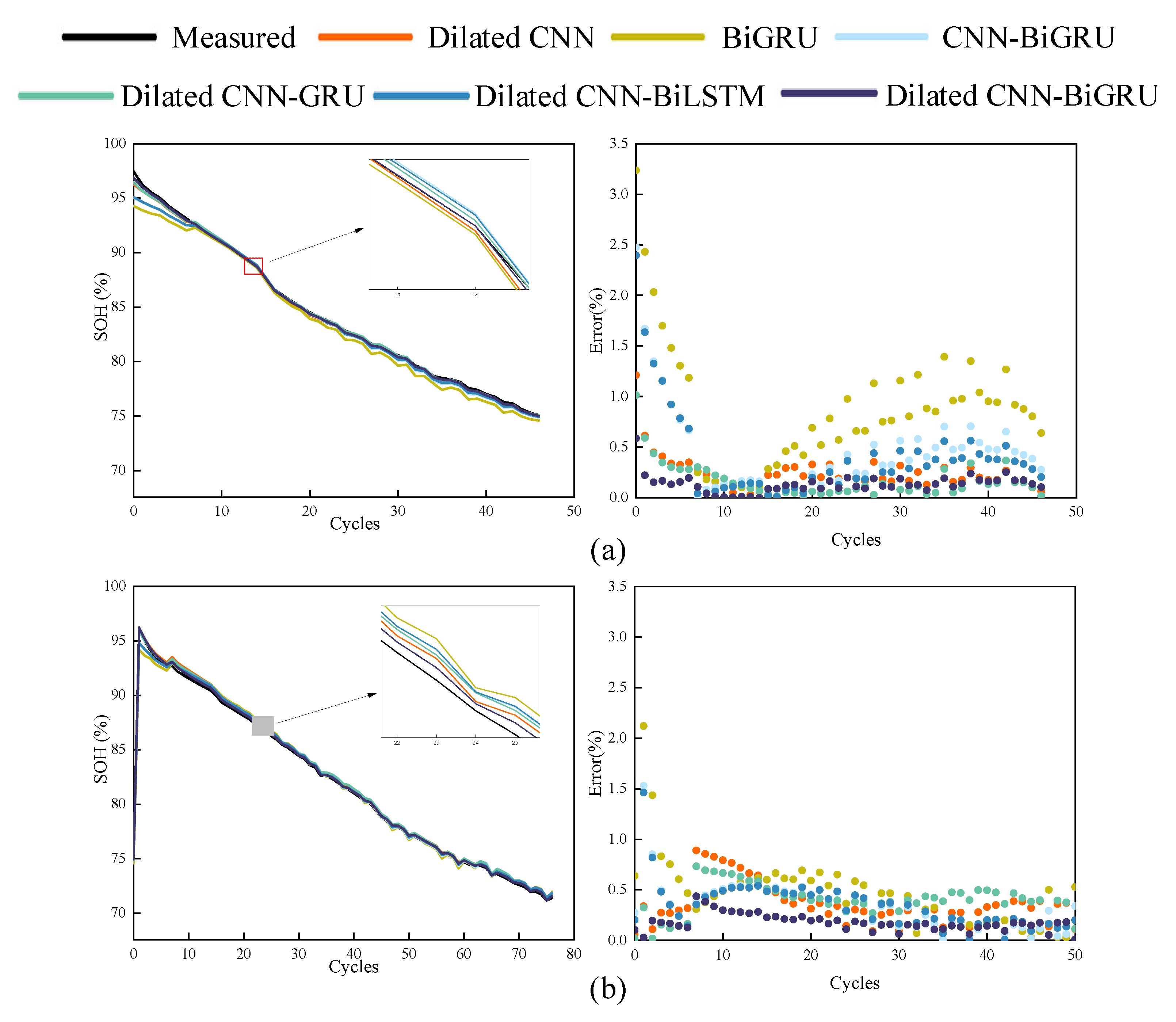
3.3. Experiment Result on NASA Dataset and Oxford Dataset
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y. On the movement simulations of electric vehicles: A behavioral model-based approach. Appl. Energy 2021, 283, 116356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tang, A.; Wang, W. A review of SOH estimation methods in Lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicle applications. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 1920–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D. Co-estimation of state-of-charge and state-of-health for lithium-ion batteries using an enhanced electrochemical model. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 2684–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, H.; Ha, J.; Kim, K.; Youn, J.; Jung, J.; Youn, B. A degenerated equivalent circuit model and hybrid prediction for state-of-health (SOH) of PEM fuel cell. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 29 September–2 October 2014; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Chen, C.; Tan, C.M.; Huang, S.C. Semi-Empirical capacity fading model for SoH estimation of Li-Ion batteries. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diab, Y.; Auger, F.; Schaeffer, E.; Chevalier, S.; Allahham, A. Real-Time Estimation of PEMFC Parameters Using a Continuous-Discrete Extended Kalman Filter Derived from a Pseudo Two-Dimensional Model. Energies 2022, 15, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Yan, J. Prognostic health condition for lithium battery using the partial incremental capacity and Gaussian process regression. J. Power Sources 2019, 421, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.; Sitapure, N.; Moon, J.; Lee, H.; Hwang, S.; Kwon, J.S. Model predictive control of Lithium-ion batteries: Development of optimal charging profile for reduced intracycle capacity fade using an enhanced single particle model (SPM) with first-principled chemical/mechanical degradation mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Luo, C.; Xue, X.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, Z.; et al. State of health (SoH) estimation and degradation modes analysis of pouch NMC532/graphite Li-ion battery. J. Power Sources 2021, 498, 229884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadabadi, K.K.; Jin, X.; Rizzoni, G. Prediction of remaining useful life for a composite electrode lithium ion battery cell using an electrochemical model to estimate the state of health. J. Power Sources 2021, 481, 228861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cui, N.; Cui, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C. Novel equivalent circuit model for high-energy lithium-ion batteries considering the effect of nonlinear solid-phase diffusion. J. Power Sources 2022, 523, 230993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Shi, Z.; Guo, D.; Dai, H.; Han, X. A simplification of the time-domain equivalent circuit model for lithium-ion batteries based on low-frequency electrochemical impedance spectra. J. Power Sources 2021, 489, 229505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.K.; Mathew, M.; Janhunen, S.; Panchal, S.; Raahemifar, K.; Fraser, R.; Fowler, M. A comprehensive equivalent circuit model for lithium-ion batteries, incorporating the effects of state of health, state of charge, and temperature on model parameters. J. Energy Storage 2021, 43, 103252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, D.; Appel, C.; Soczka-Guth, T.; Sauer, D.U. Advanced mathematical methods of SOC and SOH estimation for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 224, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, M.; Kim, G.; Park, S.; Kim, J. Integrated approach based on dual extended Kalman filter and multivariate autoregressive model for predicting battery capacity using health indicator and SOC/SOH. Energies 2020, 13, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Lao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Tian, Y.; Chen, G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, W.; Sun, W.; Lai, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Online parameter identification and state of charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on forgetting factor recursive least squares and nonlinear Kalman filter. Energies 2017, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.; Weng, C.; He, X.; Han, X.; Lu, L.; Ren, D.; Oouyang, M. Online state-of-health estimation for Li-ion battery using partial charging segment based on support vector machine. