Abstract
REMgNi4-based alloys, RE(2−x)MgxNi4 (RE: rare-earth metals; 0 < x < 2), with a AuBe5-type crystal structure, exhibit reversible hydrogen absorption and desorption reactions, which are known as hydrogen storage properties. These reactions involve formation of three hydride phases. The hydride formation pressures and hydrogen storage capacities are related to the radii of the RE(2−x)MgxNi4, which in turn are dependent on the radii and compositional ratios of the RE and Mg atoms. The crystal structures formed during hydrogen absorption reactions are the key to understanding the hydrogen storage properties of RE(2−x)MgxNi4. Therefore, in this review, we provide an overview of the crystal structures in the hydrogen absorption reactions focusing on RE(2−x)MgxNi4.
1. Introduction
Hydrogen is a unique element, since it exhibits various hydrogen states in compounds (hydrides), which are elemental hydrogen, protons, hydride ion, and covalently bonded hydrogen [1]. Such hydrogen states lead to attractive physical and material properties. For these reasons, hydrides have been focused on in relation to energy-related materials [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. In particular, hydrides (so-called material-based storage, or metal hydrides) have higher volumetric hydrogen densities than compressed H2 gas and liquid H2 [2,3,4,5,7].
To date, LaNi5-based alloys (AB5 alloys) have been used in practical applications because of their stable reversible hydrogen absorption and desorption reactions under moderate conditions (i.e., room temperature and hydrogen gas pressure less than 1 MPa). By contrast, new hydrogen storage materials have higher gravimetric hydrogen densities than the AB5 alloys (approximately 1.4 mass%) explored. In particular, Mg is a potential candidate because it is inexpensive, abundant in nature, and reacts with hydrogen to form MgH2 with high gravimetric hydrogen density (7.6 mass%) [7]. However, in order to use Mg as a practical hydrogen storage material, it is necessary to improve the thermodynamic stability of MgH2, which is −74 kJ/mol, corresponding to hydrogen release at approximately 550 K under ambient pressure. Alloying with transition metals has been attempted to improve the thermodynamic stability. Although Mg2NiH4 and Mg2FeH6 have been proposed, they are still too stable (Mg2NiH4: −62 kJ/mol H2; Mg2FeH6: −77 kJ/mol H2) to release hydrogen at ambient temperatures [7]. The value should be approximately −30 kJ/mol H2 for reversible hydrogen absorption and desorption reactions at ambient temperatures. In such hydrides, hydrogen atoms are ionically bonded with Mg in MgH2 or covalently bonded with Ni or Fe atoms in Mg2NiH4 [10] and Mg2FeH6 [11], respectively. Thus, these are ionic and complex hydrides. Qualitatively, such chemical bonding between the metal and hydrogen atoms induces hydrogen absorption and desorption reactions with high thermodynamic stability or slow kinetics. Therefore, understanding of hydrogen states in hydrides [1,12,13] is a key for development hydrogen storage materials which can operate moderate conditions. In fact, the design of intermetallic compounds that do not form ionic or complex hydrides is one approach to obtain efficient hydrogen storage materials. So far, REMgNi4-based alloys, such as RE(2−x)MgxNi4 (RE: rare-earth metals; 0 < x < 2), have been reported to exhibit reversible hydrogen absorption and desorption reactions at ambient temperatures [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. In these reactions, hydrogen atoms are located at interstitial sites in the lattice of RE(2−x)MgxNi4 and three hydride phases are formed [19,20,21,22,23,24,28,29,30,31,32,33]: REMgNi4Hx1, REMgNi4Hx2, and REMgNi4Hx3. In this paper, we refer to REMgNi4Hx1, REMgNi4Hx2, and REMgNi4Hx3 as the α-, β-, and γ-hydride phases, respectively. The experimentally reported hydride phases with their unit cell parameters, formation enthalpy of the hydrides, and hydrogen contents are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
The experimentally reported hydride phases of REMgNi4-based alloys with unit cell parameters, formation enthalpy of the hydride ΔH, and hydrogen contents (an asterisk indicates enthalpy of the hydride, which was obtained from the hydrogen release reaction).
