Ground-Source Heat Pumps with Horizontal Heat Exchangers for Space Cooling in the Hot Tropical Climate of Thailand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
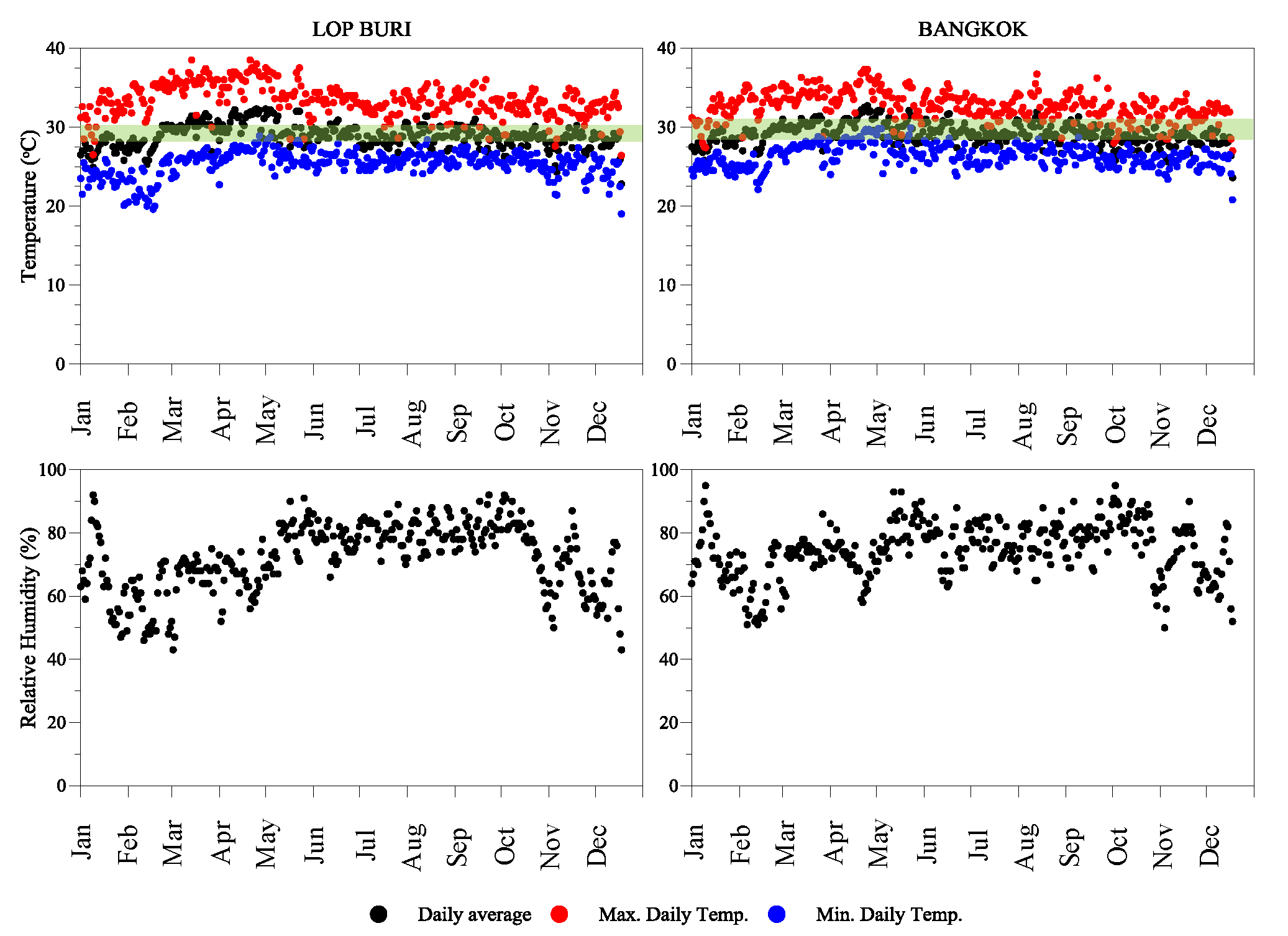
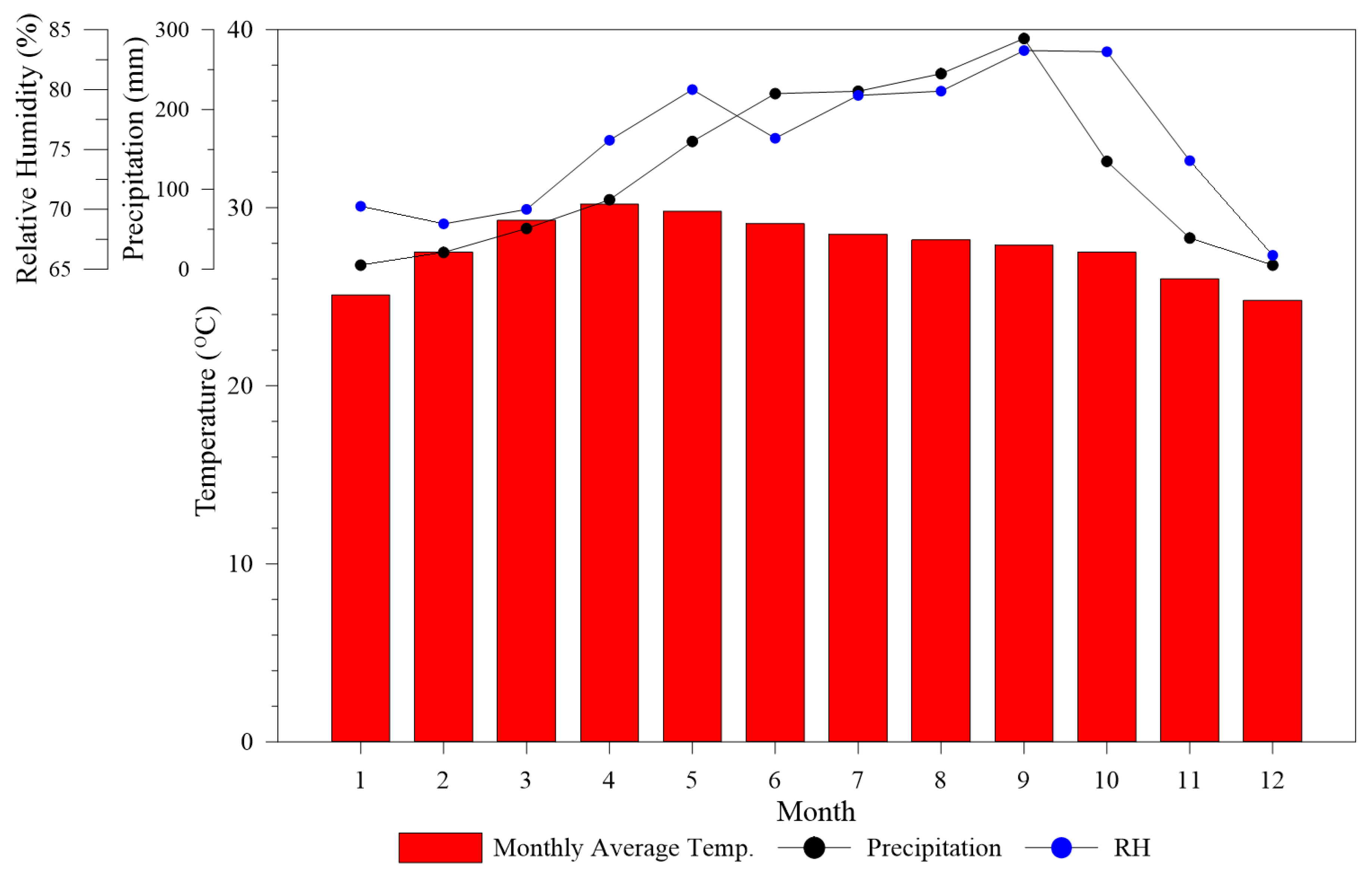
