Speed and Pressure Controls of Pumps-as-Turbines Installed in Branch of Water-Distribution Network Subjected to Highly Variable Flow Rates
Abstract
1. Introduction
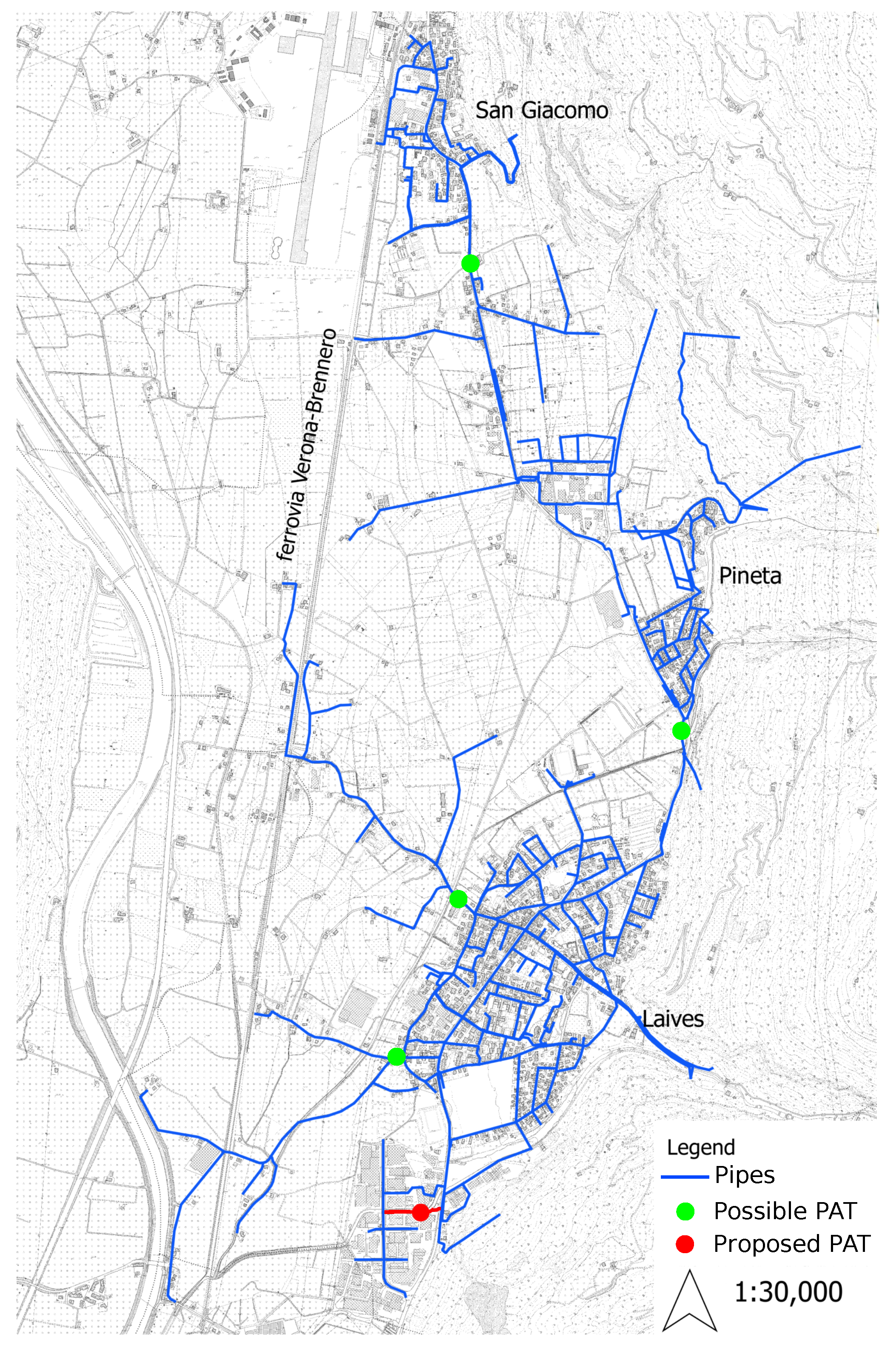
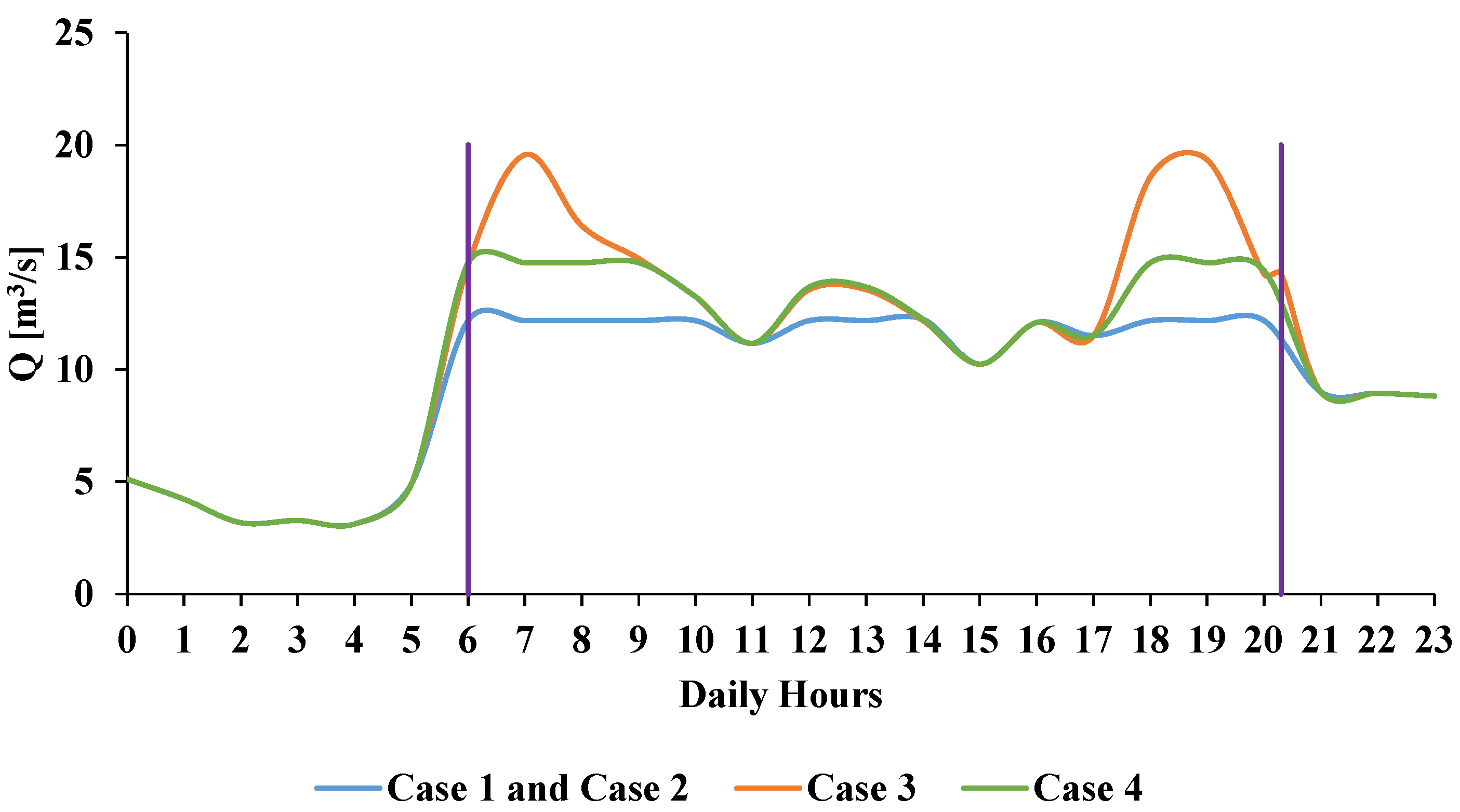
2. Case Study
3. PaT Performance
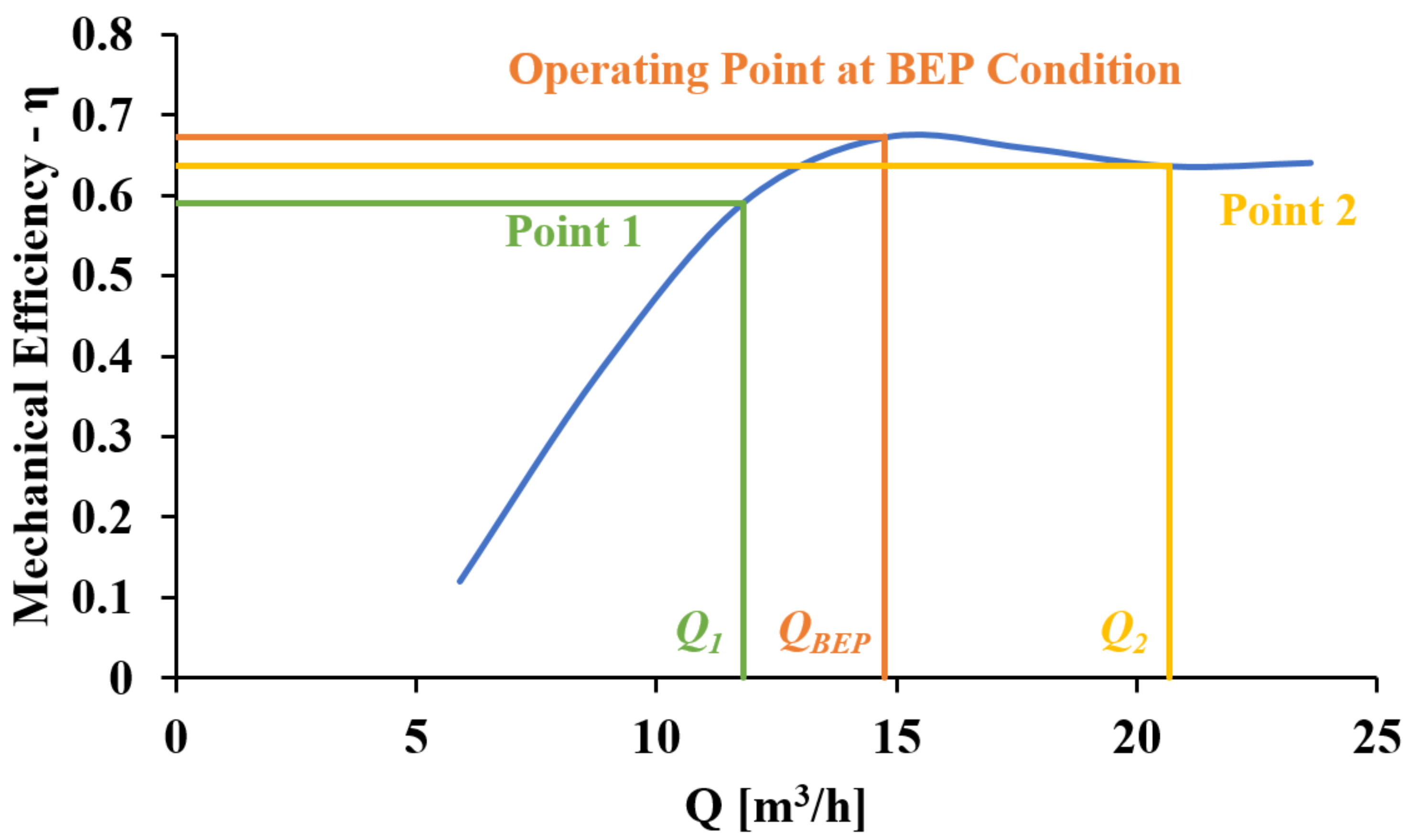
3.1. Selection of PaT Operating at Rated Conditions in Turbine Mode
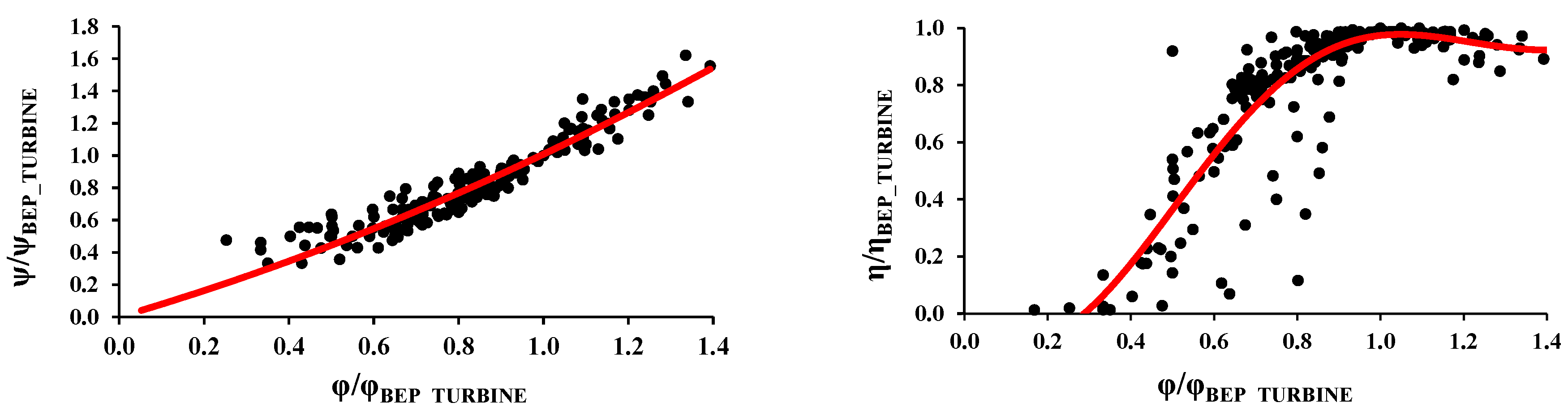
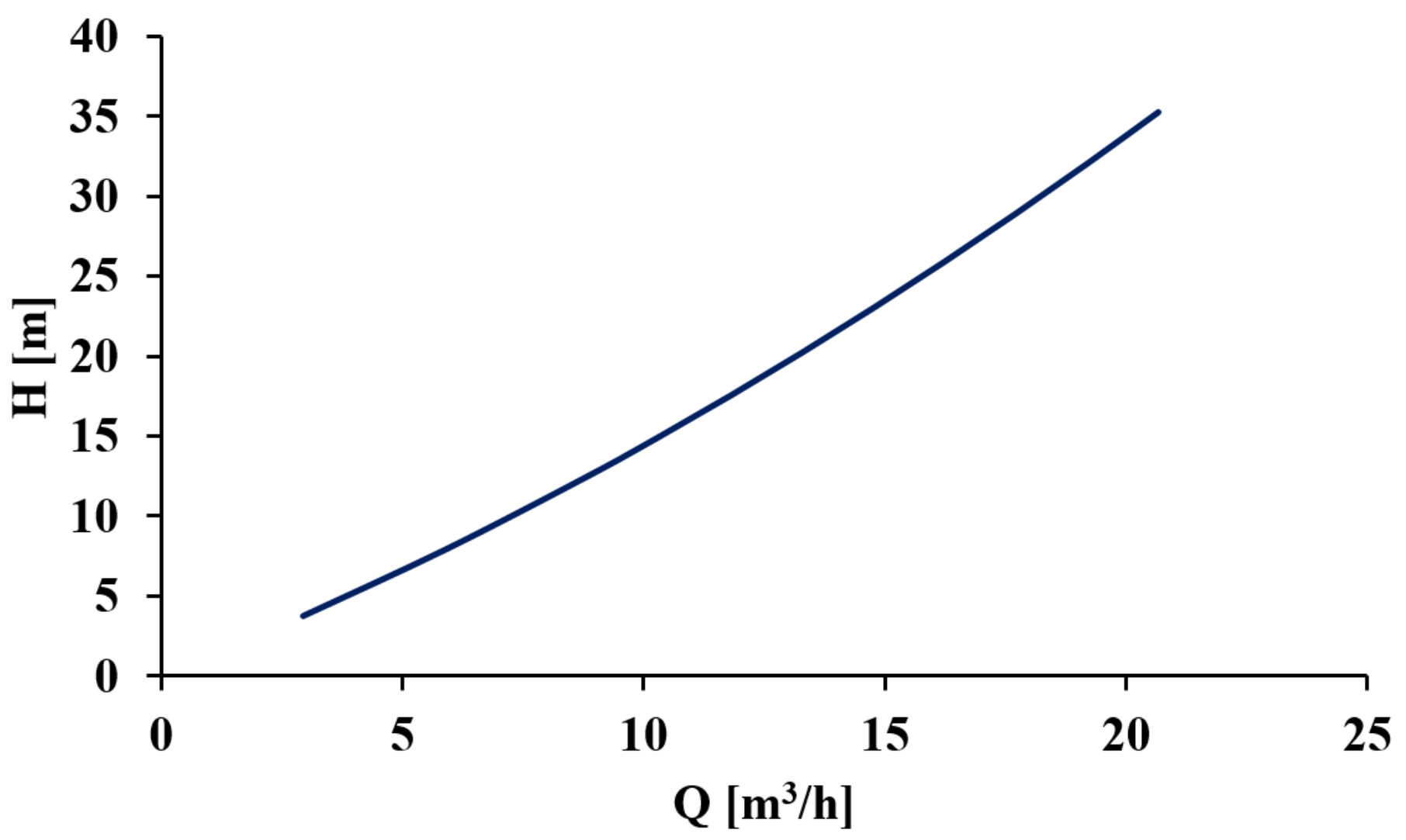
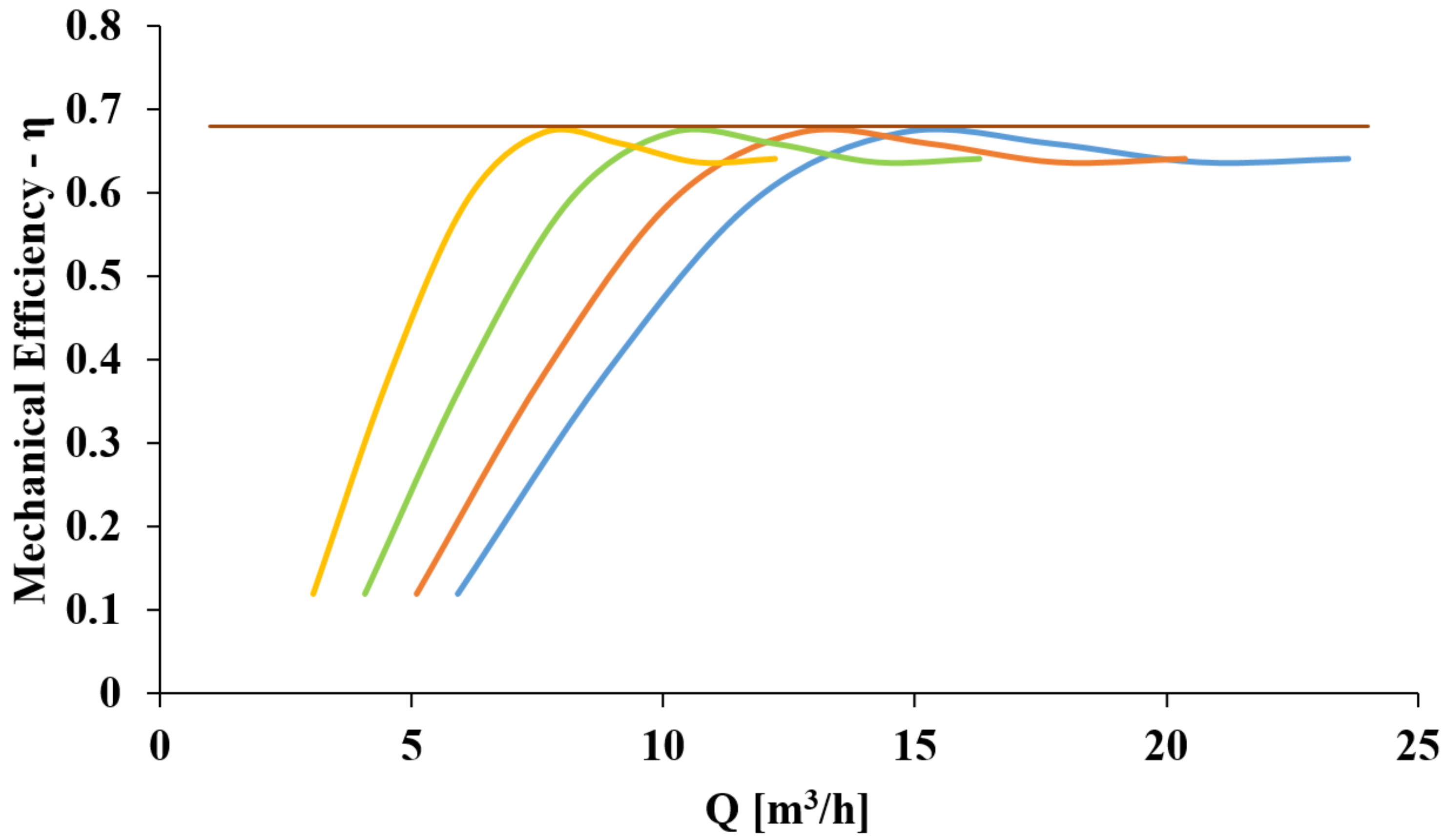
3.2. Characteristic Curves in Turbine Mode
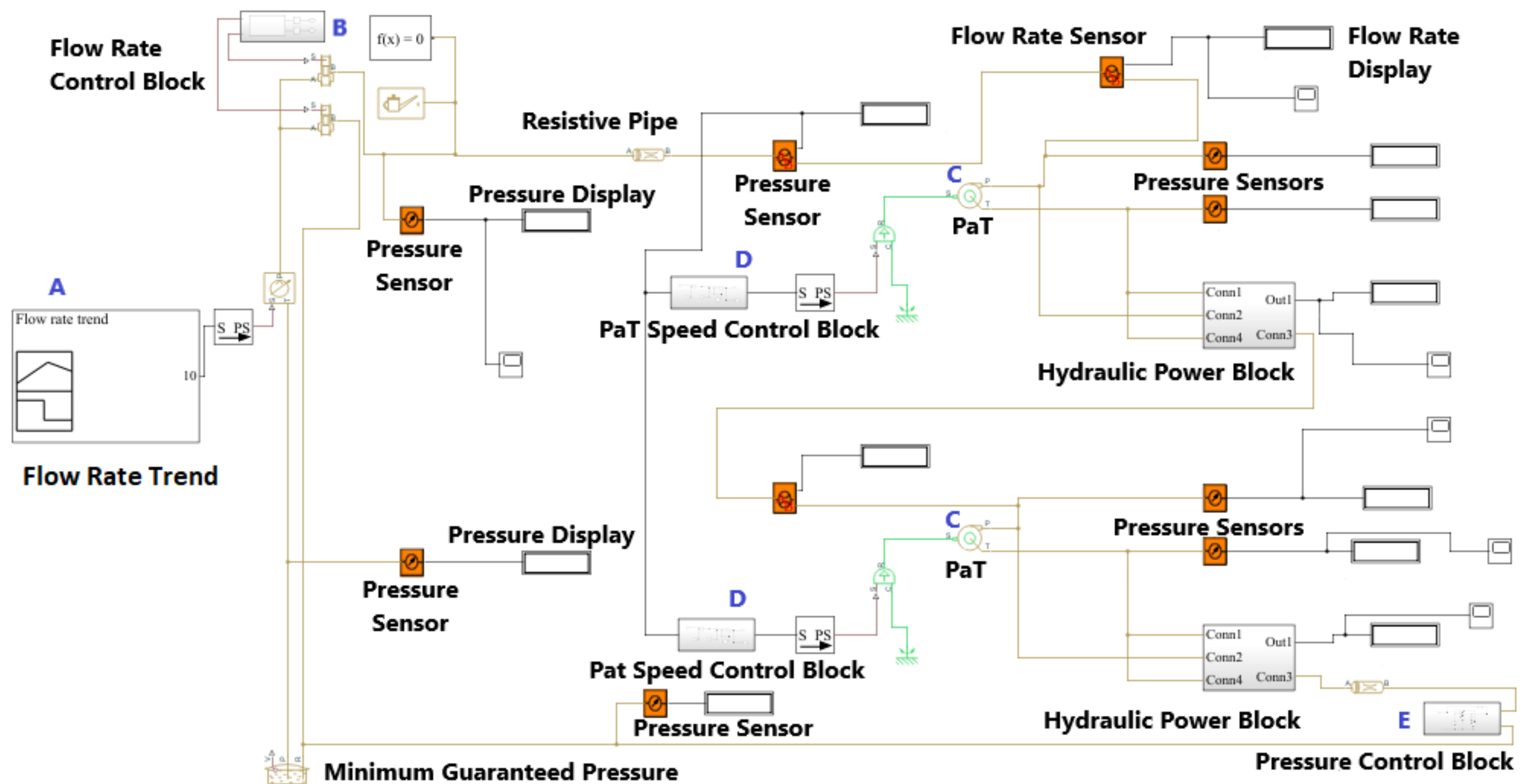
3.3. MATLAB©–Simulink Model
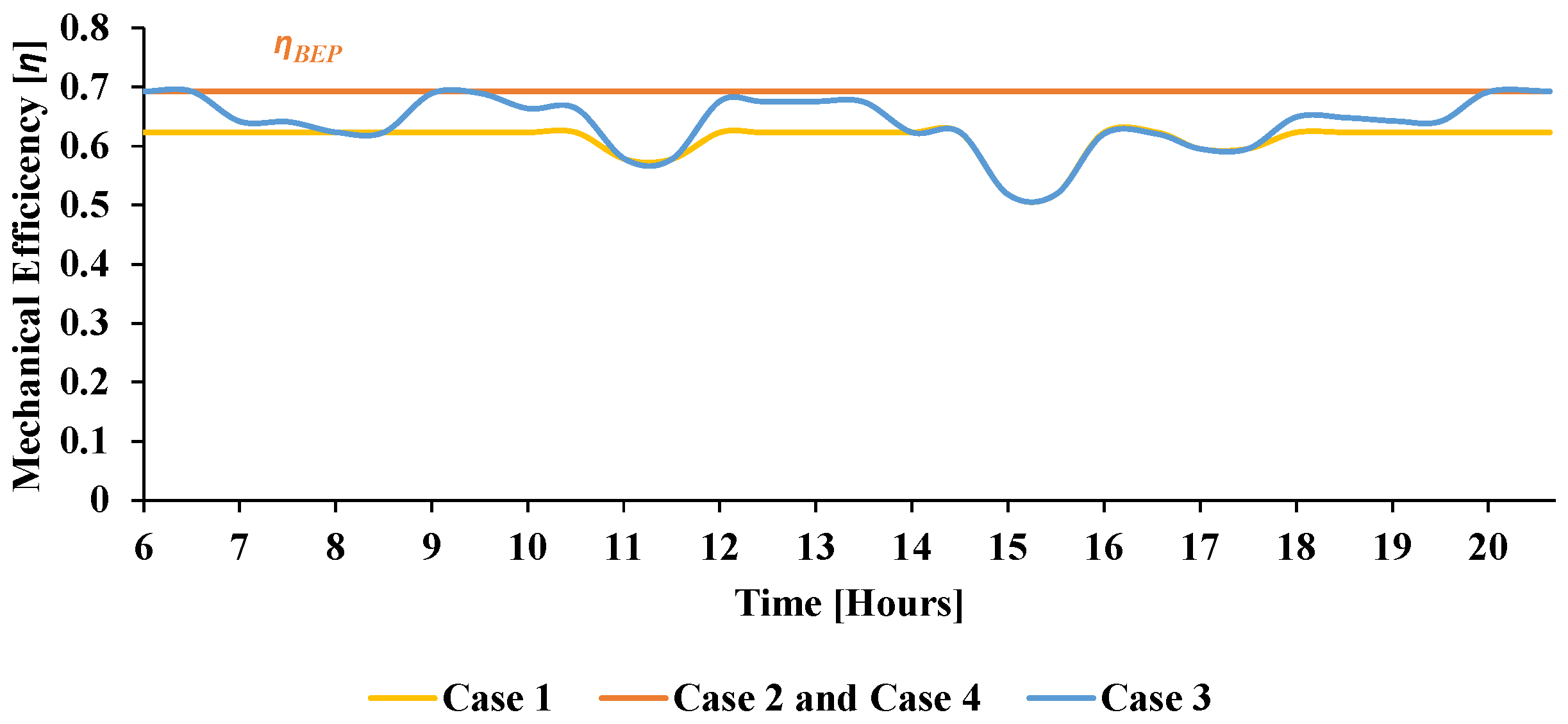
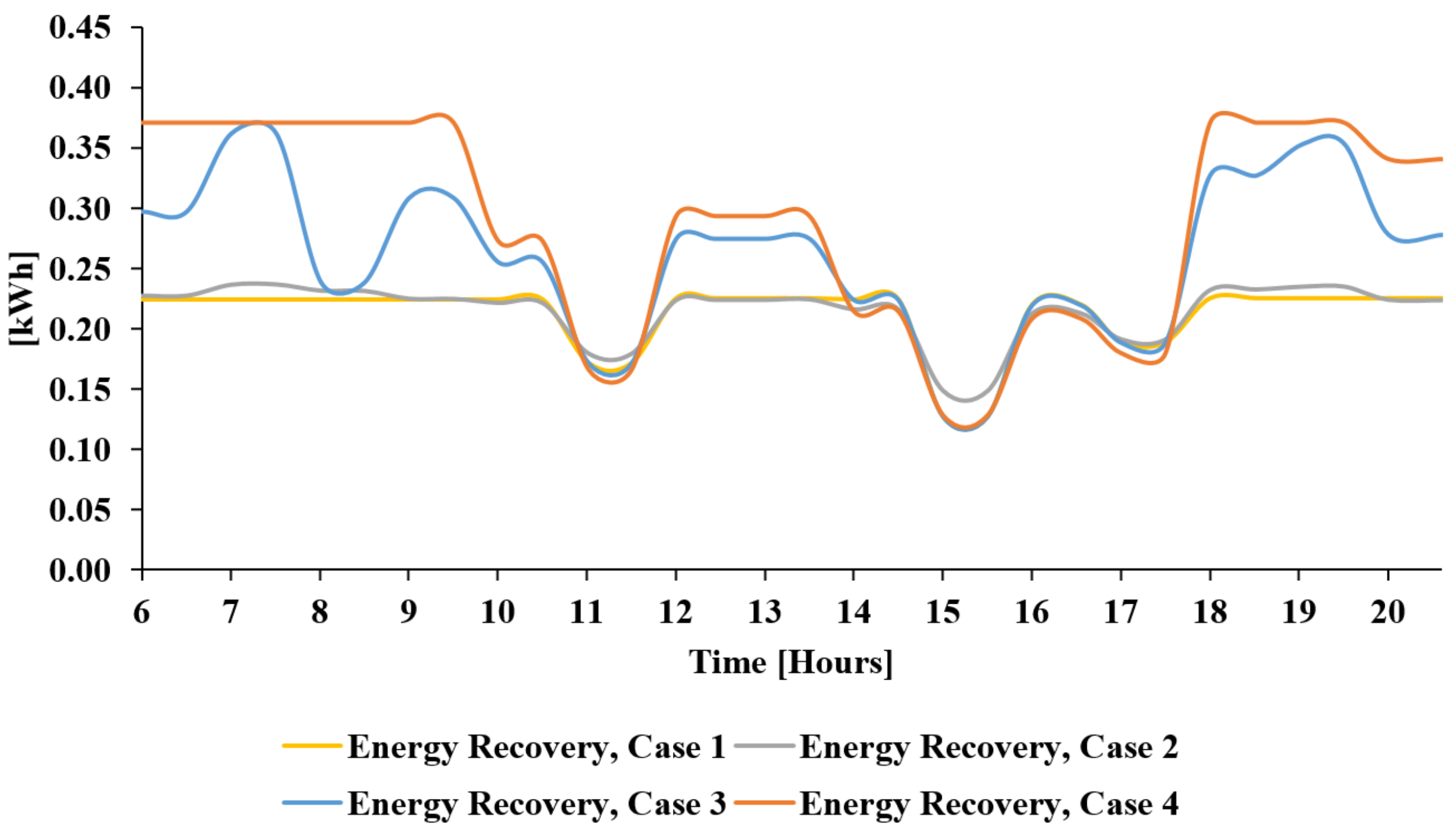
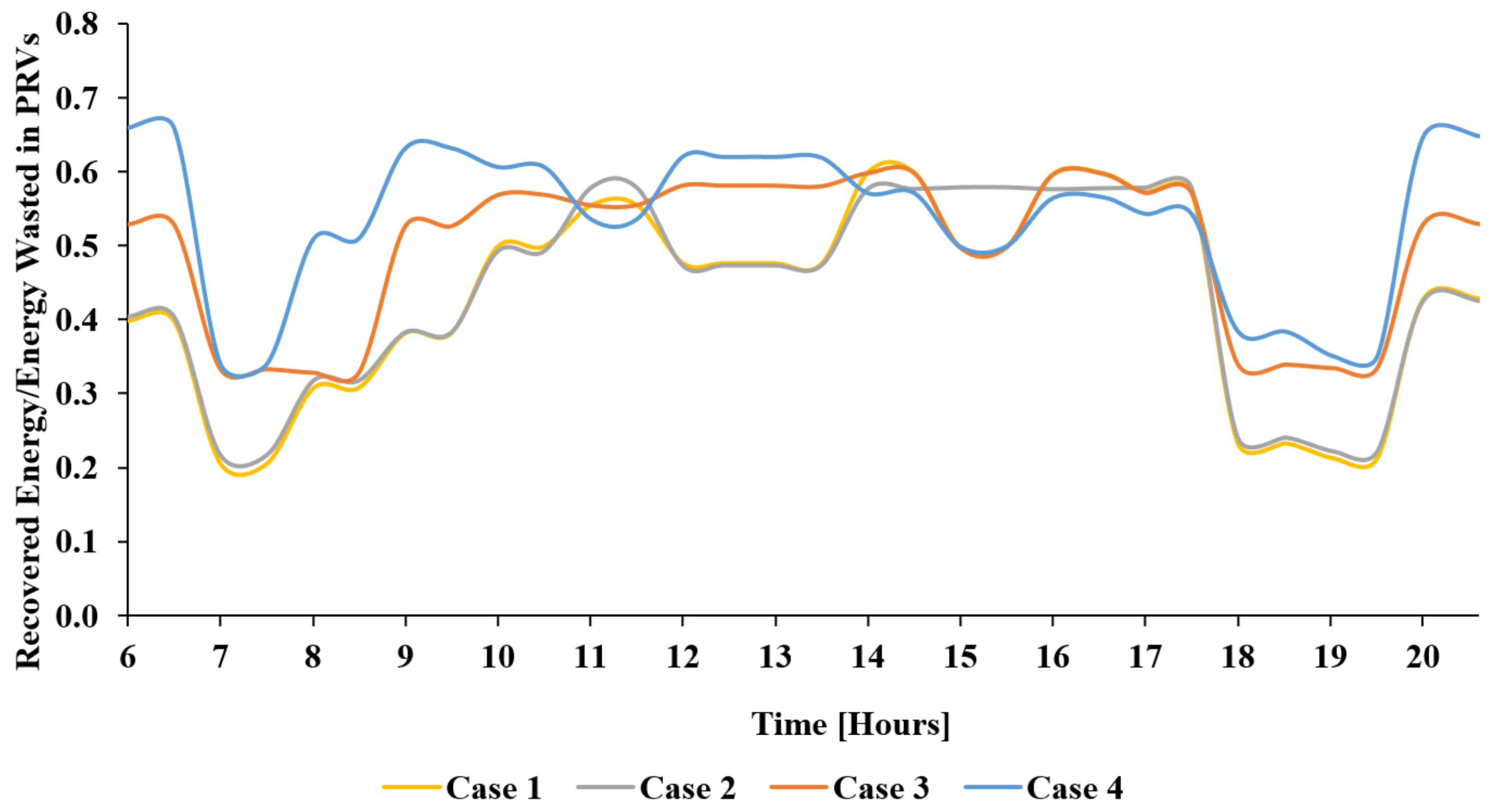
4. Results and Comments
4.1. Case 1: Basic Flow-Rate Control Strategy
4.2. Case 2: Basic Flow-Rate and Speed Control
4.3. Case 3: Advanced Speed and Flow Control
4.4. Case 4: Basic Flow-Rate and Speed Control with Reduced WDN Pressure to Bar
5. Energy and Economic Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nassar, I.A.; Hossam, K.; Abdella, M.M. Economic and environmental benefits of increasing the renewable energy sources in the power system. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Leal, V.; Oliveira, V.; Horta, I.M. A scenario-based approach for assessing the energy performance of urban development pathways. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkhair, K.S.; Rahman, K.U. Sustainable and economical small-scale and low-head hydropower generation: A promising alternative potential solution for energy generation at local and regional scale. Appl. Energy 2017, 188, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, I. Water management for sustainable and clean energy in Turkey. Energy Rep. 2015, 1, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punys, P.; Dumbrauskas, A.; Kvaraciejus, A.; Vyciene, G. Tools for Small Hydropower Plant Resource Planning and Development: A Review of Technology and Applications. Energies 2011, 4, 1258–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsialis, T.; Kougias, I.; Kazakis, N.; Theodossiou, N.; Droege, P. Supporting Renewables’ Penetration in Remote Areas through the Transformation of Non-Powered Dams. Energies 2016, 9, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkovelos, A.; Mentis, D.; Siyal, S.H.; Arderne, C.; Rogner, H.; Bazilian, M.; Howells, M.; Beck, H.; de Roo, A. A Geospatial Assessment of Small-Scale Hydropower Potential in Sub-Saharan Africa. Energies 2018, 11, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzi, M.; Rudolf, P.; ¸Stefan, D.; Nigro, A.; Rossi, M. Installation of an axial Pump-as-Turbine (PaT) in a wastewater sewer of an oil refinery: A case study. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Nigro, A.; Pisaturo, G.R.; Renzi, M. Technical and economic analysis of Pumps-as-Turbines (PaTs) used in an Italian Water Distribution Network (WDN) for electrical energy production. Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, N.; Kansoh, R.; Elbarki, W.; Fleifle, A. Pressure control for minimizing leakage in water distribution systems. Alex. Eng. J. 2017, 56, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, J.E.; Clayton, C. The effect of pressure on leakage in water distribution systems. Water Manag. 