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 8583–8592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Williams, H.; Xu, H. Human-knowledge-augmented Gaussian process regression for state-of-health prediction of lithium-ion batteries with charging curves. J. Electrochem. Energy Convers. Storage 2021, 18, 030907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zou, C.; Dorrell, D.D. State-of-health estimation for Li-ion batteries by combing the incremental capacity analysis method with grey relational analysis. J. Power Sources 2019, 410, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Liang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wen, J.; Pang, X.; Zeng, J. SOH and RUL prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on gaussian process regression with indirect health indicators. Energies 2020, 13, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, W.; Shen, W.; Liu, J. A joint grey relational analysis based state of health estimation for lithium ion batteries considering temperature effects. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 103102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.H.; Bengio, Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.; Wang, X.; He, Y. Remaining useful life and state of health prediction for lithium batteries based on empirical mode decomposition and a long and short memory neural network. Energy 2021, 232, 121022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Dong, P. Remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries based on a hybrid model combining the long short-term memory and Elman neural networks. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Mehmani, A.; Zhang, J. Deep learning-based real-time building occupancy detection using AMI data. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 4490–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shi, Y.; Liu, B.; Zuo, Y.; Fu, Z.; Ali, J. Health state estimation of lithium-ion batteries based on attention augmented BiGRU. Energy Storage Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 2326. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Xiao, F.; Li, C.; Yang, G.; Tang, X. A novel deep learning framework for state of health estimation of lithium-ion battery. J. Energy Storage 2020, 32, 101741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A.; Mohamed, A.; Hinton, G. Speech recognition with deep recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 6645–6649. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Xie, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, C.; Han, J. Deep Fisher discriminant learning for mobile hand gesture recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 77, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, B. Dilated convolution neural network for remaining useful life prediction. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2020, 20, 021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.; Lee, S.; Ward, R.; McKeown, M.J. Semi-dilated convolutional neural networks for epileptic seizure prediction. Neural Netw. 2021, 139, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, D.; Jia, M. A BiGRU method for remaining useful life prediction of machinery. Measurement 2021, 167, 108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Goebel, K.; Battery Data Set. NASA AMES Prognostics Data Repository. 2007. Available online: https://data.nasa.gov/dataset/Li-ion-Battery-Aging-Datasets/uj5r-zjdb (accessed on 13 September 2010).
- Birkl, C. Oxford Battery Degradation Dataset 1. 2017. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/intelligent-systems-division (accessed on 31 December 2016).




