Impact of Topographic Steps in the Wake and Power of a Wind Turbine: Part A—Statistics
Abstract
1. Introduction
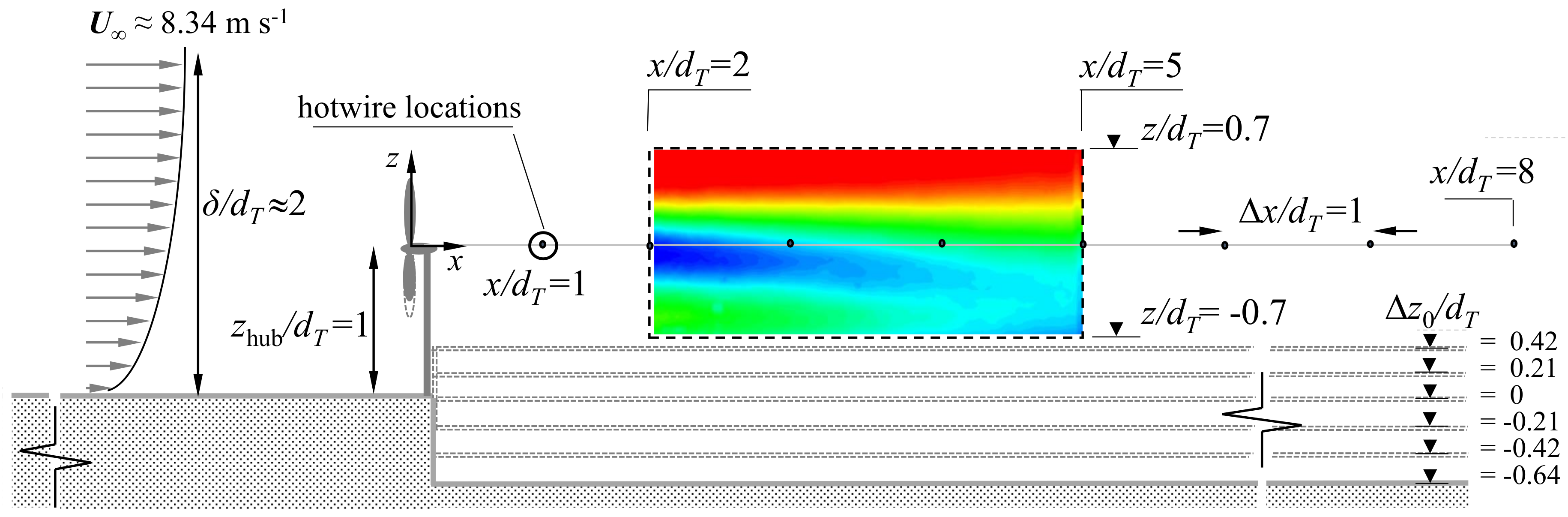
2. Experimental Set-Up
3. Results and Discussion
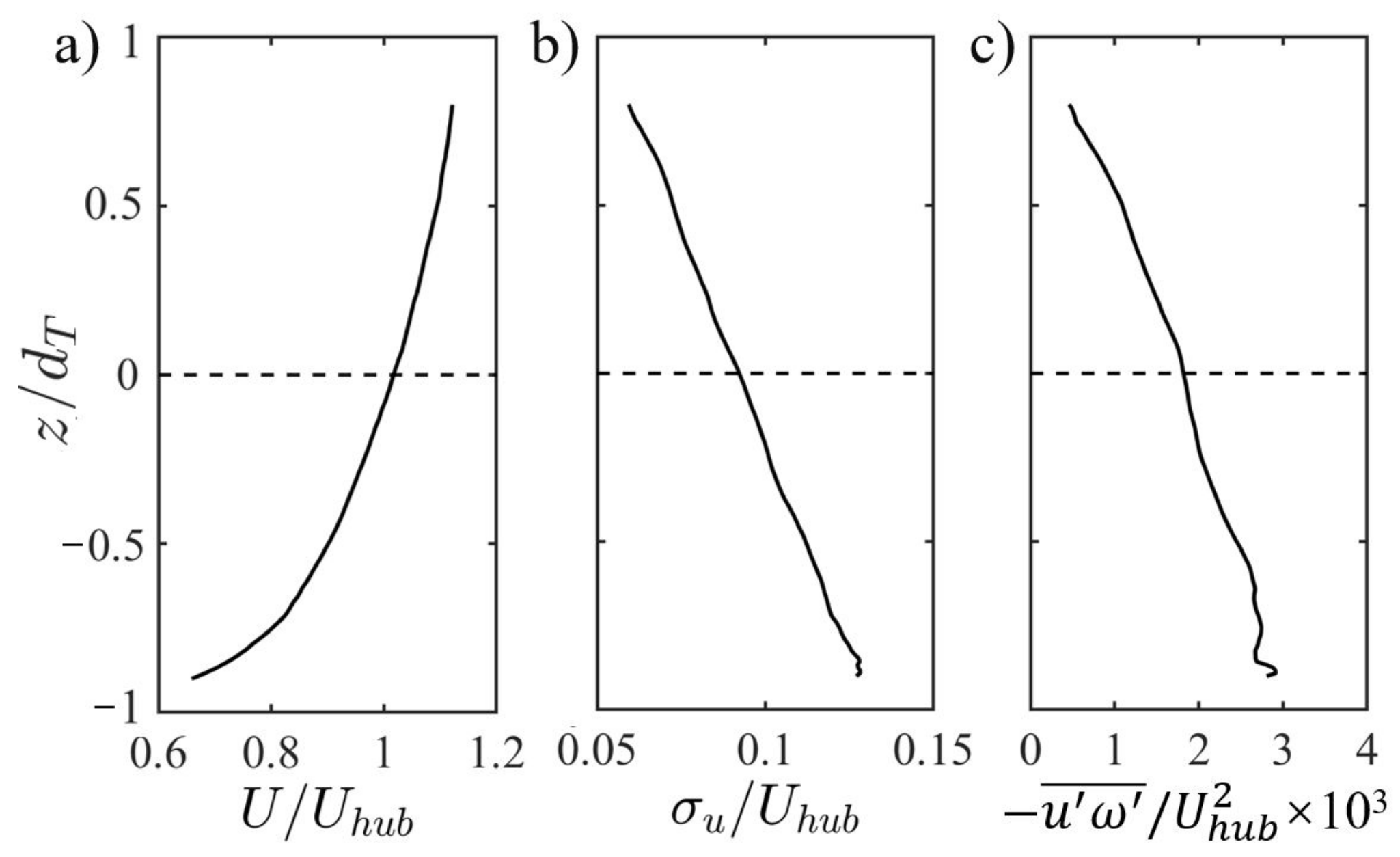
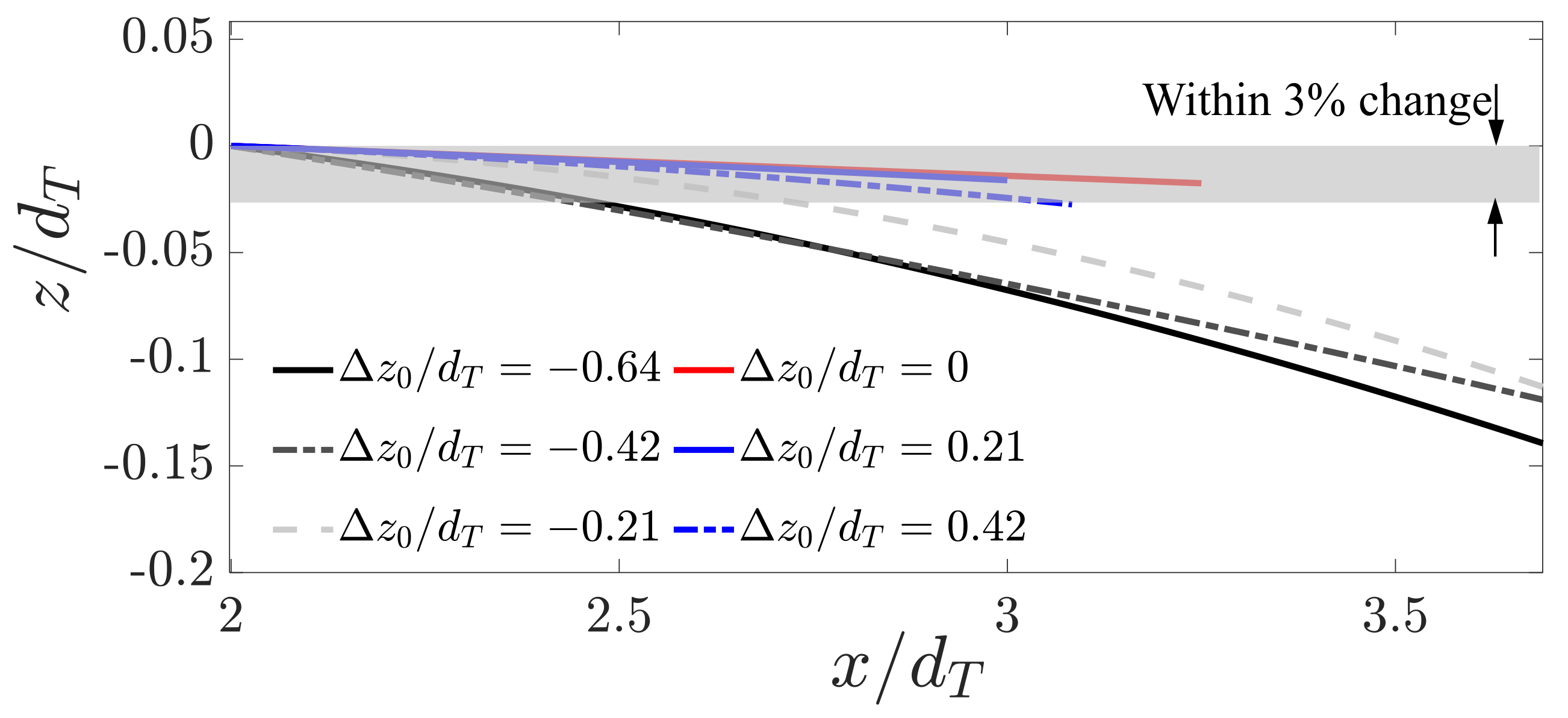
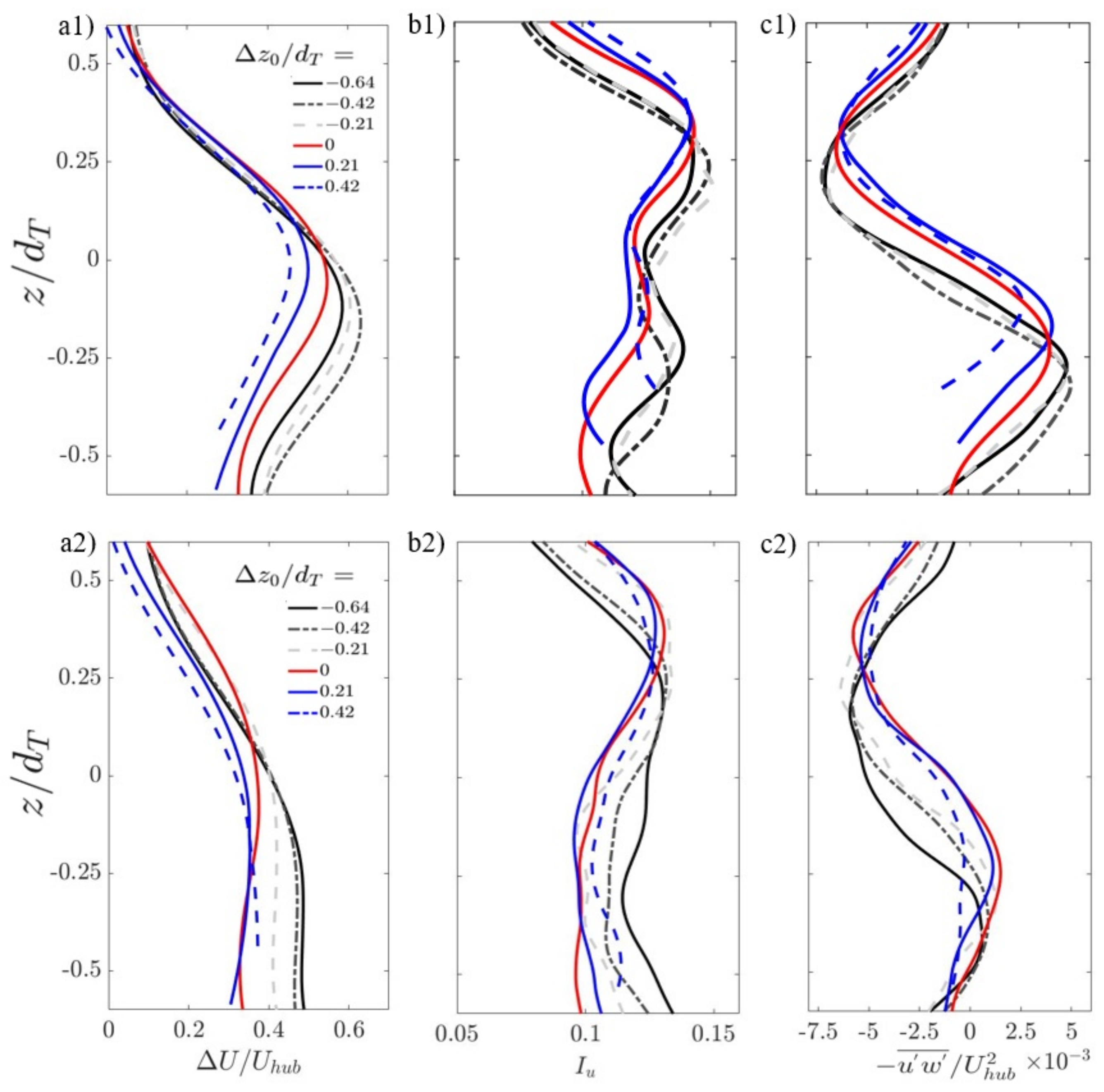
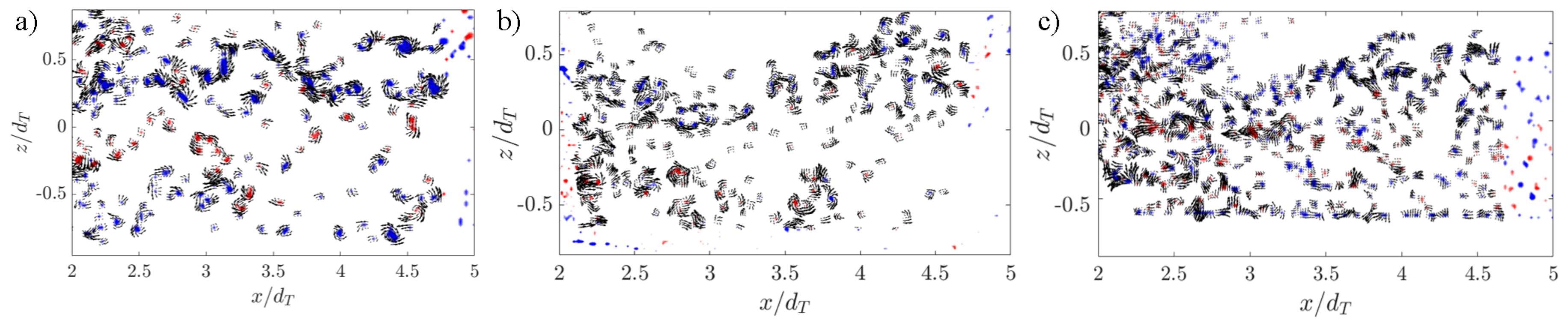
3.1. Wake Characteristics
3.2. Step-Modulated Transport of Turbulence in the Wake
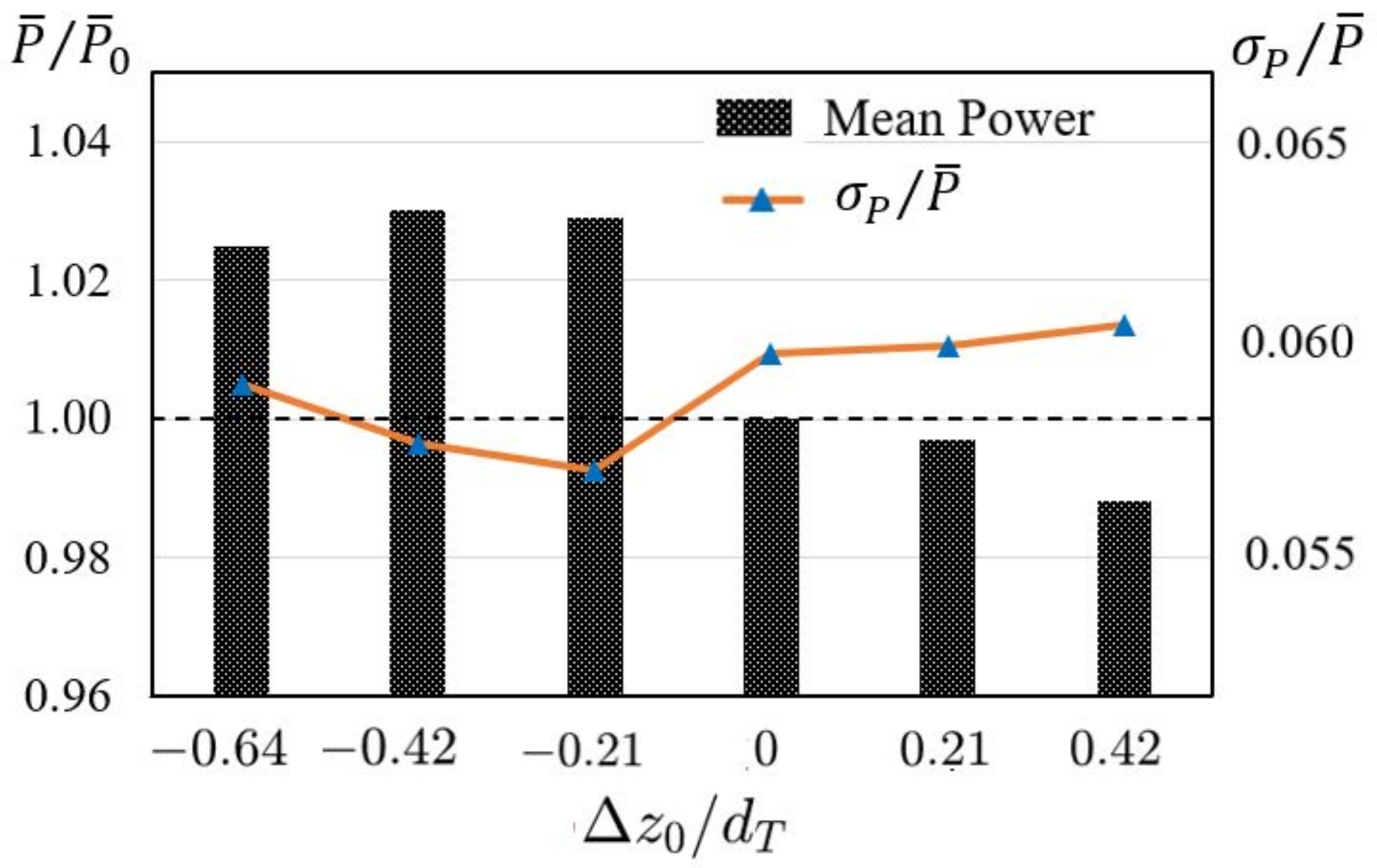
3.3. On the Power Output
4. Remarks and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TBL | Turbulence Boundary Layer |
| CTA | Constant Temperature Anemometry |
| PIV | Particle Image Velocimetry |
| FFS | Forward Facing Step |
| BFS | Backward Facing Step |
| FOV | Field of View |
References
- Kuo, J.Y.; Romero, D.A.; Beck, J.C.; Amon, C.H. Wind farm layout optimization on complex terrains–Integrating a CFD wake model with mixed-integer programming. Appl. Energy 2016, 178, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.; Rocha, A.; Santos, C.S.; Pereira, R. Wind resource modelling in complex terrain using different mesoscale–microscale coupling techniques. Appl. Energy 2013, 108, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prósper, M.A.; Otero-Casal, C.; Fernández, F.C.; Miguez-Macho, G. Wind power forecasting for a real onshore wind farm on complex terrain using WRF high resolution simulations. Renew. Energy 2019, 135, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, L.; Sørensen, J.N.; Crespo, A. Wind turbine wake aerodynamics. