Performance Improvement of a Double-Layer Microchannel Heat Sink via Novel Fin Geometry—A Numerical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overall Model Description
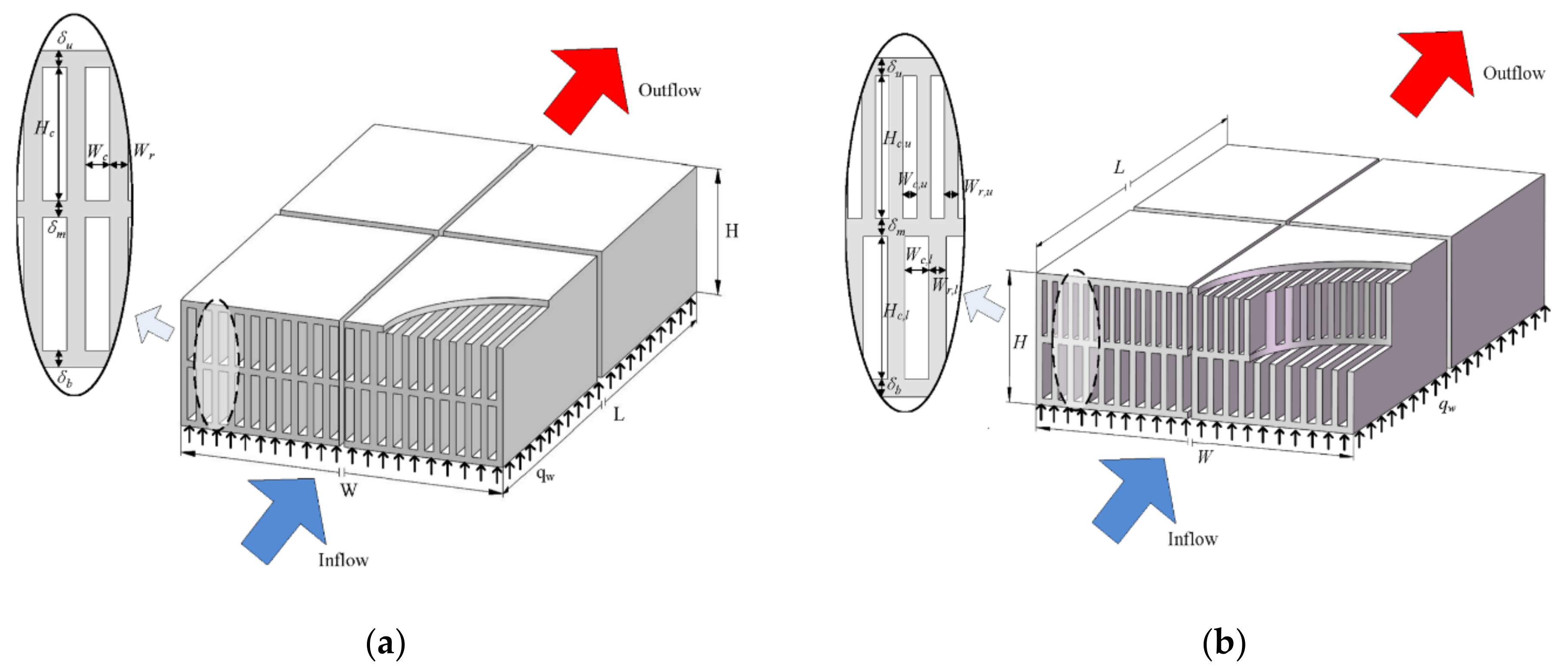
2.1. Traditional Double-Layer Microchannel Heat Sink
2.2. Definition of the Proposed Double-Layer Microchannel Sink
2.3. Material Selection
3. Analysis and Simulation Process
3.1. Assumptions and Governing Formulas
- The fluid flow is assumed incompressible and laminar, and steady state prevails.
- The influence of gravity effect and radiation is ignored.
- The thermophysical properties of fluid and solid materials are constant.
- The influence of viscous dissipation is ignored.
- No slip conditions occur at the fluid/solid interface.
- For the traditional double-layer microchannel heat sink, it is assumed that the flow of each channel is evenly distributed.