| Layer | Input [N, M] | Kernel Size | Kernel Number | Strides | Dilation Rate | Output [N, M] | Last/Next Layer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I0 | [4000, 1] | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | [4000, 1] | N/A/D1, G1 |
| DC1 | [4000, 1] | 3 | 72 | 2 | 1 | [2000, 72] | I0/P1 |
| P1 | [2000, 72] | 2 | N/A | N/A | N/A | [2000, 72] | DC1/DC2 |
| DC2 | [2000, 72] | 3 | 36 | 1 | 3 | [2000, 36] | P1/DC3 |
| DC3 | [2000, 36] | 3 | 18 | 1 | 9 | [2000, 18] | DC2/DC4 |
| DC4 | [2000, 18] | 3 | 36 | 1 | 27 | [2000, 36] | DC3/DC5 |
| DC5 | [2000, 36] | 3 | 72 | 1 | 81 | [2000, 72] | DC4/F1 |
| F1 | [2000, 72] | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2000 × 72 | DC5/D1 |
| D1 | 2000 × 72 | N/A | 100 | N/A | N/A | 100 | F1/D2 |
| D2 | 100 | N/A | 1 | N/A | N/A | 1 | D1/A1 |
| G1 | [4000, 1] | N/A | 8 | N/A | N/A | [4000, 16] | I0/G2 |
| G2 | [4000, 1] | N/A | 8 | N/A | N/A | [4000, 16] | G1/F2 |
| F2 | [4000, 1] | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 4000 × 16 | G2/D3 |
| D3 | 4000 × 16 | N/A | 100 | N/A | N/A | 100 | F2/D4 |
| D4 | 100 | N/A | 1 | N/A | N/A | 1 | D3/A1 |
| A1 | 1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1 | D2 + D4/O0 |
| O0 | 1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 1 | A1/N/A |
| Battery Number | Criteria | Dilated CNN | BiGRU | CNN-BiGRU | Dilated CNN-GRU | Dilated CNN-BiLSTM | Dilated CNN-BiGRU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0007 | MAE (%) | 1.08 | 1.12 | 0.81 | 1.35 | 1.14 | 0.80 |
| RMSE (%) | 2.07 | 1.94 | 1.42 | 2.16 | 2.37 | 1.43 | |
| B0028 | MAE (%) | 0.55 | 3.17 | 0.36 | 1.10 | 0.60 | 0.40 |
| RMSE (%) | 0.98 | 4.78 | 0.73 | 1.75 | 0.98 | 0.78 | |
| B0032 | MAE (%) | 3.92 | 4.13 | 3.86 | 3.88 | 4.47 | 2.77 |
| RMSE (%) | 5.75 | 6.03 | 5.66 | 5.72 | 6.58 | 4.76 | |
| B0036 | MAE (%) | 3.36 | 4.06 | 4.65 | 3.04 | 3.13 | 2.71 |
| RMSE (%) | 4.95 | 6.57 | 6.83 | 4.54 | 4.58 | 4.01 | |
| Overall | MAE (%) | 2.35 | 2.88 | 2.83 | 2.34 | 2.32 | 1.83 |
| RMSE (%) | 4.00 | 5.11 | 5.03 | 3.80 | 3.97 | 3.21 |
| Battery Number | Criteria | Dilated CNN | BiGRU | CNN-BiGRU | Dilated CNN-GRU | Dilated CNN-BiLSTM | Dilated CNN-BiGRU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell 4 | MAE (%) | 0.078 | 0.275 | 0.147 | 0.054 | 0.129 | 0.041 |
| RMSE (%) | 0.145 | 0.494 | 0.309 | 0.117 | 0.291 | 0.073 | |
| Cell 8 | MAE (%) | 0.108 | 0.128 | 0.097 | 0.120 | 0.100 | 0.052 |
| RMSE (%) | 0.177 | 0.241 | 0.177 | 0.187 | 0.176 | 0.083 | |
| Overall | MAE (%) | 0.097 | 0.184 | 0.116 | 0.095 | 0.111 | 0.048 |
| RMSE (%) | 0.165 | 0.359 | 0.236 | 0.164 | 0.227 | 0.080 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, C.; Gao, M. A New Hybrid Neural Network Method for State-of-Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery. Energies 2022, 15, 4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124399
Bao Z, Jiang J, Zhu C, Gao M. A New Hybrid Neural Network Method for State-of-Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery. Energies. 2022; 15(12):4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124399
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Zhengyi, Jiahao Jiang, Chunxiang Zhu, and Mingyu Gao. 2022. "A New Hybrid Neural Network Method for State-of-Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery" Energies 15, no. 12: 4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124399
APA StyleBao, Z., Jiang, J., Zhu, C., & Gao, M. (2022). A New Hybrid Neural Network Method for State-of-Health Estimation of Lithium-Ion Battery. Energies, 15(12), 4399. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124399