2. Climate of Thailand
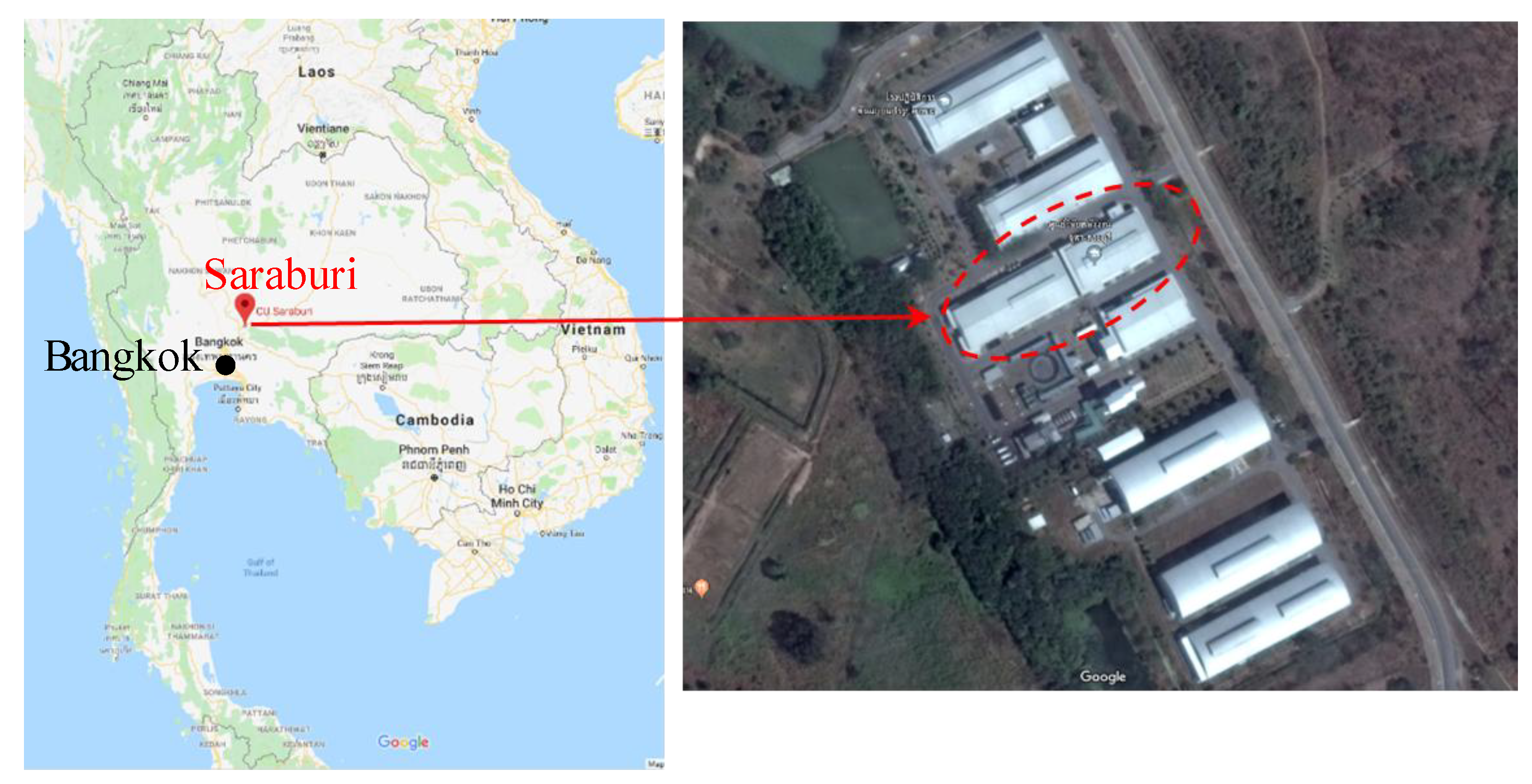
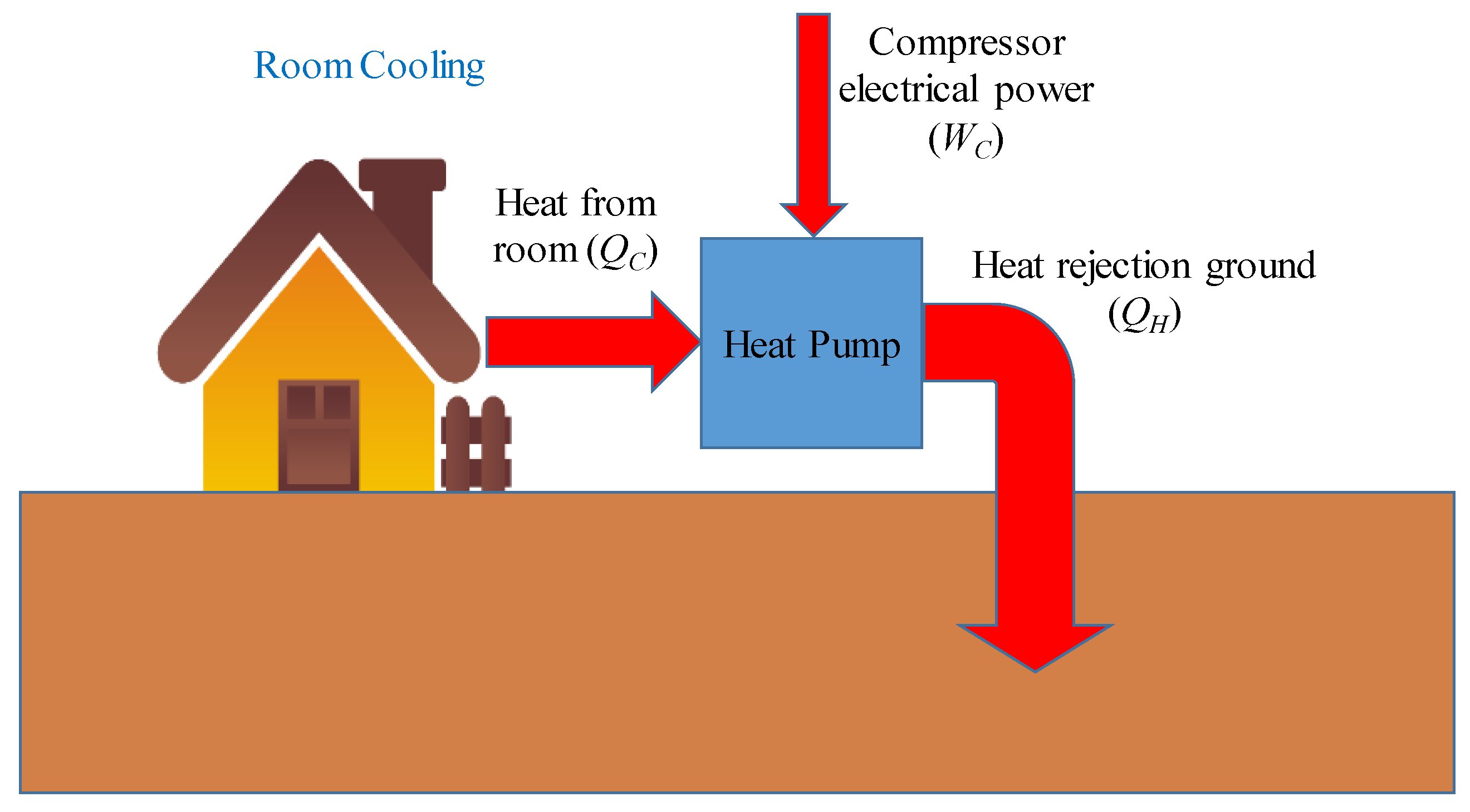
3. Configuration of the Heat Pump System
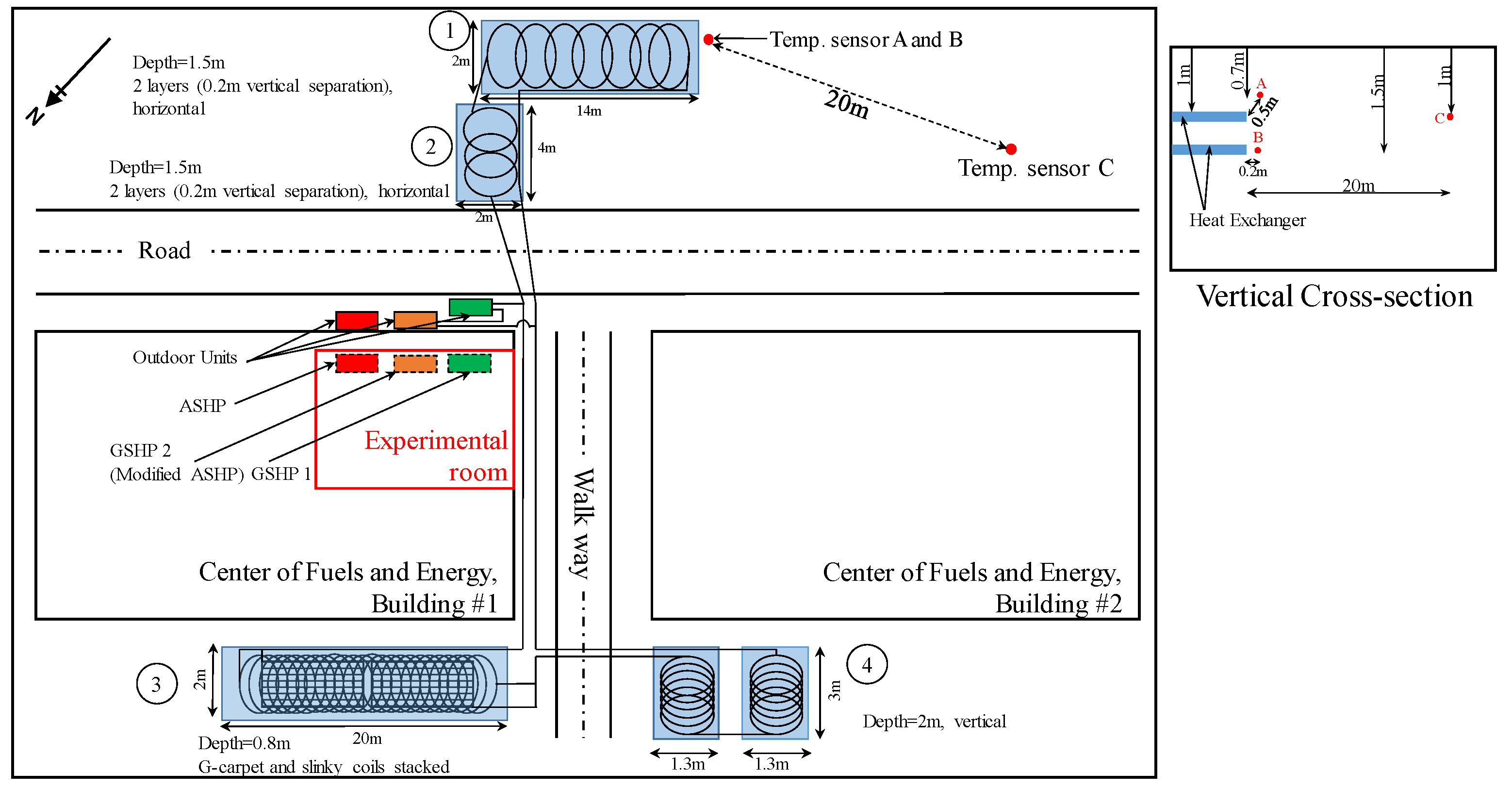
3.1. Shallow Ground Heat Exchanger