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2003, 39, 467–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migoya, E.; Crespo, A.; Garcia, J.; Moreno, F.; Manuel, F.; Jiménez, Á.; Costa, A. Comparative study of the behavior of wind-turbines in a wind farm. Energy 2007, 32, 1871–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravdahl, A.; Rorgemoen, S.; Thogersen, M. Power prediction and siting—When the terrain gets rough. In Proceedings of the World Wind Energy Conference and Exhibition, 2002 (ETA-Florence), Berlin, Germany, 2–6 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Howard, K.B.; Guala, M.; Sotiropoulos, F. Effects of a three-dimensional hill on the wake characteristics of a model wind turbine. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 025103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaviaropoulos, P.; Douvikas, D. Mean wind field prediction over complex terrain in the presence of wind turbine(s). EWEC-CONFERENCE 1999, 1208–1211. [Google Scholar]
- Politis, E.S.; Prospathopoulos, J.; Cabezon, D.; Hansen, K.S.; Chaviaropoulos, P.; Barthelmie, R.J. Modeling wake effects in large wind farms in complex terrain: The problem, the methods and the issues. Wind Energy 2012, 15, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoulis, A.; Fragoulis, A. The complex terrain wind environment and its effects on the power output and loading of wind turbines. In Proceedings of the 35th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, Reno, NV, USA, 6–9 January 1997; p. 934. [Google Scholar]
- Menke, R.; Vasiljević, N.; Hansen, K.S.; Hahmann, A.N.; Mann, J. Does the wind turbine wake follow the topography? A multi-lidar study in complex terrain. Wind Energy Sci. 2018, 3, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, T.; Li, B.; Sun, H.; Yang, H.