A New Multilevel Inverter Topology with Reduced DC Sources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The basic unit of the proposed topology generates a 13 level output voltage with a higher number of levels is possible with the generalized structure.
- A reduced voltage stress is achieved and lower number of dc voltage sources is required.
- Lower number of switching transitions improves the efficiency of the proposed topology.
- The 13 level basic unit has been discussed in detail and has been validated using a 500 W experimental setup.
2. Methodology
2.1. Description of the Proposed Topology
2.2. Comparative Study
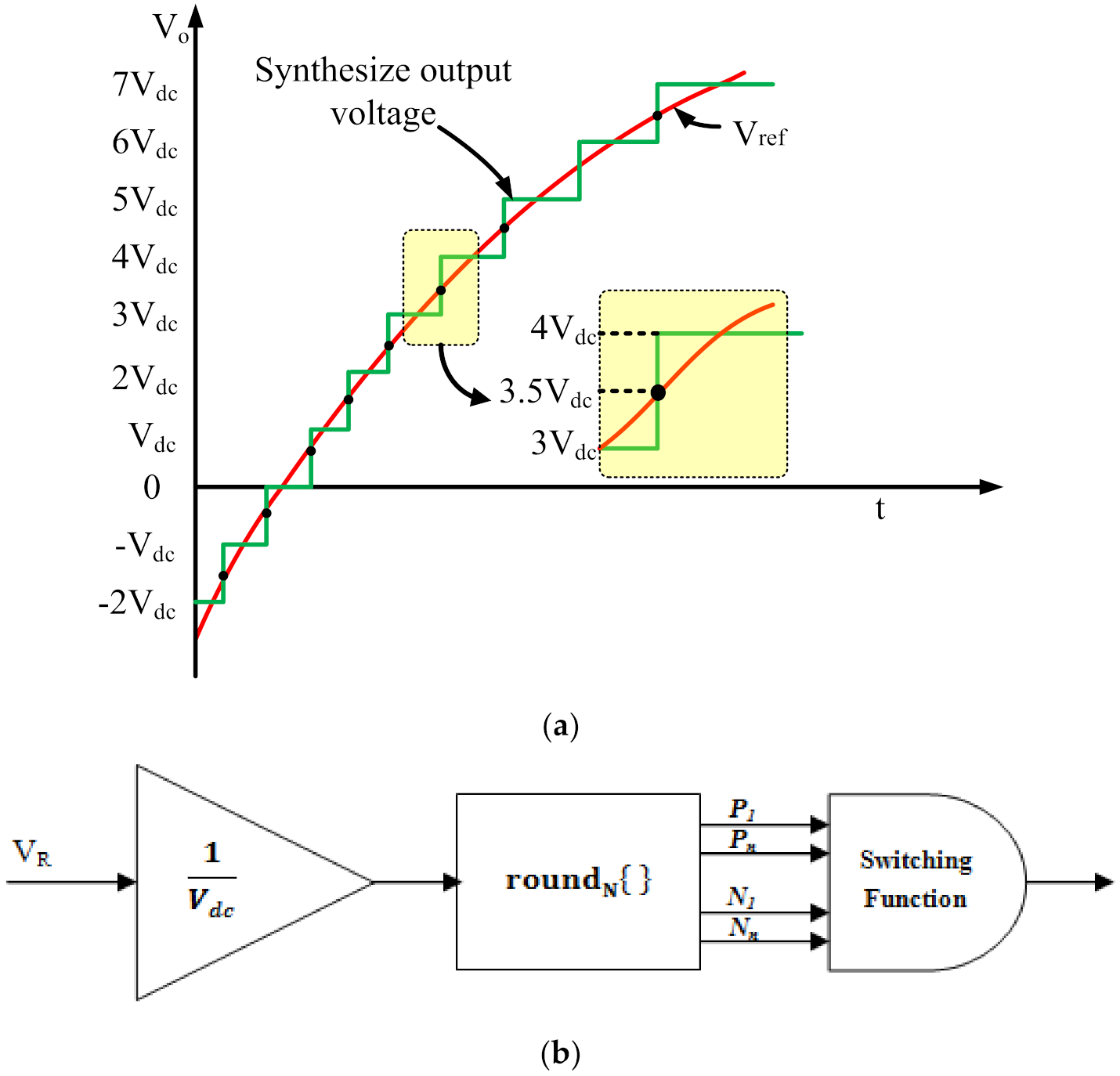
2.3. Modulation Technique
2.4. Efficiency Estimation
2.4.1. Conduction Loss
2.4.2. Switching Loss
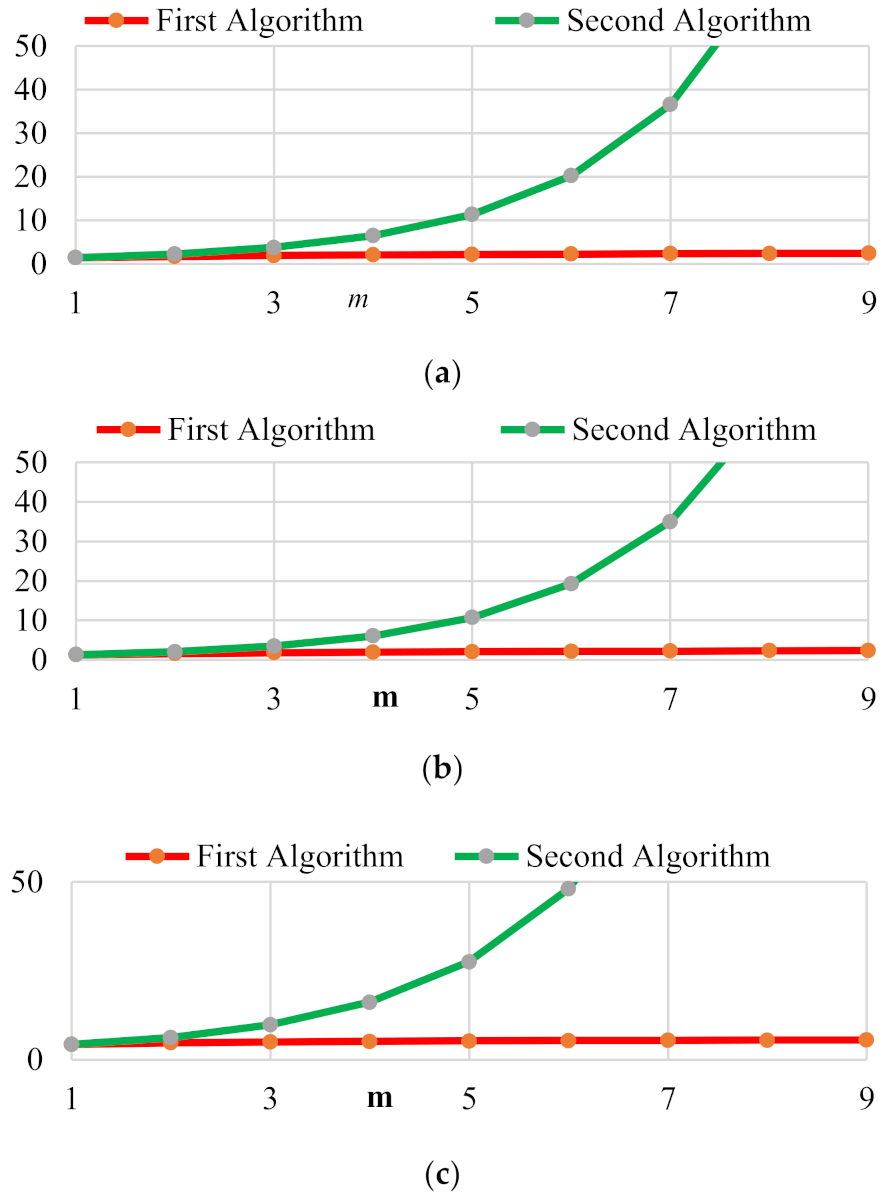
2.5. Algorithms to Fix Voltage Magnitude in Extended Topology
2.5.1. First Algorithm
2.5.2. Second Algorithm
2.6. Optimization of Structures
2.6.1. Optimization of the Proposed Cascade Converter for Maximizing the Number of Levels with Constant Power Switches
2.6.2. Optimization of the Proposed Cascade Converter for Maximizing the Number of Levels with Constant Driver Circuits
2.6.3. Optimization of the Proposed Cascade Converter for Maximizing the Number of Levels with Constant DC Sources
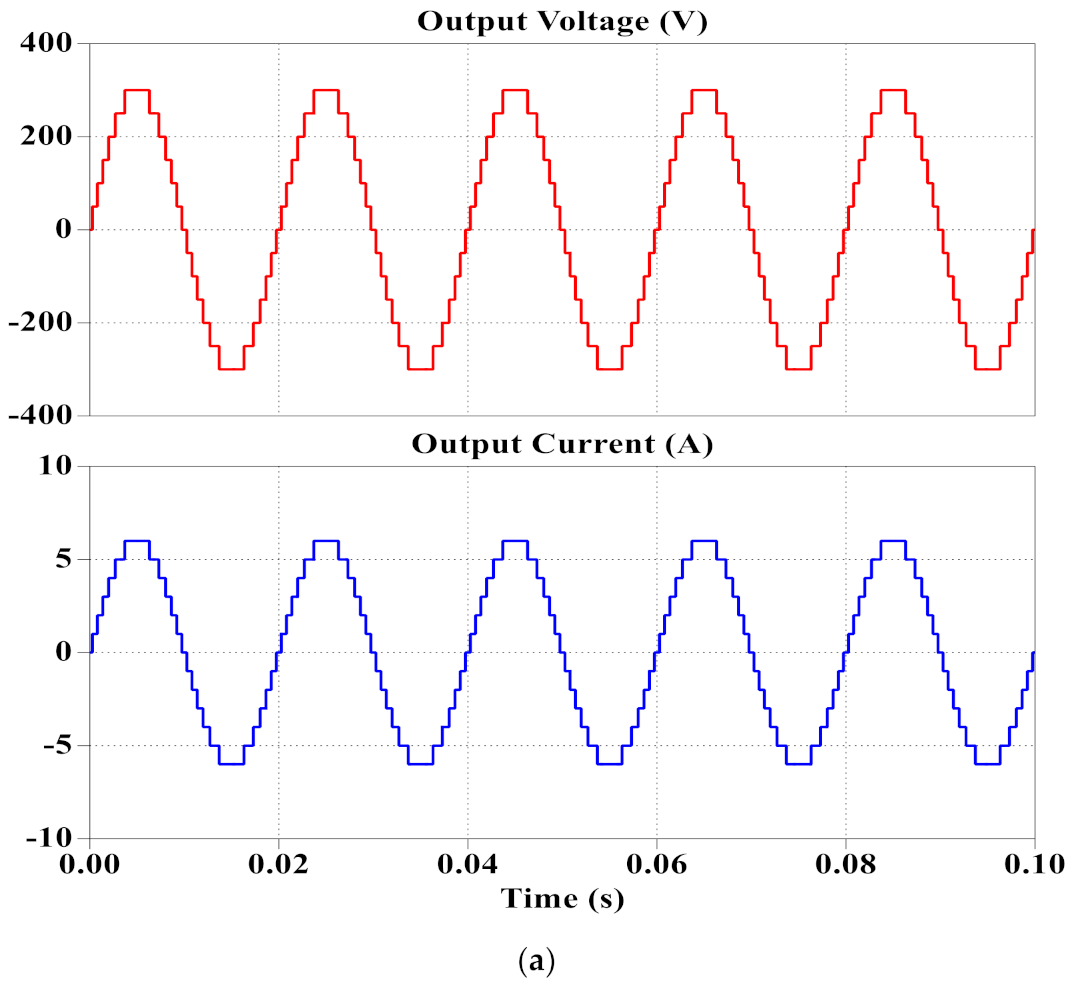
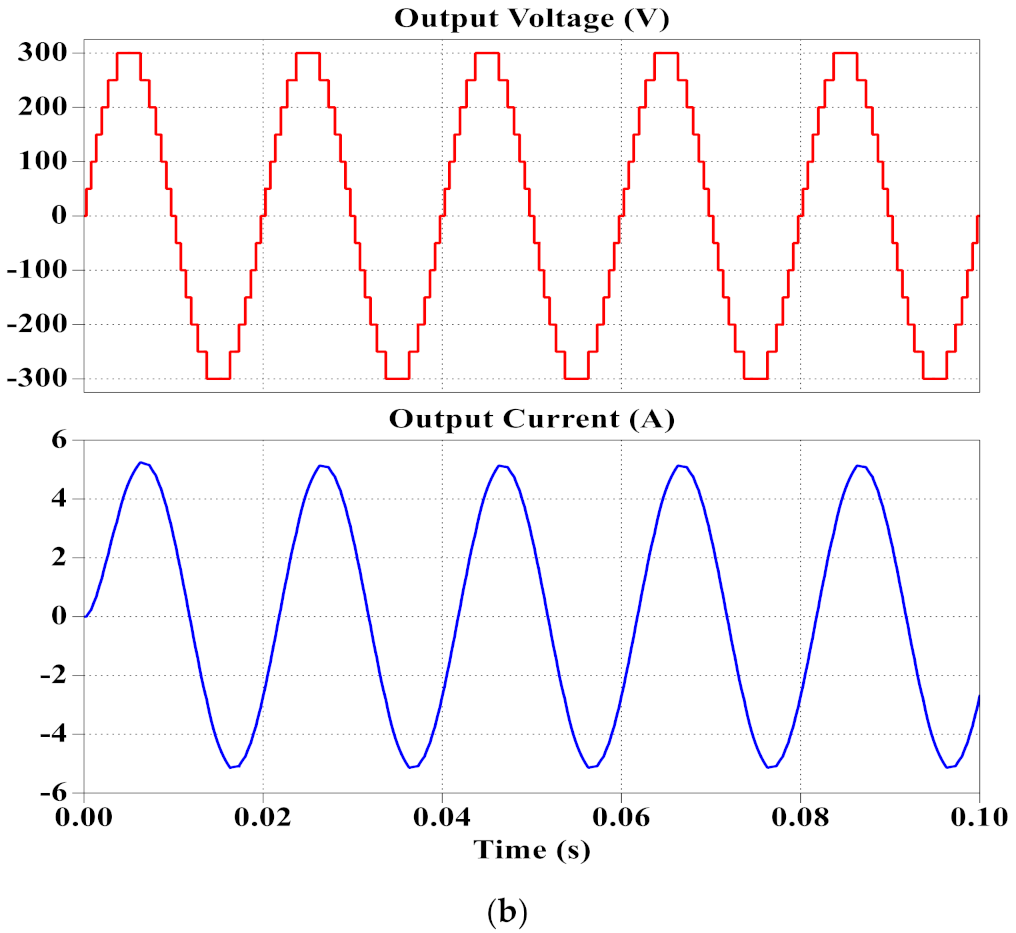
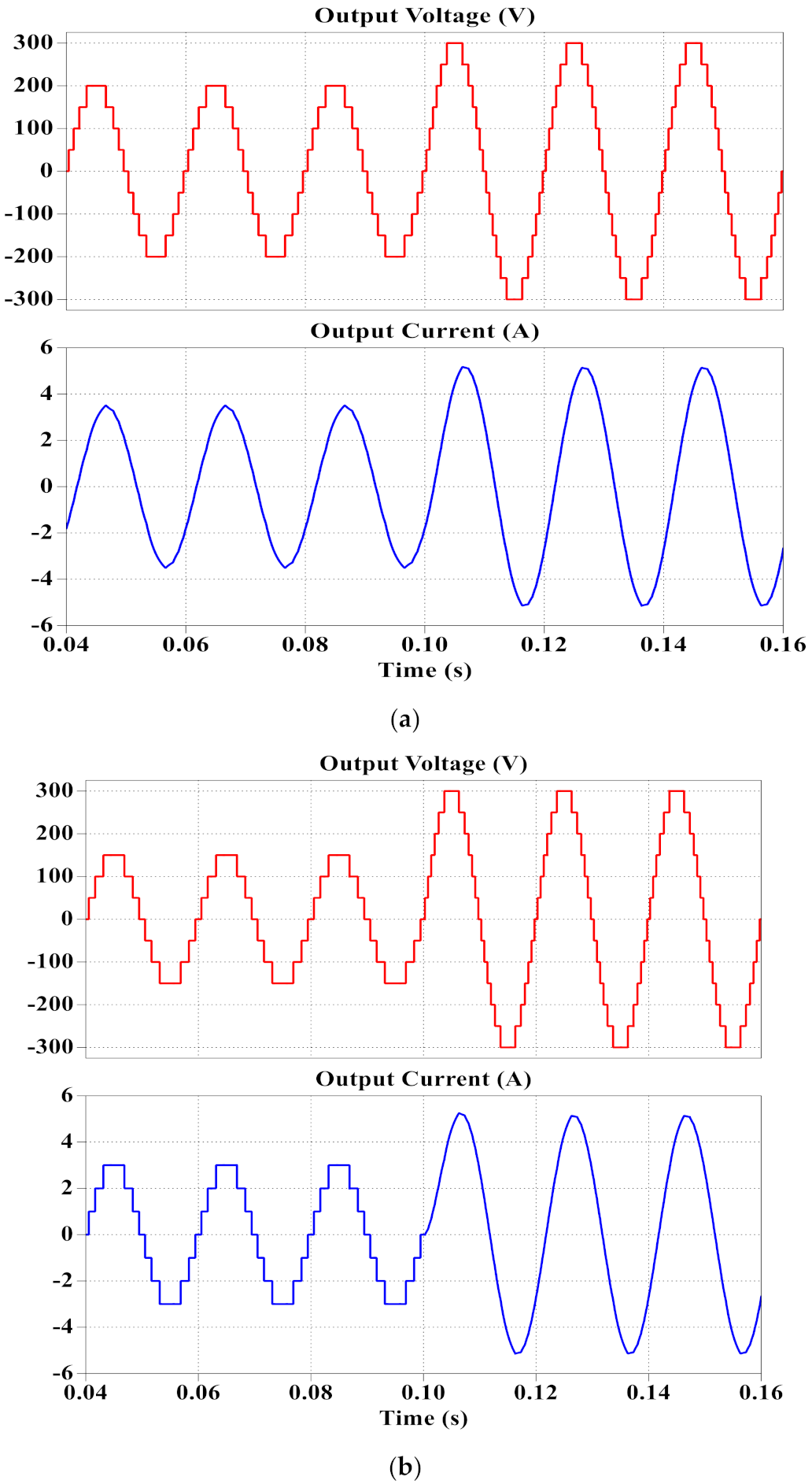
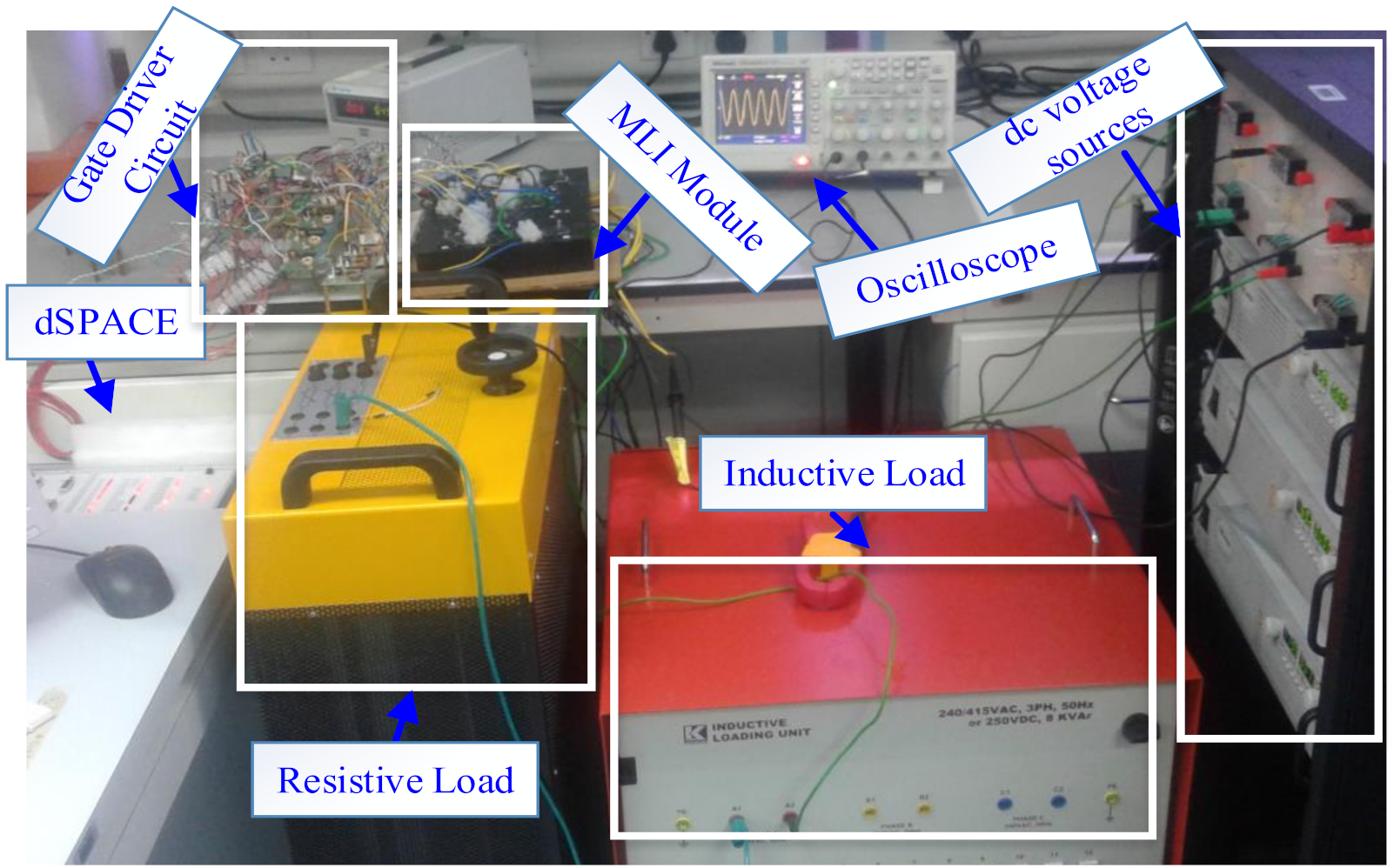
3. Simulation and Experimental Results
3.1. Simulation Results
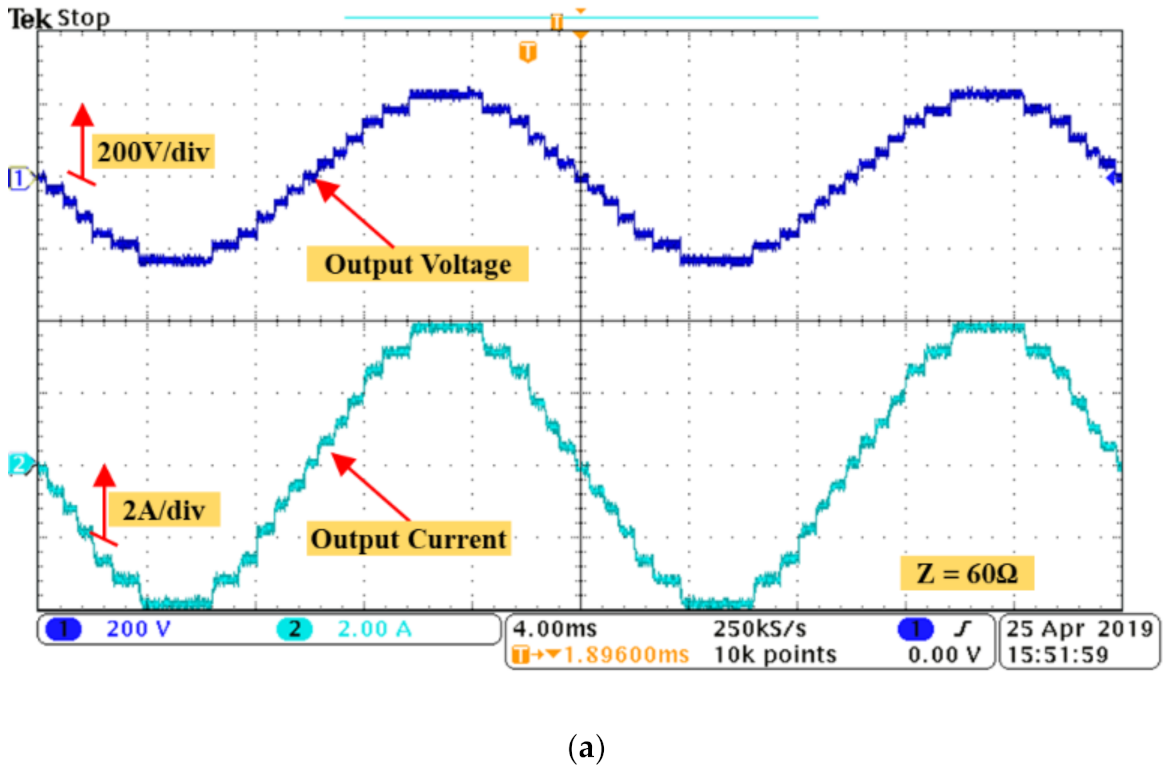
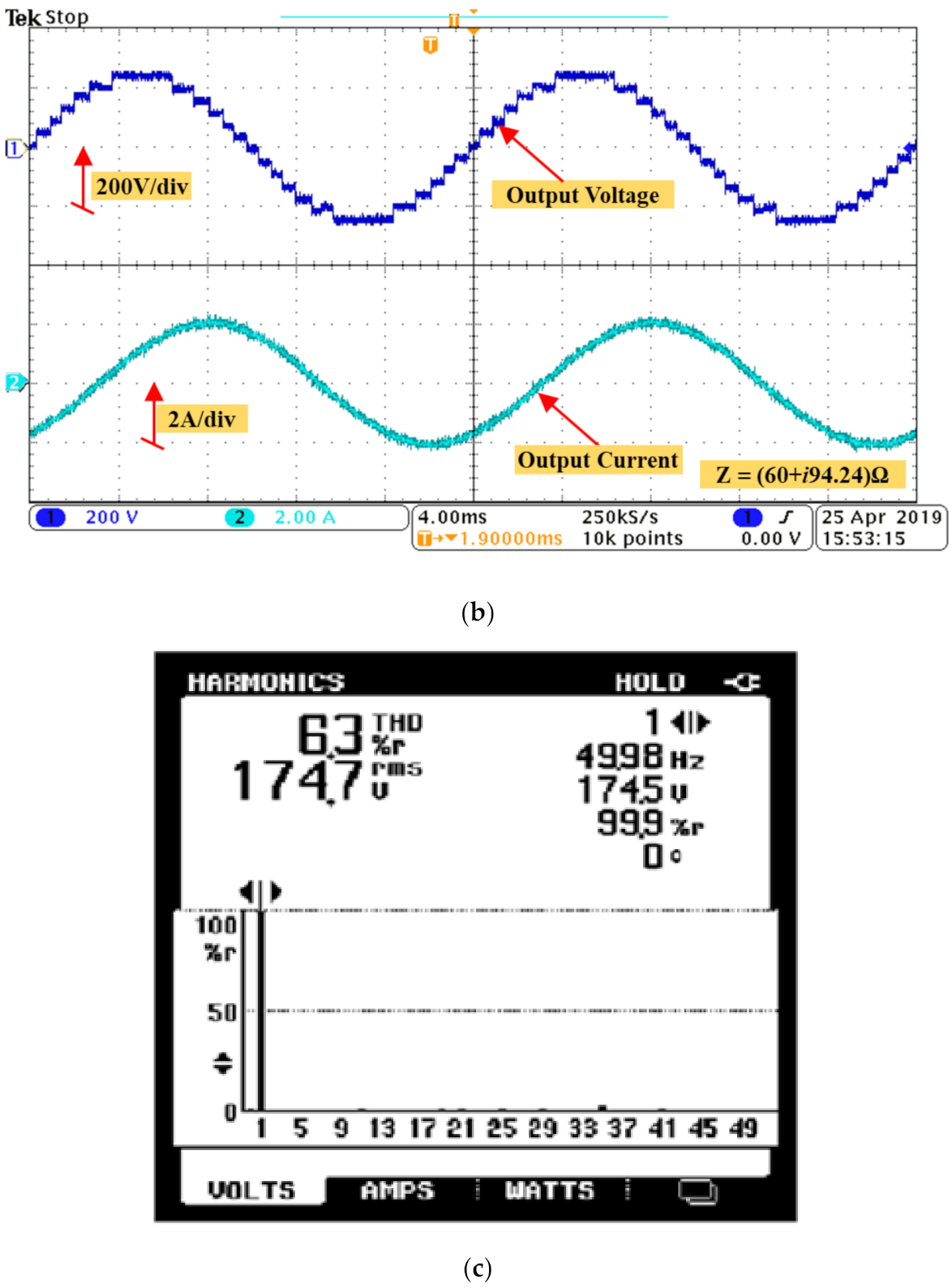
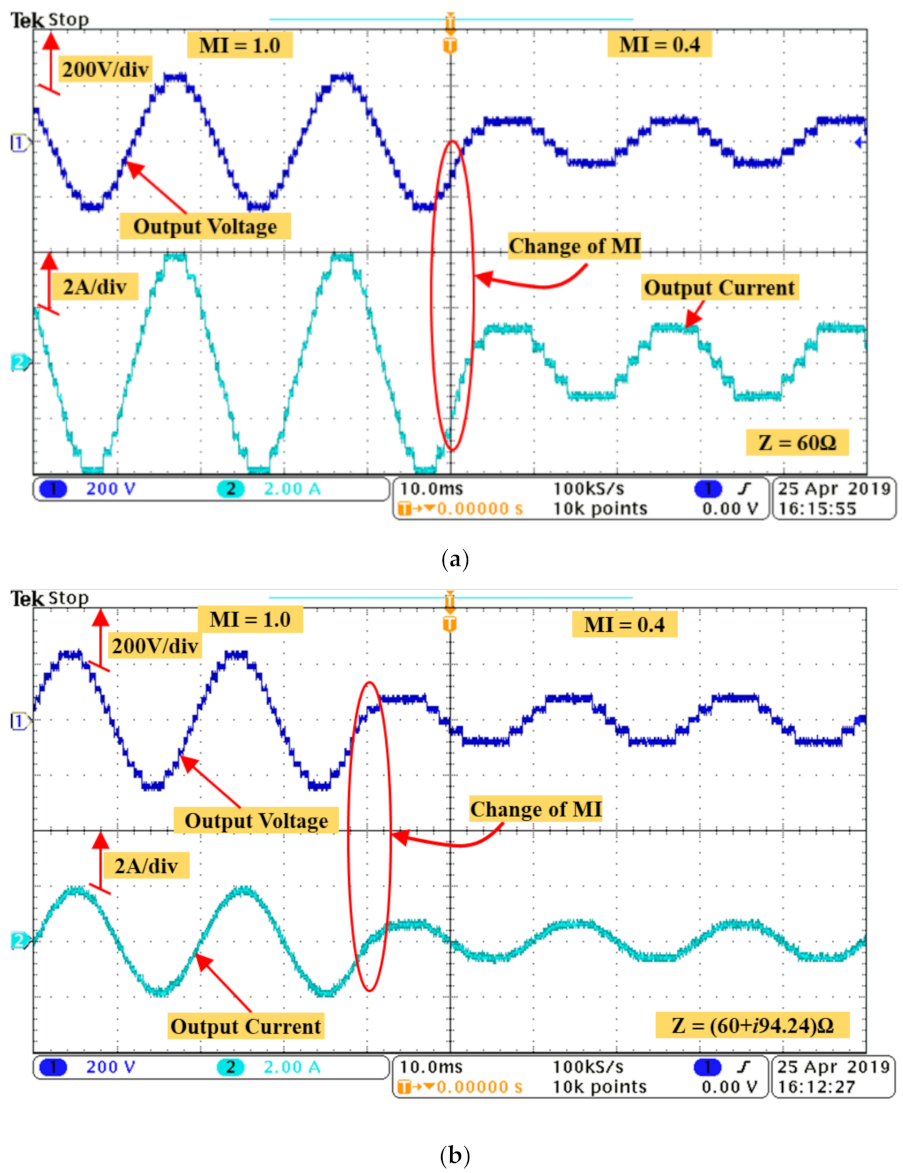
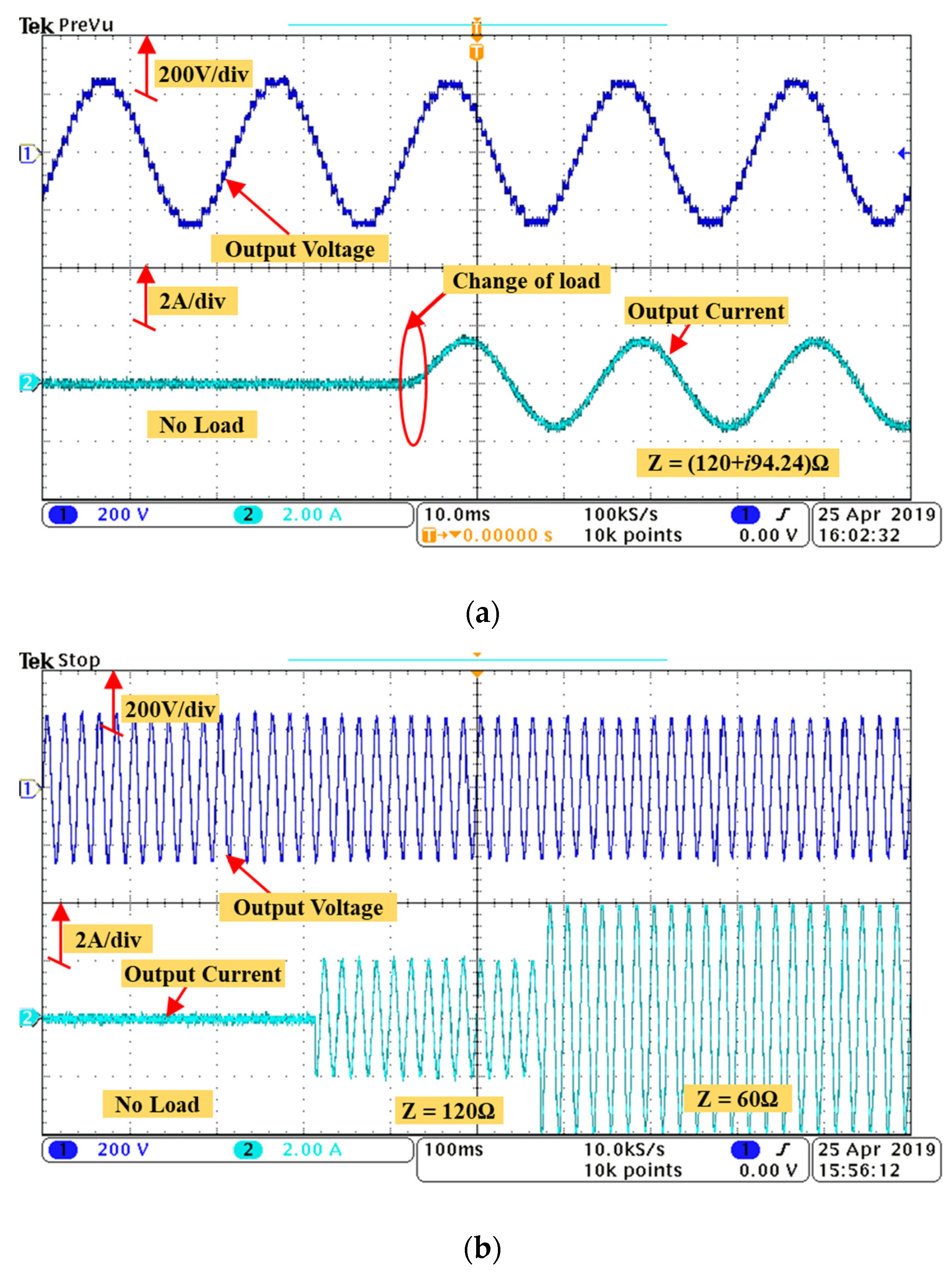