3.2. Room Cooling Experiment
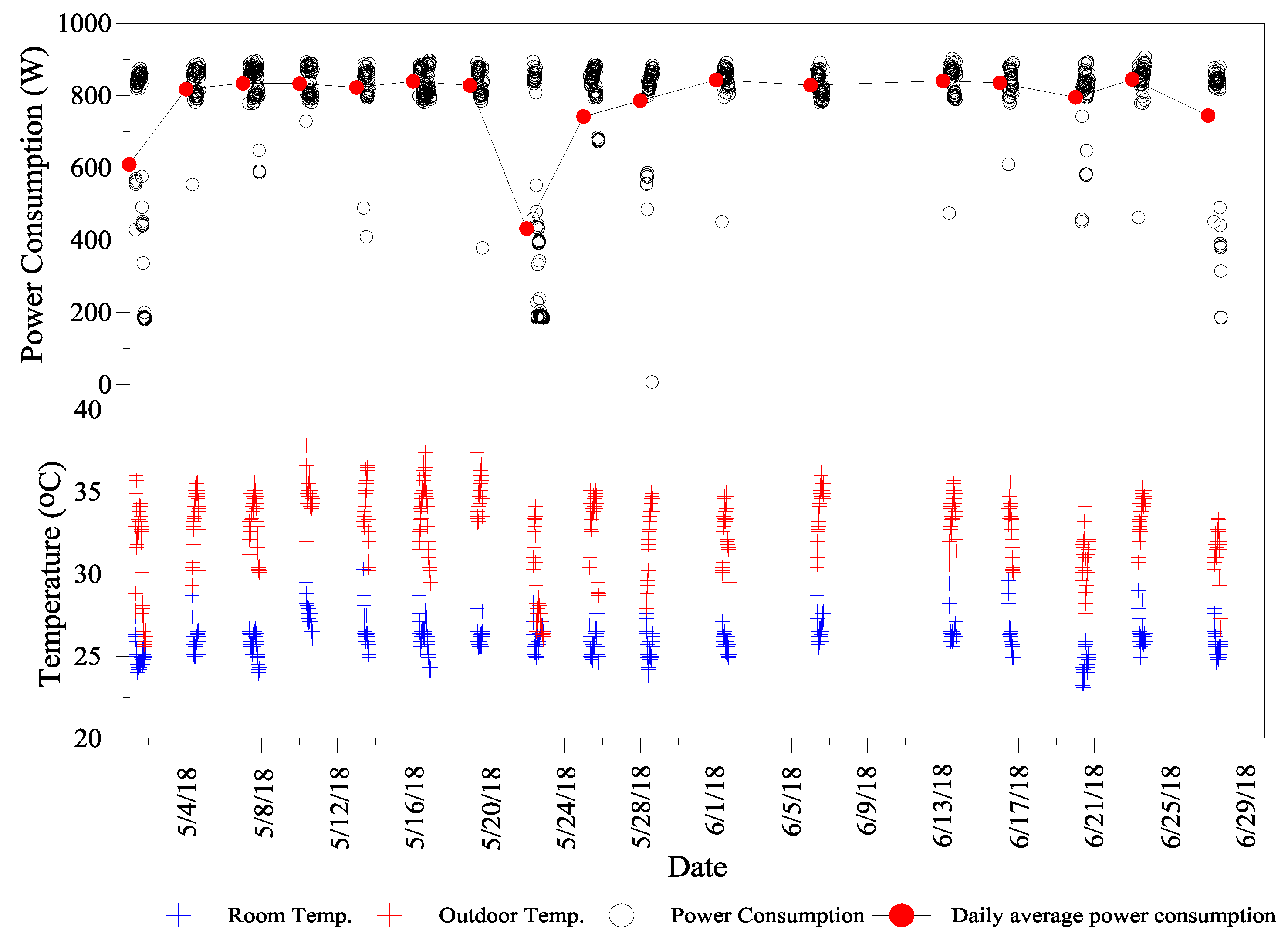
4. Data Analysis
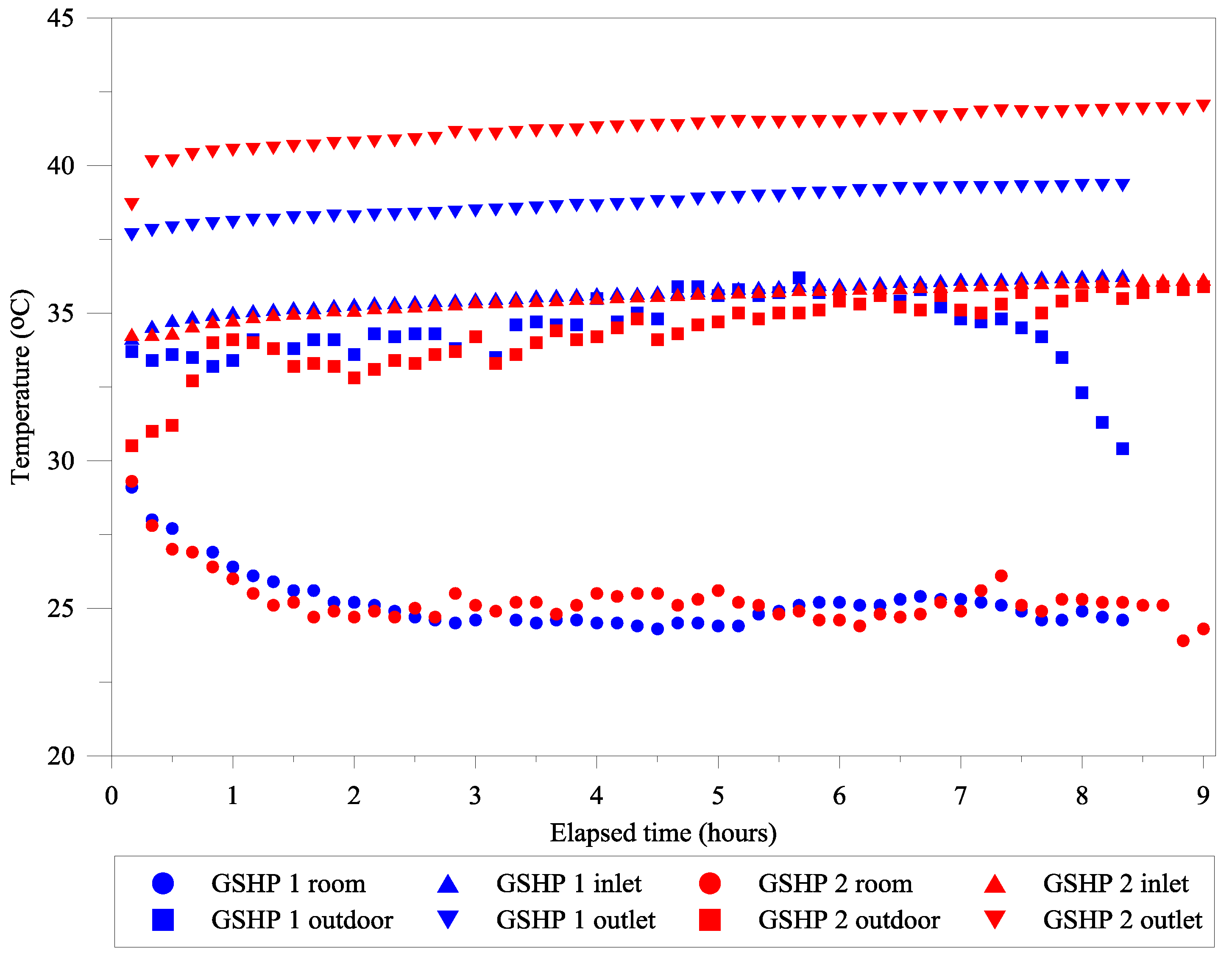
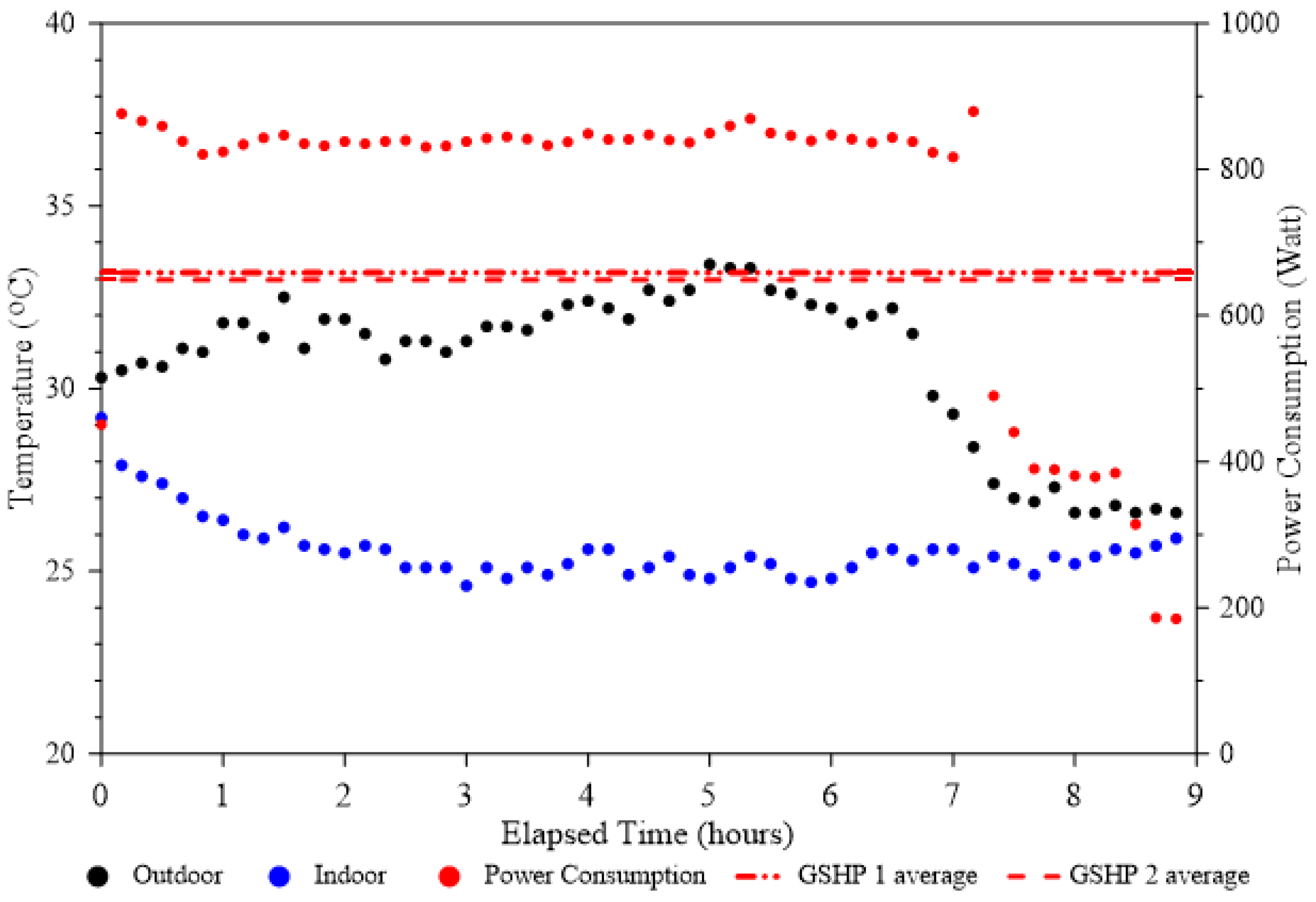
5. Results and Discussion
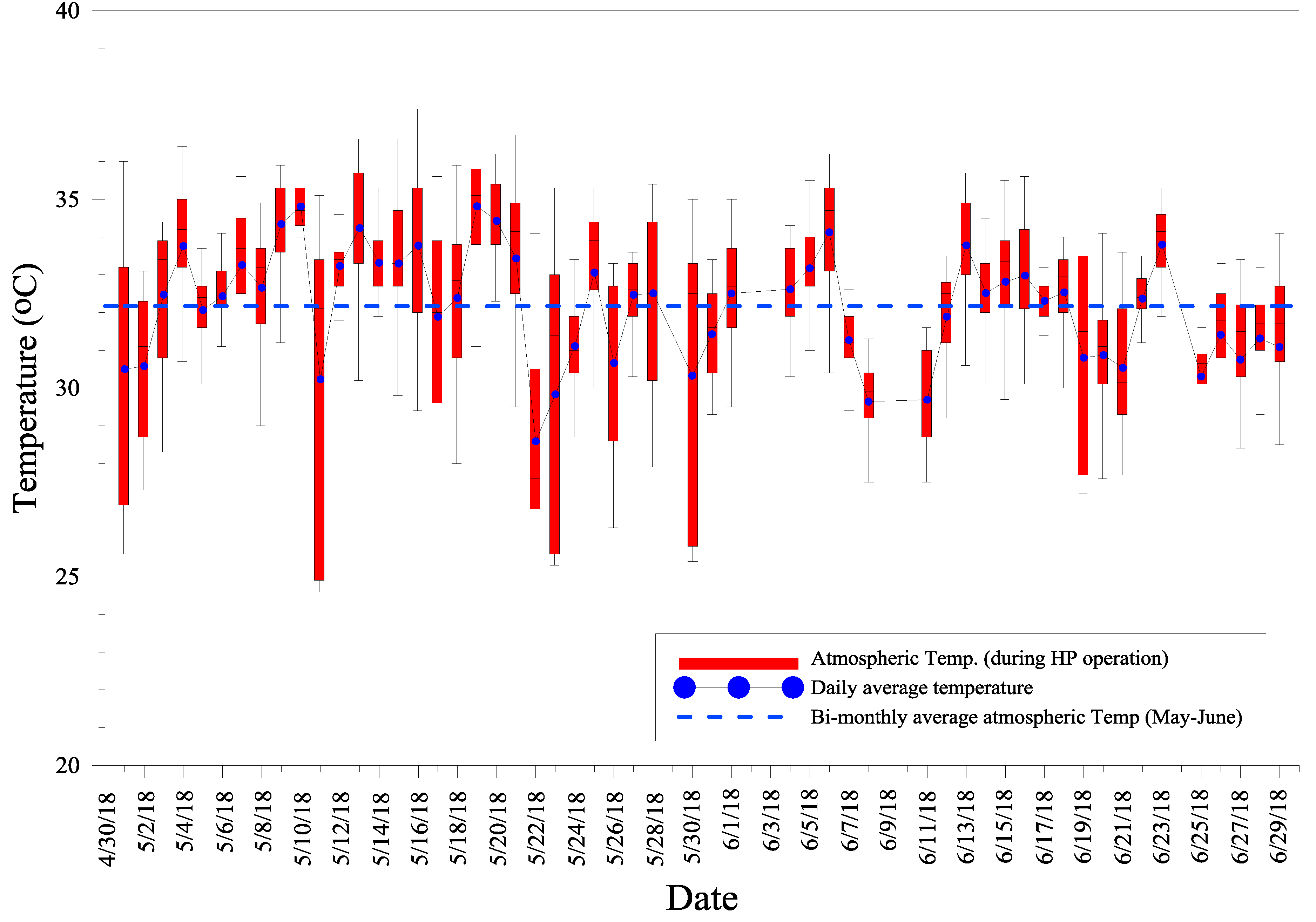