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F. Investigation of wind turbine performance coupling wake and topography effects based on LiDAR measurements and SCADA data. Appl. Energy 2019, 255, 113816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Ozbay, A.; Hu, H. Terrain effects on characteristics of surface wind and wind turbine wakes. Procedia Eng. 2015, 126, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, F.; Astolfi, D.; Mana, M.; Piccioni, E.; Becchetti, M.; Terzi, L. Investigation of terrain and wake effects on the performance of wind farms in complex terrain using numerical and experimental data. Wind Energy 2017, 20, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsoddin, S.; Porté-Agel, F. A model for the effect of pressure gradient on turbulent axisymmetric wakes. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 837, R3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Jeon, W.H. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of a Seawall’s Effect on Wind Turbine Performance. Energies 2019, 12, 3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, N.; Hamed, A.M.; Chamorro, L.P. Fractional flow speed-up from porous windbreaks for enhanced wind-turbine power. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2017, 163, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.; Johnston, J. A review of research on subsonic turbulent flow reattachment. AIAA J. 1981, 19, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziani, A.; Kerhervé, F.; Martinuzzi, R.; Keirsbulck, L. Dynamics of the recirculating areas of a forward-facing step. Exp. Fluids 2018, 59, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, A.; Tachie, M.F. Time-resolved PIV measurement of influence of upstream roughness on separated and reattached turbulent flows over a forward-facing step. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 105110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudy, L.M.; Naguib, A.M.; Humphreys, W.M., Jr. Wall-pressure-array measurements beneath a separating/reattaching flow region. Phys. Fluids 2003, 15, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoarau, C.; Borée, J.; Laumonier, J.; Gervais, Y. Analysis of the wall pressure trace downstream of a separated region using extended proper orthogonal decomposition. Phys. Fluids 2006, 18, 055107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camussi, R.; Felli, M.; Pereira, F.; Aloisio, G.; Di Marco, A. Statistical properties of wall pressure fluctuations over a forward-facing step. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 075113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, D.; Jacob, M.; Louisot, A.; Talotte, C. Forward-backward facing step pair-Aerodynamic flow, wall pressure and acoustic characterisation. In Proceedings of the 7th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference and Exhibit, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 28–30 May 2001; p. 2249. [Google Scholar]
- Largeau, J.; Moriniere, V. Wall pressure fluctuations and topology in separated flows over a forward-facing step. Exp. Fluids 2007, 42, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, H.; Nagano, Y. Investigation of turbulent boundary layer over forward-facing step via direct numerical simulation. Int. J. Heat. Fluid Flow 2010, 31, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Wang, M. Surface pressure fluctuations on steps immersed in turbulent boundary layers. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 712, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.; Goulart, P.J.; Ganapathisubramani, B. Turbulent separation upstream of a forward-facing step. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 724, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W. Experimental Study of Turbulent Boundary Layer Flows over forward Facing Steps with Different Surface Conditions. Master’s Thesis, Ontario Tech University, Oshawa, ON, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Armaly, B.F.; Durst, F.; Pereira, J.; Schönung, B. Experimental and theoretical investigation of backward-facing step flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1983, 127, 473–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isomoto, K.; Honami, S. The effect of inlet turbulence intensity on the reattachment process over a backward-facing step. J. Fluid Eng. 1989, 111, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, G.; Breuer, M.; Durst, F. Backward-facing step flows for various expansion ratios at low and moderate Reynolds numbers. J. Fluids Eng. 2004, 126, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Asai, K.; Nonomura, T.; Xi, G.; Liu, T. A review of backward-facing step (BFS) flow mechanisms, heat transfer and control. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 6, 194–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, R.J.; Meinhart, C.D.; Tomkins, C.D. Vortex organization in the outer region of the turbulent boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 2000, 422, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Jin, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chamorro, L.P. Wake and power fluctuations of a model wind turbine subjected to pitch and roll oscillations. Appl. Energy 2019, 253, 113605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohya, Y. Wind-tunnel study of atmospheric stable boundary layers over a rough surface. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2001, 98, 57–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ji, S.; Liu, B.; Chamorro, L. On the role of thickness ratio and location of axis of rotation in the flat plate motions. J. Fluids Struct. 2016, 64, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, H.; Aggarwal, R.; Singh, A.; Chamorro, L. Effects of freestream turbulence in a model wind turbine wake. Energies 2016, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hayat, I.; Jin, Y.; Chamorro, L.P. On the evolution of the integral time scale within wind farms. Energies 2018, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, H.; Johnson, E.; Barone, M.; Phillips, R.; Straka, W.; Fontaine, A.; Jonson, M. A design of a hydrofoil family for current-driven marine-hydrokinetic turbines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE), Anaheim, CA, USA, 11–15 November 2012; pp. 839–847. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.; Fontaine, A.; Jonson, M.; Meyer, R.; Straka, W.; Young, S.; van Dam, C.; Shiu, H.; Barone, M. A1: 8.7 scale water tunnel test of an axial flow water turbine. In Proceedings of the 1st Marine Energy Technology Symposium, METS13, Washington, DC, USA, 10–11 April 2013; pp. 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro, L.P.; Arndt, R.; Sotiropoulos, F. Reynolds number dependence of turbulence statistics in the wake of wind turbines. Wind Energy 2012, 15, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlak, H.; Nishino, T.; Martínez-Tossas, L.; Meneveau, C.; Sørensen, J.N. Assessment of blockage effects