3.2. Experimental Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bughneda, A.; Salem, M.; Richelli, A.; Ishak, D.; Alatai, S. Review of multilevel inverters for PV energy system applications. Energies 2021, 14, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Din, Z.; Hu, X. Hybrid Multilevel Converters: Topologies, Evolutions and Verifications. Energies 2019, 2, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, Q.; Zhang, X.; Teng, T.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z.; Lv, Q. A Comprehensive Review on Classification, Energy Management Strategy, and Control Algorithm for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. Energies 2020, 13, 5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Benedetto, M.; Lidozzi, A.; Solero, L.; Crescimbini, F.; Grbović, P.J. High-performance 3-phase 5-level e-type multilevel–multicell converters for microgrids. Energies 2021, 14, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majstorovic, M.; Rivera, M.; Ristic, L.; Wheeler, P. Comparative study of classical and mpc control for single-phase mmc based on v-hil simulations. Energies 2021, 14, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, E.; Melín, P.; Baier, C.; Espinoza, J.; Garcés, H. An Efficiency Analysis of 27 Level Single-Phase Asymmetric Inverter without Regeneration. Energies 2021, 14, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, V.; Srinivasan, G.K.; Rivera, M. Realization of 485 level inverter using tri-state architecture for renewable energy systems. Energies 2020, 13, 6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, V.; Singh, V. Compact symmetrical and asymmetrical multilevel inverter with reduced switches. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, e12458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, V.; Singh, V. Implementation of cascaded asymmetrical multilevel inverter for renewable energy integration. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2020, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Alilu, S.; Laali, S. A new general topology for cascaded multilevel inverters with reduced number of components based on developed H-bridge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3932–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishah, R.S.; Nazarpour, D.; Hosseini, S.H.; Sabahi, M. Reduction of power electronic elements in multilevel converters using a new cascade structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.K.; Jain, S. Comprehensive review of a recently proposed multilevel inverter. IET Power Electron. 2014, 7, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prem, P.; Bharanikumar, R. Design and mathematical evaluation of a new multilevel inverter topology with less circuit components for solar and wind energy conversion systems. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2017, 11, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.D.; Mekhilef, S.; Shah, N.M.; Memon, M.A. Optimal Design of a New Cascaded Multilevel Inverter Topology with Reduced Switch Count. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 24498–24510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaoud, A.; Mekhilef, S.; Ping, H.W.; Wong, K.I. A simplified structure for three-phase 4-level inverter employing fundamental frequency switching technique. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 1870–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadaei, E.; Gholamian, S.A.; Sheikholeslami, A.; Adabi, J. An Envelope Type (E-Type) Module: Asymmetric Multilevel Inverters with Reduced Components. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7148–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.P.; Sahu, L.K.; Gupta, S. Reduction in number of devices for symmetrical and asymmetrical multilevel inverters. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabalan, M.; Jeevarathinam, B.; Sandirasegarane, T. Reduced switch count pulse width modulated multilevel inverter. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadaei, E.; Sheikholeslami, A.; Gholamian, S.A.; Adabi, J. A Square T-Type (ST-Type) Module for Asymmetrical Multilevel Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prem, P.; Sathik, J.; Sivaraman, P.; Mathewsaran, A.; Aleem, S.H.E.A. A new asymmetric dual source multilevel inverter topology with reduced power switches. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. Trans. Chin. Inst. Eng. A 2019, 42, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prem, P.; Sugavanam, V.; Abubakar, A.I.; Ali, J.S.M.; Sengodan, B.C.; Krishnasamy, V.; Padmanaban, S. A novel cross-connected multilevel inverter topology for higher number of voltage levels with reduced switch count. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2020, 30, e12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.S.M.; Kannan, R. A new symmetric cascaded multilevel inverter topology using single and double source unit. J. Power Electron. 2015, 15, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramani, K.; Sathik, M.A.J.; Sivakumar, S. A new symmetric multilevel inverter topology using single and double source sub-multilevel inverters. J. Power Electron. 2015, 15, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alishah, R.S.; Hosseini, S.H.; Babaei, E.; Sabahi, M. A New General Multilevel Converter Topology Based on Cascaded Connection of Submultilevel Units with Reduced Switching Components, DC Sources, and Blocked Voltage by Switches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7157–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccella, C.; Cecati, C.; Cimoroni, M.G.; Razi, K. Analytical method for pattern generation in five-level cascaded H-bridge inverter using selective harmonic elimination. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5811–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishah, R.; Nazarpour, D.; Hosseini, S.H.; Sabahi, M. Novel topologies for symmetric, asymmetric, and cascade switched-diode multilevel converter with minimum number of power electronic components. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 5300–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neti, S.S.; Anand, V.; Singh, V. Single-Phase Generalized Switched-Capacitor Multilevel Inverter Using Reduced Number of Power Semiconductor Components with Voltage Boosting Ability. Arab J. Sci. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Laali, S.; Bayat, Z. A single-phase cascaded multilevel inverter based on a new basic unit with reduced number of power switches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.D.; Ali, J.S.M.; Mekhilef, S.; Mustafa, A.; Sandeep, N.; Almakhles, D. Reduced Switch Count Based Single Source 7L Boost Inverter Topology. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 2020, 67, 3252–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.D.; Mekhilef, S.; Mekhilef, S.; Shah, N.M.; Ali, J.S.M.; Blaabjerg, F. A new switched capacitor 7L inverter with triple voltage gain and low voltage stress. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Express Briefs 2020, 67, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.D.; Mekhilef, S.; Padmanaban, S.; Memon, M.A.; Kumar, C. Single Phase Step-up Switched-Capacitor Based Multilevel Inverter Topology with SHEPWM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 3107–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camurca, L.; Langwasser, M.; Liserre, M. Design Approach of Inductive Components in Medium Voltage Modular Multilevel Converter Considering DC Side Fault Protection Conditions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition—PEC, Virtual Conference, 14–17 June 2021; pp. 