Experimental Investigation and Benchmark Study of Oxidation of Methane–Propane–n-Heptane Mixtures at Pressures up to 100 bar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Investigated Reaction Mechanisms
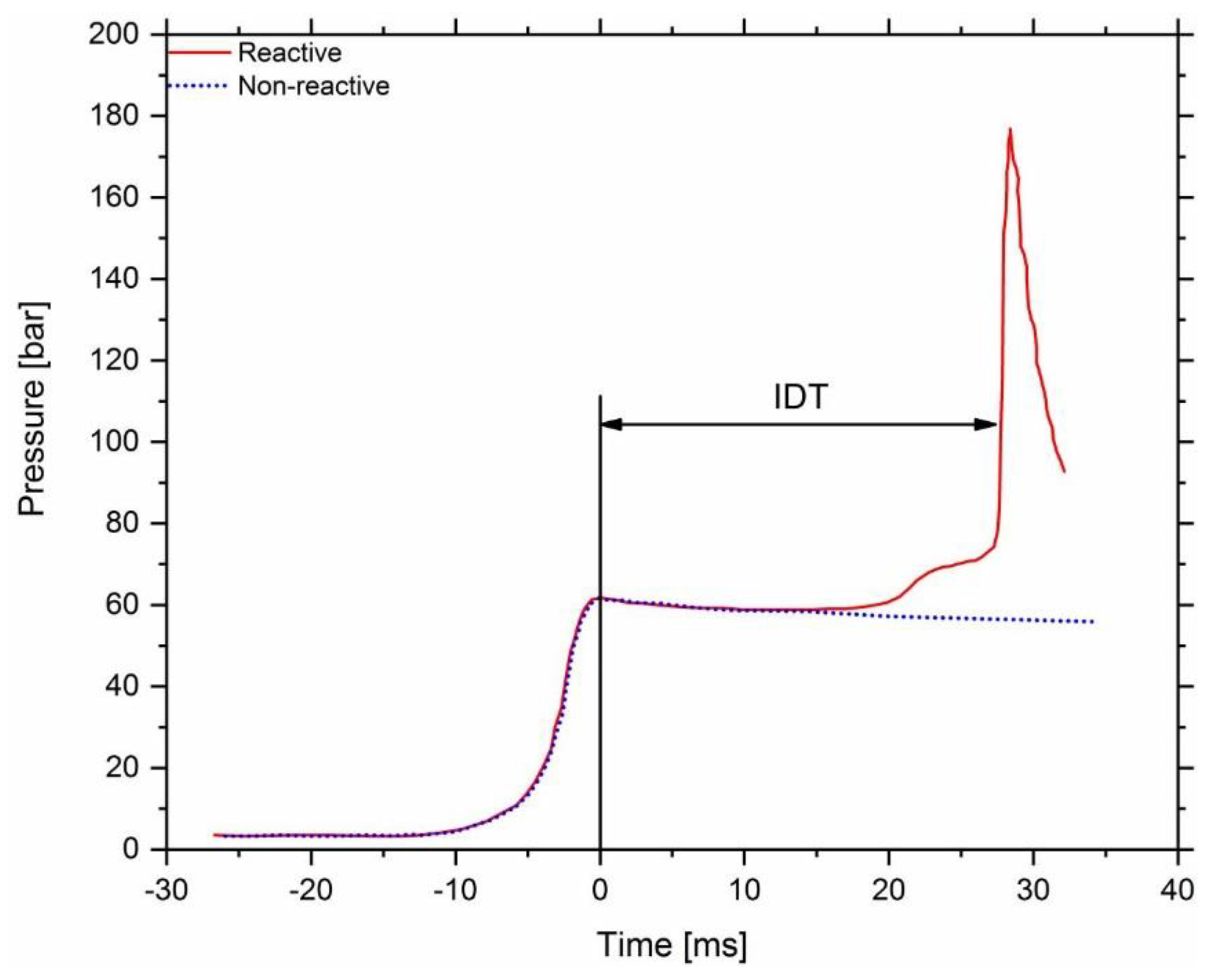
2.2. Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
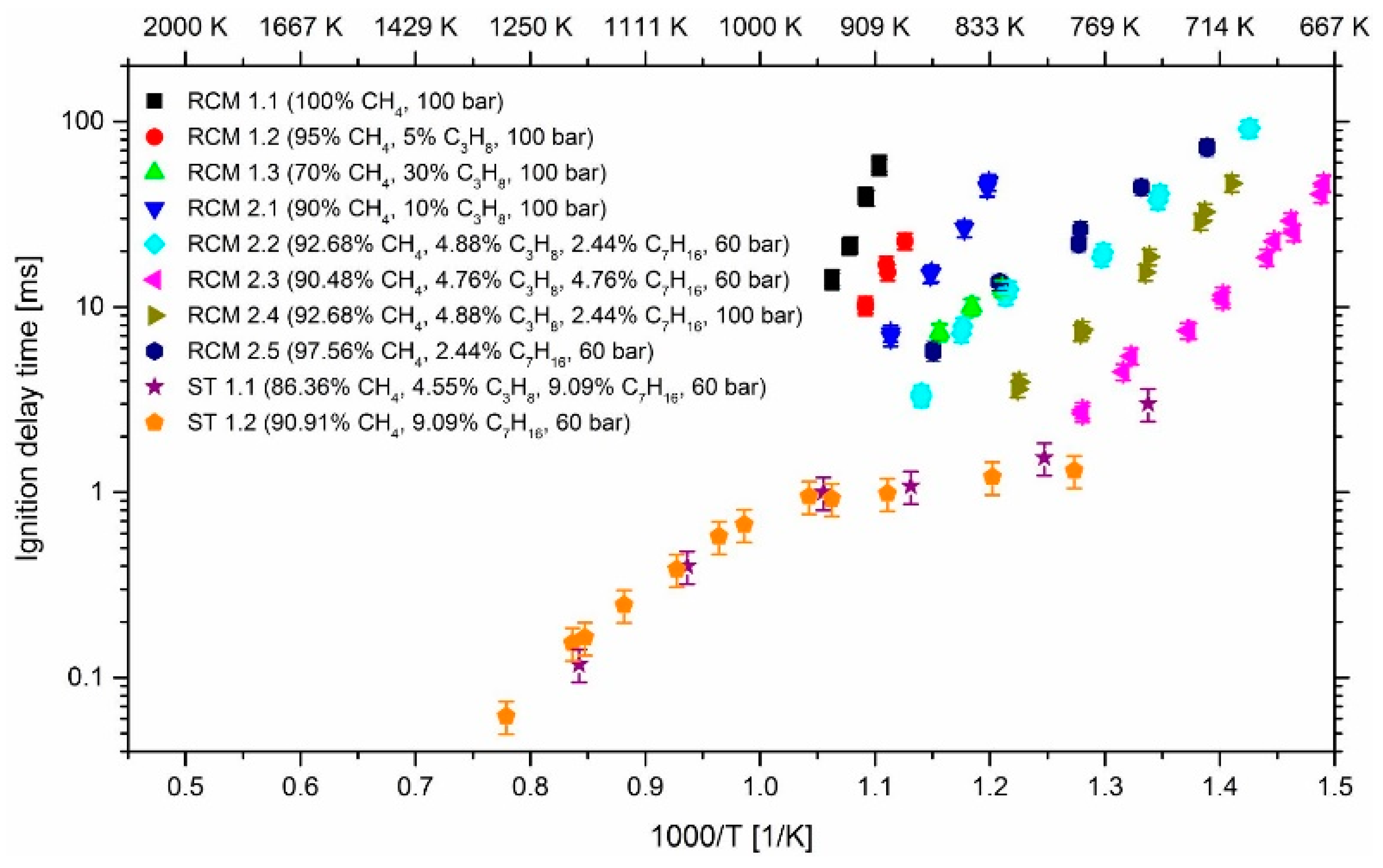
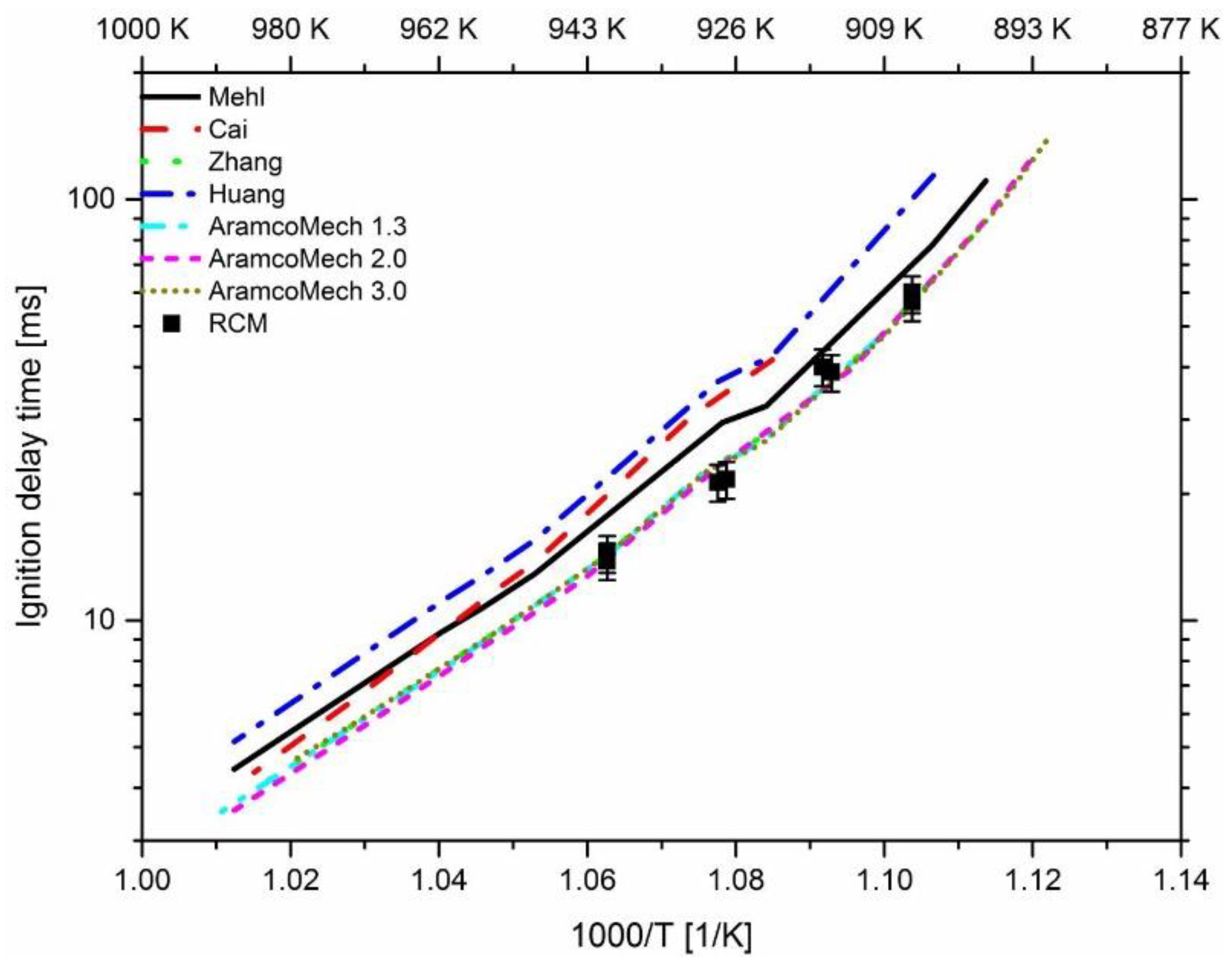
3.1. Effect of Propane
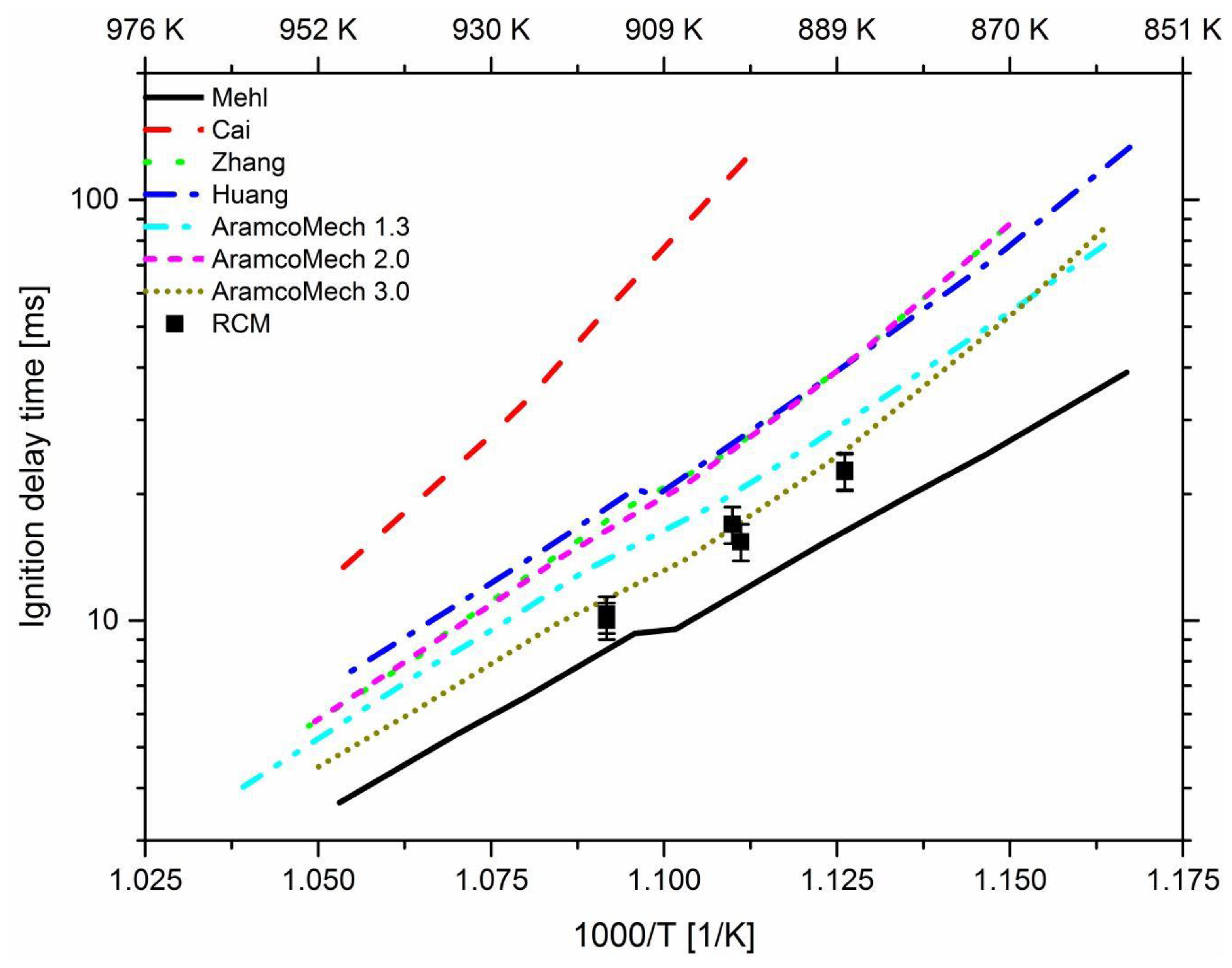
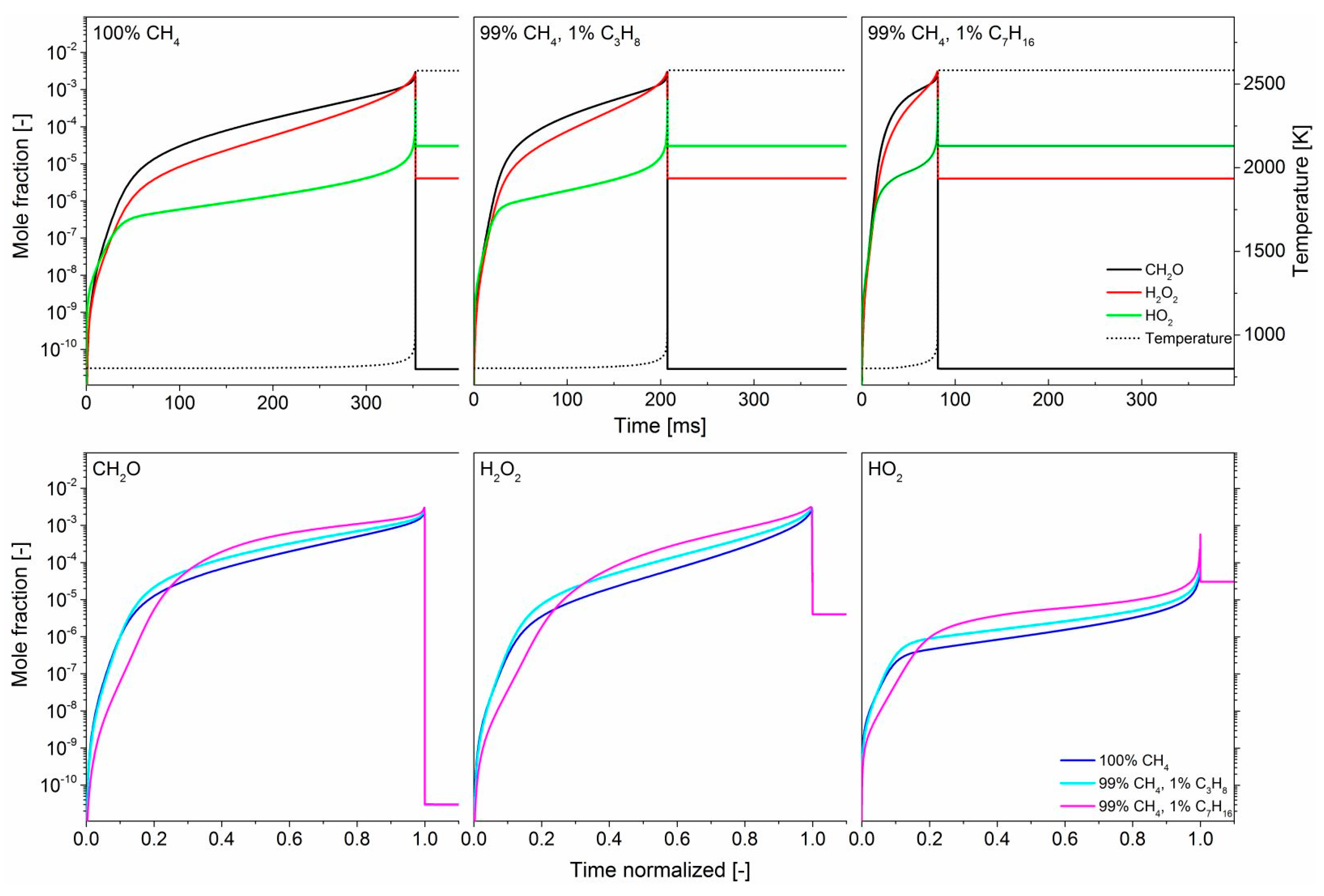
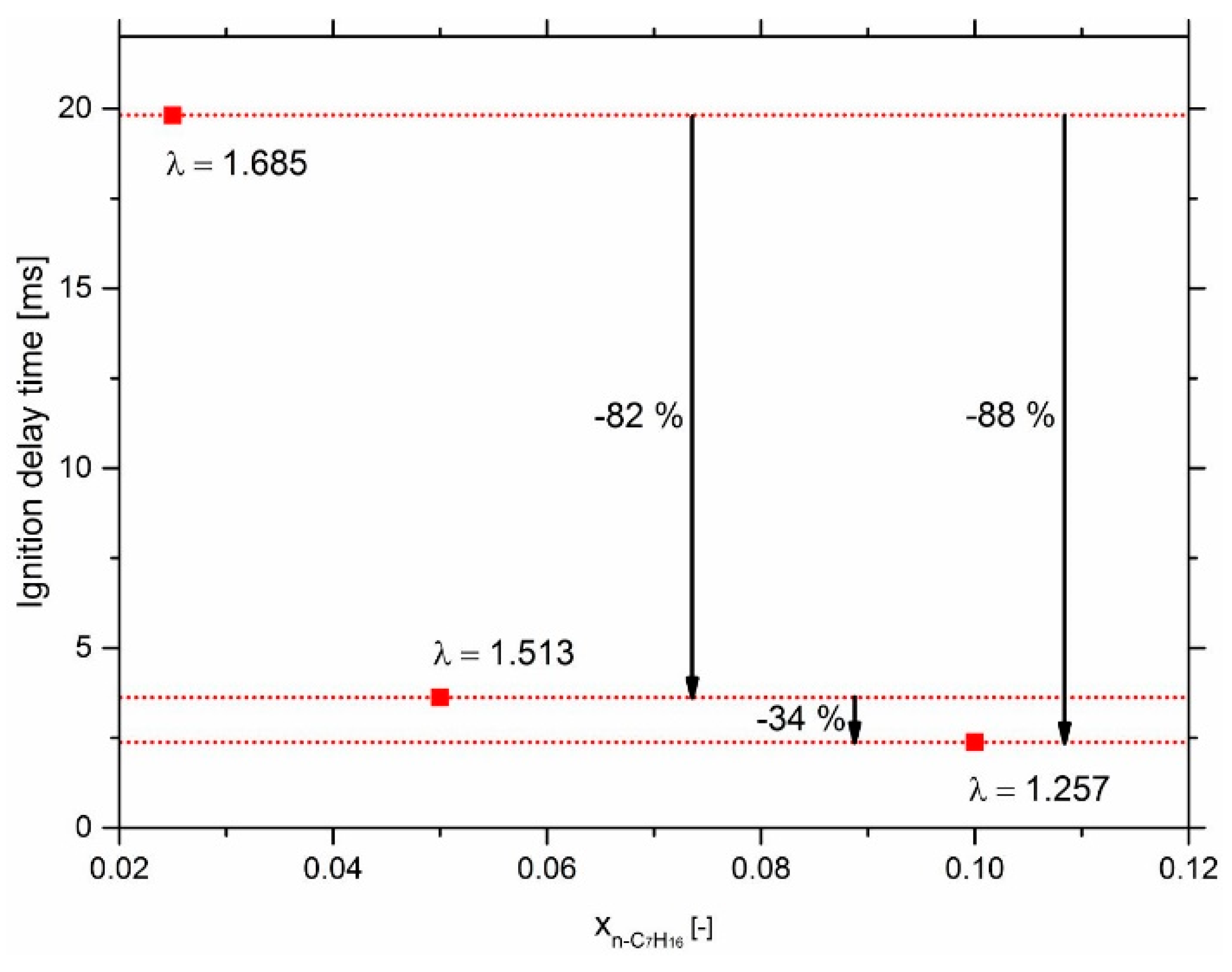
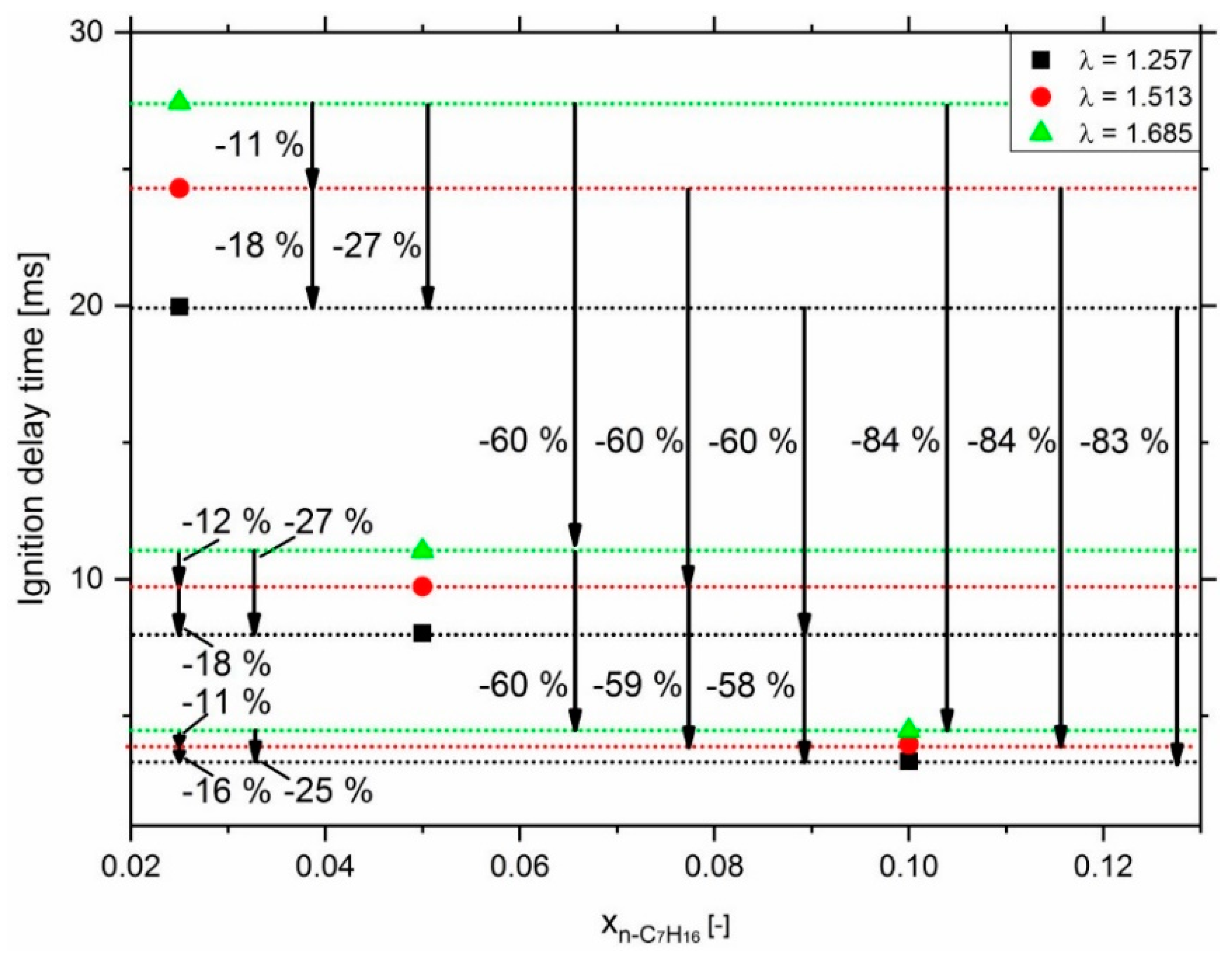
3.2. Effect of n-Heptane
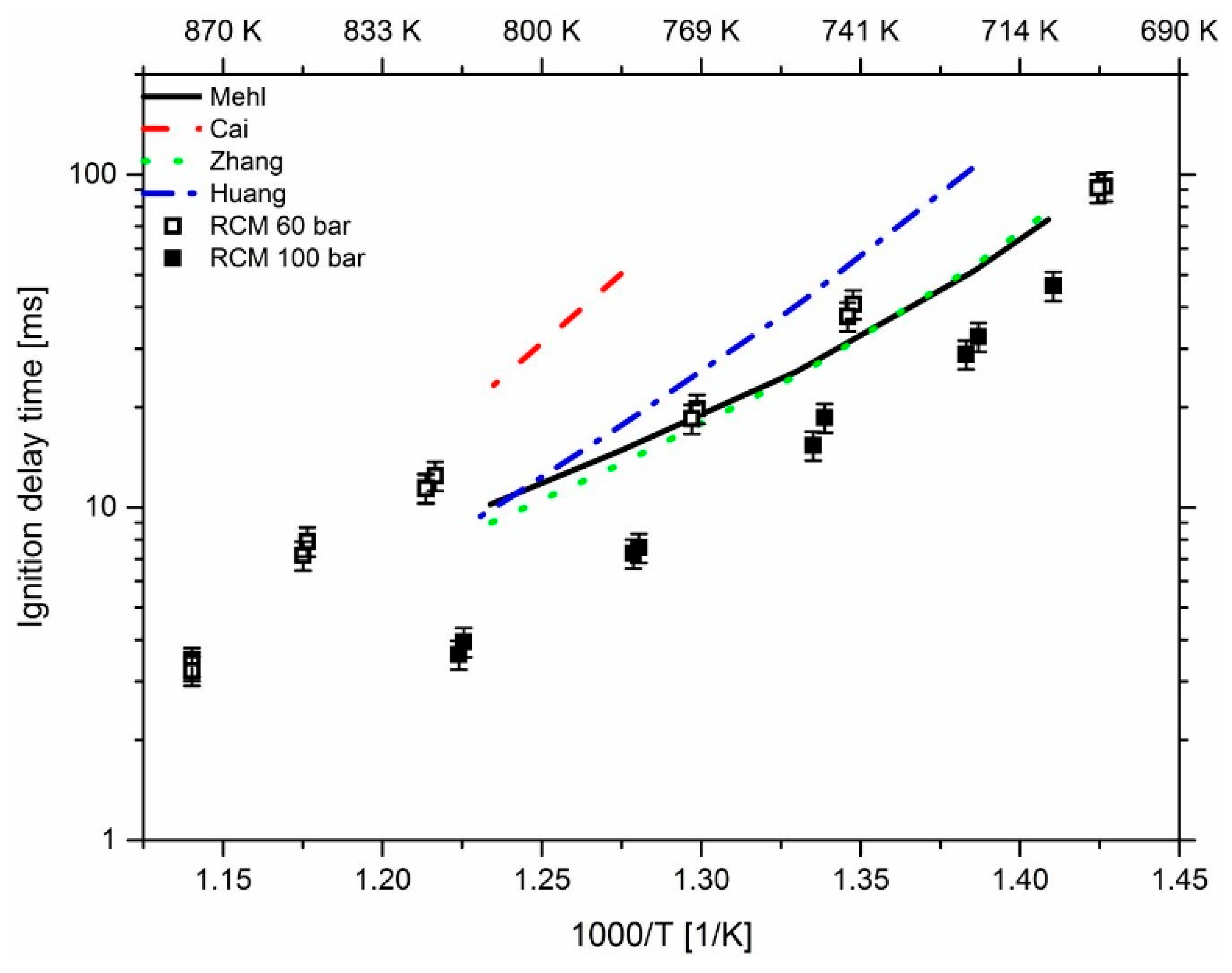
3.3. Effect of Pressure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wright, G. Fundamentals of Medium/Heavy Duty Diesel Engines; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dietsche, K.-H.; Reif, K. Kraftfahrtechnisches Taschenbuch; 28., überarb. u. erw. Aufl. 2014 ed.; Springer Vieweg: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schlick, H. Potentials and challenges of gas and dual-fuel engines for marine application. In Proceedings of the 5th Cimac Cascades, Busan, Korea, 23 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, M. Modellierung der Multikomponenten-Verdampfung im Homogenisierten Dieselmotorischen Brennverfahren; Cuvillier Verlag Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, B.; Wandel, A.P. Numerical investigation into natural gas–diesel dual-fuel engine configuration. In Proceedings of the 11th Asia-Pacific Conference on Combustion, ASPACC 2017, Sydney, Australia, 10–14 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Yao, M. A numerical investigation on methane combustion and emissions from a natural gas-diesel dual fuel engine using CFD model. Appl. Energy 2017, 205, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, W.; Fan, L.; Zhou, D.; Ma, X. Development of a skeletal mechanism for heavy-duty engines fuelled by diesel and natural gas. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 123, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ra, Y.; Chuahy, F.; Kokjohn, S. Development and validation of a reduced reaction mechanism with a focus on diesel fuel/syngas co-oxidation. Fuel 2016, 185, 663–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, L.; Ban, M.; Pirker, G.; Vujanovic, M.; Priesching, P.; Wimmer, A. Development and Validation of 3D-CFD Injection and Combustion Models for Dual Fuel Combustion in Diesel Ignited Large Gas Engines. Energies 2018, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, W.N.W.; Olsen, D.B. Computational modeling of diesel and dual fuel combustion using CONVERGE CFD software. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2016, 11, 13697–13707. [Google Scholar]
- Hockett, A.G.; Hampson, G.; Marchese, A.J. Natural gas-diesel RCCI CFD simulations using multi-component fuel surrogates. Int. J. Powertrains 2017, 6, 76–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzke, J.; Andree, S.; Theile, M.; Henke, B.; Schleef, K.; Nocke, J.; Hassel, E. Simulation of a Dual-Fuel Large Marine Engines using combined 0/1-D and 3-D Approaches. In Proceedings of the CIMAC Congress, Helsinki, Finland, 6–10 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hockett, A.; Hampson, G.; Marchese, A.J. Development and Validation of a Reduced Chemical Kinetic Mechanism for Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations of Natural Gas/Diesel Dual-Fuel Engines. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 2414–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lv, D.