In RE(2−x)MgxNi4, the atomic radii of the components, which are influenced by the addition of Mg with a smaller atomic radius than RE atoms [34], selection (radius) of the RE element, and compositional ratios, are crucial parameters for reversible hydrogen absorption and desorption reactions [14,15,16,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] and for avoiding hydrogen-induced amorphization (HIA) [35,36]. Absorbed hydrogen in RENi2 without Mg is hardly released at ambient temperature because of the considerably lower hydrogen desorption pressure than the ambient pressure. By contrast, Mg in RENi2, which forms RE(2−x)MgxNi4, leads to increased equilibrium hydrogen absorption and desorption reaction pressures [20]. The atomic radii of components can also be adjusted by the selection (radius) of RE elements and compositional ratios because the unit cell parameters also depend on the RE element [17]. This indicates that the hydrogen absorption and desorption reactions are related to the interatomic spaces between metal atoms in the crystal structure. Furthermore, the radii of the components are related to the HIA because the HIA originates in the radius ratio between RE and Ni in the case of RENi2. In REMgNi4, Mg atoms share positions with two crystallographically different atomic sites of the RE element, and the atomic radius is averaged for Mg and RE atoms. Because the Mg atom is smaller than the RE atoms, the radius ratio of the components of RE(2−x)MgxNi4 is smaller than that of pure RENi2 and leads to prevention of HIA.
For these reasons, RE(2−x)MgxNi4, with various RE elements, has been investigated. In the Refs. [18,19,20,21,22], the hydrogen storage properties and crystal structures focusing on RE = Y have been described. In the RE(2−x)MgxNi4 alloys, RE = Y is expected to have a higher gravimetric hydrogen density because Y is the lightest RE element that forms REMgNi4. However, the formation of the γ-hydride phase has not yet been reported [18,19,20,21,22]. Computational studies of YMgNi4 have been reported to investigate crystal structure and the thermodynamic stabilities [21,22]. Shtender et al. reported that the γ-hydride phase was formed by Co doping in Ni atomic sites as in YMgNi2Co2 or YMgCo4 [19]. Although most studies on RE(2−x)MgxNi4 have mainly focused on Ni [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28], Co doping at Ni atomic sites or replacement of Ni atoms with Co have also been attempted in RE = La [25], Ce [29], Pr [30], Nd [30,31], and Tb [32,33], in which, Co could lead to increased hydrogen storage capacities and decreased equilibrium hydrogen absorption reactions. A new hydride phase with a monoclinic structure has been reported [33]. The hydrogen storage properties of lanthanoids [27] and crystal structures, including local atomic arrangements focusing on RE = Pr [26,28], were studied by Sakaki et al. Systematic studies have indicated that the radii of RE atoms have a greater influence than lanthanide type on hydrogen storage properties.
Thus, hydrogen absorption and desorption reaction pressures and maintaining the crystallinities of hydrogen storage alloys can be controlled by the appropriate selection (radius) of the RE element and the compositional ratio between the RE and Mg. This is a design strategy for REMgNi4-based alloys, although the properties of other hydrogen storage alloys have been demonstrated to be controlled by the replacement of various elements. To further understand the hydrogen storage properties, with respect to the atomic arrangements, detailed analysis of crystal structures during the hydrogen absorption reactions is critical. This is because the information on metal atomic arrangements around hydrogen atoms in the crystal structures could be related to the hydrogen storage properties. The metal atomic arrangements of the α-, β-, and γ-hydride phases, which adopt different crystal structures, are maintained. However, some hydride phases have been reported to become complicated, resulting in distorted metal atomic arrangements and different hydrogen atomic positions. Herein, we provide an overview of the crystal structural changes during the hydrogen absorption reactions focusing on REMgNi4.
2. Crystal Structures
2.1. REMgNi4
REMgNi4 adopts a face-centered cubic (FCC) structure (AuBe5 type) in the space group F-43m (No. 216) with Z = 4, which resembles a Laves phase alloy with a C15-type (MgCu2 type) crystal structure in the space group Fd-3m (No. 227) with Z = 8. The crystal structures of REMgNi4 and a Laves phase alloy, RENi2, with a C15-type crystal structure, are illustrated in Figure 1.
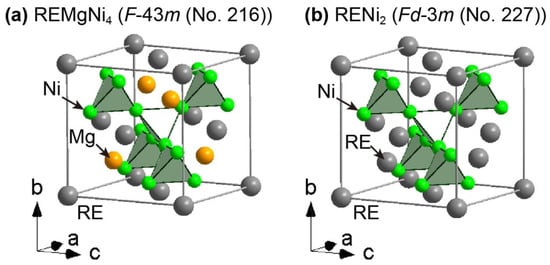
Figure 1.