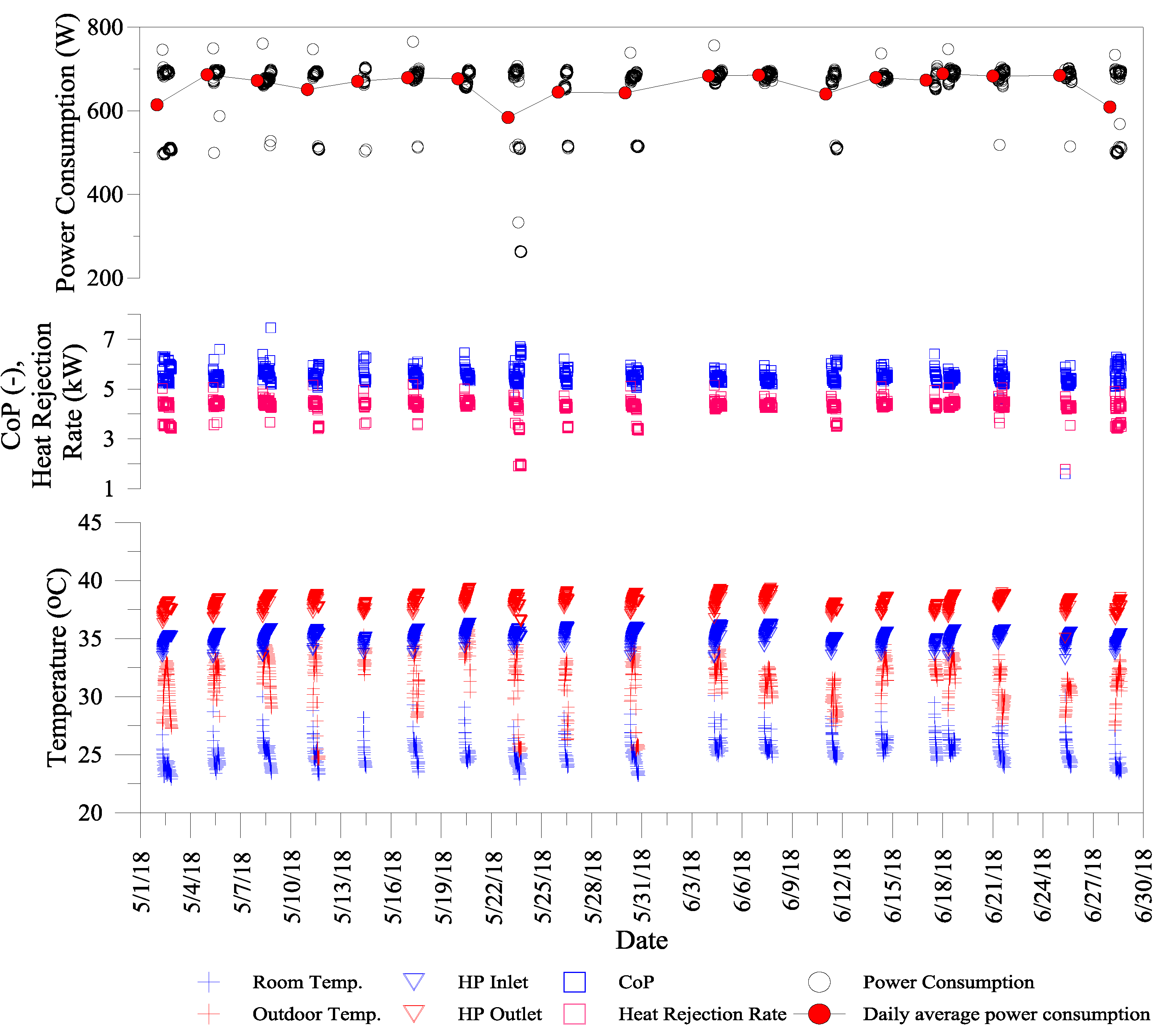
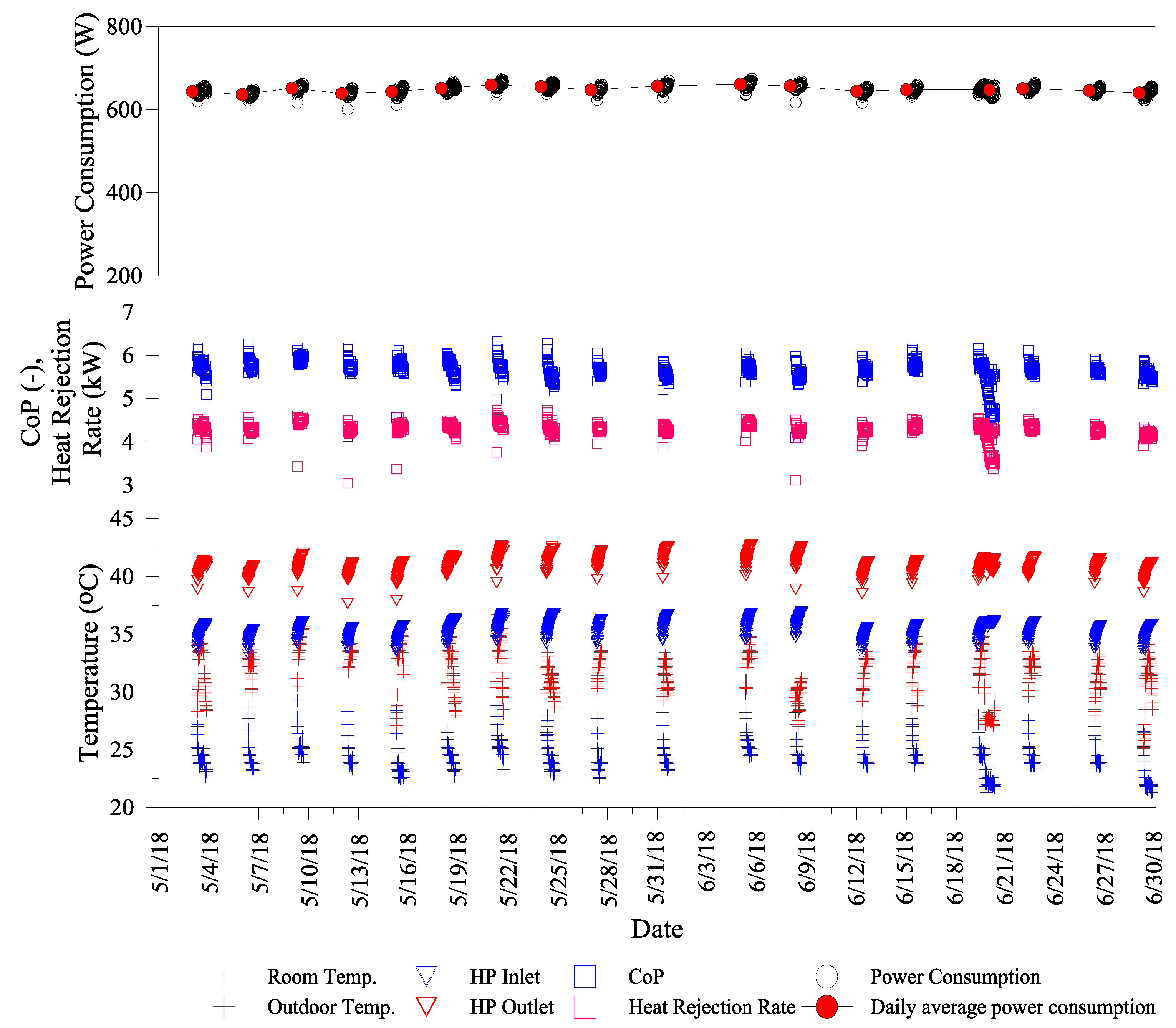
5.1. Experiment and Analysis
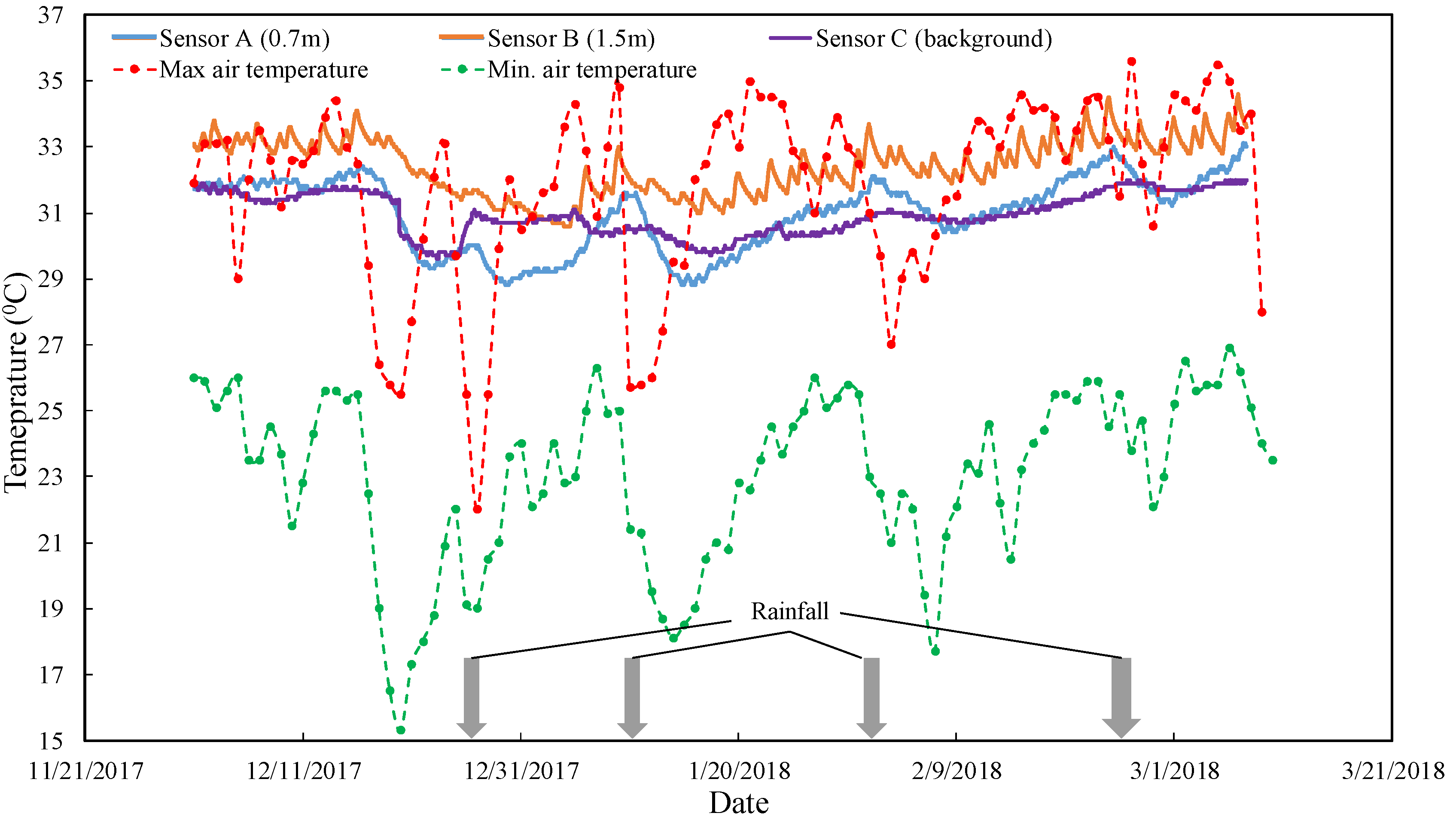
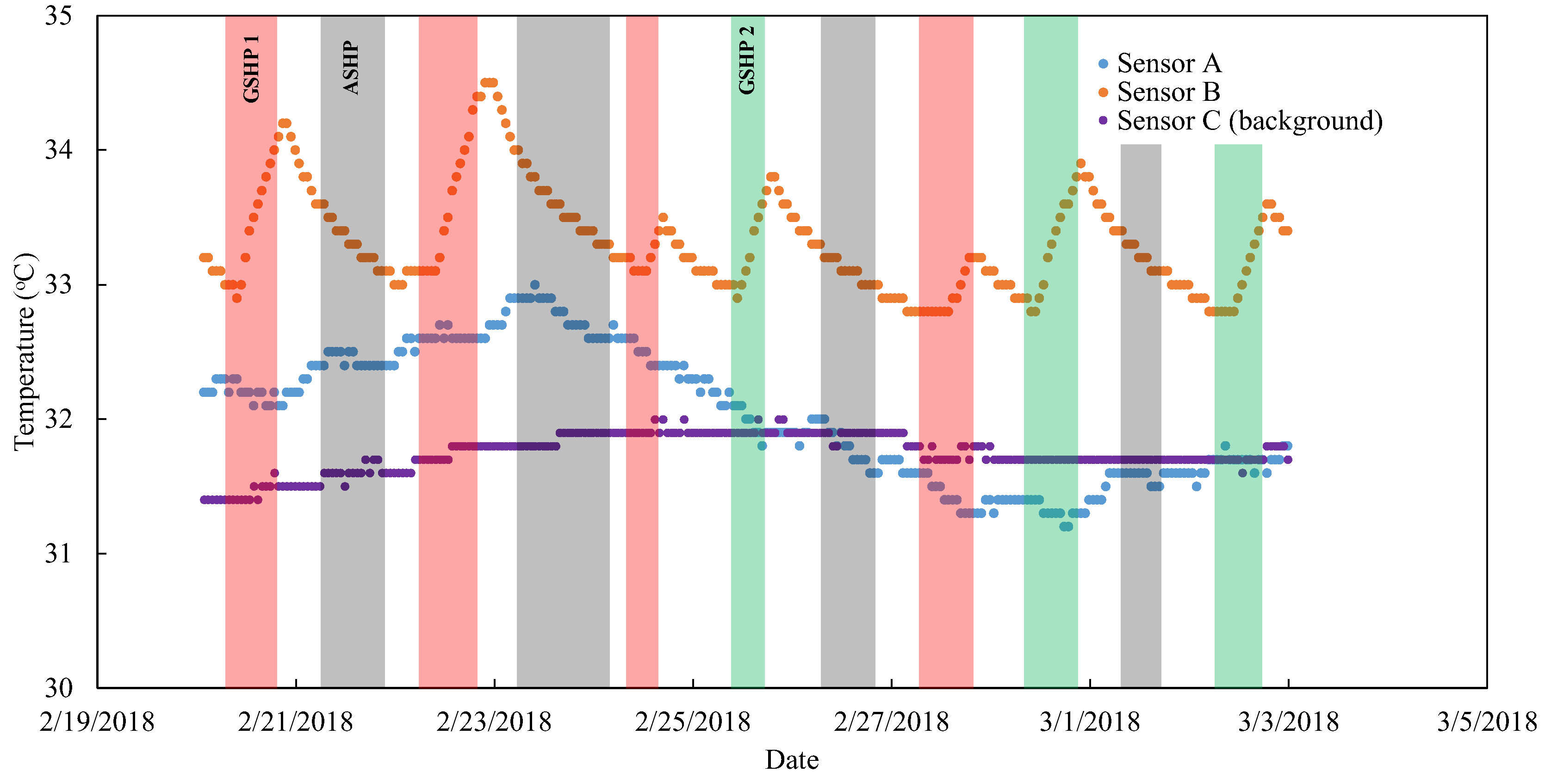
5.2. Ground Temperature Data