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Y.; Pan, M. Development of a new reduced diesel/natural gas mechanism for dual-fuel engine combustion and emission prediction. Fuel 2019, 236, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierschenk, D.M.; Pillai, M.R.; Lin, Y.; Barnett, S.A. Effect of Ethane and Propane in Simulated Natural Gas on the Operation of Ni-YSZ Anode Supported Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2010, 10, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, D.; Curran, H.J.; Simmie, J.M.; Kalitan, D.M.; Zinner, C.M.; Barrett, A.B.; Petersen, E.L.; Bourque, G. Methane/ethane/propane mixture oxidation at high pressures and at high, intermediate and low temperatures. Combust. Flame 2008, 155, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, M.; Pitz, W.J.; Westbrook, C.K.; Curran, H.J. Kinetic modeling of gasoline surrogate components and mixtures under engine conditions. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Pitsch, H. Optimized chemical mechanism for combustion of gasoline surrogate fuels. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 1623–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, H.J.; Gaffuri, P.; Pitz, W.J.; Westbrook, C.K. A comprehensive modeling study of iso-octane oxidation. Combust. Flame 2002, 129, 253–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswamy, K.; Blanquart, G.; Pitsch, H. A consistent chemical mechanism for oxidation of substituted aromatic species. Combust. Flame 2010, 157, 1879–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kazakov, A.; Dryer, F.L. Experimental and numerical studies of ethanol decomposition reactions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 