2007, 160, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, M.; Bort, C.; Bottazzi, M.; Menapace, A.; Zanfei, A. Optimal selection and monitoring of nodes aimed at supporting leakages identification in WDS. Water 2019, 11, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldarriaga, J.; Salcedo, C.A. Determination of Optimal Location and Settings of Pressure Reducing Valves in Water Distribution Networks for Minimizing Water Losses. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, R.; Abraham, E.; Parpas, P.; Stoianov, I. Optimized Control of Pressure Reducing Valves in Water Distribution Networks with Dynamic Topology. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Derakhshan, S.; Kong, F.Y. Theoretical, numerical and experimental prediction of pump as turbine performance. Renew. Energy 2012, 48, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polák, M. The Influence of Changing Hydropower Potential on Performance Parameters of Pumps in Turbine Mode. Energies 2019, 12, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binama, M.; Su, W.T.; Li, X.B.; Li, F.C.; Wei, X.Z.; An, S. Investigation on pump as turbine (PAT) technical aspects for micro hydropower schemes: A state-of-the-art review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 148–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpe, J.; Prénant, J.; Dubas, M.; Biner, H.-P. Project Charactéristiques Des Pompes Fonctionnant en Turbines; Rapport Final du Project N° 100400/150 497; Ecole d’ingénieurs de Genève, Haute école valaisanne: Genève, Switzerland, 2006; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, M.; Renzi, M. A general methodology for performance prediction of pump-as-turbines using Artificial Neural Networks. Renew. Energy 2018, 128, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, M.; Manservigi, L.; Alvisi, S.; Simani, S. Development of a physics-based model to predict the performance of pumps as turbines. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Nigro, A.; Renzi, M. Experimental and numerical assessment of a methodology for performance prediction of Pumps-as-Turbines (PaTs) operating in off-design conditions. Appl. Energy 2019, 248, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosina, E.; Buono, D.; Senatore, A. A Performance Prediction Method for Pumps as Turbines (PAT) Using a Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Modeling Approach. Energies 2017, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, A.; Derakhshan, S.; Ramos, H.M. Pumps as Turbines; Springer Tracts in Mechanical Engineering; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; p. 236. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Wang, C.; Kong, F.; Gou, Q.; Yang, S. Theoretical, experimental, and numerical study of special impeller used in turbine mode of centrifugal pump as turbine. Energy 2017, 130, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, A.; del Giudice, G.; Fecarotta, O.; Ramos, H.M. PAT Design