3.2. Simulation Domain
3.3. Simulation Methods
3.4. Study of Grid Independence
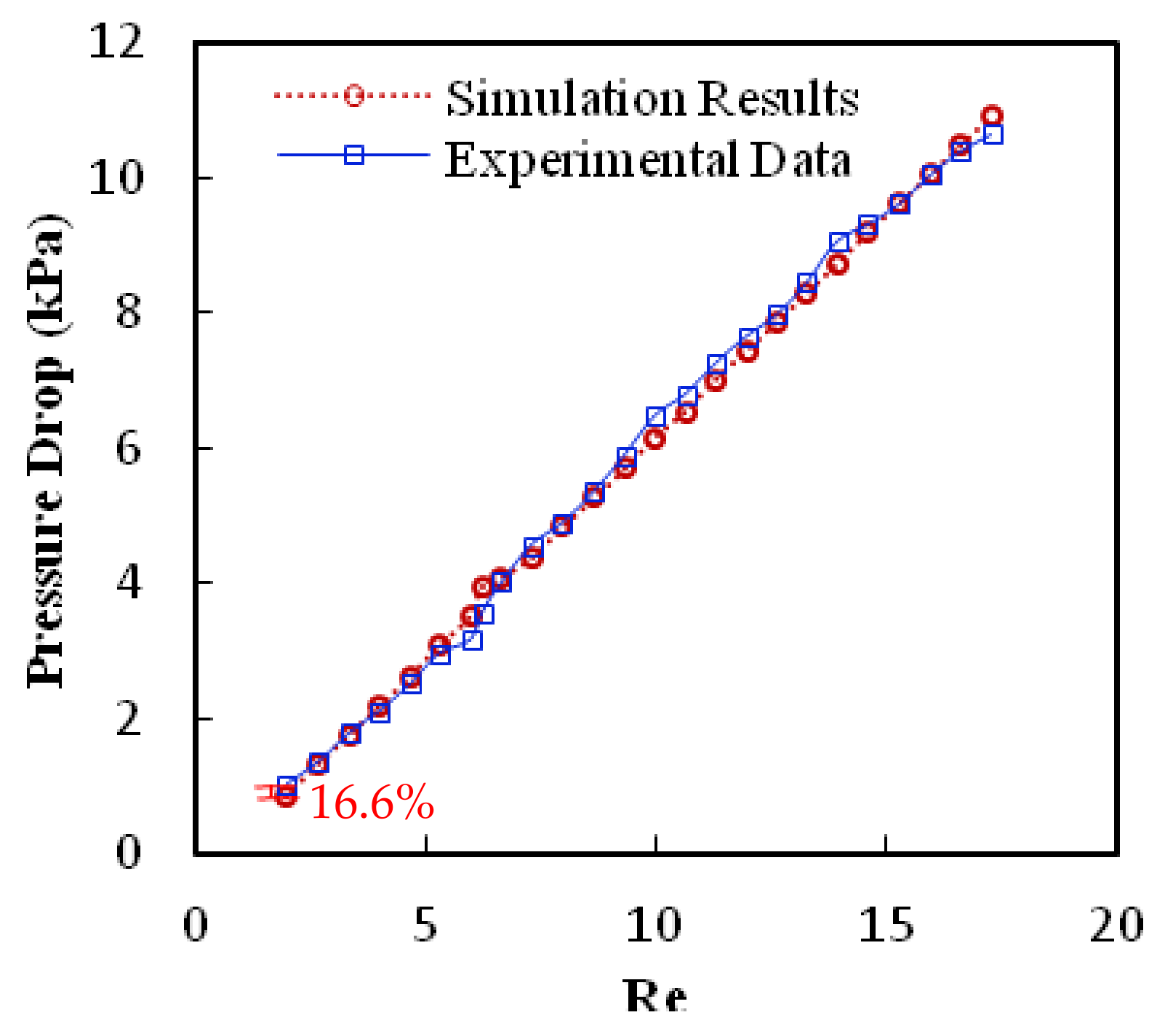
3.5. Model Validation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Pressure Drop Loss and Corresponding Pumping Power
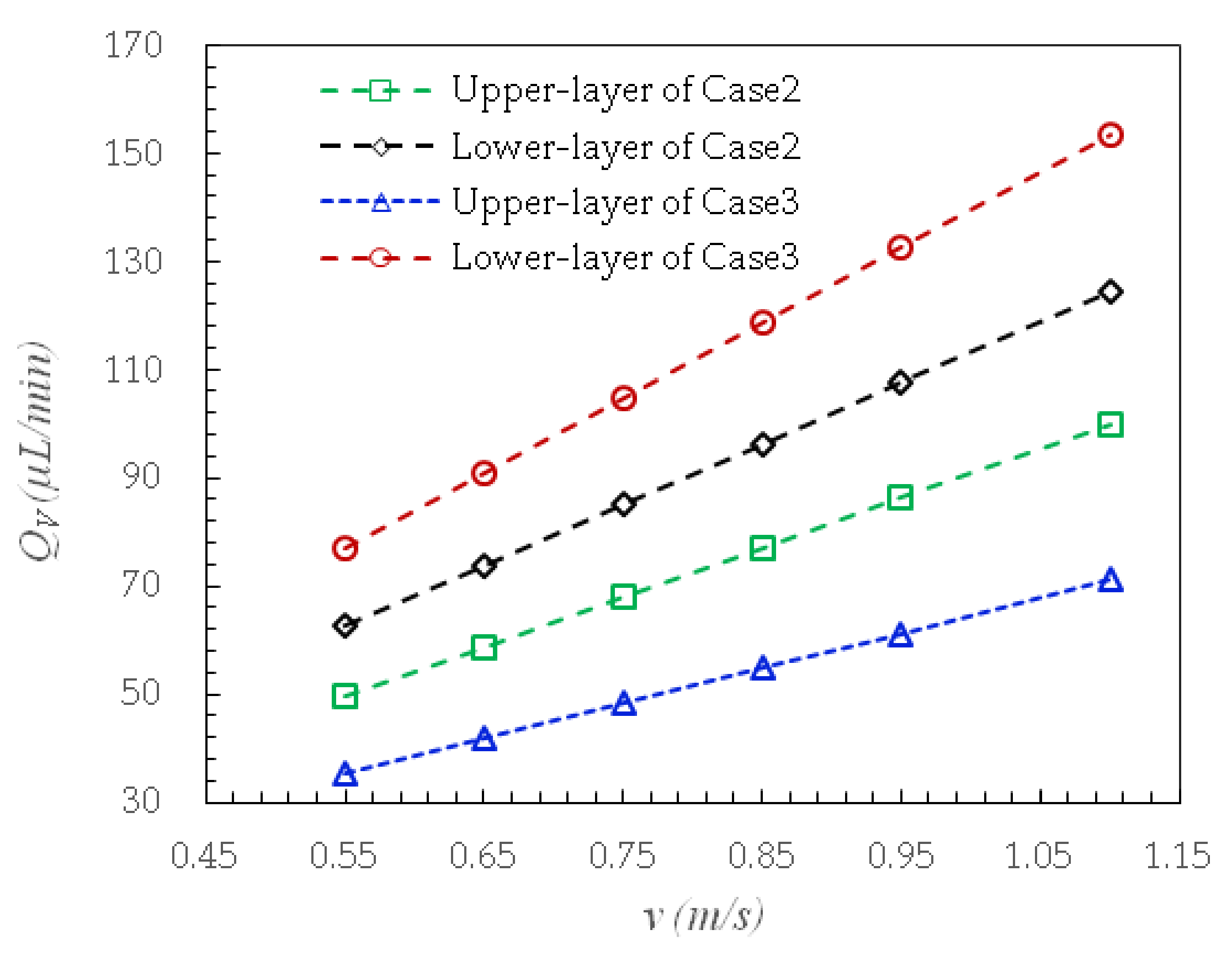
4.2. Flow Distribution and Velocity Characteristics
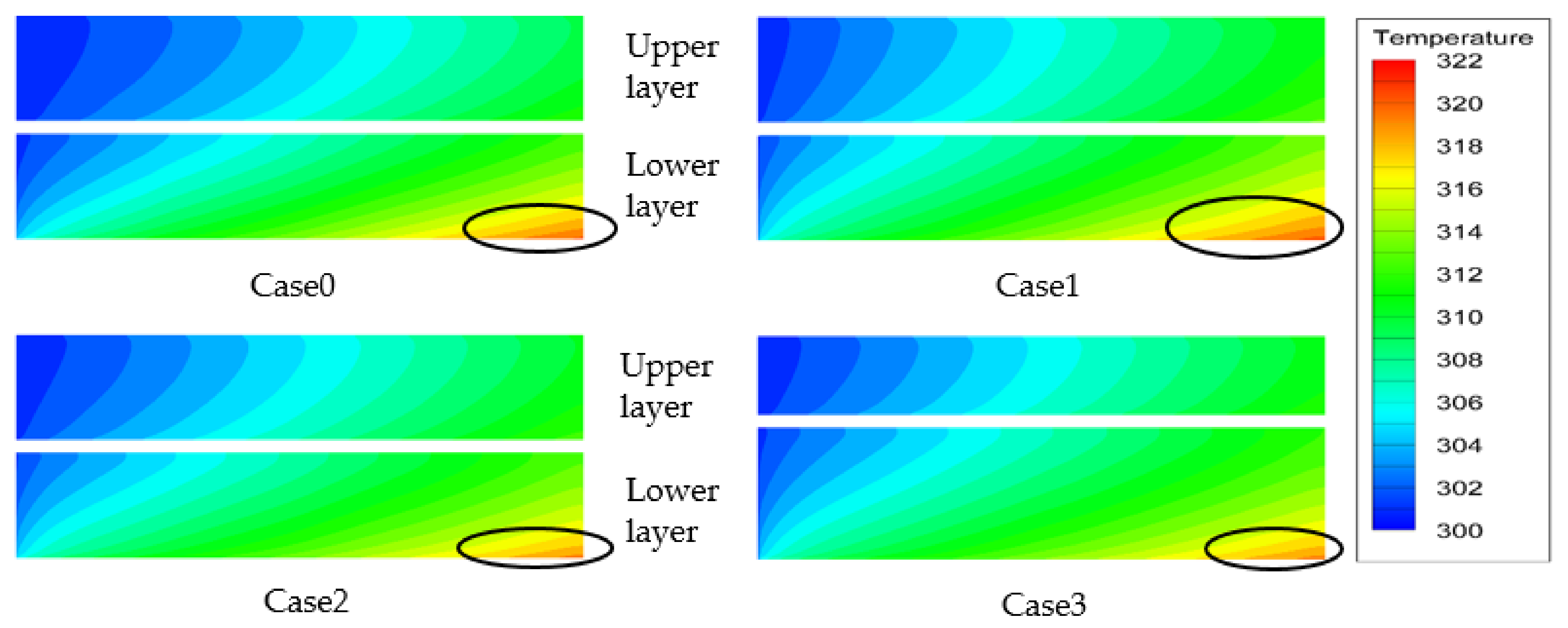
4.3. Heat Transfer Characteristics
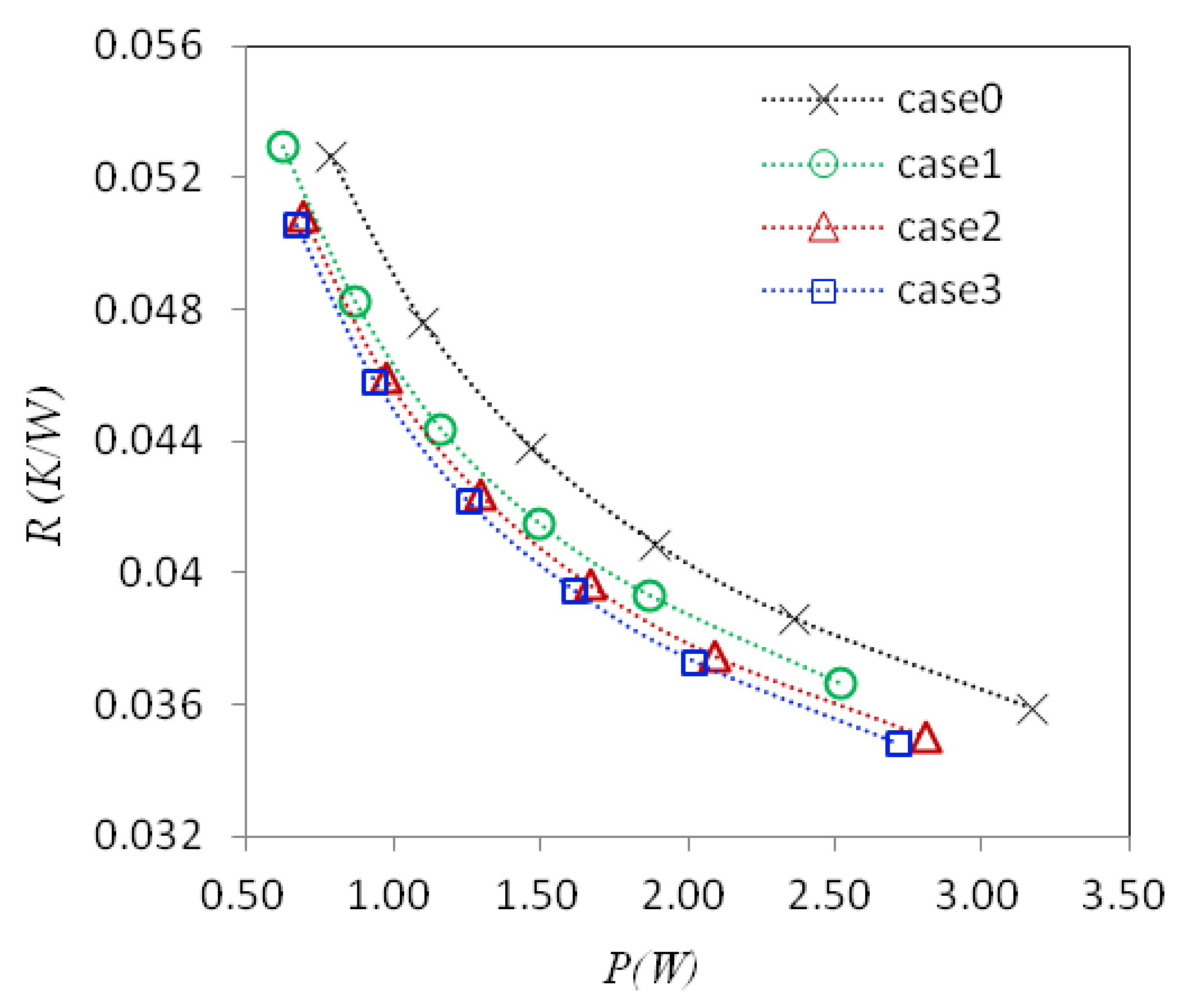
4.4. Overall Thermal Performance
5. Optimization
Optimization Method
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| tuning parameter | |
| Ab | substrate surface area of the calculation domain (m2) |
| Ac | total area of coupled wall |
| specific heat capacity in the constant pressure of working fluid | |
| Dh | hydraulic diameter of each tunnel (m) |
| h | convective heat transfer coefficient |
| H | height of the heat sink (mm) |
| height of upper channel (μm) | |
| height of lower channel (μm) | |
| , | heat conductivity of heat transfer fluid and solid silicon (W/m⋅K) |
| L | length for the designed DMHS (mm) |
| N | number of channels |
| Nu | Nusselt number |
| pressure of the working fluid (Pa) | |
| pressure of outlet (Pa) | |
| P | pump power work for the required system (W) |
| heat flux from the substrate (W/m2) | |
| total volume flow rate (L/min) | |
| R | thermal resistance (K/W) |
| Re | Reynolds number |
| thermal resistance (K/W) | |
| T | temperature on the substrate of DMHS (K) |
| average temperature of coupled wall (K) | |
| temperature of coolant at the inlet of channels (K) | |
| total temperature set at the outlet of channels (K) | |
| temperature of coolant at the outlet of channels (K) | |
| Ts | average temperature of solid (K) |
| average temperature of fluid (K) | |
| W | integrated DMHS width (m) |
| width of upper channel (μm) | |
| width of lower channel (μm) | |
| thickness of upper fin (μm) | |
| thickness of lower fin (μm) | |
| distance between the central lines of adjacent tunnels | |
| u, v, w | fluid velocities along the x, y, and z directions |
| x, y, z | spanwise, normal, and streamwise directions |
| Z | normalized variable |
| Greek Symbols | |
| pressure drop penalty (Pa) | |
| top plate thickness | |
| middle plate thickness | |
| substrate thickness | |
| fluid dynamic viscosity of working liquid (Pa⋅s) | |
| density of working liquid (kg/m3) | |
| Abbreviations | |
| DHMS | Double-layer Microchannel Heat Sink |
| HMS | Microchannel Heat Sink |
| SHMS | Single-layer Microchannel Heat Sink |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| RSM | Response Surface Methodology |
| Ave | averaged value |
| Subscripts | |
| lower channel | |
| upper channel | |
| c | channels in DMHS |
| l | lower |
| in | inlet |
| max | maximum |
| min | minimum |
| u | upper |
| rib of the lower-layer | |
| rib of the upper-layer | |
References
