Contributions and Risks of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Building Smarter Cities: Insights from a Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
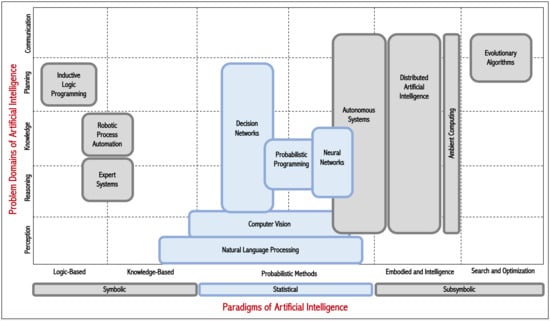
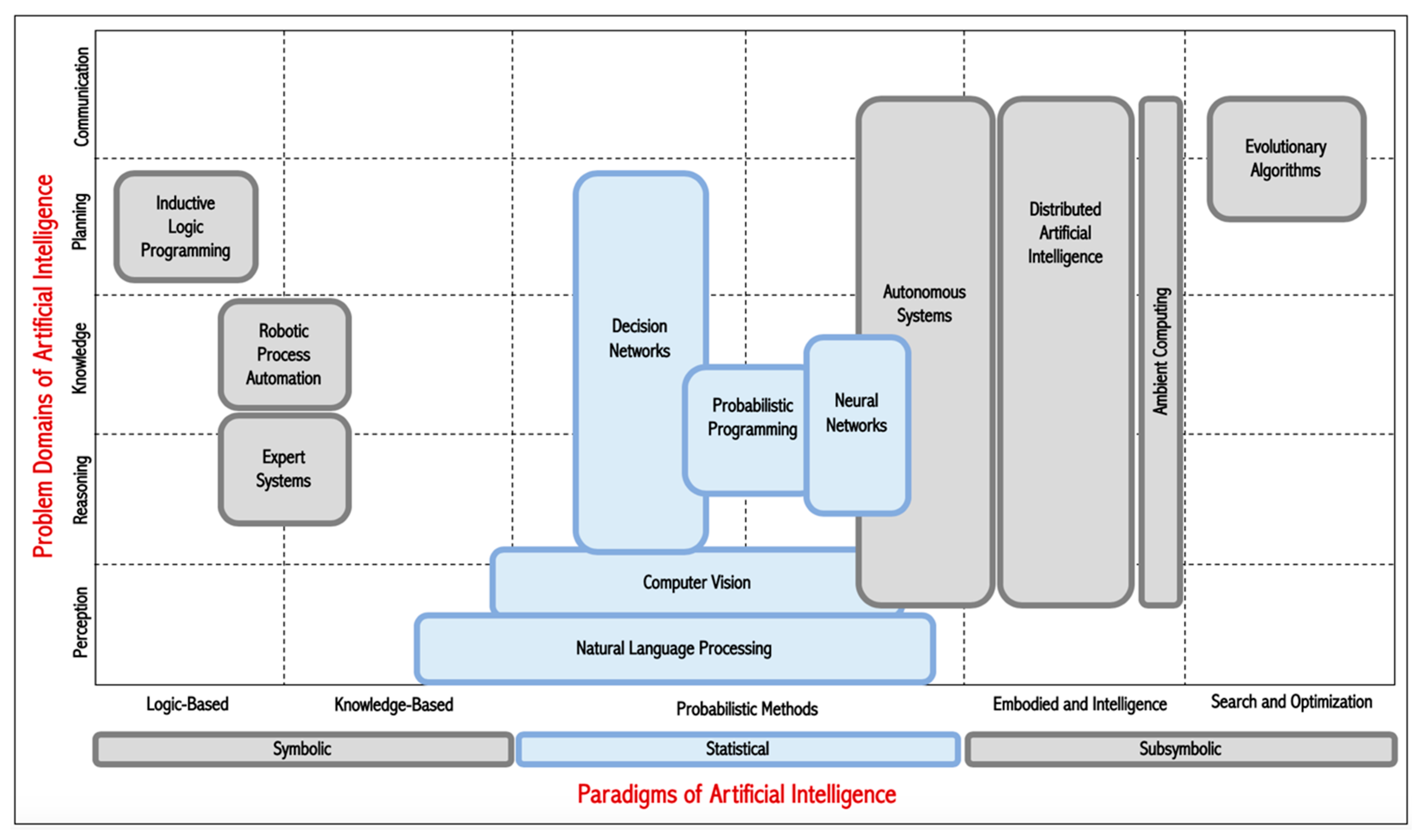
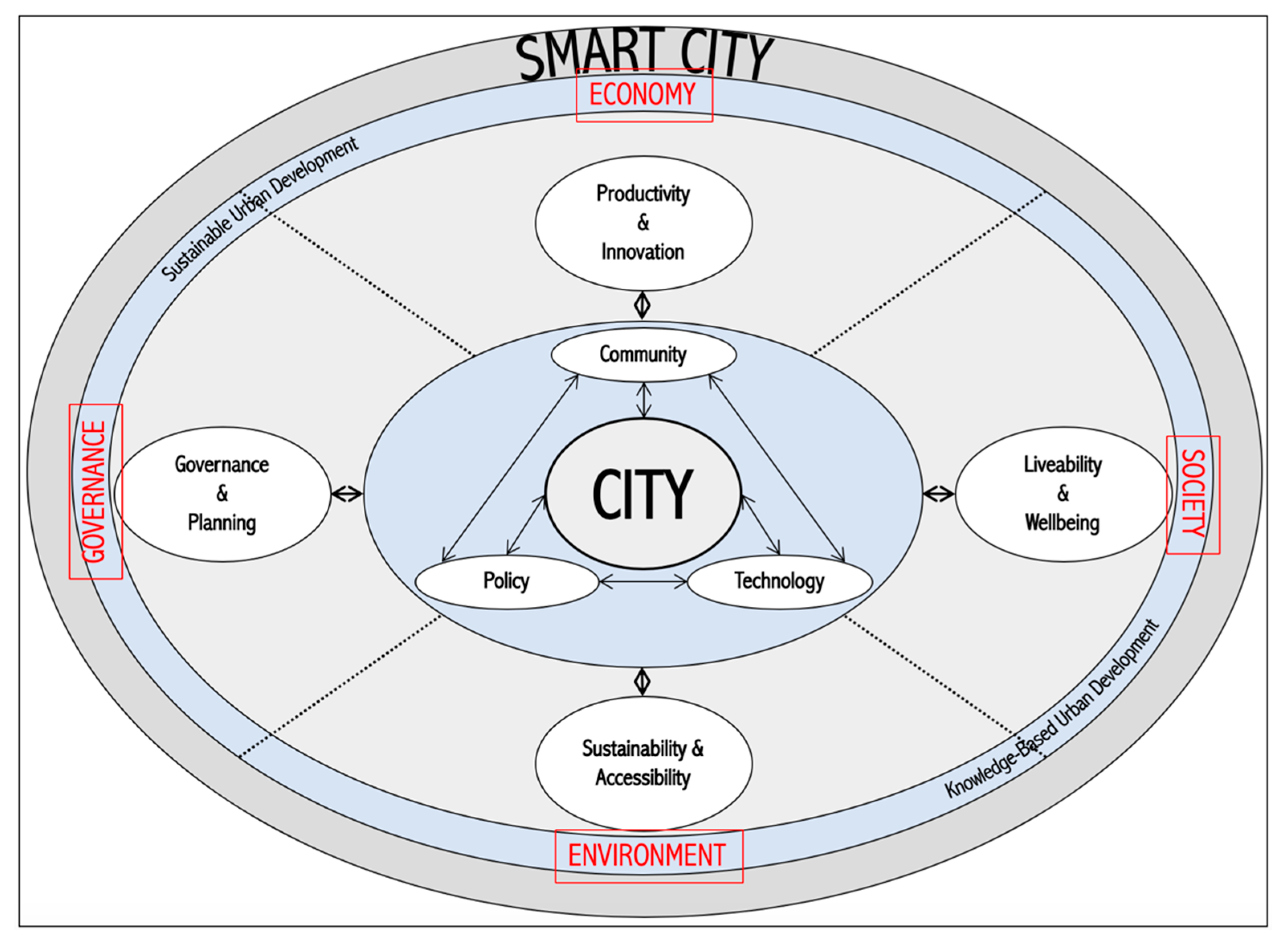
2. Conceptual and Application Background
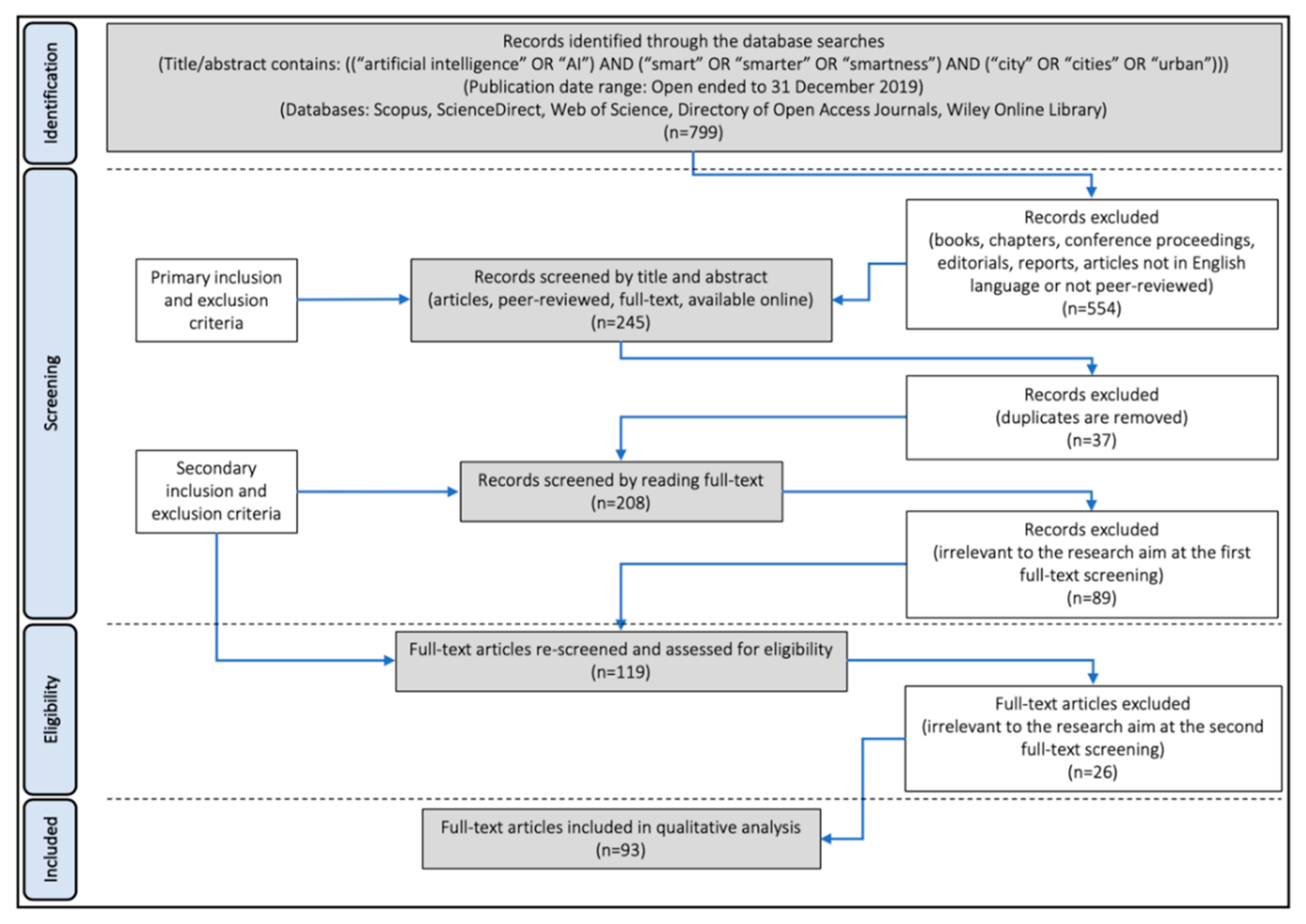
3. Materials and Method
4. Results
4.1. General Observations
4.2. AI in the Economy Dimension of Smart Cities
4.3. AI in the Society Dimension of Smart Cities
4.4. AI in the Environment Dimension of Smart Cities
4.5. AI in the Governance Dimension of Smart Cities
5. Discussion
- AI has an evident potential to provide a positive change in our cities, societies and businesses by promoting a more efficient, effective and sustainable transition/transformation;
- AI, with its technology, algorithms, and learning capabilities, can be a useful vehicle in automating the problem solving and decision-making processes; that in return could reform urban landscapes, and support the development of smarter cities;
- AI in the context of smart cities is an emerging field of research and practice. Hence, further research is needed to consolidate the knowledge in the field;
- The central focus of the literature is on AI technologies, algorithms, and their current and prospective applications;
- AI applications in the context of smart cities mainly concentrate on business efficiency, data analytics, education, energy, environmental sustainability, health, land use, security, transport, and urban management areas, and;
- Upcoming disruptions of AI on cities and societies have not been adequately investigated in the literature; thus, further investigations are needed on that issue.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Author | Title | Journal | Aim | Relevance | Domain | Paradigm | Application | Method | Technology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abduljabbar et al. [98] | Applications of artificial intelligence in transport | Sustainability | To provide an overview of AI techniques applied to transport. | Advocates that AI in the transport field is aimed at decreasing VKT thus reducing emissions and other environmental degradation. | Environment | LB KB PM ML EI SO | ES DN NN DAI EA | FS DL SI GA | Smart Transport |
| Ajerla et al. [99] | A real-time patient monitoring framework for fall detection | Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing | To develop a framework that uses edge computing to send data from wearable devices. | Describes the use of machine learning in improving fall detection devices. | Society | PM ML | NN CV | AR | IoT Smart Health |
| Alam et al. [77] | Data fusion and IoT for smart ubiquitous environments | IEEE Access | To review existing literature on data fusion and IoT with a focus on mathematical models. | Discusses the benefits of AI in relation to data fusion. | Economy | LB KB PM ML SO | ES DN NN EA | FS BN DL GA | IoT |
| Allama & Dhunny [100] | On big data, artificial intelligence and smart cities | Cities | To provide information on the use of AI and big data in smart cities. | Provides insights regarding the application of AI to public safety and security. | Governance | LB KB PM ML | ES NN | FS | IoT |
| Alsamhi et al. [101] | Survey on collaborative smart drones and internet of things for improving smartness of smart cities | IEEE Access | To show how drones and IoT can improve the smartness of cities. | Provides insights into how autonomous drones can be used for security, safety measures. | Governance | PM ML SO | NN CV EA | AR IR MV GA | IoT Drones |
| Altulyan et al. [149] | A unified framework for data integrity protection in people-centric smart cities | Multimedia Tools and Applications | To address data integrity from an end-to-end perspective. | Describes how block chain and fog computing can be used to manage data integrity. | Economy | n/a | n/a | n/a | IoT |
| Alzoubi et al. [102] | Prediction of environmental indicators in land levelling using artificial intelligence techniques | Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering | To develop AI techniques in land levelling. | Discusses using AI in land levelling. | Environment | ML | NN | n/a | n/a |
| Bajaj & Sharma [82] | Smart education with artificial intelligence-based determination of learning styles | Procedia Computer Science | To develop a framework for student learning styles using learning models and ratification intelligence. | Develops a framework for AI to improve adaptivity in teaching. | Society | LB KB PM ML EI SO | ES DN PP NN DAI EA | FS BN BPS MAS SI GA | Smart Education |
| Bennett & Hauser [137] | Artificial intelligence framework for simulating clinical decision-making | Artificial Intelligence in Medicine | To developing a framework for using AI to address healthcare challenges. | Describes how AI could lead to improvements in diagnosis and treatment. | Society | PM EI | DAI | MAS | Smart Health |
| Bose [78] | Artificial intelligence techniques in smart grid and renewable energy systems | Proceedings of the IEEE | To explain application of AI in smart grids and renewable energy systems | Provides insights into the use of smart grids for prediction, estimation and control of power systems. | Environment | LB KB ML | ES NN AS | FS DL | Smart Energy |
| Brady [103] | The challenge of big data and data science | Annual Review of Political Science | To identify innovative methods for answering previously hard-to-tackle questions about society. | Provides insights into how AI can improve decision-making, efficiency, and reduce errors and uncertainty. | Economy | ML | NN | n/a | n/a |
| Braun et al. [83] | Security and privacy challenges in smart cities | Sustainable Cities and Society | To identify possible solutions to five smart city challenges. | Provides insights into the use of AI for cyber security. | Governance | ML | NN | n/a | Smart Surveillance |
| Bui & Jung [104] | Computational negotiation-based edge analytics for smart objects | Information Sciences | To develop a computational negotiation approach on IoT systems where distributed edge devices can make their own decisions. | Describes the potential for AI and smart traffic control systems to communicate with connected-AV, and make real-time decisions to improve the efficiency of the transport network. | Economy | ML EI | AS | n/a | IoT |
| Cai et al. [105] | Deep learning-based video system for accurate and real-time parking measurement | IEEE Internet of Things Journal | To develop an accurate and real-time video system for future IoT and smart cities applications | Discusses using AI for real-time measurements to make parking more efficient. | Environment | ML | NN | DL | IoT Smart Parking |
| Casares [84] | The brain of the future and the viability of democratic governance | Futures | To identify AI implications and the potential challenges in democratic societies. | Identifies the potential for AI to contribute to public governance. | Governance | ML | NN | DL | n/a |
| Castelli et al. [144] | Predicting per capita violent crimes in urban areas | Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing | To combine a version of genetic programming with a local search method | Describes the use of AI in crime prediction and optimal allocation of law enforcement. | Governance | SO | EA | GA | n/a |
| Chassignol et al. [85] | Artificial Intelligence trends in education | Procedia Computer Science | To identify the prospective impact of AI technologies on the study process. | Identifies the potential for AI to develop innovative teaching methods, and improve student outcomes. | Society | ML | NN | n/a | Smart Education Augment. Reality Virtual Reality |
| Chatterjee et al. [164] | Success of IoT in smart cities of India | Government Information Quarterly | To combine IoT with AI in smart machines to simulate intelligent behavior and assist autonomous decision making. | Describes the use of AI to obtain data from IoT to understand acceptance of new technologies. | Governance | n/a | n/a | n/a | IoT ICT |
| Chau [69] | A review on integration of artificial intelligence into water quality modelling | Marine Pollution Bulletin | To reviewing the current state-of-the-art AI and its application in water quality modelling. | Provides insights into how AI can be used to develop more accurate water quality modelling | Environment | LB KB ML SO | ILP ES NN EA | FS DL GA | Smart Environment |
| Chen et al. [107] | An intelligent robust networking mechanism for the internet of things | IEEE Communications Magazine | To enhance the robustness of IoT topologies | Identifies how AI can reduce uncertainty in relation to robustness optimization, improve the cost and efficiency of network communications and protect against cyber-attacks. | Economy | ML SO | NN EA | DL GA | IoT Smart Energy |