Strategy for Energy Recovery in Water Distribution Networks by Electrical Regulation. Energies 2013, 6, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yang, H.; Shen, Z.; Chen, J. Micro hydro power generation from water supply system in high rise buildings using pump as turbines. Energy 2017, 137, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydon, T.; Coughlan, P.; McNabola, A. Pressure management and energy recovery in water distribution network: Development of design and selection methodologies using three pump-as-turbine case studies. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.M.; Luvizotto, E.; Brentan, B.M. Selection and location of Pumps as Turbines substituting pressure reducing valves. Renew. Energy 2017, 109, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.M.; Brentan, B.M.; Luvizotto, E. Optimal design of water supply networks using an energy recovery approach. Renew. Energy 2018, 117, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.; Terheiden, K.; Wieprecht, S. Pumps as turbines for efficient energy recovery in water supply networks. Renew. Energy 2018, 122, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Marchis, M.; Milici, B.; Volpe, R.; Messineo, A. Energy Saving in Water Distribution Network through Pump as Turbine Generators: Economic and Environmental Analysis. Energies 2016, 9, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, A.; Fecarotta, O.; del Giudice, G.; Ramos, H. Energy recovery in water systems by PATs: A comparisons among the different installation schemes. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.; Ferreira, J.P.; Covas, D.I.C.; Avellan, F. Variable speed operation of centrifugal pumps running as turbines. Experimental investigation. Renew. Energy 2019, 142, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, T.; Hardy, C.; Tichelen, P.V.; Olivier, M.; de Jaeger, E. Control of variable-speed pumps used as turbines for flexible grid-connected power generation. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2019, 176, 105962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberizzi, J.C.; Renzi, M.; Nigro, A.; Rossi, M. Study of a Pump as Turbine (PaT) speed control for a Water Distribution Network (WDN) in South-Tyrol subjected to high variable water flow rates. Energy Procedia 2018, 148, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzi, M.; Rossi, M. A generalized theoretical methodology to forecast flow coefficient, head coefficient and efficiency of Pumps-as-Turbines (PaTs). Energy Procedia 2019, 158, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEAB, Servizi Energia Ambiente Bolzano. Available online: https://www.seab.bz.it/it/privati/lacqua-di-bolzano (accessed on 3 December 2019).
- Singh, P.; Nestmann, F. An optimization routine on a prediction and selection model for the turbine operation of centrifugal pumps. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2010, 34, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SNPA, XII Rapporto Qualità Dell’Ambiente Urbano—Edizione 2016. Available online: http://www.isprambiente.gov.it/it/pubblicazioni/stato-dellambiente/xii-rapporto-qualita-dell2019ambiente-urbano-edizione-2016 (accessed on 3 December 2019).