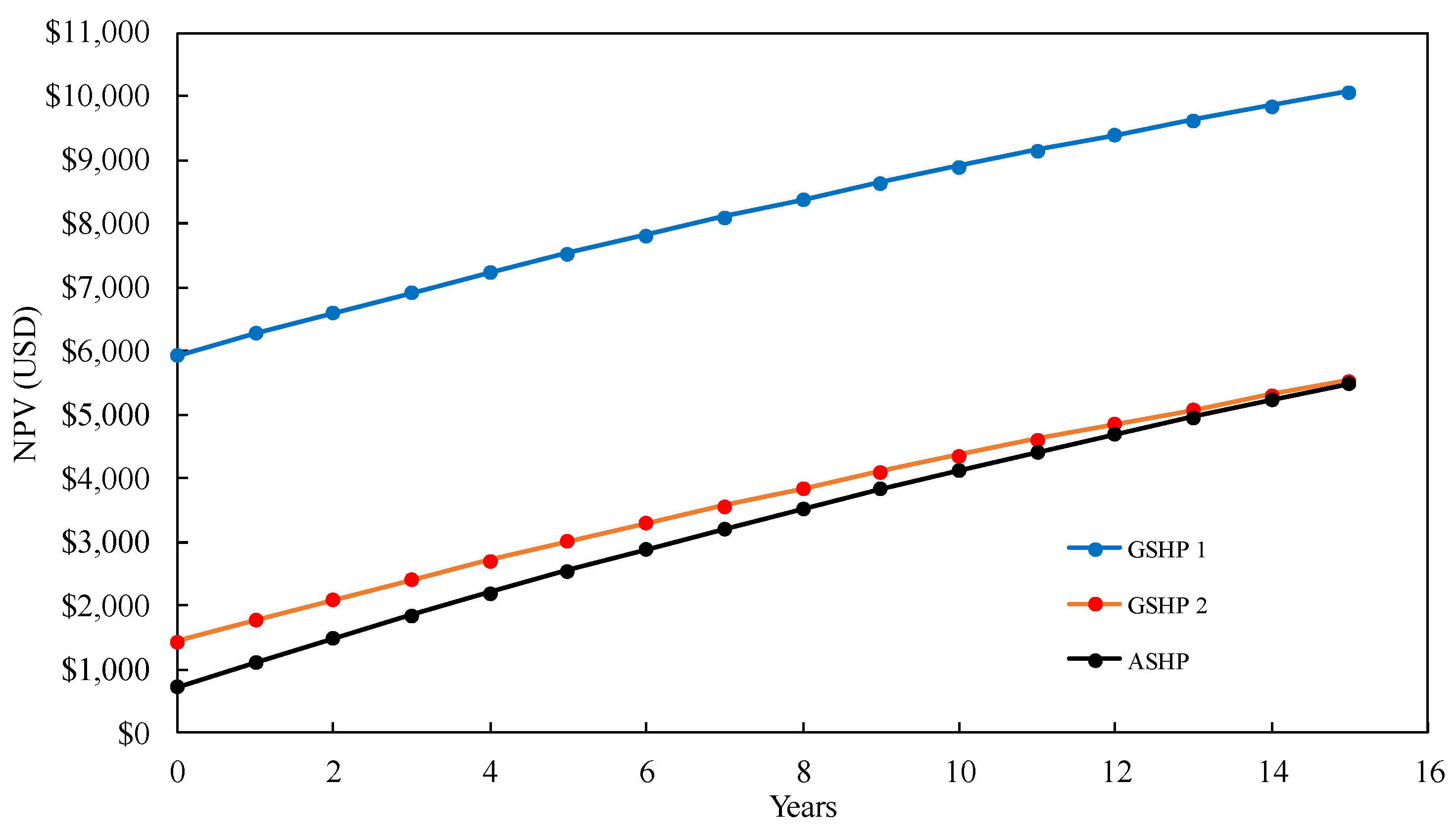
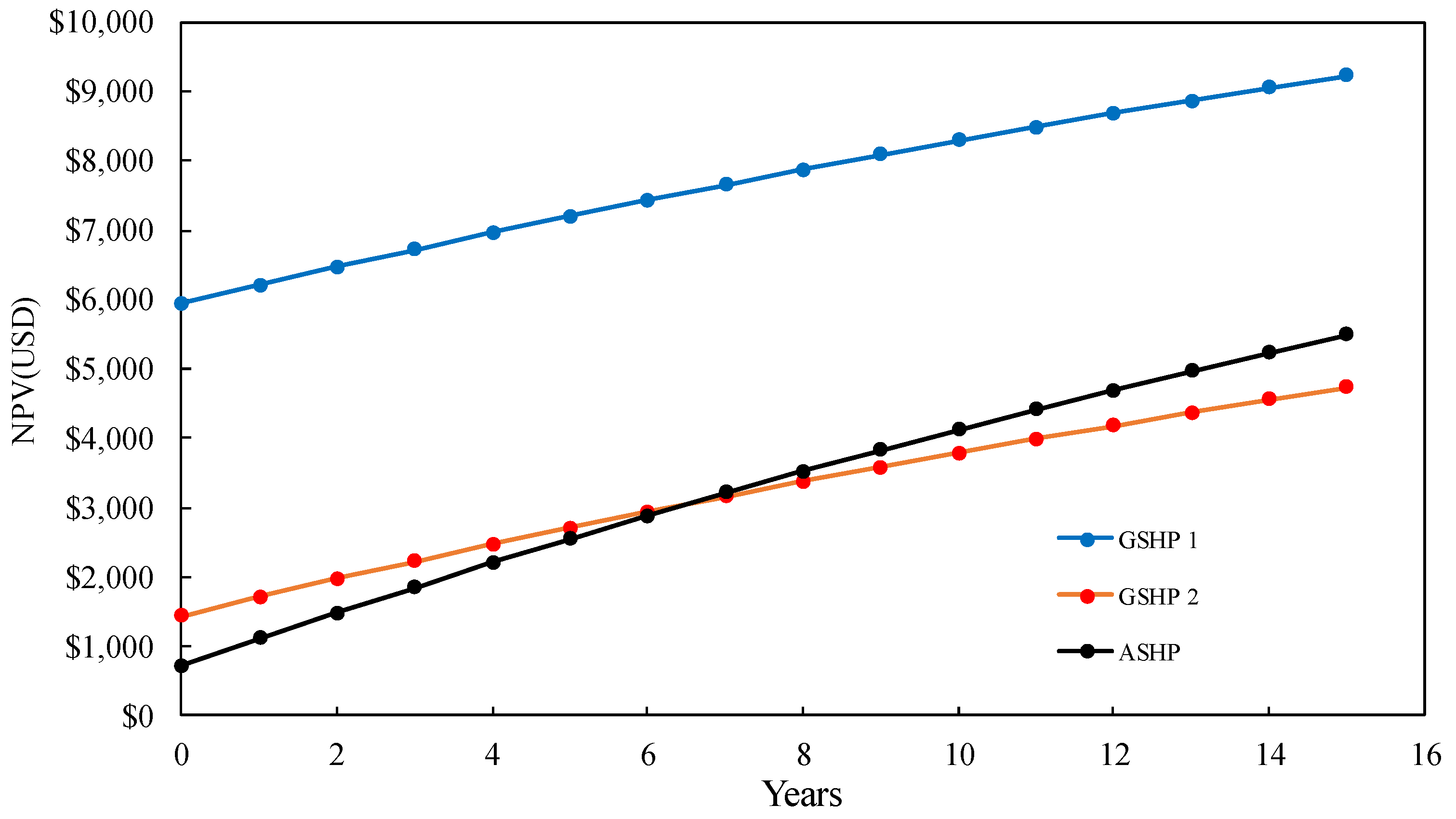
5.3. Life-Cycle Cost Analyses of the Potential Annual CO2 Reduction
- Thailand and other southeast Asian countries are experiencing rapid economic and industrial growth [73].