| Chen et al. [106] | Cognitive-LPWAN | IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking | To provide information regarding current wireless communication technologies, and other technologies | Provides insights into how AI can be used to improve communication networks | Economy | ML | NN | DL | IoT |
| Chmiel [74] | INSIGMA | Multimedia Tools and Applications | To investigate using intelligent transport systems for improving safety, mobility and environmental outcomes. | Describes using intelligent transport systems to improve congestion. | Environment | PM ML | CV | IR MV | Smart Transport |
| Chui et al. [86] | Energy sustainability in smart cities | Energies | To show ways in which AI can support energy sustainability. | Provides insights in the use of AI to monitor energy consumption. | Environment | ML SO | EA | GA | IoT Smart Energy |
| Cortes et al. [136] | Artificial intelligence and environmental decision support systems | Applied intelligence | To provide an overview of the impact of AI on environmental decision support systems. | Identifies how AI can assist in environmental decision-making | Environment | LB KB PM | Expert System DN | n/a | Smart Environment |
| Cui et al. [108] | Big data analytics and network calculus enabling intelligent management of autonomous vehicles in a smart city | IEEE Internet of Things Journal | To develop a new online AV fleet management scheme that controls congestion in cities. | Discusses using AI to reduce travel time in AV. | Environment | ML | n/a | n/a | IoT Smart Transport |
| De Paz et al. [75] | Intelligent system for lighting control in smart cities | Information Sciences | To develop a new intelligent lighting system for cities. | Describes the use of AI to control public lighting to optimize power usage. | Environment | PM ML EI | CV NN DAI | IR MV MAS | Smart Energy |
| Desouza et al. [109] | Designing, developing, and deploying artificial intelligence systems | Business Horizons | To reflect and provide insights from AI projects in the public sector. | Discusses how cognitive computing systems are able simulate human thought and learning and can be used for fraud detection, decision-support, and online assistance. | Governance | ML | NN | DL | n/a |
| Devedzic [147] | Web intelligence and artificial intelligence in education | Educational Technology & Society | To survey important aspects of web intelligence in the context of AI in education | Discusses how AI can improve adaptability in learning environments, and create more comfortable learning environments. | Society | EI | DAI | ABM | Smart Education |
| Din et al. [110] | Machine learning in the internet of things | Future Generation Computer Systems | To examine different IoT based machine learning mechanisms | Identifies machine learning as an important component for IoT particularly regarding data management. | Economy | ML | NN | DL | IoT |
| Dobrescu & Dobrescu [87] | Artificial intelligence (AI) | Global Economic Observer | To present trends, analyses and perceptions of AI. | Presents the benefits and disadvantages of integration of AI into all areas of socio-economic life | Society | PM ML | NLP CV NN | DL IR NLU NLG | n/a |
| Dong et al. [111] | Energy-efficient fair cooperation fog computing in mobile edge networks for smart city | IEEE Internet of Things Journal | To examine the convexity of the optimization problem and design a fairness cooperation algorithm. | Identifies IoT and AI as two of the most important technologies to help enable smart cities particularly regarding big data analysis. | Economy | ML | n/a | n/a | IoT |
| Drigas & Ioannidou [71] | Artificial intelligence in special education | International Journal of Engineering Education | To review studies that use AI methods in making accurate diagnosis. | Discusses how AI can stimulate problem solving, particularly in special needs students, to enhance the way children interact with their environment. | Society | LB KB ML | ES NN | FS | Smart Education |
| Edwards et al. [88] | I, teacher: using artificial intelligence (AI) and social robots in communication and instruction | Communication Education | To argue the importance of using AI in teaching. | Examines the role of teacher in an AI enabled education system. | Society | ML | NLP | NLG | Social Robots Smart Education |
| Eldrandaly et al. [148] | PTZ-surveillance coverage based on artificial intelligence for smart cities | International Journal of Information Management | To develop AI algorithm for adjusting the orientation of pan-tilt-zoom surveillance cameras. | Discusses the use of AI technology to automatically improve the field of view of surveillance cameras | Governance | EI | DAI | SI | IoT Smart Surveillance |
| Falco et al. [162] | A master attack methodology for an AI-based automated attack planner for smart cities | IEEE Access | To identify solutions for cyber safety of critical infrastructure. | Identifies the potential for automated tools to evaluate cyber threats to infrastructure. | Governance | n/a | n/a | n/a | IoT |
| Feng & Xu [63] | Hybrid artificial intelligence approach to urban planning | Expert Systems | To present a hybrid AI system for use in urban planning. | Describers how AI can assist with knowledge-based decision making. | Environment | LB KB ML | ES NN | FS DL | n/a |
| Fernández et al. [138] | An intelligent surveillance platform for large metropolitan areas with dense sensor deployment | Sensors | To maximize the number of deployable units in surveillance while minimizing costs. | Presents an intelligent surveillance platform for surveillance of public spaces | Governance | PM | CV | IR | Smart Surveillance |
| Garlík [79] | The application of artificial Intelligence in the process of optimizing energy consumption in intelligent areas | Neural Network World | To monitor and control the operation of selected smart objects. | Discusses the use of AI for energy optimization | Environment | ML SO | NN EA | GA | Smart Energy |
| Guilherme [153] | AI and education | AI & Society | To identify use of AI in assessing education and the relations between teachers and students, and students and students. | Identifies new roles for teachers in education. | Society | n/a | n/a | n/a | Smart Education |
| Guo & Li [89] | The application of medical artificial intelligence technology in rural areas of developing countries | Health Equity | To review the literature concerning the prospects of medical AI technology, and application in rural areas. | Identifies AI as a means to improve equality between rural and urban health areas. | Society | ML | NN | n/a | Smart Health |
| Guo et al. [90] | Artificial intelligence-based semantic internet of things in a user-centric smart city | Sensors | To discuss the links between AI and IoT in the context of smart city | Describes how AI can contribute to environmental monitoring. | Environment | PM ML | DN NN | BN DL | IoT |
| Håkansson [91] | Ipsum: an approach to smart volatile ICT-infrastructures for smart cities and communities | Procedia Computer Science | To create smart volatile ICT infrastructures in cities. | Discusses using AI for customized health care. | Society | ML | n/a | n/a | IoT ICT Cyber-Physical Smart Infrastructure |
| Hanson & Marshall [67] | Artificial intelligence applications in the intensive care unit | Critical Care Medicine | To review application of AI in intensive care. | Describes how AI as a monitoring tool can assist intensive care providers and resulting in reduced costs and improved patient outcomes | Society | LB KB ML SO | ES NN EA | FS DL GA | Smart Health |
| Hariri et al. [112] | Uncertainty in big data analytics | Journal of Big Data | To review big data analytics. | Identifies AI techniques as beneficial to the accurate and timely analysis of big data. | Economy | LB KB PM ML SO | ES DN EA | FS BN | IoT |
| Ibrahim et al. [113] | URBAN-i: from urban scenes to mapping slums, transport modes, and pedestrians in cities using deep learning and computer vision | Environment and Planning B | To develop framework for multipurpose realistic-dynamic urban modelling using deep CNN | Describes using deep learning to differentiate spatial structures. | Environment | PM ML | CV NN | IR DL | n/a |
| Inclezan & Prádanos [156] | Overview: a critical view on smart cities and AI | Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research | To advocate using AI to solve urban problems. | Reflects, critically, on the optimistic viewpoint of AI in relation to its potential to respond to urban problems (e.g. congestion, population growth, energy efficiency, environmental degradation and safety). | Environment | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Iqbal et al. [114] | Intelligent remote monitoring of parking spaces using licensed and unlicensed wireless technologies | IEEE Network | To develop an intelligent parking system model | Describes using AI for parking utilization and optimization. | Environment | PM ML | CV NN | AR IR MV DL | IoT Smart Parking |