on the wake characteristics and power of wind turbines. Renew. Energy 2016, 93, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, N.; Hamed, A.M.; Chamorro, L.P. An Experimental Study on the Effects of Winglets on the Wake and Performance of a ModelWind Turbine. Energies 2015, 8, 11955–11972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragheb, M.; Ragheb, A.M. Wind turbines theory-the betz equation and optimal rotor tip speed ratio. Fund. Adv. Top. Wind Power 2011, 1, 19–38. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, M.; Willert, C.E.; Scarano, F.; Kähler, C.J.; Wereley, S.T.; Kompenhans, J. PIV uncertainty and measurement accuracy. In Particle Image Velocimetry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 203–241. [Google Scholar]
- Adrian, L.; Adrian, R.J.; Westerweel, J. Particle Image Velocimetry; Number 30; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, M.M. The evolution of strained turbulent plane wakes. J. Fluid Mech. 2002, 463, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.O.; Liu, X. An experimental investigation of symmetric and asymmetric turbulent wake development in pressure gradient. Phys. Fluids 2004, 16, 1725–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.S.; Koo, E.; Mu noz-Esparza, D.; Jin, E.K.; Linn, R.; Lee, J.S. Turbulent kinetics of a large wind farm and their impact in the neutral boundary layer. Energy 2016, 95, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Schröder, A. Analysis of flapping motion of reattaching shear layer behind a two-dimensional backward-facing step. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 115104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Adrian, R.J.; Balachandar, S.; Kendall, T. Mechanisms for generating coherent packets of hairpin vortices in channel flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1999, 387, 353–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratha, D.; Sarkar, A. Analysis of flow over backward facing step with transition. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2015, 9, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleel, C.; Shaija, A.; Jayaraj, S. On simulation of backward facing step flow using immersed boundary method. Am. J. Fluid Dyn. 2013, 3, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro, L.P.; Arndt, R.A. Non-uniform velocity distribution effect on the Betz–Joukowsky limit. Wind Energy 2013, 16, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Cheng, S.; Lu, F.; Zheng, Y.; Chamorro, L.P. Impact of Topographic Steps in the Wake and Power of a Wind Turbine: Part A—Statistics. Energies 2020, 13, 6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13236411
Zhang B, Cheng S, Lu F, Zheng Y, Chamorro LP. Impact of Topographic Steps in the Wake and Power of a Wind Turbine: Part A—Statistics. Energies. 2020; 13(23):6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13236411
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Buen, Shyuan Cheng, Fanghan Lu, Yuan Zheng, and Leonardo P. Chamorro. 2020. "Impact of Topographic Steps in the Wake and Power of a Wind Turbine: Part A—Statistics" Energies 13, no. 23: 6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13236411
APA StyleZhang, B., Cheng, S., Lu, F., Zheng, Y., & Chamorro, L. P. (2020). Impact of Topographic Steps in the Wake and Power of a Wind Turbine: Part A—Statistics. Energies, 13(23), 6411. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13236411