Crystal structures of (a) REMgNi4 in the space group (F-43m (No. 216) and (b) RENi2 in the space group Fd-3m (No. 227, origin choice 1). Crystal structures of REMgNi4 and RENi2 were drawn based on crystallographic parameters of Y1.06Mg0.94Ni4.00 [20] and YNi2 [37], respectively. The RE, Mg, and Ni atoms are represented by grey, orange, and green spheres, respectively.
The differences between the two crystal structures are apparent at the (0, 0, 0) and (1/4, 1/4, 1/4) atomic sites. In the REMgNi4, the RE and Mg atoms are located at (0, 0, 0) and (1/4, 1/4, 1/4), respectively, such that the atoms are distinguishable. In the RENi2, RE atoms are located at both (0, 0, 0) and (1/4, 1/4, 1/4), with the latter position generated by the RE atoms at (0, 0, 0) due to the symmetry operation of the space group Fd-3m (No. 227, origin choice 1). Therefore, the atoms at (0, 0, 0) and (1/4, 1/4, 1/4) are indistinguishable. To understand the differences in X-ray diffraction patterns, a Laves phase alloy, CaNi2, is considered in this paper although Ca is not a rare earth metal element. CaNi2 has a Laves phase alloy, and Ca1–xMgxNi2 has been reported [14,17]. In Ca1–xMgxNi2, some of the Ca atoms in the CaNi2 Laves phase alloy are replaced by Mg atoms in a disordered arrangement. This indicates that Ca1–xMgxNi2 has a C15-type (MgCu2 type) crystal structure in the space group Fd-3m (No. 227) with Z = 8. If Ca and Mg atoms are ordered arrangements with x = 0.5, the crystal structure of Ca0.5Mg0.5Ni2 (= CaMgNi4) is described in the space group F-43m (No. 216) as well as REMgNi4. Simulated X-ray diffraction patterns of Ca0.5Mg0.5Ni2 in the space group Fd-3m (No. 227) and hypothetical CaMgNi4 in the space group F-43m (No. 216) are shown in Figure 2.
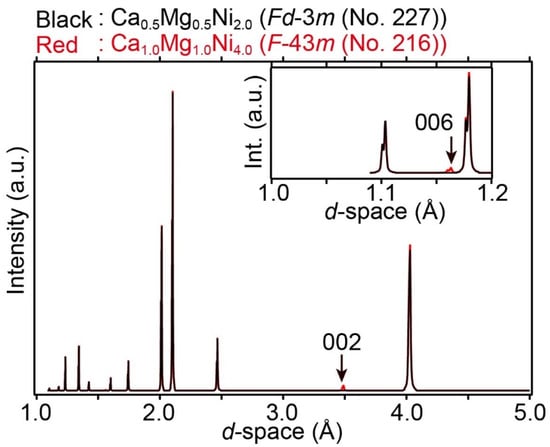
Figure 2.
Simulated X-ray diffraction patterns of (black) Ca0.5Mg0.5Ni2.0 in the space group Fd-3m (No. 227) and (red) hypothetical Ca1.0Mg1.0Ni4.0 in the space group F-43m (No. 216). For the simulation, Cu Kα radiation (wavelength λ = 1.5406 and 1.5444 Å for Kα1 and Kα2, respectively) was used. For the simulation, unit cell parameters of (Ca, Mg)Ni2 were used [14]. Inset shows an enlarged pattern at 1.0 ≤ d ≤ 1.2 Å of the X-ray diffraction of Ca0.5Mg0.5Ni2.0 and Ca1.0Mg1.0Ni4.0. (002) and (006) reflection, which are the systematic absence of the space group Fd-3m (No. 227), are indicated by arrows.
The differences between the two diffraction patterns are apparent in the (00l) reflections, which appear at d = 3.49 Å (002) and d = 1.16 Å (006). In the case of Fd-3m (No. 227), the (002) and (006) reflections are forbidden because of the systematic absences (l: 4n) in the space group, although their reflections appear in the space group F-43m (No. 216). Therefore, the (00l) reflections indicate the crystal structure-types. In REMgNi4-based alloys in the space group F-43m (No. 216), some of the RE atoms are replaced by Mg atoms and vice versa (RE(2−x)MgxNi4, 0 < x < 2). Although the arrangement of the RE and Mg atoms is disordered, their site occupations at (0, 0, 0) and (1/4, 1/4, 1/4) differ. In RE(2−x)MgxNi4, hydrogen absorption and desorption pressures (so-called plateau pressures) increase with increasing amounts of Mg, owing to a decreasing unit cell size that restricts the space available to hydrogen atomic sites. Affinities between metal and hydrogen atoms would relate with the reactions.