- The ground-source heat pump is a relatively mature technology.
- A single-function heat pump (only for cooling) is less complicated than those with reversible functions (cooling and heating).
- Labor cost is relatively low; installation cost can be further reduced by a proper arrangement and design.
5.4. Future Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. Southeast Asia Energy Outlook 2017; IEA: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Energy of The Kingdom of Thailand. Energy Statistic of Thailand; Ministry of Energy of The Kingdom of Thailand: Bangkok, Thailand, 2018.
- Lee, Z.H.; Sethupathi, S.; Lee, K.T.; Bhatia, S.; Mohamed, A.R. An Overview on Global Warming in Southeast Asia: CO2emission Status, Efforts Done, and Barriers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 28, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Air Conditioner Demand by Region. Available online: https://www.google.com.tw/url?sa=t[&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwi5xO3GrLDhAhXUc94KHWfCCesQFjAAegQIAxAC&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.jraia.or.jp%2Fenglish%2FWorld_AC_Demand.pdf&usg=AOvVaw1q-QotBU5B0pLSdNOuxDBq (accessed on 24 February 2019).
- Kwong, Q.J.; Adam, N.M.; Sahari, B.B. Thermal Comfort Assessment and Potential for Energy Efficiency Enhancement in Modern Tropical Buildings: A Review. Energy Build. 2014, 68, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Watanabe, M. Effectiveness of Promoting Energy Efficiency in Thailand: The Case of Air Conditioners; IDE Discussion Papers No. 577; Institute of Developing Economies: Chiba, Japan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cazelles, P. Promotion of Higher Efficiency Air Conditioners in Asean: A Regional Policy Roadmap; European Copper Institute: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sahakian, M. Keeping Cool in Southeast Asia Energy Consumption and Urban Air-Conditioning; Palgrave Macmillan: Basingstoke, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Supasa, T.; Hsiau, S.-S.; Lin, S.-M.; Wongsapai, W.; Wu, J.-C. Household Energy Consumption Behaviour for Different Demographic Regions in Thailand from 2000 to 2010. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriamonkul, W.; Intarajinda, R.; Tongsuk, N.; Saengsuwan, S. Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Air Conditioning System for Residential Sector in Thailand. GMSARN Int. J. 2011, 5, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Parkpoom, S.; Harrison, G.P. Analyzing the Impact of Climate Change on Future Electricity Demand in Thailand. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 23, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifwidodo, S.D.; Tanaka, T. The Characteristics of Urban Heat Island in Bangkok, Thailand. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifwidodo, S.; Chandrasiri, O. Urban Heat Island and Household Energy Consumption in Bangkok, Thailand; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 79. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, Y. New Countermeasures for Mitigating the Heat Island Effect - District Heat Supply Systems, Underground Thermal Energy Storage, Systems Using Underground as a Heat Sink (in Japanese). J. Jpn. Soc. Energy Resour. 2001, 22, 306–310. [Google Scholar]
- Genchi, Y.; Kikegawa, Y.; Inaba, A. CO2payback-Time Assessment of a Regional-Scale Heating and Cooling System Using a Ground Source Heat-Pump in a High Energy-Consumption Area in Tokyo. Appl. Energy 2002, 71, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasare, R.R.; Saha, S.K. Numerical Study of Horizontal Ground Heat Exchanger for High Energy Demand Applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2015, 85, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congedo, P.M.; Colangelo, G.; Starace, G. CFD Simulations of Horizontal Ground Heat Exchangers: A Comparison among Different Configurations. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2012, 33–34, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa Omer, A. Ground-Source Heat Pumps Systems and Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 344–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Lee, S.-R.; Yoon, S.; Jeon, J.-S. Evaluation of Geometric Factors Influencing Thermal Performance of Horizontal Spiral-Coil Ground Heat Exchangers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 144, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Nishi, K.; Komaniwa, Y.; Chou, N. Numerical Modeling of Slinky-Coil Horizontal Ground Heat Exchangers. Geothermics 2012, 41, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Yamasaki, S.; Maehara, T.; Ishikami, T.; Chou, N. Numerical Simulation and Sensitivity Study of Double-Layer Slinky-Coil Horizontal Ground Heat Exchangers. Geothermics 2013, 47, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sipio, E.; Bertermann, D. Soil Thermal Behavior in Different Moisture Condition: An Overview of ITER Project from Laboratory to Field Test Monitoring. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertermann, D.; Klug, H.; Morper-Busch, L. A Pan-European Planning Basis for Estimating the Very Shallow Geothermal Energy Potentials. Renew. Energy 2015, 75, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, P.; Adamovský, R.; Šedová, M. Temperatures and Heat Flows in a Soil Enclosing a Slinky Horizontal Heat Exchanger. Energies 2014, 7, 972–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, H.; Koyun, A.; Temir, G. Heat Transfer of Horizontal Parallel Pipe Ground Heat Exchanger and Experimental Verification. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2009, 29, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.; Tarnawski, V.; Aittomäki, A. Effect of Soil Type and Moisture Content on Ground Heat Pump Performance: Effet Du Type et de l’humidité Du Sol Sur La Performance Des Pompes à Chaleur à Capteurs Enterrés. Int. J. Refrig. 1998, 21, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.J.; Chou, S.K.; Yang, W.M. Advances in Heat Pump Systems: A Review. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 3611–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarin, R.M.; Castellotti, F. A New Heat Pump Desiccant Dehumidifier for Supermarket Application. Energy Build. 