7671–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoureux, N.; Desgroux, P.; El Bakali, A.; Pauwels, J.F. Experimental and numerical study of the role of NCN in prompt-NO formation in low-pressure CH4-O2-N2 and C2H2-O2-N2 flames. Combust. Flame 2010, 157, 1929–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Banyon, C.; Bugler, J.; Curran, H.J.; Rodriguez, A.; Herbinet, O.; Battin-Leclerc, F.; B’Chir, C.; Heufer, K.A. An updated experimental and kinetic modeling study of n-heptane oxidation. Combust. Flame 2016, 172, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, C.-W.; Somers, K.P.; Zhang, K.; Curran, H.J. The oxidation of 2-butene: A high pressure ignition delay, kinetic modeling study and reactivity comparison with isobutene and 1-butene. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugler, J.; Somers, K.P.; Silke, E.J.; Curran, H.J. Revisiting the Kinetics and Thermodynamics of the Low-Temperature Oxidation Pathways of Alkanes: A Case Study of the Three Pentane Isomers. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 7510–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Banyon, C.; Togbé, C.; Dagaut, P.; Bugler, J.; Curran, H.J. An experimental and kinetic modeling study of n-hexane oxidation. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 4194–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugler, J.; Marks, B.; Mathieu, O.; Archuleta, R.; Camou, A.; Grégoire, C.; Heufer, K.A.; Petersen, E.L.; Curran, H.J. An ignition delay time and chemical kinetic modeling study of the pentane isomers. Combust. Flame 2016, 163, 138–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, M.; Reitz, R.D. Development of a Reduced Primary Reference Fuel Mechanism for Internal Combustion Engine Combustion Simulations. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 7843–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcy, D.; Mehl, M.; Simmie, J.M.; Würmel, J.; Metcalfe, W.K.; Westbrook, C.K.; Pitz, W.J.; Curran, H.J. An experimental and modeling study of the shock tube ignition of a mixture of n-heptane and n-propylbenzene as a surrogate for a large alkyl benzene. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, W.K.; Burke, S.M.; Ahmed, S.S.; Curran, H.J. A Hierarchical and Comparative Kinetic Modeling Study of C1−C2 Hydrocarbon and Oxygenated Fuels. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2013, 45, 638–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, D.; Kalitan, D.M.; Aul, C.J.; Petersen, E.L.; Bourque, G.; Curran, H.J. Oxidation of C1−C5 Alkane Quinternary Natural Gas Mixtures at High Pressures. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, M.; Yue, Z.; Jia, M.; Reitz, R.D. A reduced toluene reference fuel chemical kinetic mechanism for combustion and polycyclic-aromatic hydrocarbon predictions. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 2390–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Reitz, R.D. Modeling Diesel Engine NOx and Soot Reduction with Optimized Two-Stage Combustion; SAE International in United States: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.-W.; Li, Y.; Burke, U.; Banyon, C.; Somers, K.P.; Ding, S.; Khan, S.; Hargis, J.W.; Sikes, T.; Mathieu, O.; et al. An experimental and chemical kinetic modeling study of 1,3-butadiene combustion: Ignition delay time and laminar flame speed measurements. Combust. Flame 2018, 197, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LOGEsoft. Available online: http://www.logesoft.com (accessed on 16 May 2019).