2.2. α-Hydride Phase (REMgNi4Hx1)
The crystal structure of the α-hydride phase has been reported in the hydrogen absorption reactions of LaMgNi4 (Figure 3). This hydride phase is formed at 0.5 MPa at 373 K [24]. The unit cell is slightly expanded compared with that of the alloy phase, and hydrogen atoms were located in a tetrahedral site coordinated by four Ni atoms. We recently reported that the alloy phases of Y(2−x)MgxNi4 (0 < x < 2) with larger unit cell parameters (Y >> Mg) form the α-hydride phase, which correspond to lower reversible hydrogen storage capacities because the α-hydride phase is thermodynamically stable and does not release hydrogen at 323 K. In the case where there are more Y atoms than Mg atoms (Y >> Mg in Y(2−x)MgxNi4 (0 < x < 2)), after hydrogen absorption, poor crystallinity (hydrogen-induced amorphization (HIA) [35,36]) has also been observed [20]. HIA is related to the atomic radii of the components. Thus, in general, less Mg decreases the reversible hydrogen storage capacity through α-hydride phase formation and results in HIA, although the precise values of Mg depend on the RE elements.
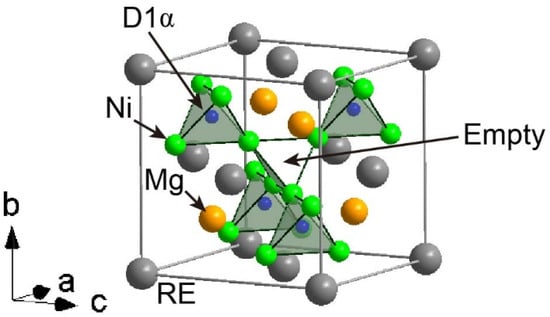
Figure 3.
Crystal structure of α hydride based on LaMgNi4D0.75 [24]. The RE, Mg, and Ni D atoms are represented by grey, orange, and green spheres, respectively. The corner-shared tetrahedra formed by four Ni atoms are represented as the green polyhedra. The D atoms in the crystal structure are indicated as D1α.
2.3. β-Hydride Phase (REMgNi4Hx2)
The β-hydride phase is formed at a hydrogen pressure less than 10 MPa below 373 K. Therefore, the β-hydride phase is mainly obtained as the hydride phase of RE(2−x)MgxNi4 under a moderate hydrogen pressure range.
The β-hydride phase adopts an orthorhombic unit cell in the space group Pmn21 (No. 31) with Z = 2. Although the crystal system is different from the alloy phase, the same metal atomic arrangements of REMgNi4 (but distorted) were found in the crystal structure (Figure 4).
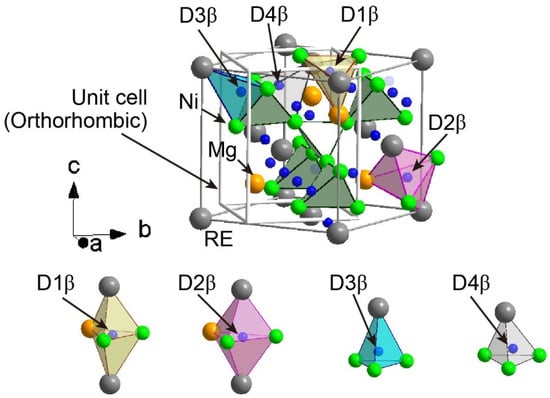
Figure 4.
Crystal structure of β hydride, based on Y1.06Mg0.94Ni4.00D3.86 [20]. The Y, Mg, and Ni D atoms are represented by grey, orange, and green circles, respectively. Parts of Mg atoms are replaced by Y atoms. The corner-shared tetrahedra formed by four Ni atoms are represented as the green polyhedra. The original orthorhombic unit cell is represented as white line. The grey lines connect the Y atoms in Y1.06Mg0.94Ni4.00D3.86 to compare it with the unit cell of REMgNi4 (Figure 1). In the local atomic arrangements around the D atoms, the hydrogen sites in the triangular bipyramid, and the tetrahedra are represented as yellow (D1β), pink (D2β), cyan (D3β), and green (D4β) polyhedral, respectively.