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, A.; Monopoli, V.G.; Tcai, A.; Leon, J.I.; Buticchi, G.; Vazquez, S.; Liserre, M.; Franquelo, L.G. Discontinuous-PWM Method for Multilevel N-Cell Cascaded H-Bridge Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 7996–8005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

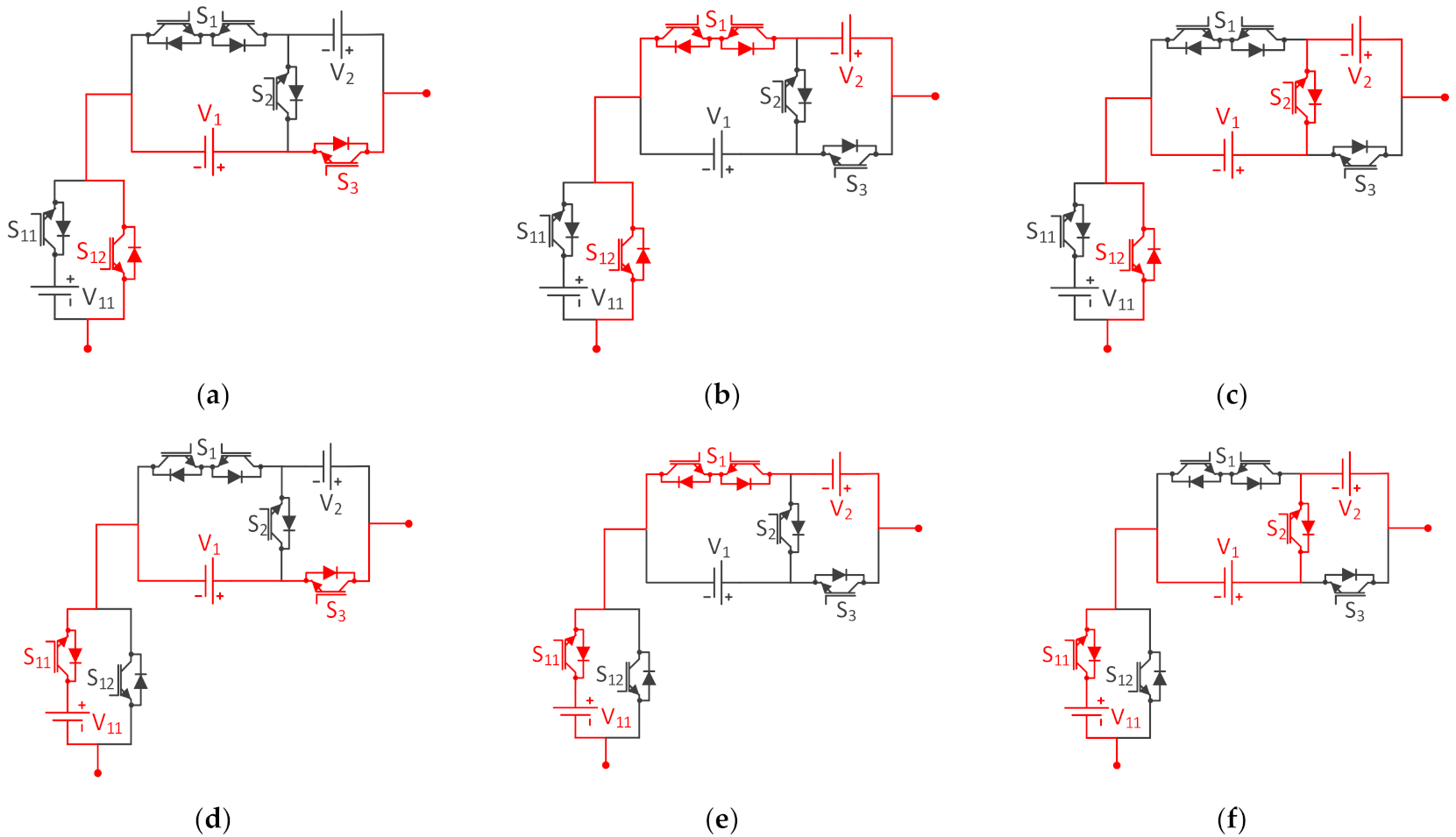
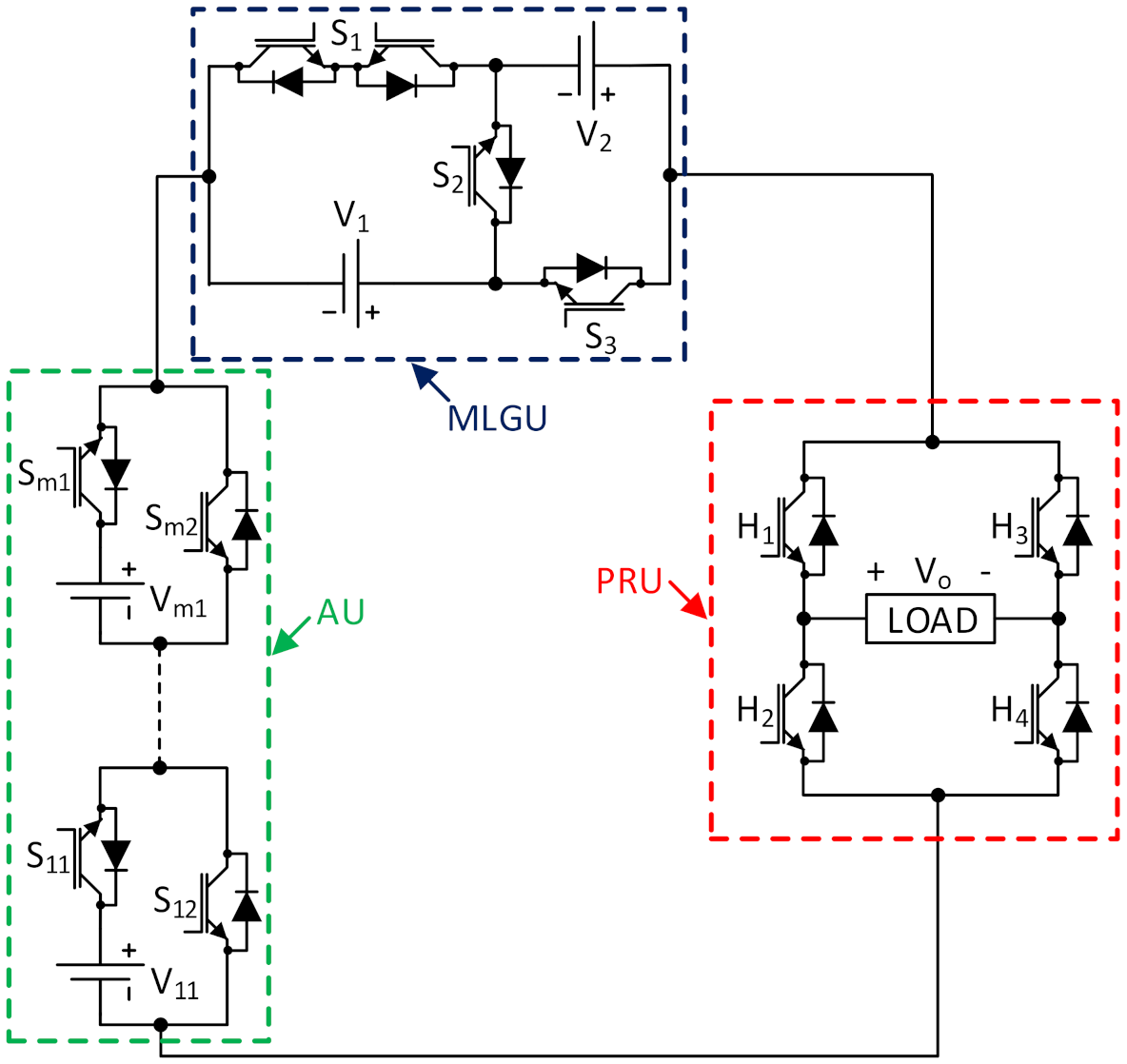

| S1 | S2 | S3 | S11 | S12 | S21 | S22 | --- | Sm1 | Sm2 | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | Load Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | V1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | V2 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | V1 + V2 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | V11 + V1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | V11 + V2 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | V11 + V1+ V2 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | V21 + V11 + V1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -- | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | V21 + V11 + V2 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -- | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | V21 + V11 + V1+ V1 |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -- | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Vm1 + V21 + V11 + V1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -- | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Vm1 + V21 + V11 + V2 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -- | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | Vm1 + V21 + V11 + V1 + V1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −V1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −V2 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −(V1 + V2) |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −(V11 + V1) |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −(V11 + V2) |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | -- | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −(V11 + V1+ V2) |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | - | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −(V21 + V11 + V1) |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -- | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −(V21 + V11 + V2) |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -- | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −(V21 + V11 + V1+ V1) |
| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -- | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −(Vm1 + V21 + V11 + V1) |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -- | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −(Vm1 + V21 + V11 + V2) |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | -- | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | −(Vm1 + V21 + V11 + V1 + V1) |
| S.No | Parameter | [13] | [20] | [21] | [19] | [17] | [18] | [24] | [28] | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Number of independent sources | 6 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 3 |
| 2 | Number of capacitors | - | 4 | - | - | 3 | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | Number of IGBTs | 10 | 9 | 14 | 12 | 8 | 10 | 16 | 16 | 10 |
| 4 | Number of drivers | 8 | 7 | 13 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 7 |
| 5 | Number of diodes | 1 | - | - | - | 14 | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | Cost of IGBT in USD (at 1 USD per IGBT) | 10 | 9 | 14 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 16 | 16 | 10 |
| 7 | Cost of Driver in USD (at 5.25 USD per IGBT) | 42 | 36.75 | 68.25 | 47.25 | 42 | 52.5 | 63 | 73.5 | 36.75 |
| 8 | Cost of diodes in USD (at 3.63 USD per diode) | 3.63 | - | - | - | 50.82 | - | - | - | - |
| 9 | Cost of capacitor in USD (at 1.82 USD per capacitor) | - | 7.28 | - | - | 5.46 | - | - | - | - |
| 10 | Total cost (USD) | 80.63 | 75.03 | 113.25 | 81.2 | 141.28 | 86.5 | 113 | 126.5 | 66.75 |
| 11 | Experimental output power (W) | 32 | 450 | 170 | 240 | 64 | 300 | 570 | 125 | 500 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rawa, M.; P, P.; Mohamed Ali, J.S.; Siddique, M.D.; Mekhilef, S.; Wahyudie, A.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.; Stojcevski, A. A New Multilevel Inverter Topology with Reduced DC Sources. Energies 2021, 14, 4709. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154709
Rawa M, P P, Mohamed Ali JS, Siddique MD, Mekhilef S, Wahyudie A, Seyedmahmoudian M, Stojcevski A. A New Multilevel Inverter Topology with Reduced DC Sources. Energies. 2021; 14(15):4709. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154709
Chicago/Turabian StyleRawa, Muhyaddin, Prem P, Jagabar Sathik Mohamed Ali, Marif Daula Siddique, Saad Mekhilef, Addy Wahyudie, Mehdi Seyedmahmoudian, and Alex Stojcevski. 2021. "A New Multilevel Inverter Topology with Reduced DC Sources" Energies 14, no. 15: 4709. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154709
APA StyleRawa, M., P, P., Mohamed Ali, J. S., Siddique, M. D., Mekhilef, S., Wahyudie, A., Seyedmahmoudian, M., & Stojcevski, A. (2021). A New Multilevel Inverter Topology with Reduced DC Sources. Energies, 14(15), 4709. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14154709