| Jha et al. [80] | Renewable energy | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews | To summarize reviews and state-of-the-art research outcomes related to renewable energies | Describes the use of AI to achieve renewable energy goals | Environment | PM ML EI SO | DN PP NN DAI EA | BN BPS GA MAS SI | Smart Energy |
| Khalifa [161] | Smart cities: opportunities, challenges, and security threats | Journal of Strategic Innovation and Sustainability | To discuss the importance and consequences of smart city development. | Identifies the opportunity for AI and smart cities to achieve better security measures | Governance | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Kopytko et al. [92] | Smart home and artificial intelligence as environment for the implementation of new technologies | Path of Science | To determine smart homes and AI as combined innovative tools. | Provides insights into the use of AI in smart homes to achieve energy savings. | Environment | LB KB ML SO | ES NN DAI EA | FS DL MAS GA | IoT Smart Homes |
| Kundu [115] | Blockchain and trust in a smart city | Environment and Urbanization Asia | To provide insights into institutions that can be governed on blockchain through smart contracts. | Identifies trust as a fundamental part of smart city governance. | Governance | ML | n/a | n/a | IoT Blockchain |
| Le et al. [116] | A comparative study of PSO-ANN, GA-ANN, ICA-ANN, and ABC-ANN in estimating the heating load of buildings’ energy efficiency for smart city planning | Applied Sciences | To propose four new AI techniques for forecasting the heating load of buildings | Discusses the use of AI to improve energy efficiency in buildings | Environment | ML EI SO | NN DAI EA | DL SI GA | Smart Energy |
| Leung et al. [117] | AI-based sensor information fusion for supporting deep supervised learning | Sensors | To present an AI-based system which supports deep supervised learning of transport data collected from sensors | Describes using AI-based sensor to collect data from multiple sources. | Environment | ML | NN | DL | IoT GNS GPS GIS |
| Li et al. [118] | Intelligent metasurface imager and recognizer | Light: Science & Applications | To propose the use of a smart metasurface imager and recognizer, empowered by a network of ANN to control data flow | Identifies the potential for AI enabled sensors and other devices to monitor health. | Society | ML | NN CV | DL MV | IoT Smart Surveillance |
| Liu et al. [93] | Object tracking in vary lighting conditions for fog based intelligent surveillance of public spaces | IEEE Access | To improve the robustness and accuracy of the correlation filter-based trackers for handling intense illumination change. | Describes the use of intelligent surveillance systems in detecting abnormal circumstances, identifying and tracking targets. | Governance | PM ML | CV | AR IR MV | Smart Surveillance |
| Liu et al. [119] | Modeling and simulation of robot inverse dynamics using LSTM-based deep learning algorithm for smart cities and factories | IEEE Access | To highlight the influence of the hyper-parameter settings on model performance and to explore the applicability of the Long Short-Term Memory model. | Develops a model that uses deep learning to make robots more responsive to uncertainty. | Economy | ML | NN | DL | Robotics |
| Lukowicz & Slusalle [94] | How to avoid an AI interaction singularity | Interactions | To advocate for AI systems to focus on enhancing human cognitive capabilities, and develop creativity, inventiveness, and intuition, trust, ethics, and values | Discusses goals required to improve AI decision-making. | Economy | PM ML | CV NLP | IR NLU | n/a |
| Lytras et al. [120] | Data analytics in smart healthcare | Applied Sciences | To identify use of AI to improve quality of life and relieve medical shortages | Describes how smart healthcare analytics can improve quality of life for patients. | Society | ML | NN | DL | IoT Smart Health |
| Martins [95] | Towards smart city innovation | Revista de Tecnologia da Informação e Comunicação | To analyze the impact and perspectives on adopting software-defined networking and AI for smart city projects. | Describes how cognitive processing could allow innovative solutions to complex problems. | Governance | ML | NN | DL | n/a |
| McArthur et al [140] | The roles of artificial intelligence in education | Journal of Educational Technology | To summarize current applications of ideas from Al to education field. | Identifies future uses of AI in the education field. | Society | LB KB | ES | n/a | Smart Education |
| Meena et al. [145] | Mobile power infrastructure planning and operational management for smart city applications | Energy Procedia | To maximize the profit of utility and electric vehicle owners. | Provides insights into the use of AI to optimize energy consumption particularly electrical vehicles. | Environment | SO | EA | GA | IoT |
| Muhammad et al. [121] | Intelligent and energy-efficient data prioritization in green smart cities | IEEE Communications Magazine | To highlight the key challenges of data prioritization, its future requirements, and propositions for integration into green smart cities | Discusses the use of AI to improve the efficiency of data prioritization. | Environment | ML | NN | DL | IoT |
| Nápoles et al. [96] | MUSA–I: towards new social tools for advanced multi-modal transportation in smart cities | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute Proceedings | To describe the general architecture and current implementation of an explicit multi-modal transport demand system for smart cities. | Discusses using AI for transport demand management. | Environment | PM ML | CV | AR IR MV | Smart Transport |
| Neuhauser et al. [142] | Using design science and artificial intelligence to improve health communication | Patient Education and Counselling | To describe how the use of AI can improve the effectiveness of health communication. | Discusses how AI can improve the effectiveness of communication in health settings. | Society | LB KB | ES | n/a | Smart Health |
| Noorbakhsh-Sabet [122] | Artificial intelligence transforms the future of healthcare | The American Journal of Medicine | To review the applications for machine learning in healthcare. | Identifies AI potential to increase learning and decision support in the health sector. | Society | ML | NN | DL | Smart Health |
| Park et al. [123] | Dependable fire detection system with multifunctional artificial intelligence framework | Sensors | To propose new fire detection system using a multifunctional AI framework and data transfer delay minimization mechanism. | Describes how machine learning can improve fire detection systems. | Governance | ML | NN | DL | IoT Smart Fire Detection |
| Patel et al. [70] | The coming of age of artificial intelligence in medicine | Path of Science | To analyze discussions which reflect on AI in the medical research field. | Discusses the use of AI in medical care. | Society | KB PM ML EI | ES DN NN DAI | BN ABM | Smart Health |
| Pence [152] | Artificial intelligence in higher education | Journal of Educational Technology Systems | To explore the use of AI in education | Identifies the need for education to be adaptive in the face of rapid technology advances, and changes to employment. | Society | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Pieters [141] | Explanation and trust | Ethics and Information Technology | To investigate the relationship between explanation and trust in the context of AI | Describes the importance on online security for trust in AI systems. | Governance | LB KB | ES | n/a | n/a |
| Ponce & Gutiérrez [124] | An indoor predicting climate conditions approach using internet-of-things and artificial hydrocarbon networks | Measurement | To predict the temperature of remote locations using field sensors and information from network. | Identifies methods of incorporating AI in weather monitoring to better predict changes. | Environment | ML | NN | n/a | IoT Artificial Hydrocarbon Networks |
| Puri et al. [125] | Hybrid artificial intelligence and internet of things model for generation of renewable resource of energy | IEEE Access | To develop an IoT based system to generate electrical energy from multiple sensors. | Provides insights into the use of piezoelectric sensors to generate energy from body heat. | Environment | ML | NN | n/a | IoT Smart Energy |