Hydrogen atoms are located inside the triangular bipyramids and tetrahedra. The triangular bipyramid is formed by two RE, one Mg, and two Ni atoms, and the tetrahedron is formed by one RE and three Ni atoms. When there are more RE atoms than Mg atoms, the volumes of the hydrogen atomic sites are expanded, and the hydrogen storage capacities are increased [20]. As mentioned above, increasing the volume of the unit cell induces the formation of thermodynamically stable α-hydride phases, which are responsible for the lower reversible hydrogen storage capacities reported for Y(2−x)MgxNi4 (0 < x < 2) [20]. In Y(2−x)MgxNi4 (0 < x < 2), the alloys with slightly more Y atoms than Mg atoms exhibited the highest reversible hydrogen storage capacities [20]. The affinity of metal atoms around hydrogen atoms is speculated to be related to hydrogen storage properties, in addition to the space available to the hydrogen atomic sites.
To date, the β-hydride has been reported to have three crystallographically different hydrogen atomic sites (D1β, D2β, and D3β), and Y(2−x)MgxNi4 (0 < x < 2) has one extra hydrogen atomic site (D4β in Figure 4). The amount of extra D4β hydrogen atomic sites increased with increasing amounts of Y atoms, and the positions were the same as those of the hydrogen atoms in the γ-hydride phase. Although the γ-hydride phase of Y(2−x)MgxNi4 (0 < x < 2) could not be observed [20], an increase in the occupancies of D4β might lead to the formation of the γ-hydride phase (the hydrogen atomic positions in the γ-hydride phase are shown in the next section). Notably, the extra hydrogen atomic sites have H–H interatomic distances shorter than 2.1 Å, which correspond to the shortest H–H interatomic distances in hydrides [38]. Although hydrogen atomic pairs with short interatomic distances might not simultaneously exist at each atomic site, such short H–H interatomic distances have been reported in the γ hydride [28] as well as the other hydrides [39,40,41].
Related to the β-hydride phase with the orthorhombic unit cell, a TbMgCo4 hydride phase with a monoclinic unit cell in the space group Pm (No. 6) has been reported [33]. The details of hydrogen atomic positions in the monoclinic structure are not presented in the Ref. [33].
2.4. Y-Hydride Phase (REMgNi4Hx3)
The γ-hydride phase formed at higher hydrogen pressures and had higher storage capacities than the α and β hydrides. As mentioned above, the hydrogen pressure depends on the types of RE and the compositional ratios between the RE and Mg atoms. This is because the equilibrium hydrogen pressure for the γ-hydride phase decreases if the β hydride is formed at a lower pressure. A larger unit cell size and lower amounts of Mg induce the absorption of hydrogen at lower hydrogen pressures and form a thermodynamically stable α-hydride phase with lower reversible hydrogen storage capacities. Thus, it is important to form the γ-hydride phase at a lower equilibrium hydrogen pressure without the formation of the α-hydride phase to maintain higher hydrogen storage capacities. In addition to optimizing the compositional ratios between RE and Mg, another approach is the replacement of a portion of the Ni atoms with transition metals (e.g., Co) [19,29,30,31,32,33]. With the replacement of Ni with Co, the hydrogen storage capacity of YMgCo4 was found to be higher than that of LaNi5 [19].
The γ-hydride phase has an FCC crystal structure in the space group F-43m (No. 216) with Z = 4 (Figure 5). Two crystal structure models have been reported. One is LaMgNi4H4.85, wherein hydrogen atoms are located inside the triangular bipyramid coordinated by two La, one Mg, and two Ni atoms and a tetrahedron coordinated by four Ni atoms. The hydrogen atoms in the tetrahedron (1/2, 1/2, 1/2) have different atomic positions from hydrogen atoms (3/4, 3/4, 3/4) in the α-hydride phase. The other is Pr0.6Mg1.4Ni4H3.6, wherein a portion of the Mg atoms are located at the Pr atomic positions. The hydrogen atoms inside the triangular bipyramid are coordinated by two Pr (Mg), one Mg, and two Ni atoms and a tetrahedron coordinated by one Pr (Mg) and three Ni atoms. The difference between LaMgNi4H4.85 and Pr0.6Mg1.4Ni4H3.6 is the hydrogen atomic sites in the tetrahedral sites (see Figure 5). The hydrogen atomic sites in Pr0.6Mg1.4Ni4H3.6 are similar to those of the β hydride (see Figure 4 and Figure 5b). In particular, the D2γ hydrogen atomic site has the same local atomic arrangements as D4β in the β hydride, Y1.06Mg0.94Ni4D3.86 (Figure 4). D4β atoms, which were observed in Y1.06Mg0.94Ni4.00D3.86 as extra hydrogen atomic sites with short D–D interatomic distances of less than 2.1 Å, are speculated to be a bridge between the β- and γ-hydride phases.