- Schmidt, R.R.; Notohardjono, B.D. High-end server low-temperature cooling. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2002, 46, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullius, J.F.; Vajtai, R.; Bayazitoglu, Y. A Review of Cooling in Microchannels. Heat Transf. Eng. 2011, 32, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckerman, D.; Pease, R. High-performance heat sinking for VLSI. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 1981, 2, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Mudawar, I. Experimental and numerical study of pressure drop and heat transfer in a single-phase micro-channel heat sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 2549–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Garimella, S. Investigation of Liquid Flow in Microchannels. In Proceedings of the 8th AIAA/ASME Joint Thermophysics and Heat Transfer Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 24–26 June 2002; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Dirker, J.; Meyer, J.P.; Garach, D.V. Inlet flow effects in micro-channels in the laminar and transitional regimes on single-phase heat transfer coefficients and friction factors. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 77, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiselj, I.; Hetsroni, G.; Mavko, B.; Mosyak, A.; Pogrebnyak, E.; Segal, Z. Effect of axial conduction on the heat transfer in micro-channels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2004, 47, 2551–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.-S.; Garimella, S.V.; Liu, D. Investigation of heat transfer in rectangular microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 48, 1688–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Kota, K.; Tao, W.; Joshi, Y. Parametric Numerical Study of Flow and Heat Transfer in Microchannels with Wavy Walls. J. Heat Transf. 2011, 133, 051702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, M.; Valipour, M.S.; Saedodin, S. Analytical Study of Heat Flux Splitting in Micro-channels Filled with Porous Media. Transp. Porous Media 2015, 109, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Qiu, Y.; Kim, C.N. An improved porous medium model for microchannel heat sinks. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 2512–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, C.; Vafai, K. Analysis of double slip model for a partially filled porous microchannel—An exact solution. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 2018, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, M.; Valipour, M.S.; Saedodin, S. Conjugate Heat Transfer Inside Microchannels Filled with Porous Media: An Exact Solution. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2016, 30, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Ma, D.; Zhai, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Du, M. Experimental and numerical study of fluid flow and heat transfer characteristics in microchannel heat sink with complex structure. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Sundén, B. Analysis of micro-channel heat sinks with rectangular-shaped flow obstructions. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2016, 69, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Wang, C.-C.; Xie, G. A parametric study on thermal performance of microchannel heat sinks with internally vertical bifurcations in laminar liquid flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 117, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Zhao, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, X.