- AEEG, Relazione Annuale Sullo Stato Dei Servizi E Sull’Attività Svolta. Available online: https://www.arera.it/it/dati/eepcfr2.htm (accessed on 3 December 2019).
- Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Fang, Z.; Shao, J.; Li, J. Optimal design of a high efficiency LLC resonant converter with a narrow frequency range for voltage regulation. Energies 2018, 11, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
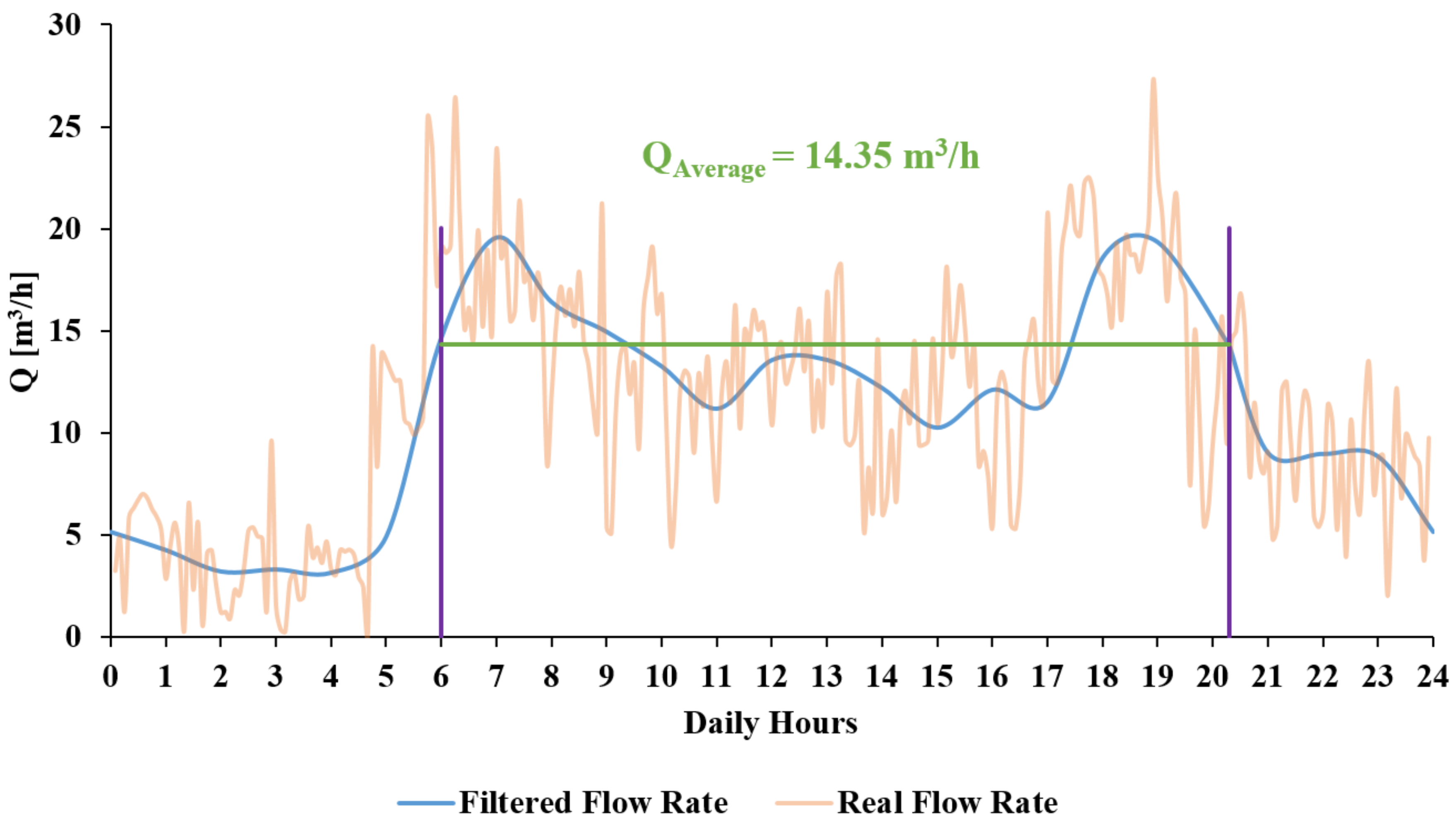

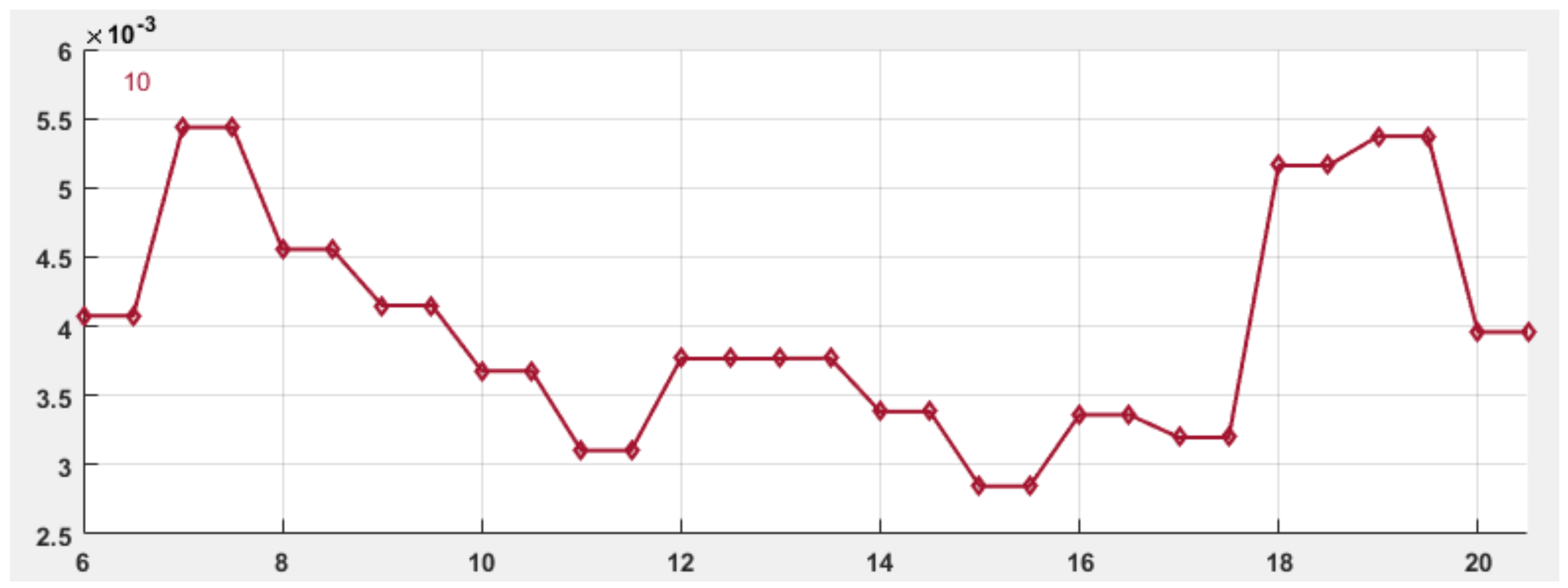

| Hour | 6:00 | 7:00 | 8:00 | 9:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 | 20:30 |
| 14.67 | 19.57 | 16.40 | 14.94 | 13.24 | 11.17 | 13.56 | 13.56 | 12.18 | 10.24 | 12.10 | 11.51 | 18.58 | 19.34 | 14.25 |
| Pump Mode | Turbine Mode | |
|---|---|---|
| Flow rate (m3/h) | 13 | |
| Head (m) | 20 | |
| Mechanical efficiency (-) | ||
| Rotational speed (rpm) | 2900 | 2900 |
| Specific speed (rad/s) | ||
| Impeller diameter (m) |
| BEP Flow Rate Offset (%) | Flow Rate (m3/h) | (-) | Head (m) | (-) | Mechanical Efficiency (-) | Mechanical Power (KW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14.35 | ||||||
| Operating Strategy | Pressure Constraint (Bar) | |
|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Flow-rate control | 4 |
| Case 2 | Flow-rate and | 4 |
| speed control | ||
| Case 3 | Speed control | 4 |
| Case 4 | Flow-rate and | 3.5 |
| speed control |
| Energy Recovery | Economic Saving | % with Respect | Not Recovered | % of Recovered | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| to Case 1 | Energy | ||||