| Quan et al. [146] | Artificial intelligence-aided design | Environment and Planning B | To develop a smart design framework which uses AI to assist urban design decision-making. | Provides insights into the use of AI in the design process | Environment | SO | EA | GA | Smart Design |
| Rahman et al. [126] | Blockchain and IoT-based cognitive edge framework for sharing economy services in a smart city | IEEE Access | To propose blockchain-based infrastructure to support security- and privacy-oriented spatio-temporal smart contract services. | Identifies benefits of AI in helping with data collection, fusing information from multiple sources. | Economy | ML | NN | DL | IoT Blockchain |
| Ramesh et al. [68] | Artificial intelligence in medicine | Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England | To explore the proficiency of AI in medicine. | Provides insights into how AI can help with the analysis of complex medical data. | Society | LB KB ML SO | ES NN EA | FS DL GA | Smart Health |
| Reaz [73] | Artificial intelligence techniques for advanced smart home implementation | Acta Technica Corvininesis-Bulletin of Engineering | To develop a platform which serves as a reference point for developing more cutting-edge smart home technologies. | Identifies how AI can be used to provide more efficient power consumption | Environment | LB KB PM ML EI | ES CV NN AS DAI | FS AR MAS | Smart Home |
| Rho et al. [72] | Advanced issues in artificial intelligence and pattern recognition for intelligent surveillance system in smart home environment | Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence | To review topics strongly related to the intelligent surveillance systems in smart homes. | Describes the use of AI in home surveillance systems | Governance | ML | n/a | n/a | Smart Surveillance Smart Homes |
| Roll & Wylie [143] | Evolution and revolution in artificial intelligence in education | International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education | To review papers to identify the focus and typical scenarios that occupy the field of AI and education. | Describes how AI will impact the job market and create effective educational system. | Society | LB KB | ES | n/a | Smart Education |
| Ruohomaa et al. [127] | Towards smart city concept in small cities | Technology Innovation Management Review | To present the practical viewpoints, cases and experiences relating to the planning of smart cities. | Identifies shared learning and cooperation as important factors in increasing innovation and growth in smart cities. | Economy | ML | n/a | n/a | IoT |
| Sgantzos & Grigg [128] | Artificial intelligence implementations on the blockchain | Future Internet | To reveal the potential combined applications of AI and blockchain. | Describes the potential for AI to be an independent source of knowledge and innovation. | Economy | ML EI SO | NN DAI EA | MAS GA | IoT Blockchain |
| Shi et al. [129] | Smart textile-integrated microelectronic systems for wearable applications | Advanced Materials | To provide an overview of the progress of the smart textile field. | Describes the use of smart textiles for health care monitoring. | Society | ML | NN | n/a | Smart Textiles |
| Soomro et al. [130] | Smart city big data analytics | Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery | To present classification model that studies four aspects of research in the big data analytics domain. | Provides insights into the potential for machine learning to complete complex statistical analysis and make more informed decisions. | Economy | ML SO | NN EA | GA | n/a |
| Stefanelli [139] | The socio-organizational age of artificial intelligence in medicine | Artificial Intelligence in Medicine | To explore the great challenges for AI in medicine. | Identifies AI as an effective way to manage medical knowledge, and increase resources for patient care. | Society | KB | n/a | n/a | Smart Health |
| Streitz [131] | Beyond ‘smart-only’ cities: redefining the ‘smart-everything’ paradigm | Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing | To present the various manifestations of the smart everything paradigm. | Identifies the need for privacy-by-design to empower people and enforce a citizen centric approach to data collection. | Governance | ML | NN | DL | IoT |
| Syifa et al. [132] | An artificial intelligence application for post-earthquake damage mapping in Palu, Central Sulawesi, Indonesia | Sensors | To develop a classification of pre- and post-earthquake satellite images using ANN and support vector machine classifiers. | Provides insights into the use of AI subsets artificial neural networks and support vector machine classifiers to identify areas affected by earthquakes | Governance | ML | NN | n/a | n/a |
| Wan & Hwang [97] | Value-based deep reinforcement learning for adaptive isolated intersection signal control | IET Intelligent Transport Systems | To identify the use of reinforcement learning in signal controls. | Describes using traffic signal control methods for transport system optimization. | Environment | PM ML | PP NN | DL | Smart Transport |
| Wang & Srinivasan [81] | A review of artificial intelligence-based building energy use prediction | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews | To better understand of the use of ensemble models for predicting building energy use. | Discusses the use of AI in building use energy predictions. | Environment | PM ML | PP NN | n/a | n/a |
| Wang et al. [133] | Exploring the application of artificial intelligence technology for identification of water pollution characteristics and tracing the source of water quality pollutants | Science of The Total Environment | To develop an AI scheme for identifying spatiotemporal water quality distributions and the relationships between water quality indicators and industrial point sources of pollutants. | Identifies the potential for AI to monitor water pollutant levels and changes | Environment | ML | NN | DL | Smart Environment |
| Wei et al. [134] | Conventional models and artificial intelligence-based models for energy consumption forecasting: a review | Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering | To review conventional models and AI based models in energy consumption forecasting. | Describes how Ai can be used in energy forecasting to assist with identifying inefficiencies in energy consumption and pollution prevention. | Environment | PM ML EI SO | DN NN DAI EA | BN DL SI GA | Smart Energy |
| Wogu et al. [135] | Artificial intelligence, smart classrooms and online education in the 21st century | Journal of Cases on Information Technology | To investigate impact of AI innovations in the education sector and on human development | Describes the potential changes AI will bring to the education sector. | Society | ML | n/a | n/a | Smart Education |
| Wu & Silva [26] | Artificial intelligence solutions for urban land dynamics | Journal of Planning Literature | To increase understanding of how AI approaches urban and land dynamics modelling processes. | Discusses the use of AI in identifying the dynamics of urban land use. | Environment | KB ML EI SO | ES NN DAI EA | FS ABM SI GA | n/a |
| Yu et al. [150] | Decentralized big data auditing for smart city environments leveraging blockchain technology | IEEE Access | To design a blockchain instantiation and conduct a comparison between the existing and proposed schemes. | Identifies the potential for AI to processing and analyzing large amounts of data | Economy | n/a | n/a | n/a | Blockchain |
| Yun et al. [76] | Not deep learning but autonomous learning of open innovation for sustainable artificial intelligence | Sustainability | To build an interaction model between direct and autonomous learning. | Investigates the potential for AI to develop autonomous learning capabilities. | Economy | ML EI | AS DAI | SI | n/a |
| Zou et al. [157] | Exploring urban population forecasting and spatial distribution modeling with artificial intelligence technology | Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences | To improve the precision of small area population forecasting. | Describes the use of AI in population forecasting | Environment | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
References