-D.; Yan, W.-M. A new scheme for reducing pressure drop and thermal resistance simultaneously in microchannel heat sinks with wavy porous fins. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 111, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, M.; Daneshipour, M.; Valipour, M.S.; Rafee, R.; Saedodin, S. Enhancing heat transfer in microchannel heat sinks using converging flow passages. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 92, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Gao, J. Influence of geometric parameters on flow and heat transfer performance of micro-channel heat sinks. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 107, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A.; Almogbel, M. Constructal T-shaped fins. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 43, 2101–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almogbel, M.A. Constructal tree-shaped fins. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2005, 44, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, G.; Rocha, L.A.O. Constructal design of Y-shaped assembly of fins. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 49, 4552–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K. Thermal optimization of branched-fin heat sinks subject to a parallel flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 77, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Shen, H.; Wang, C.-C. Parametric study on thermal performance of microchannel heat sinks with internal vertical Y-shaped bifurcations. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 90, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Sunden, B.; Xie, G. Laminar thermal performance of microchannel heat sinks with constructal vertical Y-shaped bifurcation plates. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 73, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafai, K.; Zhu, L. Analysis of two-layered micro-channel heat sink concept in electronic cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1999, 42, 2287–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafai, K.; Zhu, L. Multi-Layered Micro-Channel Heat Sink, Devices and Systems Incorporating Same. U.S. Patent 6,675,875, 13 January 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vafai, K.; Khaled, A.-R. Analysis of flexible microchannel heat sink systems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2005, 48, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, A.-R.; Vafai, K. Control of exit flow and thermal conditions using two-layered thin films supported by flexible complex seals. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2004, 47, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, A.-R.; Vafai, K. Cooling augmentation using microchannels with rotatable separating plates. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 3732–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Vafai, K. A comparative analysis of innovative microchannel heat sinks for electronic cooling. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 76, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, M.H.; Khiabani, R.H. Forced Convective Heat Transfer in Parallel Flow Multilayer Microchannels. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 129, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levac, M.L.-J.; Soliman, H.M.; Ormiston, S.J. Three-dimensional analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer in single- and two-layered micro-channel heat sinks. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 47, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Liu, Y.; Sundén, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J. Numerical Investigation of Heat Transfer and Pressure Loss of Double-Layer Microchannels for Chip Liquid Cooling. In Proceedings of the Heat Transfer Enhancement for Practical Applications; Fire and Combustion; Multi-Phase Systems; Heat Transfer in Electronic Equipment; Low Temperature Heat Transfer, Rio Grande, PR, USA, 8–12 July 2012; Volume 2, pp. 575–583. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Liu, Y.; Sunden, B.; Zhang, W. Computational Study and Optimization of Laminar Heat Transfer and Pressure Loss of Double-Layer Microchannels for Chip Liquid Cooling. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2013, 5, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-C.; Muezzin, F.N.A. Heat transfer of a parallel flow two-layered microchannel heat sink. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 49, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.-C.; Yan, W.-M.; Li, W.-P. Analysis of heat transfer characteristics of double-layered microchannel heat sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 3090–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, T.-C.; Yan, W.-M.; Wang, X.-D.; Huang, Y.-X. Optimal design of geometric parameters of double-layered microchannel heat sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 3262–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Zhang, X.-X.; Wang, X.-D. Optimization of geometry and flow rate distribution for double-layer microchannel heat sink. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 78, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Tseng, K. Parametric study on the performance of double-layered microchannels heat sink. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 80, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.; Wang, X.-D.; Wang, T.-H.; Yan, W.-M. Optimization of thermal resistance and bottom wall temperature uniformity for double-layered microchannel heat sink. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 93, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakanova, A.; Yin, S.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Leong, K. Optimization and comparison of double-layer and double-side micro-channel heat sinks with nanofluid for power electronics cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 65, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y. Numerical simulation of stacked microchannel heat sink with mixing-enhanced passive structure. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 34, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, P.; Lin, N.; Miao, J.; Wong, W.K.; Choon, T.K. Silicon nanopillars based 3D stacked microchannel heat sinks concept for enhanced heat dissipation applications in MEMS packaging. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 141, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, A.K.M.M.; Khan, J.A. Numerical Analysis of Single Phase Multi Layered Micro-Channel Heat Sink with Inter-Connects Between Vertical Channels. In Proceedings of the 2010 14th International Heat Transfer Conference, Washington, WA, USA, 8–13 August 2010; Volume 6, pp. 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Lio, X.B.; Liu, W. Cooling behavior in a novel heat sink based on multilayer staggered honeycomb structure. In Proceedings of the Asme Micro/Nanoscale Heat and Mass Transfer International Conference; 2010; pp. 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.; Singh, P.P.; Garg, H. Numerical Analysis of Trapezoidal Shape Double Layer Microchannel Heat Sink. Int. J. Mech. Ind. Eng. 2014, 3, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.; Wang, X.-D.; Wang, T.-H. An improved design of double-layered microchannel heat sink with truncated top channels. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 79, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.; Wang, X.-D.; Wang, T.-H.; Yan, W.-M. Multi-parameter optimization of flow and heat transfer for a novel double-layered microchannel heat sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 84, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Xia, G.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Characteristics of entropy generation and heat transfer in double-layered micro heat sinks with complex structure. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 103, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, J. Thermodynamic analysis of the effect of channel geometry on heat transfer in double-layered microchannel heat sinks. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 143, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osanloo, B.; Mohammadi-Ahmar, A.; Solati, A.; Baghani, M. Performance enhancement of the double-layered micro-channel heat sink by use of tapered channels. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 102, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-C.; Ang, M.-L. Thermal hydraulic performance of a double-layer microchannel heat sink with channel contraction. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 81, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabandeh, E.; Rozati, S.A.; Joshaghani, M.; Akbari, O.A.; Akbari, S.; Toghraie, D. Thermal performance improvement in water nanofluid/GNP–SDBS in novel design of double-layer microchannel heat sink with sinusoidal cavities and rectangular ribs. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 136, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Wang, S.-L.; Wang, X.-D.; Wang, T.-H. Selected porous-ribs design for performance improvement in double-layered microchannel heat sinks. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 137, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-L.; Li, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-D.; Lu, G. Flow and heat transfer characteristics in double-layered microchannel heat sinks with porous fins. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 93, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, H.; Shen, S.; Ma, S. A Novel Double-layered Heat Sink for High Power Electronics. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 20th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (EPTC), Singapore, 4–7 December 2018; pp. 686–690. [Google Scholar]