| Case 1 | 4637 | 979 | - | 7833 | 37 |
| Case 2 | 4706 | 994 | 1.5 | 7764 | 38 |
| Case 3 | 5699 | 1204 | 23 | 6771 | 46 |
| Case 4 | 6307 | 1332 | 36 | 6163 | 51 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alberizzi, J.C.; Renzi, M.; Righetti, M.; Pisaturo, G.R.; Rossi, M. Speed and Pressure Controls of Pumps-as-Turbines Installed in Branch of Water-Distribution Network Subjected to Highly Variable Flow Rates. Energies 2019, 12, 4738. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244738
Alberizzi JC, Renzi M, Righetti M, Pisaturo GR, Rossi M. Speed and Pressure Controls of Pumps-as-Turbines Installed in Branch of Water-Distribution Network Subjected to Highly Variable Flow Rates. Energies. 2019; 12(24):4738. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244738
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlberizzi, Jacopo Carlo, Massimiliano Renzi, Maurizio Righetti, Giuseppe Roberto Pisaturo, and Mosè Rossi. 2019. "Speed and Pressure Controls of Pumps-as-Turbines Installed in Branch of Water-Distribution Network Subjected to Highly Variable Flow Rates" Energies 12, no. 24: 4738. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244738
APA StyleAlberizzi, J. C., Renzi, M., Righetti, M., Pisaturo, G. R., & Rossi, M. (2019). Speed and Pressure Controls of Pumps-as-Turbines Installed in Branch of Water-Distribution Network Subjected to Highly Variable Flow Rates. Energies, 12(24), 4738. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244738