2007, 39, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aynur, T.N.; Hwang, Y.; Radermacher, R. Integration of Variable Refrigerant Flow and Heat Pump Desiccant Systems for the Cooling Season. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2010, 30, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgener, O.; Hepbasli, A. A Parametrical Study on the Energetic and Exergetic Assessment of a Solar-Assisted Vertical Ground-Source Heat Pump System Used for Heating a Greenhouse. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zheng, M.; Kong, F.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Bai, T. Numerical Simulation of Solar Assisted Ground-Source Heat Pump Heating System with Latent Heat Energy Storage in Severely Cold Area. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2008, 28, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, H.; Esen, M.; Ozsolak, O. Modelling and Experimental Performance Analysis of Solar-Assisted Ground Source Heat Pump System. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 2017, 29, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawlader, M.N.A.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Jahangeer, K.A. Performance of Evaporator-Collector and Air Collector in Solar Assisted Heat Pump Dryer. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruelisauer, M.; Meggers, F.; Leibundgut, H. Choosing Your Heat Sink for Cooling in Tropical Climates. In Proceedings of the 5th International Building Physics Conference (IBPC), Kyoto, Japan, 28–31 May 2012; pp. 1339–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Permchart, W.; Tanatvanit, S. Study on Using the Ground as A Heat Sink for A 12,000-Btu/h Modified Air Conditioner. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2009, 3, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Yasukawa, K.; Uchida, Y.; Tenma, N.; Taguchi, Y.; Muraoka, H.; Ishii, T.; Suwanlert, J.; Buapeng, S.; Nguyen, T.H. Groundwater Temperature Survey for Geothermal Heat Pump Application in Tropical Asia. Bull. Geol. Surv. Jpn. 2009, 60, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, K.; Takashima, I.; Uchida, Y. Geothermal Heat Pump Application for Space Cooling in Kamphaengphet, Thailand. Bull. Geol. Surv. Jpn. 2009, 60, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Yasukawa, K.; Tenma, N.; Taguchi, Y.; Suwanlert, J.; Buapeng, S. Subsurface Thermal Regime in the Chao-Phraya Plain, Thailand. Bull. Geol. Surv. Jpn. 2009, 60, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokchai, S.; Chotpantarat, S.; Takashima, I.; Uchida, Y.; Widiatmojo, A.; Yasukawa, K.; Charusiri, P. A Pilot Study on Geothermal Heat Pump (GHP) Use for Cooling Operations, and on GHP Site Selection in Tropical Regions Based on a Case Study in Thailand. Energies 2018, 11, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, D.; Choudhary, R.; Soga, K. Risk Based Lifetime Costs Assessment of a Ground Source Heat Pump (GSHP) System Design: Methodology and Case Study. Build. Environ. 2013, 60, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorollahi, Y.; Bigdelou, P.; Pourfayaz, F.; Yousefi, H. Numerical Modeling and Economic Analysis of a Ground Source Heat Pump for Supplying Energy for a Greenhouse in Alborz Province, Iran. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, H.; Inalli, M.; Esen, M. A Techno-Economic Comparison of Ground-Coupled and Air-Coupled Heat Pump System for Space Cooling. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, H.; Inalli, M.; Esen, M. Technoeconomic Appraisal of a Ground Source Heat Pump System for a Heating Season in Eastern Turkey. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 1281–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, G.H.; Lee, S.R.; Yoon, S.; Kim, M.J. Optimum Design of Horizontal Ground-Coupled Heat Pump Systems Using Spiral-Coil-Loop Heat Exchangers. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Rayegan, R.; Tao, Y. Case Study of Ground-Source Heat Pump Applications in Hot and Humid Climates. J. Archit. Eng. 2014, 21, 5014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedari, J.; Sangprajak, A.; Hirunlabh, J. Thailand Climatic Zones. Renew. Energy 2002, 25, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco, D.A.; Muñoz-Mejías, M.; Pino-Sepúlveda, R.; Ortega-Aguilera, R.; García-Herrera, C. Thermal Simulation of a Social Dwelling in Chile: Effect of the Thermal Zone and the Temperature-Dependant Thermophysical Properties of Light Envelope Materials. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 112, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffell, I.; Brett, D.; Brandon, N.; Hawkes, A. A Review of Domestic Heat Pumps. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9291–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Cao, B.; Ji, W.; Ouyang, Q.; Lin, B.; Zhu, Y. The Underlying Linkage between Personal Control and Thermal Comfort: Psychological or Physical Effects? Energy Build. 2016, 111, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, R.L.; Cheng, M.J.; Lin, T.P.; Ho, M.C. Thermal Perceptions, General Adaptation Methods and Occupant’s Idea about the Trade-off between Thermal Comfort and Energy Saving in Hot-Humid Regions. Build. Environ. 2009, 44, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feriadi, H.; Wong, N.H. Thermal Comfort for Naturally Ventilated Houses in Indonesia. Energy Build. 2004, 36, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedari, J.; Yamtraipat, N.; Pratintong, N.; Hirunlabh, J. Thailand Ventilation Comfort Chart. Energy Build. 2000, 32, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.H.; Feriadi, H.; Lim, P.Y.; Tham, K.W.; Sekhar, C.; Cheong, K.W. Thermal Comfort Evaluation of Naturally Ventilated Public Housing in Singapore. Build. Environ. 2002, 37, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.H.; Khoo, S.S. Thermal Comfort in Classrooms in the Tropics. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djamila, H.; Chu, C.M.; Kumaresan, S. Field Study of Thermal Comfort in Residential Buildings in the Equatorial Hot-Humid Climate of Malaysia. Build. Environ. 2013, 62, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, F. Adaptive Thermal Comfort Standards in the Hot-Humid Tropics. Energy Build. 