- Tänzler, A.G. Experimentelle Untersuchung eines Dual-Fuel-Brennverfahrens für schwere Nutzfahrzeugmotoren; Springer Fachmedien: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachler, R.F.; Ramalingam, A.K.; Heufer, K.A.; Winter, F. Reduction and validation of a chemical kinetic mechanism including necessity analysis and investigation of CH4/C3H8 oxidation at pressures up to 120 bar using a rapid compression machine. Fuel 2016, 172, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, U.; Beeckmann, J.; Kopp, W.A.; Uygun, Y.; Olivier, H.; Leonhard, K.; Pitsch, H.; Heufer, K.A. A comprehensive experimental and kinetic modeling study of butanone. Combust. Flame 2016, 168, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Vranckx, S.; Heufer, K.A.; Khomik, S.V.; Uygun, Y.; Olivier, H.; Fernandez, R.X. On the Chemical Kinetics of Ethanol Oxidation: Shock Tube, Rapid Compression Machine and Detailed Modeling Study. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 2012, 226, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, A.; Zhang, K.; Dhongde, A.; Virnich, L.; Sankhla, H.; Curran, H.; Heufer, K.A. An RCM experimental and modeling study on CH4 and CH4/C2H6 oxidation at pressures up to 160 bar. Fuel 2017, 206, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, C. Gaseq—A Chemical Equilibrium Program for Windows. Available online: http://www.gaseq.co.uk/ (accessed on 29 September 2017).
- Shock & Detonation Toolbox—Cantera 2.1. Available online: http://shepherd.caltech.edu/EDL/public/cantera/html/SD_Toolbox/ (accessed on 29 September 2017).
- Goodwin, D.G.; Moffat, H.K.; Speth, R.L. Cantera: An Object-Oriented Software Toolkit for Chemical Kinetics, Thermodynamics, and Transport Processes; Version 2.2. 1; Cantera Developers: Warrenville, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Minwegen, H.; Burke, U.; Heufer, K.A. An experimental and theoretical comparison of C3–C5 linear ketones. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, S.M.; Burke, U.; Mc Donagh, R.; Mathieu, O.; Osorio, I.; Keesee, C.; Morones, A.; Petersen, E.L.; Wang, W.; DeVerter, T.A.; et al. An experimental and modeling study of propene oxidation. Part 2: Ignition delay time and flame speed measurements. Combust. Flame 2015, 162, 296–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.