- Salimpour, M.R.; Al-Sammarraie, A.T.; Forouzandeh, A.; Farzaneh, M. Constructal Design of Circular Multilayer Microchannel Heat Sinks. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2019, 11, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, K.; Khan, A.A.; Kim, K.-Y. Performance Analysis of Double-Layer Microchannel Heat Sink With Various Microchannel Shapes. Heat Transf. Res. 2018, 49, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Xie, G. Comparative study for convective heat transfer of counter-flow wavy double-layer microchannel heat sinks in staggered arrangement. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 137, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Xie, G.; Wang, C.-C. The numerical simulation with staggered alternation locations and multi-flow directions on the thermal performance of double-layer microchannel heat sinks. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 163, 114332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Xie, G.; Wang, C.-C. Heat transfer and thermodynamic analysis by introducing multiple alternation structures into double-layer microchannel heat sinks. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 145, 105975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, E.; Akbari, O.A.; Sarafraz, M.M.; Abbas, T.; Safaei, M.R. Heat Transfer of Oil/MWCNT Nanofluid Jet Injection Inside a Rectangular Microchannel. Symmetry 2019, 11, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadsetani, R.; Sheikhzadeh, G.A.; Hajmohammadi, M.R.; Safaei, M.R. Introduce a novel configurationof microchannel andhigh-conductivity insertsfor cooling of disc-shaped electronic components. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2019, 30, 2845–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasteh, H.; Mashayekhi, R.; Goodarzi, M.; Motaharpour, S.H.; Dahari, M.; Toghraie, D. Heat and fluid flow analysis of metal foam embedded in a double-layered sinusoidal heat sink under local thermal non-equilibrium condition using nanofluid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 1461–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, M.; D’Orazio, A.; Karimipour, A.; Abdollahi, A.; Safaei, M.R. Lattice Boltzmann method to simulate convection heat transfer in a microchannel under heat flux Gravity and inclination angle on slip-velocity. Int. J. Numer. Method H 2019, 30, 3371–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, K.; Sekimura, M.; Minakami, K.; Iwasaki, H.; Ishizuka, M. Development of Micro Channel Heat Exchanging. JSME Int. J. Ser. B 2001, 44, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papautsky, I.; Brazzle, J.; Ameel, T.; Frazier, A. Laminar fluid behavior in microchannels using micropolar fluid theory. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1999, 73, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, D.; Webb, R. Forced convection heat transfer in helically rib-roughened tubes. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1980, 23, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi-Gorji, M.; Pourmehran, O.; Hatami, M.; Ganji, D.D. Statistical optimization of microchannel heat sink (MCHS) geometry cooled by different nanofluids using RSM analysis. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2015, 130, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Hatami, M.; Song, D.; Jing, D. Design of microchannel heat sink with wavy channel and its time-efficient optimization with combined RSM and FVM methods. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 103, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Case0 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 400 | 400 |
| Case1 | 70 | 50 | 70 | 50 | 400 | 400 |
| Case2 | 40 | 40 | 70 | 50 | 400 | 400 |
| Case3 | 40 | 40 | 70 | 50 | 300 | 500 |
| Density (kg/m3) | Specific Heat (J/(kg⋅K)) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m⋅K)) | Viscosity (kg/m⋅s)) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purified Water | 998.2 | 4182 | 0.6 | 1.003 × 10−3 |
| Silicon | 2330 | 710 | 148 |
| Mesh I | Mesh II | Mesh III | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max. Temp. (K) | 320.32 | 320.33 | 320.39 |
| Pressure drop, Pa | 169.93 | 169.56 | 168.78 |
| Difference | Baseline | 0.003% 0.22% | 0.02% 0.68% |
| No. | Wr | Wc | Hc | Δp (bar) | Rth | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. Data | Simulation Data | Deviation | |||||
| 1 | 56 | 44 | 320 | 15 | 0.110 | 0.109 | 0.91% |
| 2 | 55 | 45 | 287 | 17 | 0.113 | 0.113 | 0.00% |
| 3 | 50 | 50 | 302 | 31 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.00% |
| Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper limit value () | 0.55 | 30 | 40 | 300 |
| Average value () | 0.65 | 40 | 50 | 400 |
| Lower limit value () | 0.75 | 50 | 60 | 500 |
| Coded Factors (after Normalization) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Average value () | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ) | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| Case4 | 42 | 38 | 66 | 54 | 300 | 500 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.-D.; Chen, M.-R.; Wu, J.-H.; Hung, K.-S.; Wang, C.-C. Performance Improvement of a Double-Layer Microchannel Heat Sink via Novel Fin Geometry—A Numerical Study. Energies 2021, 14, 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123585
Zhang Y-D, Chen M-R, Wu J-H, Hung K-S, Wang C-C. Performance Improvement of a Double-Layer Microchannel Heat Sink via Novel Fin Geometry—A Numerical Study. Energies. 2021; 14(12):3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123585
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yong-Dong, Miao-Ru Chen, Jung-Hsien Wu, Kuo-Shu Hung, and Chi-Chuan Wang. 2021. "Performance Improvement of a Double-Layer Microchannel Heat Sink via Novel Fin Geometry—A Numerical Study" Energies 14, no. 12: 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123585
APA StyleZhang, Y.-D., Chen, M.-R., Wu, J.-H., Hung, K.-S., & Wang, C.-C. (2021). Performance Improvement of a Double-Layer Microchannel Heat Sink via Novel Fin Geometry—A Numerical Study. Energies, 14(12), 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14123585