- Oreskes, N. The scientific consensus on climate change. Science 2004, 306, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.; Nuccitelli, D.; Green, S.A.; Richardson, M.; Winkler, B.; Painting, R.; Skuce, A. Quantifying the consensus on anthropogenic global warming in the scientific literature. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 024024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Foth, M.; Kamruzzaman, M. Towards post-anthropocentric cities: Reconceptualizing smart cities to evade urban ecocide. J. Urban Technol. 2019, 26, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanamge, N.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Goonetilleke, A.; Kamruzzaman, M. Determining disaster severity through social media analysis: Testing the methodology with South East Queensland Flood tweets. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 42, 101360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotto, D.; Philippi, A.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M. Aligning urban policy with climate action in the global South: Are Brazilian cities considering climate emergency in local planning practice? Energies 2019, 12, 3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Xu, R.; Abramson, M.J.; Li, S.; Guo, Y. Bushfires in Australia: A serious health emergency under climate change. Lancet Planet. Health 2020, 4, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenmin, L.; Espinosa, P. Tackling climate change to accelerate sustainable development. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinniburgh, C. Can extinction rebellion survive? Dissent 2020, 67, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomitsch, M.; Haeusler, M.H. Infostructures: Towards a complementary approach for solving urban challenges through digital technologies. J. Urban Technol. 2015, 22, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M. Does smart city policy lead to sustainability of cities? Land Use Policy 2018, 73, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Inkinen, T. Geographies of Disruption: Place Making for Innovation in the Age of Knowledge Economy; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M. Smart cities and mobility: Does the smartness of Australian cities lead to sustainable commuting patterns? J. Urban Technol. 2019, 26, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbolino, R.; De Simone, L.; Carlucci, F.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Ioppolo, G. Towards a sustainable industrial ecology: Implementation of a novel approach in the performance evaluation of Italian regions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M.D.; Buys, L.; Perveen, S. Smart Cities of the Sunshine State: Status of Queensland’s Local Government Areas. Available online: https://eprints.qut.edu.au/118349/ (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Desouza, K.C.; Swindell, D.; Smith, K.L.; Sutherland, A.; Fedorschak, K.; Coronel, C. Local government 2035: Strategic trends and implications of new technologies. Issues Technol. Innov. 2015, 27, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Kyriazopoulou, C. Smart city technologies and architectures: A literature review. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Smart Cities and Green ICT Systems, Lisbon, Portugal, 20–22 May 2015; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ab-Rahman, A.; Hamid, U.Z.; Chin, T.A. Emerging technologies with disruptive effects: A review. Perintis e-J. 2017, 7, 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Gatzweiler, F.W. Advancing urban health and wellbeing through collective and artificial intelligence: A system approach 3.0. In Urban Health and Wellbeing Programme; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- King, B.A.; Hammond, T.; Harrington, J. Disruptive technology: Economic consequences of artificial intelligence and the robotics revolution. J. Strateg. Innov. Sustain. 2017, 12, 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Tegmark, M. Life 3.0: Being Human in the Age of Artificial Intelligence; Knopf: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yigitcanlar, T. Technology and the City: Systems, Applications and Implications; Routledge: Abingdon upon Thames, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Batty, M. Artificial intelligence and smart cities. Environ. Plan. Urban Anal. City Sci. 2018, 45, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalkoff, R.J. Artificial Intelligence: An Engineering Approach; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Pannu, A. Artificial intelligence and its application in different areas. Artif. Intell. 2015, 4, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Corea, F. AI Knowledge Map: How to Classify AI Technologies. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2018/08/22/ai-knowledge-map-how-to-classify-ai-technologies/#5e99db627773 (accessed on 18 January 2020).
- Wu, N.; Silva, E.A. Artificial intelligence solutions for urban land dynamics: A review. J. Plan. Lit. 2010, 24, 246–265. [Google Scholar]
- Jiafeng, Z.; Tian, L.; Lin, Z. Artificial intelligence approach to creative data manipulation for optimisation of livelihood oriented urban planning and management. Int. J. Perform. Eng. 2019, 15, 602–610. [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz, B.W.; Weyerer, J.C.; Geyer, C. Artificial intelligence and the public sector: Applications and challenges. Int. J. Public Adm. 2019, 42, 596–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendling, J.; Decker, G.; Hull, R.; Reijers, H.A.; Weber, I. How do machine learning, robotic process automation, and blockchains affect the human factor in business process management? Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2018, 43, 297–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, A.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Currie, G. Understanding autonomous vehicles: A systematic literature review on capability, impact, planning and policy. J. Transp. Land Use 2019, 12, 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Times. ANA Starts Testing Semi-Autonomous Bus at Haneda Airport for Passengers and Staff. Available online: https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2020/01/22/national/ana-starts-testing-autonomous-bus-operation-haneda-airport/#.XjN_rGgzZnI (accessed on 31 January 2020).
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Wilson, M.; Kamruzzaman, M. Disruptive impacts of automated driving systems on the built environment and land use: An urban planner’s perspective. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Foth, M.; Sabatini-Marques, J.; da Costa, E.; Ioppolo, G. Can cities become smart without being sustainable? A systematic review of the literature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 45, 348–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston Chronicle. Robot Police Coming to Houston Transit Center, Rail Platform, Park and Ride Lot. Available online: https://www.houstonchronicle.com/news/transportation/article/Robot-police-coming-to-Houston-transit-center-14999004.php (accessed on 23 January 2020).
- Washington Post. One Solution for Keeping Traffic Stops from Turning Violent: A Robot that Separates Police Officers from Drivers. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2019/05/14/one-solution-keeping-traffic-stops-turning-violent-robot-that-separates-police-officers-drivers (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Swindell, D.; Desouza, K.C.; Hudgens, R. Dubai Offers Lessons for Using Artificial Intelligence in Local Government; Brookings: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.W.; Lee, H.W.; Liu, C.H. A review of artificial intelligence algorithms used for smart machine tools. Inventions 2018, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, K.C.; Smith, K.L. Big Data and Planning; American Planning Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; Volume 585, pp. 2–102. [Google Scholar]
- Desouza, K.C. Delivering Artificial Intelligence in Government: Challenges and Opportunities; IBM Center for the Business of Government: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Thakuriah, P.V.; Tilahun, N.Y.; Zellner, M. Seeing Cities through Big Data; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sadilek, A.; Kautz, H.; DiPrete, L.; Labus, B.; Portman, E.; Teitel, J.; Silenzio, V. Deploying nEmesis: Preventing foodborne illness by data mining social media. In Proceedings of the 13th IAAI Conference on AI, Seattle, WA, USA; 2016; pp. 3982–3989. [Google Scholar]
- BBC. Durham Police AI to Help with Custody Decisions. Available online: http://www.bbc.com/news/technology-39857645 (accessed on 31 January 2020).
- Accenture. Accenture Helps Seattle Police Department Implement Data Analytics Platform. Available online: https://newsroom.accenture.com/news/accenture-helps-seattle-police-department-implement-data-analytics-platform.htm (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Fastcompany. San Diego’s Massive, 7-Year Experiment with Facial Recognition Technology Appears to be a Flop. Available online: https://www.fastcompany.com/90440198/san-diegos-massive-7-year-experiment-with-facial-recognition-technology-appears-to-be-a-flop (accessed on 17 February 2020).