2004, 36, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryś, K.; Bryś, T.; Sayegh, M.A.; Ojrzyńska, H. Subsurface Shallow Depth Soil Layers Thermal Potential for Ground Heat Pumps in Poland. Energy Build. 2018, 165, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, M.; Bernier, M.; Coquet, Y.; Philippe, M. A Simple Heat and Moisture Transfer Model to Predict Ground Temperature for Shallow Ground Heat Exchangers. Renew. Energy 2017, 103, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, M.; Philippe, M.; Coquet, Y. A Field Experiment to Assess the Influence of Heat and Mass Transfer at the Soil Surface on Shallow Ground Heat Exchanger Performances. In Proceedings of the World Geothermal Congress, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, H.; Simunek, J.; Mohanty, B. Numerical Analysis of Coupled Water, Vapor, and Heat Transport in the Vadose Zone. Vadose Zone J. 2006, 5, 784–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi-Fare, O.; Basu, P. Influences of Ground Saturation and Thermal Boundary Condition on Energy Harvesting Using Geothermal Piles. Energy Build. 2018, 165, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, G. Dynamic Thermal Performance of Horizontal Ground Source Heat Pumps – The Impact of Coupled Heat and Moisture Transfer. Energy 2018, 152, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Toride, N.; Šimůnek, J. Water and Vapor Movement with Condensation and Evaporation in a Sandy Column. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts, A.B.; Cameron, D.A.; Ward, J. Improving the Performance of Ground Coupled Heat Exchangers in Unsaturated Soils. Energy Build. 2015, 104, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, K.K.; Misra, R.; Yadav, T.; Agrawal, G.D.; Jamuwa, D.K. Experimental Study to Investigate the Effect of Water Impregnation on Thermal Performance of Earth Air Tunnel Heat Exchanger for Summer Cooling in Hot and Arid Climate. Renew. Energy 2018, 120, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Dong, Y. Closed-Form Equation for Thermal Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils at Room Temperature. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, X. Research of Heat and Moisture Transfer Influence on the Characteristics of the Ground Heat Pump Exchangers in Unsaturated Soil. Energy Build. 2016, 130, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cai, G.; Liu, S.; Puppala, A.J. Investigation on Thermal Characteristics and Prediction Models of Soils. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 106, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, G.H.; Lee, S.R.; N.V., N.; Yoon, S. A New Performance Evaluation Algorithm for Horizontal GCHPs (Ground Coupled Heat Pump Systems) That Considers Rainfall Infiltration. Energy 2015, 83, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Rayegan, R. A Comparison of Deterministic and Probabilistic Life Cycle Cost Analyses of Ground Source Heat Pump (GSHP) Applications in Hot and Humid Climate. Energy Build. 2012, 55, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saner, D.; Juraske, R.; Kübert, M.; Blum, P.; Hellweg, S.; Bayer, P. Is It Only CO2that Matters? A Life Cycle Perspective on Shallow Geothermal Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 1798–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, P.; Saner, D.; Bolay, S.; Rybach, L.; Blum, P. Greenhouse Gas Emission Savings of Ground Source Heat Pump Systems in Europe: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithayasrichareon, P.; MacGill, I.F. Portfolio Assessments for Future Generation Investment in Newly Industrializing Countries - A Case Study of Thailand. Energy 2012, 44, 1044–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
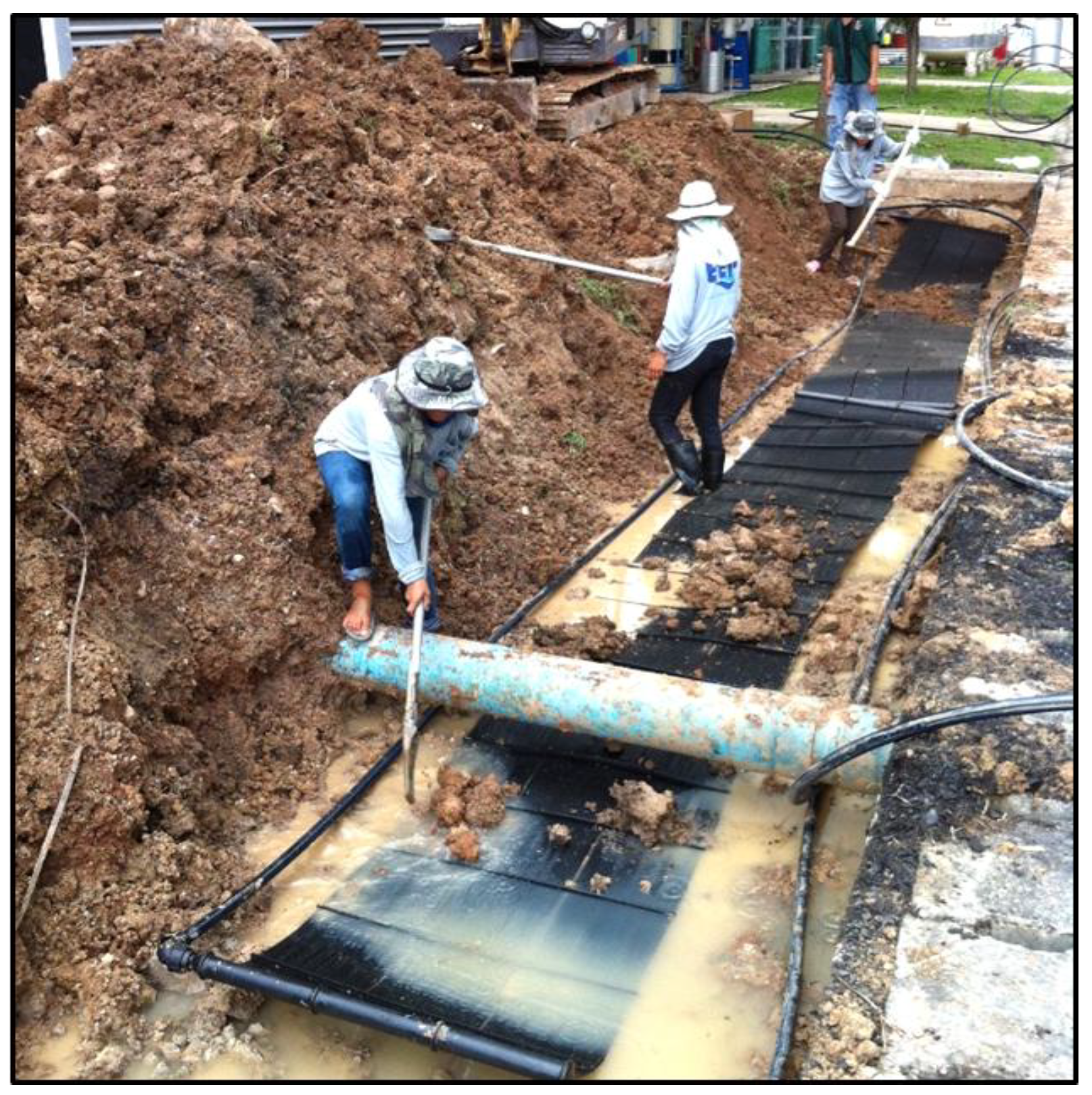
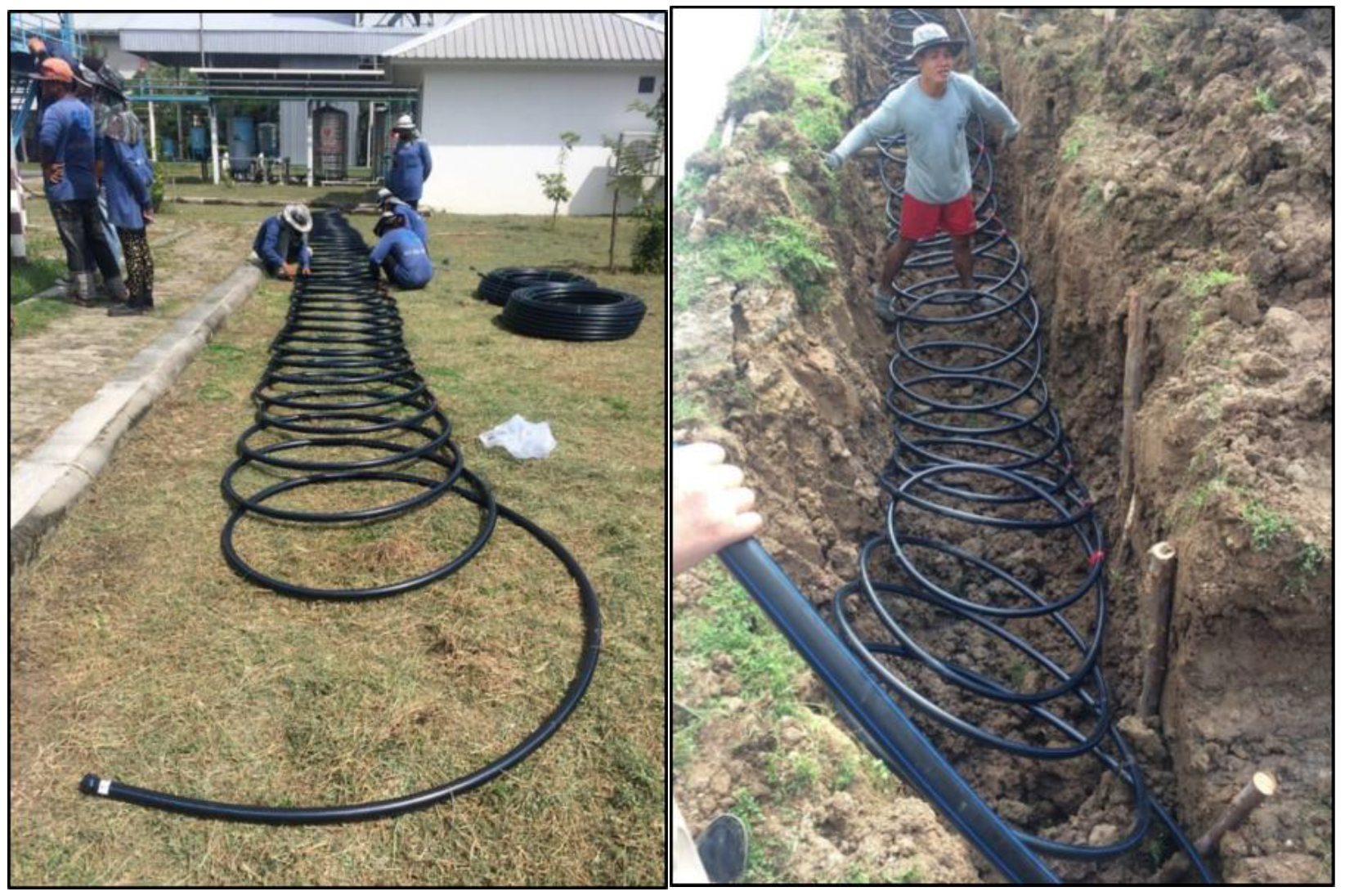
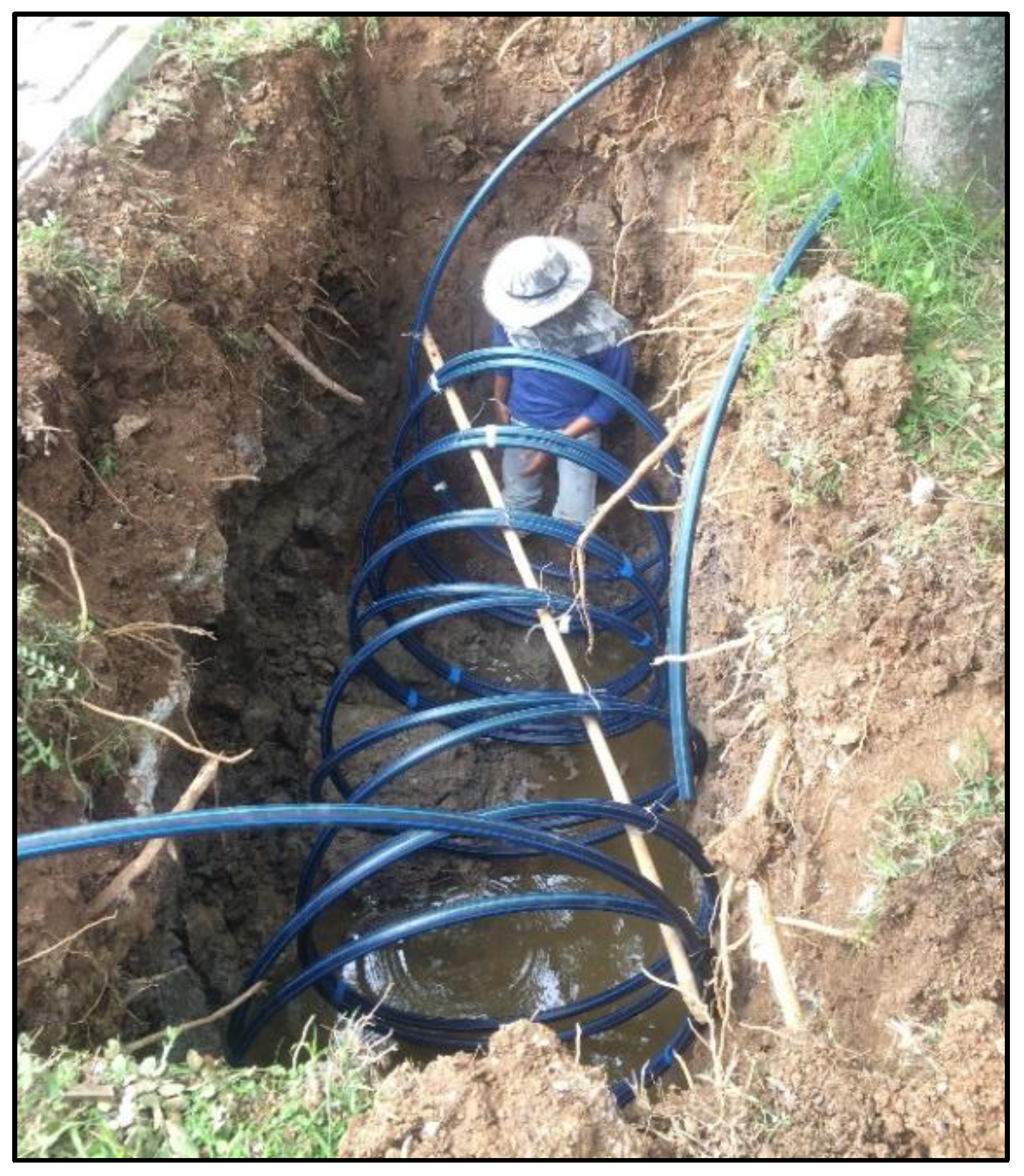
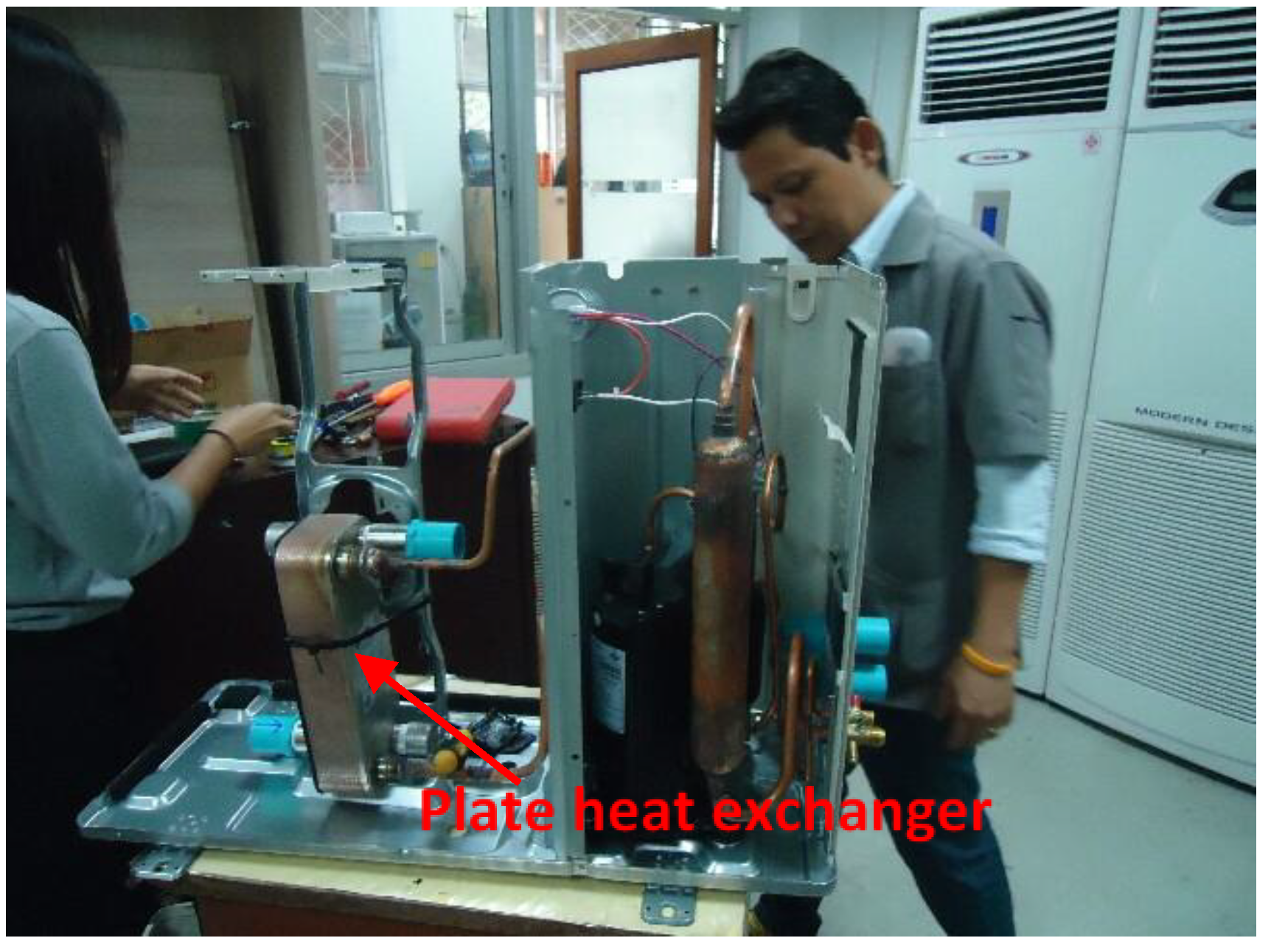





| Heat Pump | Cooling Capacity (kW) | Heating Capacity (kW) | Inverter | Refrigerant | Energy Rating1 | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSHP 1 | 4 | 5 | Yes | R410a | - | Imported from Japan |
| GSHP 2 | N/A2 | - | No | R410a | N/A3 | Replaced with 7.03 kW Water-R410A plate heat exchanger |
| ASHP | 3.5 | - | Yes | R410a | 5 stars | - |
| Sensor Location | Sensor Type | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Indoor air temp. | T type thermocouple | +/−0.5 °C |
| Atmospheric air temp. | T type thermocouple | +/−0.5 °C |
| Heat transfer fluid inlet | Pt100 platinum resistance | +/−0.2 °C |
| Heat transfer fluid outlet | Pt-100 platinum resistance | +/−0.2 °C |
| Ground Temperatures | NTC thermistor | +/−0.2 °C |
| Heat Pump | Life-Cycle Cost | Cost1 |
|---|---|---|
| GSHP 1 | Total cost | 5700 |
| GSHP 2 | Total cost | 900 |
| Ground Heat Exchanger | Material cost | 225 |
| Installation cost | 360 | |
| ASHP | Unit cost | 630 |
| Installation cost | 90 | |
| Others | Electricity cost | 0.1352 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Widiatmojo, A.; Chokchai, S.; Takashima, I.; Uchida, Y.; Yasukawa, K.; Chotpantarat, S.; Charusiri, P. Ground-Source Heat Pumps with Horizontal Heat Exchangers for Space Cooling in the Hot Tropical Climate of Thailand. Energies 2019, 12, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071274
Widiatmojo A, Chokchai S, Takashima I, Uchida Y, Yasukawa K, Chotpantarat S, Charusiri P. Ground-Source Heat Pumps with Horizontal Heat Exchangers for Space Cooling in the Hot Tropical Climate of Thailand. Energies. 2019; 12(7):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071274
Chicago/Turabian StyleWidiatmojo, Arif, Sasimook Chokchai, Isao Takashima, Yohei Uchida, Kasumi Yasukawa, Srilert Chotpantarat, and Punya Charusiri. 2019. "Ground-Source Heat Pumps with Horizontal Heat Exchangers for Space Cooling in the Hot Tropical Climate of Thailand" Energies 12, no. 7: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071274
APA StyleWidiatmojo, A., Chokchai, S., Takashima, I., Uchida, Y., Yasukawa, K., Chotpantarat, S., & Charusiri, P. (2019). Ground-Source Heat Pumps with Horizontal Heat Exchangers for Space Cooling in the Hot Tropical Climate of Thailand. Energies, 12(7), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12071274