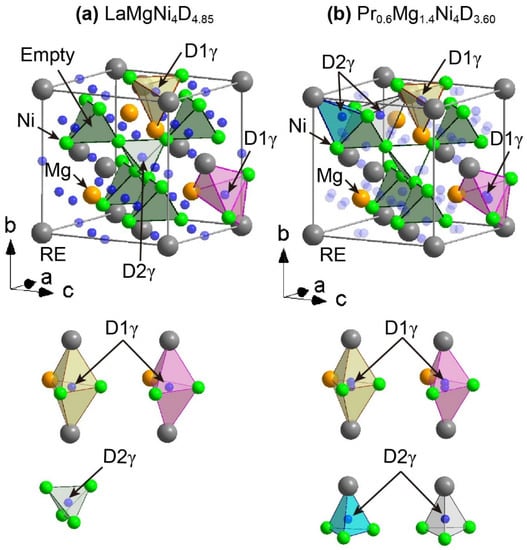
Figure 5.
Crystal structures of γ hydride phases based on (a) LaMgNi4D4.85 [24] and (b) Pr0.6Mg1.4Ni4D3.60. [28]. The La (Pr), Mg, and Ni D atoms are represented by grey, orange, and green spheres, respectively. Parts of Pr atoms are replaced by Mg atoms in Pr0.6Mg1.4Ni4D3.60. The corner-shared tetrahedra formed by four Ni atoms are represented as the green polyhedra. The original orthorhombic unit cell is represented as white line. In the local atomic arrangements around the D atoms, the hydrogen sites (D1γ) in the triangular bipyramid are represented as yellow and pink polyhedra. In the local atomic arrangements around the D atoms, the hydrogen sites (D2γ) in the tetrahedra are represented as green (LaMgNi4D4.85), cyan (Pr0.6Mg1.4Ni4D3.60), and grey (Pr0.6Mg1.4Ni4D3.60) polyhedra.
3. Conclusions
REMgNi4-based alloys, RE(2−x)MgxNi4 (RE: rare-earth metals; 0 < x < 2), form three hydride phases—the α-, β-, and γ-hydride phases—during the hydrogen absorption reactions.
In this paper, we provided overview of the crystal structures of the α-, β-, and γ-hydride phases. The α-hydride phase has hydrogen atoms inside the tetrahedra, while the β- and γ-hydride phases have similar hydrogen atoms inside the triangular bipyramid and tetrahedron. In particular, the β-hydride phase of Y(2−x)MgxNi4 (0 < x < 2) has an extra hydrogen atomic site with a short H–H interatomic distance of less than 2.1 Å, which has not been reported for other β-hydride phases. The atomic site has the same local atomic arrangement as the hydrogen atomic site in the γ-hydride phase and may be a bridge between the β- and γ-hydride phases.
The higher hydrogen pressures required for the formation of the γ-hydride phase (with higher hydrogen storage capacity) could be decreased by increasing the unit cell sizes of the RE(2−x)MgxNi4 with higher amounts of RE than Mg. Although RE(2−x)MgxNi4 with RE >> Mg has larger unit cell sizes, it leads to the formation of a thermodynamically stable α-hydride phase and a decrease in the reversible hydrogen storage capacity. Thus, the compositional ratios between RE and Mg should be optimized. In addition to the optimization of the compositional ratios, replacing Ni with Co can lead to the γ-hydride phase having a hydrogen storage capacity greater that of the hydrogen storage alloy, LaNi5, without the formation of a thermodynamically stable α-hydride phase. For the reason, the REMgNi4 based alloys, RE(2−x)MgxNi4 (RE: rare-earth metals; 0 < x < 2), have potential as hydrogen storage materials that could replace LaNi5.