- Madaio, M.; Haimson, O.L.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Hinds-Aldrich, M.; Dilkina, B.; Chau, D.H.P. Identifying and Prioritizing Fire Inspections: A Case Study of Predicting Fire Risk in Atlanta; Bloomberg: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Han, H.; Kamruzzaman, M. Approaches, advances, and applications in the sustainable development of smart cities: A commentary from the guest editors. Energies 2019, 12, 4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New York Times. Another Hacked Florida City Pays a Ransom, This Time for $460,000. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2019/06/27/us/lake-city-florida-ransom-cyberattack.html (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- MIT News. System Predicts 85 Percent of Cyber-Attacks Using Input from Human Experts. Available online: http://news.mit.edu/2016/ai-system-predicts-85-percent-cyber-attacks-using-input-human-experts-0418 (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Smith, S.F.; Barlow, G.J.; Xie, X.F.; Rubinstein, Z.B. Smart urban signal networks: Initial application of the SURTRAC adaptive traffic signal control system. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling, Rome, Italy, 10–14 June 2013; pp. 434–442. [Google Scholar]
- Curbed. Criticism Mounts over Detroit Police Department’s Facial Recognition Software. Available online: https://detroit.curbed.com/2019/7/8/20687045/project-green-light-detroit-facial-recognition-technology (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- The Guardian. What is Fake News? How to Spot It and What You Can Do to Stop It. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/media/2016/dec/18/what-is-fake-news-pizzagate (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Washington Post. N.C. Man Told Police He Went to D.C. Pizzeria with Gun to Investigate Conspiracy Theory. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/local/wp/2016/12/04/d-c-police-respond-to-report-of-a-man-with-a-gun-at-comet-ping-pong-restaurant (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Azcentral. A Slashed Tire, A Pointed Gun, Bullies on the Road: Why do Waymo Self-Driving Vans Get So Much Hate? Available online: https://www.azcentral.com/story/money/business/tech/2018/12/11/waymo-self-driving-vehicles-face-harassment-road-rage-phoenix-area/2198220002 (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Selby, J.D.; Desouza, K.C. Fragile cities in the developed world: A conceptual framework. Cities 2019, 91, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, K.C.; Selby, J.D. How Technological Progress Can Cause Urban Fragility; Brookings Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- NHTSA. The Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) or Autopilot Systems May Not Function as Designed, Increasing the Risk of a Crash. Available online: https://static.nhtsa.gov/odi/inv/2016/INCLA-PE16007-7876.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- CNN. Chrysler Recalls 1.4 Million Hackable Cars. Available online: http://money.cnn.com/2015/07/24/technology/chrysler-hack-recall/index.html (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- CNN. Chryslers Can be Hacked over the Internet. Available online: http://money.cnn.com/2015/07/21/technology/chrysler-hack/index.html (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Slate. Autonomous Vehicles will Cost Local Governments Big Bucks. Available online: http://www.slate.com/blogs/future_tense/2015/06/16/autonomous_vehicles_will_cost_local_governments_big_bucks.html (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Az Central. Self-Driving Cars may Cost Cities. Available online: http://www.azcentral.com/story/news/arizona/politics/2015/07/01/self-driving-cars-cityrevenue/29598929 (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Buys, L.; Ioppolo, G.; Sabatini-Marques, J.; da Costa, E.M.; Yun, J.J. Understanding ‘smart cities’: Intertwining development drivers with desired outcomes in a multidimensional framework. Cities 2018, 81, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Han, H.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Ioppolo, G.; Sabatini-Marques, J. The making of smart cities: Are Songdo, Masdar, Amsterdam, San Francisco and Brisbane the best we could build? Land Use Policy 2019, 88, 104187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Xu, L. An intelligent decision support system for fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of urban development. Expert Syst. Appl. 1999, 16, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, R.; Mahajan, P. Artificial intelligence research in India: A scientometric analysis. Sci. Technol. Libr. 2016, 35, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarynskyy, O.; Makarynska, D.; Kuhn, M.; Featherstone, W.E. Predicting sea level variations with artificial neural networks at Hillarys Boat Harbour, Western Australia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, K.; Haque, M.M.; Rahman, A.; Shamseldin, A.Y.; Shoaib, M. Flood estimation in ungauged catchments: Application of artificial intelligence-based methods for Eastern Australia. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2017, 31, 1499–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.W.; Marshall, B.E. Artificial intelligence applications in the intensive care unit. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, A.N.; Kambhampati, C.; Monson, J.R.; Drew, P.J. Artificial intelligence in medicine. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2004, 86, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, K.W. A review on integration of artificial intelligence into water quality modelling. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.L.; Shortliffe, E.H.; Stefanelli, M.; Szolovits, P.; Berthold, M.R.; Bellazzi, R.; Abu-Hanna, A. The coming of age of artificial intelligence in medicine. Artif. Intell. Med. 2009, 46, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drigas, A.S.; Ioannidou, R.E. Artificial intelligence in special education: A decade review. Int. J. Eng. Educ. 2012, 28, 1366. [Google Scholar]
- Rho, S.; Min, G.; Chen, W. Advanced issues in artificial intelligence and pattern recognition for intelligent surveillance system in smart home environment. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2012, 25, 1299–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaz, M.B. Artificial intelligence techniques for advanced smart home implementation. Acta Tech. Corvininesis Bull. Eng. 2013, 6, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chmiel, W.; Dańda, J.; Dziech, A.; Ernst, S.; Kadłuczka, P.; Mikrut, Z.; Pawlik, P.; Szwed, P.; Wojnicki, I. INSIGMA: An intelligent transportation system for urban mobility enhancement. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 10529–10560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paz, J.F.; Bajo, J.; Rodríguez, S.; Villarrubia, G.; Corchado, J.M. Intelligent system for lighting control in smart cities. Inf. Sci. 2016, 372, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Lee, D.; Ahn, H.; Park, K.; Yigitcanlar, T. Not deep learning but autonomous learning of open innovation for sustainable artificial intelligence. Sustainability 2016, 8, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Mehmood, R.; Katib, I.; Albogami, N.N.; Albeshri, A. Data fusion and IoT for smart ubiquitous environments: A survey. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 9533–9554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, B.K. Artificial intelligence techniques in smart grid and renewable energy systems: Some example applications. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 2262–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlík, B. The application of artificial intelligence in the process of optimizing energy consumption in intelligent areas. Neural Netw. World 2017, 27, 415–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Bilalovic, J.; Jha, A.; Patel, N.; Zhang, H. Renewable energy: Present research and future scope of artificial intelligence. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Srinivasan, R.S. A review of artificial intelligence-based building energy use prediction: Contrasting the capabilities of single and ensemble prediction models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, R.; Sharma, V. Smart education with artificial intelligence-based determination of learning styles. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 132, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Fung, B.C.; Iqbal, F.; Shah, B. Security and privacy challenges in smart cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casares, A.P. The brain of the future and the viability of democratic governance: The role of artificial intelligence, cognitive machines, and viable systems. Futures 2018, 103, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassignol, M.; Khoroshavin, A.; Klimova, A.; Bilyatdinova, A. Artificial intelligence trends in education: A narrative overview. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 136, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, K.; Lytras, M.; Visvizi, A. Energy sustainability in smart cities: Artificial intelligence, smart monitoring, and optimization of energy consumption. Energies 2018, 11, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrescu, E.M.; Dobrescu, E.M. Artificial intelligence (AI): The technology that shapes the world. Glob. Econ. Obs. 2018, 6, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, C.; Edwards, A.; Spence, P.R.; Lin, X. I, teacher: Using artificial intelligence (AI) and social robots in communication and instruction. Commun. Educ. 2018, 67, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, B. The application of medical artificial intelligence technology in rural areas of developing countries. Health Equity 2018, 2, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Lu, Y.; Gao, H.; Cao, R. Artificial intelligence-based semantic internet of things in a user-centric smart city. Sensors 2018, 18, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, A. Ipsum: An approach to smart volatile ICT-infrastructures for smart cities and communities. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 126, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopytko, V.; Shevchuk, L.; Yankovska, L.; Semchuk, Z.; Strilchuk, R. Smart home and artificial intelligence as environment for the implementation of new technologies. Traektoriâ Nauk. Path Sci. 2018, 4, 2007–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, S.; Muhammad, K.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Doctor, F. Object tracking in vary lighting conditions for fog based intelligent surveillance of public spaces. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 29283–29296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukowicz, P.; Slusallek, P. How to avoid an AI interaction singularity. Interactions 2018, 25, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.S. Towards smart city innovation under the perspective of software-defined networking, artificial intelligence and big data. Rev. Tecnol. Inf. Comun. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nápoles, V.M.; Rodríguez, M.D.; Páez, D.G.; Penelas, J.L.; García-Ochoa, A.G.; Pérez, A.L. MUSA–I: Towards new social tools for advanced multi-modal transportation in smart cities. Multidiscip. Digit. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2018, 2, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.H.; Hwang, M.C. Value-based deep reinforcement learning for adaptive isolated intersection signal control. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 12, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljabbar, R.; Dia, H.; Liyanage, S.; Bagloee, S. Applications of artificial intelligence in transport: An overview. Sustainability 2019, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajerla, D.; Mahfuz, S.; Zulkernine, F. A real-time patient monitoring framework for fall detection. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, Z.; Dhunny, Z.A. On big data, artificial intelligence and smart cities. Cities 2019, 89, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsamhi, S.H.; Ma, O.; Ansari, M.S.; Almalki, F.A. Survey on collaborative smart drones and internet of things for improving smartness of smart cities. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128125–128152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, I.; Delavar, M.R.; Mirzaei, F.; Arrabi, B.N. Prediction of environmental indicators in land leveling using artificial intelligence techniques. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, H.E. The challenge of big data and data science. Annu. Rev. Political Sci. 2019, 22, 297–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, K.H.; Jung, J.J. Computational negotiation-based edge analytics for smart objects. Inf. Sci. 2019, 480, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.Y.; Alvarez, R.; Sit, M.; Duarte, F.; Ratti, C. Deep learning-based video system for accurate and real-time parking measurement. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 7693–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Miao, Y.; Jian, X.; Wang, X.; Humar, I. Cognitive-LPWAN: Towards intelligent wireless services in hybrid low power wide area networks. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2019, 3, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Qiu, T.; Zhou, X.; Li, K.; Atiquzzaman, M. An intelligent robust networking mechanism for the internet of things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.C.; Ni, W.; Lin, I.C.; Tao, X.; Zhang, P. Big data analytics and network calculus enabling intelligent management of autonomous vehicles in a smart city. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 2021–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, K.C.; Dawson, G.S.; Chenok, D. Designing, developing, and deploying artificial intelligence systems: Lessons from and for the public sector. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 63, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, I.U.; Guizani, M.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Hassan, S.; Korotaev, V.V. Machine learning in the internet of things: Designed techniques for smart cities. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 100, 826–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y. Energy-efficient fair cooperation fog computing in mobile edge networks for smart city. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 7543–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, R.H.; Fredericks, E.M.; Bowers, K.M. Uncertainty in big data analytics: Survey, opportunities, and challenges. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.R.; Haworth, J.; Cheng, T. Urban-i: From urban scenes to mapping slums, transport modes, and pedestrians in cities using deep learning and computer vision. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, R.; Maniak, T.; Karyotis, C. Intelligent remote monitoring of parking spaces using licensed and unlicensed wireless technologies. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, D. Blockchain and trust in a smart city. Environ. Urban. Asia 2019, 10, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.; Nguyen, H.; Dou, J.; Zhou, J. A comparative study of PSO-ANN, GA-ANN, ICA-ANN, and ABC-ANN in estimating the heating load of buildings’ energy efficiency for smart city planning. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.K.; Braun, P.; Cuzzocrea, A. AI-based sensor information fusion for supporting deep supervised learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Shuang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Wei, M.; Liu, C.; Hao, C.; Qiu, C.W.; Cui, T.J. Intelligent metasurface imager and recognizer. Light Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, L.; Hao, B.; Yang, L.; Hu, T.; Xue, T.; Wang, S. Modeling and simulation of robot inverse dynamics using LSTM-based deep learning algorithm for smart cities and factories. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 173989–173998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytras, M.D.; Chui, K.T.; Visvizi, A. Data analytics in smart healthcare: The recent developments and beyond. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, K.; Lloret, J.; Baik, S.W. Intelligent and energy-efficient data prioritization in green smart cities: Current challenges and future directions. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorbakhsh-Sabet, N.; Zand, R.; Zhang, Y.; Abedi, V. Artificial intelligence transforms the future of healthcare. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, S.; Yun, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, W.T. Dependable fire detection system with multifunctional artificial intelligence framework. Sensors 2019, 19, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, H.; Gutiérrez, S. An indoor predicting climate conditions approach using Internet-of-Things and artificial hydrocarbon networks. Measurement 2019, 135, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, V.; Jha, S.; Kumar, R.; Priyadarshini, I.; Abdel-Basset, M.; Elhoseny, M.; Long, H.V. A hybrid artificial intelligence and internet of things model for generation of renewable resource of energy. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 111181–111191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rashid, M.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Hassanain, E.; Alhamid, M.F.; Guizani, M. Blockchain and IoT-based cognitive edge framework for sharing economy services in a smart city. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 18611–18621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruohomaa, H.; Salminen, V.; Kunttu, I. Towards a smart city concept in small cities. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2019, 9, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgantzos, K.; Grigg, I. Artificial intelligence implementations on the blockchain: Use cases and future applications. Future Internet 2019, 11, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Shu, L.; Yang, Y.; Chai, Y. Smart textile-integrated microelectronic systems for wearable applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 32, 1901958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, K.; Bhutta, M.N.; Khan, Z.; Tahir, M.A. Smart city big data analytics: An advanced review. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2019, 9, e1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streitz, N. Beyond ‘smart-only’ cities: Redefining the ‘smart-everything’ paradigm. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2019, 10, 791–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syifa, M.; Kadavi, P.R.; Lee, C.W. An artificial intelligence application for post-earthquake damage mapping in Palu, Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. Sensors 2019, 19, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yao, J.; Wang, G.; Hao, F.; Shrestha, S.; Xue, B.; Peng, Y. Exploring the application of artificial intelligence technology for identification of water pollution characteristics and tracing the source of water quality pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Li, C.; Peng, X.; Zeng, F.; Lu, X. Conventional models and artificial intelligence-based models for energy consumption forecasting: A review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 181, 106187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wogu, I.A.; Misra, S.; Assibong, P.A.; Apeh, H.A.; Olu-Owolabi, F.E.; Awogu-Maduagwu, E.A. Artificial intelligence, smart class rooms and online education in the 21st century: Implications for human development. J. Cases Inf. Technol. 2018, 21, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortès, U.; Sànchez-Marrè, M.; Ceccaroni, L.; R-Roda, I.; Poch, M. Artificial intelligence and environmental decision support systems. Appl. Intell. 2000, 13, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.C.; Hauser, K. Artificial intelligence framework for simulating clinical decision-making: A Markov decision process approach. Artif. Intell. Med. 2013, 57, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Calavia, L.; Baladrón, C.; Aguiar, J.; Carro, B.; Sánchez-Esguevillas, A.; Alonso-López, J.; Smilansky, Z. An intelligent surveillance platform for large metropolitan areas with dense sensor deployment. Sensors 2013, 13, 7414–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanelli, M. The socio-organizational age of artificial intelligence in medicine. Artif. Intell. Med. 2001, 23, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, D.; Lewis, M.; Bishary, M. The roles of artificial intelligence in education: Current progress and future prospects. J. Educ. Technol. 2005, 1, 42–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieters, W. Explanation and trust: What to tell the user in security and AI? Ethics Inf. Technol. 2011, 13, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhauser, L.; Kreps, G.L.; Morrison, K.; Athanasoulis, M.; Kirienko, N.; Van Brunt, D. Using design science and artificial intelligence to improve health communication: ChronologyMD case example. Patient Educ. Couns. 2013, 92, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roll, I.; Wylie, R. Evolution and revolution in artificial intelligence in education. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Education 2016, 26, 582–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, M.; Sormani, R.; Trujillo, L.; Popovič, A. Predicting per capita violent crimes in urban areas: An artificial intelligence approach. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2017, 8, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, N.K.; Parashar, S.; Swarnkar, A.; Gupta, N.; Niazi, K.R.; Bansal, R.C. Mobile power infrastructure planning and operational management for smart city applications. Energy Procedia 2017, 142, 2202–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.J.; Park, J.; Economou, A.; Lee, S. Artificial intelligence-aided design: Smart design for sustainable city development. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2019, 46, 1581–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devedzic, V. Web Intelligence and artificial intelligence in education. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2004, 7, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Eldrandaly, K.A.; Abdel-Basset, M.; Abdel-Fatah, L. PTZ-surveillance coverage based on artificial intelligence for smart cities. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2019, 49, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altulyan, M.; Yao, L.; Kanhere, S.S.; Wang, X.; Huang, C. A unified framework for data integrity protection in people-centric smart cities. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 79, 4989–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, Z.; Sinnott, R.O. Decentralized big data auditing for smart city environments leveraging blockchain technology. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 6288–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, S.; Easpaig, G.; Nic, B.; Fox, R. Virtually caring: A qualitative study of internet-based mental health services for LGBT young adults in rural Australia. Rural Remote Health 2020, 20, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pence, H.E. Artificial intelligence in higher education: New wine in old wineskins? J. Educ. Technol. Syst. 2019, 48, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, A. AI and education: The importance of teacher and student relations. AI Soc. 2019, 34, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Conversation. COVID-19 Death Toll Estimated to Reach 3900 by Next Friday, According to AI Modelling. Available online: https://theconversation.com/covid-19-death-toll-estimated-to-reach-3-900-by-next-friday-according-to-ai-modelling-133052 (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- Lin, Y.P.; Petway, J.R.; Lien, W.Y.; Settele, J. Blockchain with artificial intelligence to efficiently manage water use under climate change. Environments 2018, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inclezan, D.; Prádanos, L.I. A critical view on smart cities and AI. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2017, 60, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Min, Y. Exploring urban population forecasting and spatial distribution modelling with artificial intelligence technology. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2019, 119, 295–310. [Google Scholar]
- Rolnick, D.; Donti, P.L.; Kaack, L.H.; Kochanski, K.; Lacoste, A.; Sankaran, K.; Luccioni, A. Tackling climate change with machine learning. arXiv preprint arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.05433. [Google Scholar]
- O’Gorman, P.A.; Dwyer, J.G. Using machine learning to parameterize moist convection: Potential for modeling of climate, climate change, and extreme events. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2018, 10, 2548–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, K.; Deo, R.; Apan, A.A. Drought modelling based on artificial intelligence and neural network algorithms: A case study in Queensland, Australia. In Climate Change Adaptation in Pacific Countries; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 177–198. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, E. Smart cities: Opportunities, challenges, and security threats. J. Strateg. Innov. Sustain. 2019, 14, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Falco, G.; Viswanathan, A.; Caldera, C.; Shrobe, H. A master attack methodology for an AI-based automated attack planner for smart cities. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 48360–48373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanamge, N.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Goonetilleke, A.; Kamruzzaman, M. Can volunteer crowdsourcing reduce disaster risk? A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 35, 101097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Kar, A.K.; Gupta, M.P. Success of IoT in smart cities of India: An empirical analysis. Gov. Inf. Q. 2018, 35, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Tong, S.; Fang, Z.; Qu, Z. Frontiers: Machines vs. humans: The impact of artificial intelligence chatbot disclosure on customer purchases. Mark. Sci. 2019, 38, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T. Smart cities: An effective urban development and management model? Aust. Plan. 2015, 52, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotta, M.J.; Sell, D.; Pacheco, R.C.; Yigitcanlar, T. Digital commons and citizen coproduction in smart cities: Assessment of Brazilian municipal e-government platforms. Energies 2019, 12, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T. Smart city policies revisited: Considerations for a truly smart and sustainable urbanism practice. World Technopolis Rev. 2018, 7, 97–112. [Google Scholar]
- Rjab, A.B.; Mellouli, S. Smart cities in the era of artificial intelligence and internet of things: Literature review from 1990 to 2017. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research: Governance in the Data Age, Delft, The Netherlands, 30 May–1 June 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, B.; Hendry, D.G. Value Sensitive Design: Shaping Technology with Moral Imagination; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- LSE. Why Low Trust in Government May Mean Americans Don’t Want Anything Done about Inequality. Available online: https://blogs.lse.ac.uk/usappblog/2019/12/23/why-low-trust-in-government-may-mean-americans-dont-want-anything-done-about-inequality (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Morishita, L.; van Zyl, D. Exploring the significance of earning a social license to operate in an urban setting. Geo-Resour. Environ. Eng. 2017, 2, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yuttapongsontorn, N.; Desouza, K.C.; Braganza, A. Complexities of large-scale technology project failure: A forensic analysis of the Seattle popular monorail authority. Public Perform. Manag. Rev. 2008, 31, 443–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mergel, I.; Desouza, K.C. Implementing open innovation in the public sector: The case of Challenge. gov. Public Adm. Rev. 2013, 73, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, K.C.; Bhagwatwar, A. Technology-enabled participatory platforms for civic engagement: The case of US cities. J. Urban Technol. 2014, 21, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Research on the evaluation of urban open data. World J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 5, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perng, S.Y.; Kitchin, R.; Mac Donncha, D. Hackathons, entrepreneurial life and the making of smart cities. Geoforum 2018, 97, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNN. Artist Uses 99 Phones to Trick Google into Traffic Jam Alert. Available online: https://us.cnn.com/style/article/artist-google-traffic-jam-alert-trick-scli-intl/index.html (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- Desouza, K.C. Agile Information Systems: Conceptualization, Construction, and Management; Routledge: Abingdon upon Thames, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R.T.; Kunene, K.N.; Islam, M.S. Frugal information systems (IS). Inf. Technol. Dev. 2013, 19, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planetizen. Our Fragile Emerging Megacities: A Focus on Resilience. Available online: https://www.planetizen.com/node/67338 (accessed on 19 February 2020).