-J.; Curran, H.J. Using rapid compression machines for chemical kinetics studies. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2014, 44, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.L.; Hanson, R.K. Nonideal effects behind reflected shock waves in a high-pressure shock tube. Shock Waves 2001, 10, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heufer, K.A.; Olivier, H. Determination of ignition delay times of different hydrocarbons in a new high pressure shock tube. Shock Waves 2010, 20, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, S.; Winter, F. Comparing the Influence of Propane and n-Heptane Addition on Methane Ignition. In Proceedings of the 8th European Combustion Meeting, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 18–21 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cord, M.; Husson, B.; Lizardo Huerta, J.C.; Herbinet, O.; Glaude, P.A.; Fournet, R.; Sirjean, B.; Battin-Leclerc, F.; Ruiz-Lopez, M.; Wang, Z.; et al. Study of the low temperature oxidation of propane. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 12214–12228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.L.; Kalitan, D.M.; Simmons, S.; Bourque, G.; Curran, H.J.; Simmie, J.M. Methane/propane oxidation at high pressures: Experimental and detailed chemical kinetic modeling. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Ramalingam, A.; Minwegen, H.; Heufer, K.A.; Pitsch, H. Impact of exhaust gas recirculation on ignition delay times of gasoline fuel: An experimental and modeling study. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffner, M.; Jud, M.; Sattelmayer, T. Reaction Kinetics Analysis of Dual Fuel Internal Combustion Engines Based on Ignition Delay Times Using n-Heptane/Methane Fuel Blends. In Proceedings of the 8th European Combustion Meeting, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 18–21 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Steen, H. Handbuch des Explosionsschutzes; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]


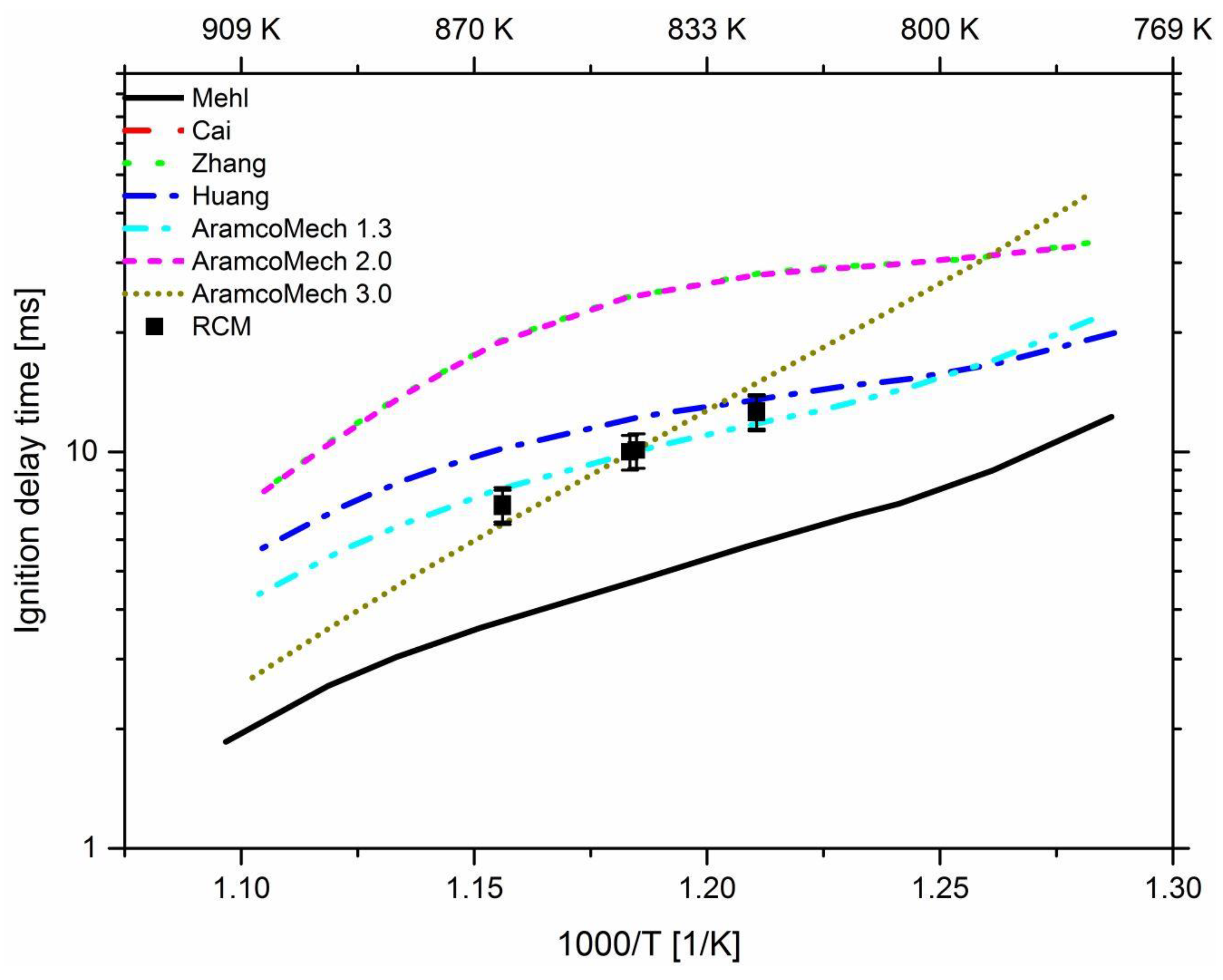