Author Contributions
T.S. conceived and wrote the manuscript. S.-i.O. supervised and discussed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by JST SICORP, grant number JPMJSC 1802 and MEXT/JSPS KAKENHI “Hydrogenomics”, grant number JP18H05513.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Takagi, S.; Orimo, S. Recent progress in hydrogen-rich materials from the perspective of bonding flexibility of hydrogen. Scr. Mater. 2015, 109, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.; Züttel, A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 2001, 414, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Züttel, A. Materials for hydrogen storage. Mater. Today 2003, 6, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimo, S.; Nakamori, Y.; Eliseo, J.R.; Züttel, A.; Jensen, C.M. Complex hydrides for hydrogen storage. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4111–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberle, U.; Felderhoff, M.; Schüth, F. Chemical and physical solutions for hydrogen storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6608–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Oguchi, H.; Toyama, N.; Sato, T.; Takagi, S.; Otomo, T.; Arunkumar, D.; Kuwata, N.; Kawamura, J.; Orimo, S. A complex hydride lithium superionic conductor for high-energy-density all-solid-state lithium metal batteries. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirscher, M.; Yartys, V.A.; Baricco, M.; Bellosta von Colbe, J.; Blanchard, D.; Bowman, R.C.; Broom, D.P.; Buckley, C.E.; Chang, F.; Chen, P.; et al. Materials for hydrogen-based energy storage e past, recent progress and future outlook. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 827, 153548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Ikeshoji, T.; Sato, T.; Orimo, S. Pseudorotating hydride complexes with high hydrogen coordination: A class of rotatable polyanions in solid matter. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 173901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisu, K.; Kim, S.; Shinohara, T.; Zhao, K.; Züttel, A.; Orimo, S. Monocarborane cluster as a stable fluorine-free calcium battery electrolyte. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolliker, P.; Yvon, K.; Jorgensen, J.D.; Rotella, F.J. Structural studies of the hydrogen storage material Mg2NiH4. 2. Monoclinic low-temperature structure. Inorg. Chem. 1986, 25, 3590–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didisheim, J.-J.; Zolliker, P.; Yvon, K.; Fischer, P.; Schefer, J.; Gubelmann, M.; Williams, A.F. Dimagnesium iron (II) hydride, Mg2FeH6, containing octahedral FeH64– anions. Inorg. Chem. 1984, 23, 1953–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J.; Daemen, L.L.; Cheng, Y.; Orimo, S. Evidence of intermediate hydrogen states in the formation of a complex hydride. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Daemen, L.L.; Cheng, Y.; Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J.; Ikeda, K.; Aoki, T.; Otomo, T.; Orimo, S. Hydrogen-release reaction of a complex transition metal hydride with covalently bound hydrogen and hydride ions. ChemPhysChem 2019, 20, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terashita, N.; Akiba, E. Hydriding Properties of (Mg1–xMx)Ni2 C15–Type Laves Phase Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1890–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhanga, H.; Zhenga, X.; Tianb, X.; Liuc, Y.; Lia, X. New approaches for rare earth-magnesium based hydrogen storage alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2017, 27, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, P.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.F. Room Temperature Metal Hydrides for Stationary and Heat Storage Applications: A Review. Front. Energy Res. 2021, 9, 616115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadir, K.; Noréus, D.; Yamashita, I. Structural Determination of AMgNi4 (Where A = Ca, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, and Y) in the AuBe5 Type Structure. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 345, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aono, K.; Orimo, S.; Fujii, H. Structural and Hydriding Properties of MgYNi4: A new intermetallic compound with C15b-type Laves phase structure. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 309, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtender, V.V.; Denys, R.V.; Paul–Boncour, V.; Riabov, A.B.; Zavaliy, I.Y. Hydrogenation Properties and Crystal Structure of YMgT4 (T = Co, Ni, Cu) Compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 603, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Mochizuki, T.; Ikeda, K.; Honda, T.; Otomo, T.; Sagayama, H.; Yang, H.; Luo, W.; Lombardo, L.; Züttel, A.; et al. Crystal Structural Investigations for Understanding the Hydrogen Storage Properties of YMgNi4–Based Alloys. ASC Omega 2020, 5, 31192–31198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigent, J.; Gupta, M. Ab initio study of the hydrogenation properties of Mg-based binary and ternary compounds Mg2X (X= Ni, Si) and YMgNi4. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 446–447, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roquefere, J.-G.; Matar, S.F.; Bobet, J.-L. Stability of the hydrides REMgNi4H4 (RE = Y, Gd) from first principles. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 7858–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guénée, L.; Favre–Nicolin, V.; Yvon, K. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Hydrogenation Properties of the Ternary Compounds LaNi4Mg and NdNi4Mg. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 348, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotard, J.-N.; Sheptyakov, D.; Yvon, K. Hydrogen Induced Site Depopulation in the LaMgNi4–Hydrogen System. Z. Kristallogr. 2008, 223, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yuan, Z.; Bu, W.; Jia, Z.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effect of elemental substitution on the structure and hydrogen storage properties of LaMgNi4 alloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 93, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaki, K.; Terashita, N.; Tsunokake, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Akiba, E. In Situ X-ray Diffraction Study of Phase Transformation of Mg2−xPrxNi4 during Hydrogenation and Dehydrogenation (x = 0.6 and 1.0). J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaki, K.; Terashita, N.; Tsunokake, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Akiba, E. Effect of Rare Earth Elements and Alloy Composition on Hydrogenation Properties and Crystal Structures of Hydrides in Mg2−xRExNi4. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 19156–19163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaki, K.; Terashita, N.; Kim, H.; Proffen, T.; Majzoub, E.H.; Tsunokake, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Akiba, E. Crystal Structure and Local Structure of Mg2−xPrxNi4 (x = 0.6 and 1.0) Deuteride Using in Situ Neutron Total Scattering. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 7010–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denys, R.V.; Riabov, A.B.; Černý, R.; Koval’chuk, I.V.; Zavaliy, I.Y. New CeMgCo4 and Ce2MgCo9 compounds: Hydrogenation properties and crystal structure of hydrides. J. Solid State Chem. 2012, 187, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbovytskyya, Y.; Opryska, V.; Paul-Boncourb, V.; Zavaliya, I.; Berezovetsa, V.; Lyutyya, P.; Kosarchyna, Y. Solid Gas and Electrochemical Hydrogenation of the Selected Alloys (R’,R’’)2-xMgxNi4-yCoy (R’, R’’ = Pr, Nd; x = 0.8–1.2; y = 0–2). J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 876, 160155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtender, V.V.; Denys, R.V.; Paul–Boncour, V.; Verbovytskyy, Y.V.; Zavaliy, I.Y. Effect of Co substitution on hydrogenation and magnetic properties of NdMgNi4 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 639, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtender, V.V.; Denys, R.V.; Zavaliy, I.Y.; Zelinska, O.Y.; Paul-Boncour, V.; Pavlyuk, V.V. Phase equilibriain the Tb-Mg-Co system at 500 ºC, crystal structure and hydrogenation properties of selected compounds. J. Solid State Chem. 2015, 232, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtender, V.V.; Paul–Boncour, V.; Denys, R.V.; Crivello, J.-C.; Zavaliy, I.Y. TbMgNi4-xCox−(H,D)2 System. I: Synthesis, Hydrogenation Properties, and Crystal and Electronic Structures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, J.C. Atomic radii in crystal. J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 41, 3199–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Masumoto, T. Solid State Amorphization of Intermetallic Compounds by Hydrogenation. J. Alloys Compd. 1993, 194, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Li, X.-G.; Masumoto, T. Differential thermal analysis of hydrogen-induced amorphization in C15 Laves phase GdFe2. Acta Metall. Mater. 1992, 40, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, M.R.; del Moral, A. Magnetostriction and thermal expansion in rare earth-Ni2 intermetallic compounds. Proc-Int. Conf. Magn. Rare-Earths Actin. 1983, 1, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Switendick, A.C. Band Structure Calculations for Metal Hydrogen Systems. Z. Phys. Chem. 1979, 117, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgschulte, A.; Terreni, J.; Billeter, E.; Daemen, L.; Cheng, Y.; Pandey, A.; Łodziana, Z.; Hemley, R.J.; Ramirez–Cuesta, A.J. Inelastic Neutron Scattering Evidence for Anomalous H–H Distances in Metal Hydrides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yartys, V.A.; Denys, R.D.; Hauback, B.C.; Fjellvåg, H.; Bulyk, I.I.; Riabov, A.B.; Kalychak, Y.M. Short hydrogen–hydrogen separations in novel intermetallic hydrides, RE3Ni3In3D4 (RE = La, Ce and Nd). J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 330–332, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajeeston, P.; Ravindran, P.; Vidya, R.; Kjekshus, A.; Fjellvåg, H.; Yartys, V.A. Short hydrogen–hydrogen separation in RNiInH1.333 (R = La, Ce, Nd). Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).