- Purao, S.R.; Desouza, K.C.; Becker, J. Investigating failures in large-scale public sector projects with sentiment analysis. e-Serv. J. 2012, 8, 84–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, K.C.; Hunter, M.; Yigitcanlar, T. Under the hood: A look at techno-centric smart city development. Public Manag. 2019, 12, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurthy, R.; Smith, K.L.; Desouza, K.C. Urban informatics: Critical data and technology considerations. In Seeing Cities Through Big Data; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 163–188. [Google Scholar]
- Wired. A Deep Flaw in Your Car Lets Hackers Shut Down Safety Features. Available online: https://www.wired.com/story/car-hack-shut-down-safety-features (accessed on 14 February 2020).
- BBC. China Coronavirus: Misinformation Spreads Online About Origin and Scale. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/blogs-trending-51271037 (accessed on 20 February 2020).
- BBC. Burned to Death Because of a Rumour on WhatsApp. Available online: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-latin-america-46145986 (accessed on 30 December 2019).
- Gherhes, V.; Obrad, C. Technical and humanities students’ perspectives on the development and sustainability of artificial intelligence (AI). Sustainability 2018, 10, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Conversation. Australian Police are Using the Clearview AI Facial Recognition System with No Accountability. Available online: https://theconversation.com/australian-police-are-using-the-clearview-ai-facial-recognition-system-with-no-accountability-132667 (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- The Conversation. Airlines Take no Chances with Our Safety. And Neither Should Artificial Intelligence. Available online: https://theconversation.com/airlines-take-no-chances-with-our-safety-and-neither-should-artificial-intelligence-132580 (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- The Verge. IBM’s Watson Gave Unsafe Recommendations for Treating Cancer. Available online: https://www.theverge.com/2018/7/26/17619382/ibms-watson-cancer-ai-healthcare-science (accessed on 12 March 2020).
- NTSB. Preliminary Report Released for Crash Involving Pedestrian, Uber Technologies, Inc., Test Vehicle. Available online: https://www.ntsb.gov/news/press-releases/Pages/NR20180524.aspx (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- The Conversation. Microsoft’s Racist Chatbot Tay Highlights How Far AI is from being Truly Intelligent. Available online: https://theconversation.com/microsofts-racist-chatbot-tay-highlights-how-far-ai-is-from-being-truly-intelligent-56881 (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Forbes. Is Artificial Intelligence Dangerous? 6 AI Risks Everyone Should Know About. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2018/11/19/is-artificial-intelligence-dangerous-6-ai-risks-everyone-should-know-about/#65ee8ba22404 (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- The Conversation. To Protect us from the Risks of Advanced Artificial Intelligence, We Need to Act Now. Available online: https://theconversation.com/to-protect-us-from-the-risks-of-advanced-artificial-intelligence-we-need-to-act-now-107615 (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Medium. Summary of EU White Paper on Artificial Intelligence: A European Approach to Excellence and Trust. Available online: https://medium.com/@tibastar/summary-of-eu-white-paper-on-artificial-intelligence-a-european-approach-to-excellence-and-trust-e04a1a018b5 (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- EU. On Artificial Intelligence: A European Approach to Excellence and Trust. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/info/files/commission-white-paper-artificial-intelligence-feb2020_en.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- The Guardian. Elon Musk: Regulate AI to Combat ’Existential Threat’ before It’s too Late. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2017/jul/17/elon-musk-regulation-ai-combat-existential-threat-tesla-spacex-ceo (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- Schleiger, E.; Hajkowicz, S. Artificial Intelligence in Australia Needs to Get Ethical, So We Have a Plan. Available online: https://www.themandarin.com.au/107060-artificial-intelligence-in-australia-needs-to-get-ethical-so-we-have-a-plan (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Nica, E.; Manole, C.; Stan, C.I. A laborless society? How highly automated environments and breakthroughs in artificial intelligence bring about innovative kinds of skills and employment disruptions, altering the nature of business process and affecting the path of economic growth. J. Self-Gov. Manag. Econ. 2018, 6, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Gunkel, D.J. The Machine Question: Critical Perspectives on AI, Robots, and Ethics; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Makridakis, S. The forthcoming artificial intelligence (AI) revolution: Its impact on society and firms. Futures 2017, 90, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhnejad, Y.; Yigitcanlar, T. Scientific landscape of sustainable urban and rural areas research: A systematic scientometric analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smashing Magazine. How AI is Helping Solve Climate Change. Available online: https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2019/09/ai-climate-change (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Vella, K.; Desouza, K.; Butler, L.; Kankanamge, N. Smart City or Not? Now You Can See How Yours Compares. Available online: https://eprints.qut.edu.au/180751/ (accessed on 15 March 2020).
| Selection Criteria |
|---|
|
| Category | Element | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| AI paradigms | Machine learning | [26]; [63]; [67,68,69,70]; [71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135] |
| Probabilistic methods | [70]; [73,74,75]; [77]; [80,81,82]; [87]; [90]; [93,94]; [96,97,98,99,100,101]; [112,113,114]; [134]; [136,137,138] | |
| Knowledge-based | [26]; [63]; [67,68,69,70,71]; [73]; [77,78]; [82]; [92]; [98]; [100]; [112]; [136]; [139,140,141,142,143] | |
| Search and optimization | [26]; [67,68,69]; [77]; [79,80]; [82]; [86]; [92]; [98]; [101]; [106]; [112]; [116]; [128]; [130]; [134]; [144,145,146] | |
| Logic-based | [63]; [67,68]; [69]; [71]; [73]; [77,78]; [82]; [92]; [98]; [100]; [112]; [136]; [140,141,142,143] | |
| Embodied intelligence | [26]; [70]; [73]; [75,76]; [80]; [82]; [98]; [104]; [116]; [128]; [134]; [137]; [147] | |
| AI applications | Neural networks | [26]; [63]; [67,68,69,70]; [71]; [73]; [75]; [77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85]; [87]; [89,90]; [92]; [95]; [97,98,99,100,101,102,103]; [105,106,107]; [109,110,111,112]; [116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126]; [128,129,130,131,132,133,134] |
| Evolutionary algorithms | [26]; [67,68,69]; [77]; [79,80]; [82]; [86]; [92]; [98]; [101]; [106]; [112]; [116]; [128]; [130]; [134]; [144,145,146] | |
| Expert systems | [26]; [63]; [67,68,69,70]; [71]; [73]; [77,78]; [82]; [92]; [98]; [100]; [112]; [136]; [140,141,142,143] | |
| Distributed artificial intelligence | [26]; [70]; [73]; [75,76]; [80]; [82]; [92]; [98]; [116]; [128]; [134]; [137]; [147,148] | |
| Computer vision | [73,74,75]; [87]; [93,94]; [96]; [99]; [101]; [113,114]; [118]; [138] | |
| Decision networks | [70]; [77]; [80]; [82]; [90]; [98]; [112]; [134]; [136] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yigitcanlar, T.; Desouza, K.C.; Butler, L.; Roozkhosh, F. Contributions and Risks of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Building Smarter Cities: Insights from a Systematic Review of the Literature. Energies 2020, 13, 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13061473
Yigitcanlar T, Desouza KC, Butler L, Roozkhosh F. Contributions and Risks of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Building Smarter Cities: Insights from a Systematic Review of the Literature. Energies. 2020; 13(6):1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13061473
Chicago/Turabian StyleYigitcanlar, Tan, Kevin C. Desouza, Luke Butler, and Farnoosh Roozkhosh. 2020. "Contributions and Risks of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Building Smarter Cities: Insights from a Systematic Review of the Literature" Energies 13, no. 6: 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13061473
APA StyleYigitcanlar, T., Desouza, K. C., Butler, L., & Roozkhosh, F. (2020). Contributions and Risks of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Building Smarter Cities: Insights from a Systematic Review of the Literature. Energies, 13(6), 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13061473