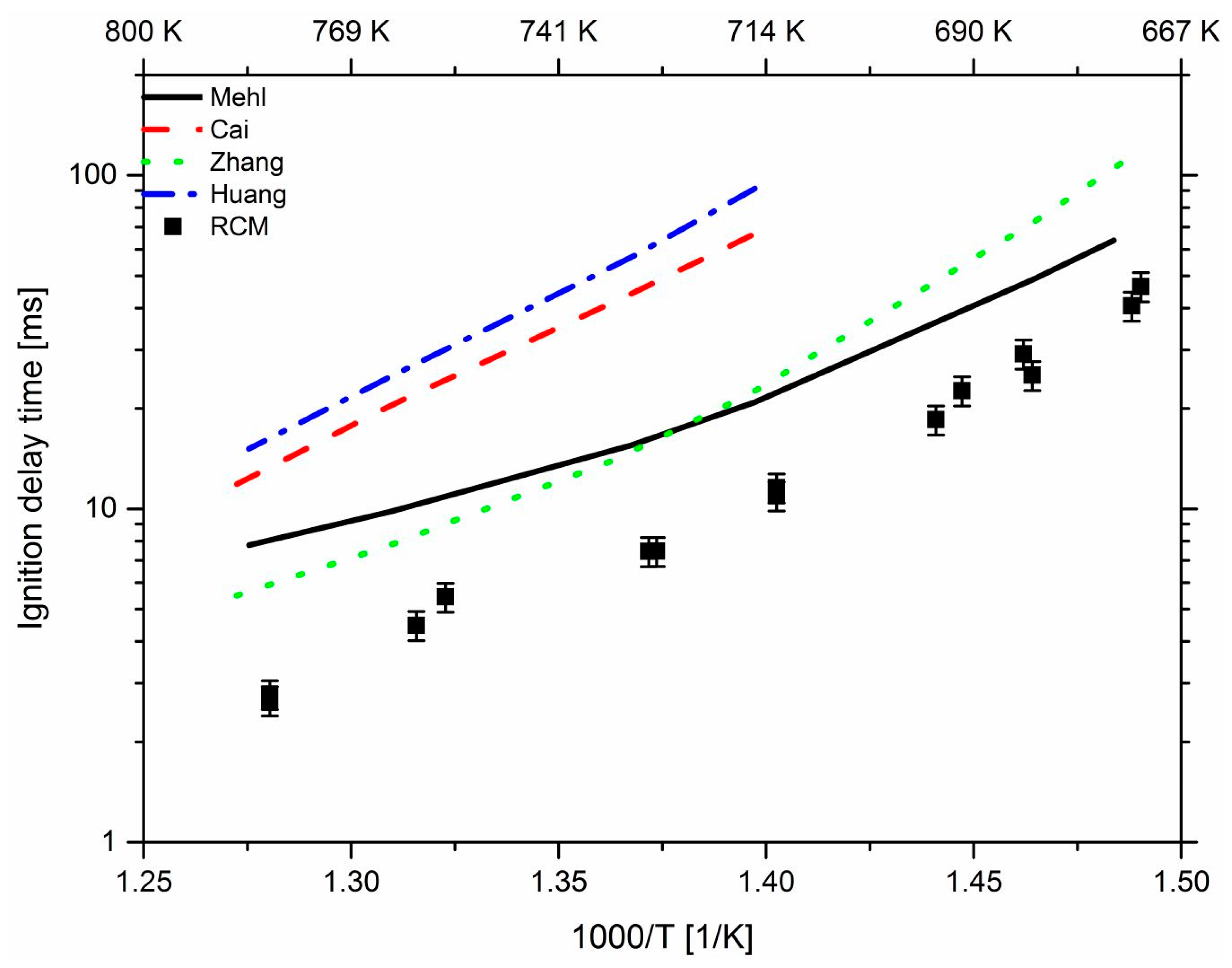
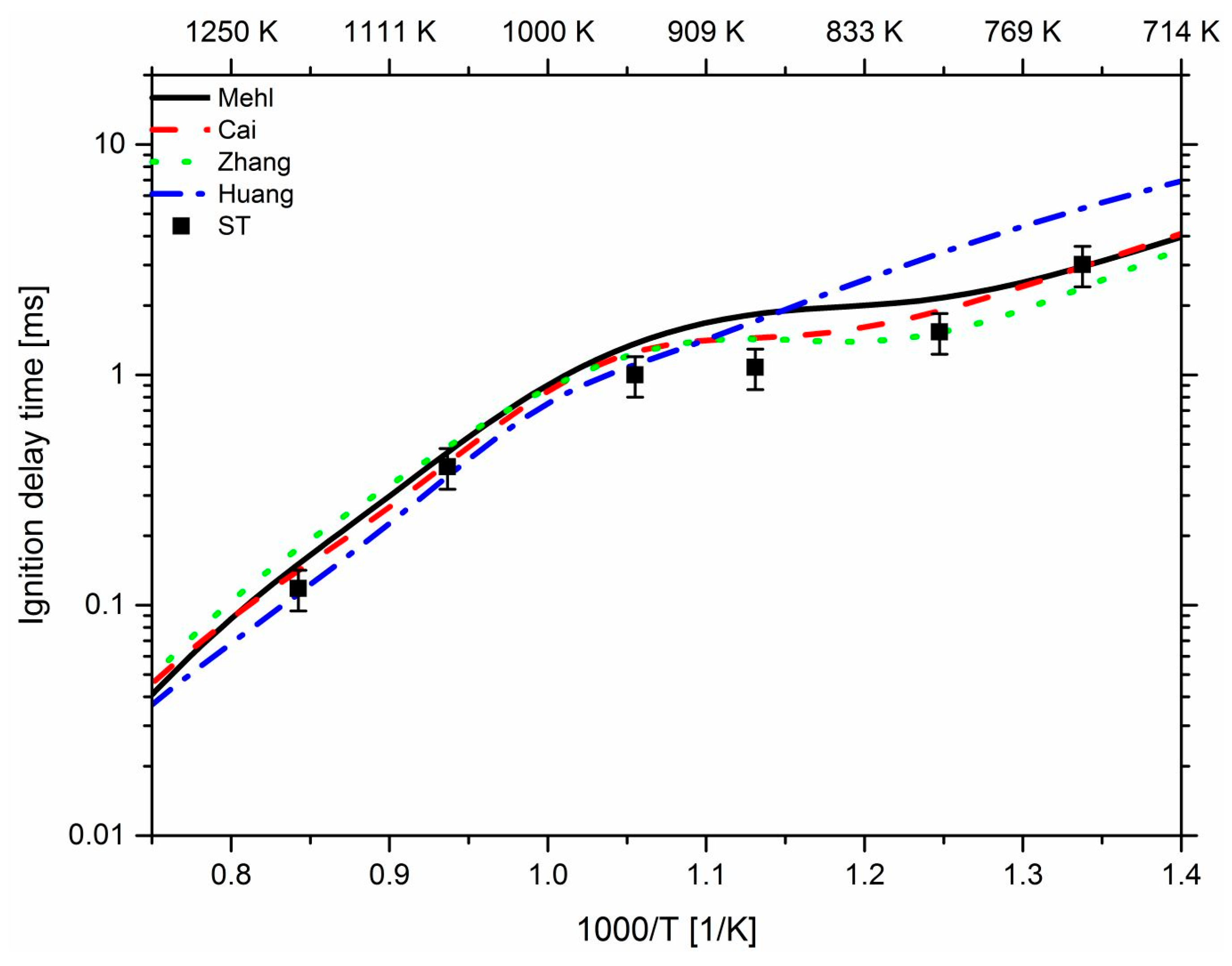
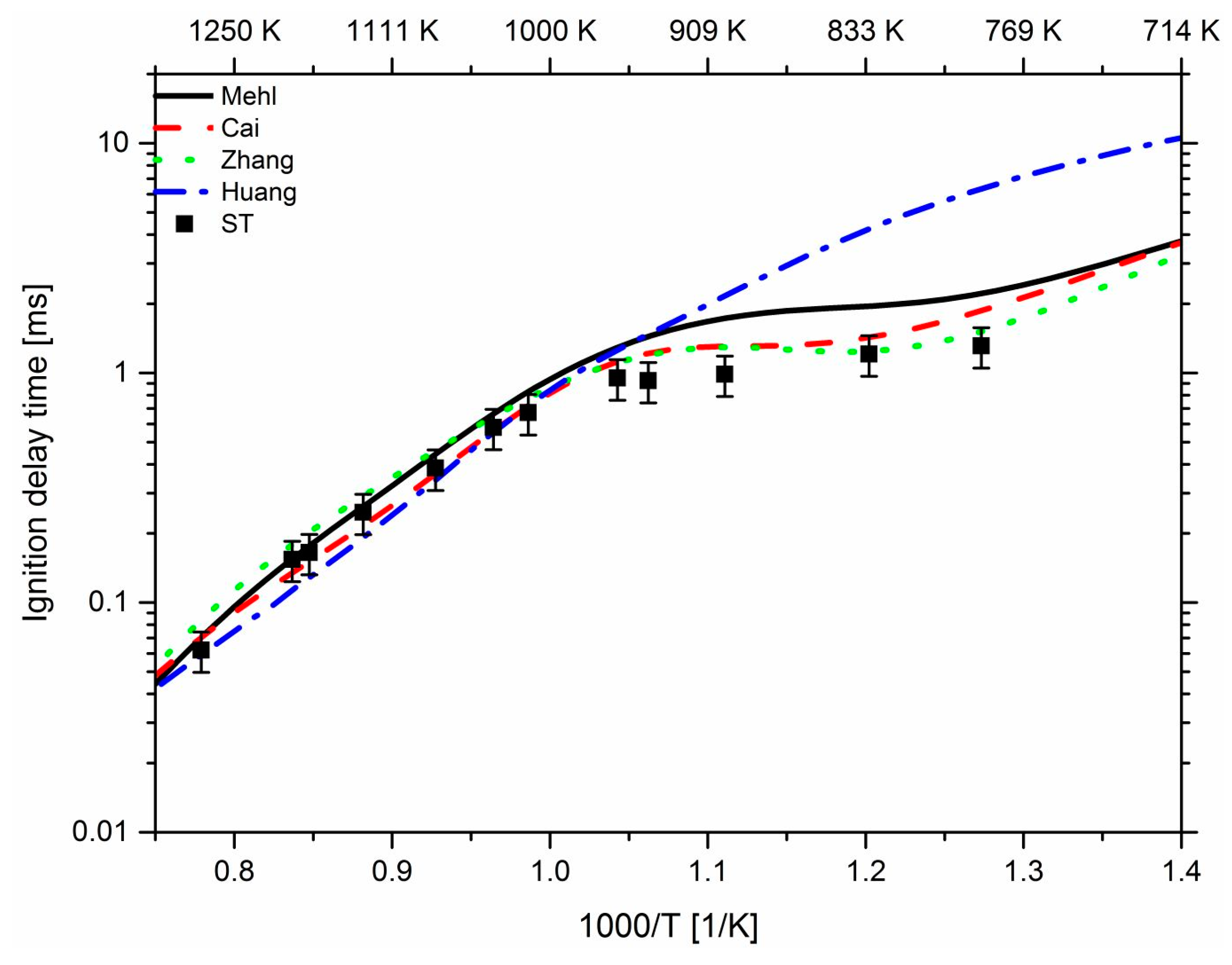
| Test Facility | Test Series | Fuel Composition | Pressure | Temperature | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 (mol %) | C3H8 (mol %) | xn-C7H16 Defined by (1) | (bar) | (K) | |||
| Rapid compression machine | RCM1.1 | 100 | 0 | - | 100 | 906–941 | [37] |
| RCM1.2 | 95 | 5 | - | 100 | 888–916 | [37] | |
| RCM1.3 | 70 | 30 | - | 100 | 826–865 | [37] | |
| RCM2.1 | 90 | 10 | - | 100 | 803–898 | this study | |
| RCM2.2 | 95 | 5 | 0.025 | 60 | 701–877 | this study | |
| RCM2.3 | 95 | 5 | 0.05 | 60 | 671–781 | this study | |
| RCM2.4 | 95 | 5 | 0.025 | 100 | 709–817 | this study | |
| RCM2.5 | 100 | 0 | 0.025 | 60 | 720–869 | this study | |
| Shock tube | ST1.1 | 95 | 5 | 0.1 | 60 | 748–1187 | this study |
| ST1.2 | 100 | 0 | 0.1 | 60 | 785–1284 | this study | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schuh, S.; Ramalingam, A.K.; Minwegen, H.; Heufer, K.A.; Winter, F. Experimental Investigation and Benchmark Study of Oxidation of Methane–Propane–n-Heptane Mixtures at Pressures up to 100 bar. Energies 2019, 12, 3410. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183410
Schuh S, Ramalingam AK, Minwegen H, Heufer KA, Winter F. Experimental Investigation and Benchmark Study of Oxidation of Methane–Propane–n-Heptane Mixtures at Pressures up to 100 bar. Energies. 2019; 12(18):3410. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183410
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchuh, Sebastian, Ajoy Kumar Ramalingam, Heiko Minwegen, Karl Alexander Heufer, and Franz Winter. 2019. "Experimental Investigation and Benchmark Study of Oxidation of Methane–Propane–n-Heptane Mixtures at Pressures up to 100 bar" Energies 12, no. 18: 3410. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183410
APA StyleSchuh, S., Ramalingam, A. K., Minwegen, H., Heufer, K. A., & Winter, F. (2019). Experimental Investigation and Benchmark Study of Oxidation of Methane–Propane–n-Heptane Mixtures at Pressures up to 100 bar. Energies, 12(18), 3410. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12183410






